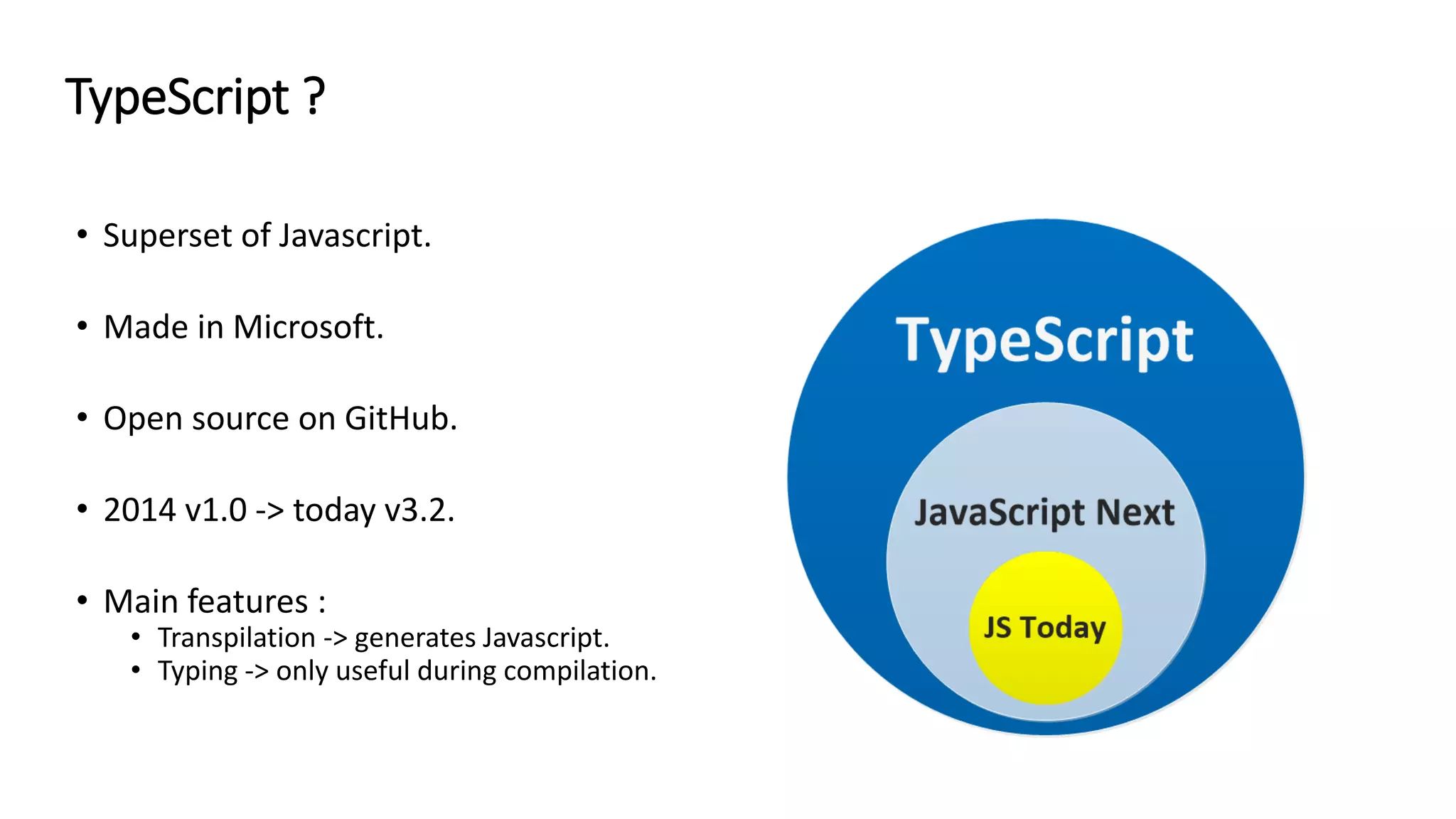
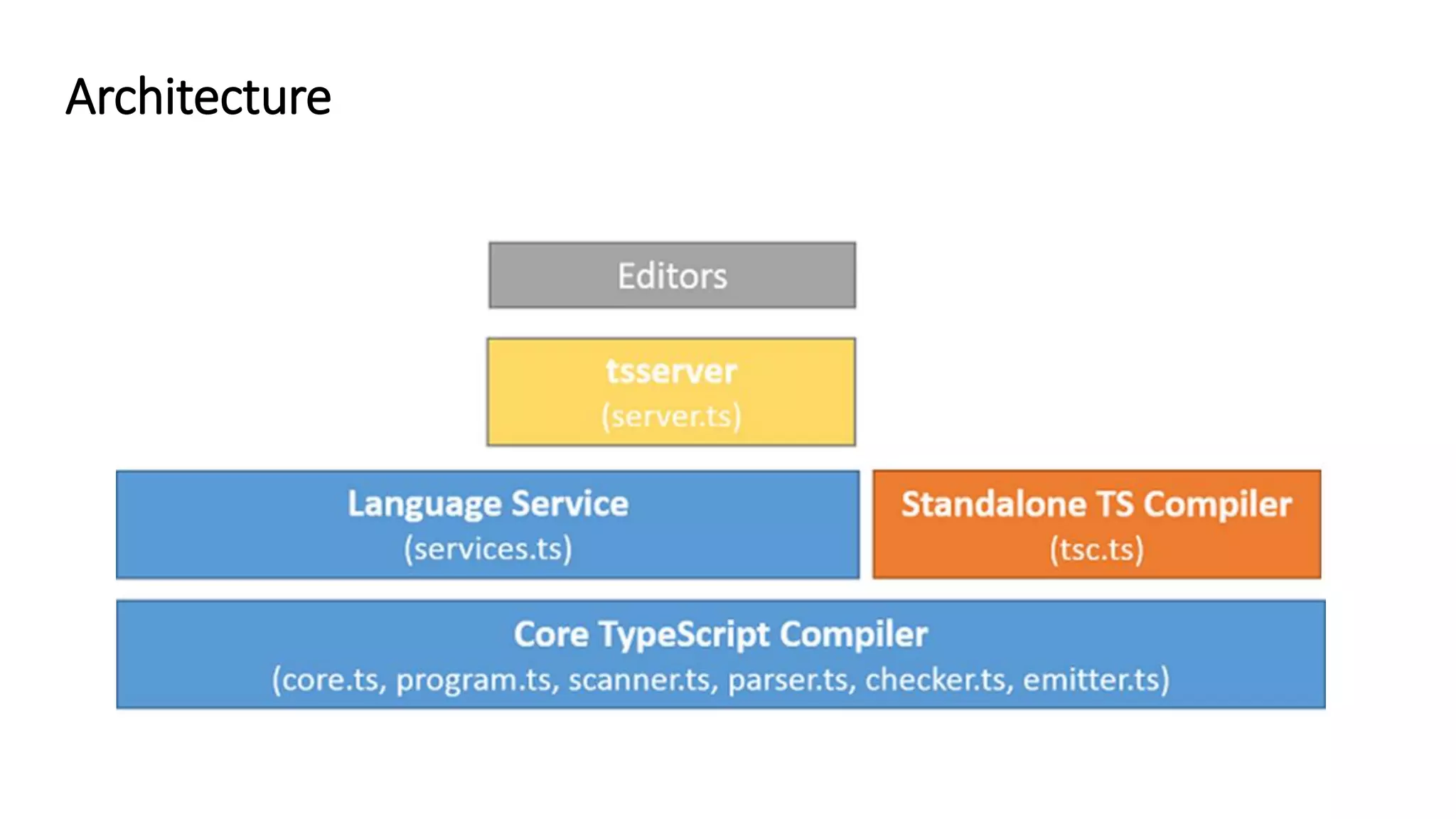
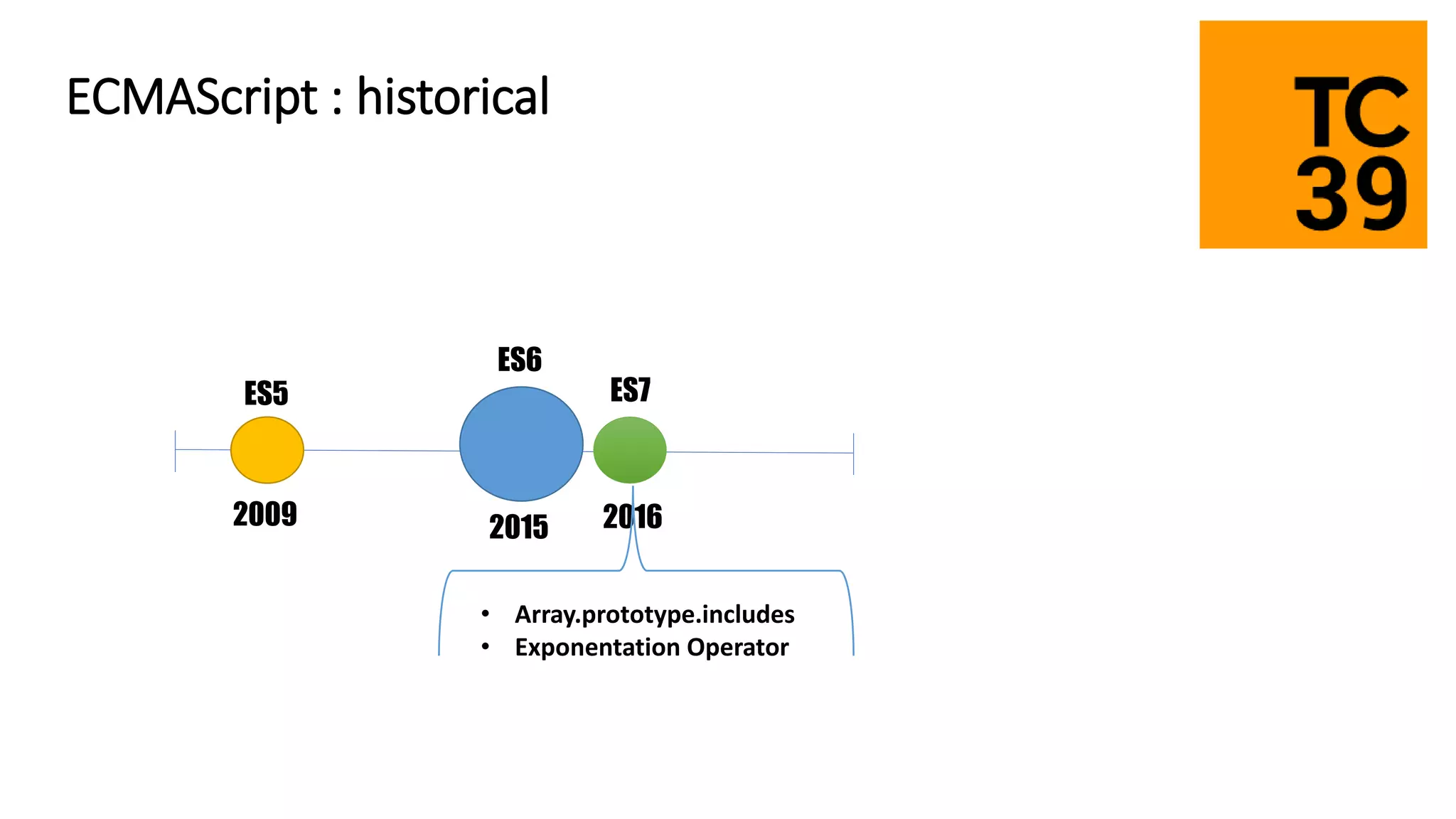
