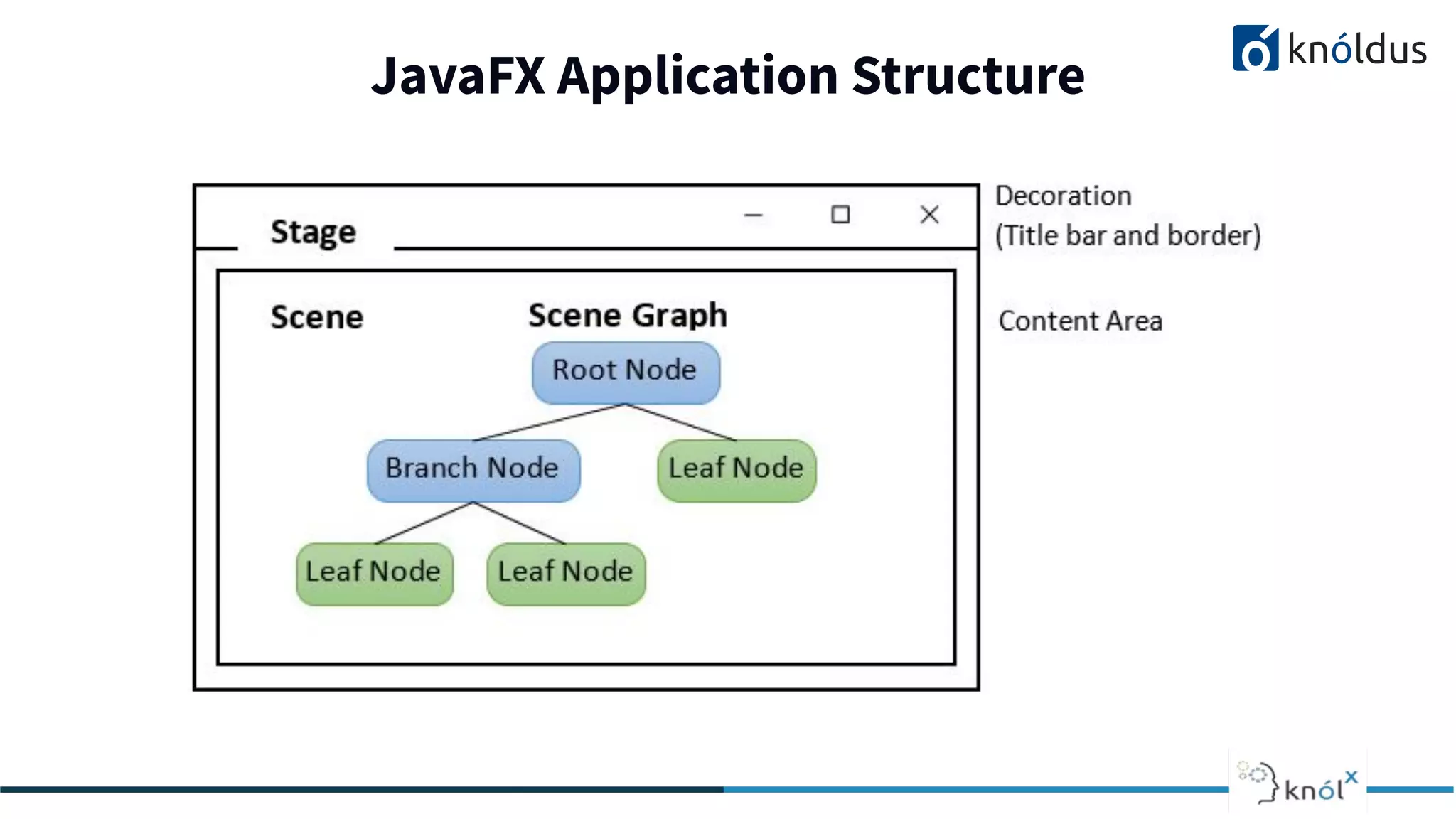
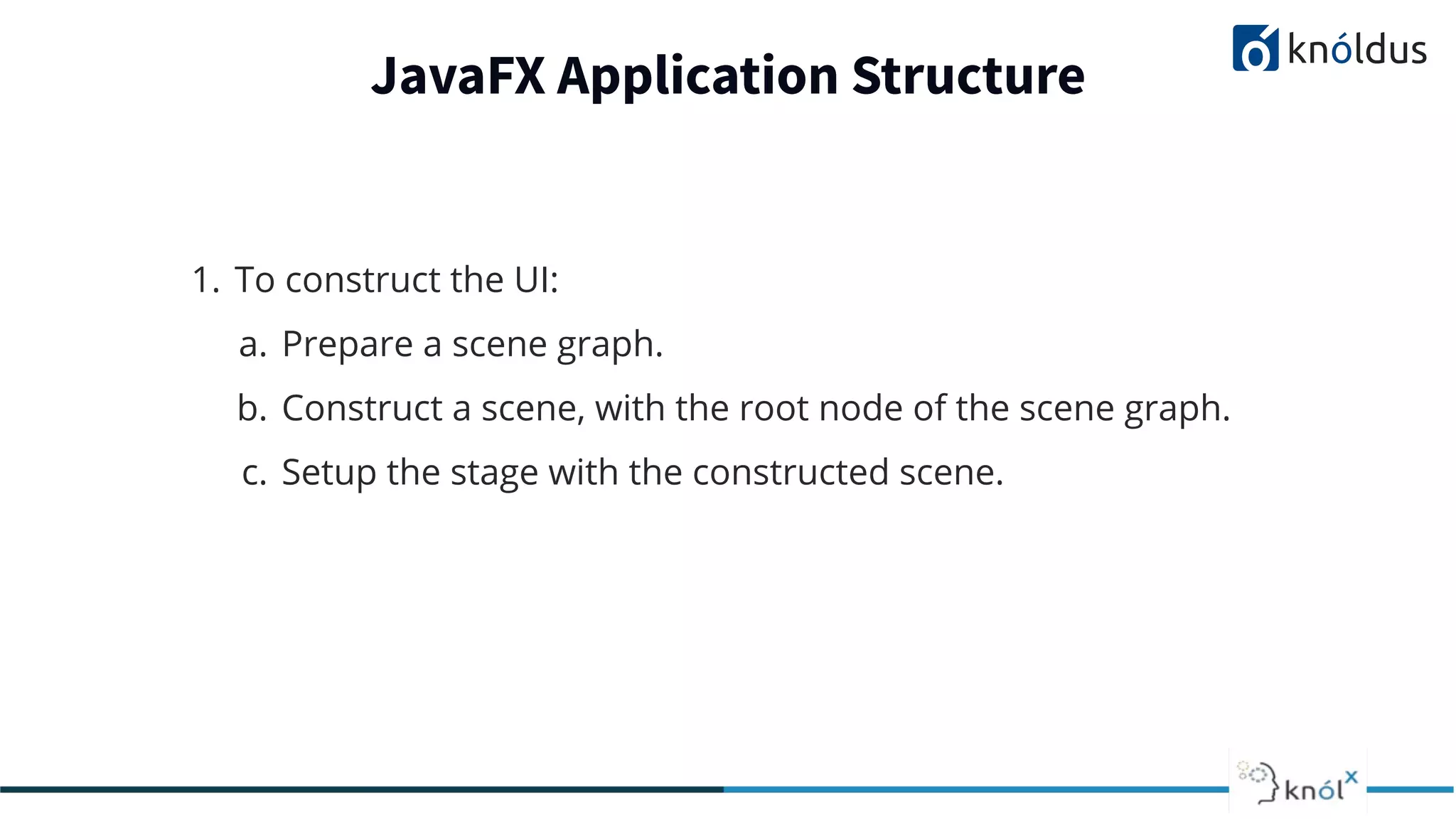
