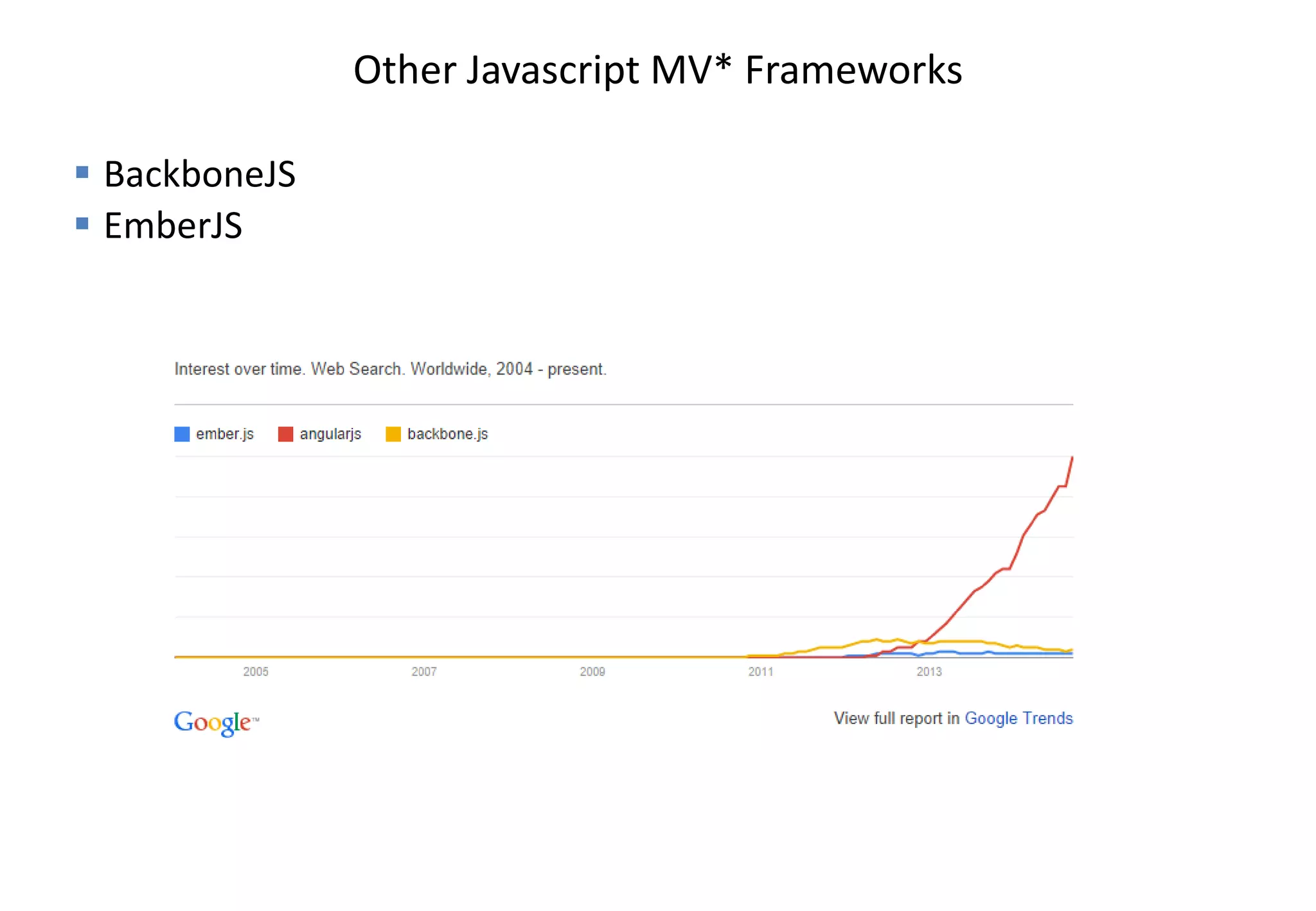
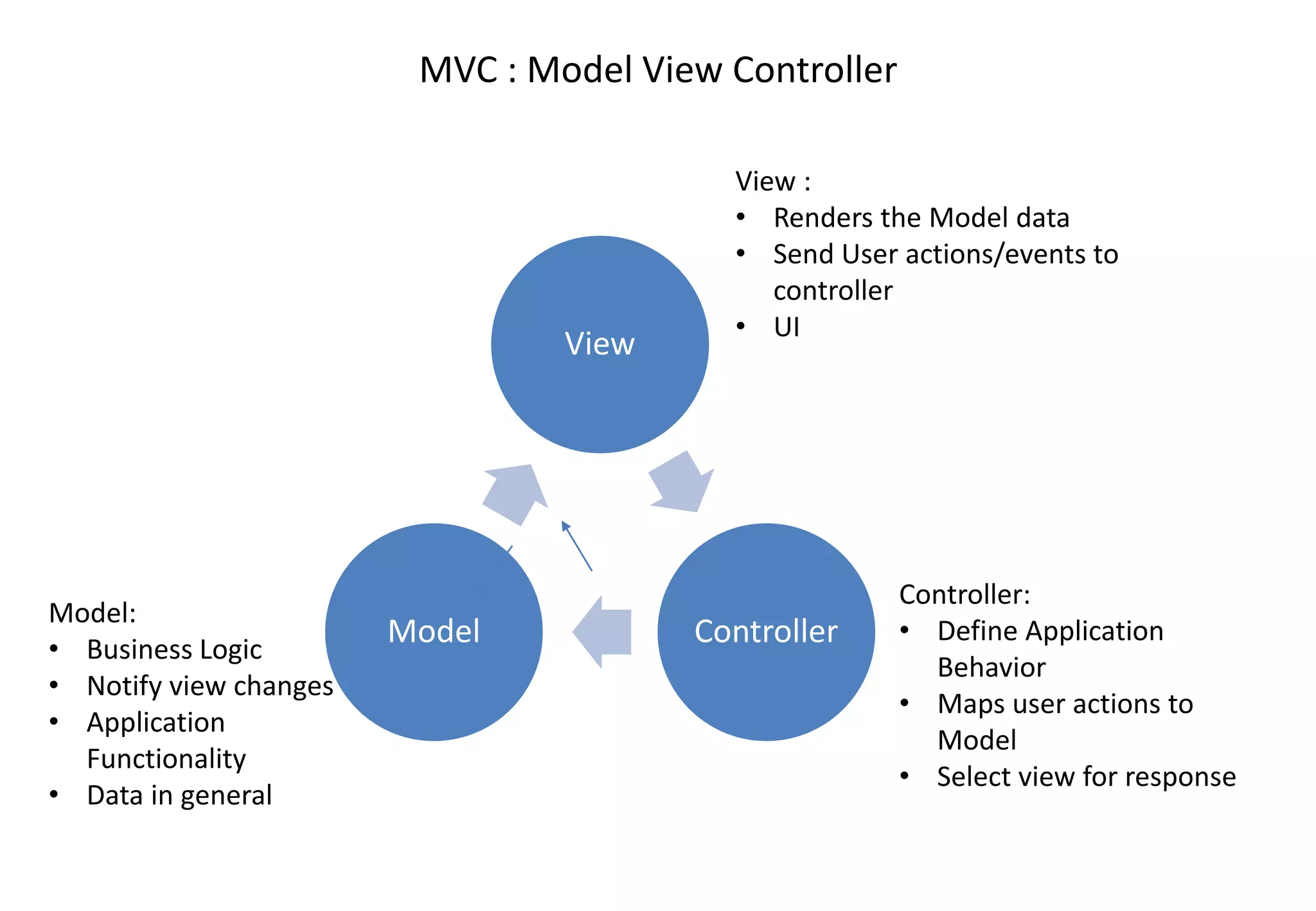
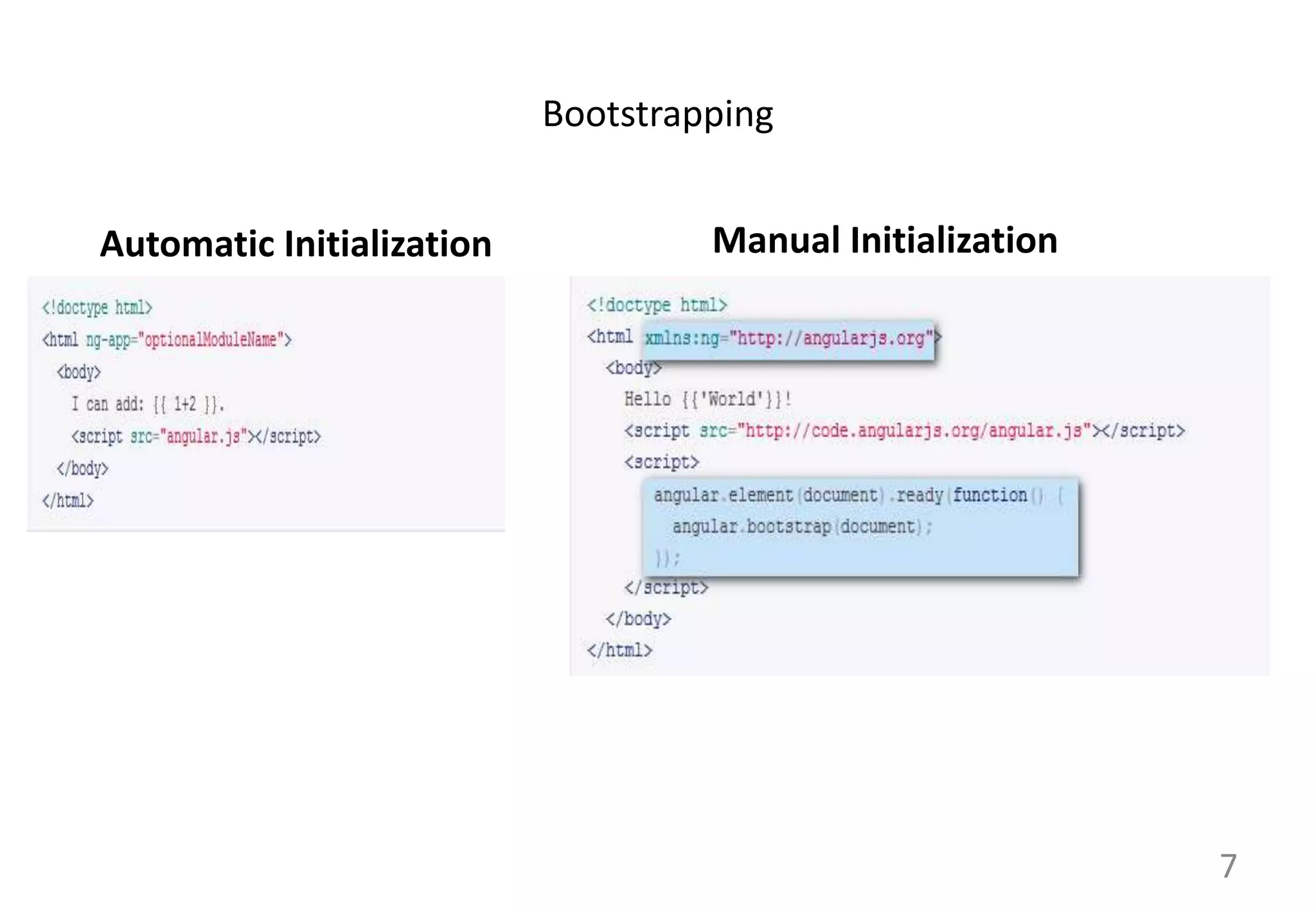
