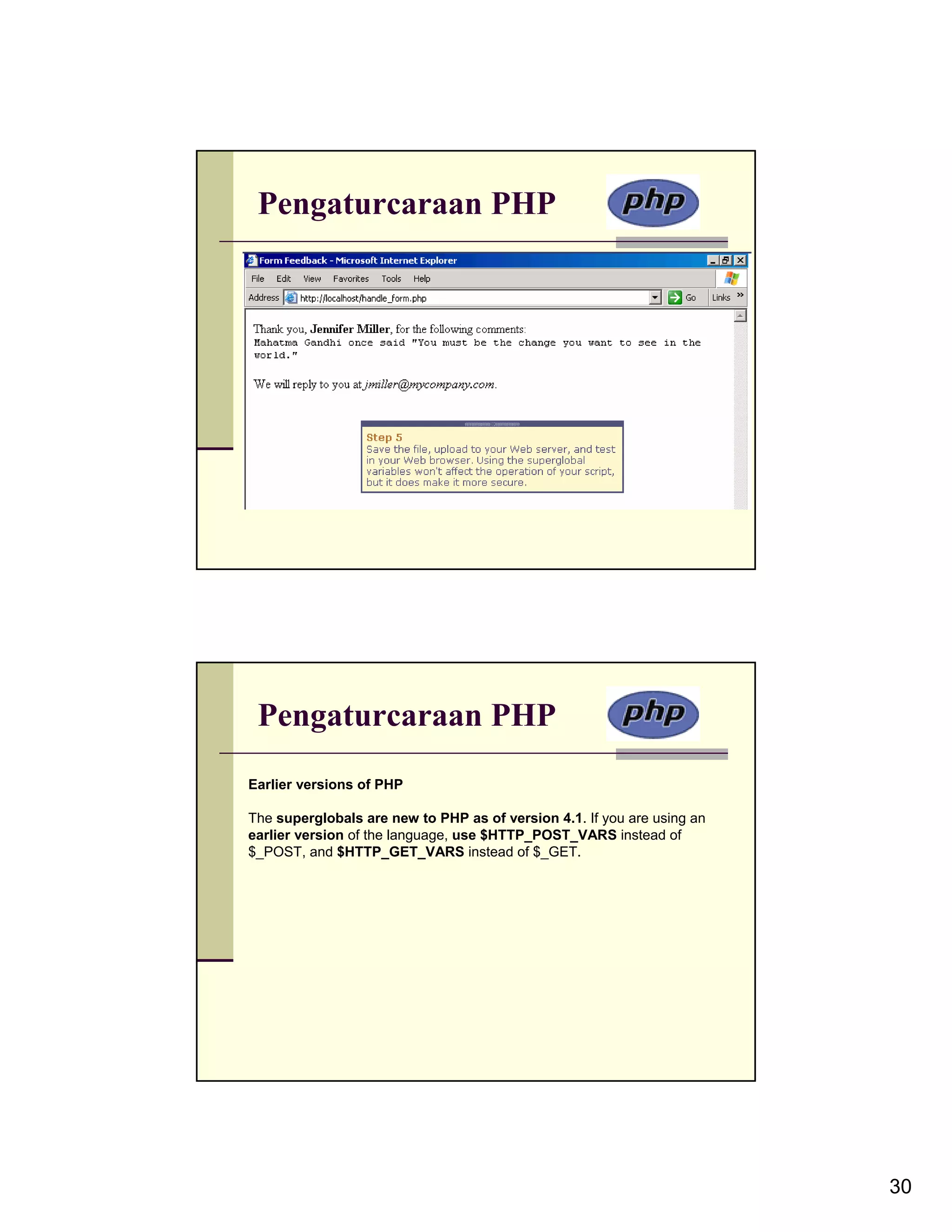
The document discusses creating and managing HTML forms with PHP. It covers creating a basic HTML form with tags like <form> and <input>, then processing the form data with a PHP script. The PHP script receives submitted data through superglobal variables like $_POST and $_GET. Form validation is also covered, using functions like empty() and conditionals to check for required fields and proper data formats. The document also discusses arrays in PHP for storing multiple submitted values, and using foreach loops to access array elements.



![Pengaturcaraan PHP Once you have an HTML form, the next step is to write a bare- bones PHP script to handle it. When we say that this script will be handling the form, we mean that it will do something with the data it receives; that is it will reiterate the data back to the Web browser. The PHP page that receives the form data will assign what the user entered into this form element to a special variable called $_REQUEST['weight']. It is very important that the spelling and capitalization match exactly, as PHP is case-sensitive when it comes to variable names. $_REQUEST['weight'] can then be used like any other variable: printed, used in mathematical computations, concatenated, and so on. Pengaturcaraan PHP Registering Globals In earlier versions of PHP, the register_globals setting was turned on by default. This feature gave PHP an ease of use by automatically turning form inputs into similarly named variables, like $name or $email (as opposed to having to refer to $_REQUEST['name'] and $_REQUEST['email'] first). As of version 4.2 of PHP, the developers behind PHP opted to turn this setting off by default because not relying on this feature improves the security of your scripts. Unfortunately, this also To work around this, there are two had the side effect that a lot of existing options. First, you could turn scripts no longer worked and many beginning programmers were stymied register_globals back on, assuming when they saw blank values in their that you have administrative control form results, error messages, or just over your PHP installation. Second, blank pages. you could start using the superglobal variables, such as $_REQUEST, $_GET, and $_POST. 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingwithphp-121217015805-phpapp02/75/Programming-with-php-7-2048.jpg)
![Pengaturcaraan PHP Pengaturcaraan PHP Following the rules outlined before, the data entered into the name form input, which has a name value of name, will be accessible through the variable $_REQUEST['name']. The data entered into the email form input, which has a name value of email, will be accessible through $_REQUEST['email']. The same applies to the entered comments data. Again, the spelling and capitalization of your variables here must exactly match the corresponding name values in the HTML form. 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingwithphp-121217015805-phpapp02/75/Programming-with-php-8-2048.jpg)


