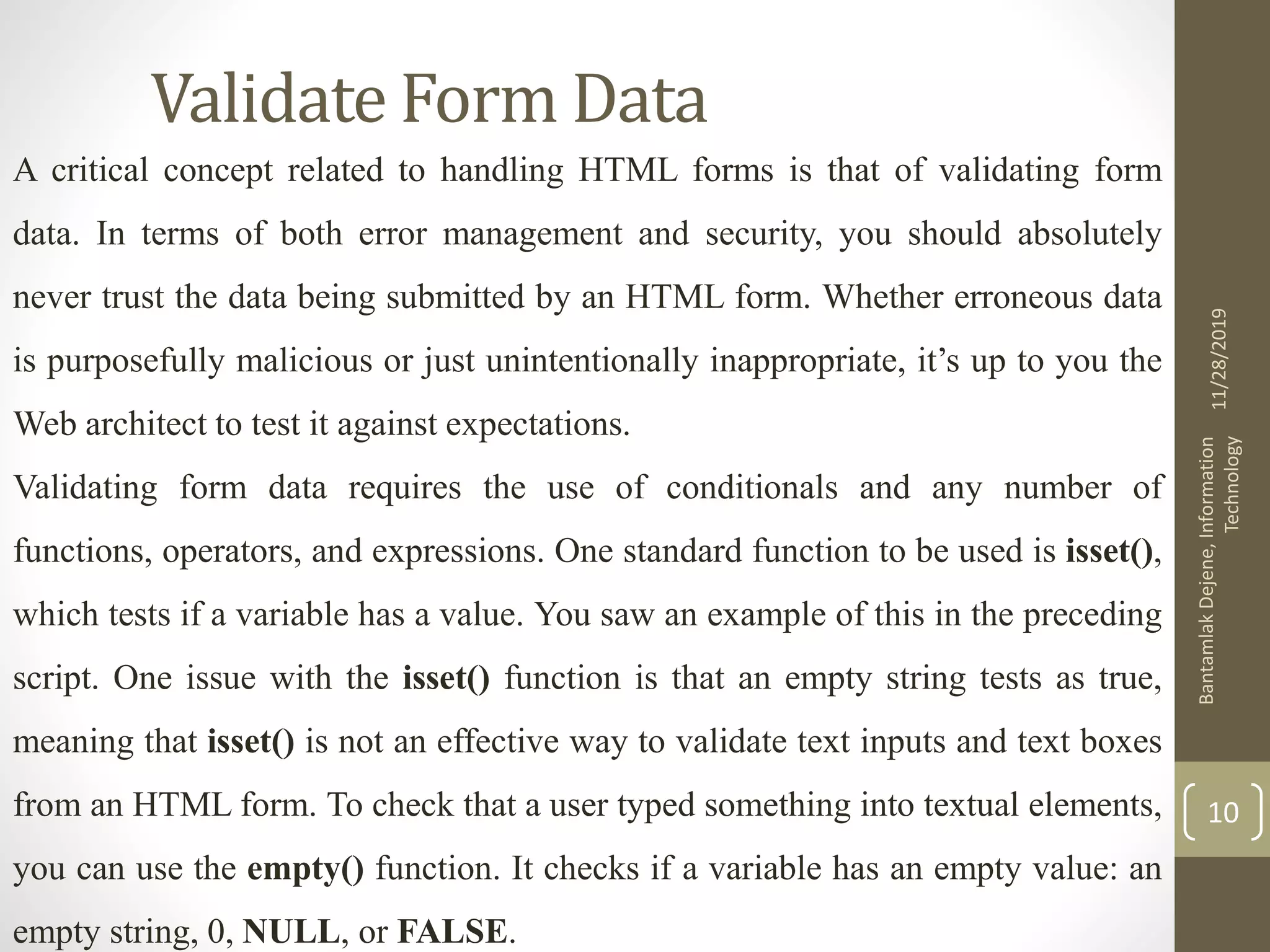
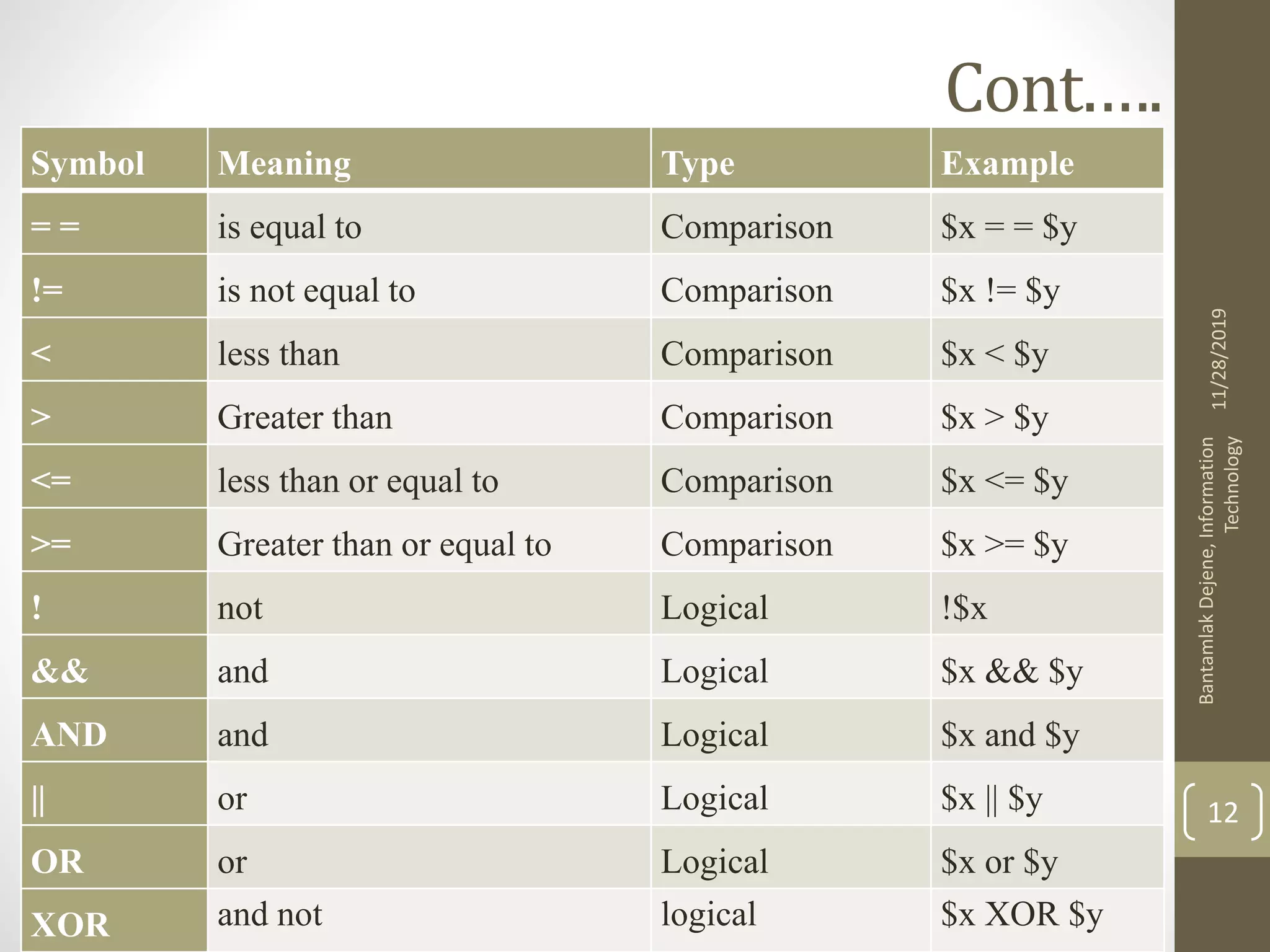
The document discusses various topics related to handling HTML forms with PHP scripts, including: - Creating an HTML form with tags like <form> and various input elements. The form directs submitted data to a PHP script. - In PHP, form data is accessed through special variables like $_REQUEST based on the input names. - A PHP script can display a form, handle form submissions, and re-display the form by checking if the request method is POST. - Form data should be validated in PHP scripts before use through functions like empty() and conditionals.




