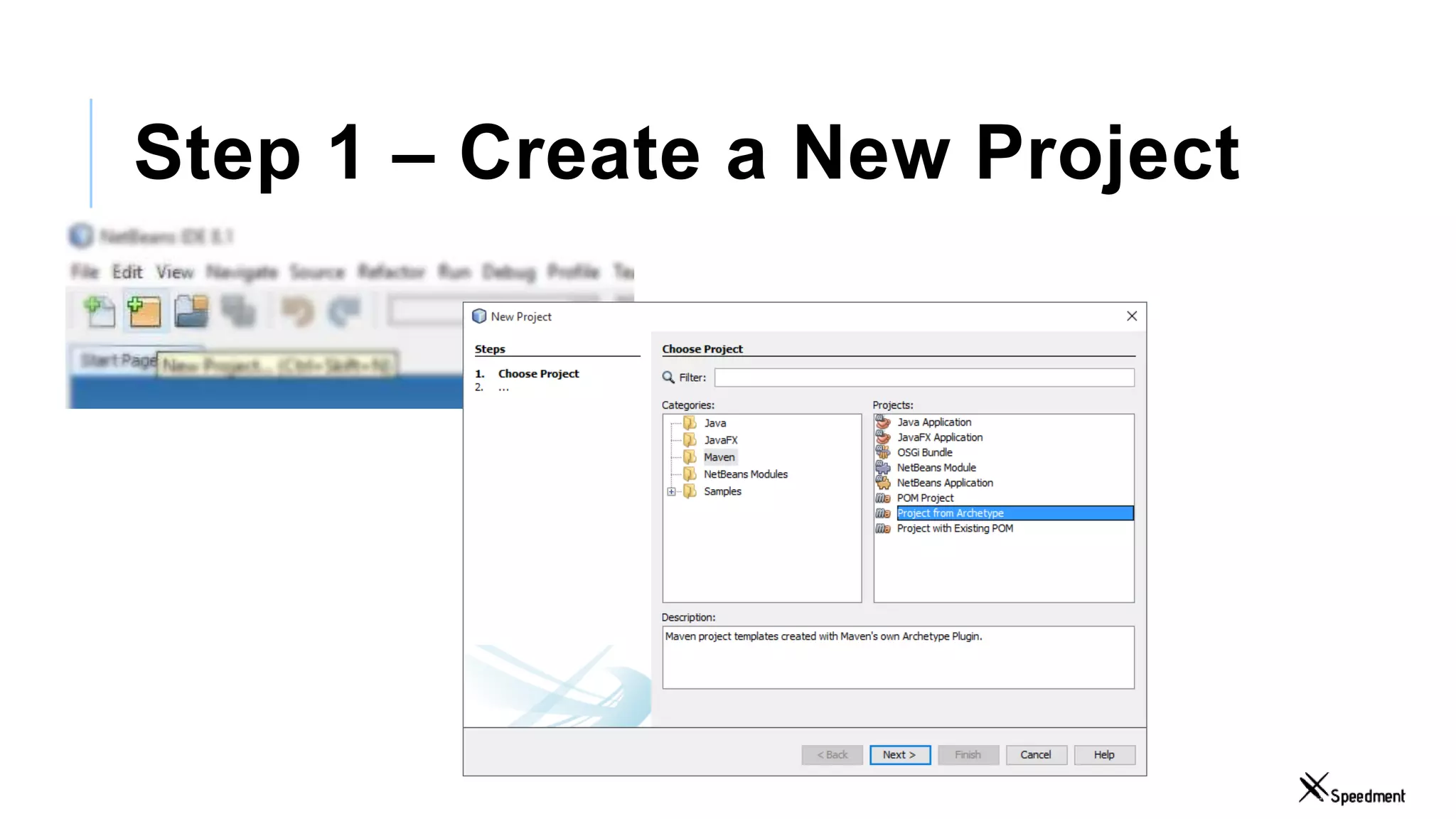
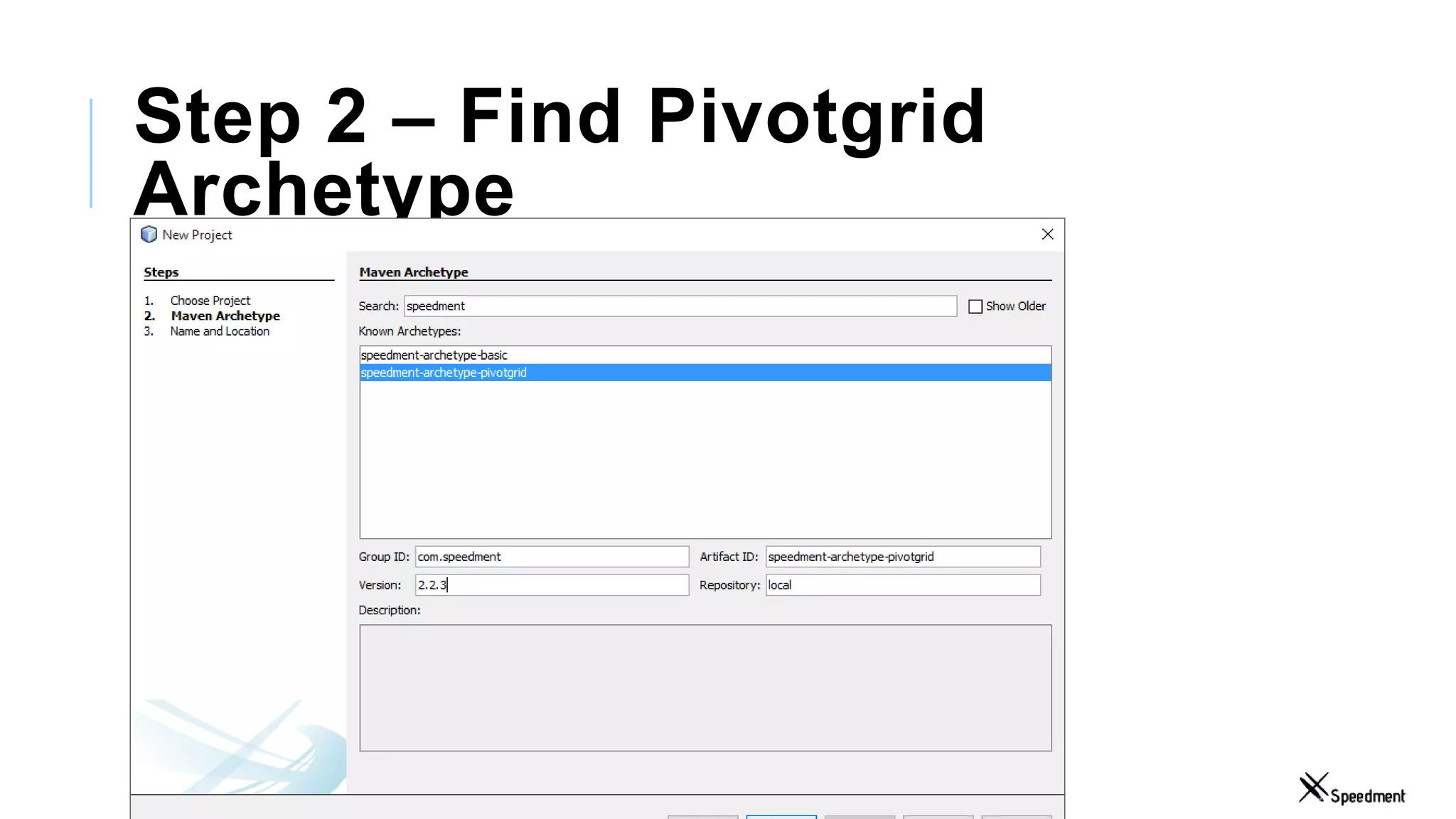
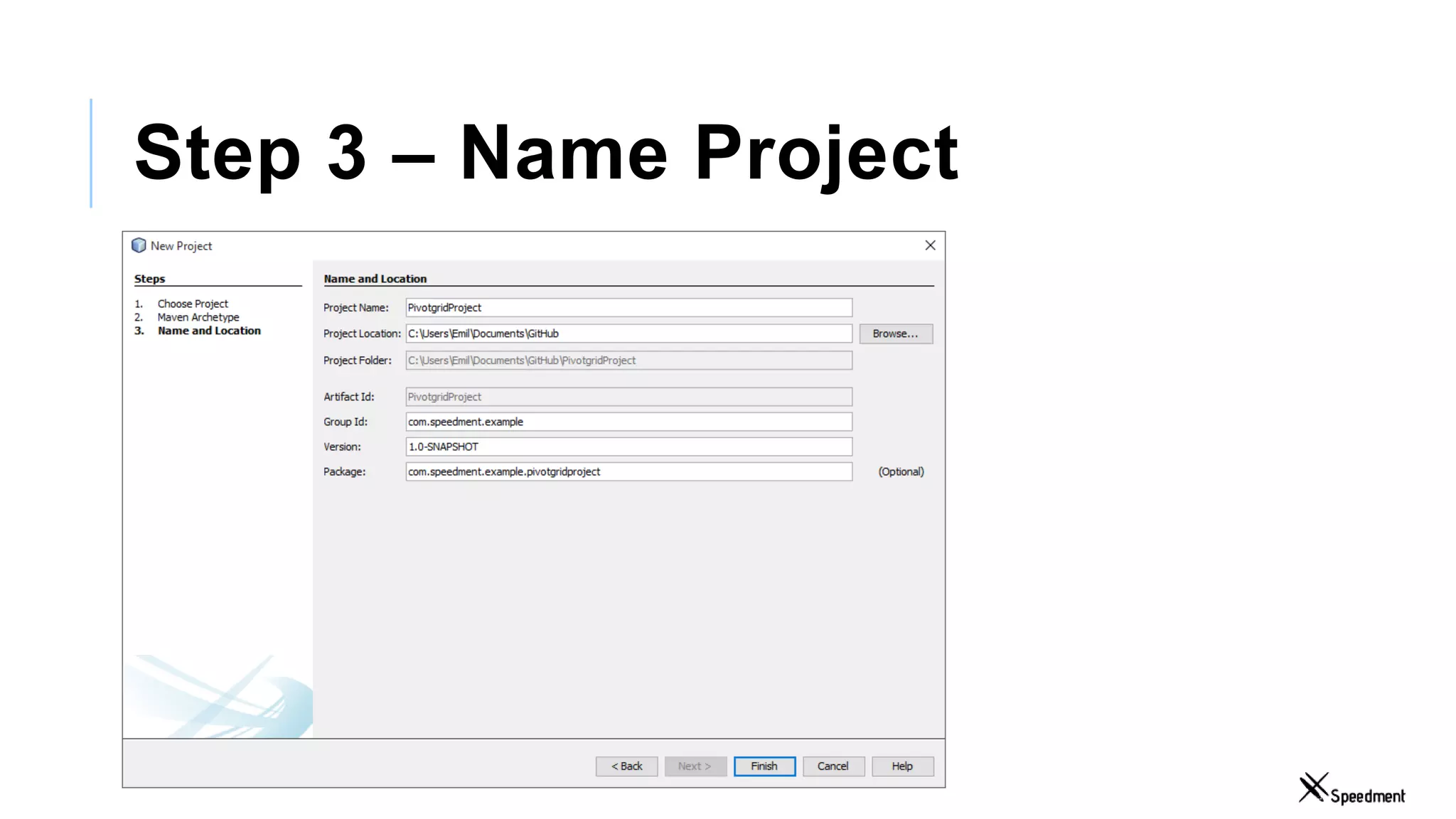
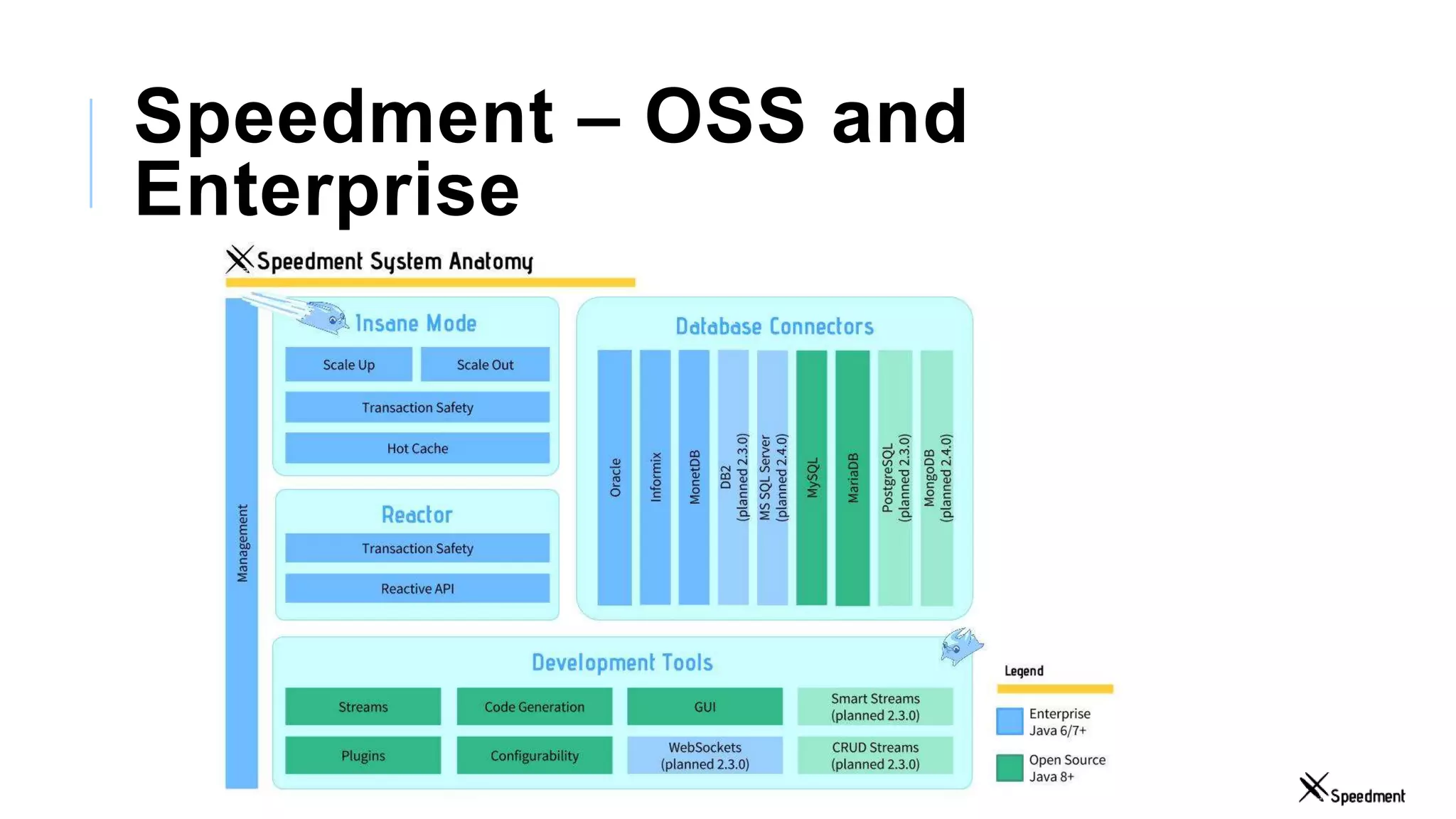
