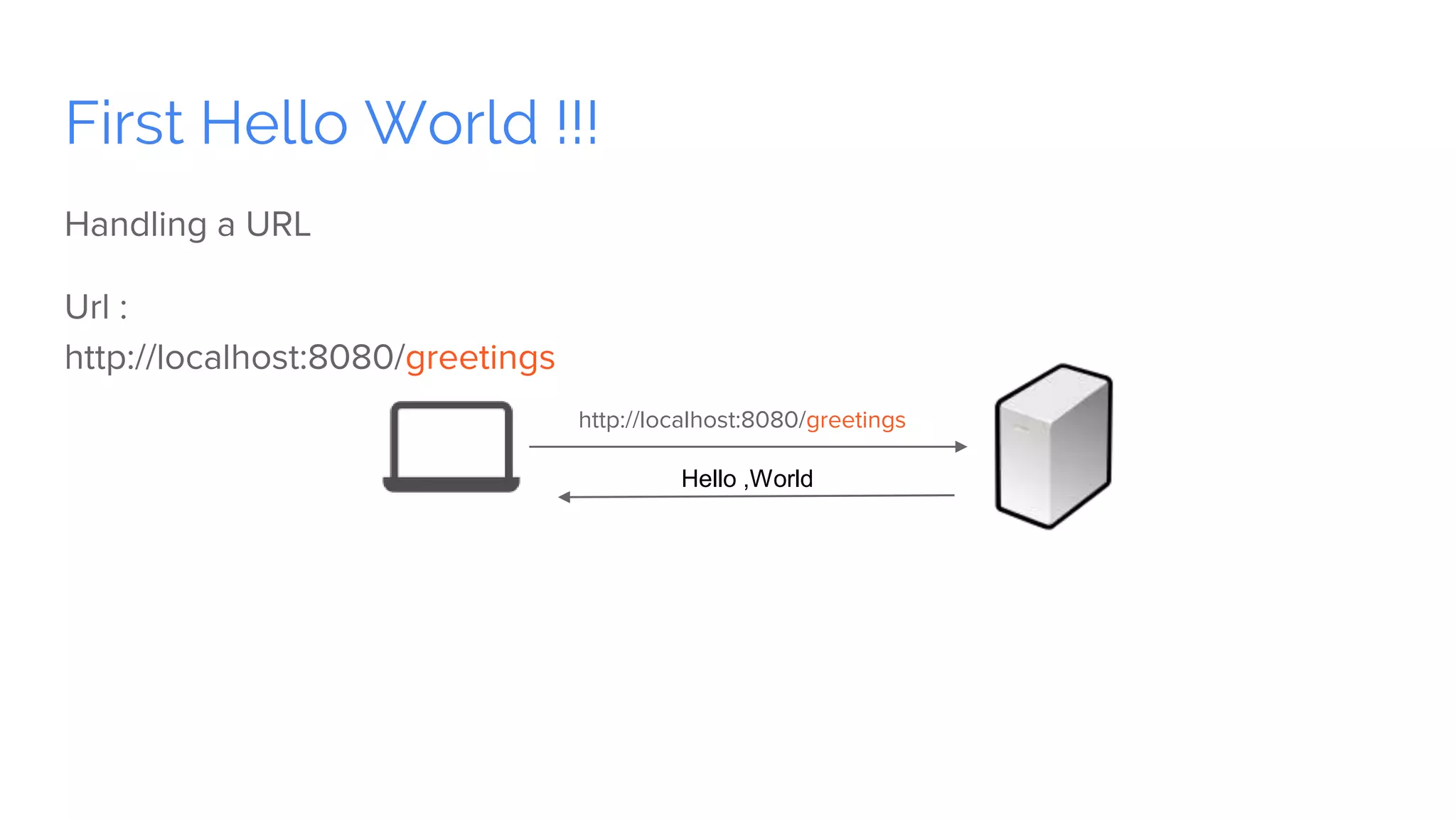
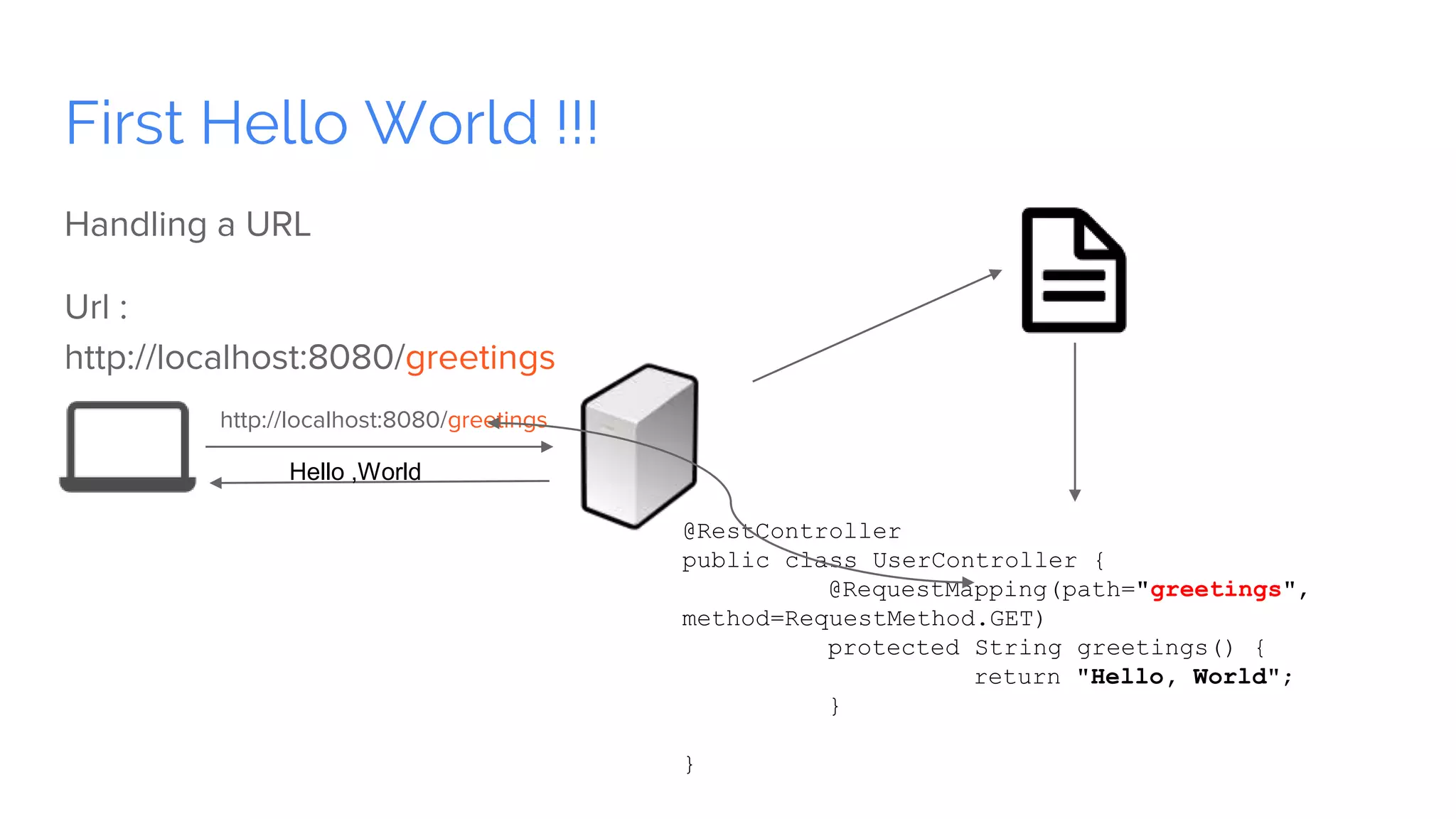
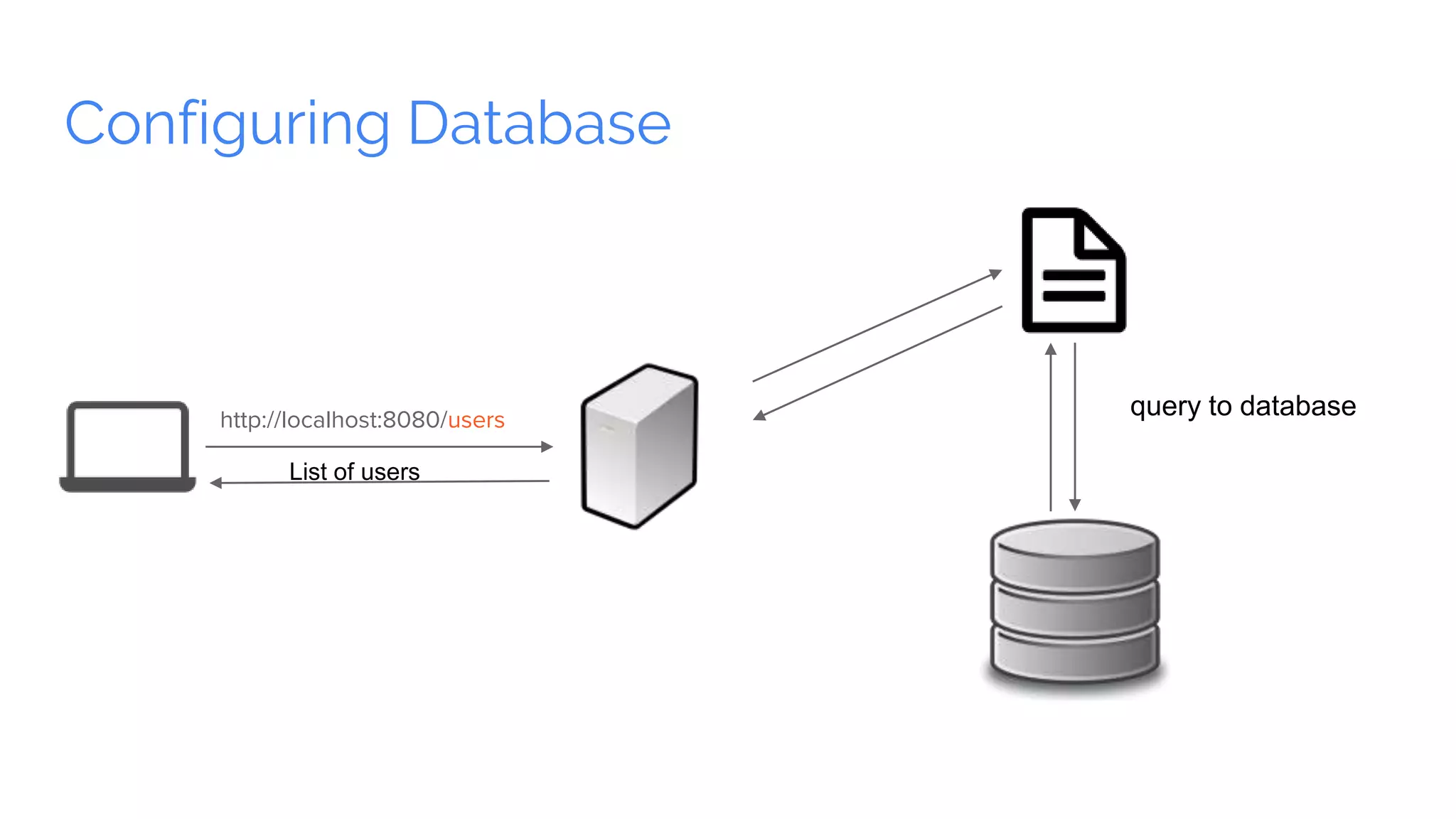