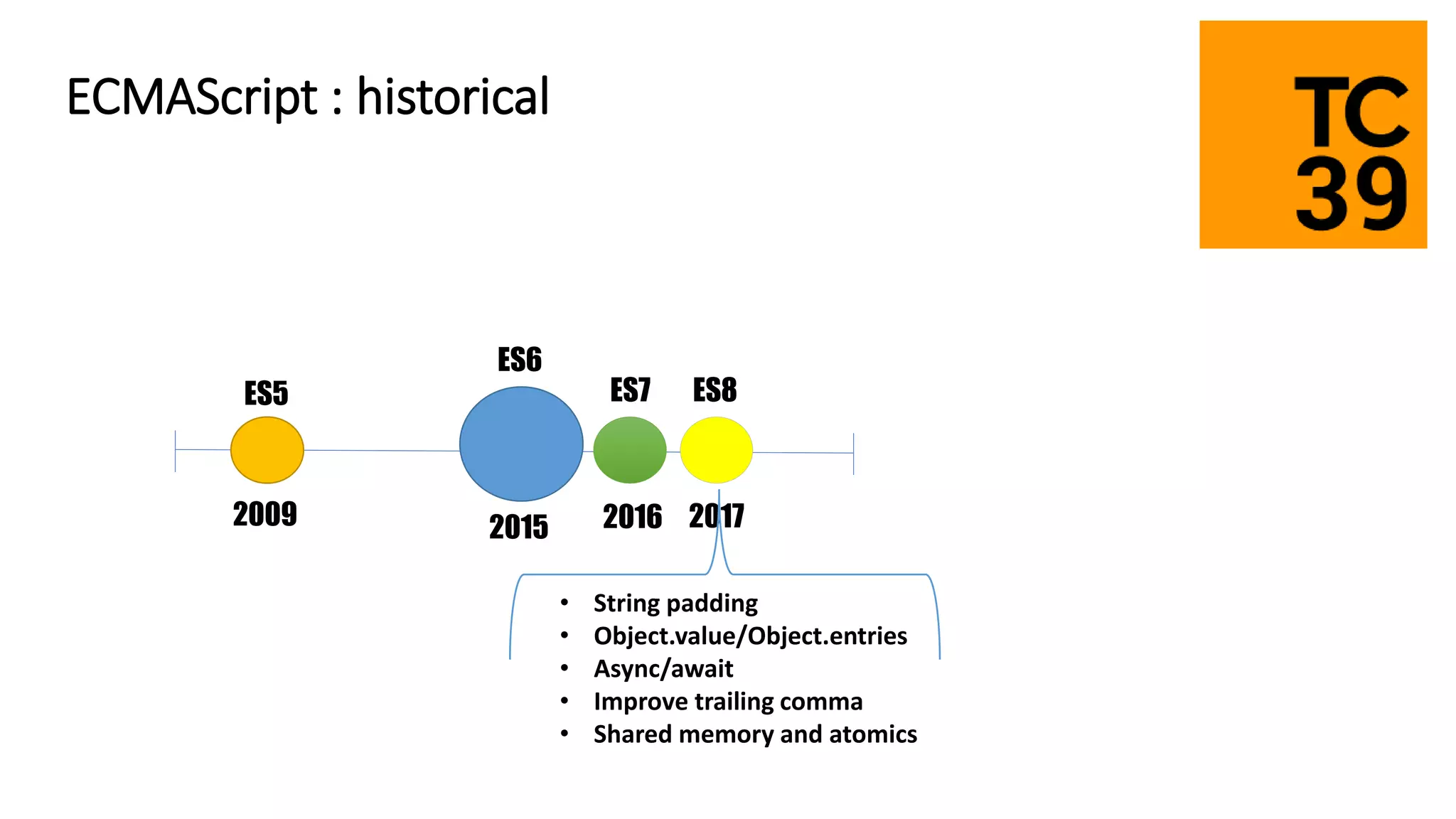
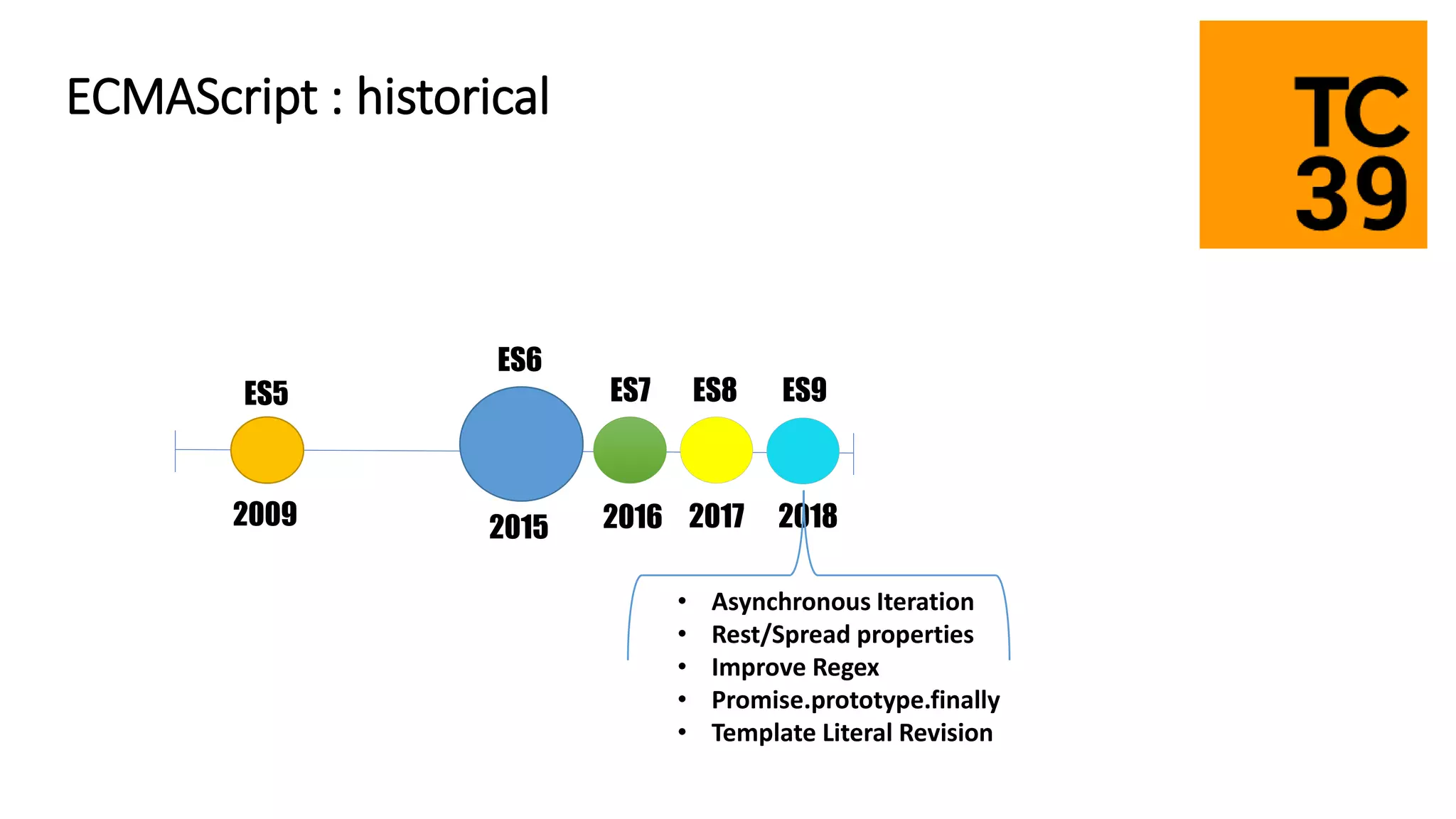
TypeScript is a superset of JavaScript that adds static typing and class-based object-oriented programming. It allows developers to migrate existing JavaScript code incrementally by adding type annotations and migrating files to the .ts extension over time. The document discusses TypeScript's architecture, transpilation to JavaScript, typing system, and provides recommendations for migrating JavaScript code to TypeScript.