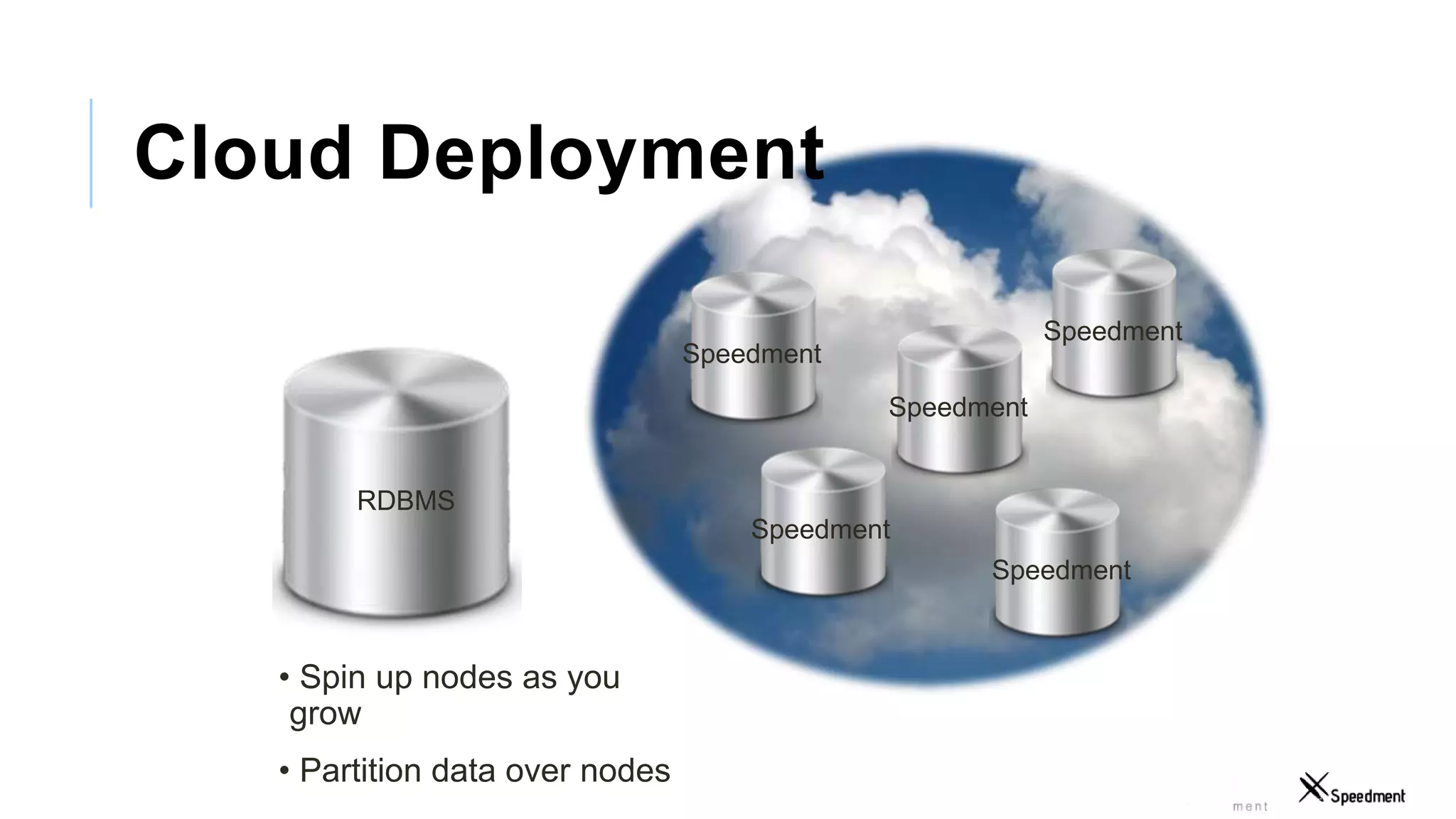
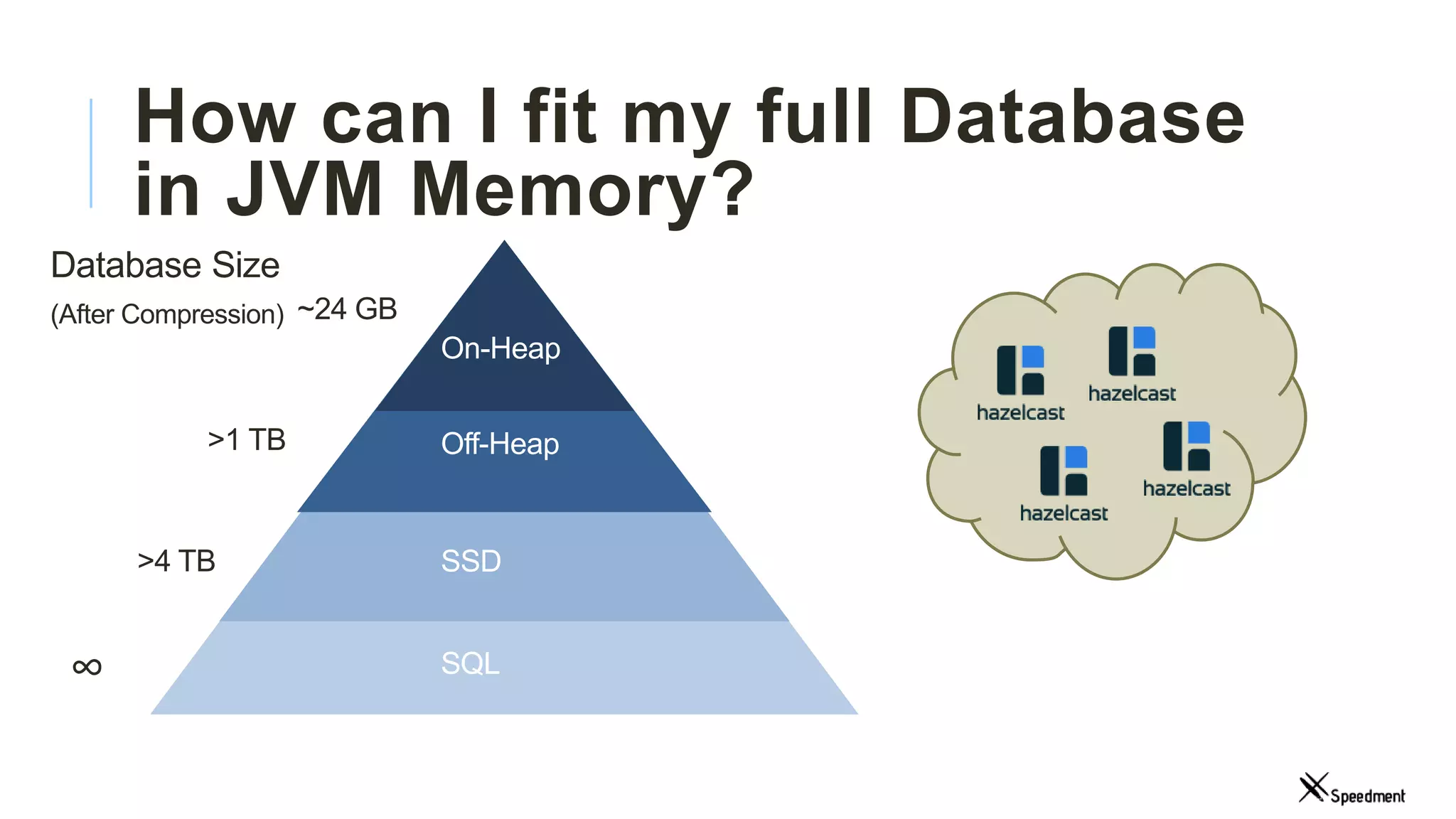
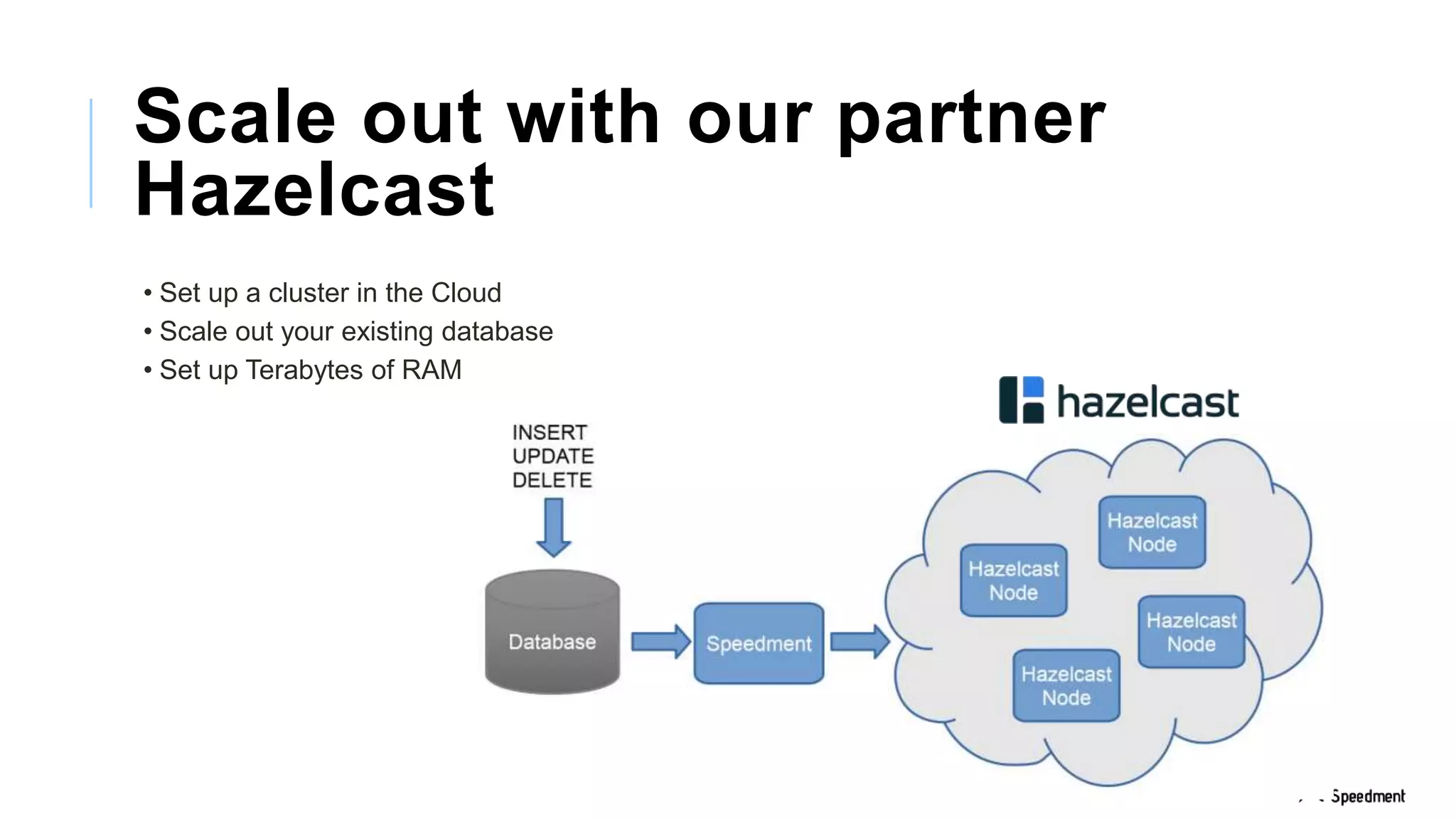