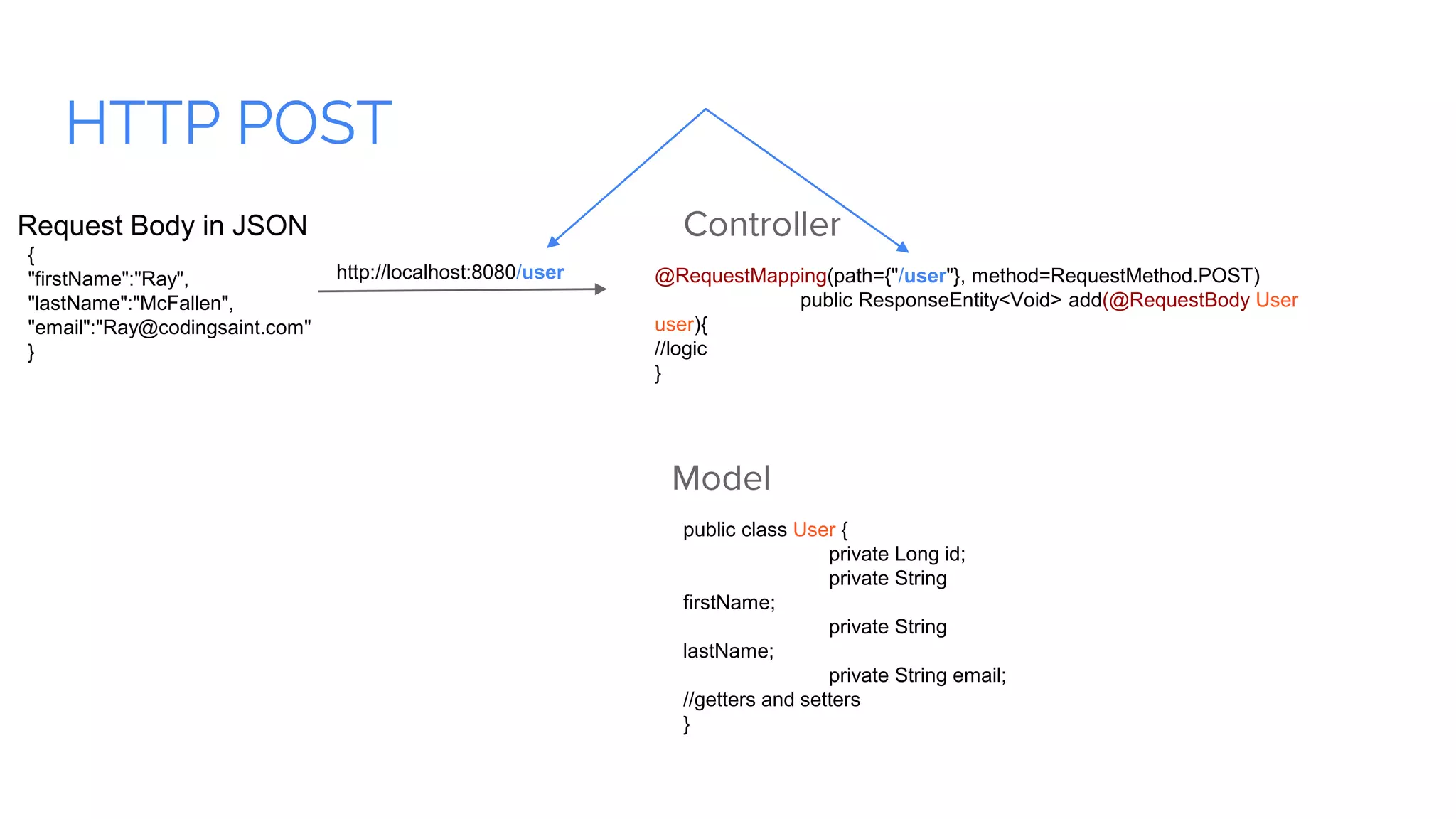
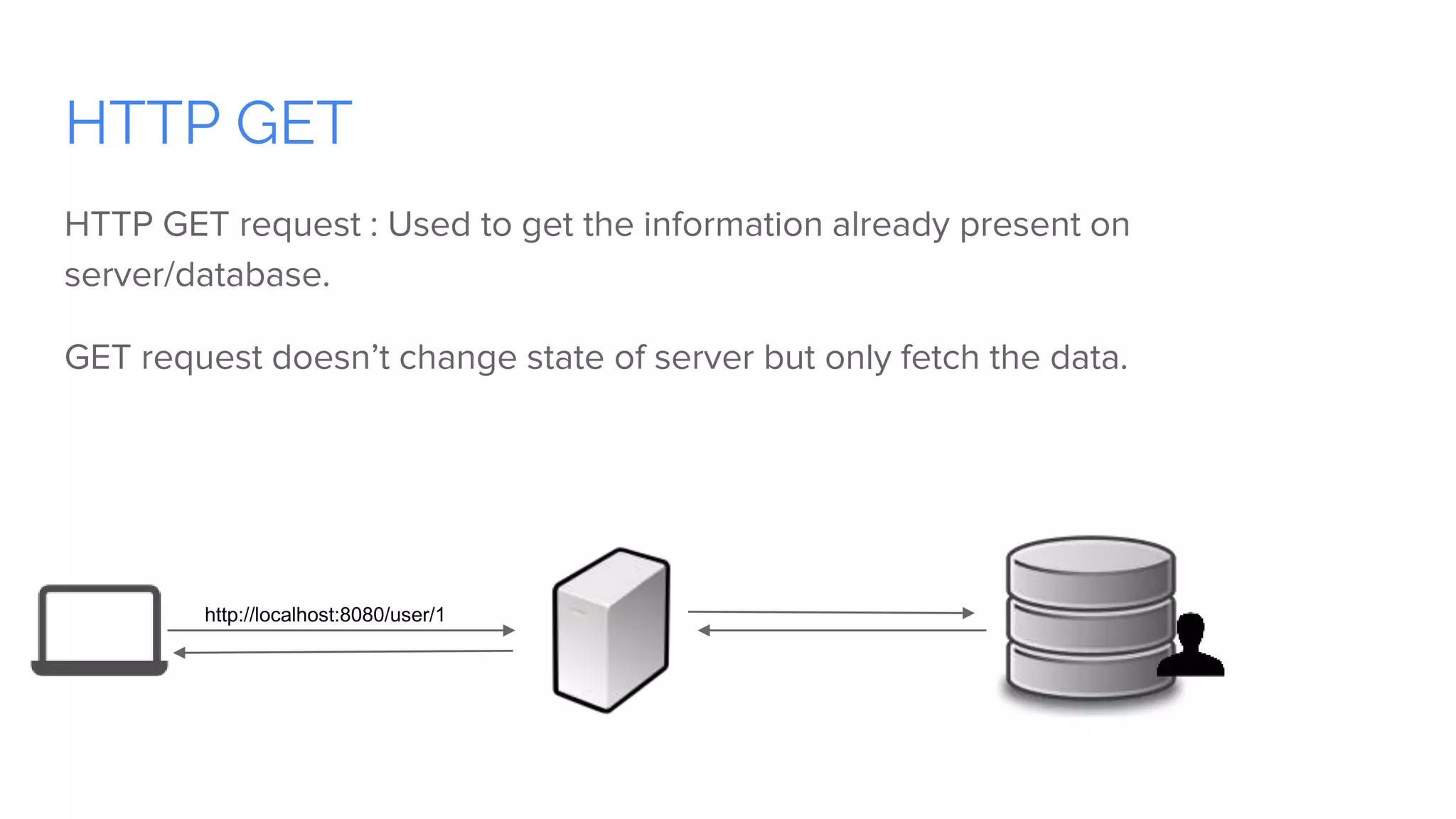
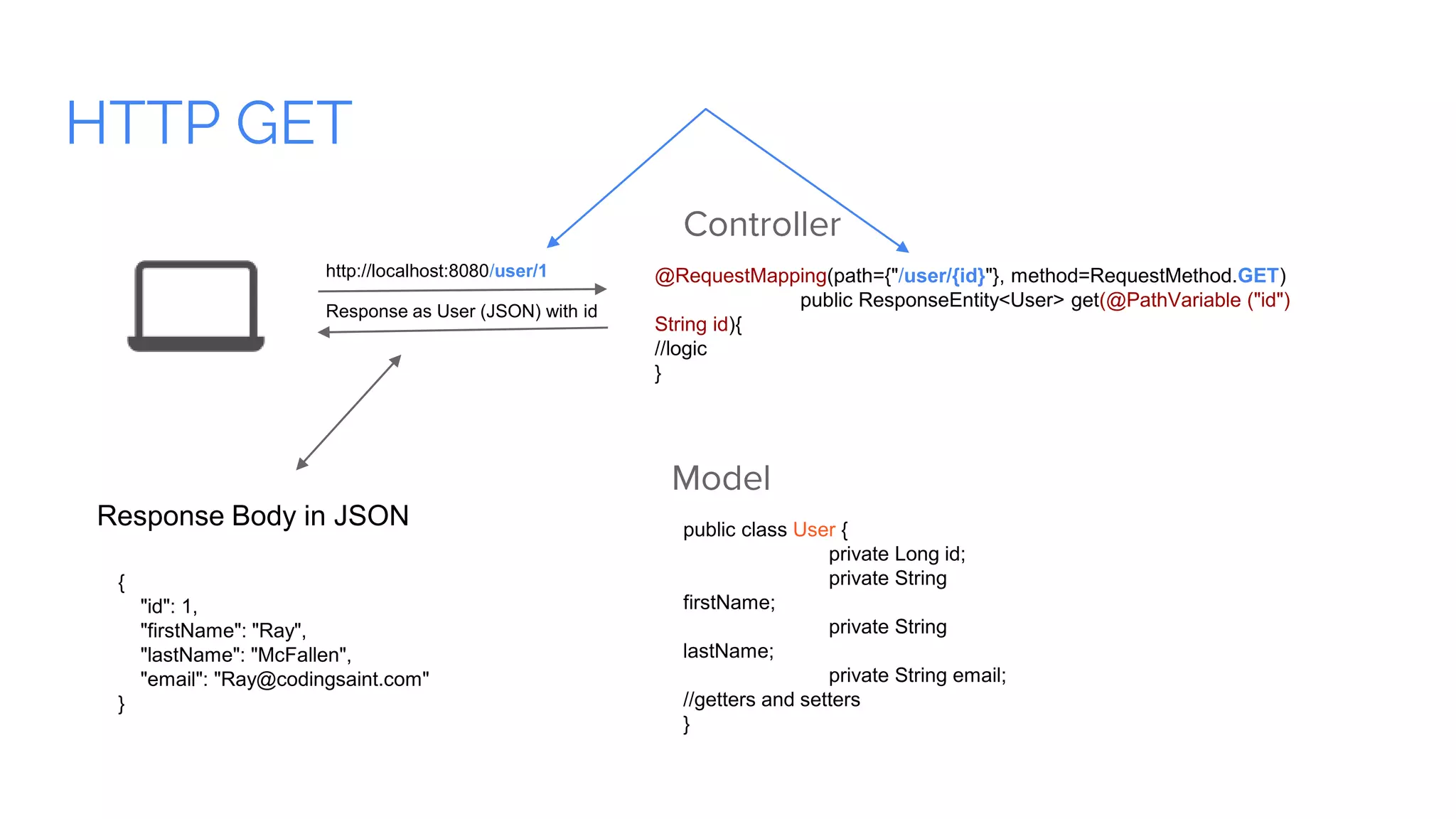
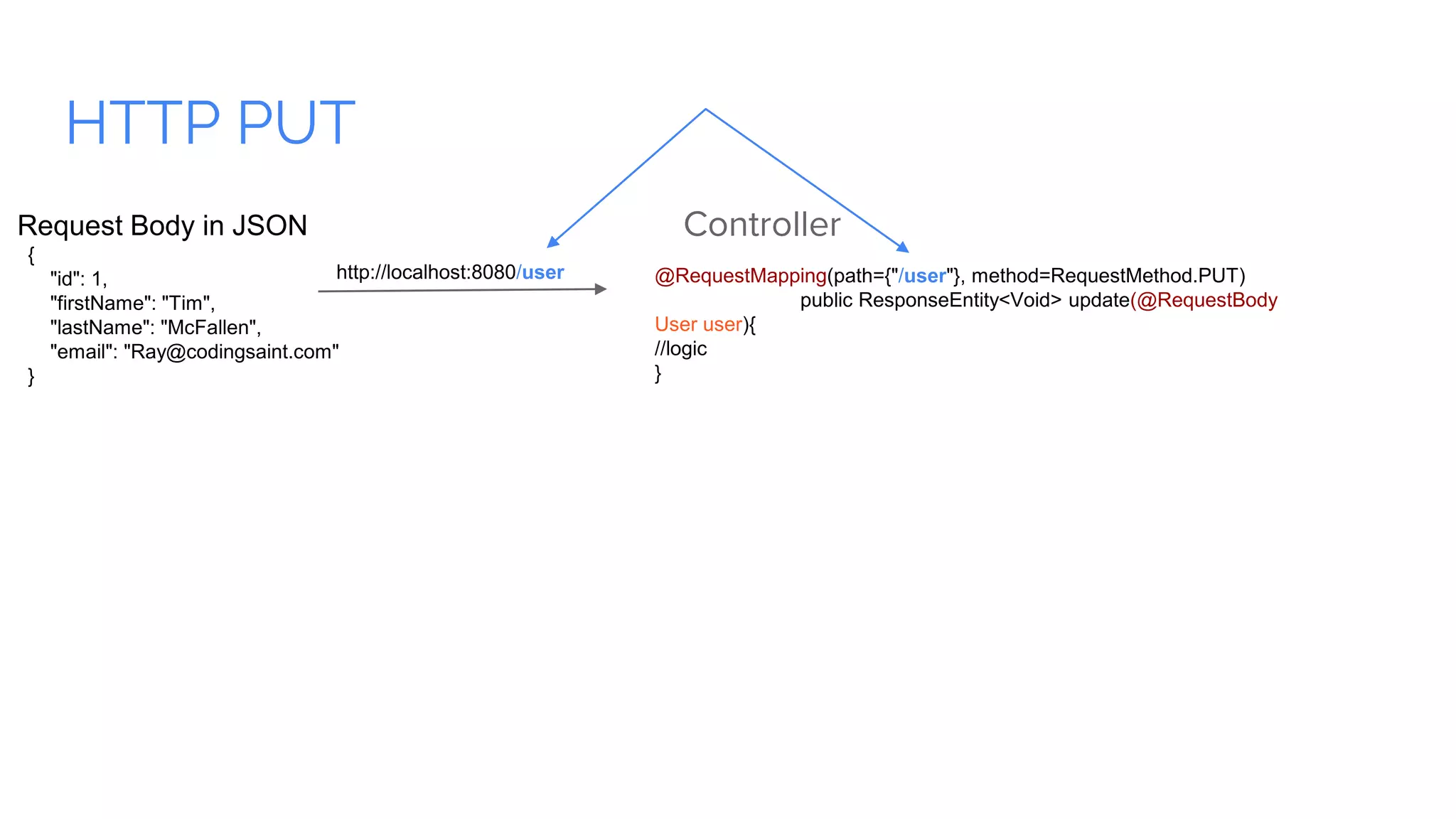
