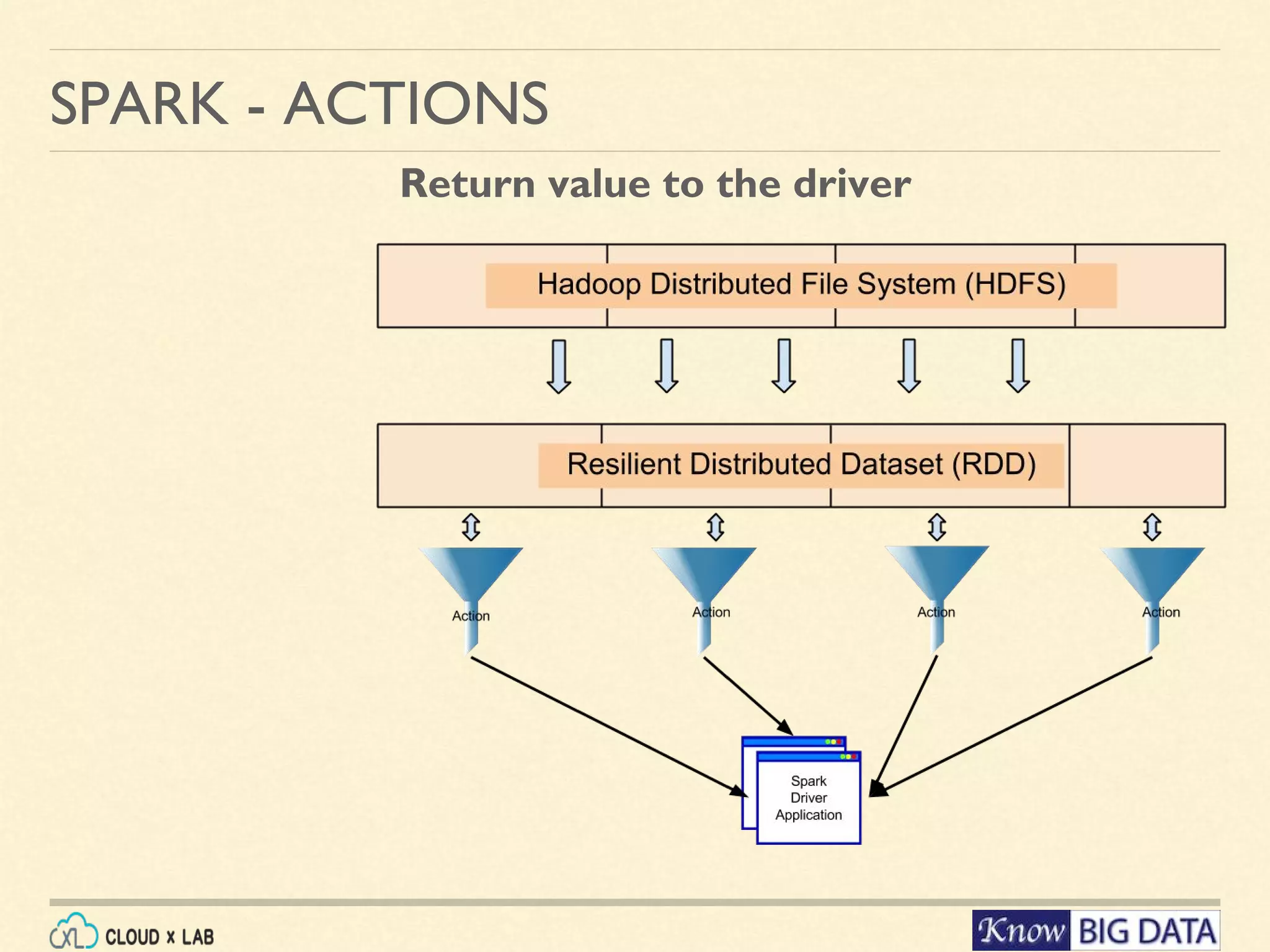
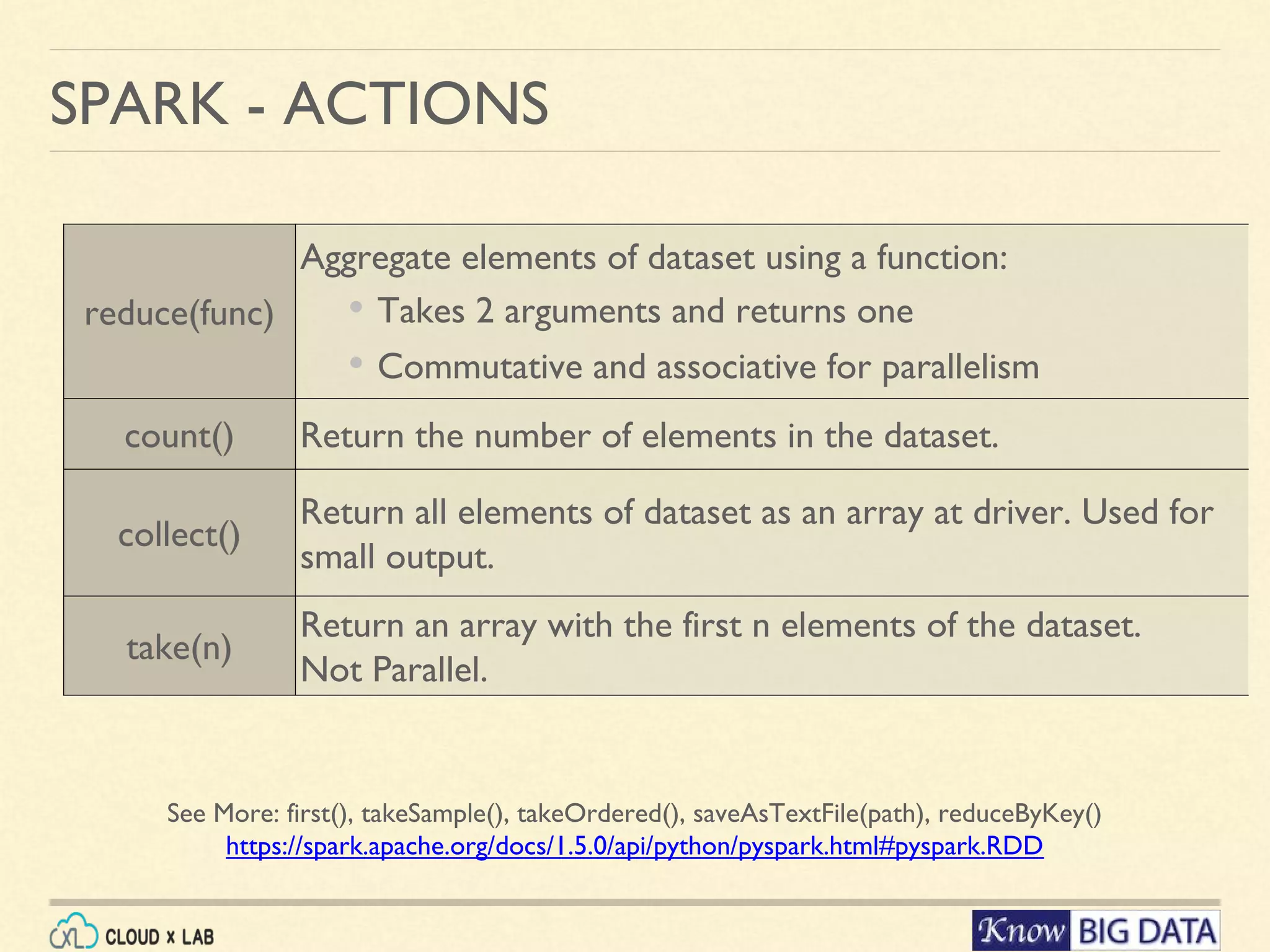
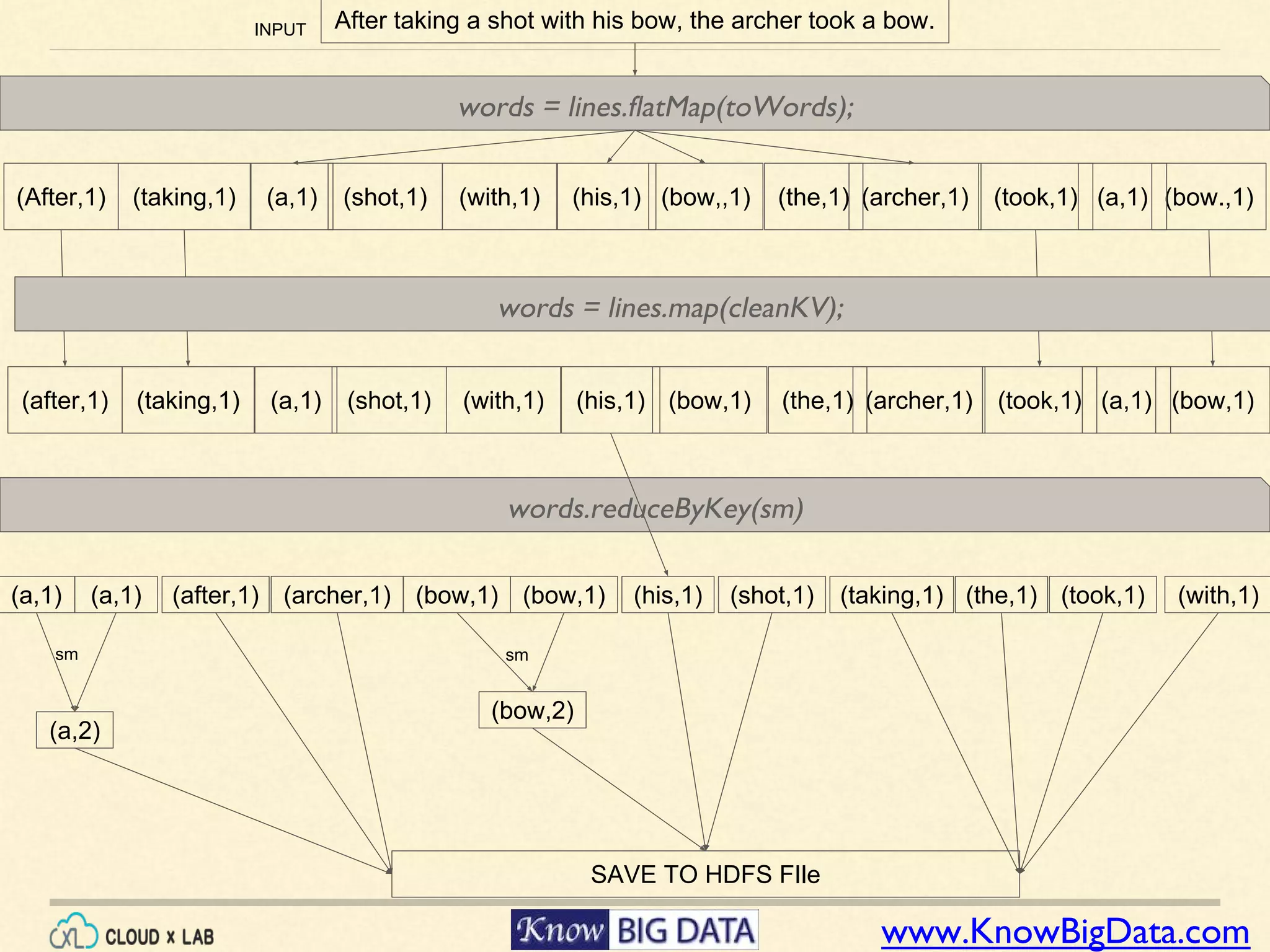
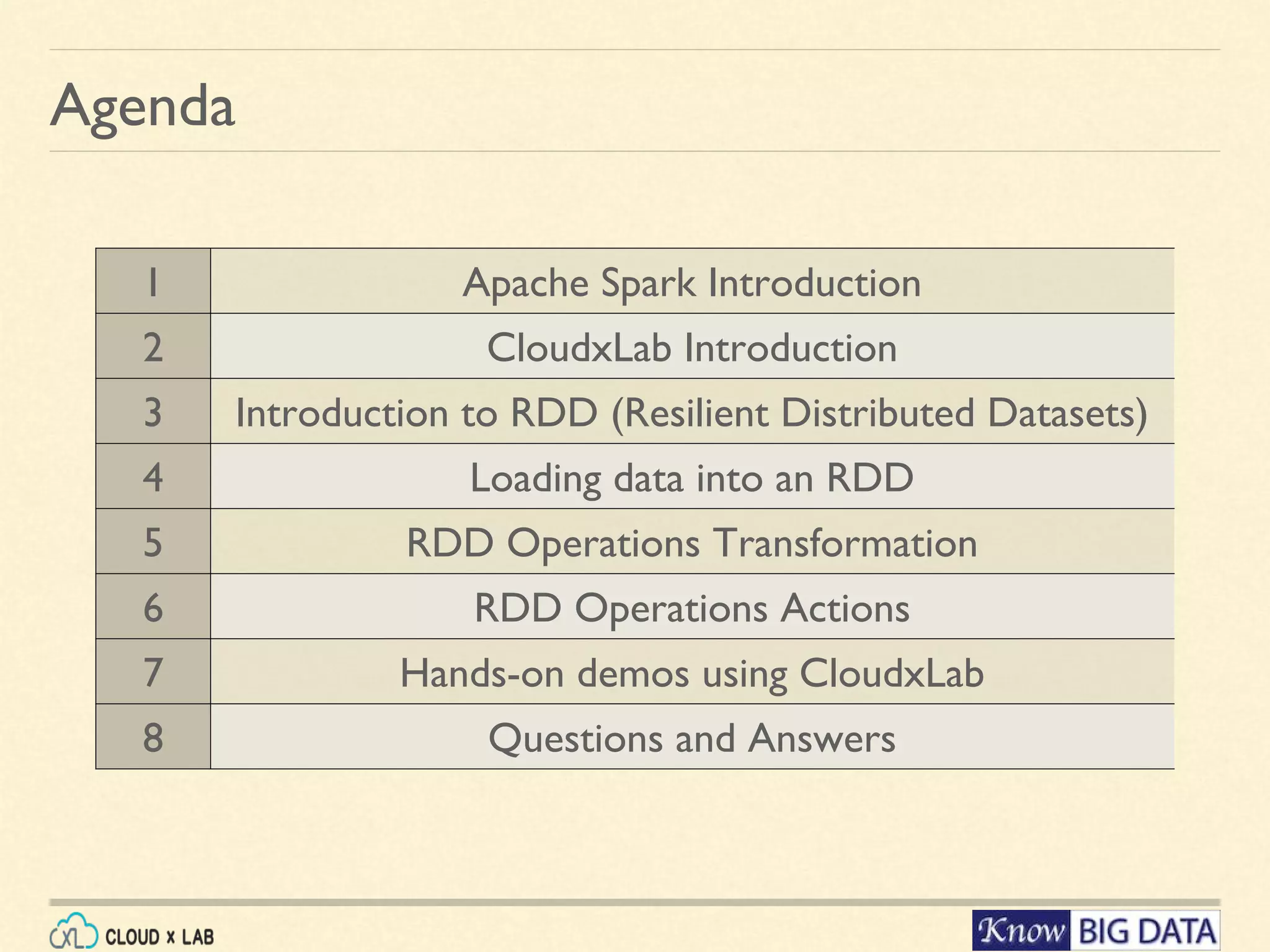
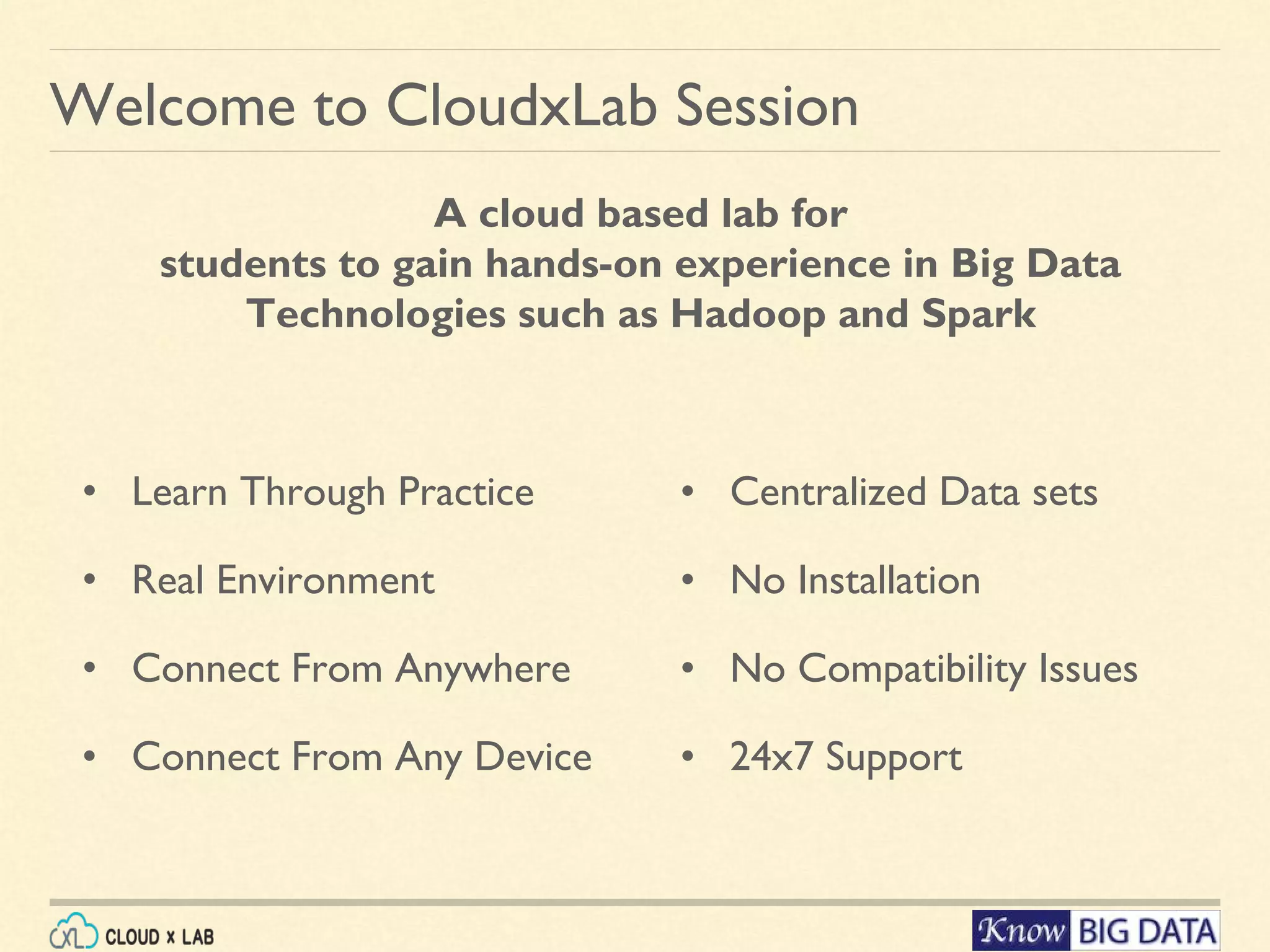
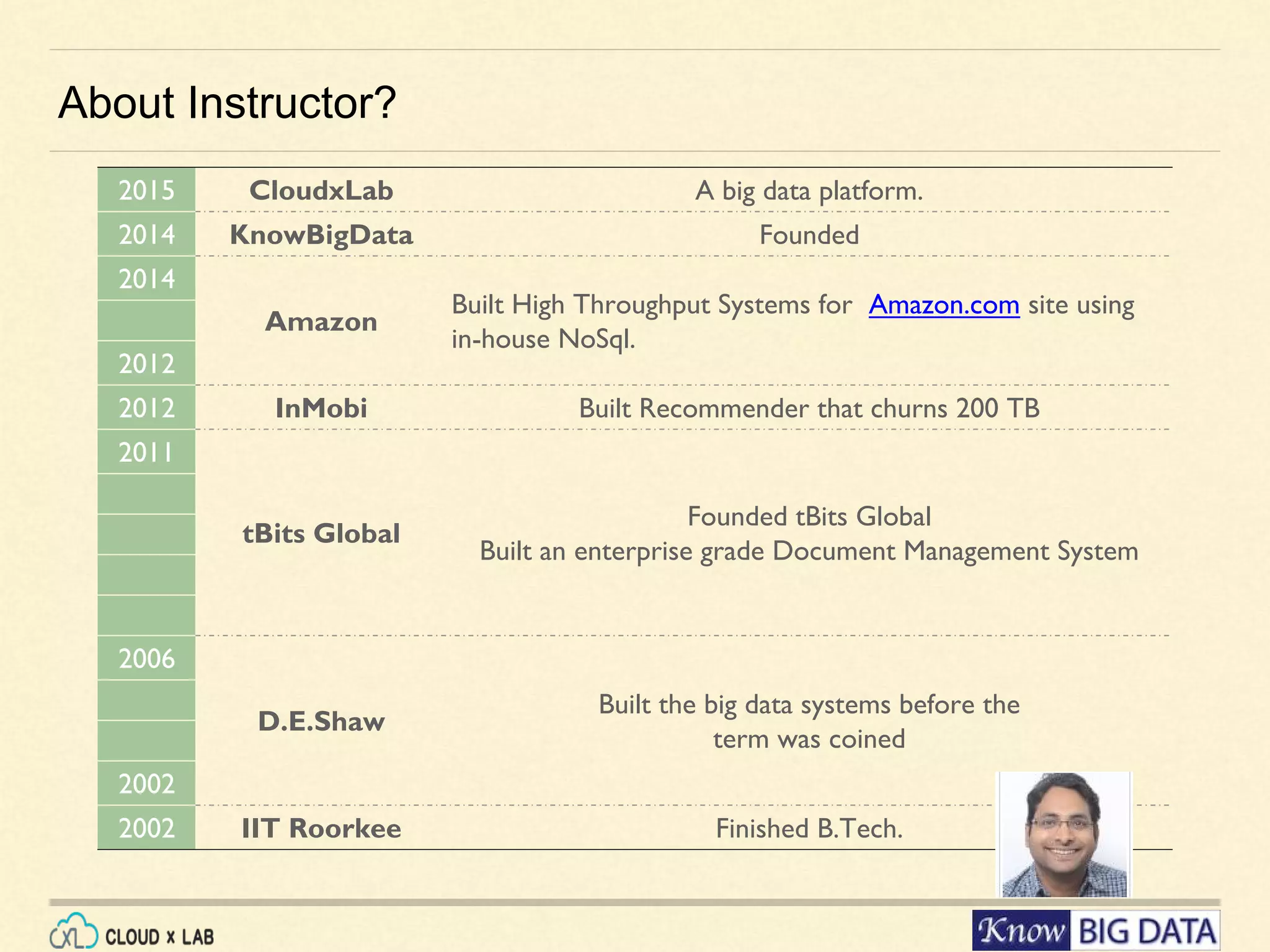
This document outlines a hands-on session on big data processing using Apache Spark, covering