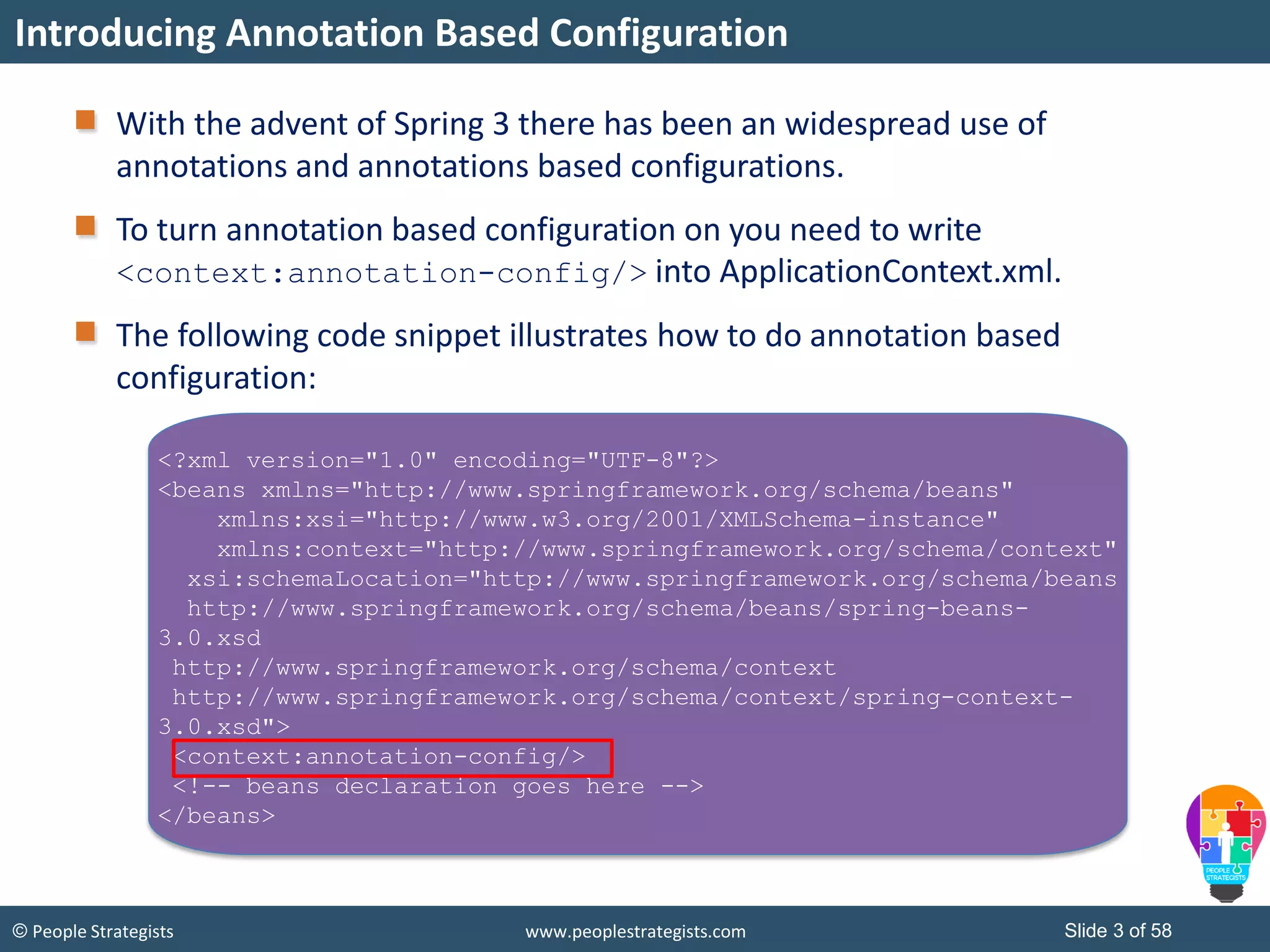
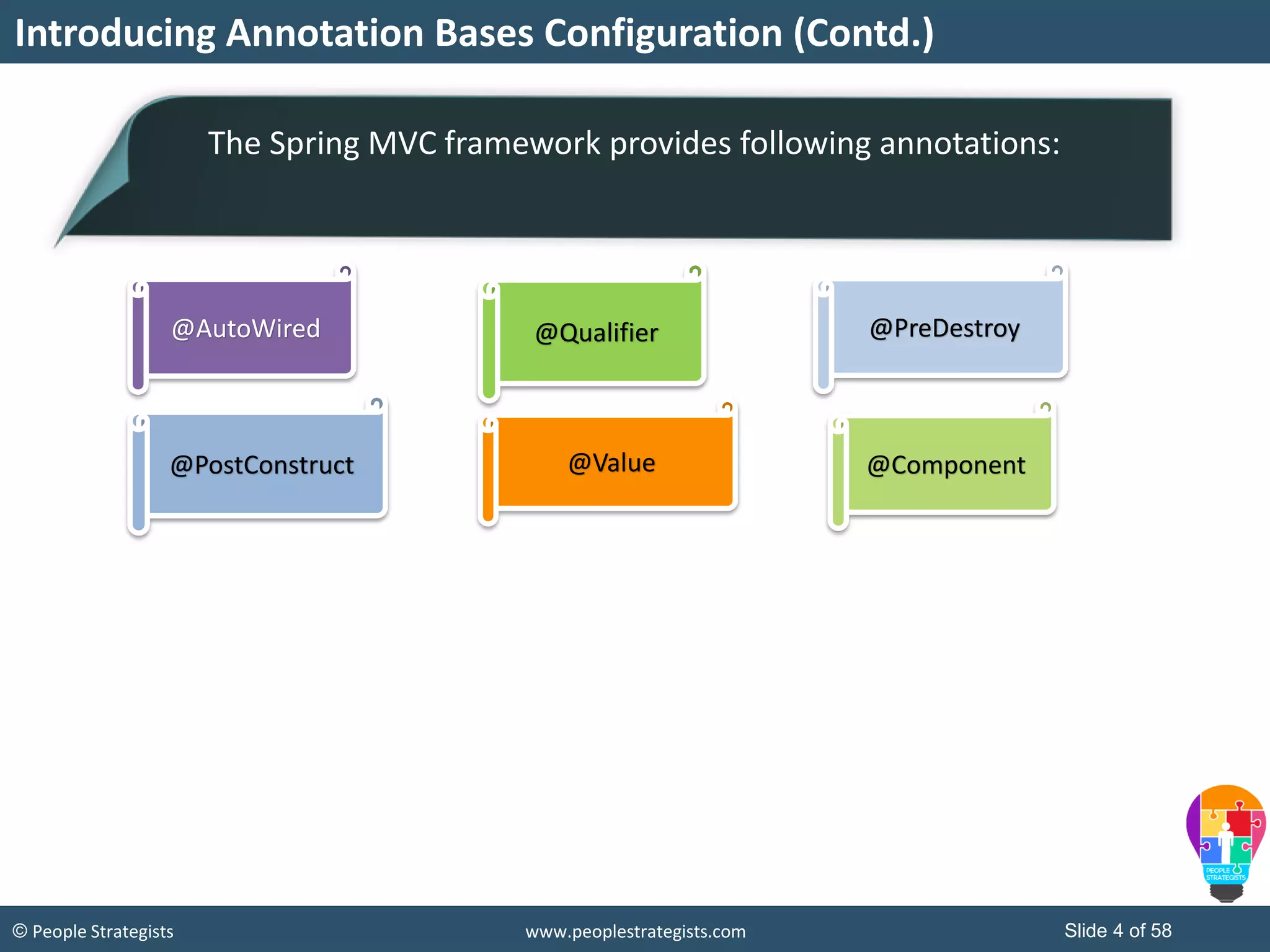
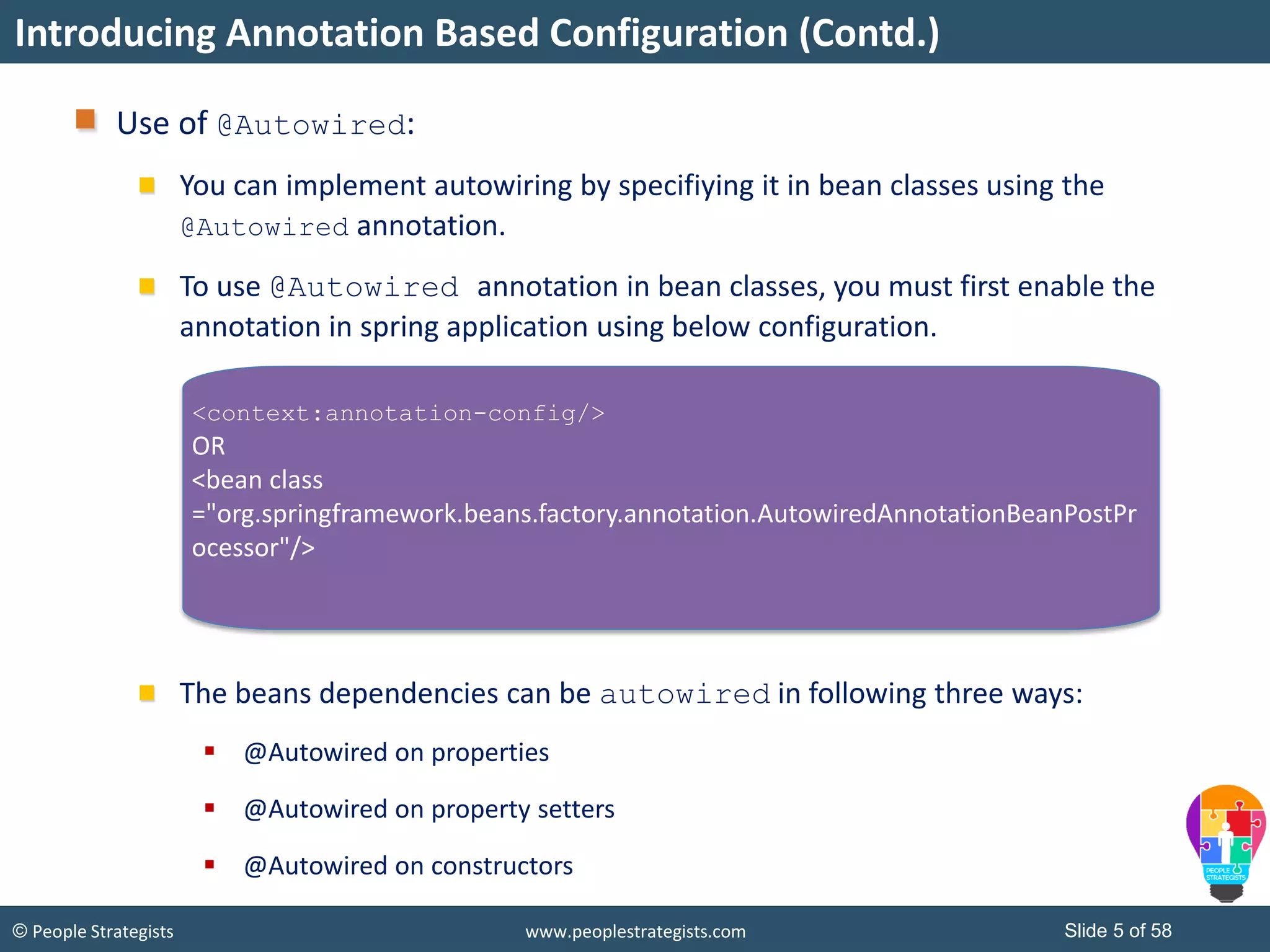
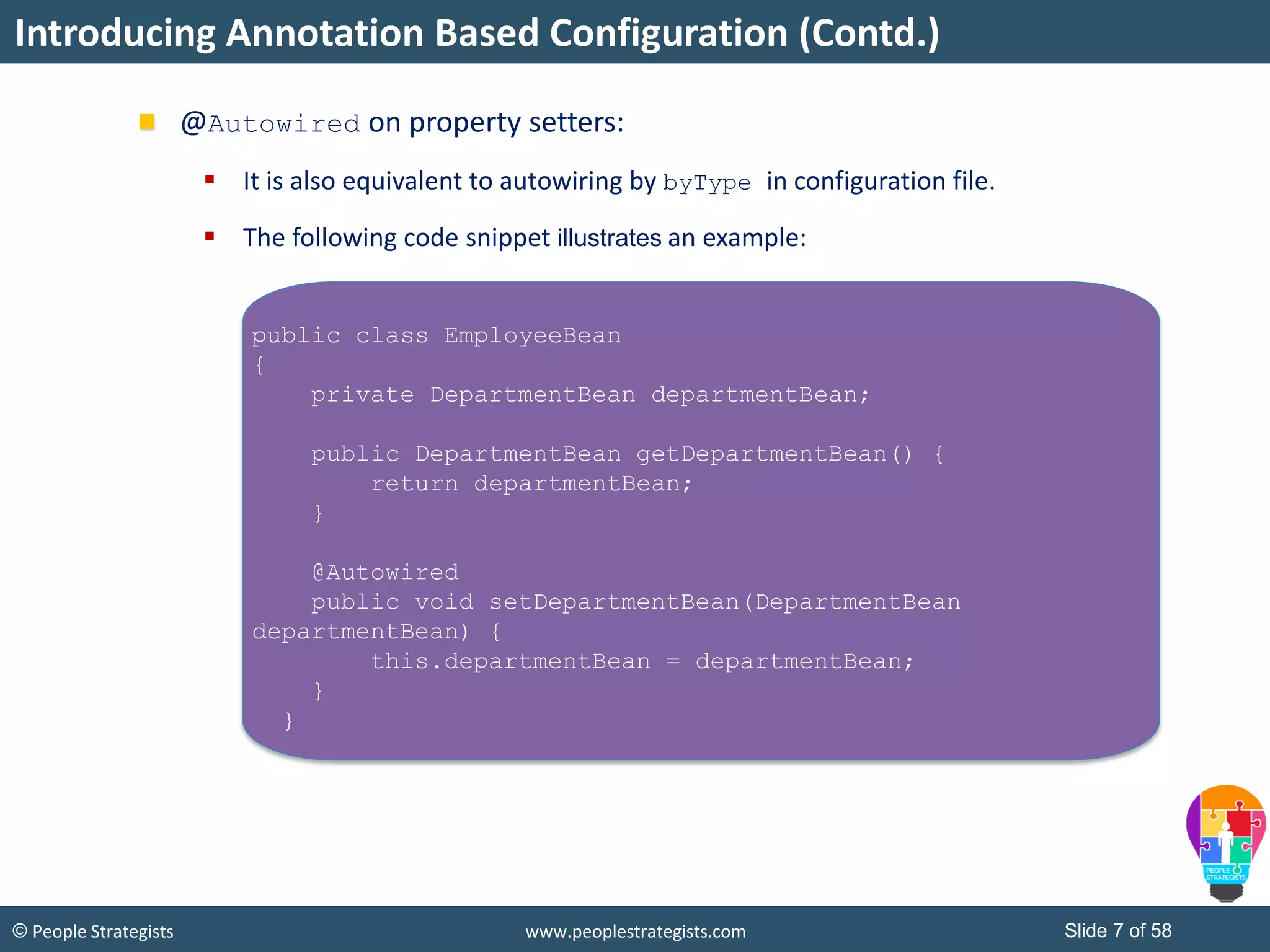
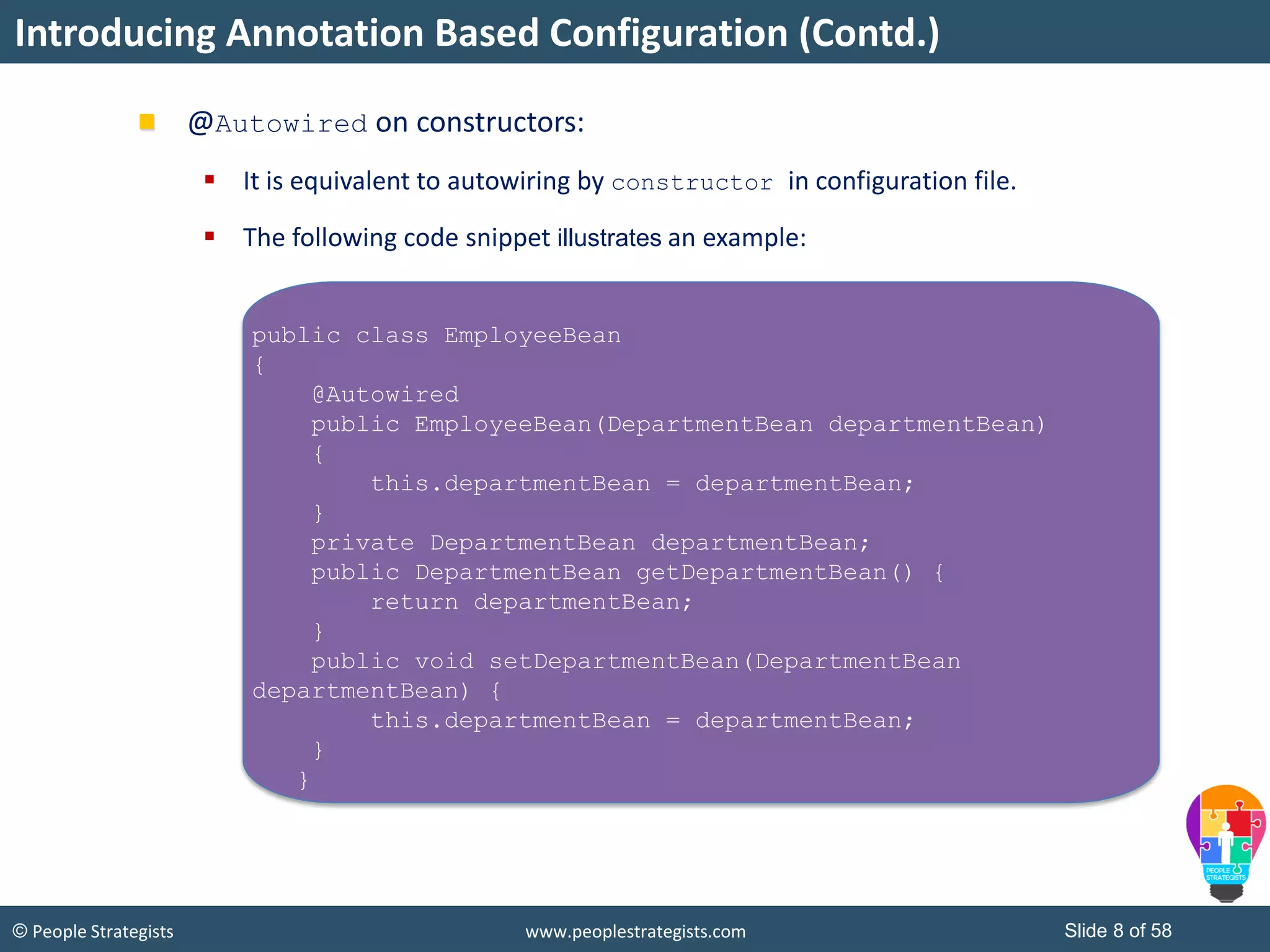
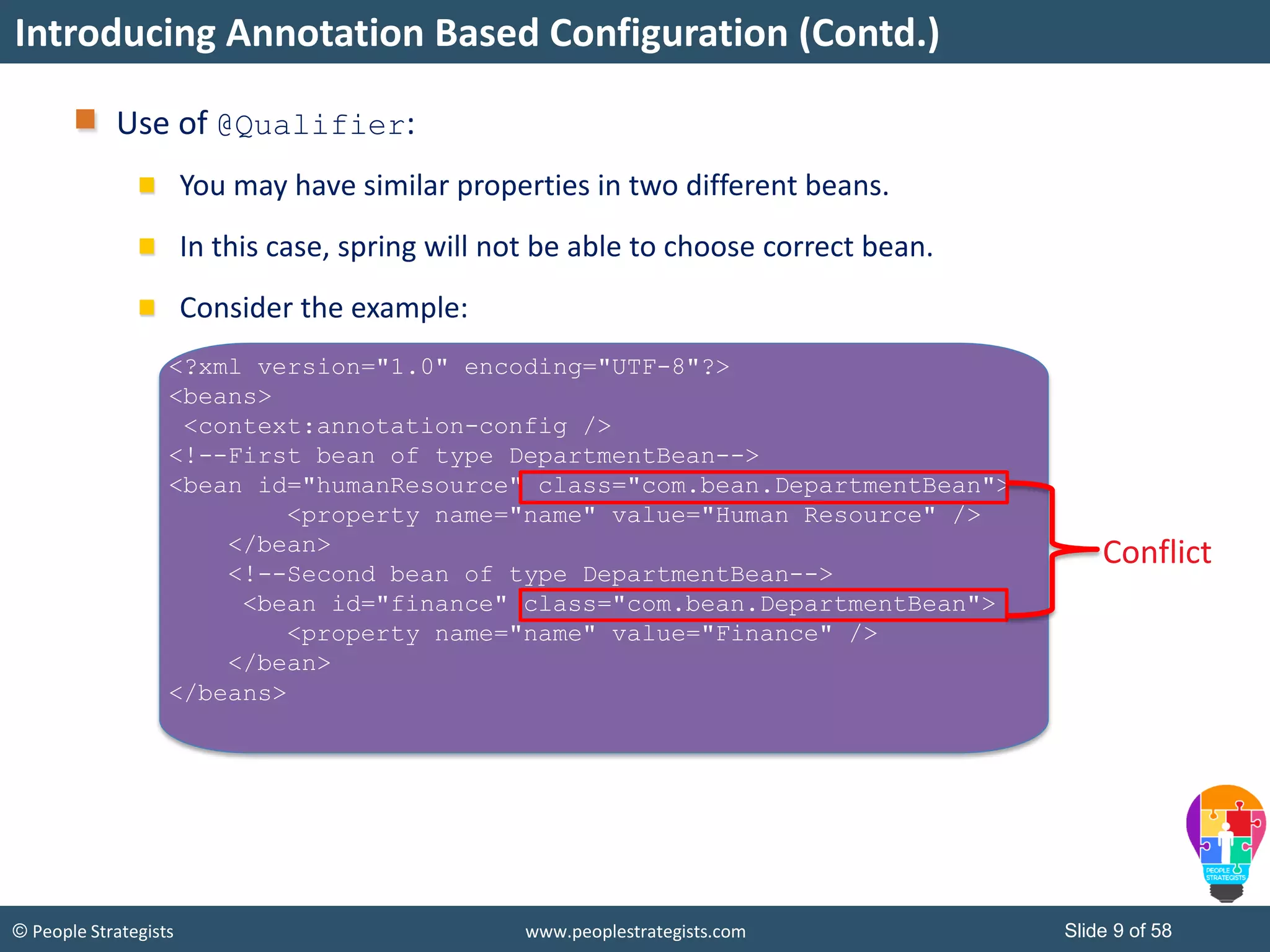