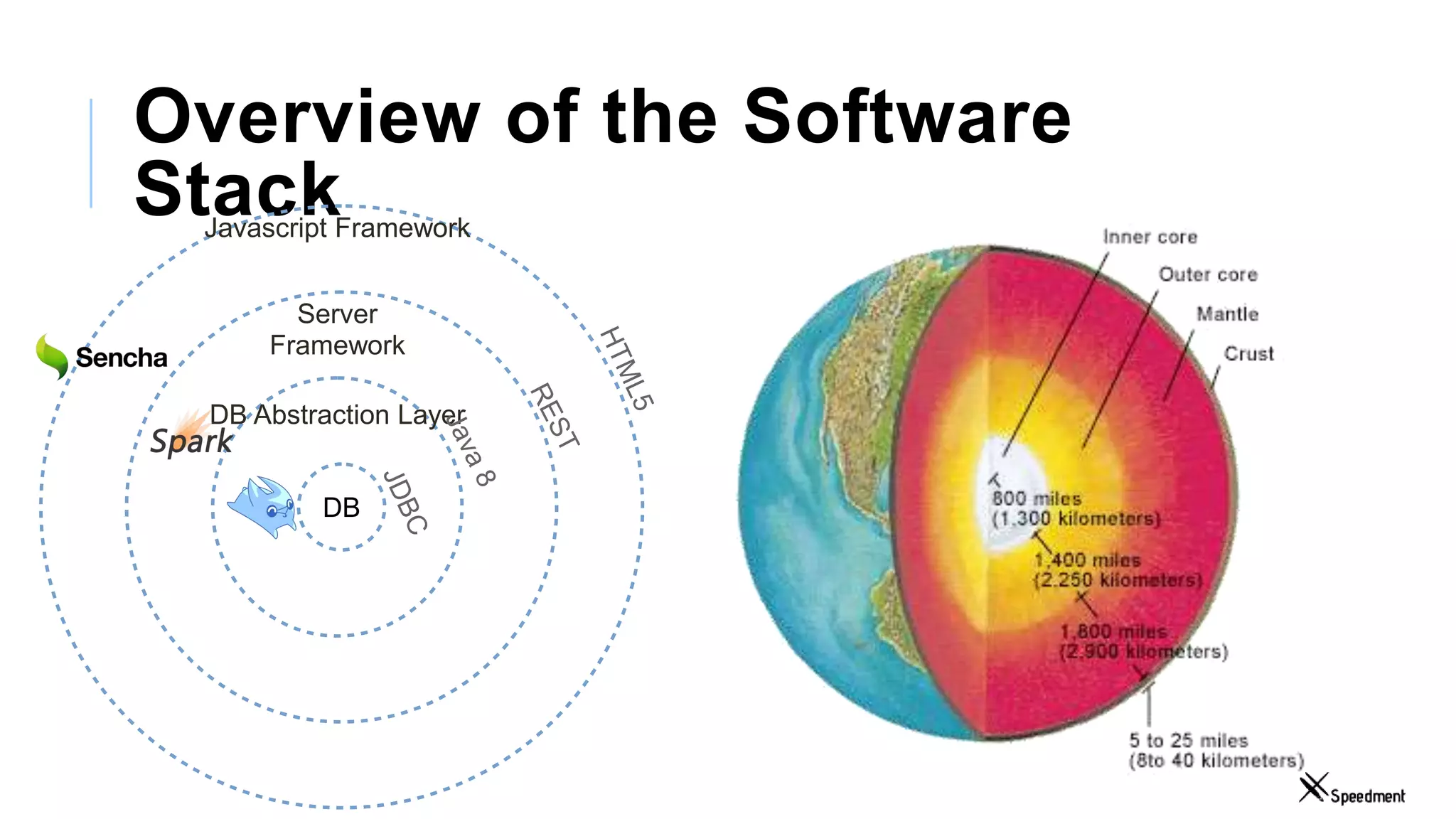
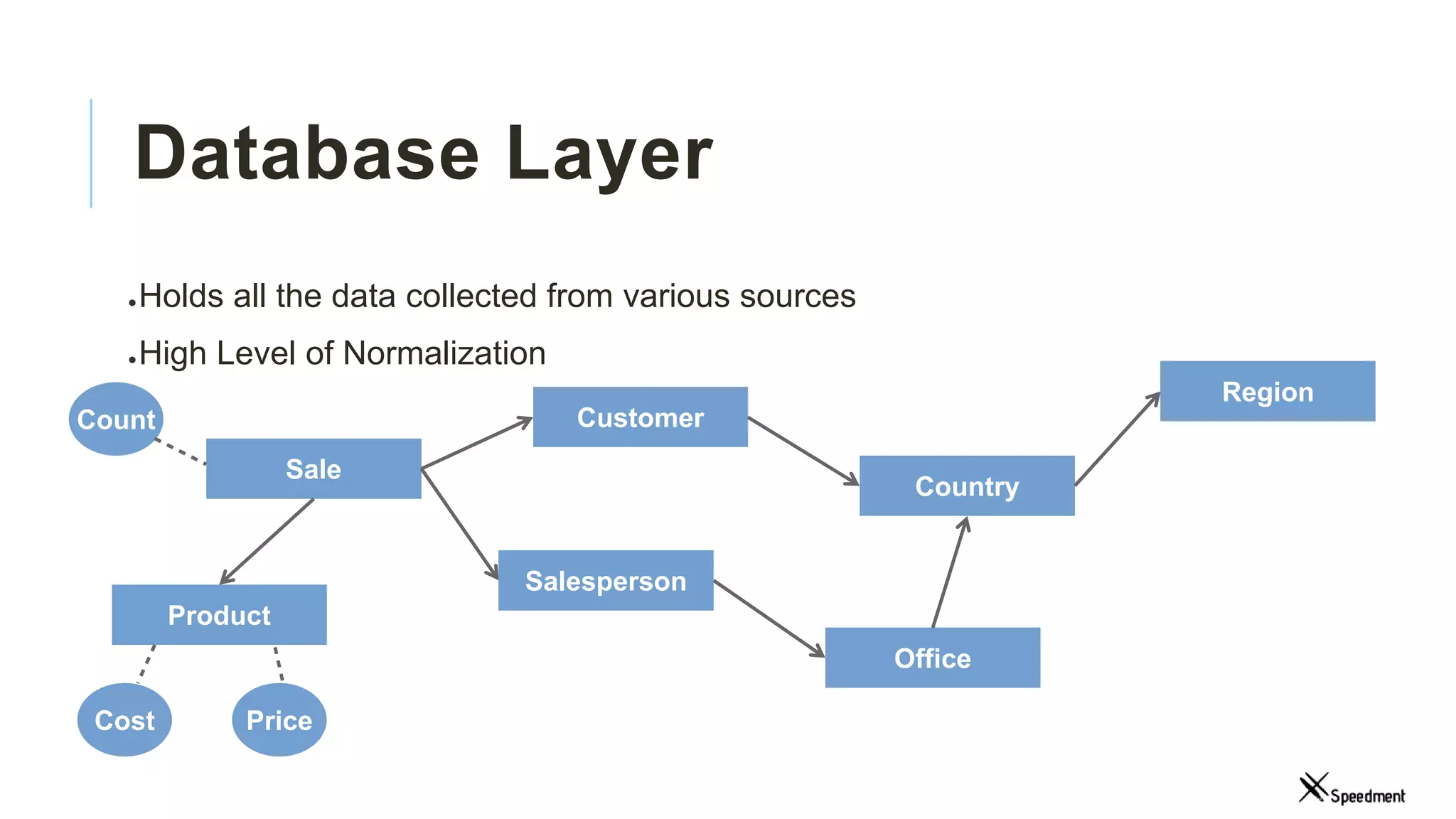
This document discusses Speedment, a Java development tool that optimizes database interactions by employing an object-oriented approach to simplify development and enhance performance. It covers the pros and cons of using Java ORM JPA, along with features such as code generation, querying with Java 8 streams, and in-memory caching to speed up applications. Additionally, it details how to integrate Speedment with Sencha for creating a REST API, providing a framework for seamless data management and client-server interaction.




