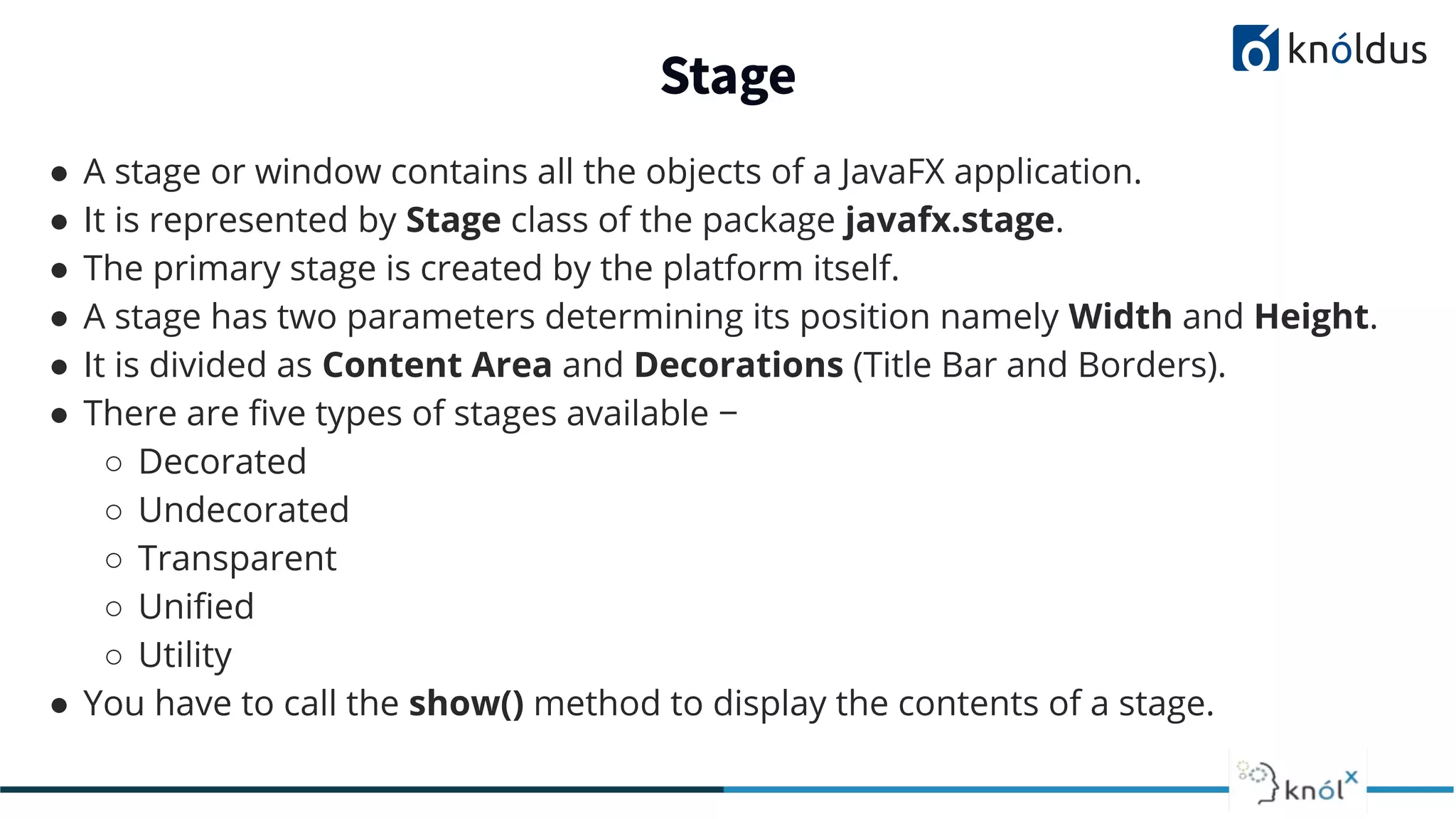
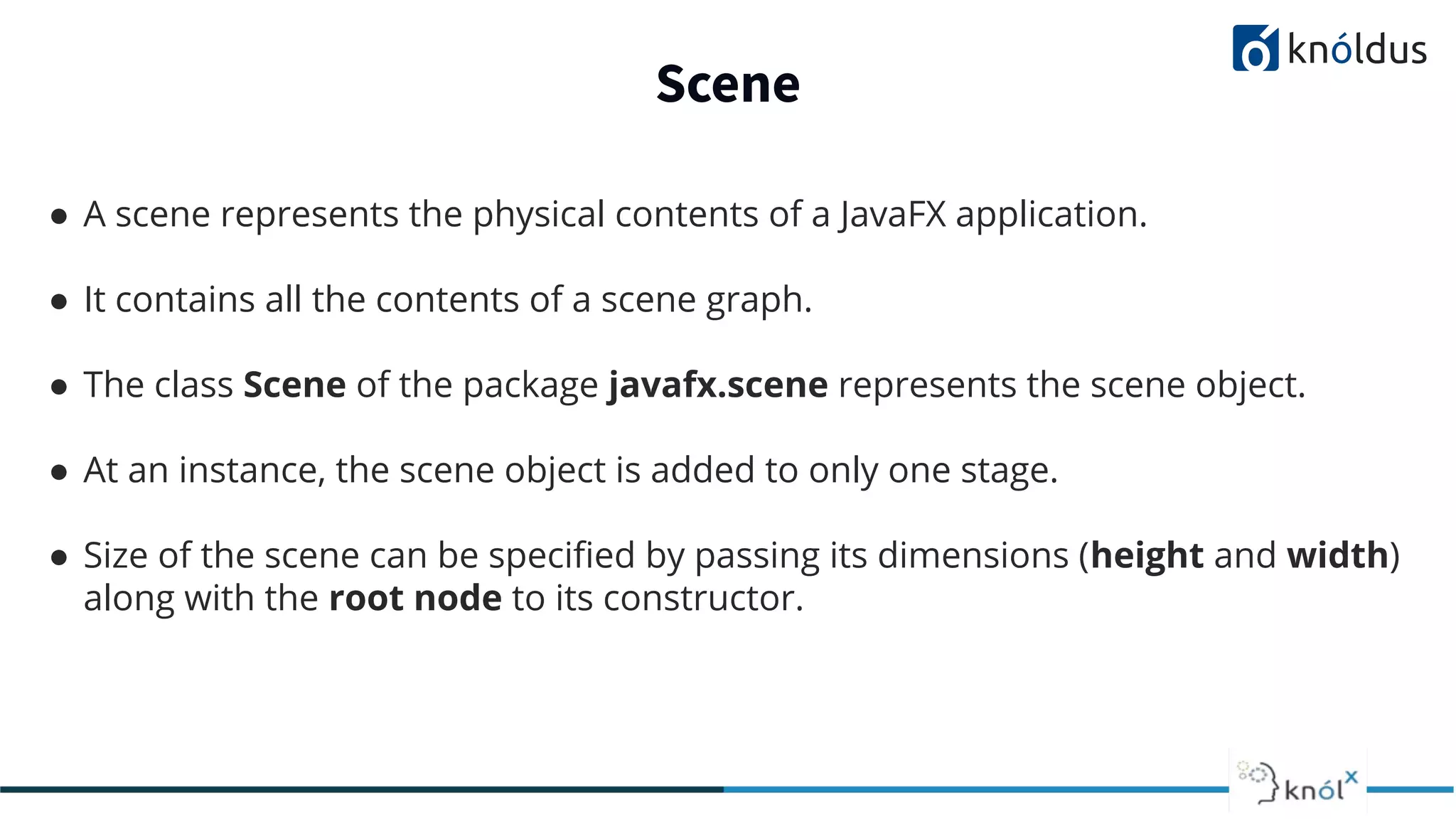
