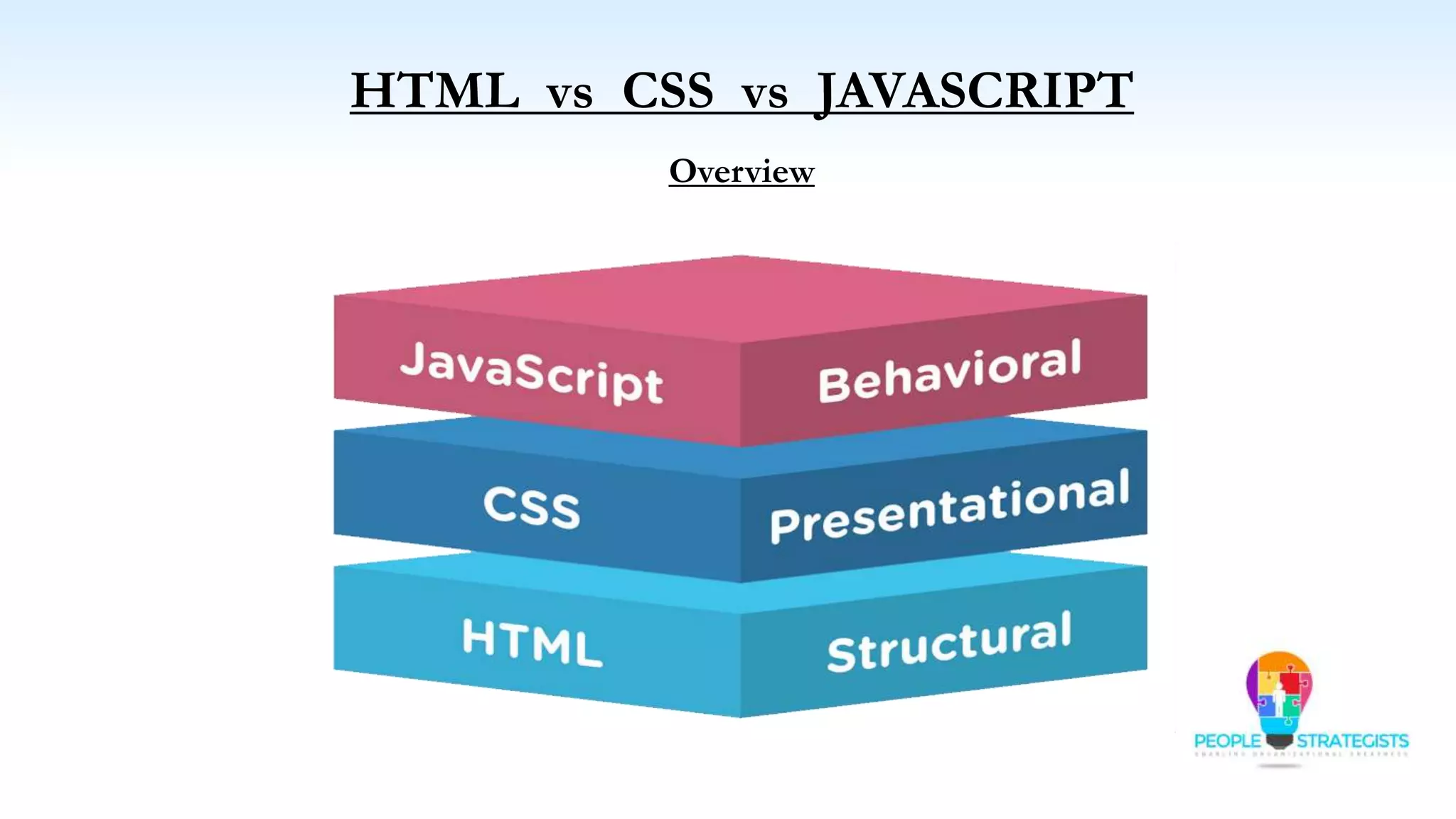
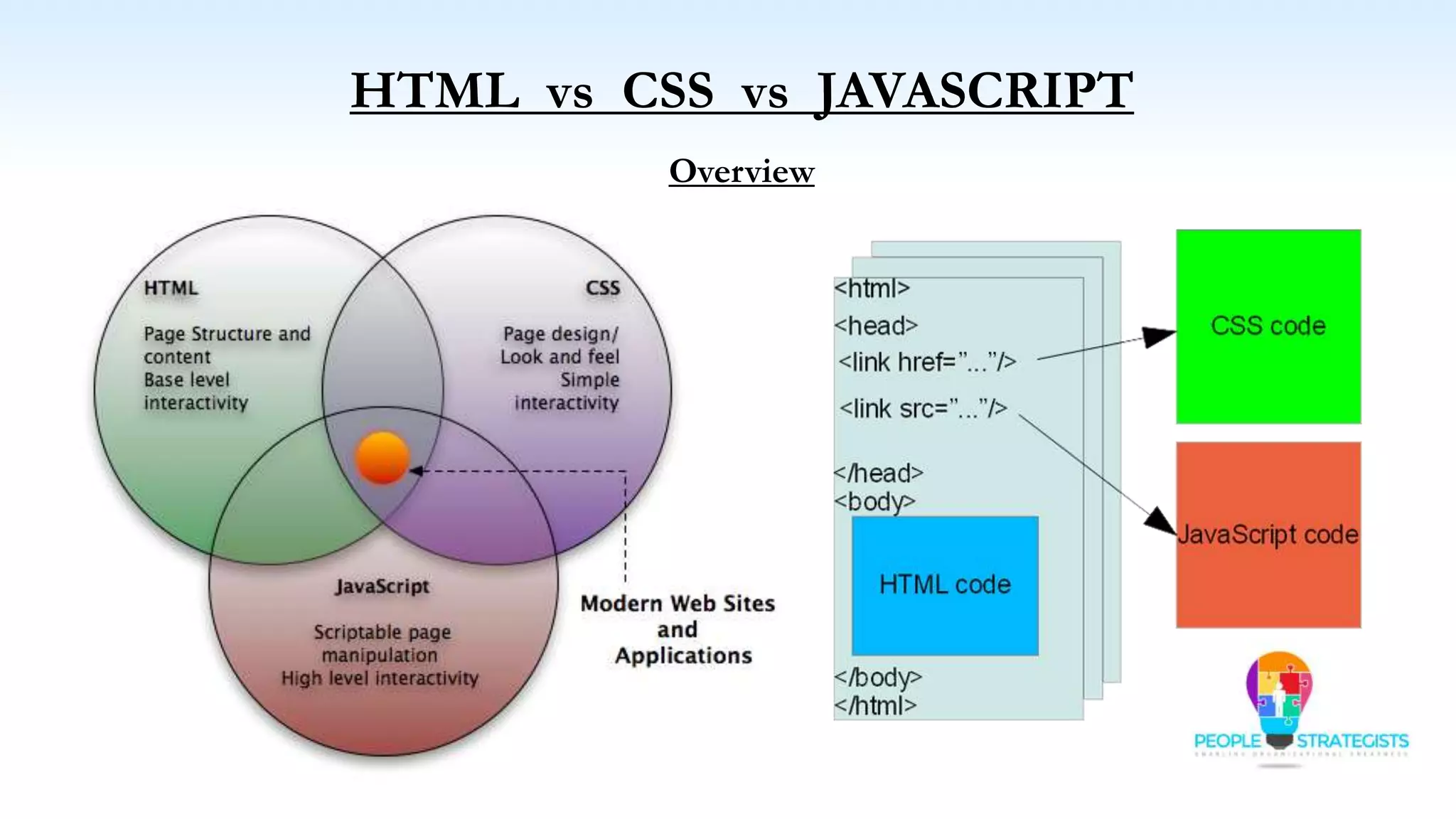
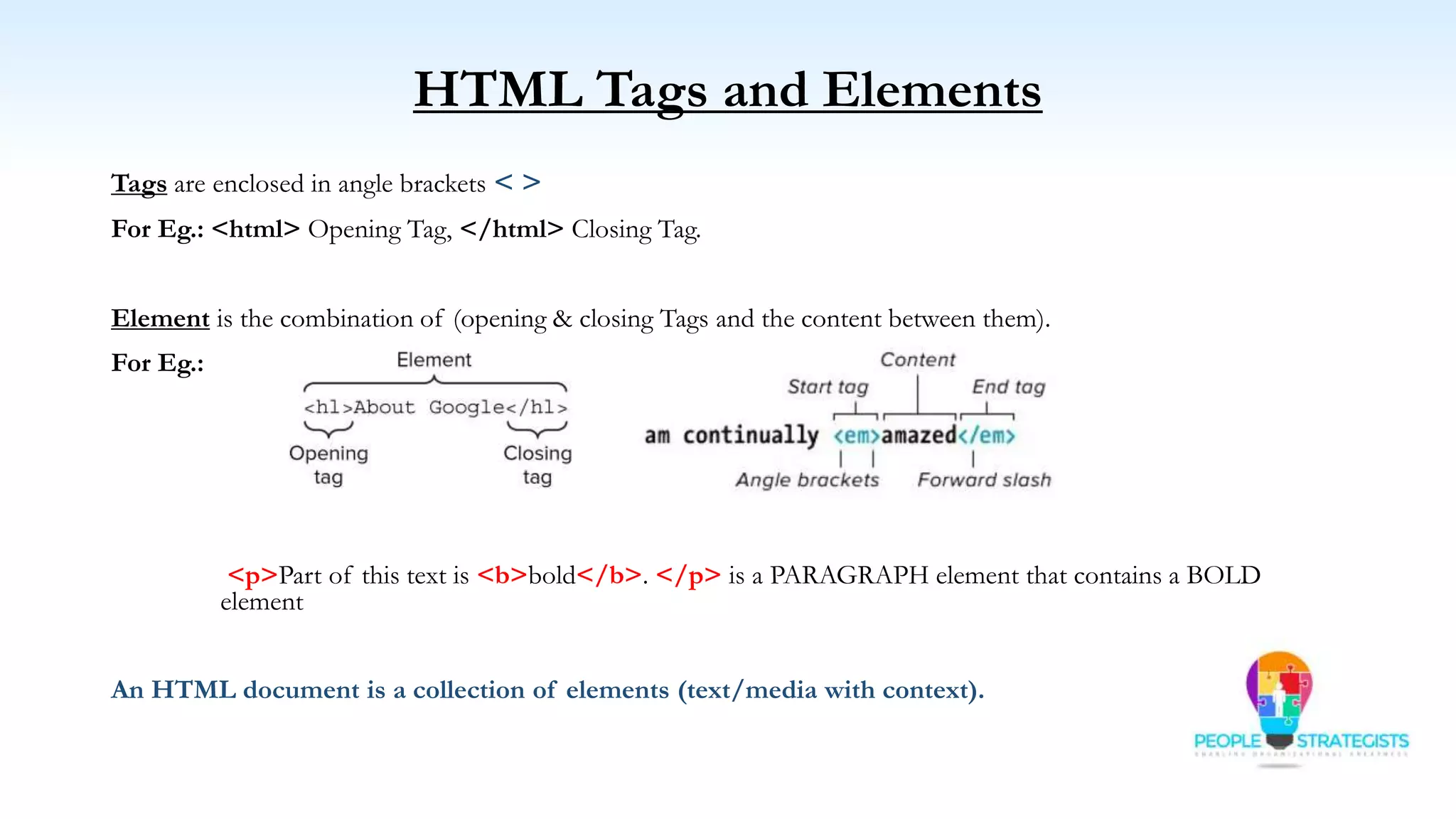
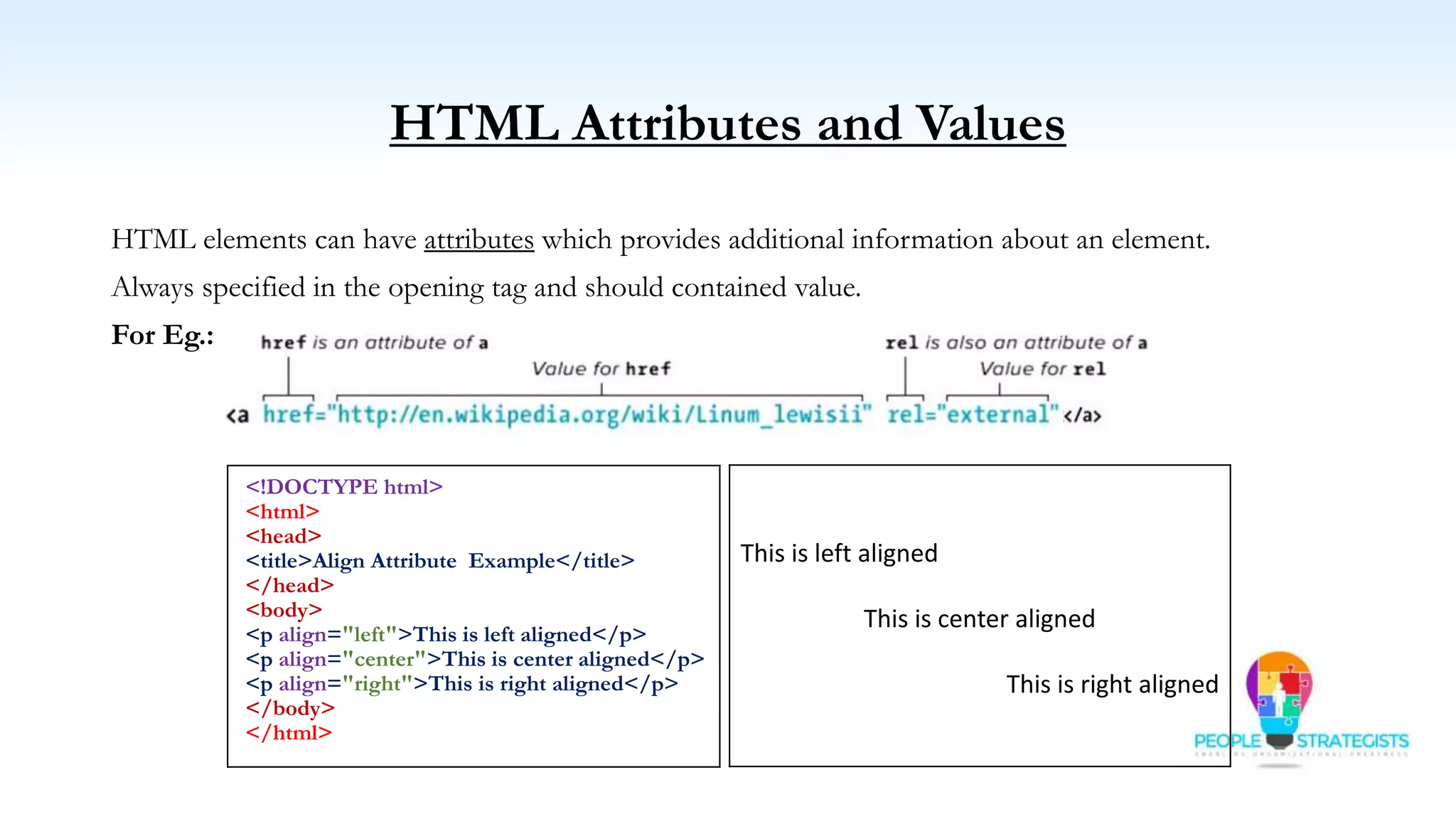
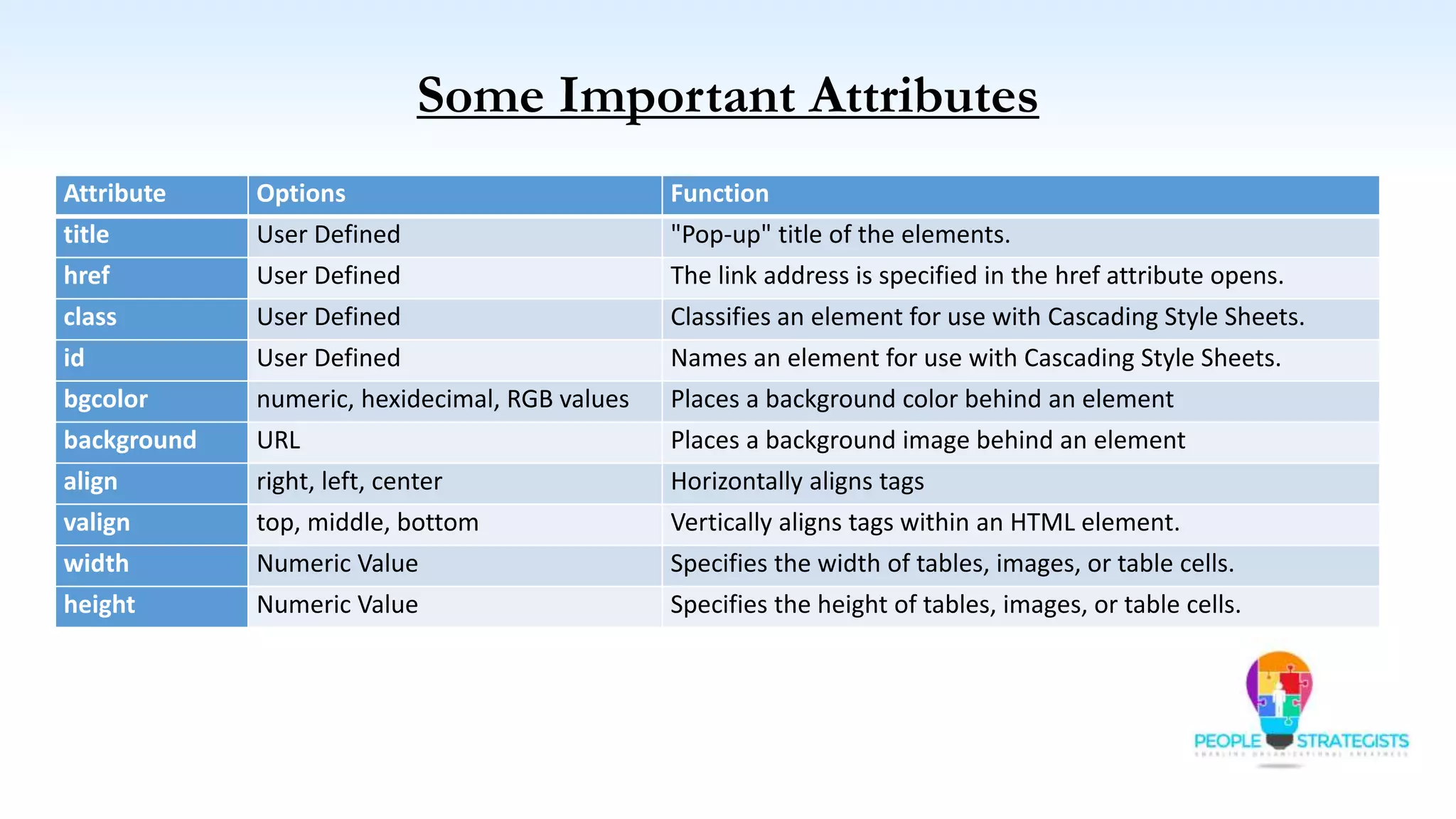