![• Files + options → tsc → core compiler → JavaScript files. • Use options : • Command line : • Configuration file aka tsconfig.json : tsc **/*.ts –-target=es5 -–sourcemap=true CLI tsc { "compilerOptions": { "target": "es5", "module": "es2015", "removeComments": true, "sourceMap": true }, "include": ["src/**/*"] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devdaysv2en-181201124048/75/TypeScript-Best-Practices-12-2048.jpg)










![• Use ES2015 -> transpile if needed. • To prevent ugly import : 1. In tsconfig.json use aliases path : 2. Don’t forget to also configure this aliases into your bundler’s config file. 3. Result : import { Animal } from "../../../../../../../core/animal"; { "compilerOptions": { "baseUrl": "./src", "paths": { "@myProject/utils/*": ["app/utils/*"], "@myPorject/core/*": ["app/core/*"] } } } import { Animal } from “@myProject/core/animal"; Module](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devdaysv2en-181201124048/75/TypeScript-Best-Practices-29-2048.jpg)
![enum Color { Red, Blue, Green } let foo: Color = Color.Red; let bar: string = Color[Color.Red]; "use strict"; var Color; (function (Color) { Color[Color["Red"] = 0] = "Red"; Color[Color["Blue"] = 1] = "Blue"; Color[Color["Green"] = 2] = "Green"; })(Color || (Color = {})); let foo = Color.Red; let bar = Color[Color.Red]; color.ts TypeScript compiler color.js Enum](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devdaysv2en-181201124048/75/TypeScript-Best-Practices-30-2048.jpg)