![Cont.…. The beauty of PHP and what makes it so easy to learn and use is how well it interacts with HTML forms. PHP scripts store the received information in special variables. For example, say you have a form with an input defined like so: <input type="text" name="city" /> Whatever the user types into that input will be accessible via a PHP variable named $_REQUEST['city']. It is very important that the spelling and capitalization match exactly! PHP is case-sensitive when it comes to variable names, so $_REQUEST['city'] will work, but $_Request['city'] and $_REQUEST['City'] will have no value. 11/28/2019 BantamlakDejene,Information Technology 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpch-2htmlformsandserversidescripting-191128093746/75/html-forms-and-server-side-scripting-5-2048.jpg)
![Cont.…. Element Name Variable Name Name $_REQUEST['name'] Email $_REQUEST['email'] comments $_REQUEST['comments'] Age $_REQUEST['age'] Gender $_REQUEST['gender'] Submit $_REQUEST['submit'] 11/28/2019 BantamlakDejene,Information Technology 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpch-2htmlformsandserversidescripting-191128093746/75/html-forms-and-server-side-scripting-6-2048.jpg)

![Cont.…. The question, then, is how to determine if the form has been submitted. The answer is simple, after a bit of explanation. When you have a form that uses the POST method and gets submitted back to the same page, two different types of requests will be made of that script. The first request, which loads the form, will be a GET request. This is the standard request made of most Web pages. When the form is submitted, a second request of the script will be made, this time a POST request (as long as the form uses the POST