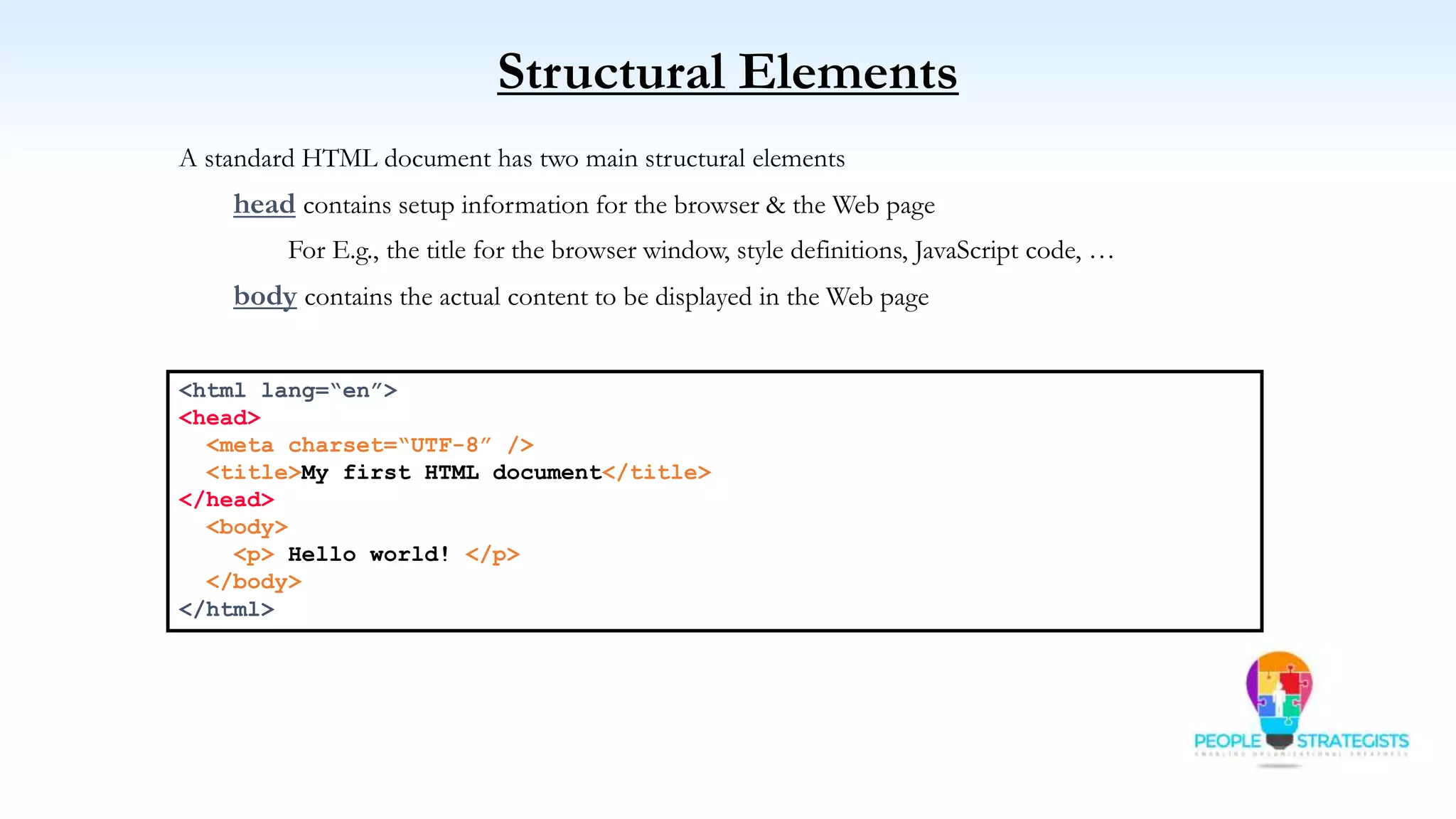
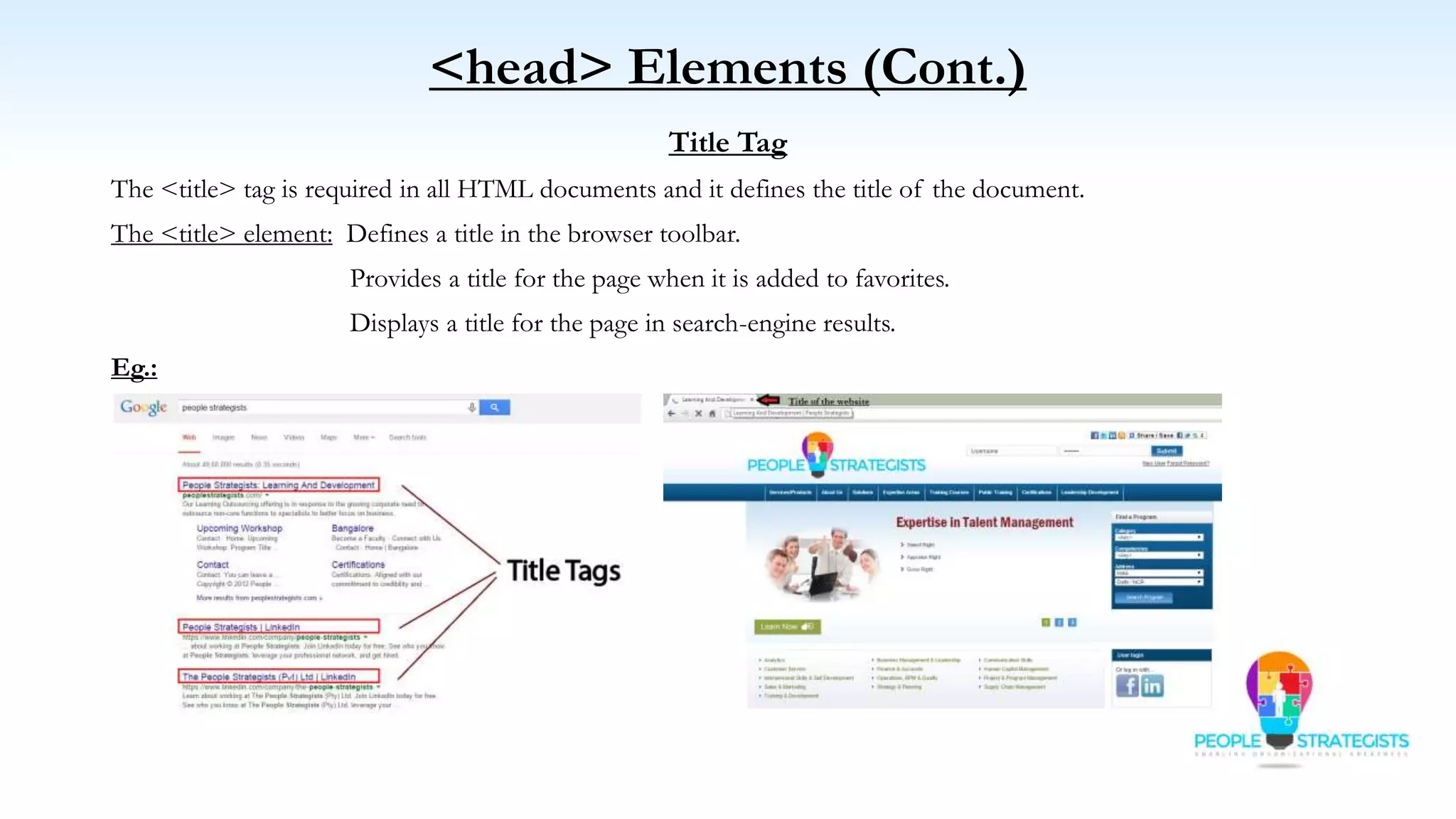
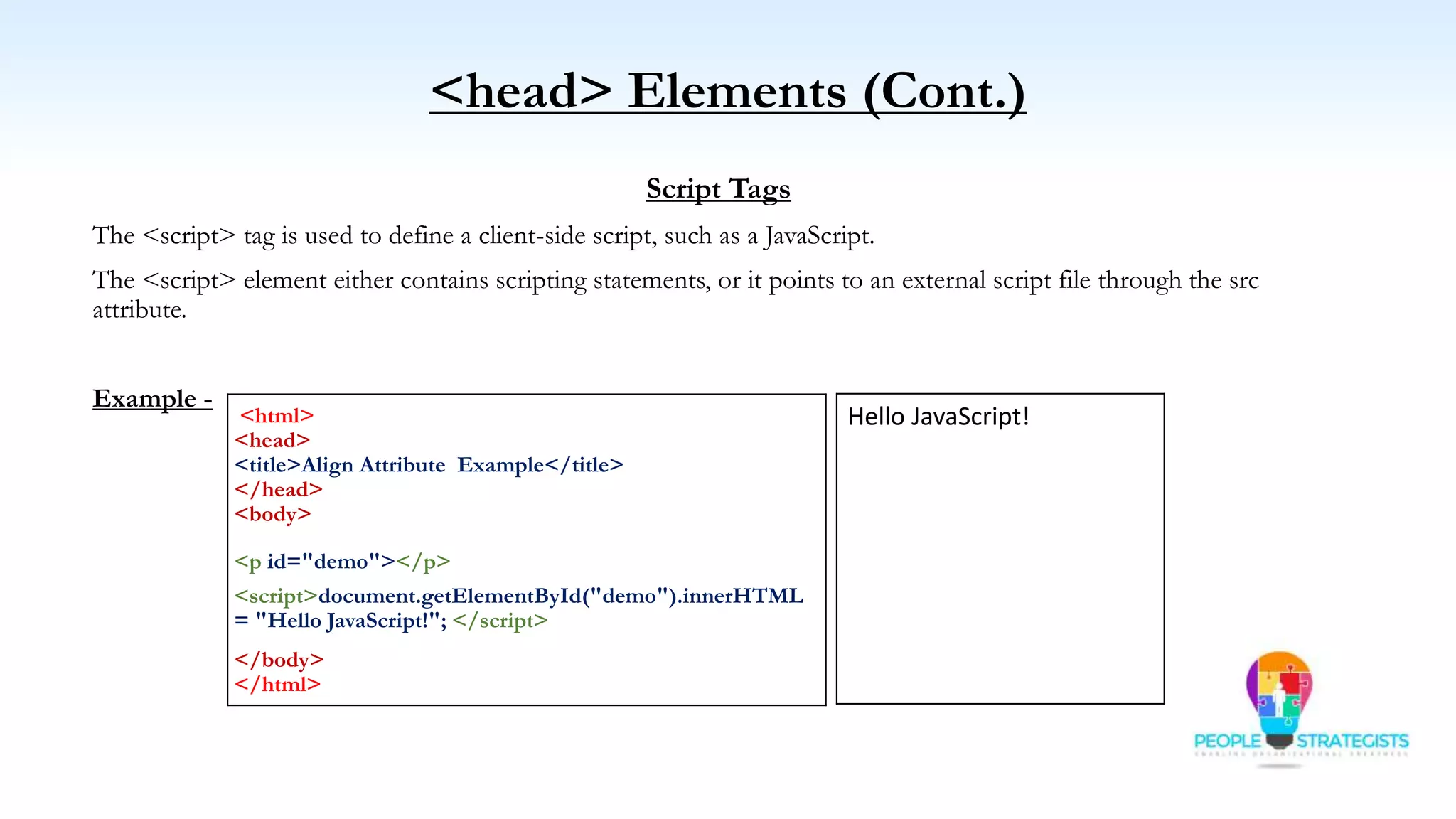
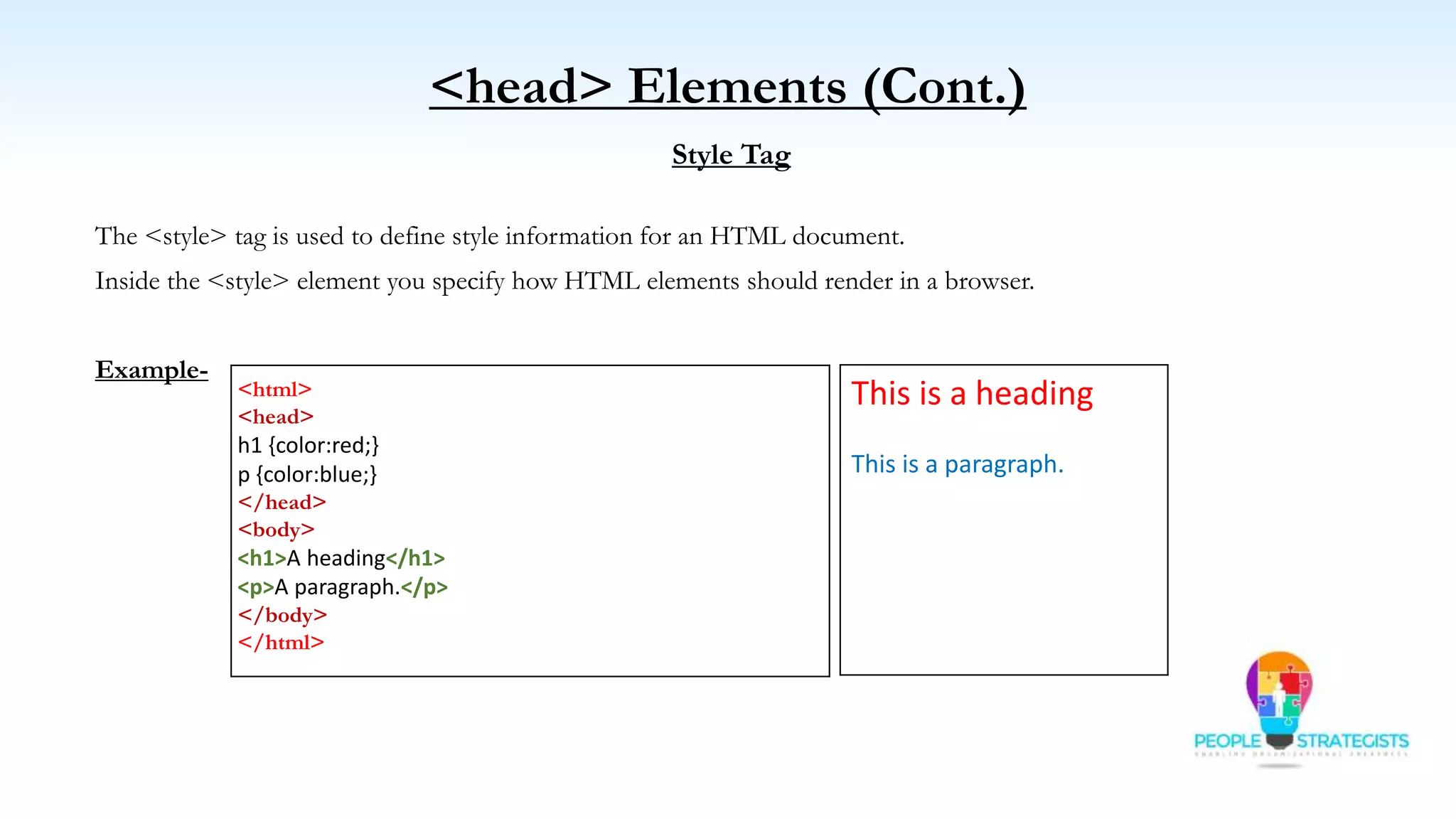
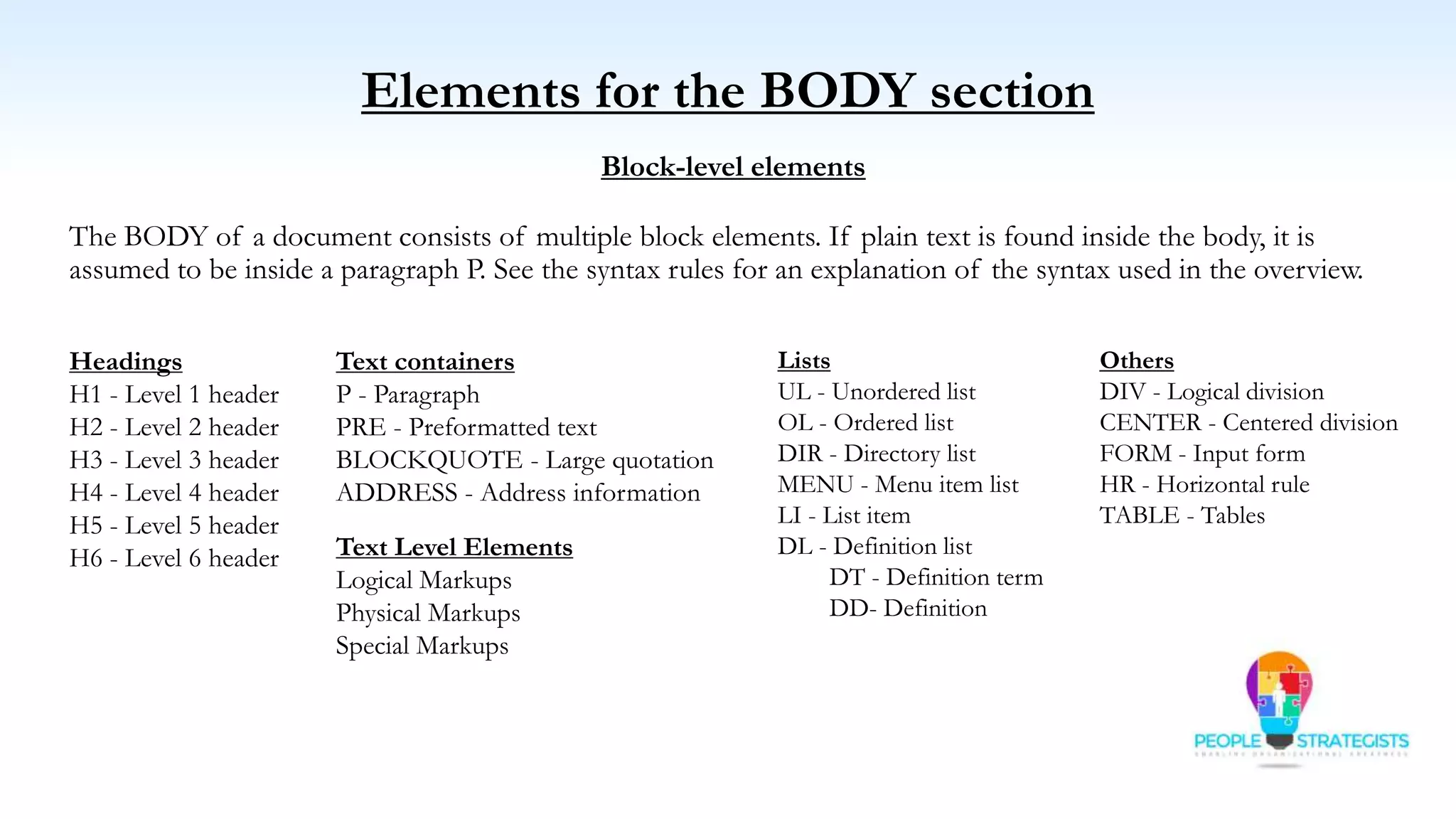
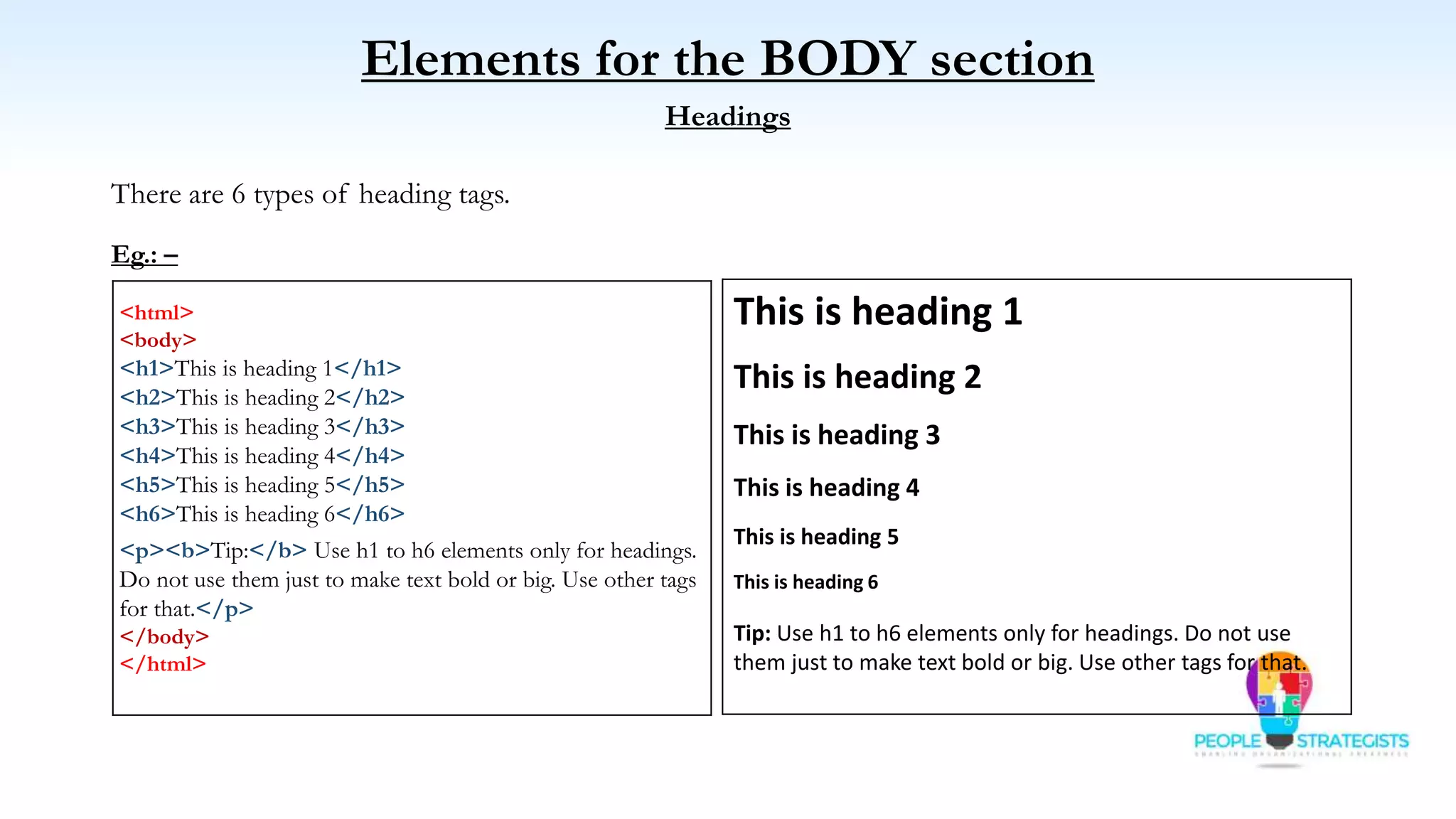