topics such as RDD operations, transformations, and actions. Participants will learn to compute the word frequency of a text file stored in HDFS, using a cloud-based lab environment offered by CloudxLab. The session also provides a brief introduction to CloudxLab's features and the instructor's background in big data technologies.



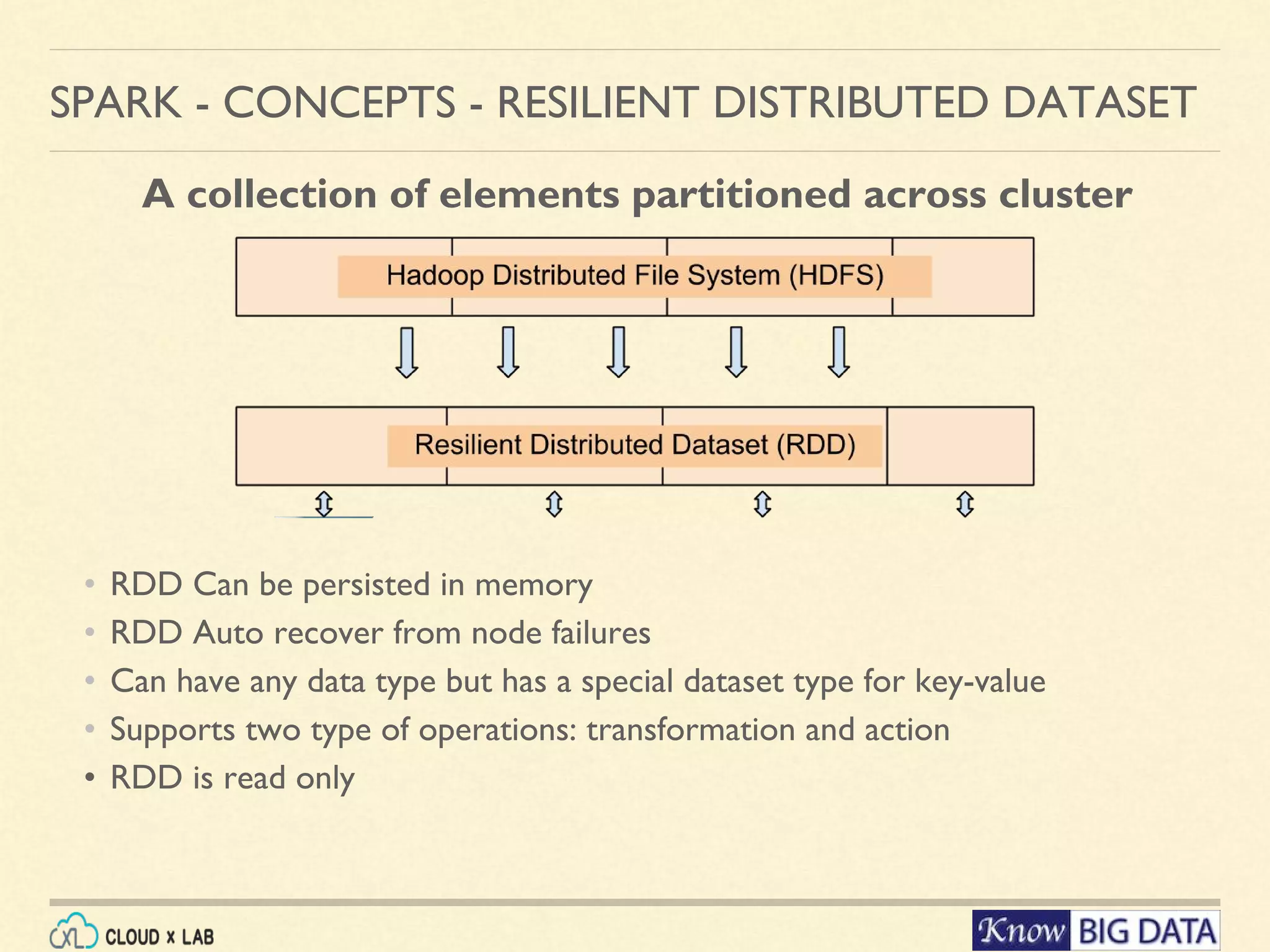
![Convert an existing array into RDD: myarray = sc.parallelize([1,3,5,6,19, 21]); SPARK - CONCEPTS - RESILIENT DISTRIBUTED DATASET Load a file From HDFS: lines = sc.textFile('/data/mr/wordcount/input/big.txt') Check first 10 lines: lines.take(10); // Does the actual execution of loading and printing 10 lines.