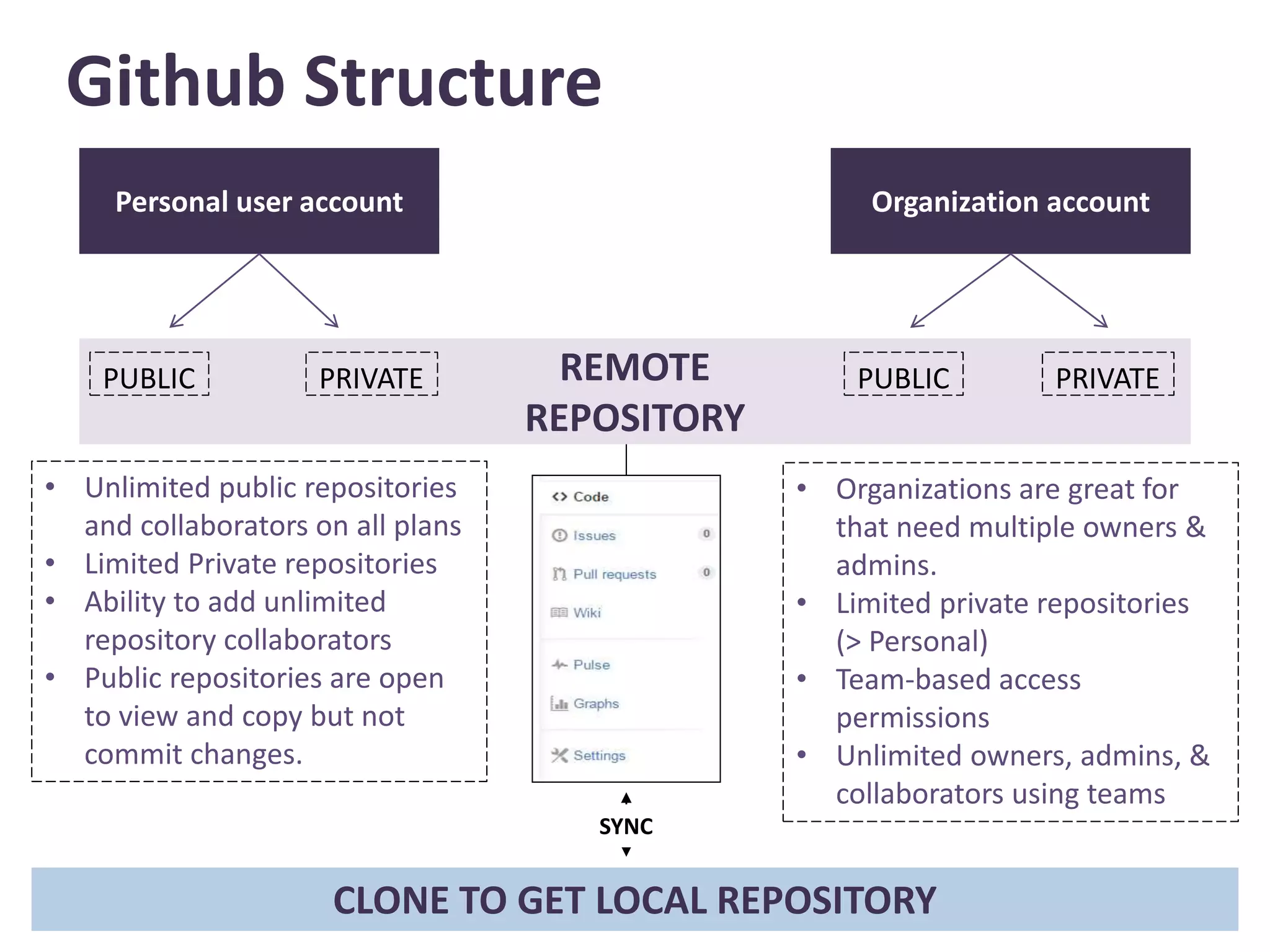
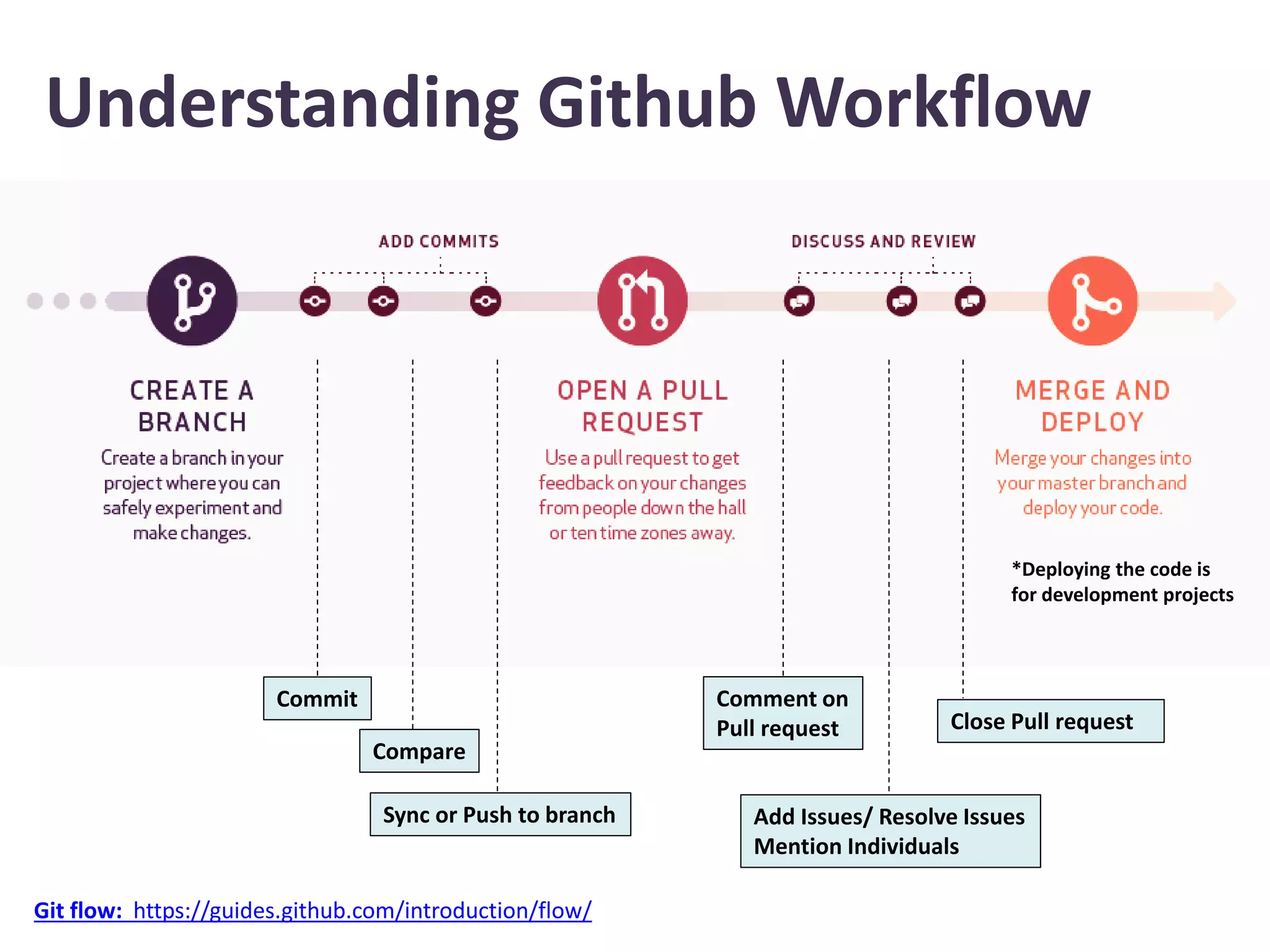
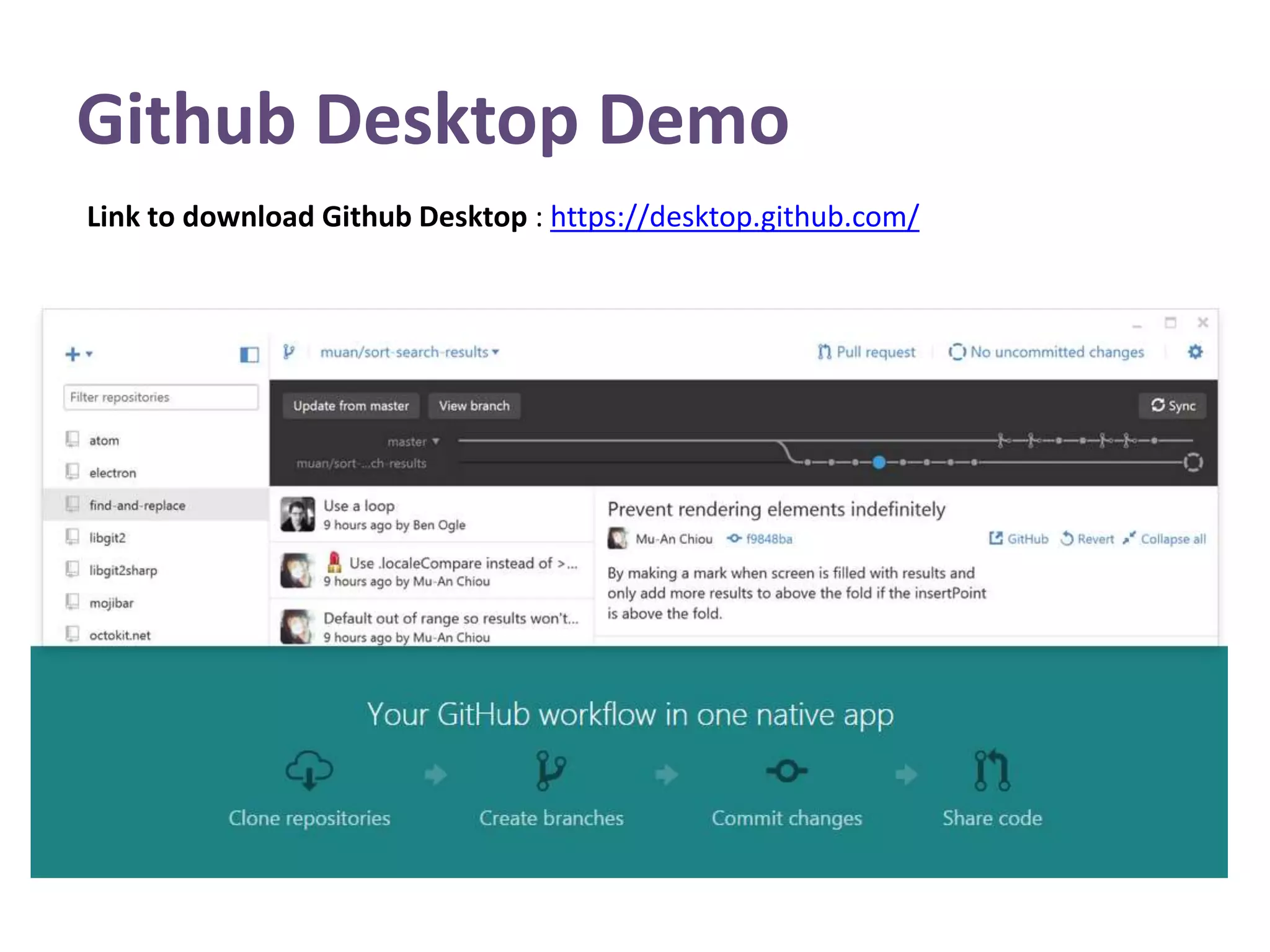
This document provides an introduction to GitHub. It defines Git as a version control system that records changes to files and allows users to revert files to earlier versions. GitHub is described as a hosting service for Git repositories that provides a graphical interface and collaboration features. The document outlines key GitHub concepts like repositories, branches, commits, forking, pull requests and issues. It also summarizes the typical GitHub workflow and includes a link to download GitHub Desktop for a demo.