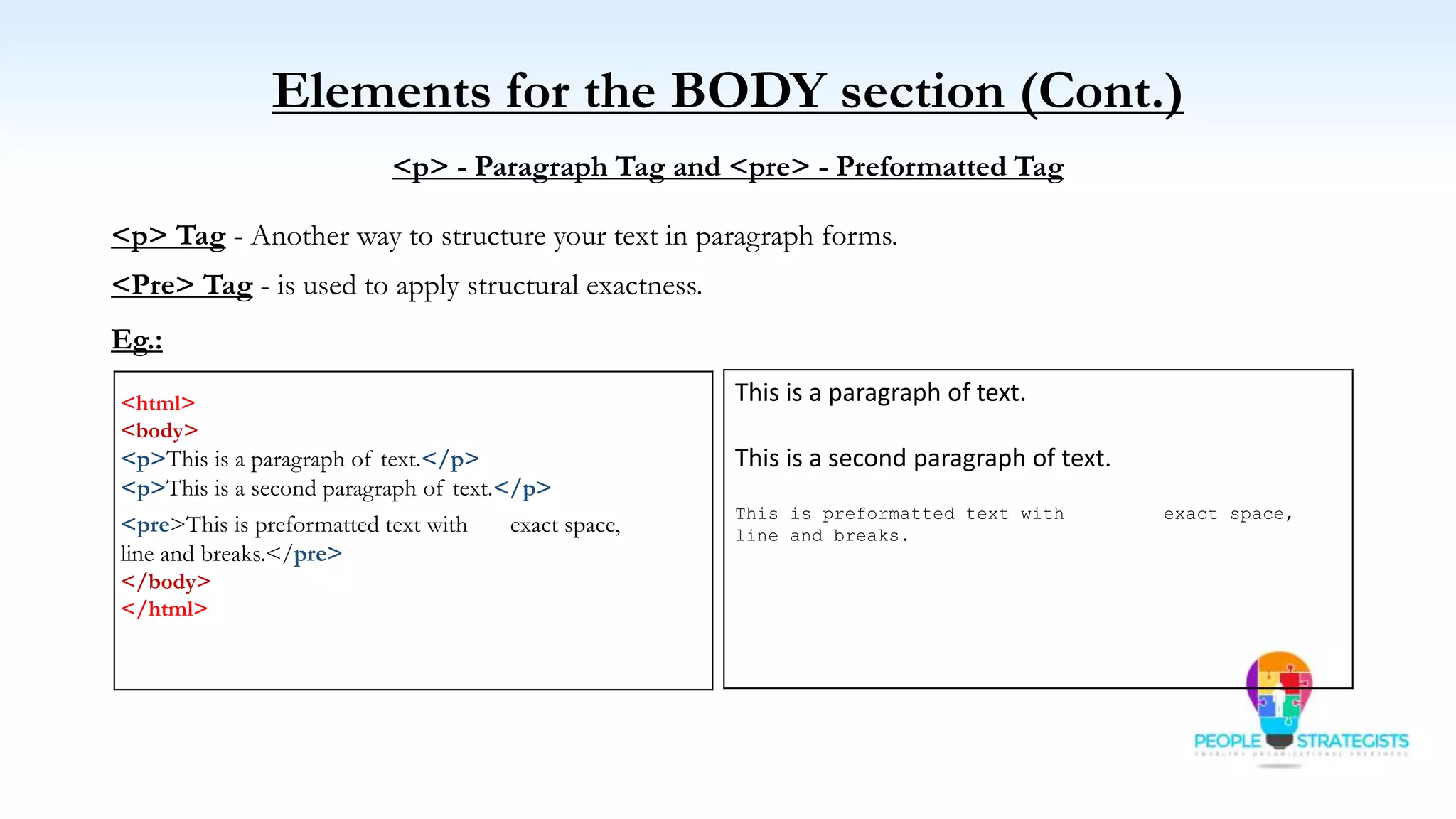
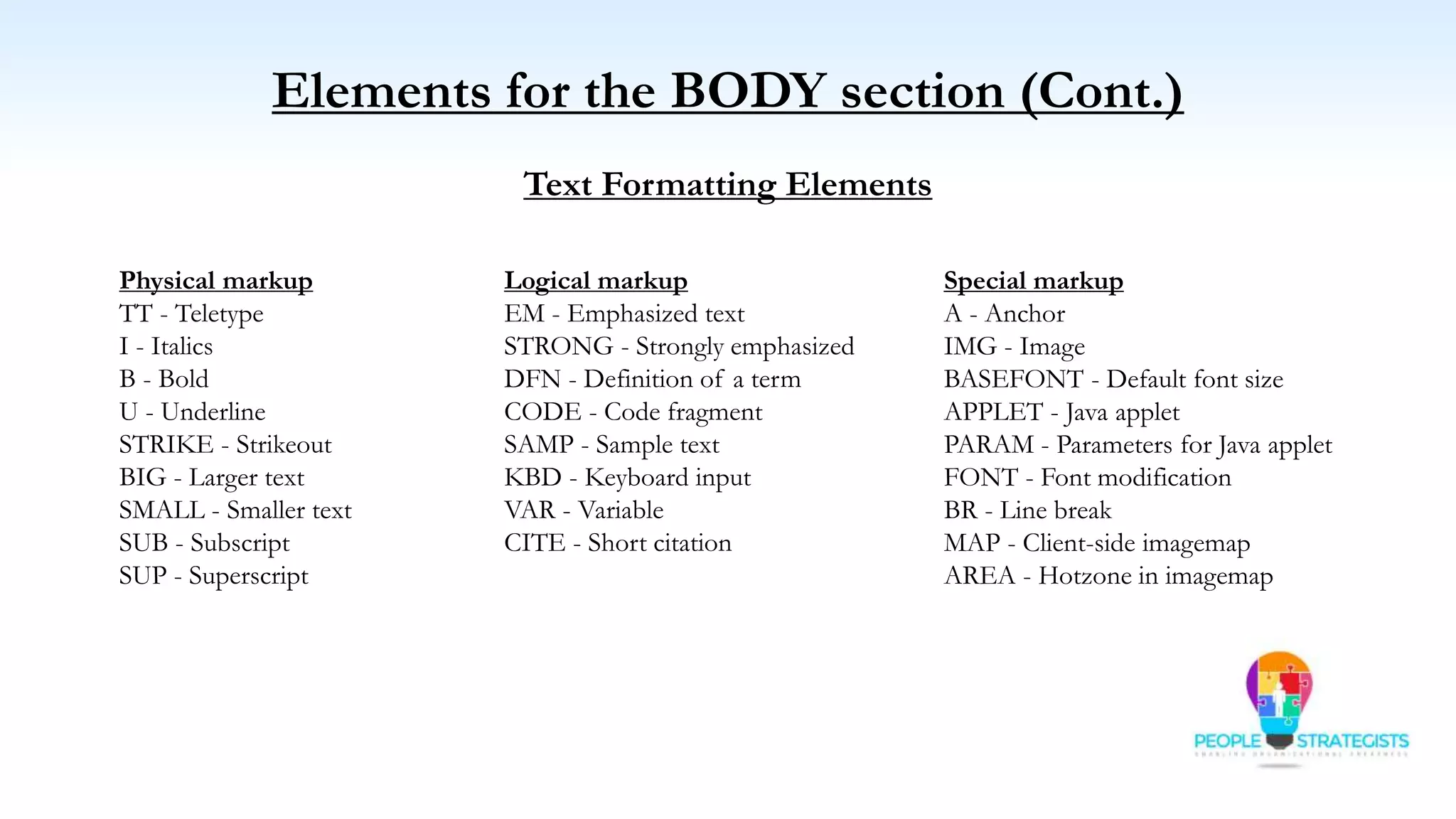
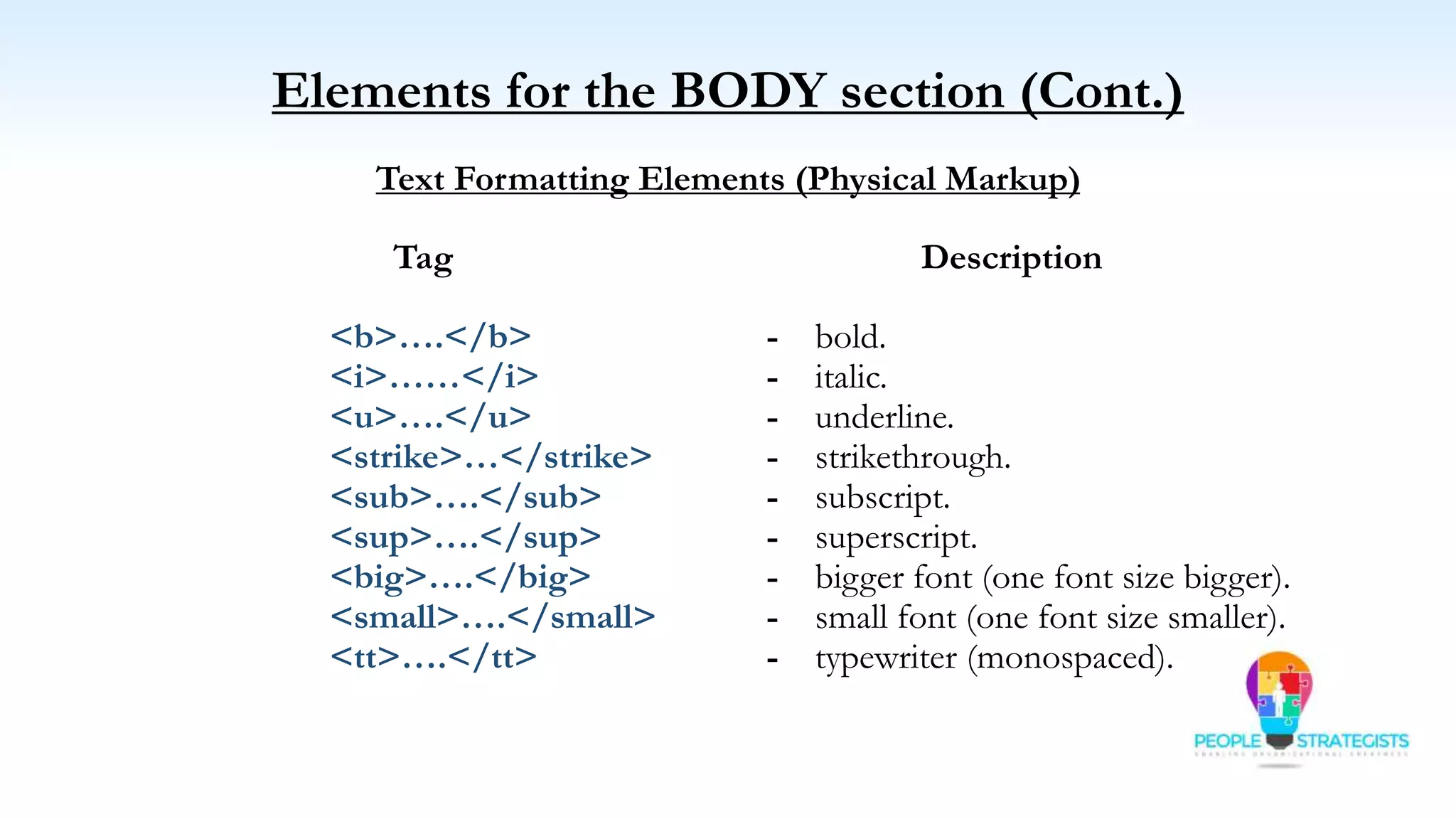
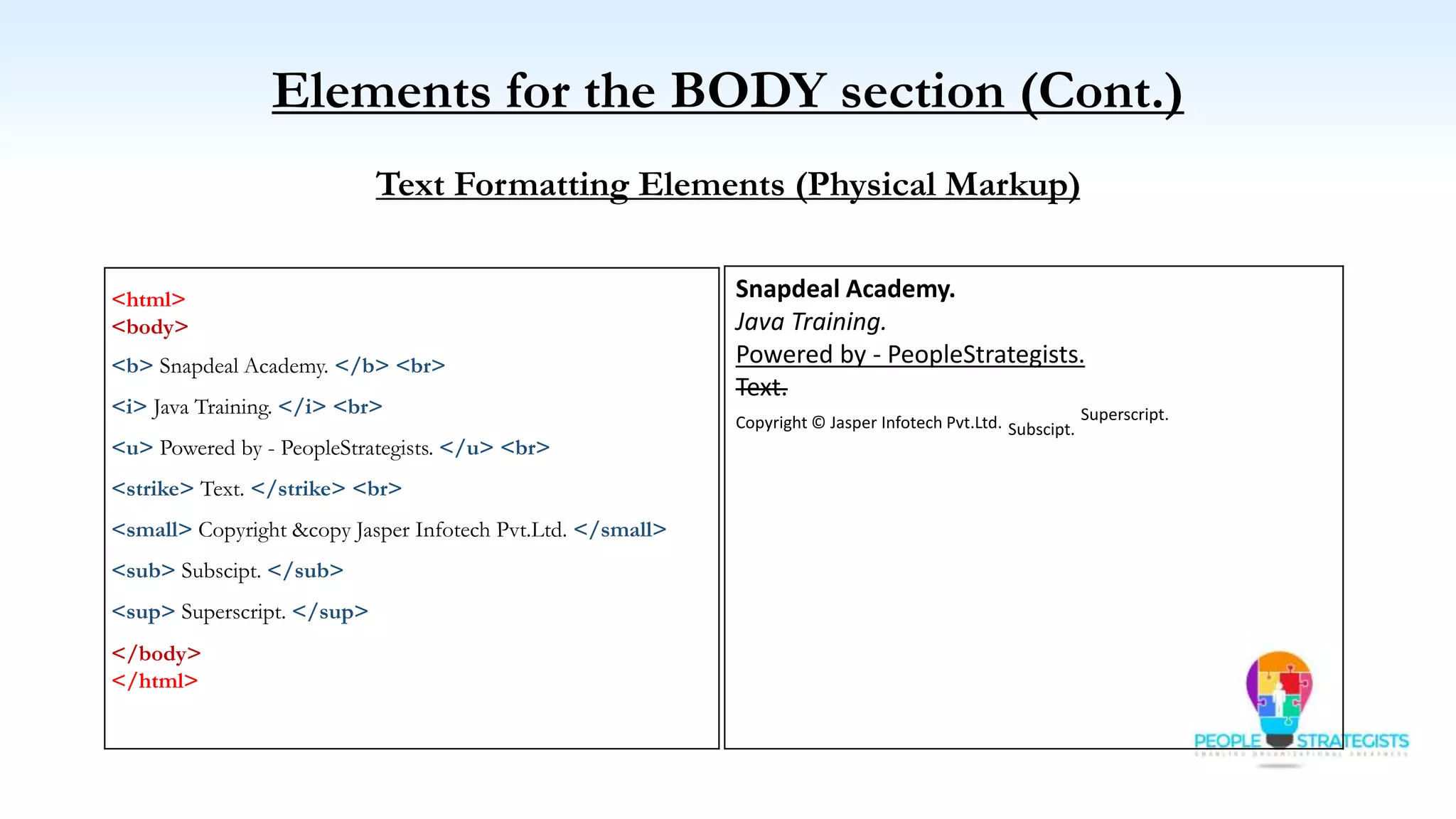
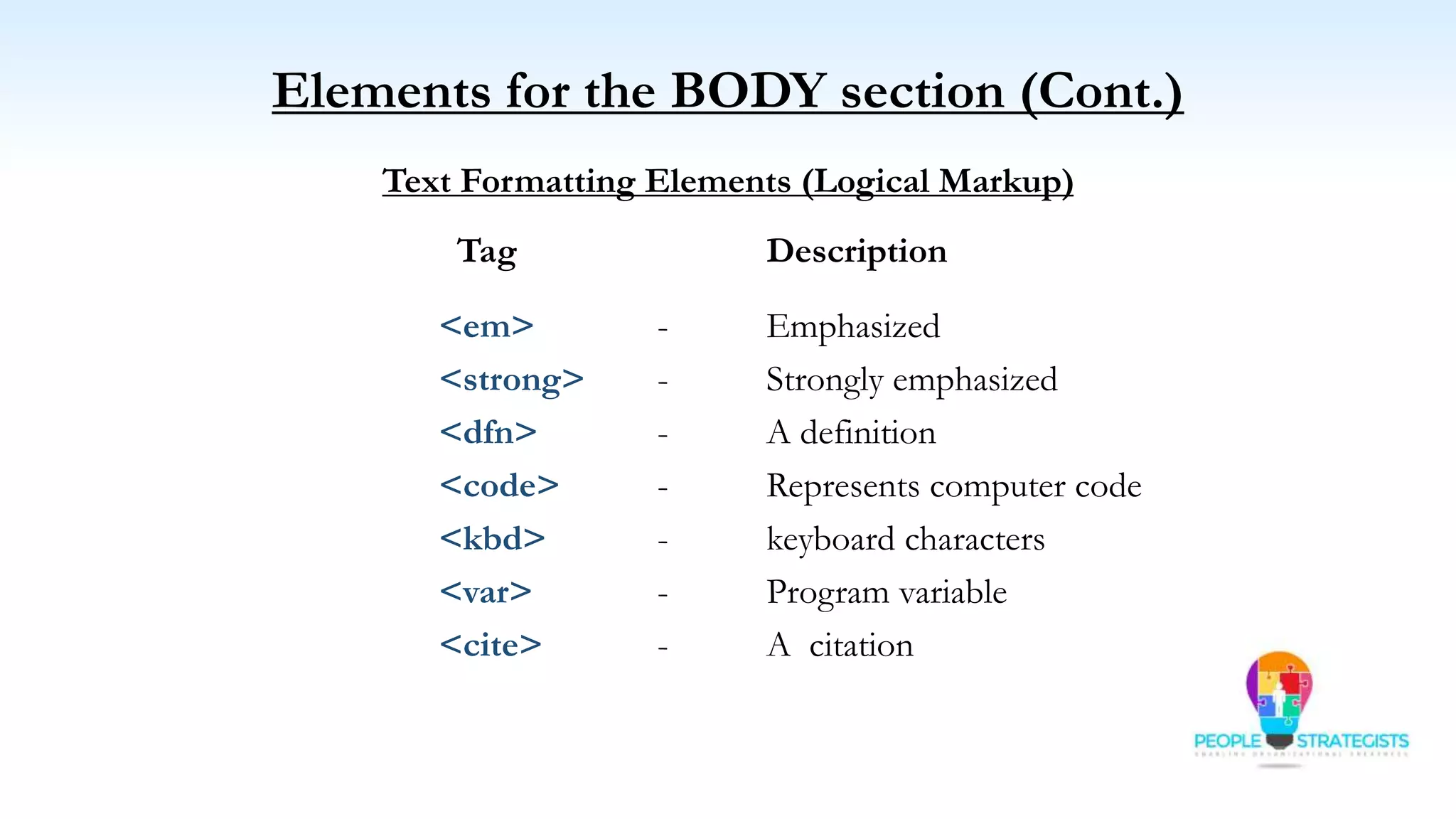