![const enum Color { Red, Blue, Green } let foo: Color = Color.Red; "use strict"; let foo = 0 /* Red */; color.ts TypeScript compiler color.js let bar: string = Color[Color.Red]; Constant Enum](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devdaysv2en-181201124048/75/TypeScript-Best-Practices-31-2048.jpg)

![class Greeter { greeting: string; constructor(message: string) { this.greeting = message; } greet() { return "Hello, " + this.greeting; } } class PoliteGreeter extends Greeter { //... } var __extends = (this && this.__extends) || (function () { var extendStatics = function (d, b) { extendStatics = Object.setPrototypeOf || ({ __proto__: [] } instanceof Array && function (d, b) { d.__proto__ = b; }) || function (d, b) { for (var p in b) if (b.hasOwnProperty(p)) d[p] = b[p]; }; return extendStatics(d, b); } return function (d, b) { extendStatics(d, b); function __() { this.constructor = d; } d.prototype = b === null ? Object.create(b) : (__.prototype = b.prototype, new __()); }; })(); var Greeter = /** @class */ (function () { function Greeter(message) { this.greeting = message; } Greeter.prototype.greet = function () { return "Hello, " + this.greeting; }; return Greeter; }()); var PoliteGreeter = /** @class */ (function (_super) { __extends(PoliteGreeter, _super); function PoliteGreeter() { return _super !== null && _super.apply(this, arguments) || this; } return PoliteGreeter; }(Greeter)); file.ts TypeScript compiler file.js TypeScript Helper](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devdaysv2en-181201124048/75/TypeScript-Best-Practices-33-2048.jpg)