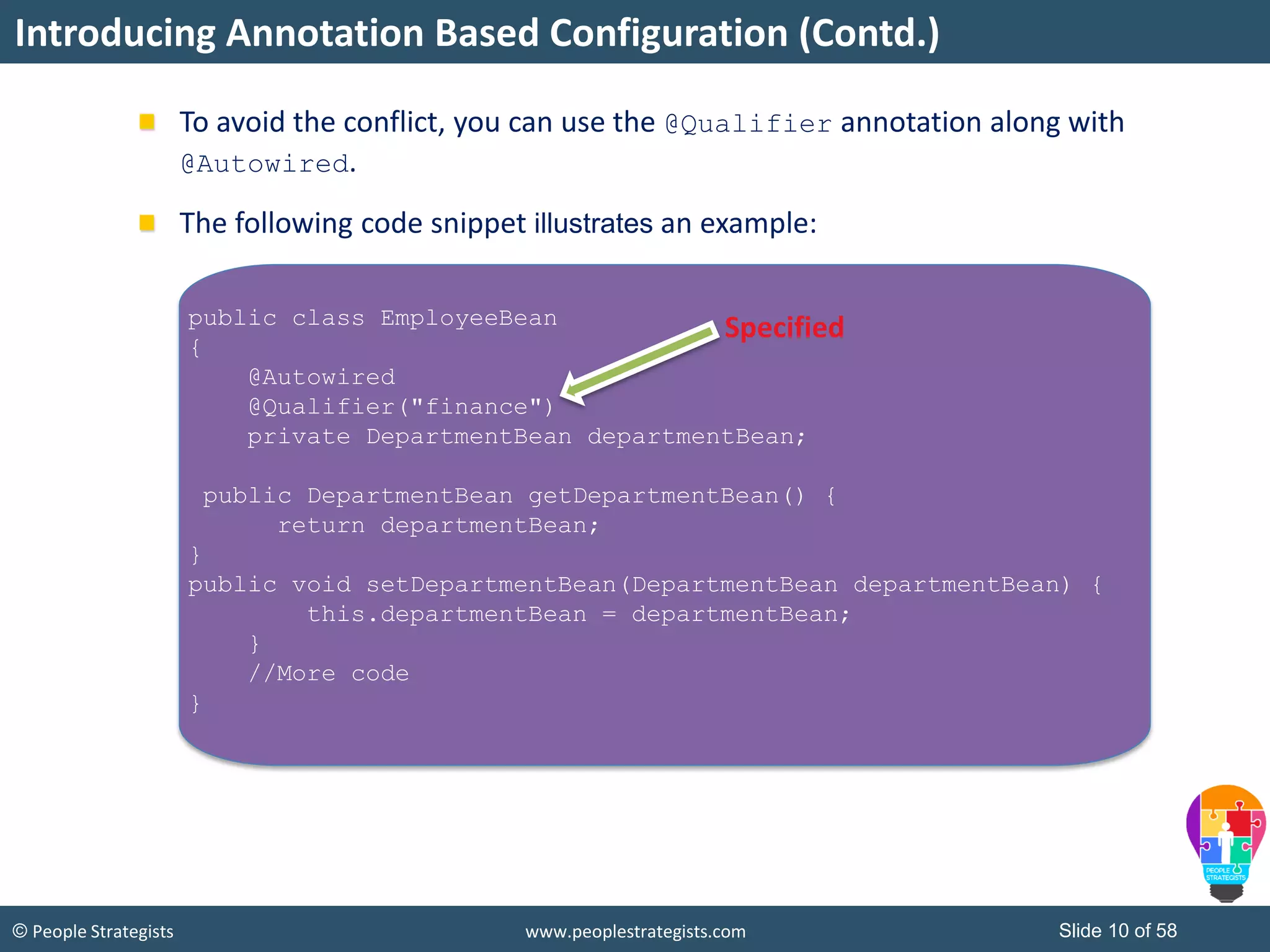
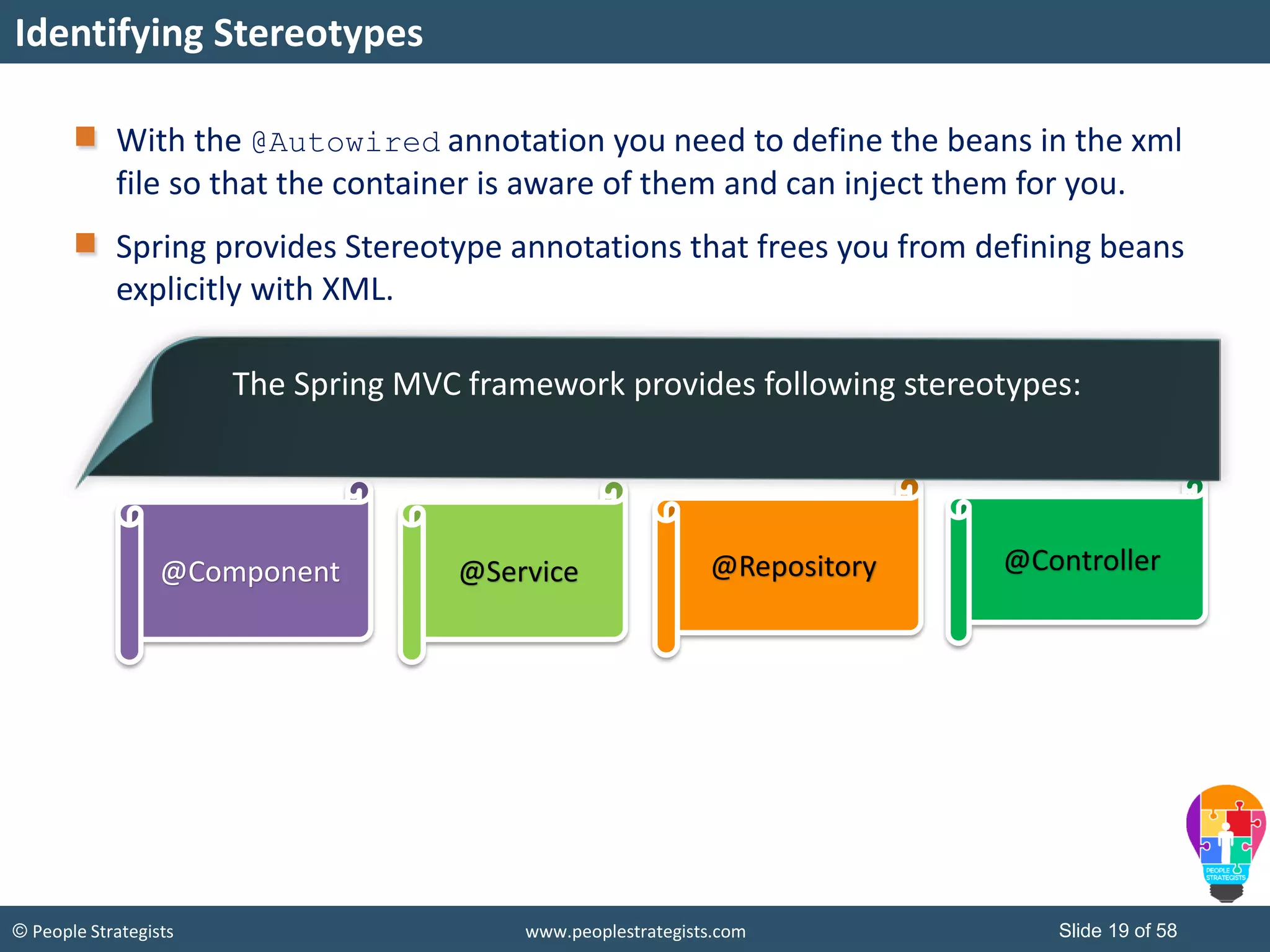
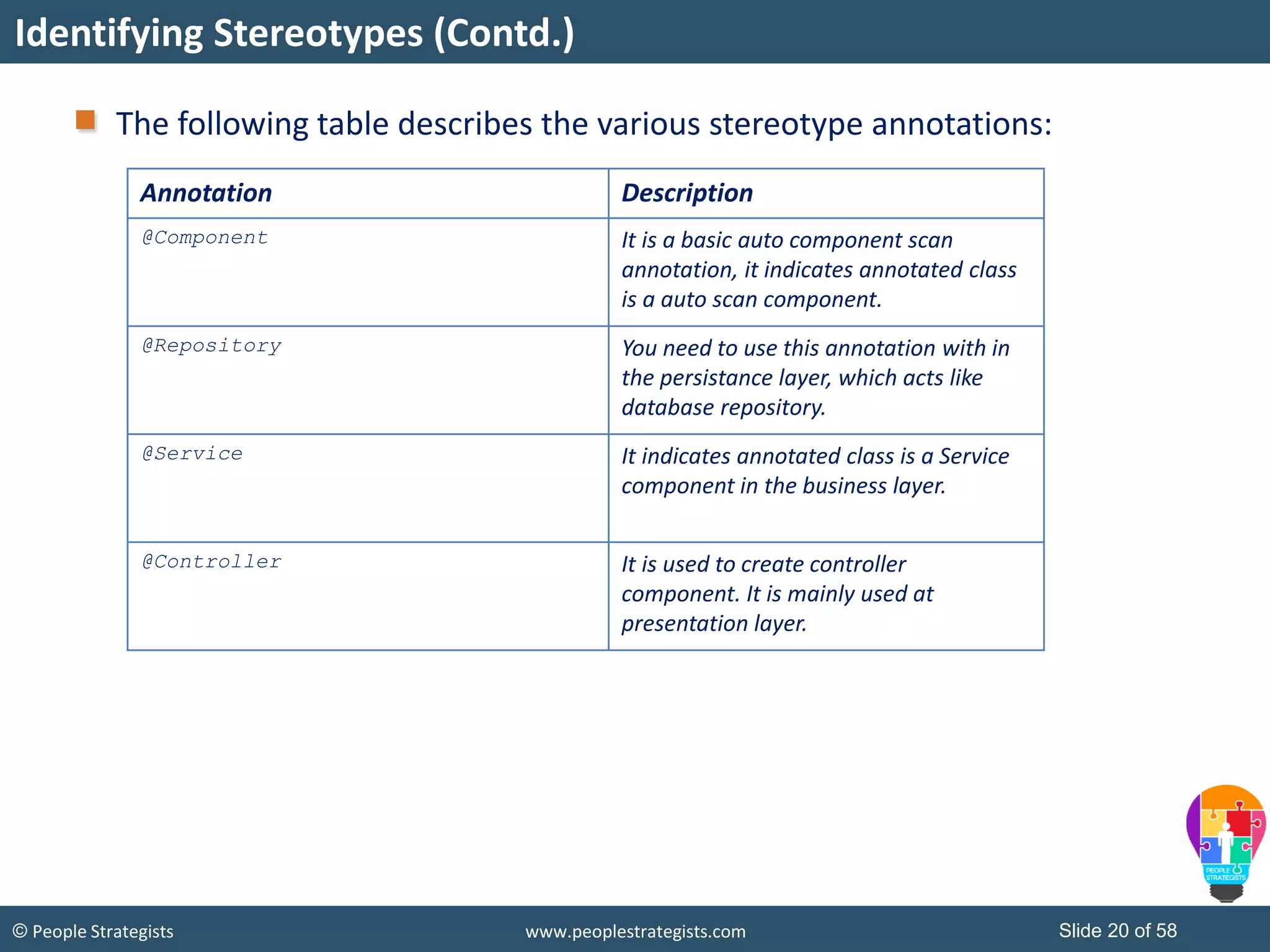
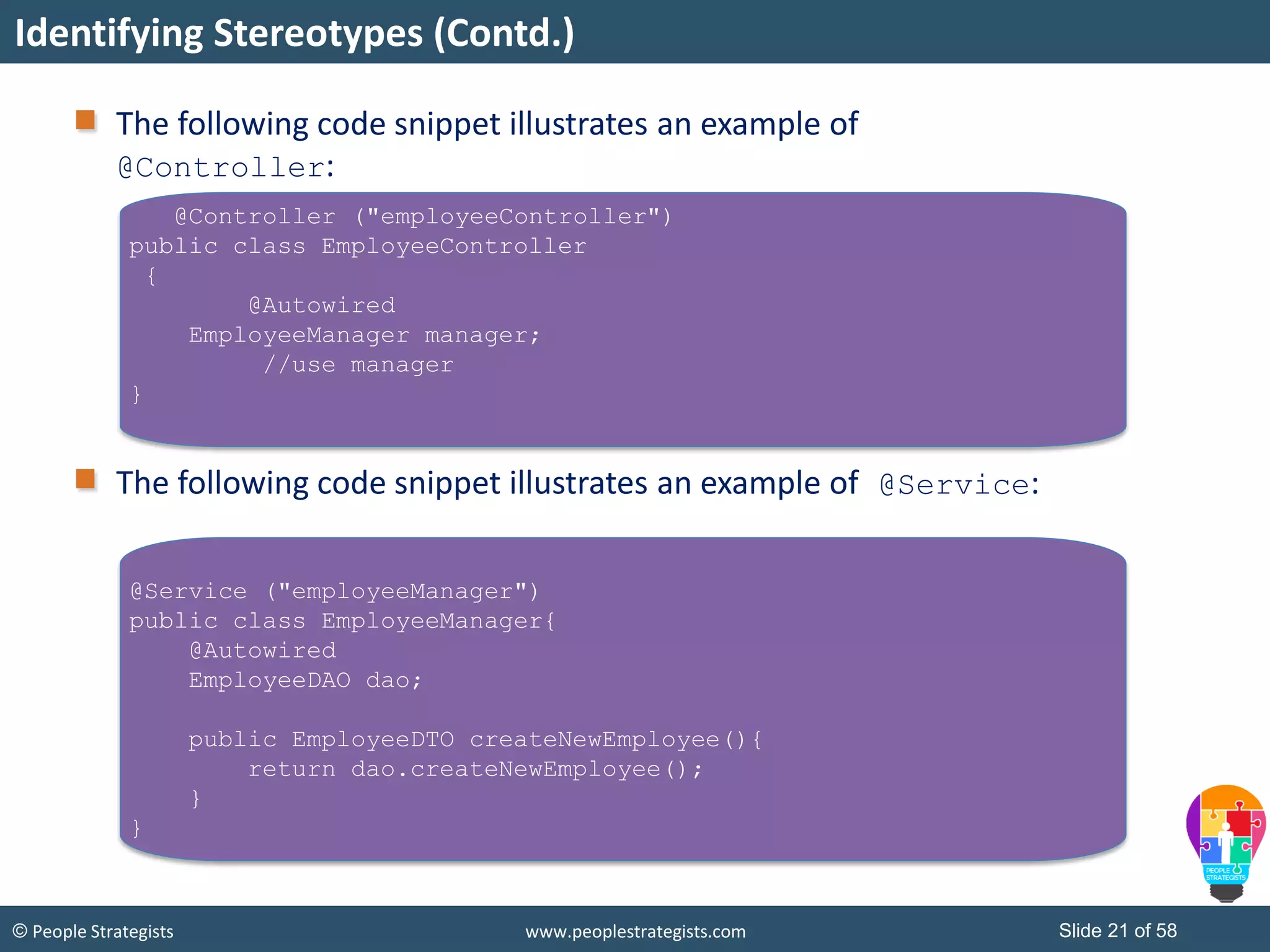
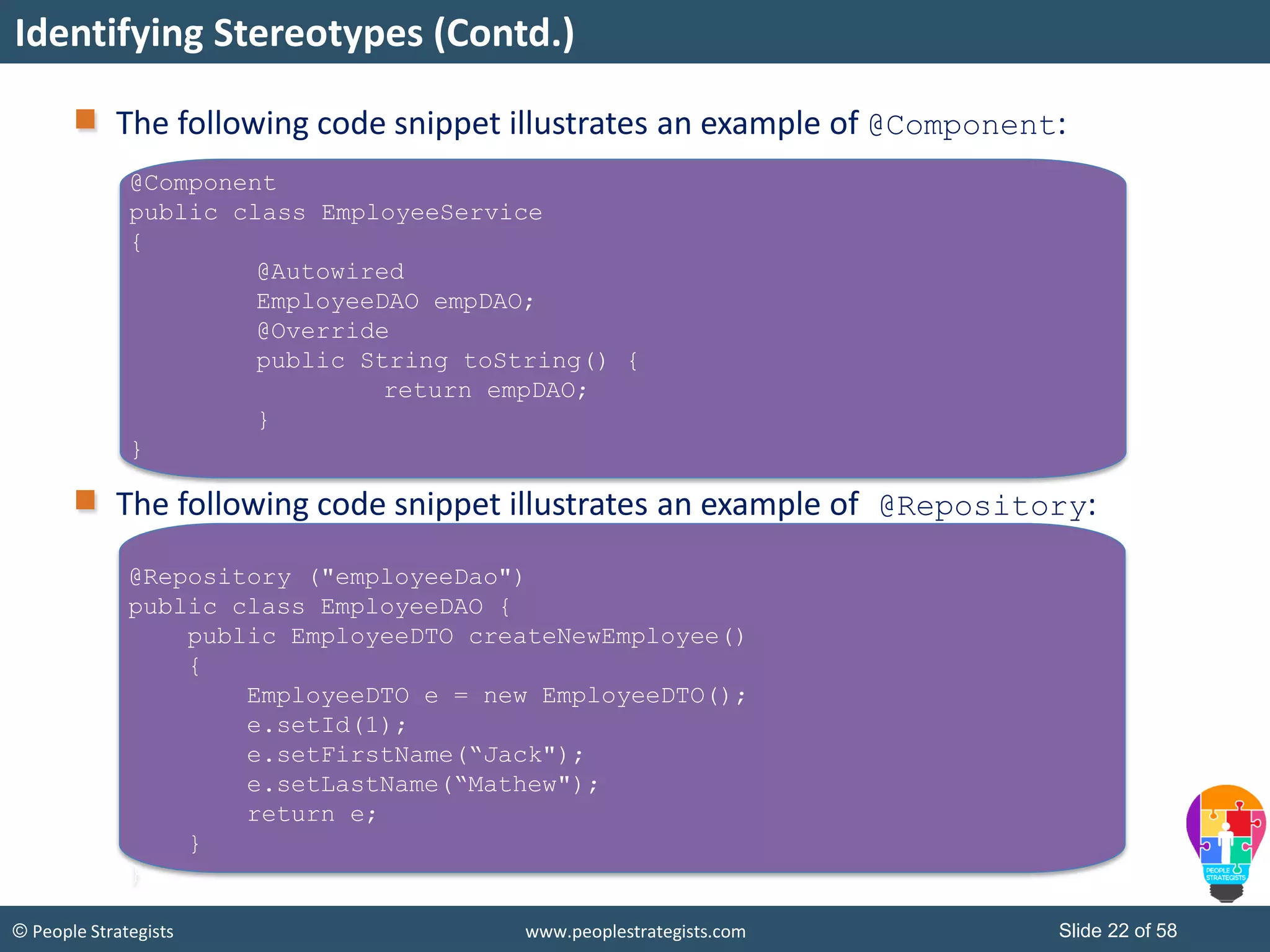
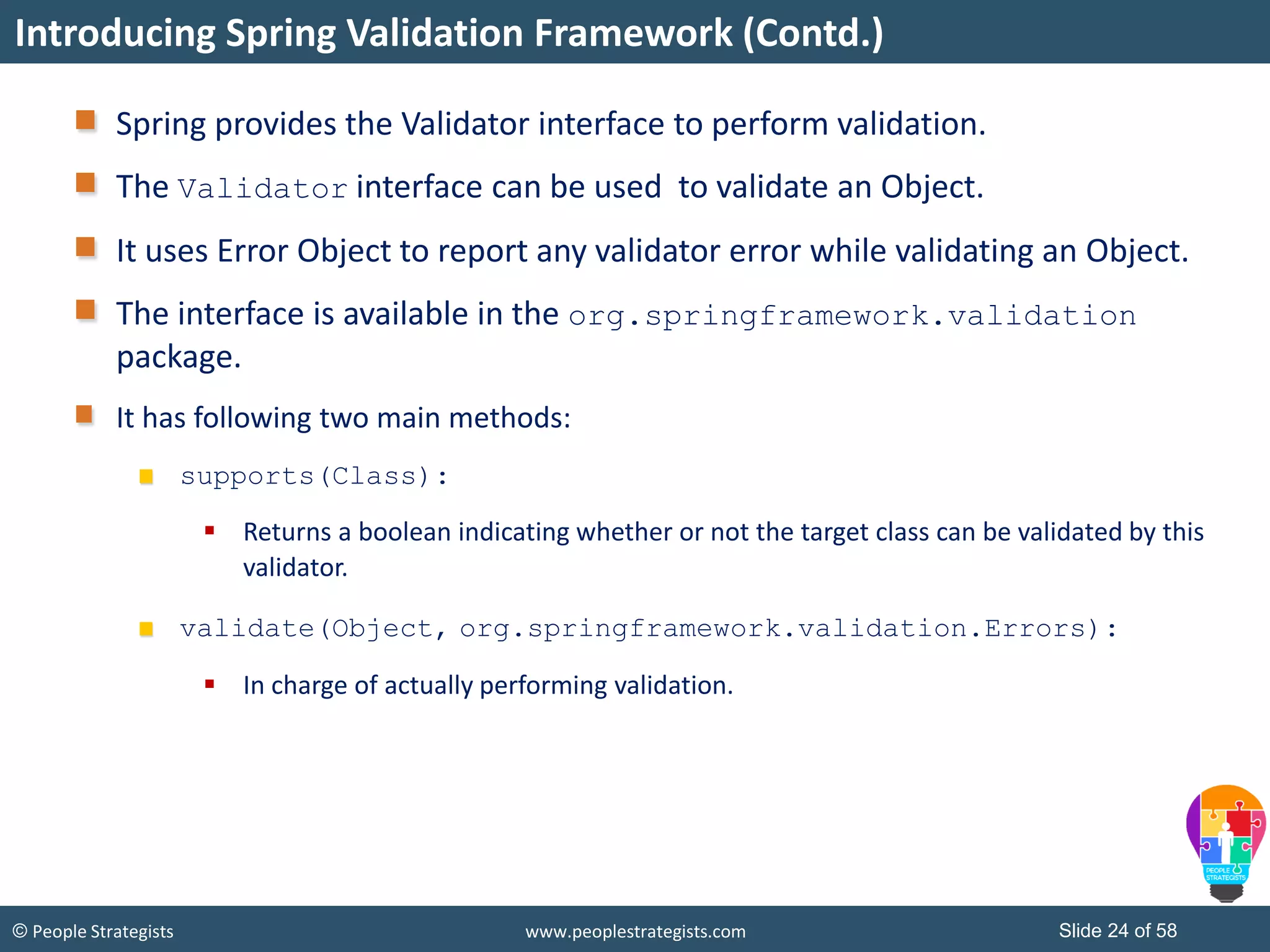