method). With this in mind, you can test for a form’s submission by checking the request method, found in the $_SERVER array: if ($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] = = 'POST') { // Handle the form. } else { // Display the form. } 11/28/2019 BantamlakDejene,Information Technology 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpch-2htmlformsandserversidescripting-191128093746/75/html-forms-and-server-side-scripting-8-2048.jpg)
![Cont.…. If you want a page to handle a form and then display it again (e.g., to add a record to a database and then give an option to add another), drop the else clause: if ($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] = = 'POST') { // Handle the form. } // Display the form. 11/28/2019 BantamlakDejene,Information Technology 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpch-2htmlformsandserversidescripting-191128093746/75/html-forms-and-server-side-scripting-9-2048.jpg)



![Cont.…. An array follows the same naming rules as any other variable. This means that you might not be able to tell that $var is an array as opposed to a string or number. The important syntactical difference arises when accessing individual array elements. To refer to a specific value in an array, start with the array variable name, followed by the key within square brackets: $band = $artists[0]; // The Mynabirds echo $states['MD']; // Maryland You can see that the array keys are used like other values in PHP: numbers (e.g., 0) are never quoted, whereas strings (MD) must be. Because arrays use a different syntax than other variables, and can contain multiple values, printing them can be trickier. This will not work: echo "My list of states: $states"; 11/28/2019 BantamlakDejene,Information Technology 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpch-2htmlformsandserversidescripting-191128093746/75/html-forms-and-server-side-scripting-16-2048.jpg)