![• Many helpers exists : • Generate in each file where are needed -> increase bundle size !!! function __assign(t: any, ...sources: any[]): any; // Helper de Object.Assign function __spread(...args: any[]): any[]; // Helper de l'opérateur spread //... TypeScript Helper : the trap](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devdaysv2en-181201124048/75/TypeScript-Best-Practices-34-2048.jpg)


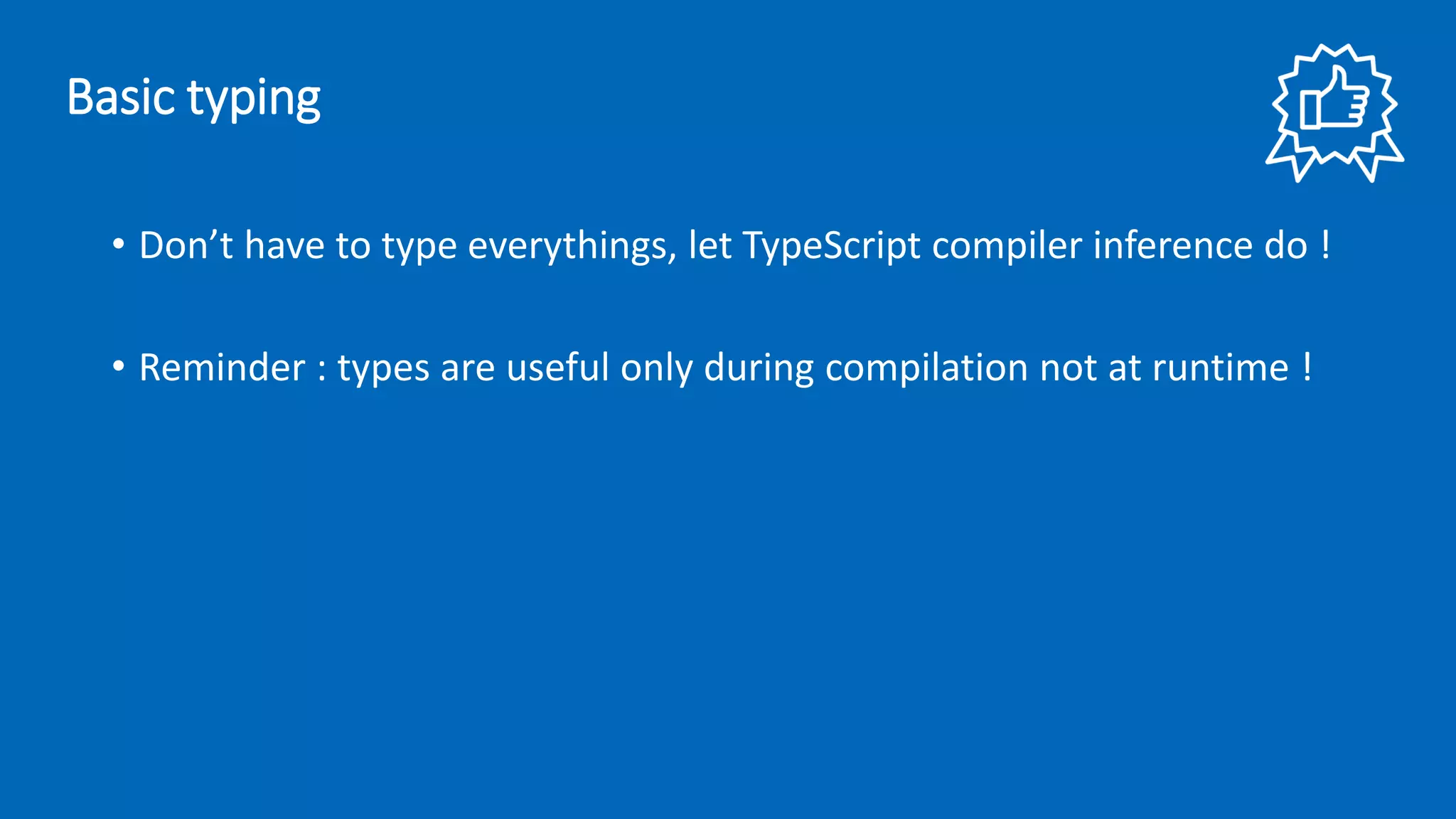
![Basic typing • boolean, number, string, array, void, null, undefined, object, any et unknow. let name: string; let list: number[] = [1, 2, 3]; function fn(param: boolean): void { // Do something }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devdaysv2en-181201124048/75/TypeScript-Best-Practices-37-2048.jpg)











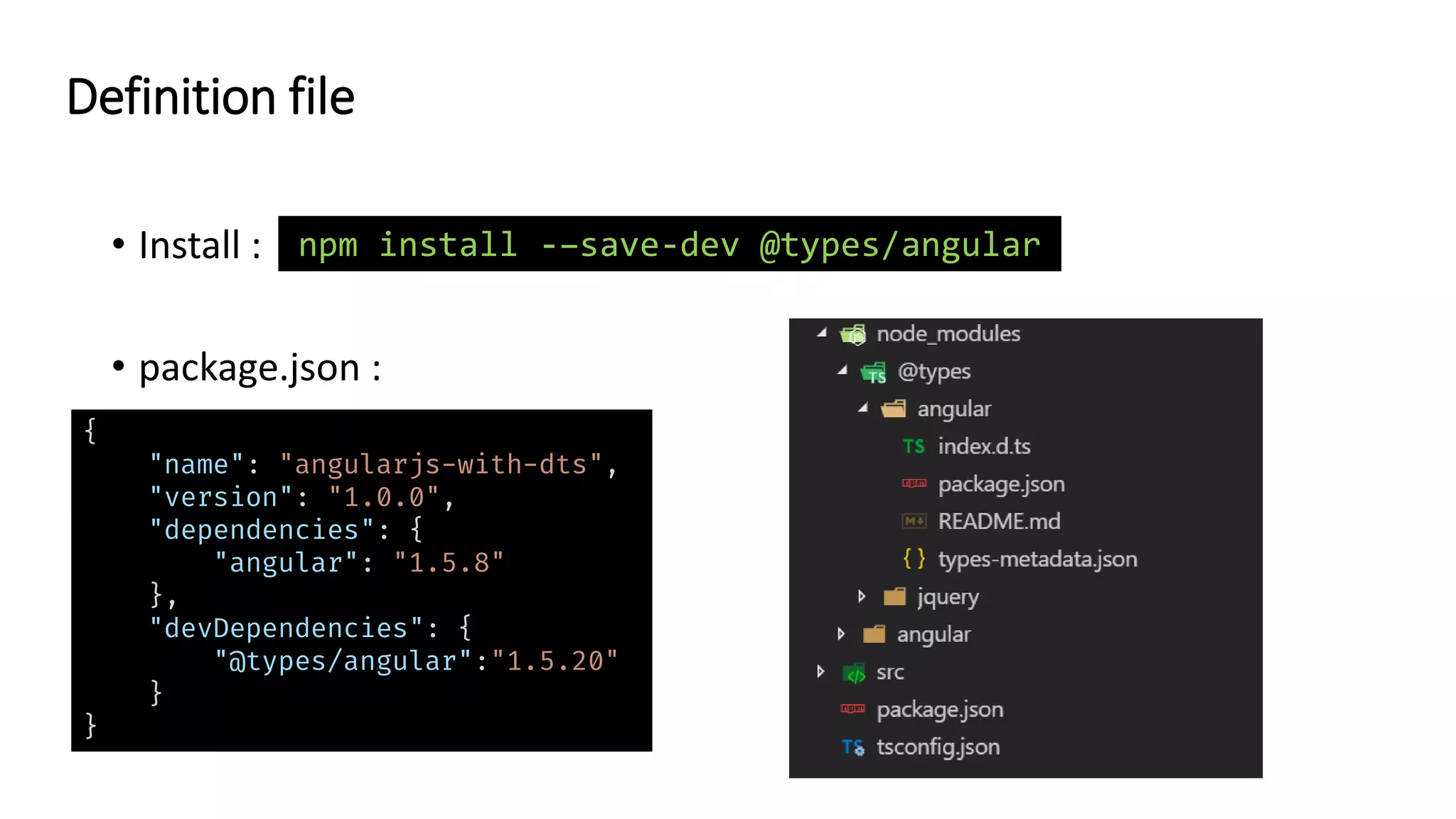
![• Alaway install .d.ts files in devDependencies. • Specify composition of lib.d.ts file according to the native Javascript features you use : Definition file { "compilerOptions": { "target": "es5", "lib": [ "dom", "es5", "es2015.collection", "es2015.iterable" ] } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devdaysv2en-181201124048/75/TypeScript-Best-Practices-51-2048.jpg)

![// @ts-check JavaScript → TypeScript : solution 1 function add(numbers) { return numbers .reduce(function(previous, next) { return previous + next; }); } var result = add([true, 2, "3"]); console.log(result); // 33 // @ts-check /** * @param {number[]} numbers */ function add(numbers) { return numbers .reduce(function(previous, next) { return previous + next; }); } var result = add([true, 2, "3"]); console.log(result); // 33 --checkJs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devdaysv2en-181201124048/75/TypeScript-Best-Practices-53-2048.jpg)