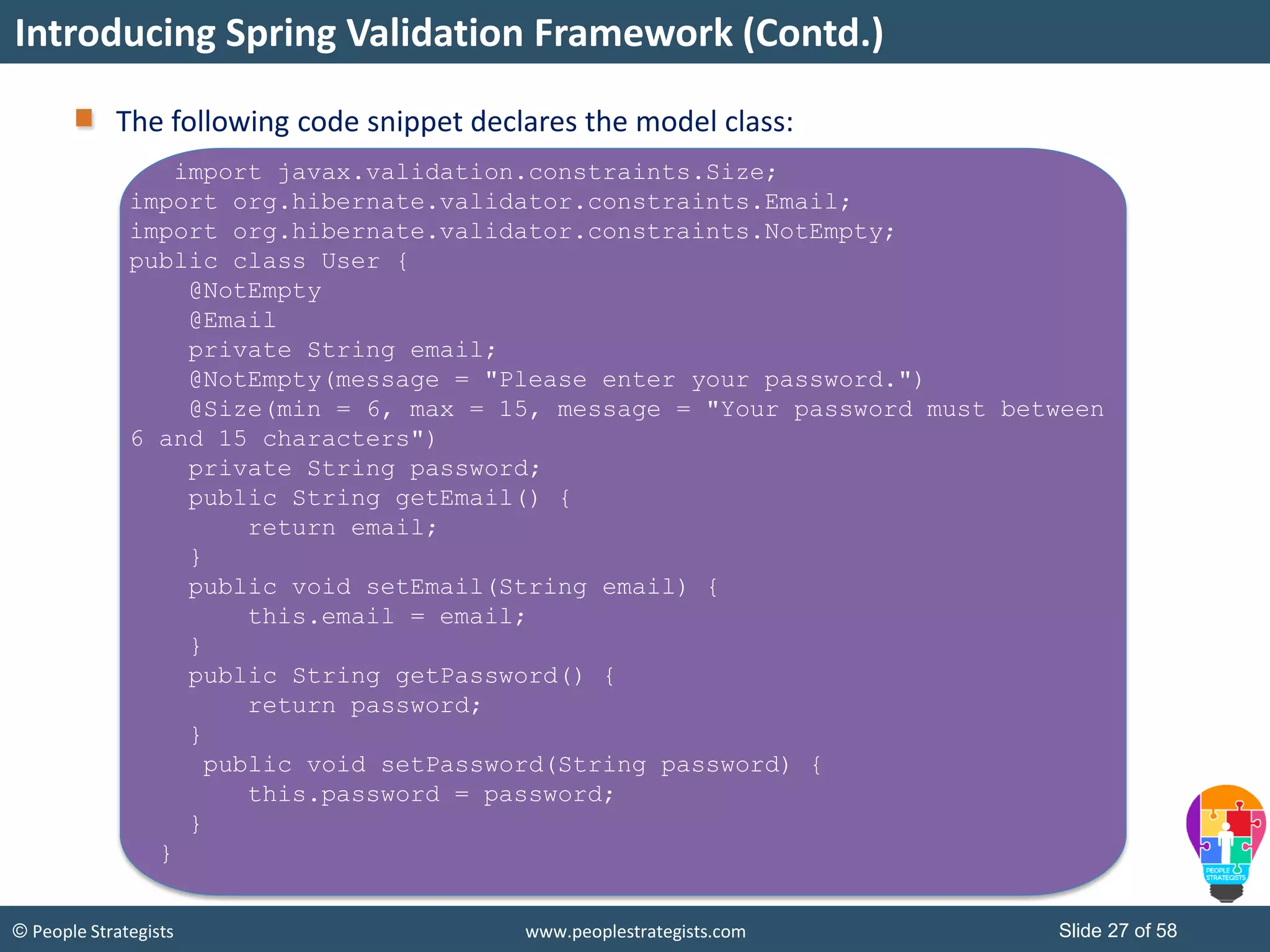
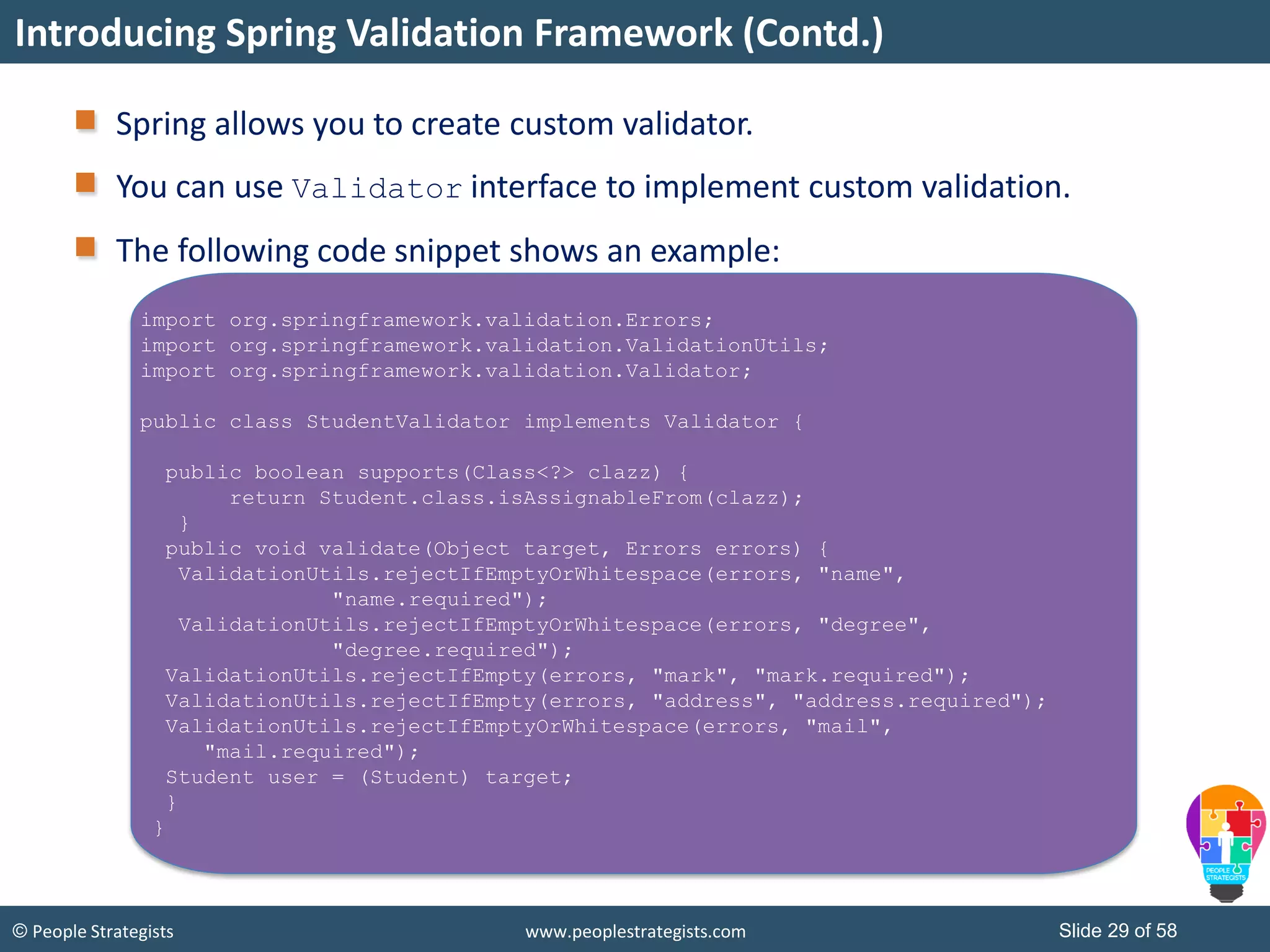
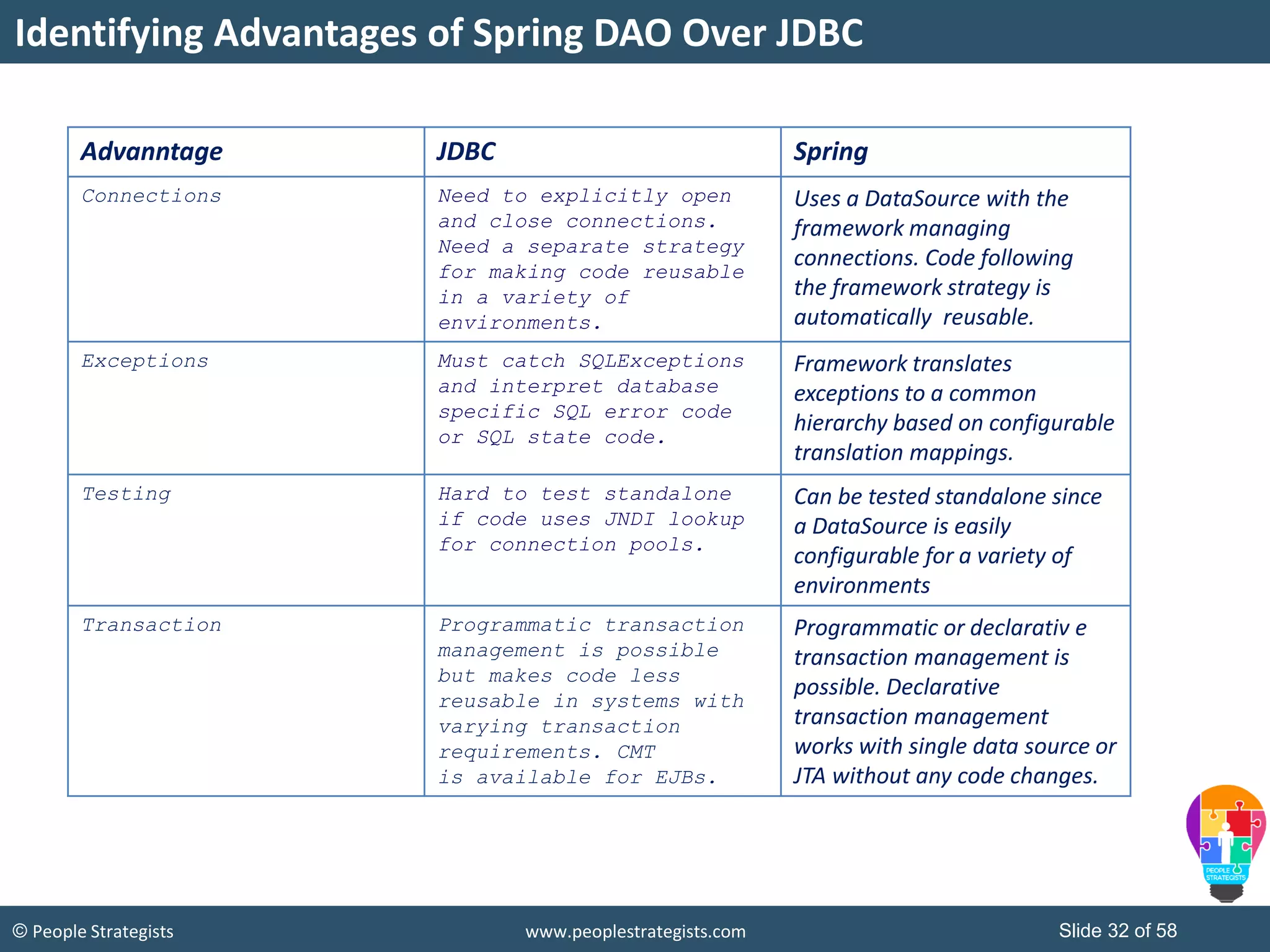
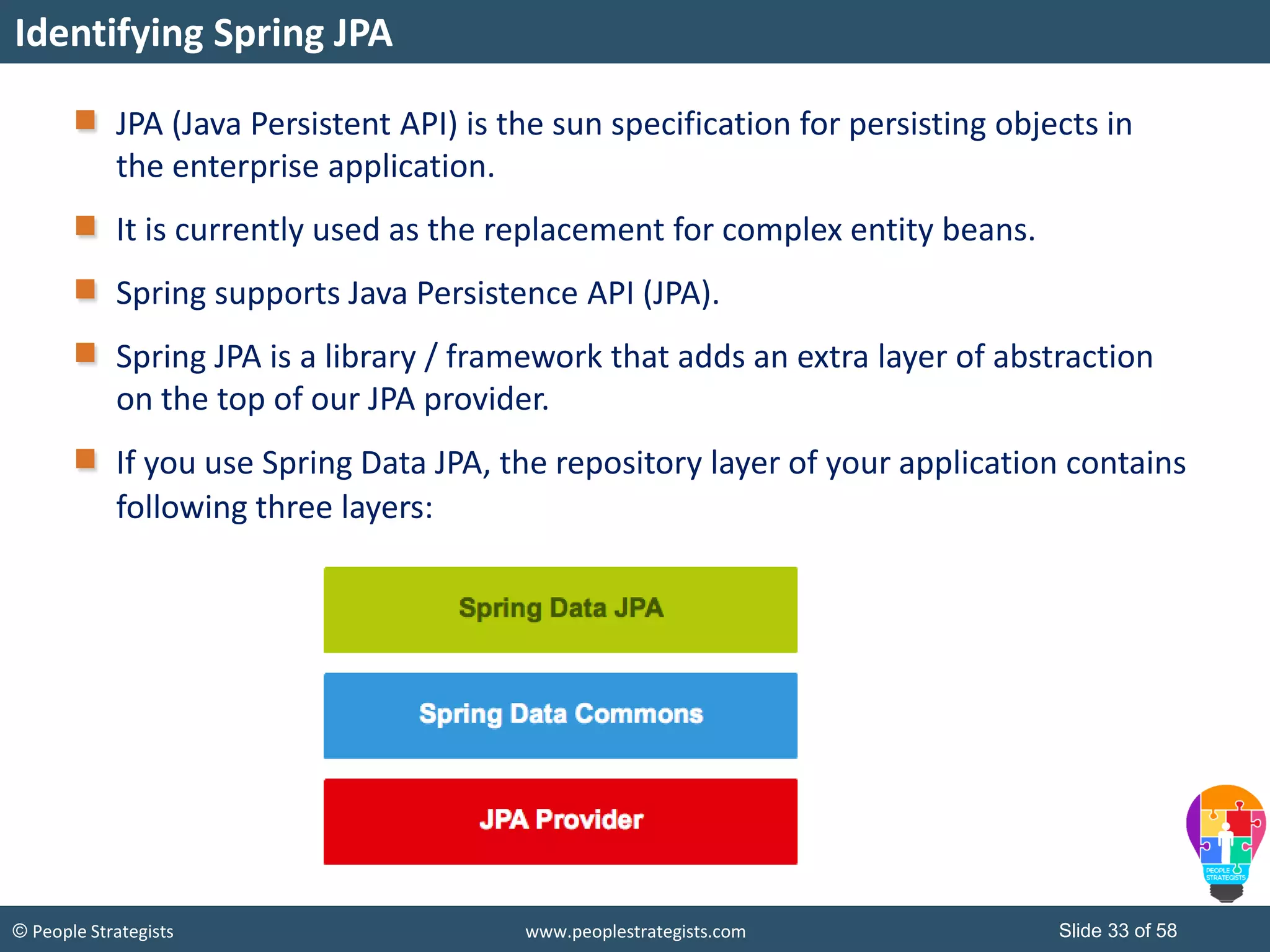
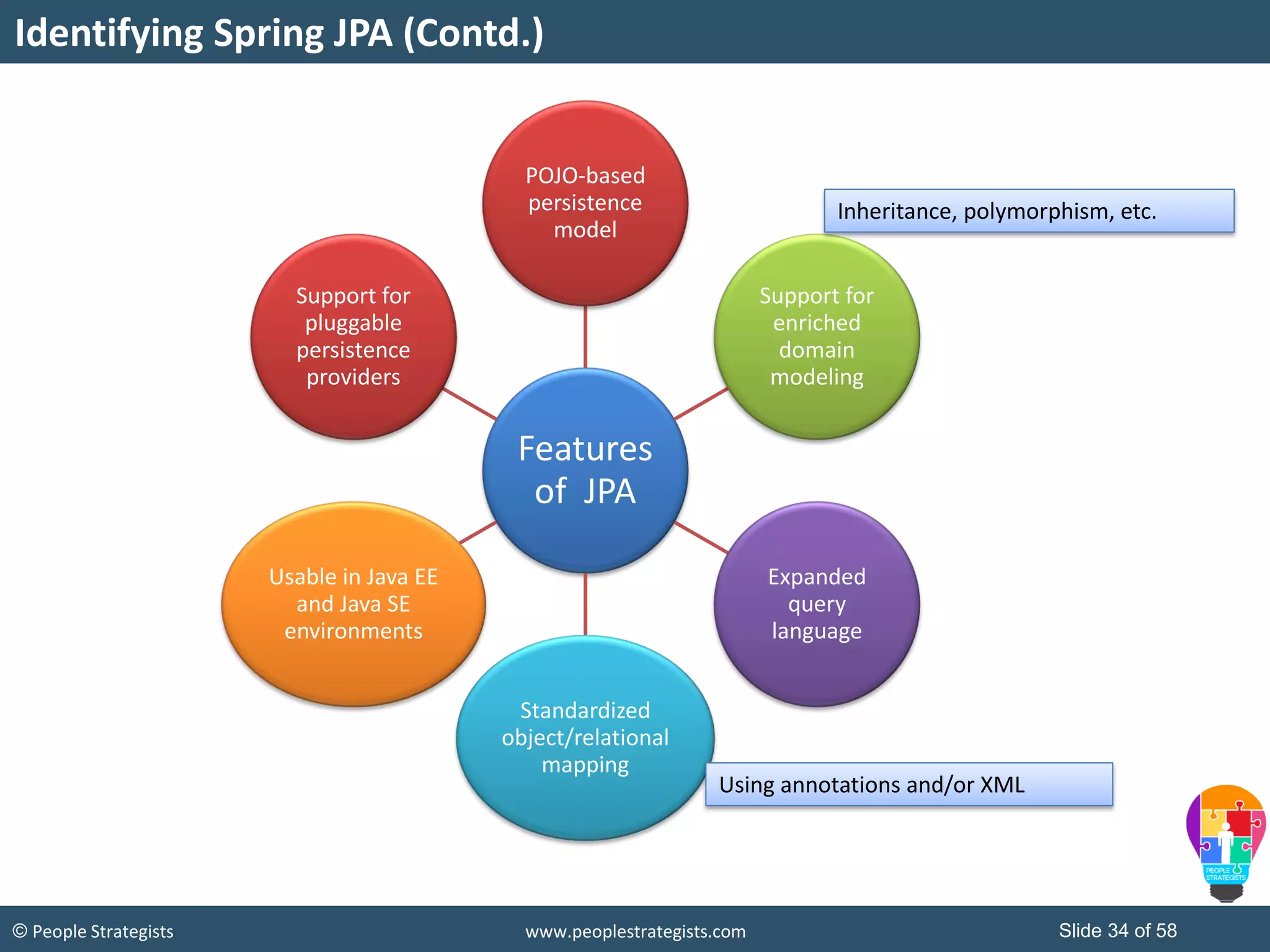
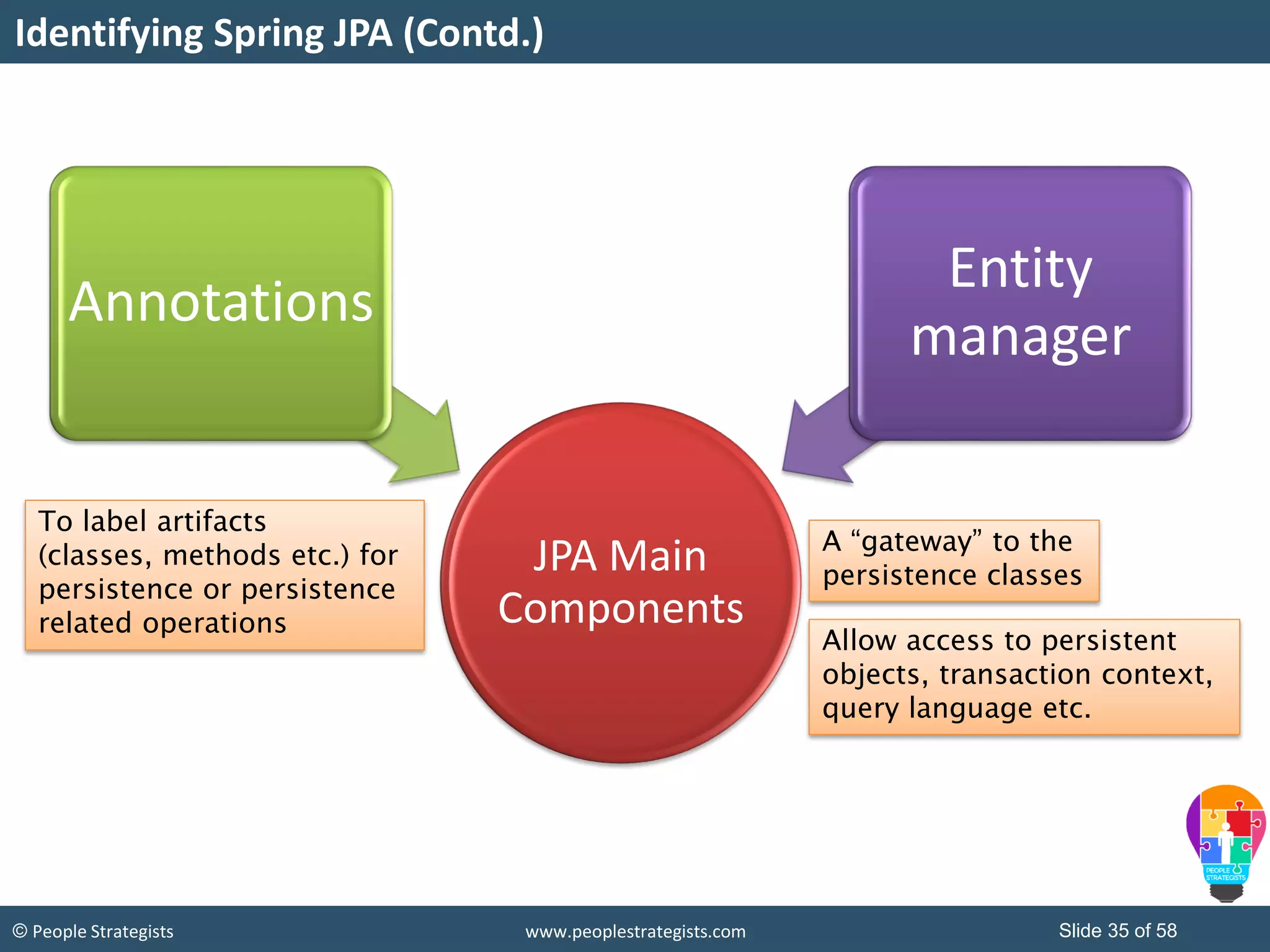