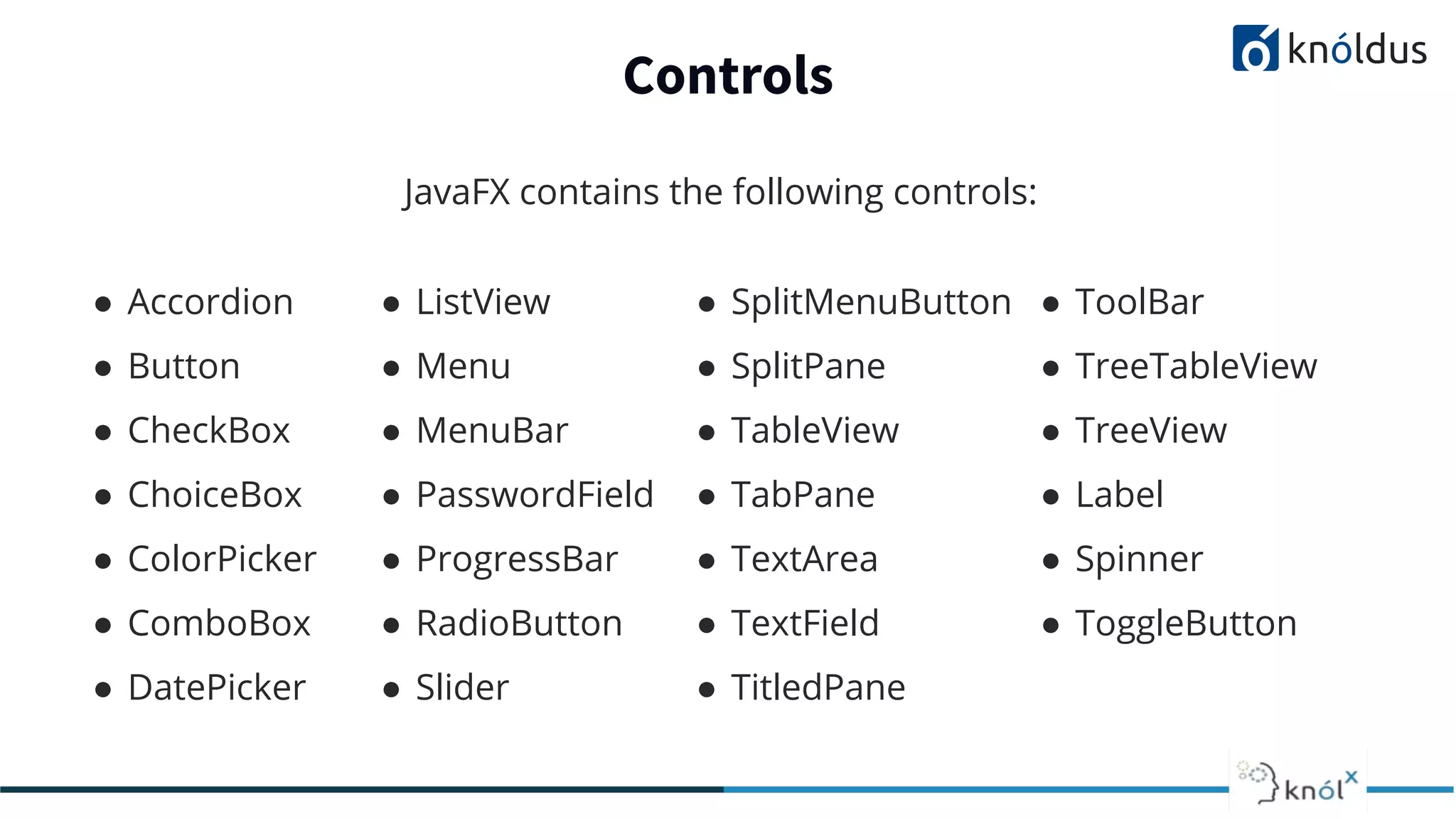
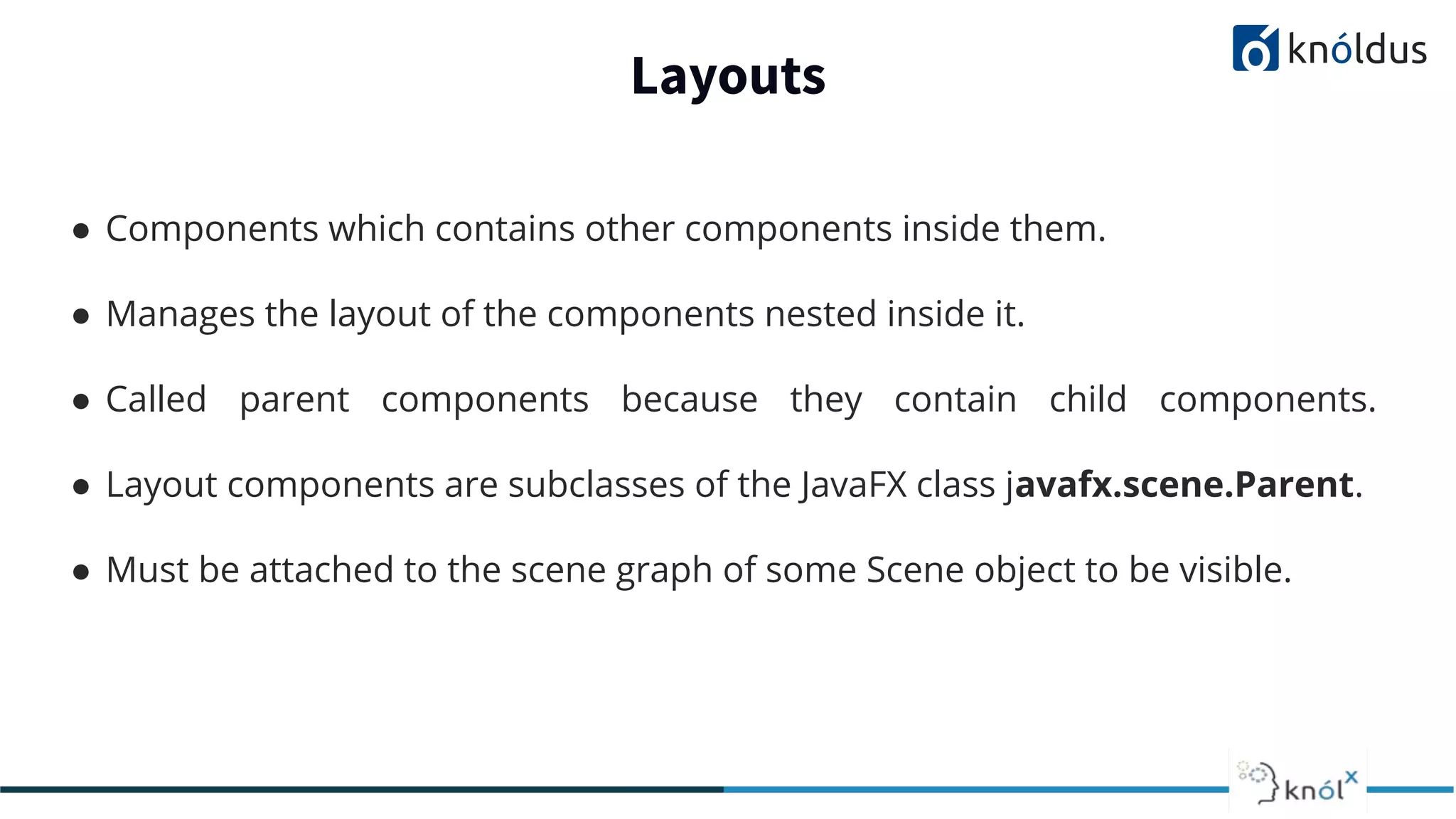