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudxlab-sparkhandsondemo-160430115026/75/Apache-Spark-Introduction-CloudxLab-10-2048.jpg)
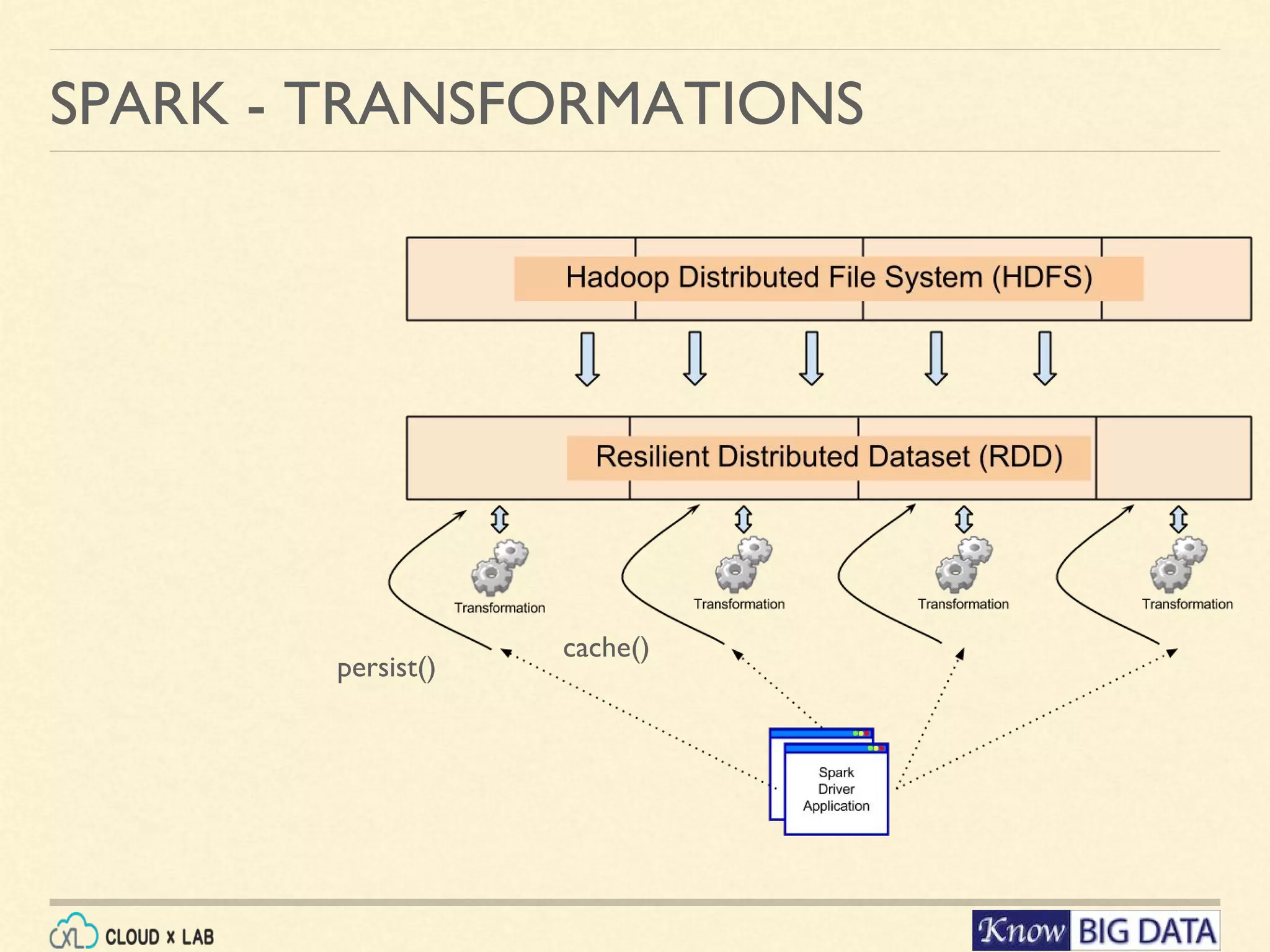
![SPARK - TRANSFORMATIONS map(func) Return a new distributed dataset formed by passing each element of the source through a function func. Analogous to foreach of pig. filter(func) Return a new dataset formed by selecting those elements of the source on which func returns true. flatMap( func) Similar to map, but each input item can be mapped to 0 or more output items groupByKey ([numTasks]) When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs, returns a dataset of (K, Iterable<V>) pairs. See More: sample, union, intersection, distinct, groupByKey, reduceByKey, sortByKey,join https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/api/java/index.html?org/apache/spark/api/java/JavaPairRDD. html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudxlab-sparkhandsondemo-160430115026/75/Apache-Spark-Introduction-CloudxLab-12-2048.jpg)

![Define a function to clean & convert to key-value: import re def cleanKV(mystr): mystr = mystr.lower() mystr = re.sub("[^0-9a-z]", "", mystr) #replace non alphanums with space return (mystr, 1); # returning a tuple - word & count SPARK - Cleaning the data Execute the map() transformation: cleanWordsKV = words.map(cleanKV); //passing “clean” function as argument Check first 10 words pairs: cleanWordsKV.take(10); // Does the actual execution of loading and printing 10 lines.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudxlab-sparkhandsondemo-160430115026/75/Apache-Spark-Introduction-CloudxLab-14-2048.jpg)