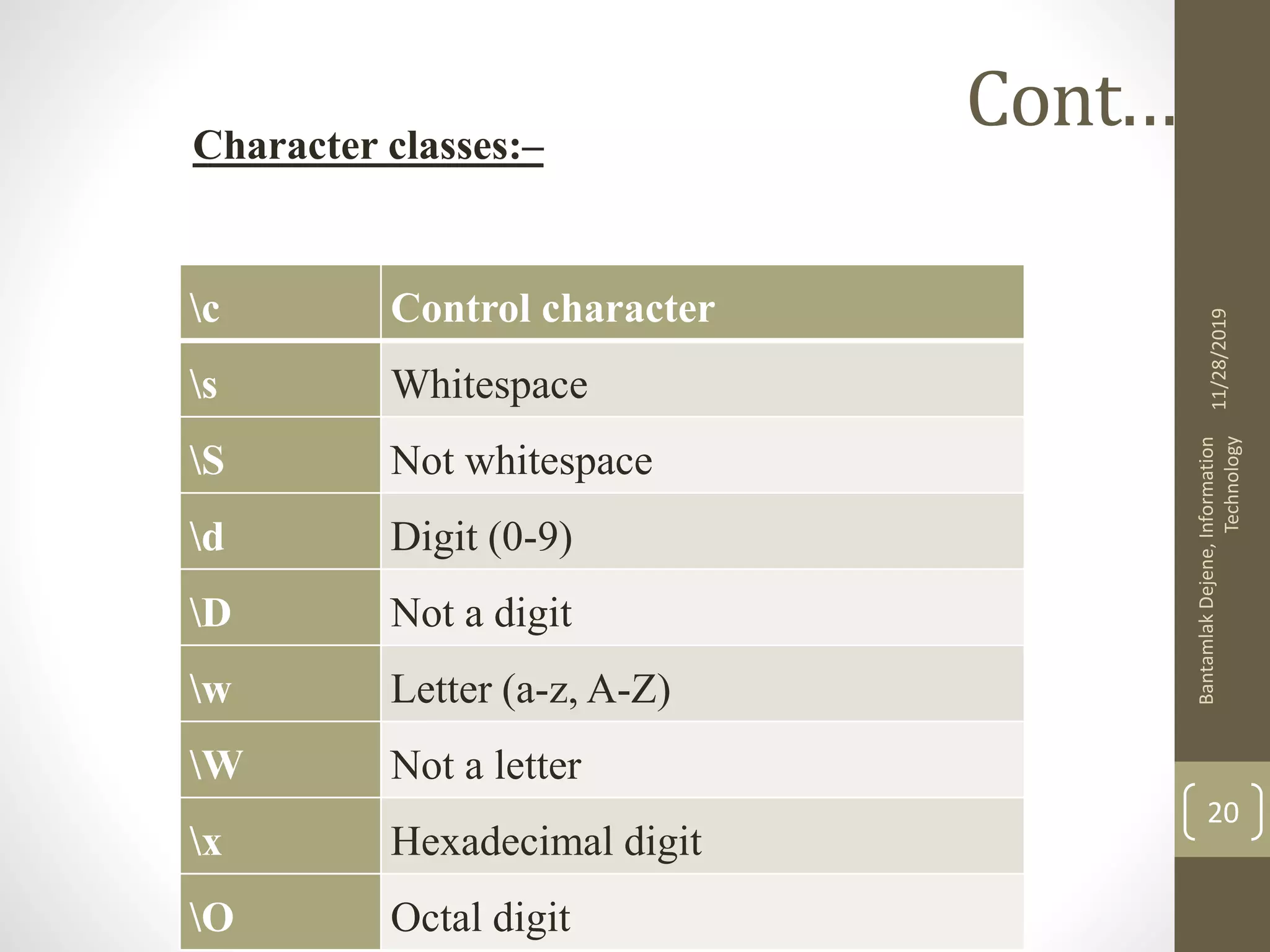
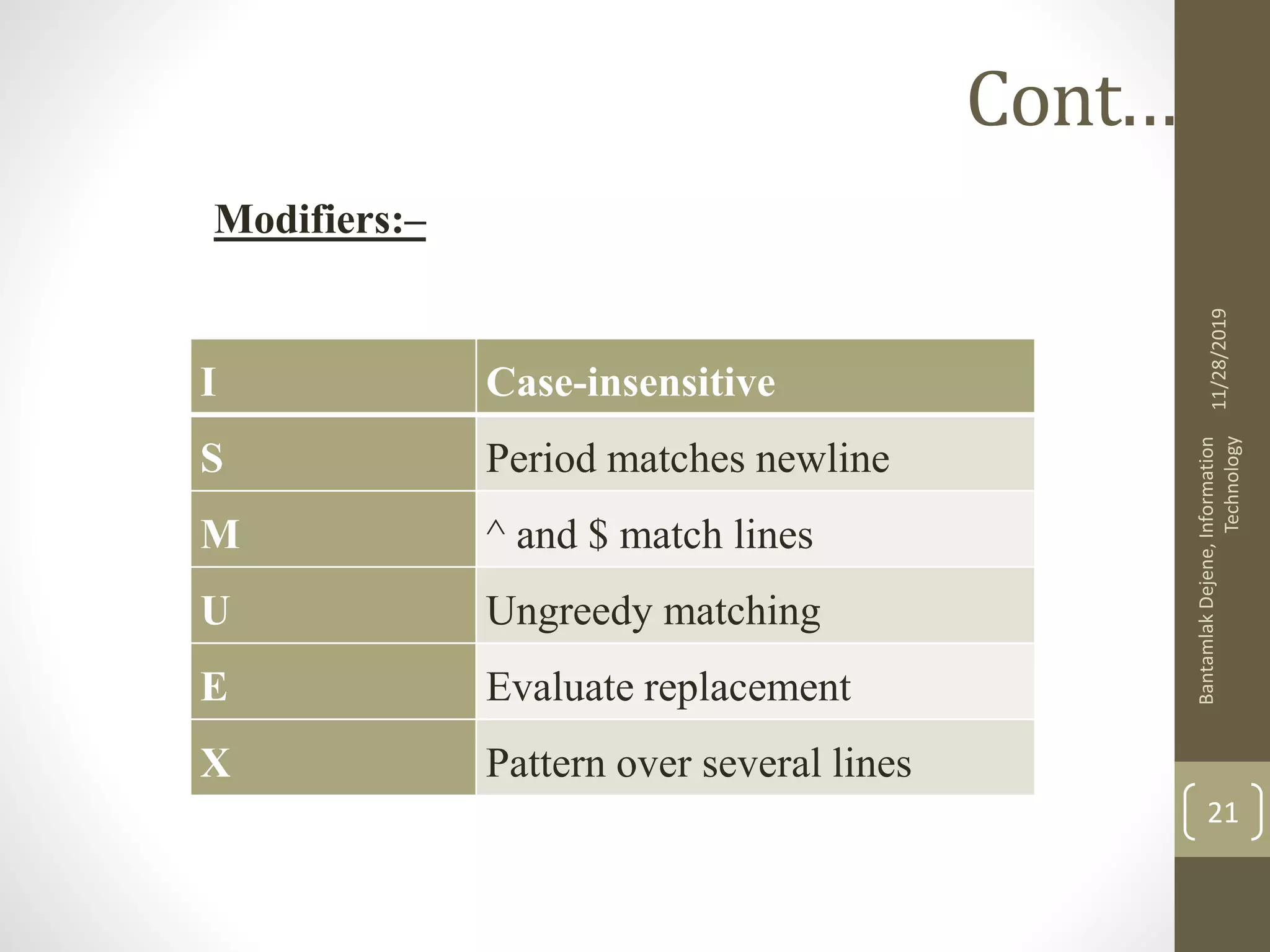
![Cont.…. ^ Start of string $ End of string . Any single character ( ) Group of expressions [] Item range (e.g. [afg] means a, f, or g) [^] Items not in range ( e.g. [^cde] means not c, d, or e ) - (dash) character range within an item range (e.g. [a-z] means a through z) | (pipe) Logical or ( e.g. (a|b) means a or b ) ? Zero or one of preceding character/item range * Zero or more of preceding character/item range + One or more of preceding character/item range {integer} Exactly integer of preceding character/item range ( e.g. a{2} ) 11/28/2019 BantamlakDejene,Information Technology 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpch-2htmlformsandserversidescripting-191128093746/75/html-forms-and-server-side-scripting-18-2048.jpg)
![Cont.…. {integer,} Integer or more of preceding character/item range ( e.g. a{2,} ) {integer, integer} From integer to integer (e.g. a{2,4} means 2 to four of a ) Escape character [:punct:] Any punctuation [:space:] Any space character [:blank:] Any space or tab [:digit:] Any digit: 0 through 9 [:alpha:] All letters: a-z and A-Z [:alnum:] All digits and letters: 0-9, a-z, and A-Z [:xdigit:] Hexadecimal digit [:print:] Any printable character [:upper:] All uppercase letters: A-Z [:lower:] All lowercase letters: a-z 11/28/2019 BantamlakDejene,Information Technology 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpch-2htmlformsandserversidescripting-191128093746/75/html-forms-and-server-side-scripting-19-2048.jpg)