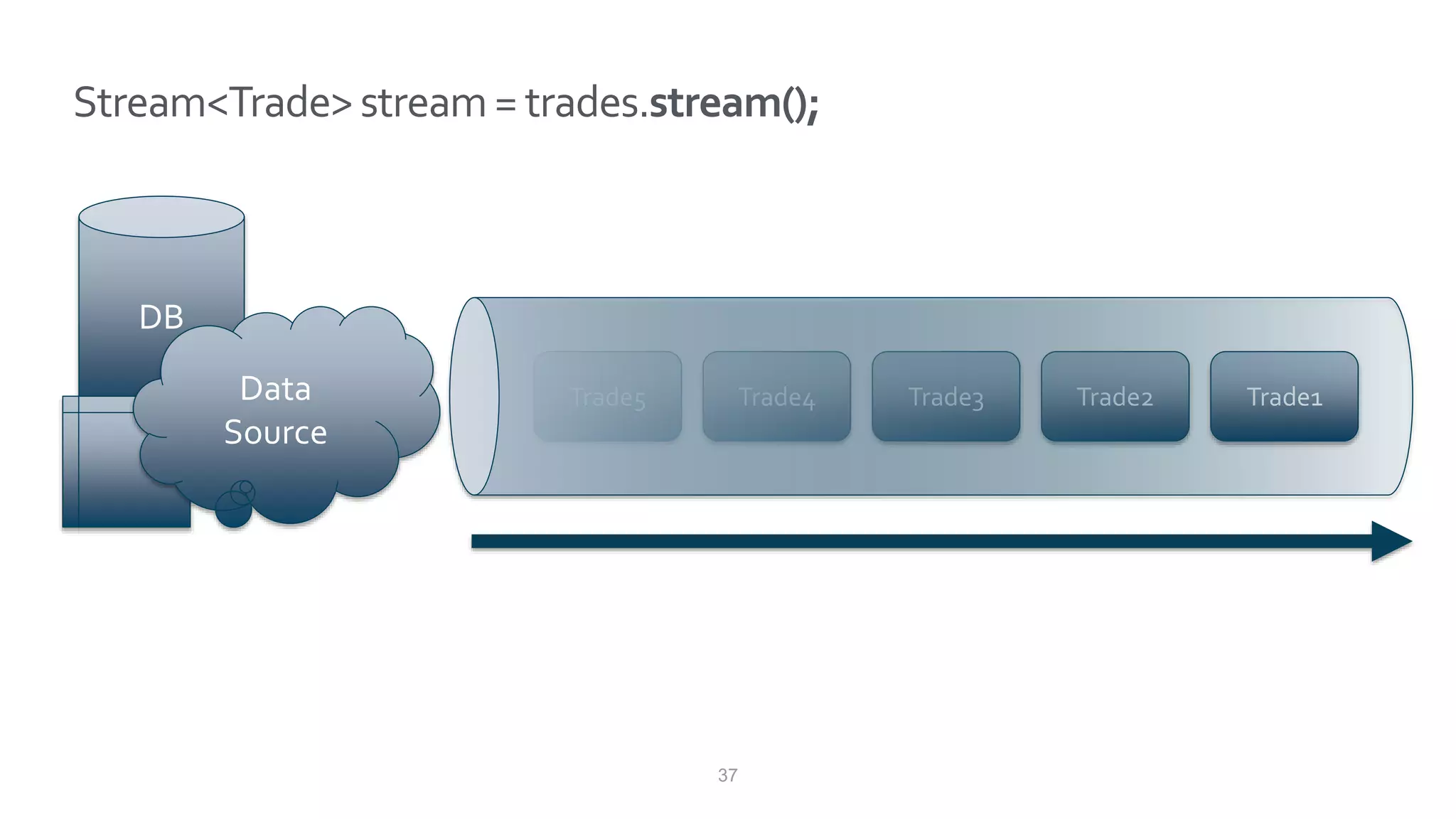
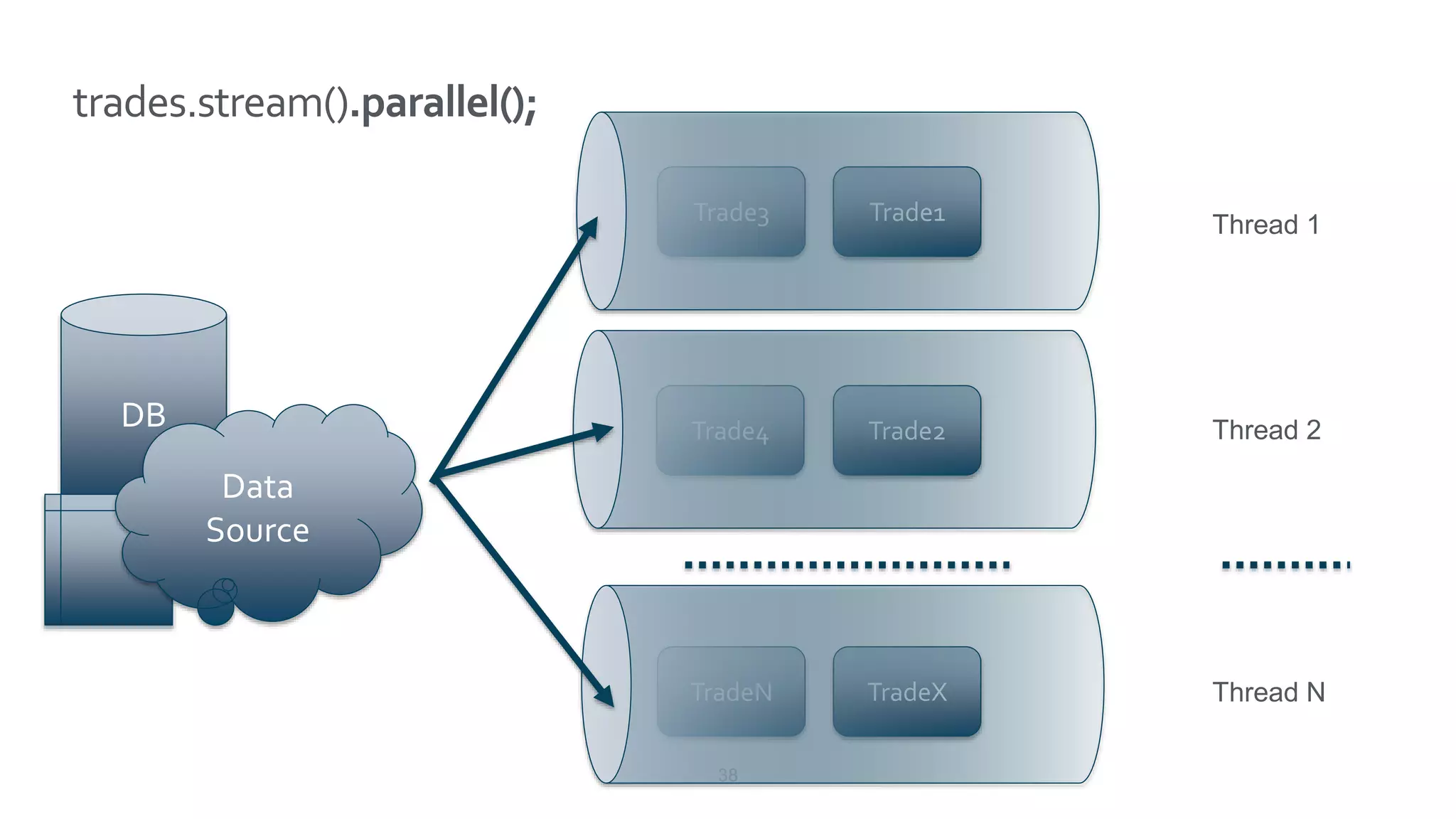
![http://localhost:4567/trades/1001/200? from=0&to=1441147840000&callback=Ext.data.JsonP.callback1 Ext.data.JsonP.callback1([ {'start':1420131600000,'stop':1420236681000,'average':100876,'open':100000,'close':102209,'high':104060,'low':98714}, {'start':1420236682000,'stop':1420243199000,'average':102339,'open':102224,'close':103348,'high':103366,'low':101603}, {'start':1420477200000,'stop':1420502399000,'average':102272,'open':103353,'close':103316,'high':103608,'low':100819}, {'start':1420563600000,'stop':1420657005000,'average':101682,'open':103315,'close':102292,'high':103755,'low':99241}, … (200 rows in