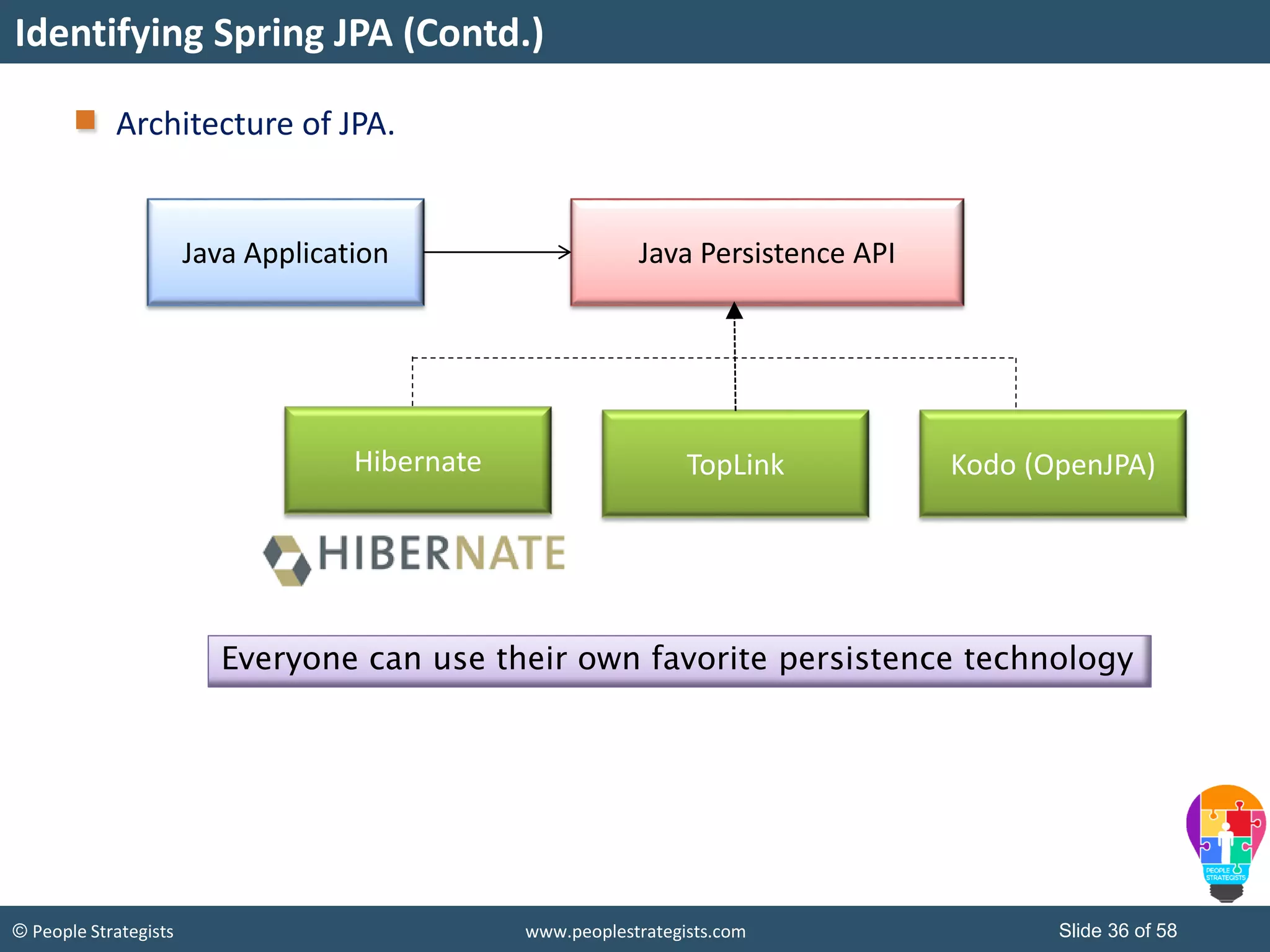
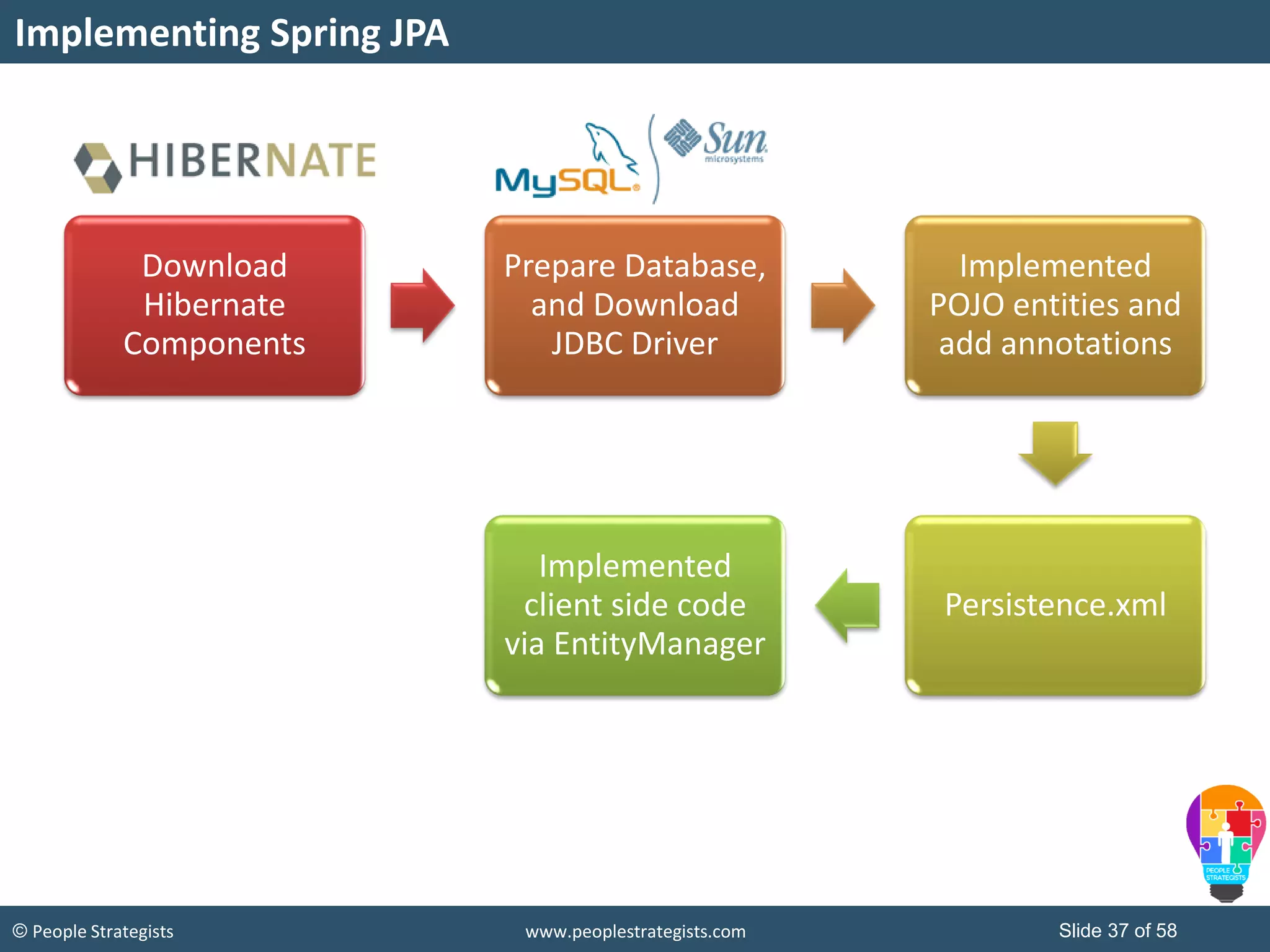
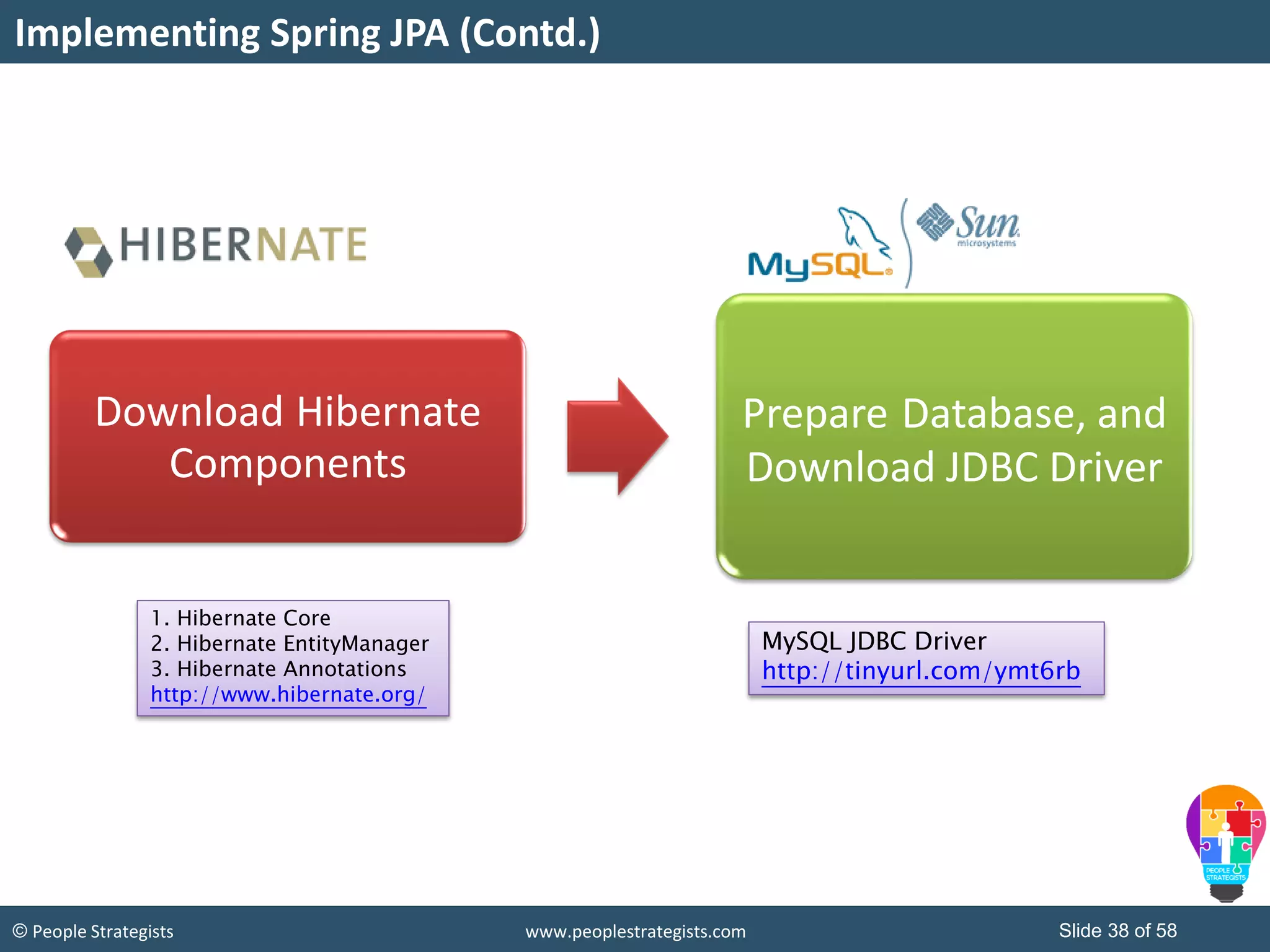
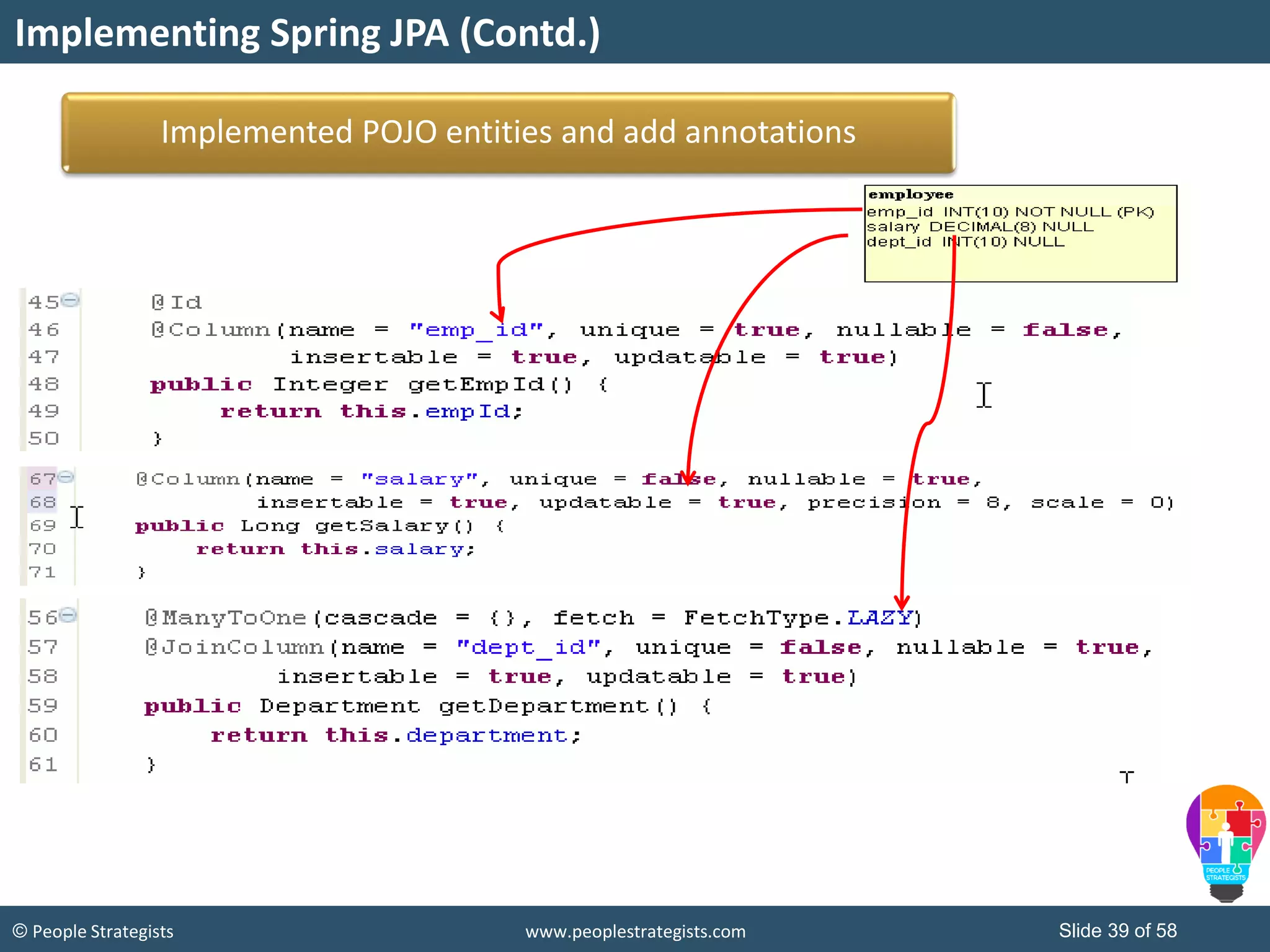
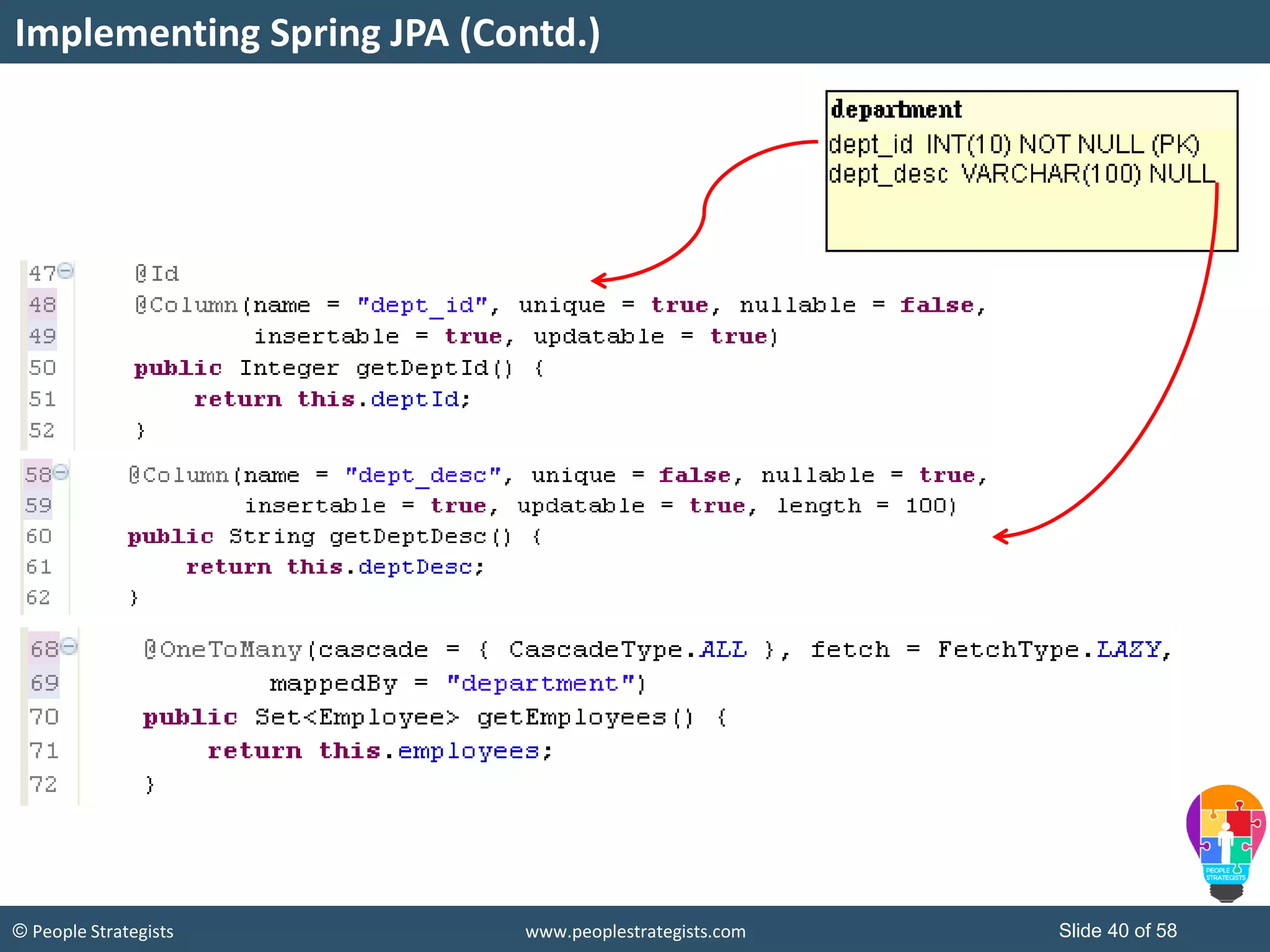
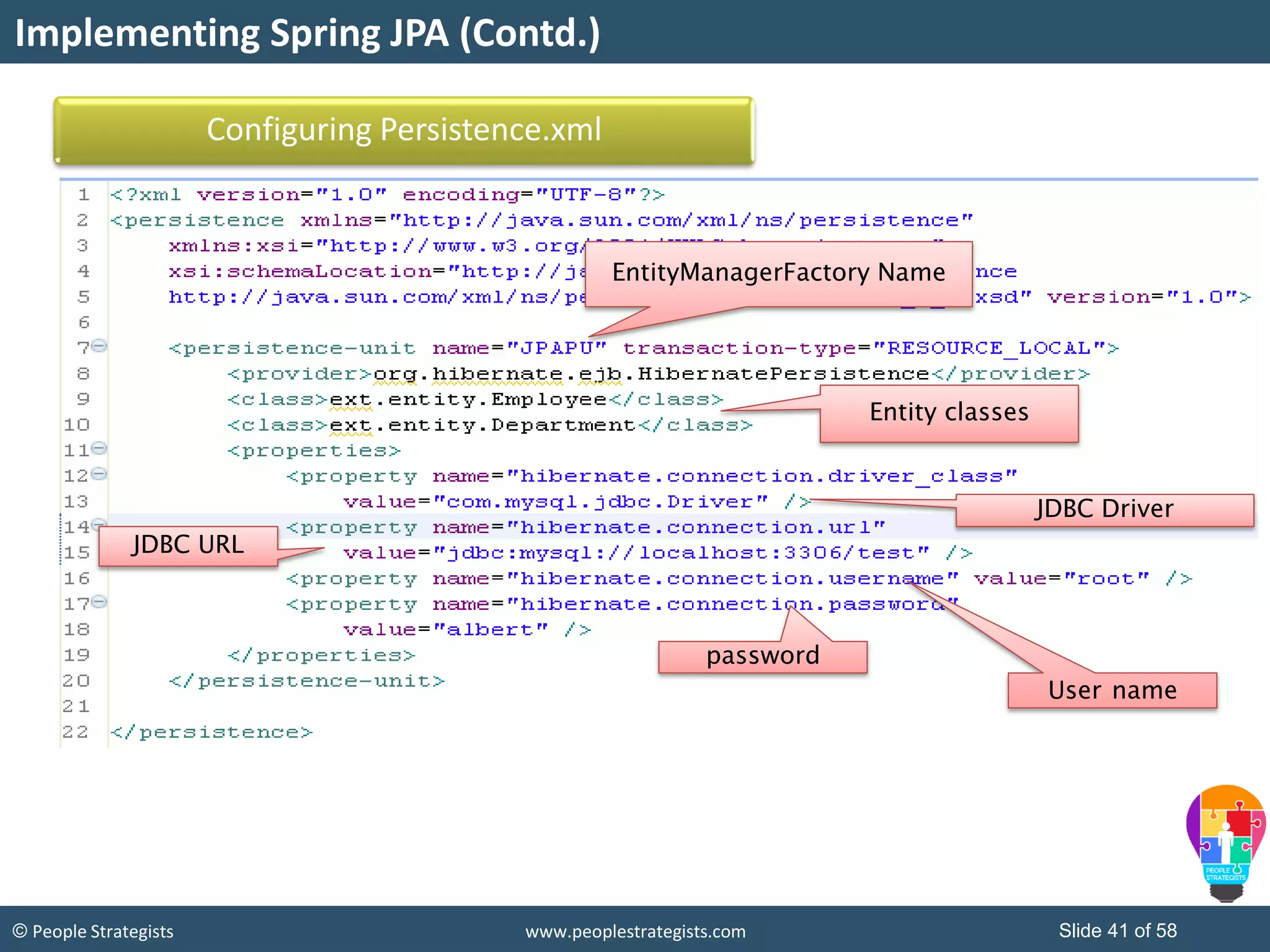