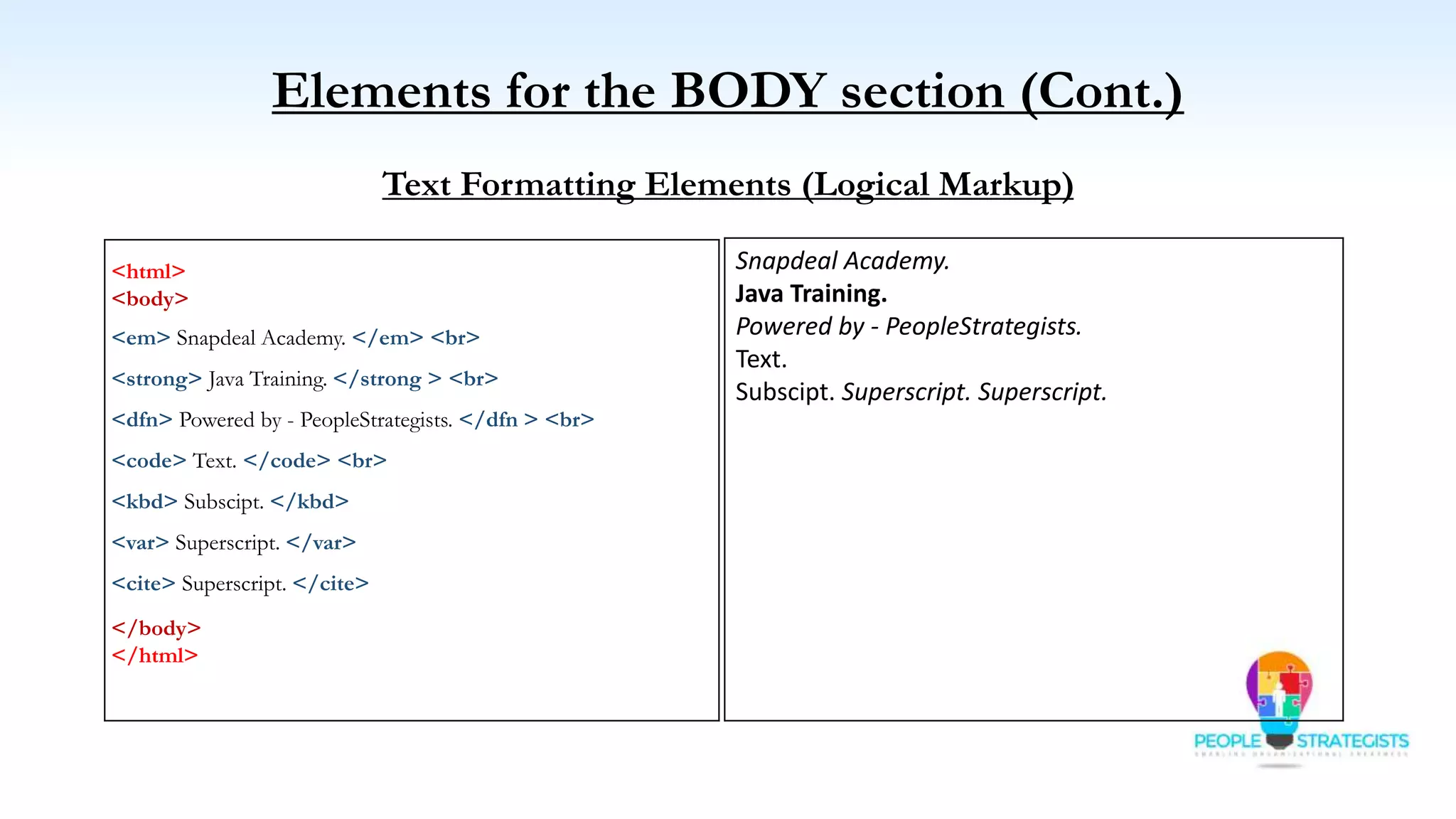
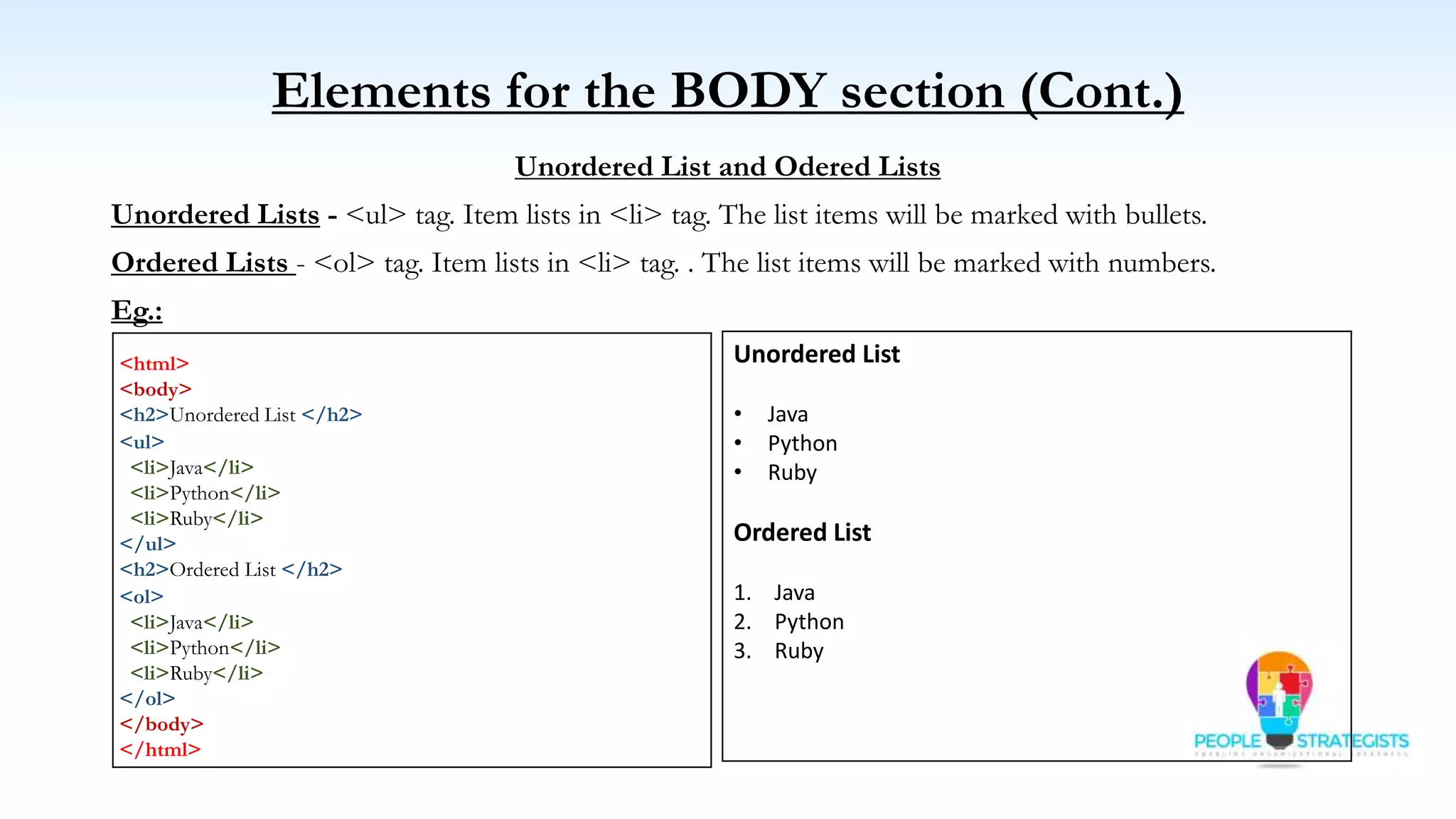
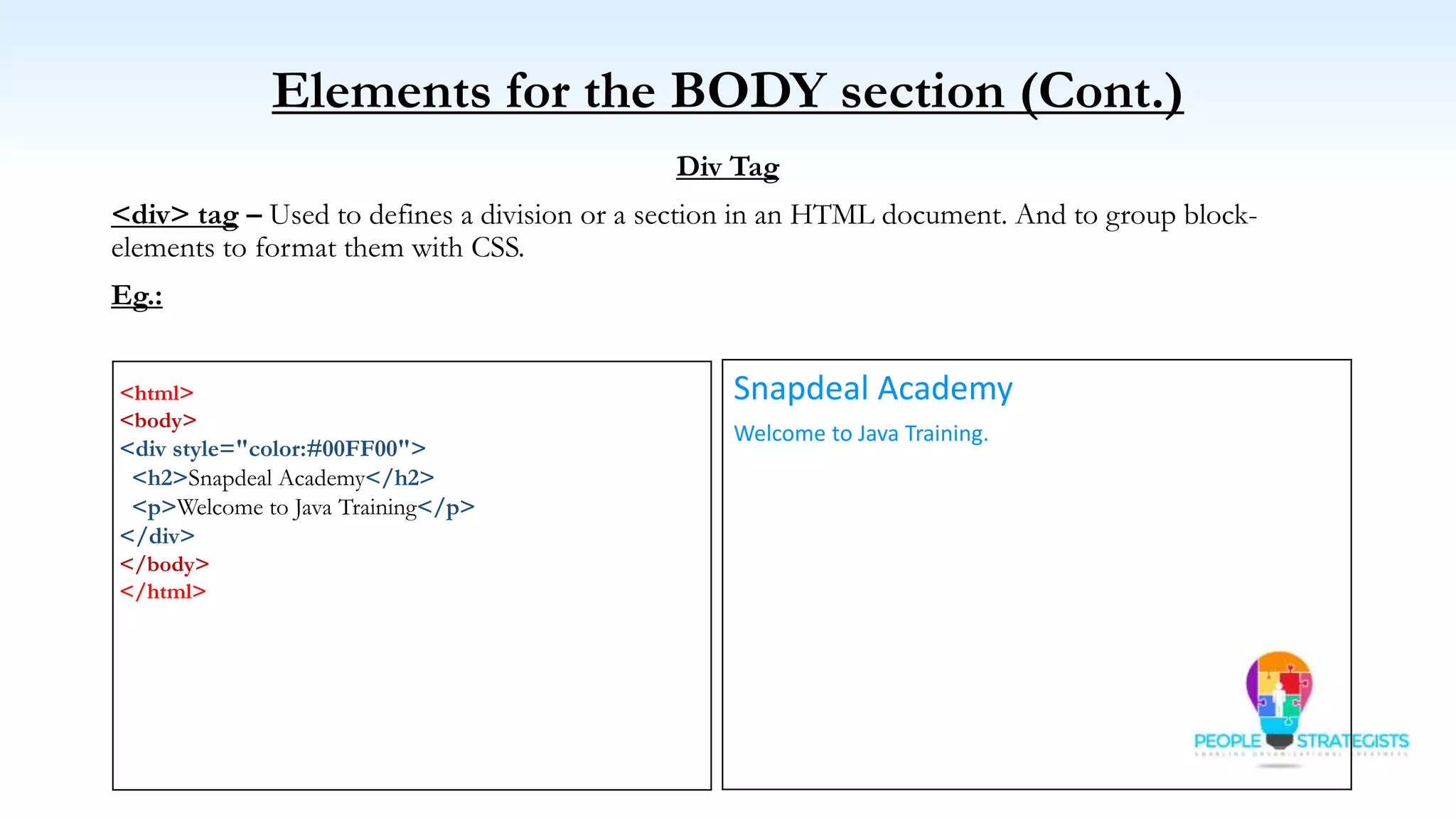
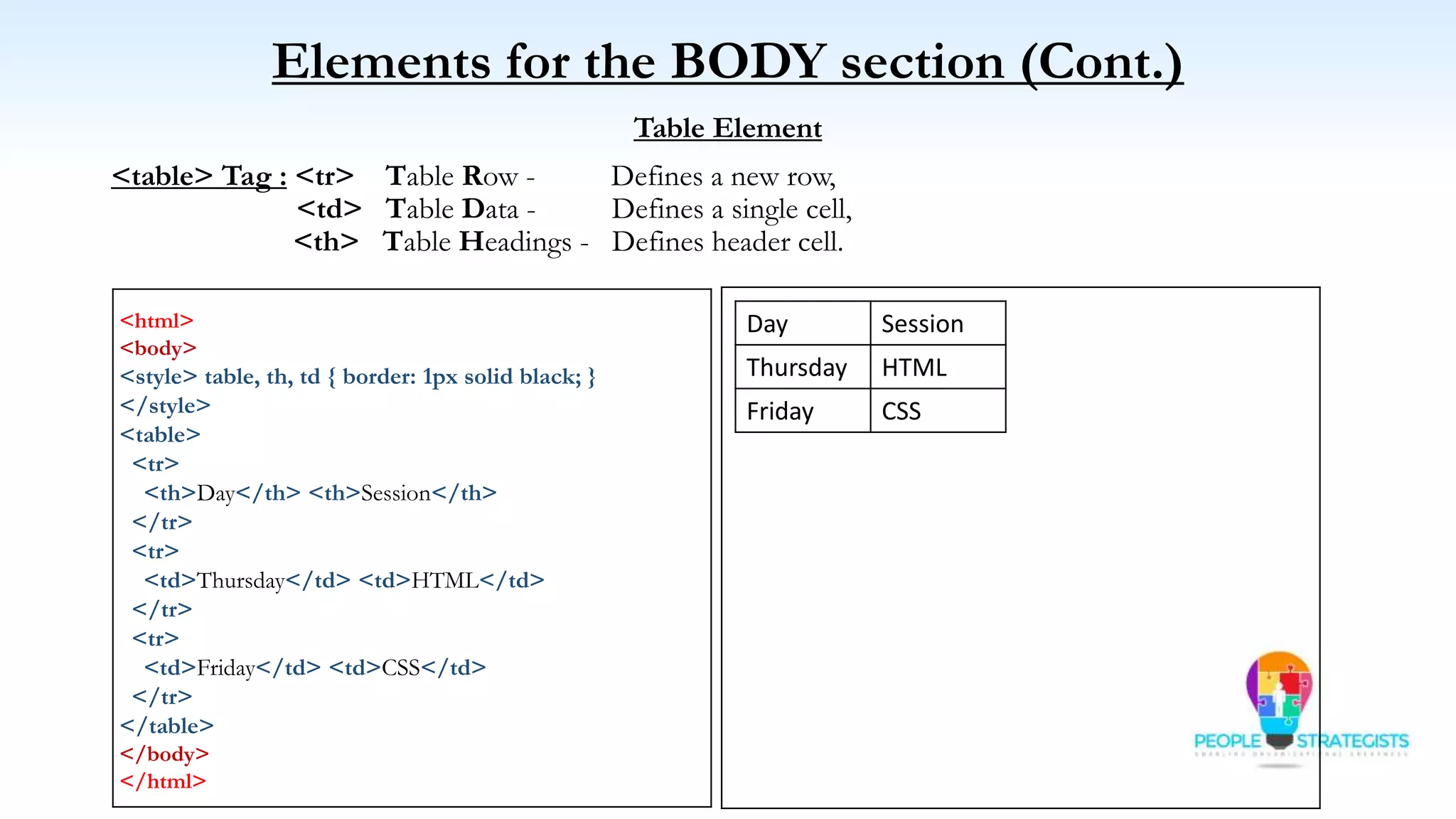
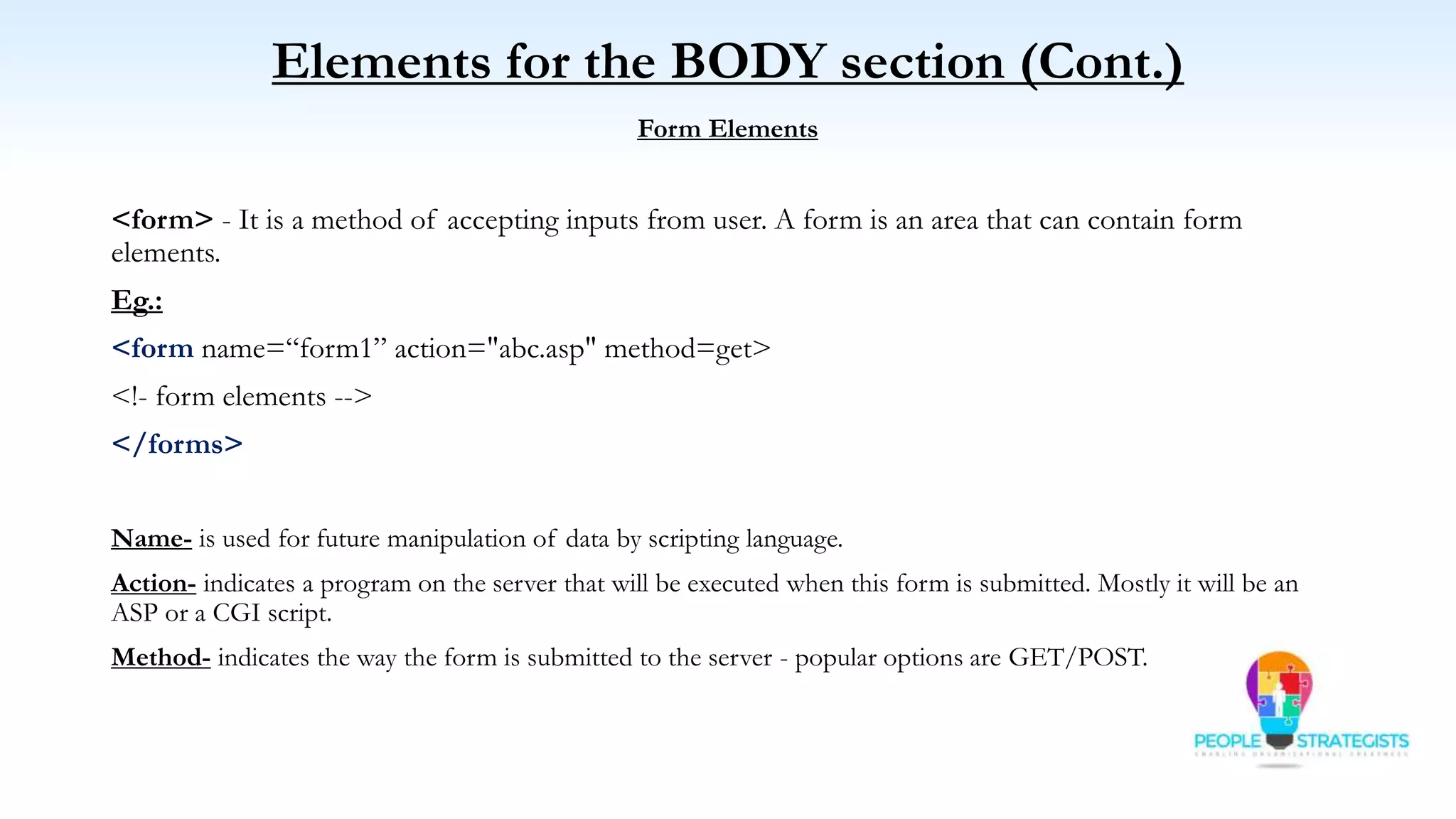