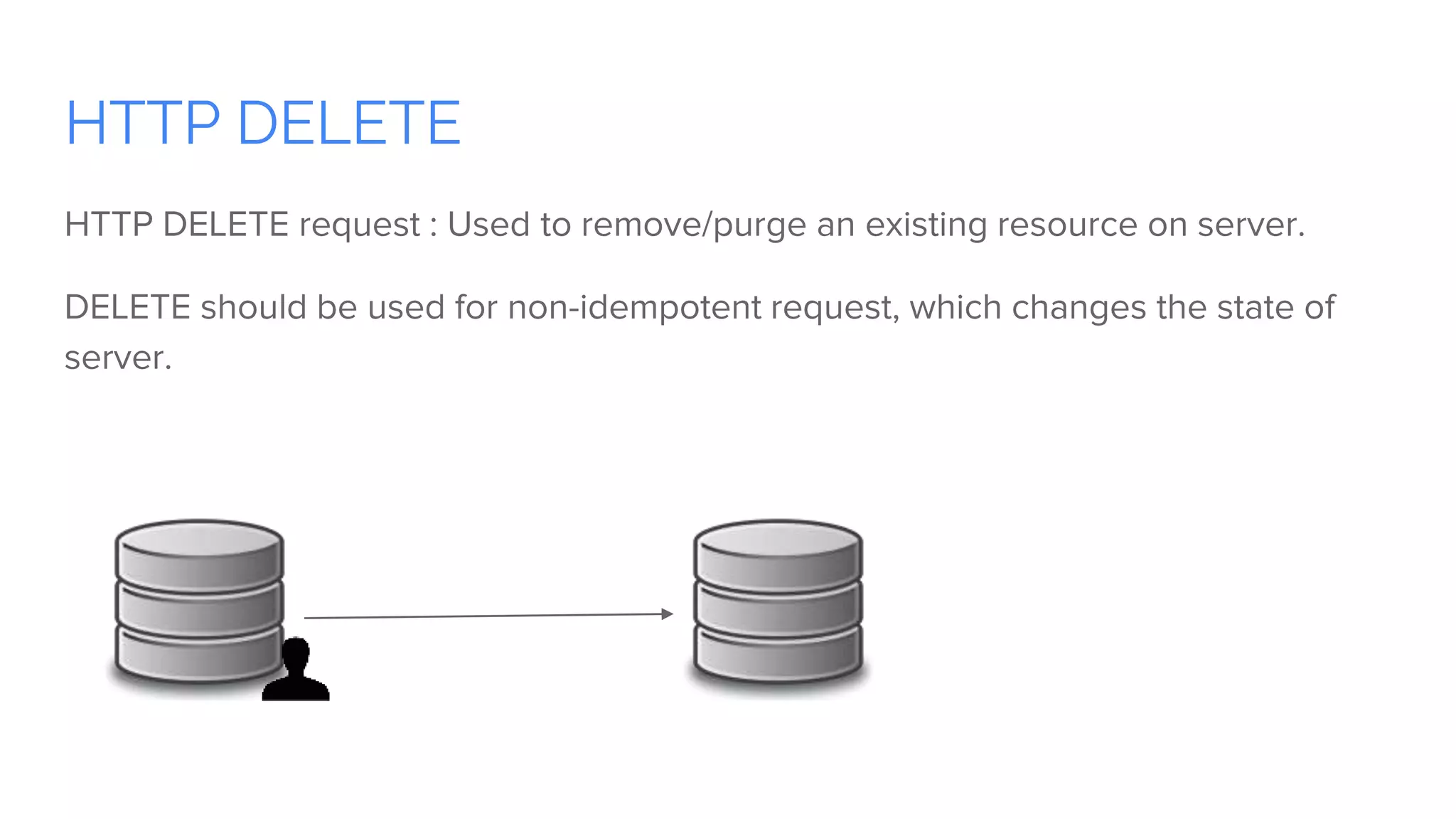
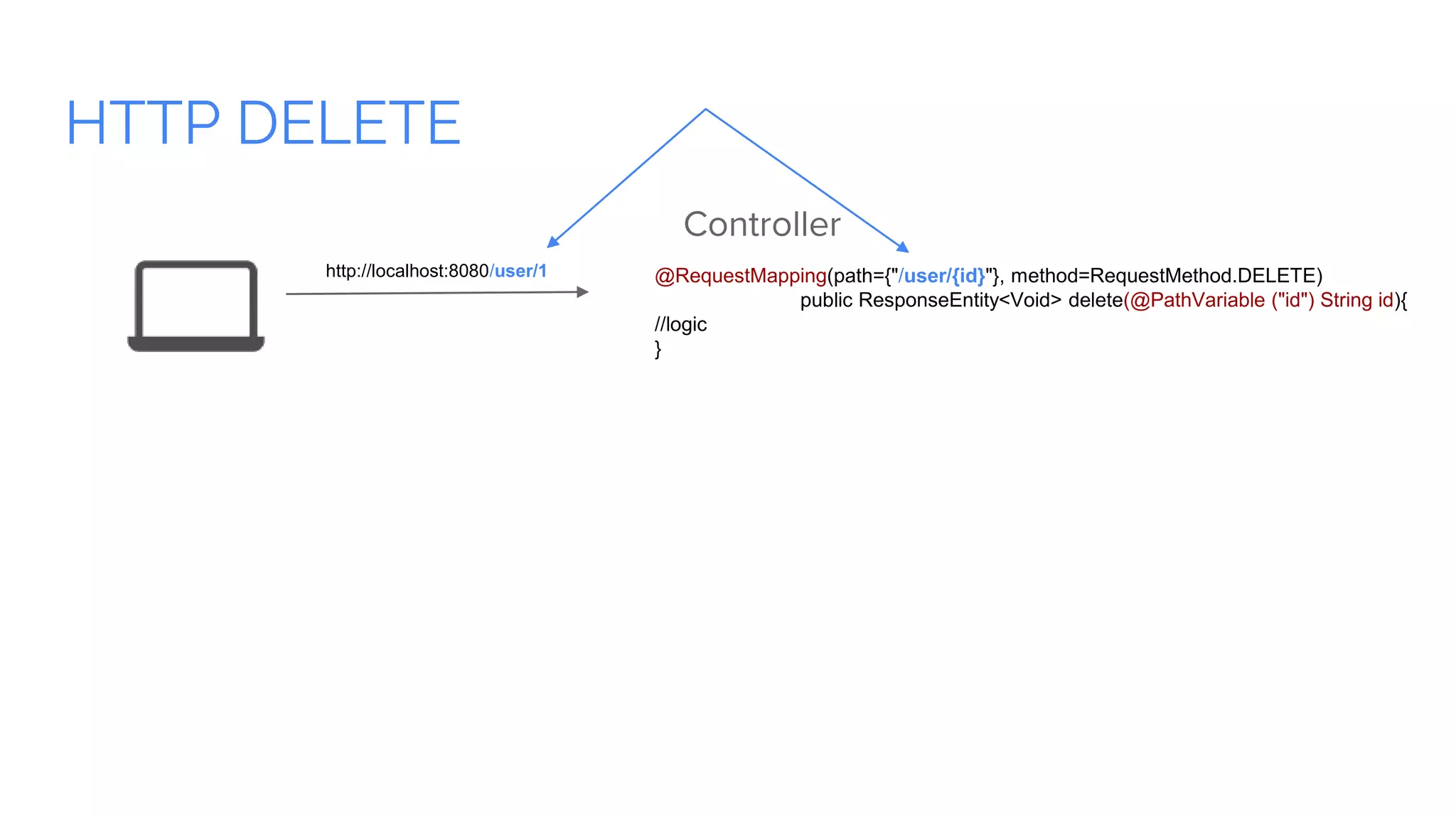
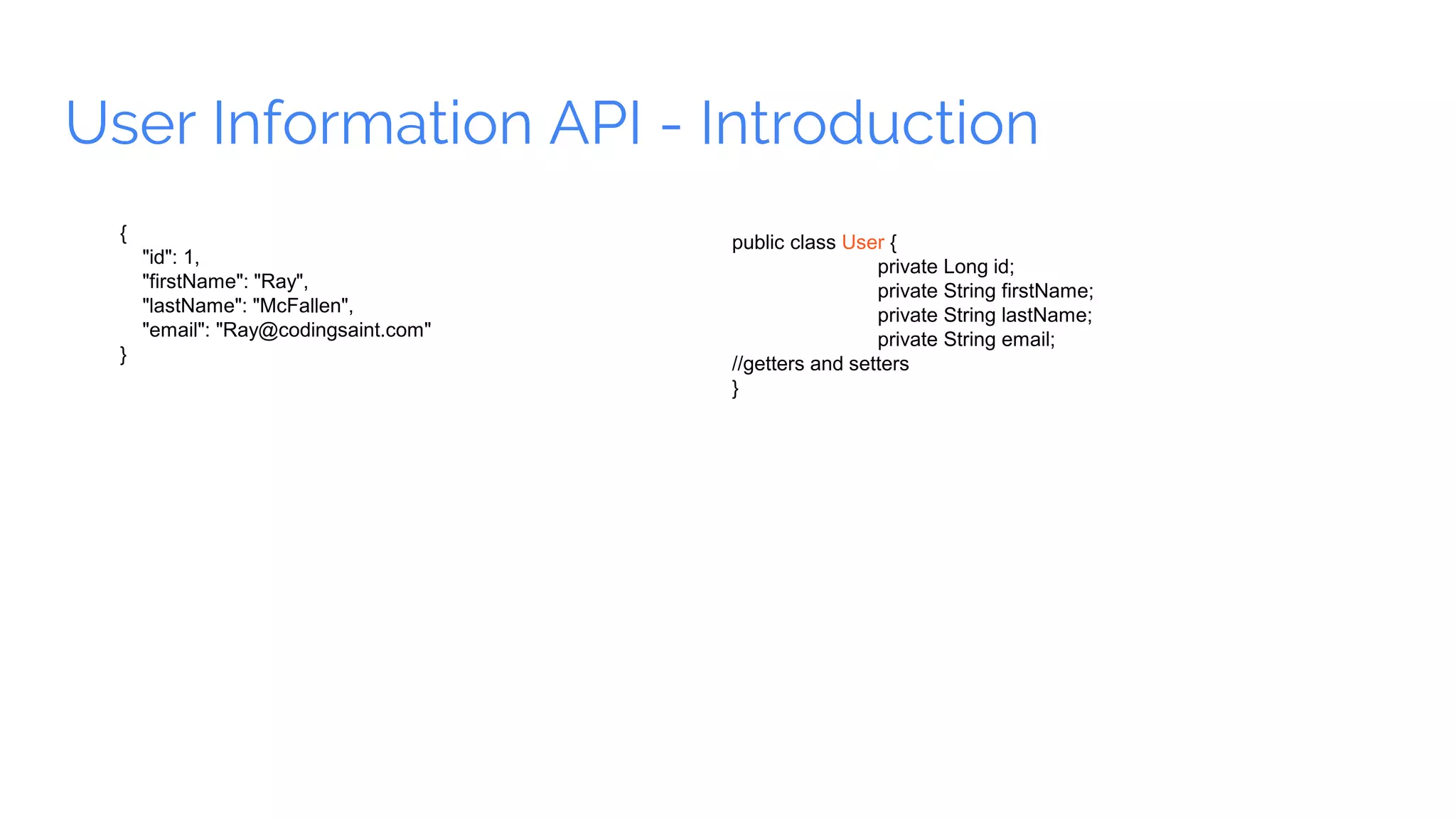
Spring Boot is a framework for creating stand-alone, production-grade Spring-based applications that can be started using java -jar without requiring any traditional application servers. It is designed to get developers up and running as quickly as possible with minimal configuration. Some key features of Spring Boot include automatic configuration, starter dependencies to simplify dependency management, embedded HTTP servers, security, metrics, health checks and externalized configuration. The document then provides examples of building a basic RESTful web service with Spring Boot using common HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, DELETE and handling requests and responses.