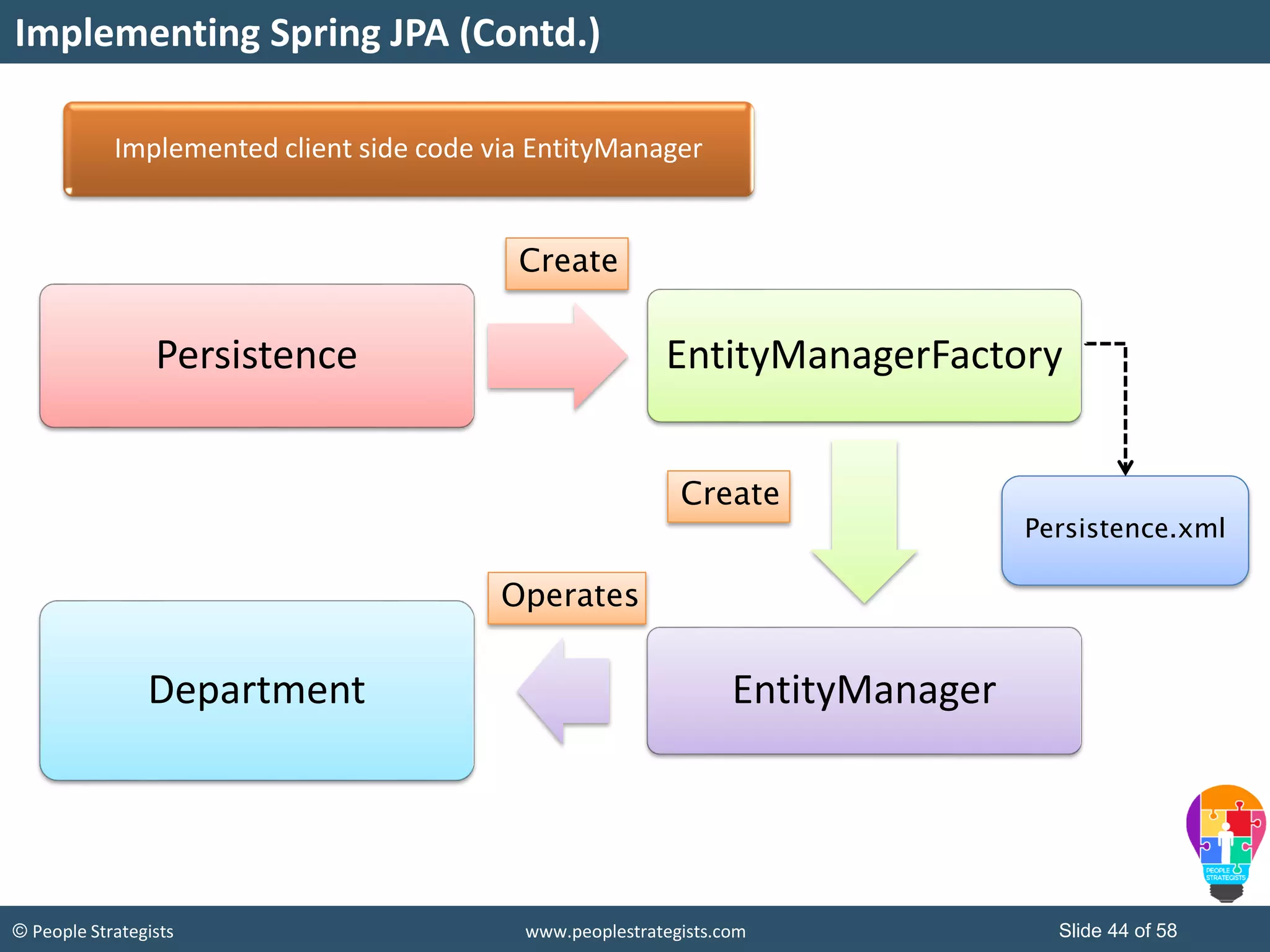
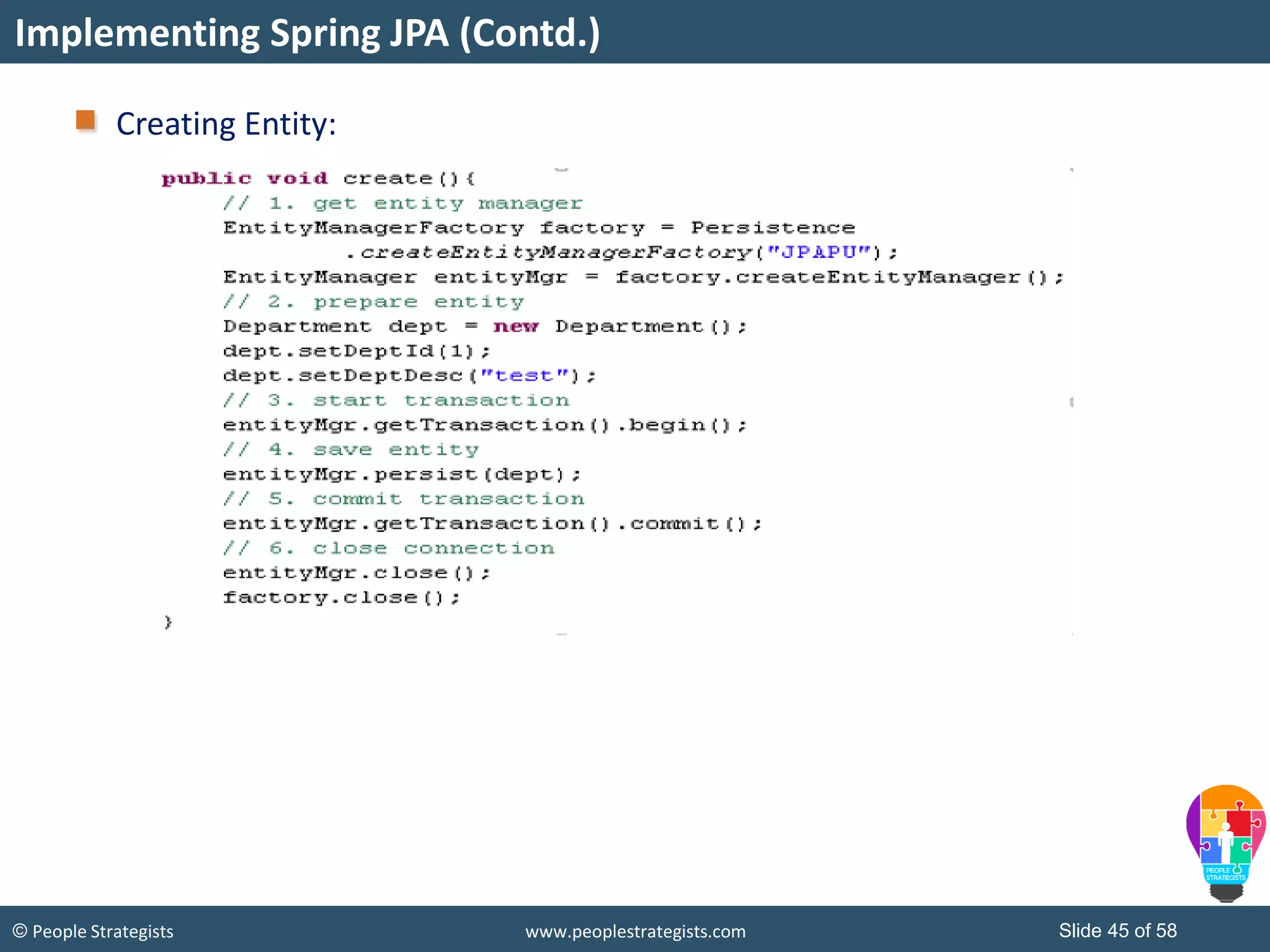
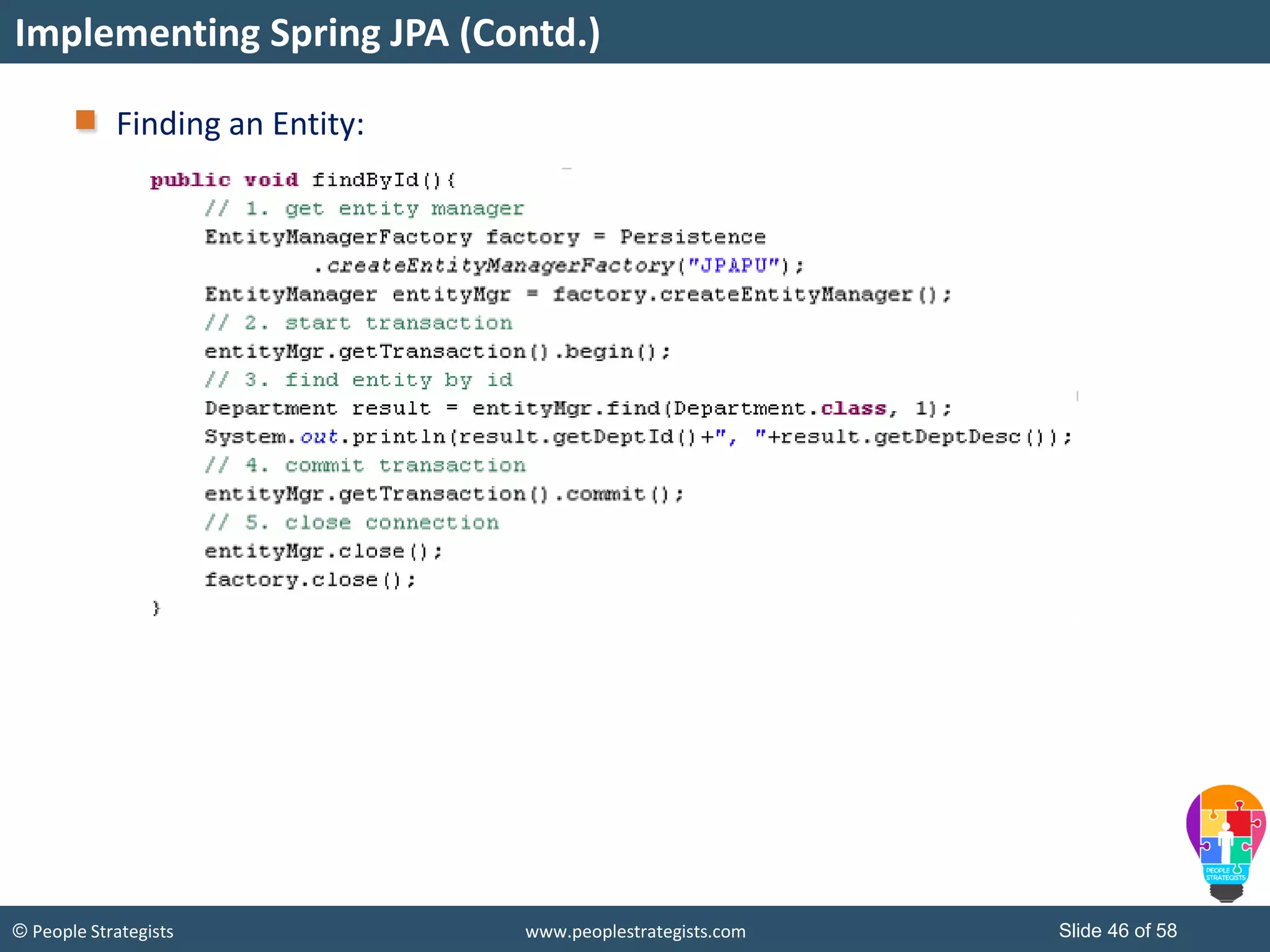
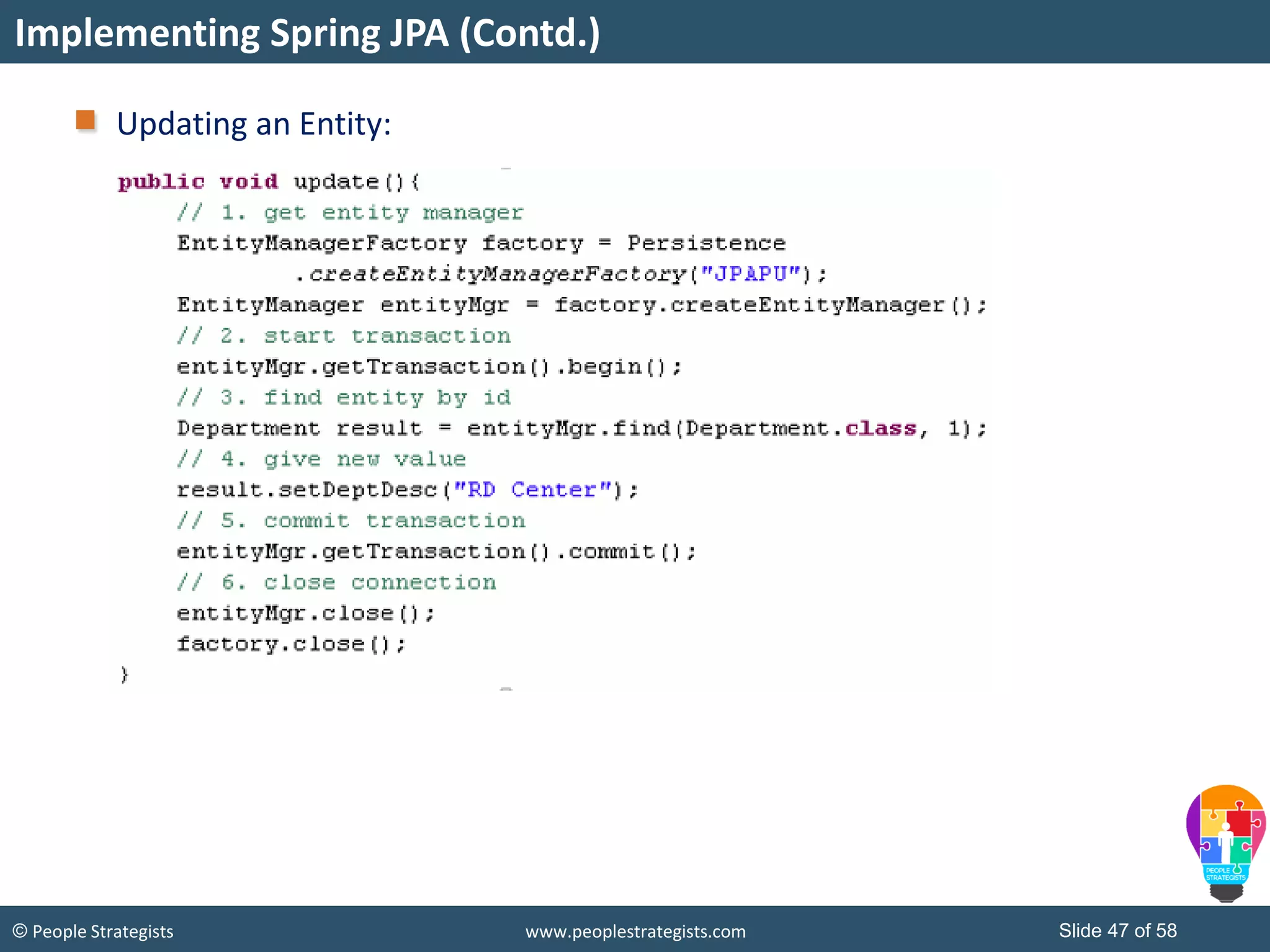
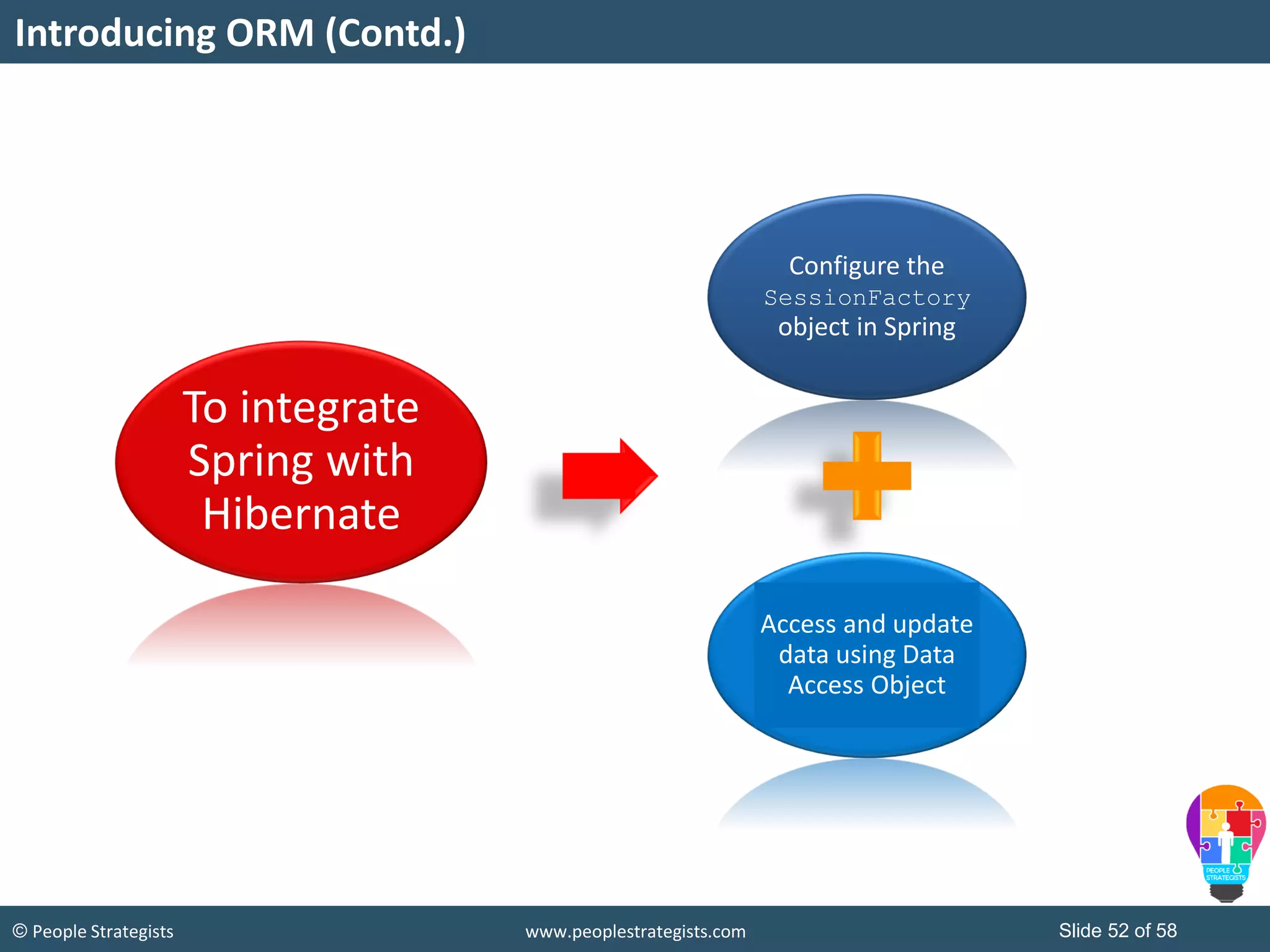
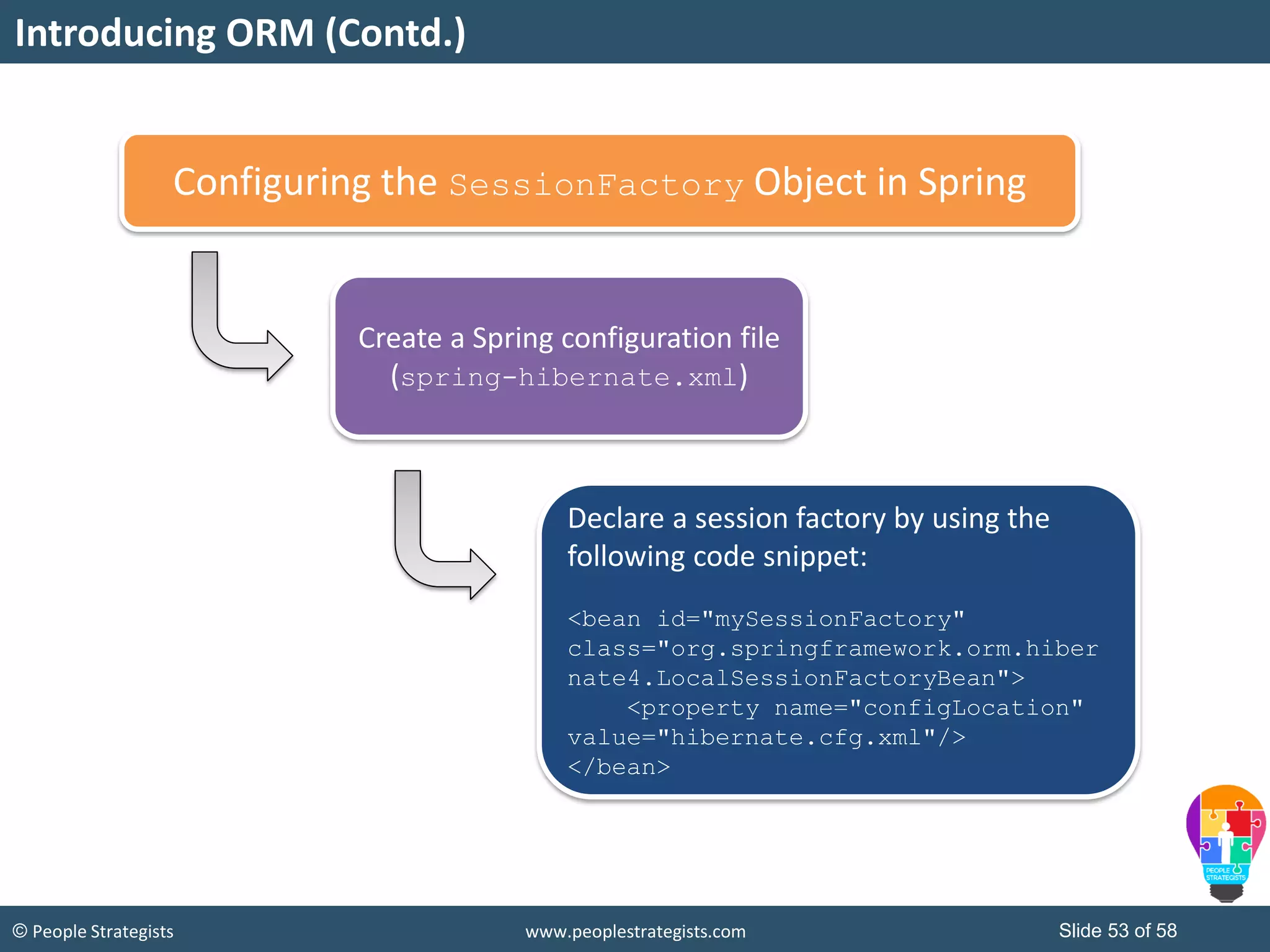
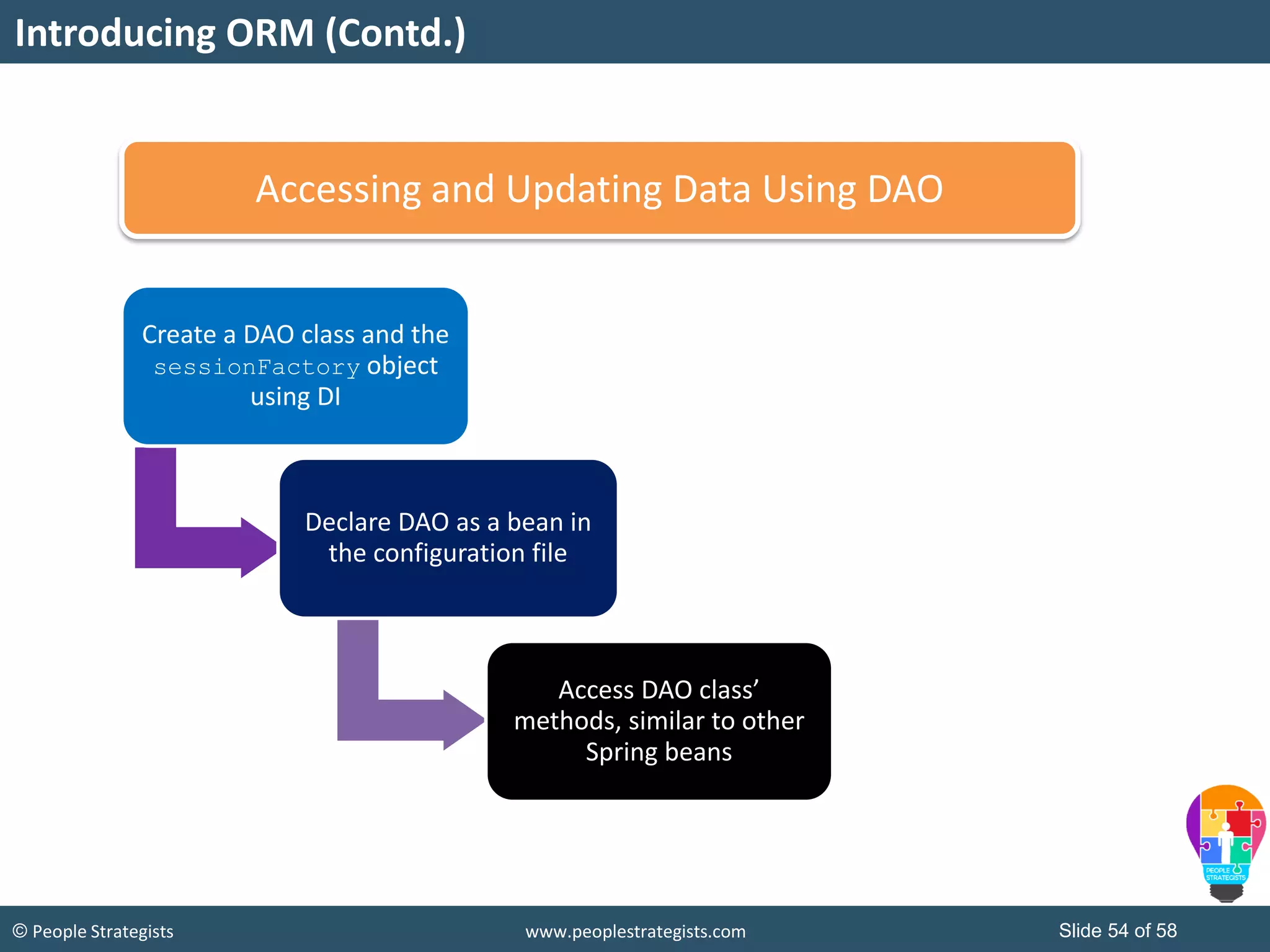