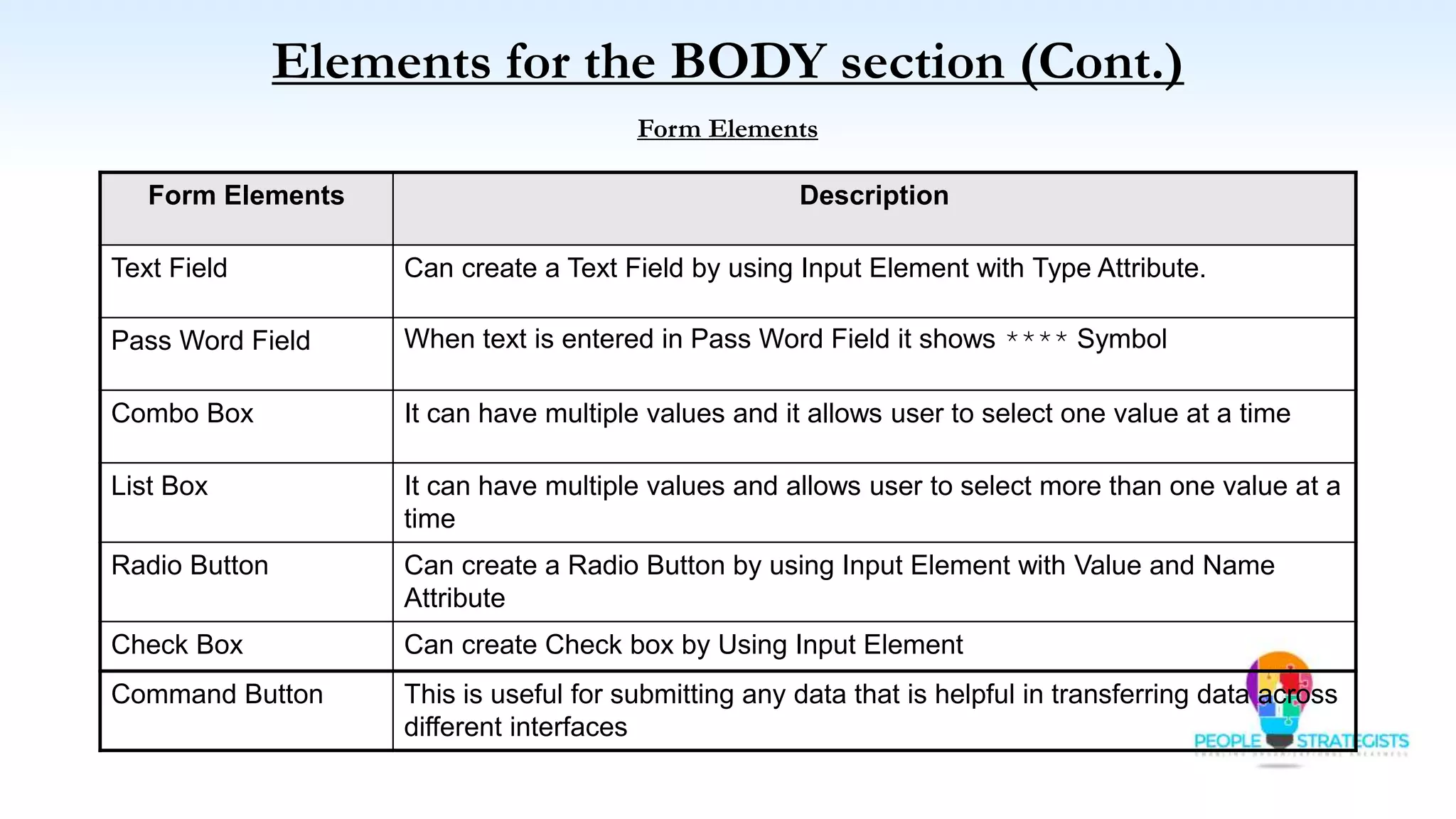
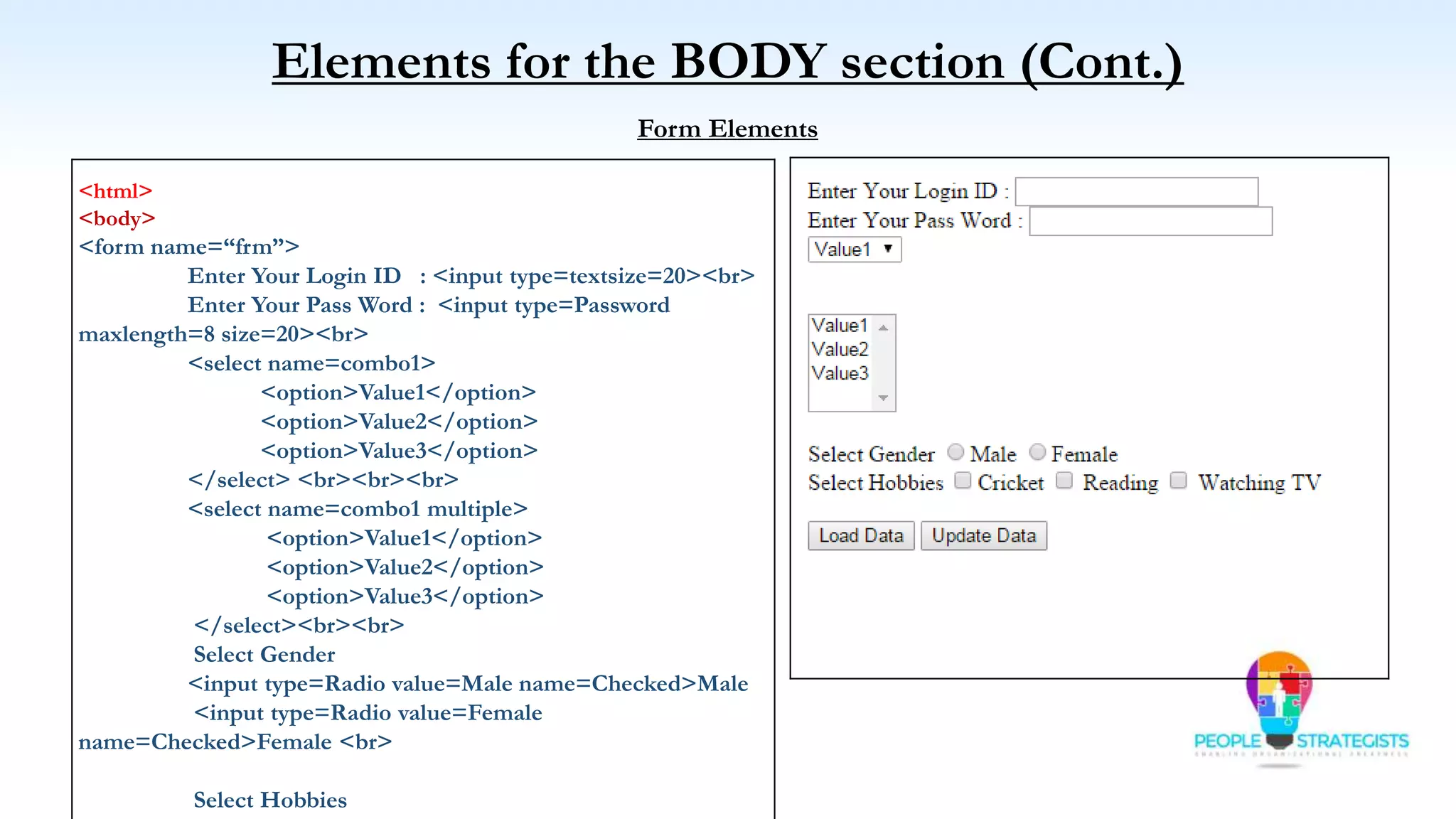
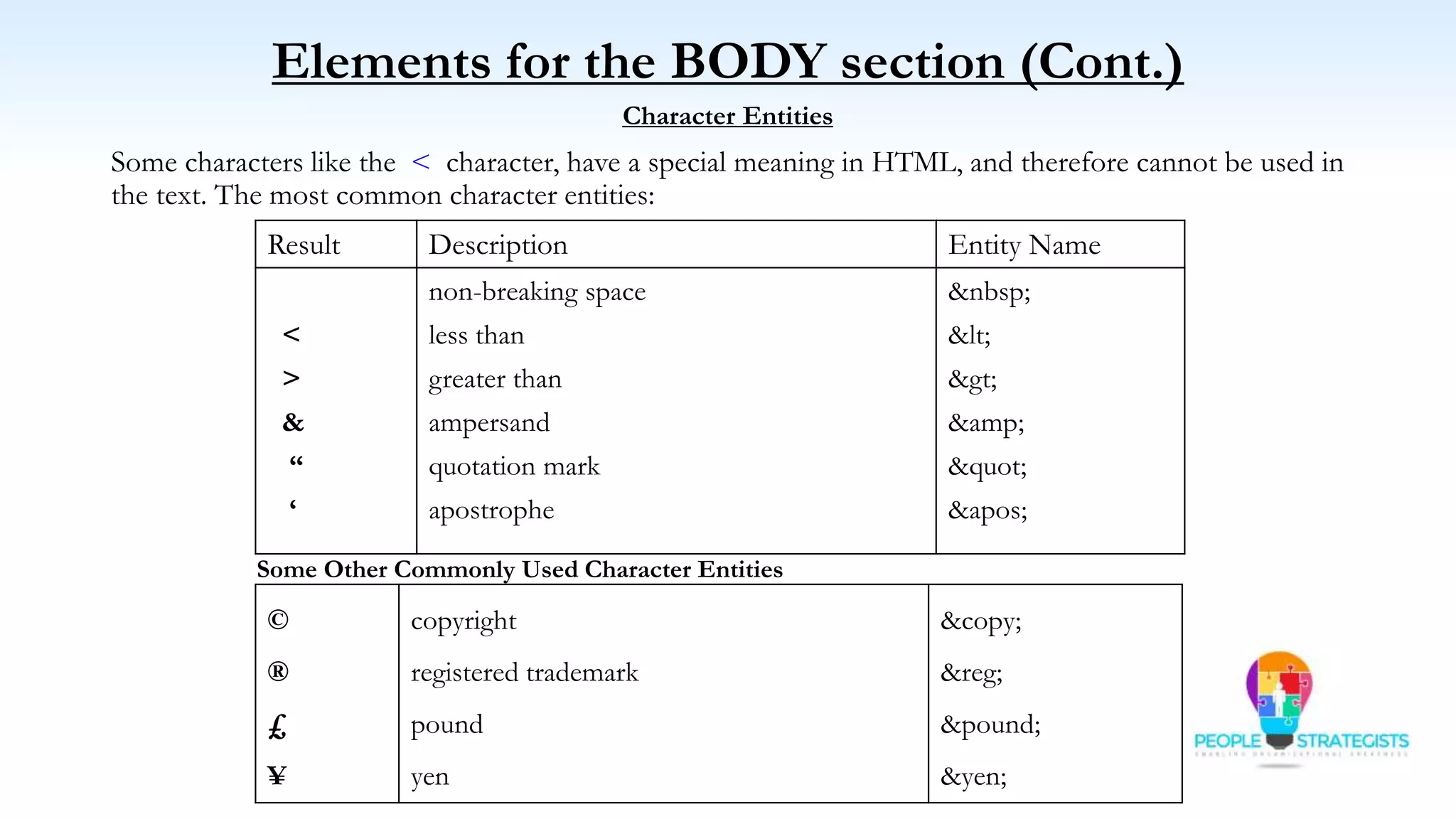
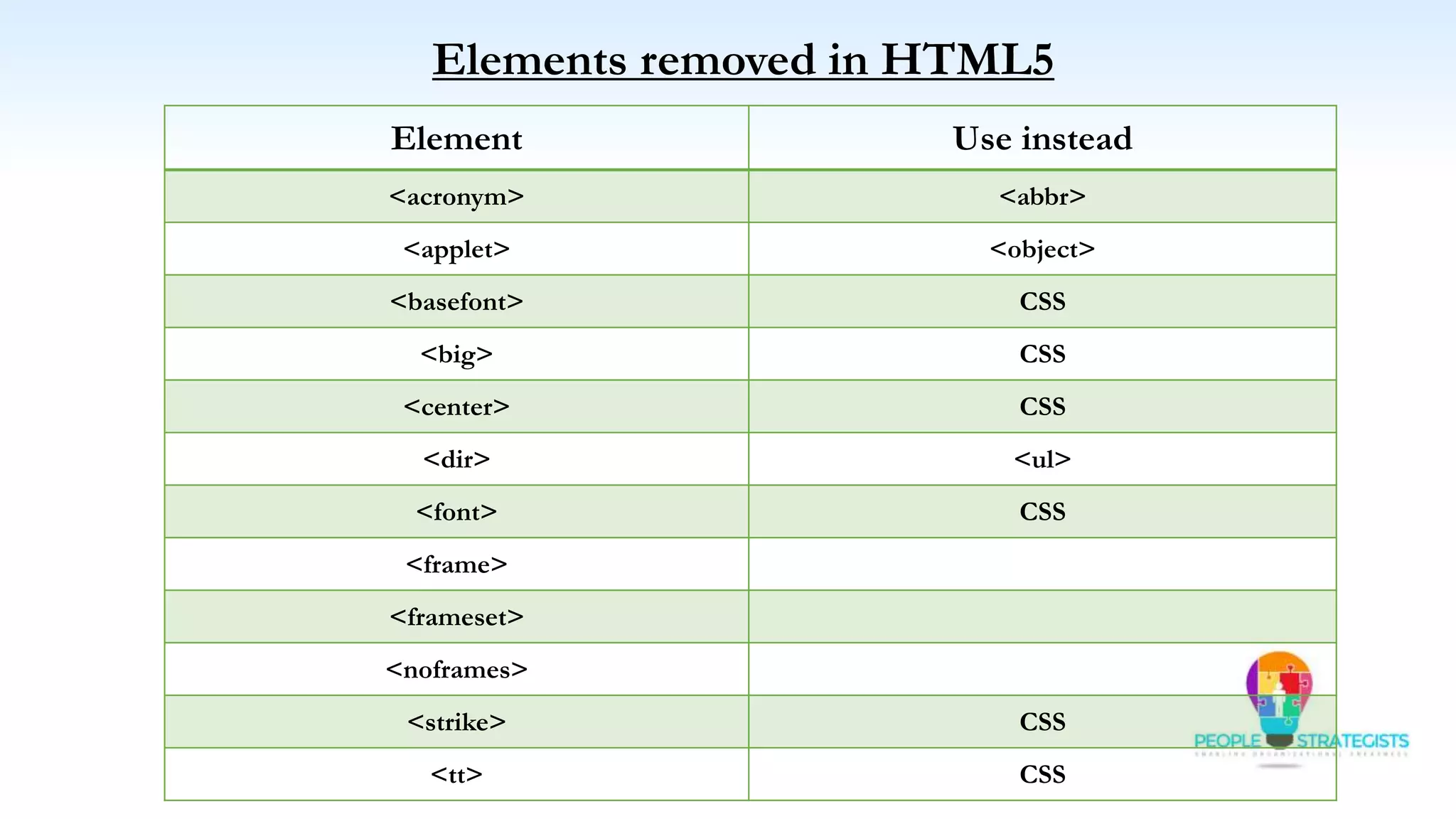
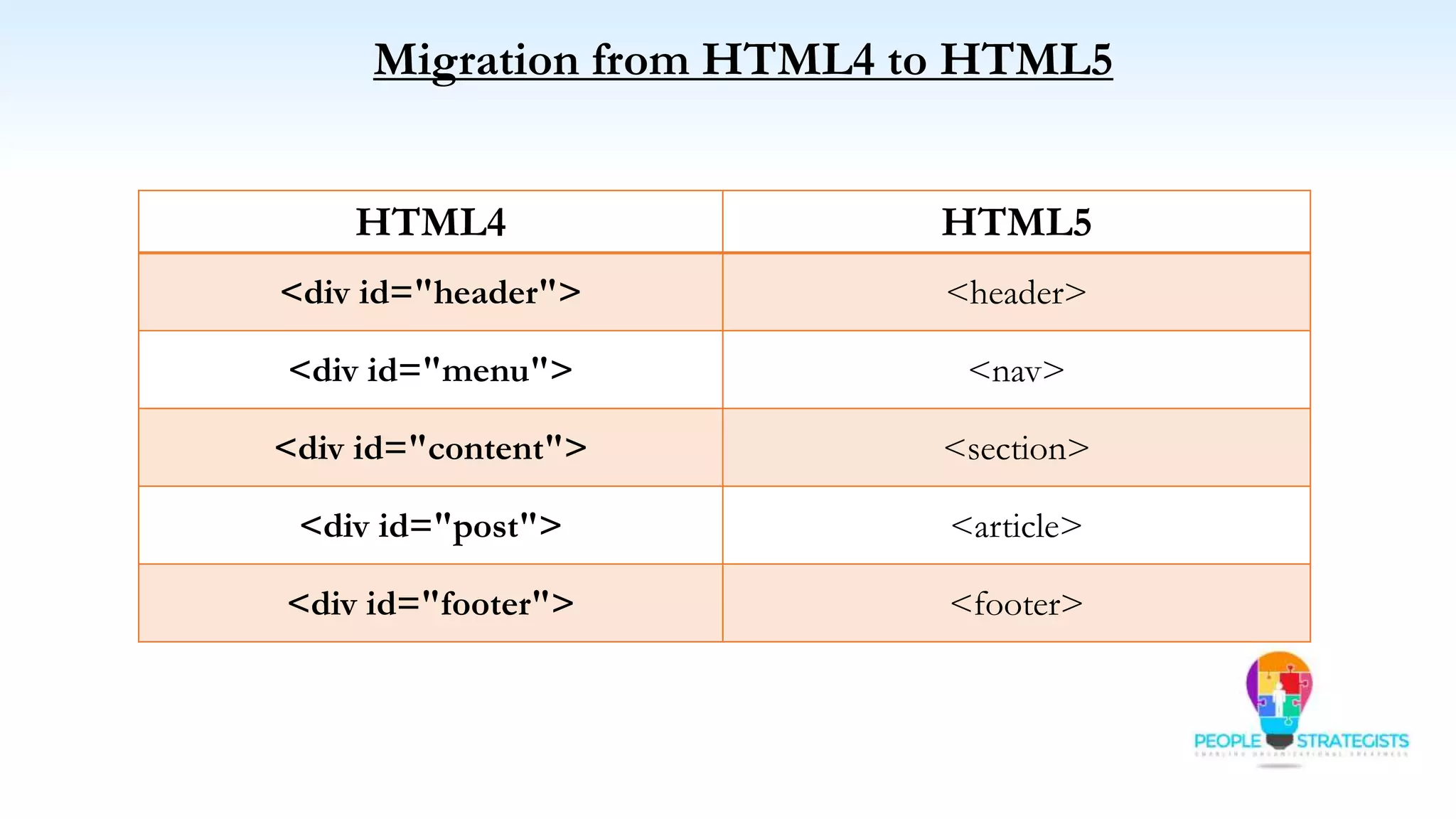
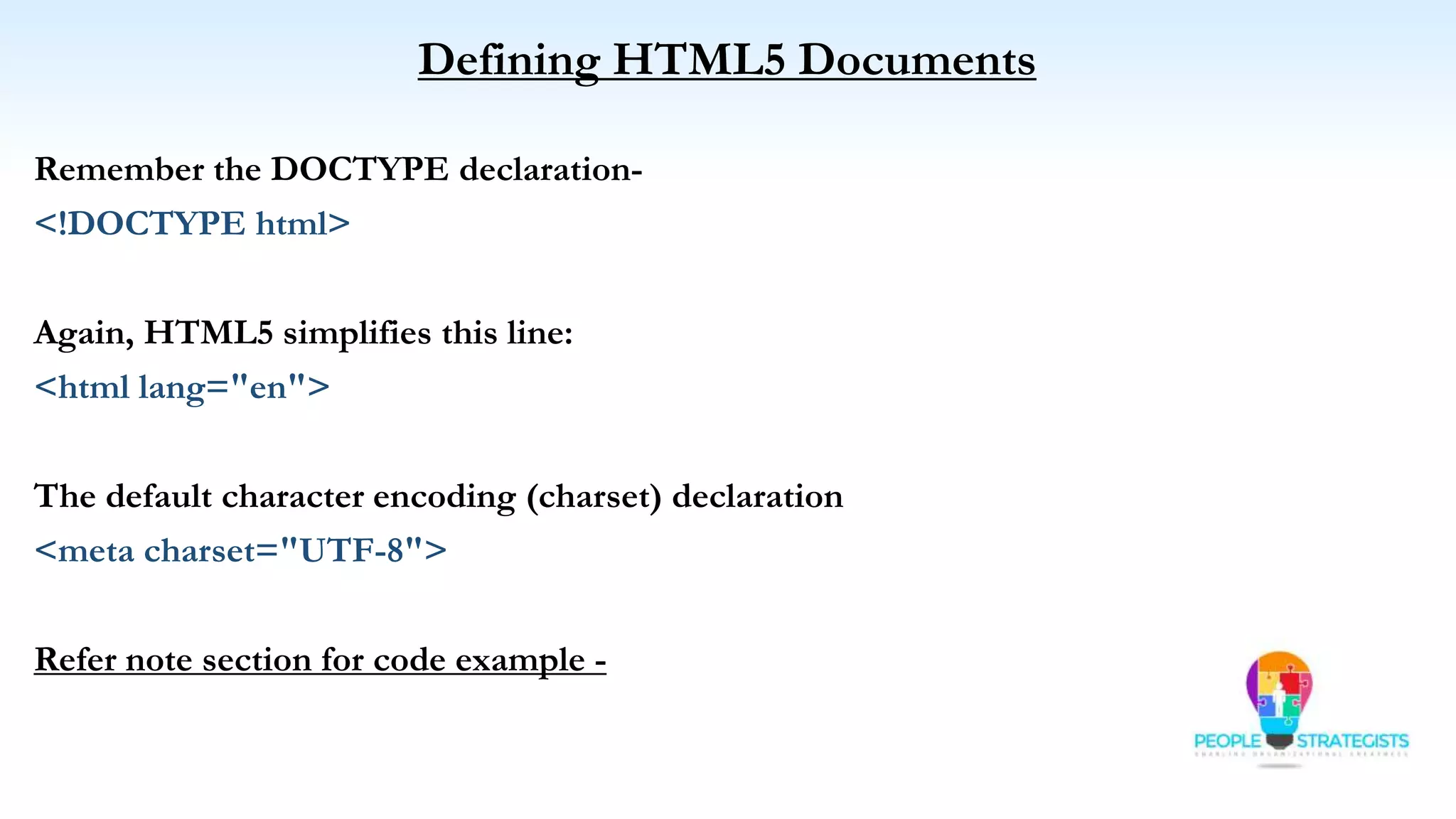