total) ... {'start':1441147839000,'stop':1441147839000,'average':142165,'open':142165,'close':142165,'high':142165,'low':142165} ]); Objectives:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meetupgbg151228-160107233714/75/DZone-Java-8-Block-Buster-Query-Databases-Using-Streams-34-2048.jpg)

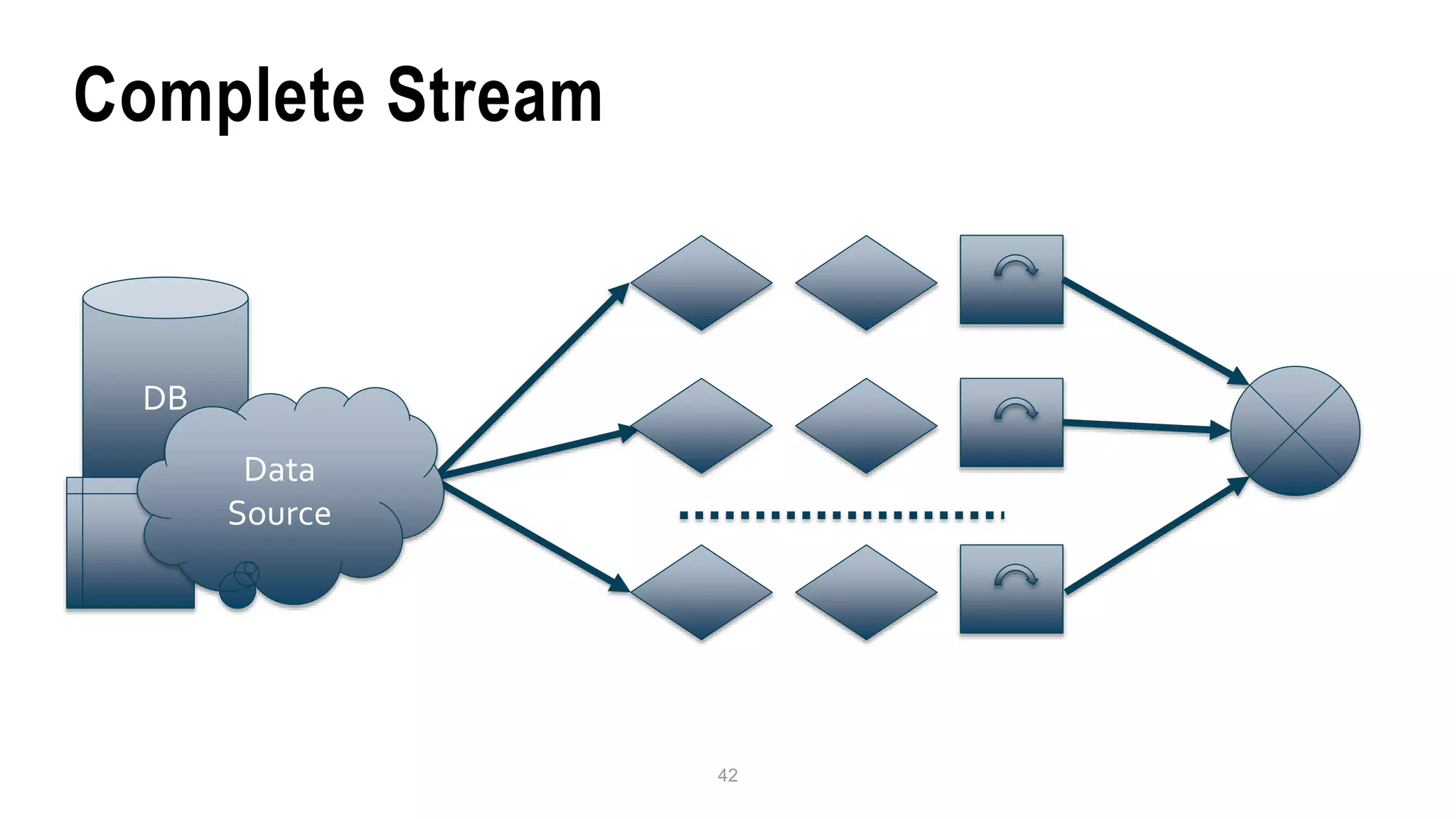



![Server Framework ●A lightweight webserver ●Separates client/server-responsabilitys ●Execute selected business logic as response to REST commands ●Low Level of Abstraction http://localhost:8123/salesinfo/ ?c=callback &filter=[{...}]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meetupgbg151228-160107233714/75/DZone-Java-8-Block-Buster-Query-Databases-Using-Streams-51-2048.jpg)