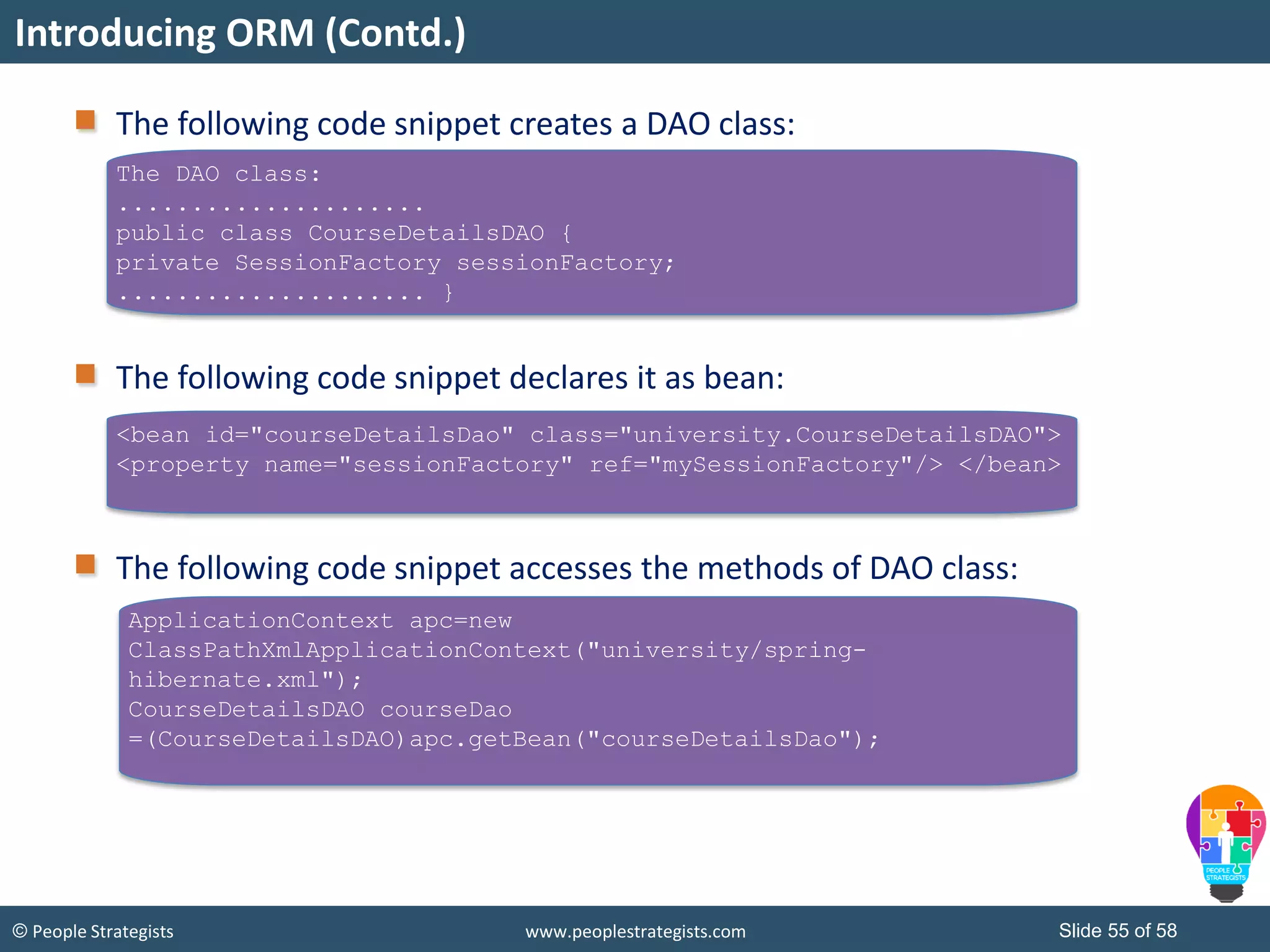
The document discusses Spring Framework and annotations-based configuration in Spring. It covers: - Enabling annotation-based configuration by adding <context:annotation-config/> to the XML file. - Common annotations like @Autowired, @Component, @Value that can be used for dependency injection and configuration. - How to implement autowiring by type, name and constructor. - Other annotations like @PostConstruct, @PreDestroy for lifecycle callbacks. - Stereotype annotations @Controller, @Service, @Repository that can be used instead of defining beans explicitly. - Spring validation support using Validator interface, validation annotations and implementing custom validators. - Spring