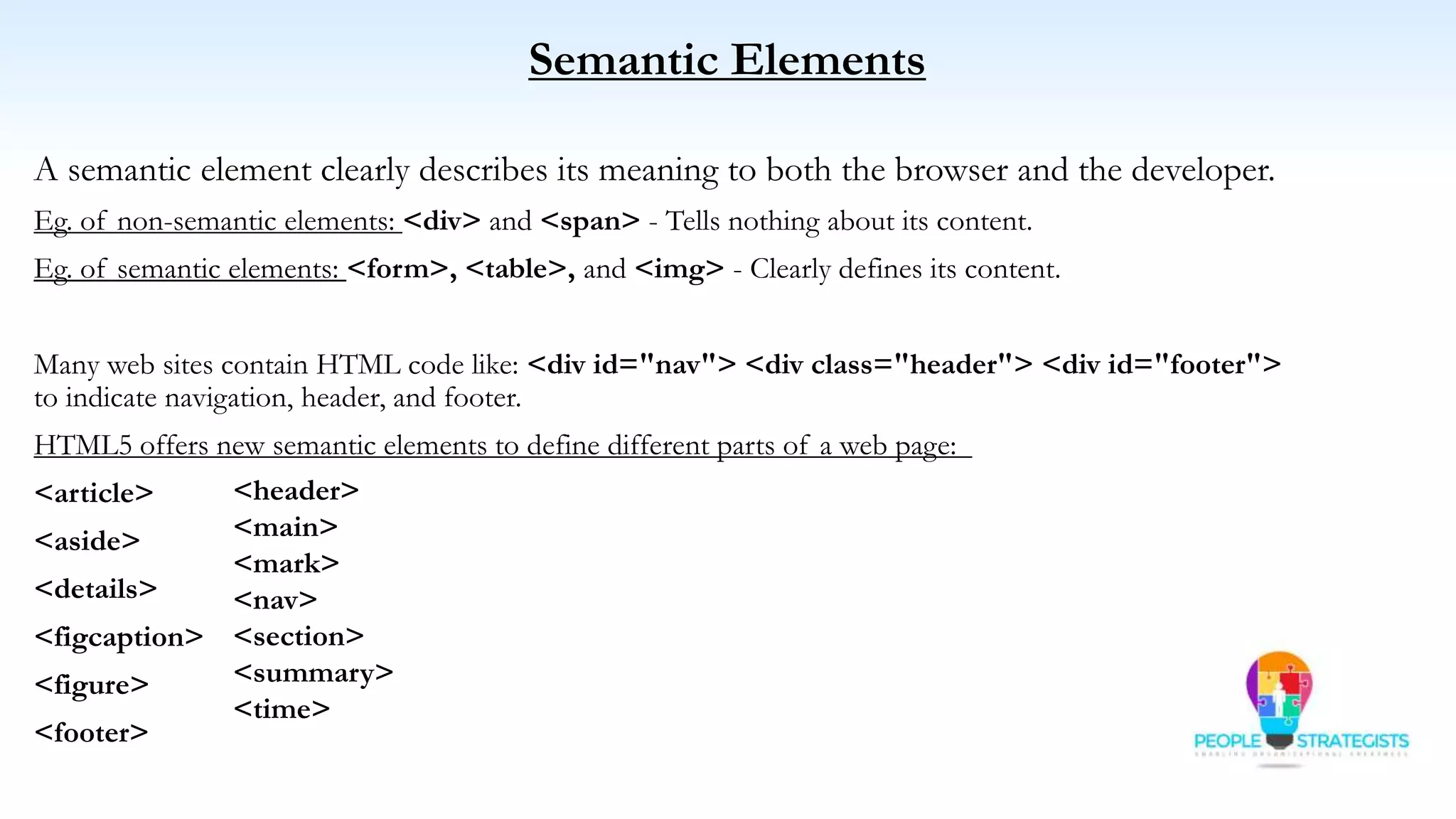
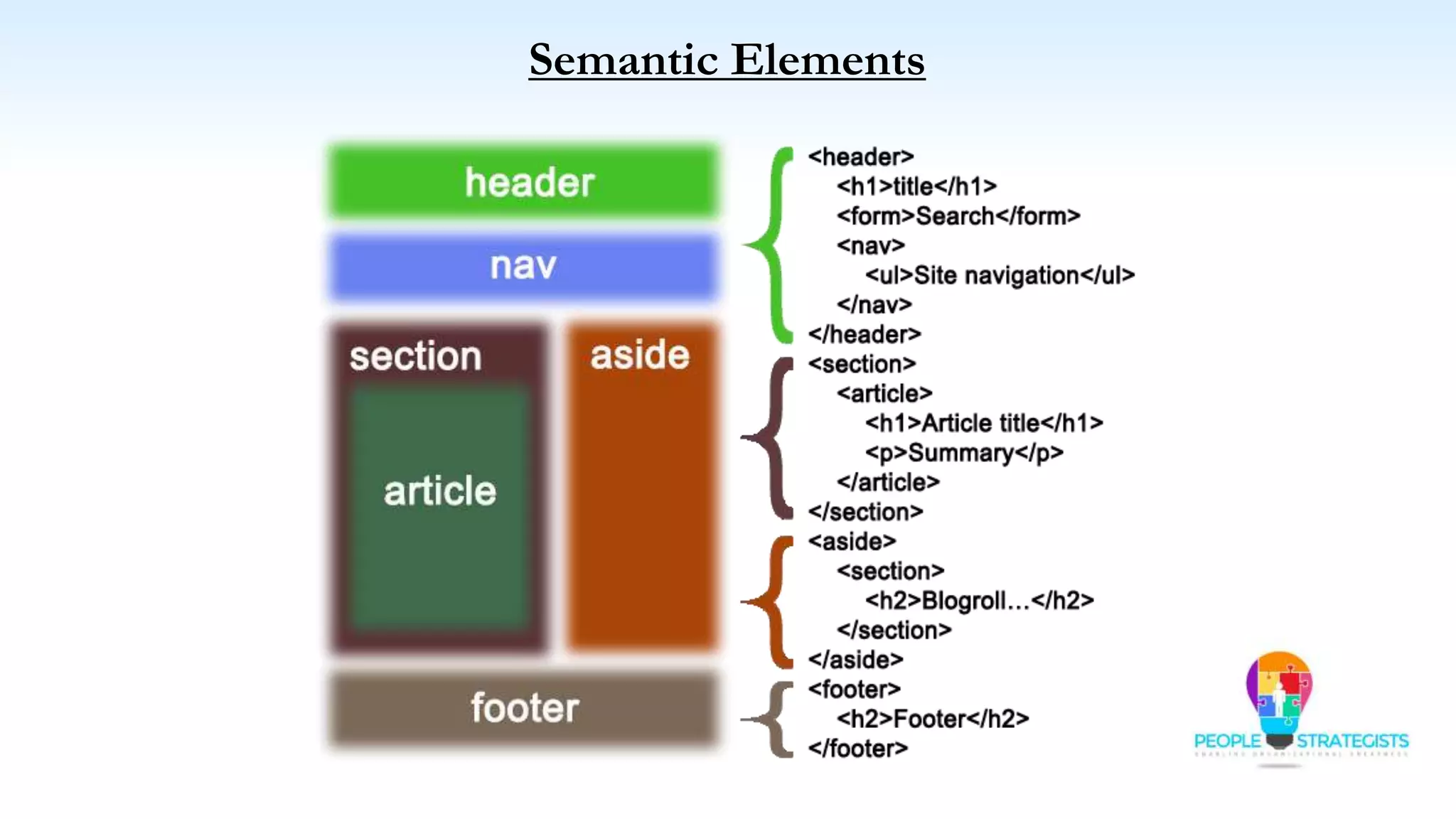
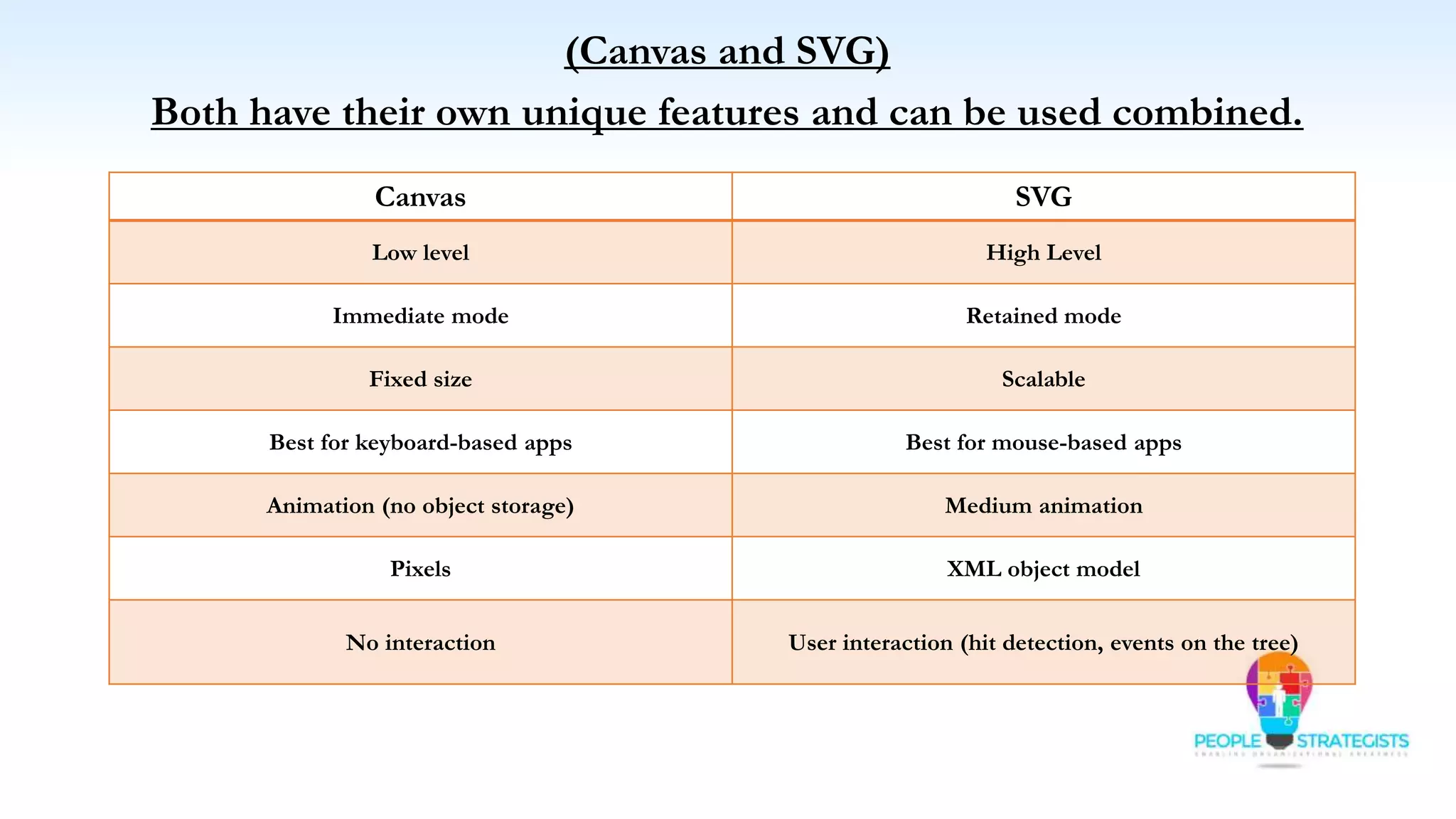
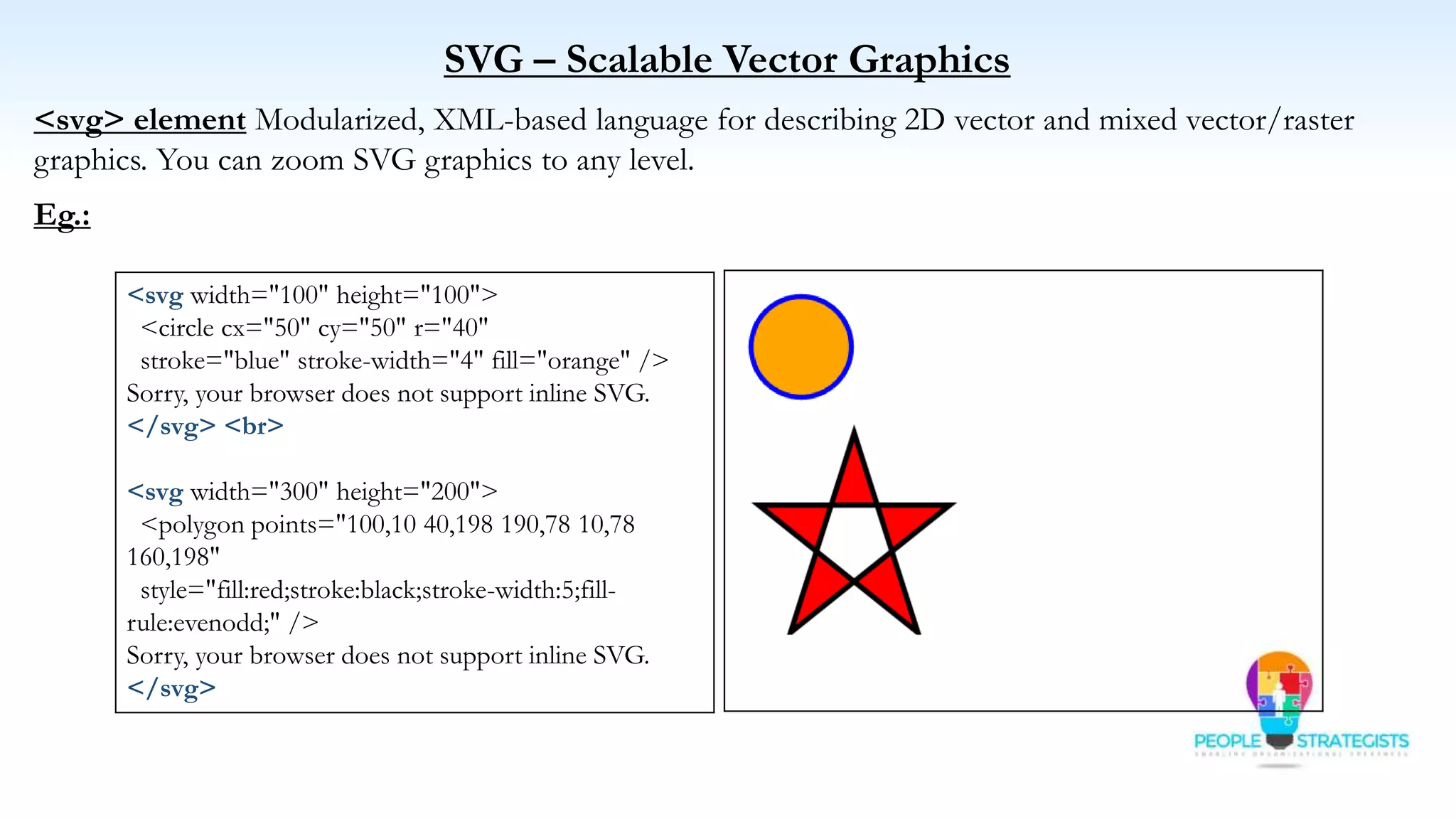
This document provides an overview of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. It discusses how HTML is used to define the structure and layout of web pages using markup tags, how CSS is used to style web pages, and how JavaScript can be used to add interactive elements. It also covers common HTML tags for headings, paragraphs, lists, and other content sections. Key elements like <head> and <body> are explained along with common tags used in each section.