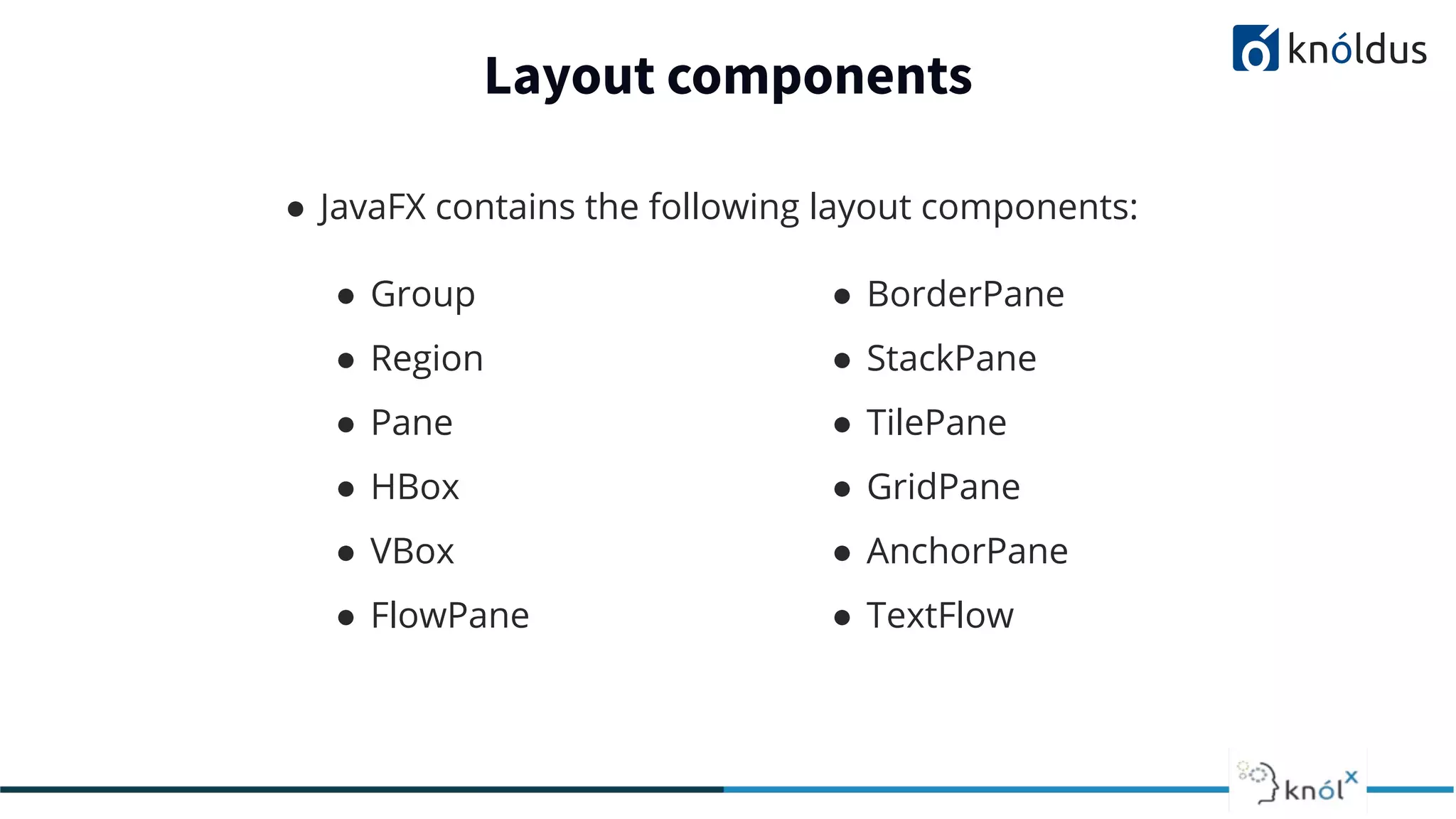
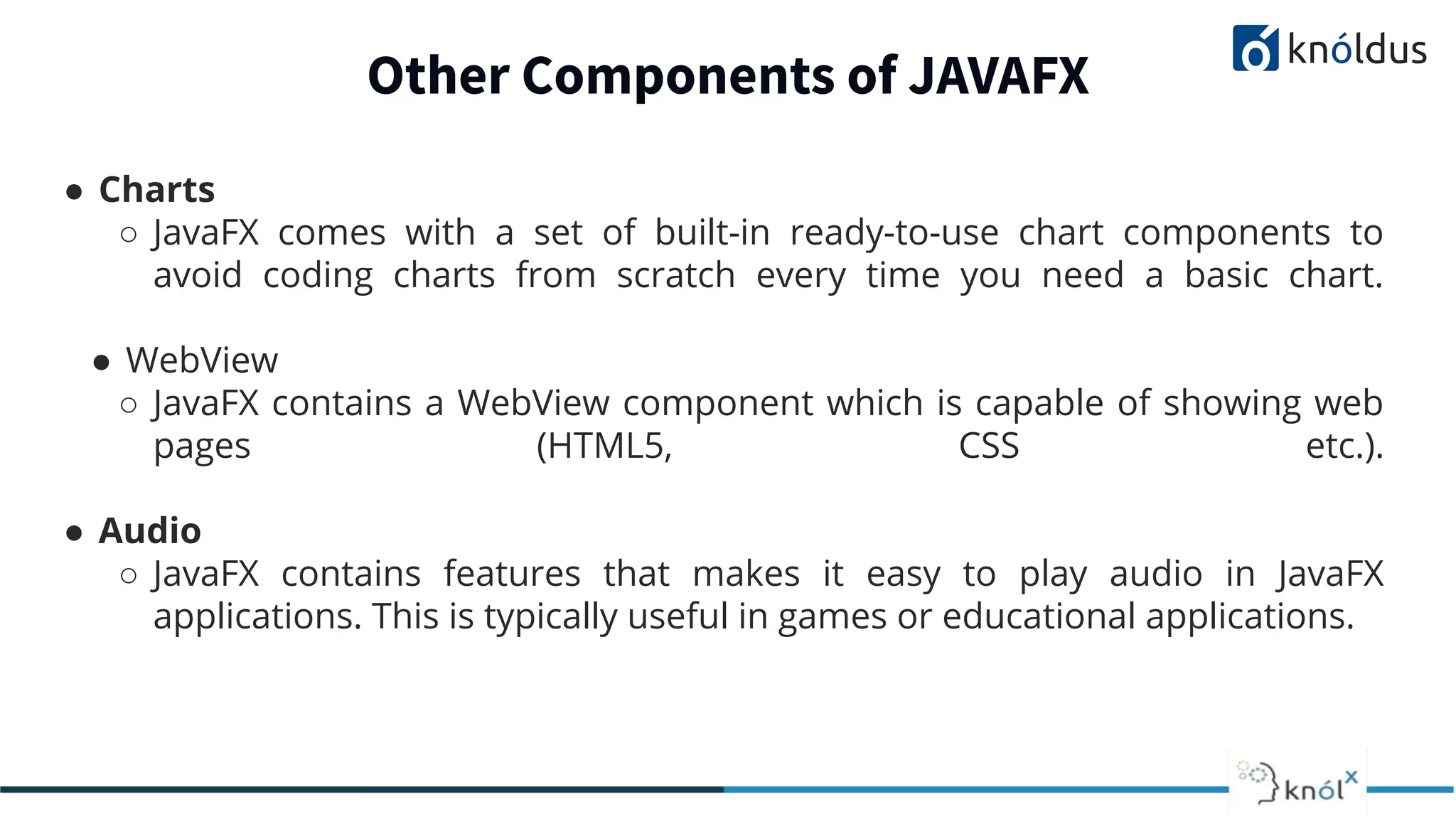
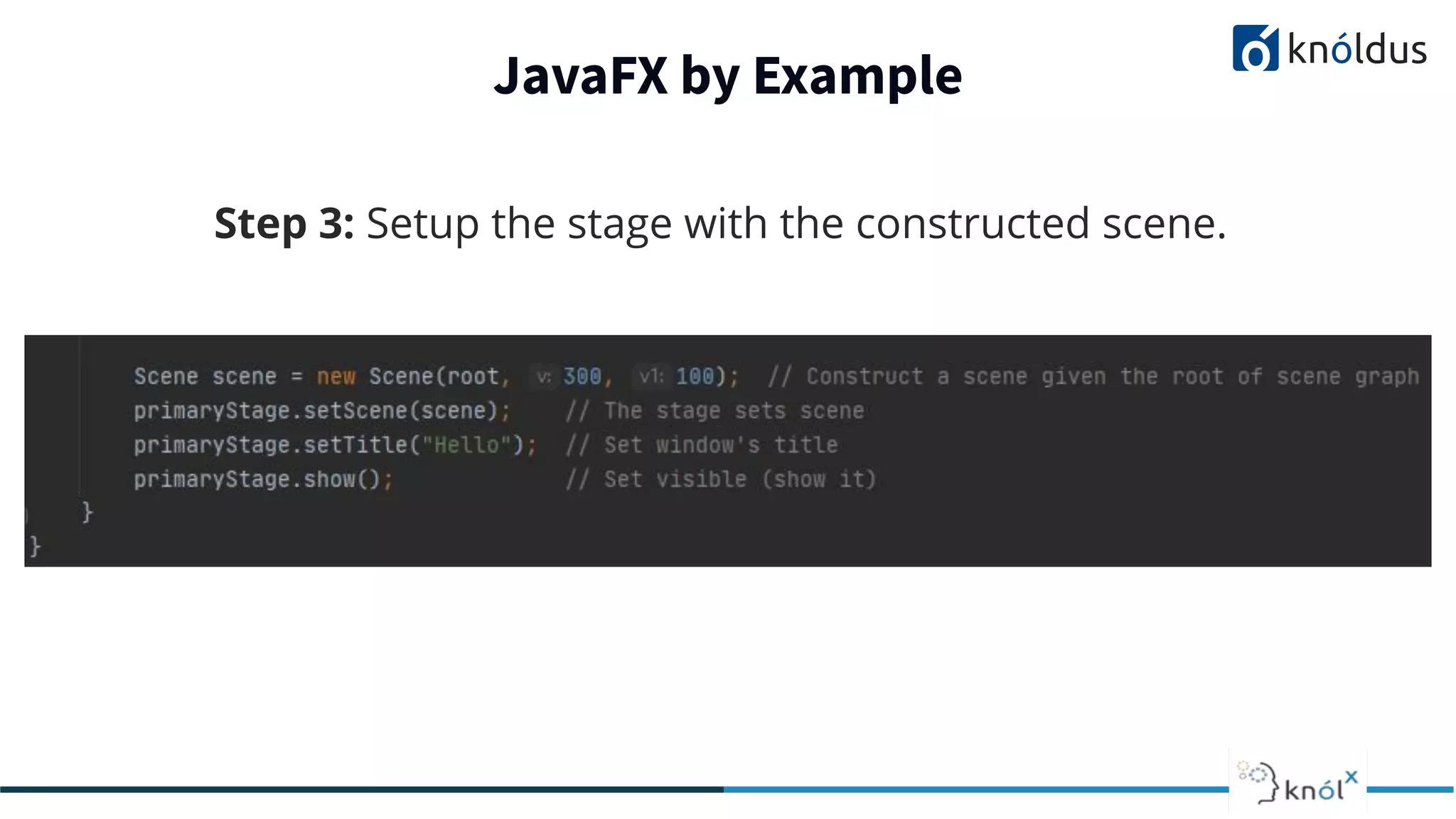
This document provides an overview of JavaFX presented by Mansi Babbar. It discusses what JavaFX is, why it is needed, its features and structure. The key components of JavaFX like controls, layouts, charts, media etc. are explained. An example JavaFX application structure and code is given. The presentation ends with a demo of JavaFX.