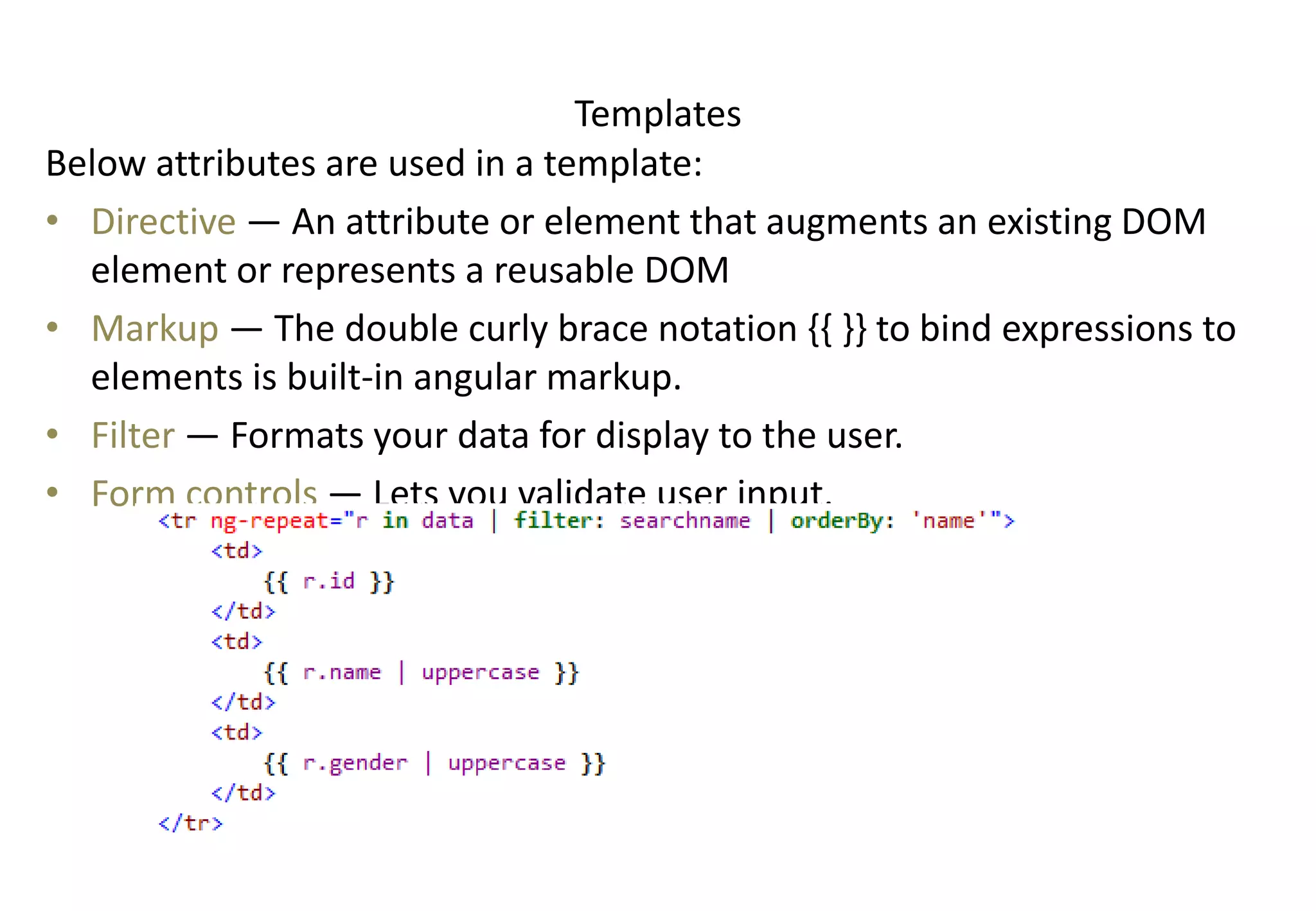
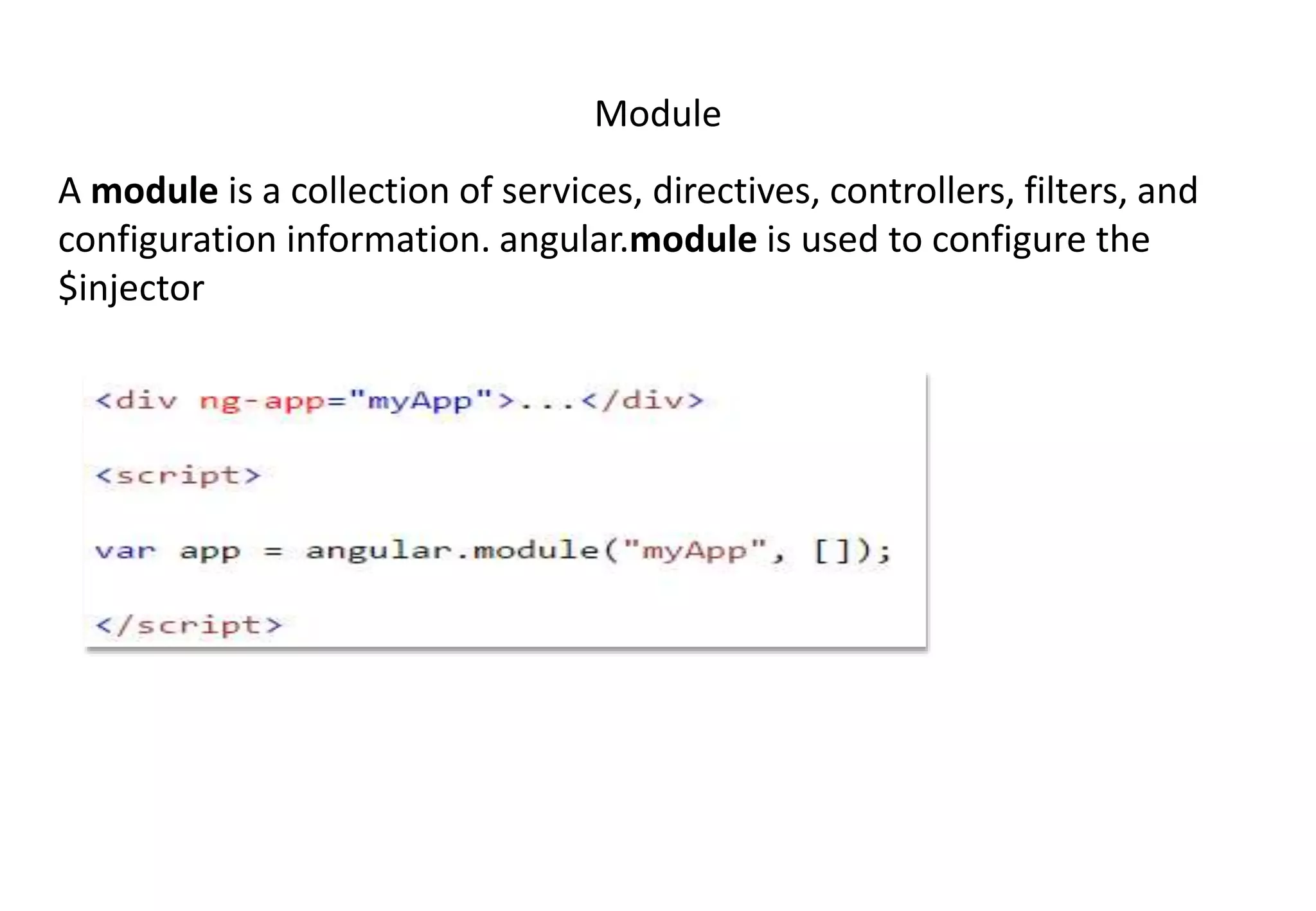