![Pengaturcaraan PHP Others way to avoid _$_REQUEST[‘variable’] extract($_GET); extract($_POST); extract($_COOKIE); User can call directly the name of variable like $name without using the method $_POST[“name”]. Managing Magic Quotes 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingwithphp-121217015805-phpapp02/75/Programming-with-php-11-2048.jpg)





![Pengaturcaraan PHP This is a simple and effective way to validate a form input (particularly a radio button, check box, or select). If the user checks either gender radio button, then $_REQUEST['gender'] will have a value, meaning that the condition isset($_REQUEST['gender']) is true. In such a case, the shorthand version of this variable — $gender — is assigned the value of $_REQUEST['gender'], repeating the technique used with $name, $email, and $comments. If the condition is not true, then $gender is assigned the value of NULL, indicating that it has no value. Notice that NULL is not in quotes. Pengaturcaraan PHP 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingwithphp-121217015805-phpapp02/75/Programming-with-php-18-2048.jpg)










![Creating and Accessing Arrays Pengaturcaraan PHP Creating Arrays Although you can use PHP-generated arrays, there will frequently be times when you want to create your own. There are two primary ways to define your own array. First, you could add one element at a time to build one, as in this example. It's important to understand that if you specify a key and a value already exists indexed with that same key, the new value will overwrite the existing one. In this example, based on the latest assignment, the value of $array['son'] is Michael and that of array[2] is orange. 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingwithphp-121217015805-phpapp02/75/Programming-with-php-31-2048.jpg)

![Accessing Arrays Individual array elements can be accessed by key (e.g., $_POST['email']). This works when you know exactly what the keys are or if you want to refer to only a single element. To access every array element, use the foreach loop. The foreach loop will iterate through every element in $array, assigning each element's value to the $value variable. In this example, you can access both the keys and values. Pengaturcaraan PHP 33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingwithphp-121217015805-phpapp02/75/Programming-with-php-33-2048.jpg)




![Pengaturcaraan PHP To access the $states array, you refer to $abbr['US'] To access Maryland, use $abbr['US']['MD'] Of course, you can still access multidimensional arrays using the foreach loop, nesting one inside another if necessary. Pengaturcaraan PHP To print out one of these values, surround the whole construct in curly braces: 38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingwithphp-121217015805-phpapp02/75/Programming-with-php-38-2048.jpg)






![Pengaturcaraan PHP $_POST['interests'] Even if the user selects only one interest, $_POST['interests'] will still be an array because the HTML name for the corresponding input is interests[] (the square brackets make it an array). select menu You can also end up with a multidimensional array by having an HTML form's select menu allow for multiple selections: ‹select name="interests[]" multiple="multiple"› ‹option value="Music"›Music‹/option› ‹option value="Movies"›Movies‹/option› ‹option value="Books"›Books‹/option› ‹option value="Skiing"›Skiing‹/option› ‹option value="Napping"›Napping‹/option› ‹/select› Arrays and Strings 45](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingwithphp-121217015805-phpapp02/75/Programming-with-php-45-2048.jpg)






![Pengaturcaraan PHP Pengaturcaraan PHP Array (Adding/Replace) In array, we can add or change content of array example 1 : $fruit = array('banana','papaya'); Cara menambah : <? $fruit[2] = “apple”; print “$fruit[2] ?> The Output apple 52](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingwithphp-121217015805-phpapp02/75/Programming-with-php-52-2048.jpg)
![Pengaturcaraan PHP Array (merging) You also can merge 2 or more array. Example 1 : $pantry = array( 1 => "apples", 2 => "oranges", 3 => "bananas" ); $pantry2 = array( 1 => "potatoes", 2 => "bread", 3 => "tomatoes" ); Pengaturcaraan PHP Array (Merging) Way to combine : <? $pantry_food = array_merge ($pantry, $pantry2); ?> The Output $pantry_food[0] = "apples"; $pantry_food[1] = "oranges"; $pantry_food[2] = "bananas"; $pantry_food[3] = "potatoes"; $pantry_food[4] = "bread"; $pantry_food[5] = "tomatoes"; 53](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingwithphp-121217015805-phpapp02/75/Programming-with-php-53-2048.jpg)