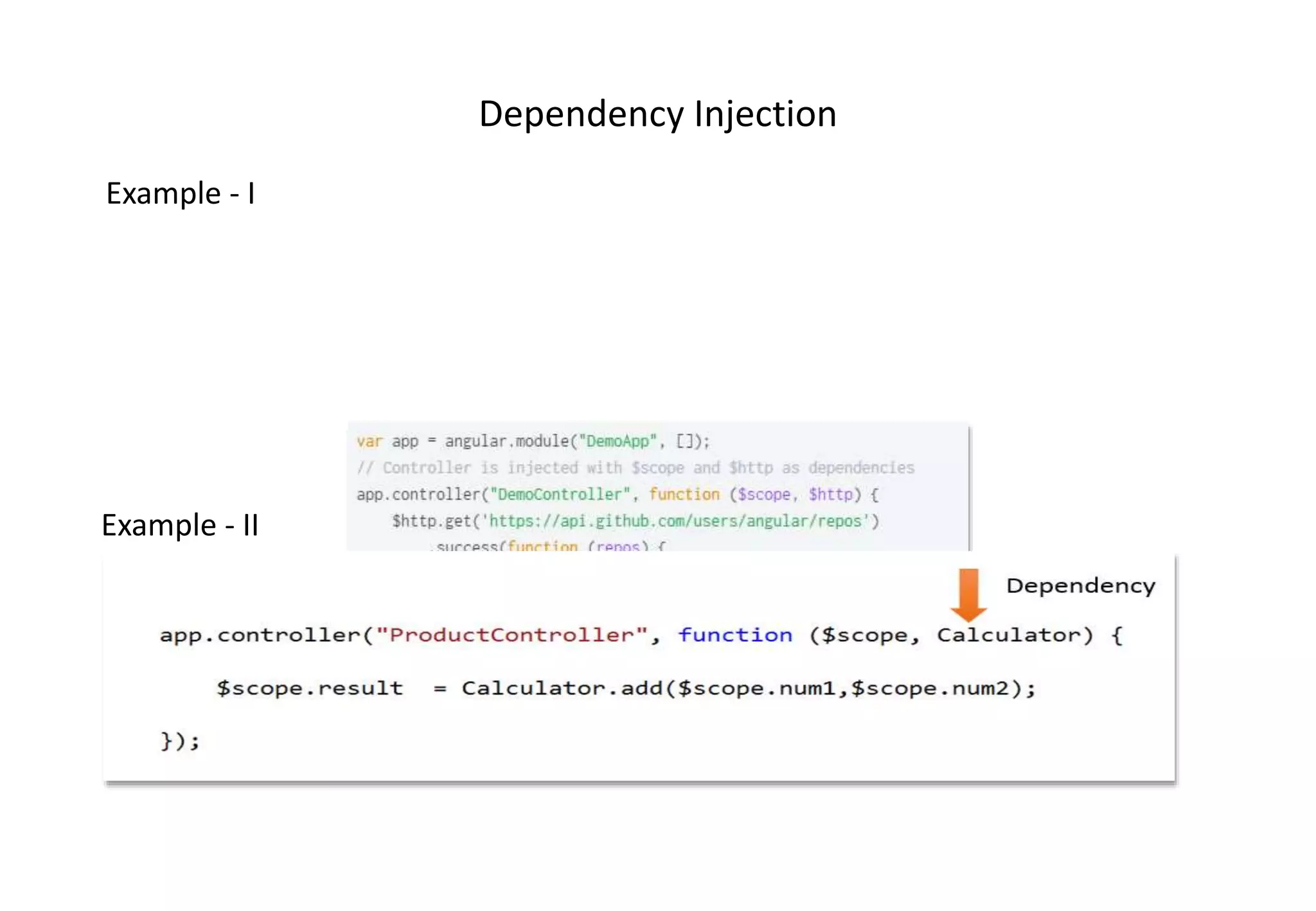
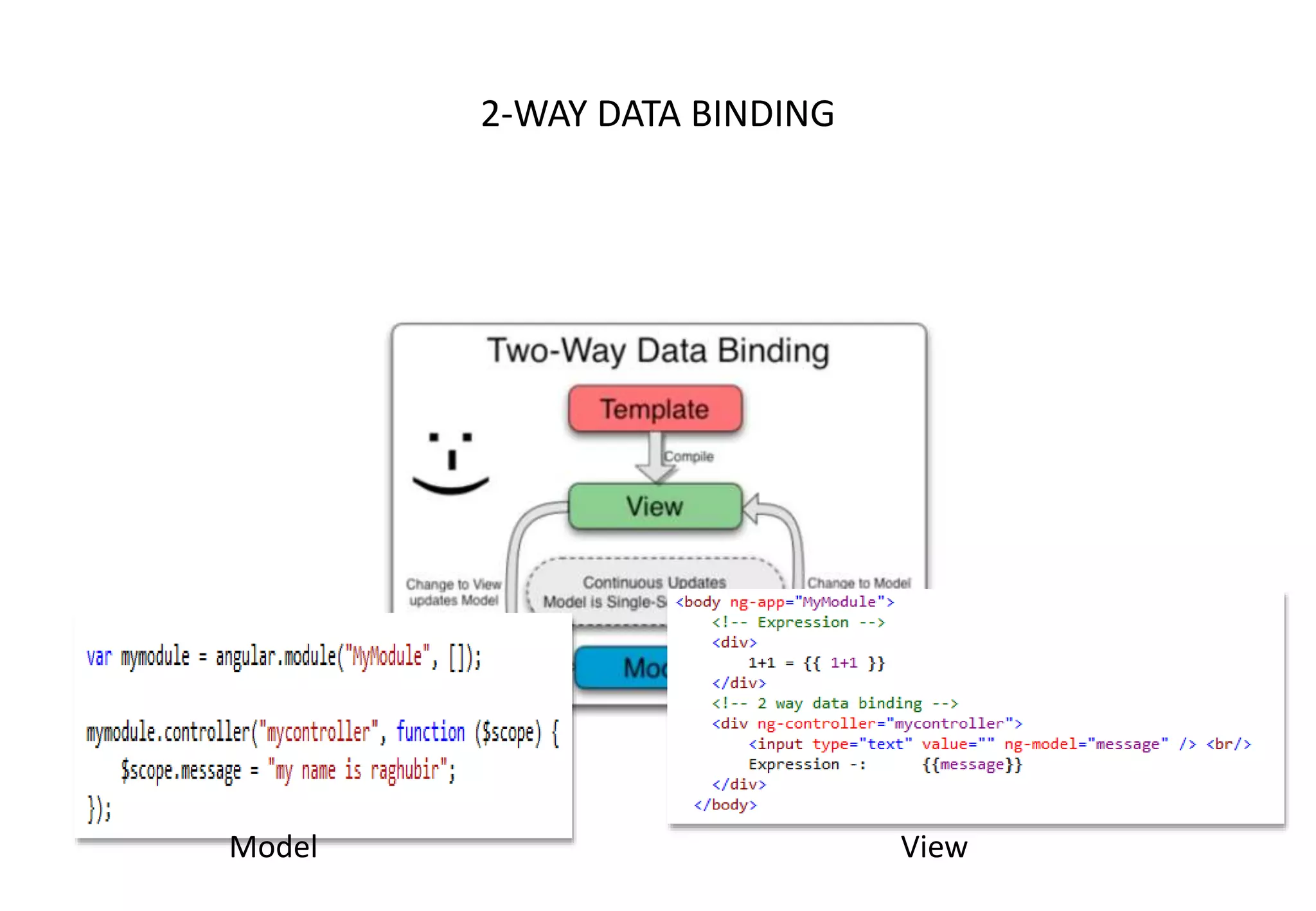
AngularJS (1.x) is a client-side framework for developing browser-based applications using model-view-whatever architecture. It was created by Google and is open source. AngularJS uses templates, modules, services, dependency injection and two-way data binding to build single page applications. Key features include bootstrapping, routing, directives and unit testing capabilities. Angular 2 is a complete rewrite of AngularJS and uses only class-based services rather than multiple options.