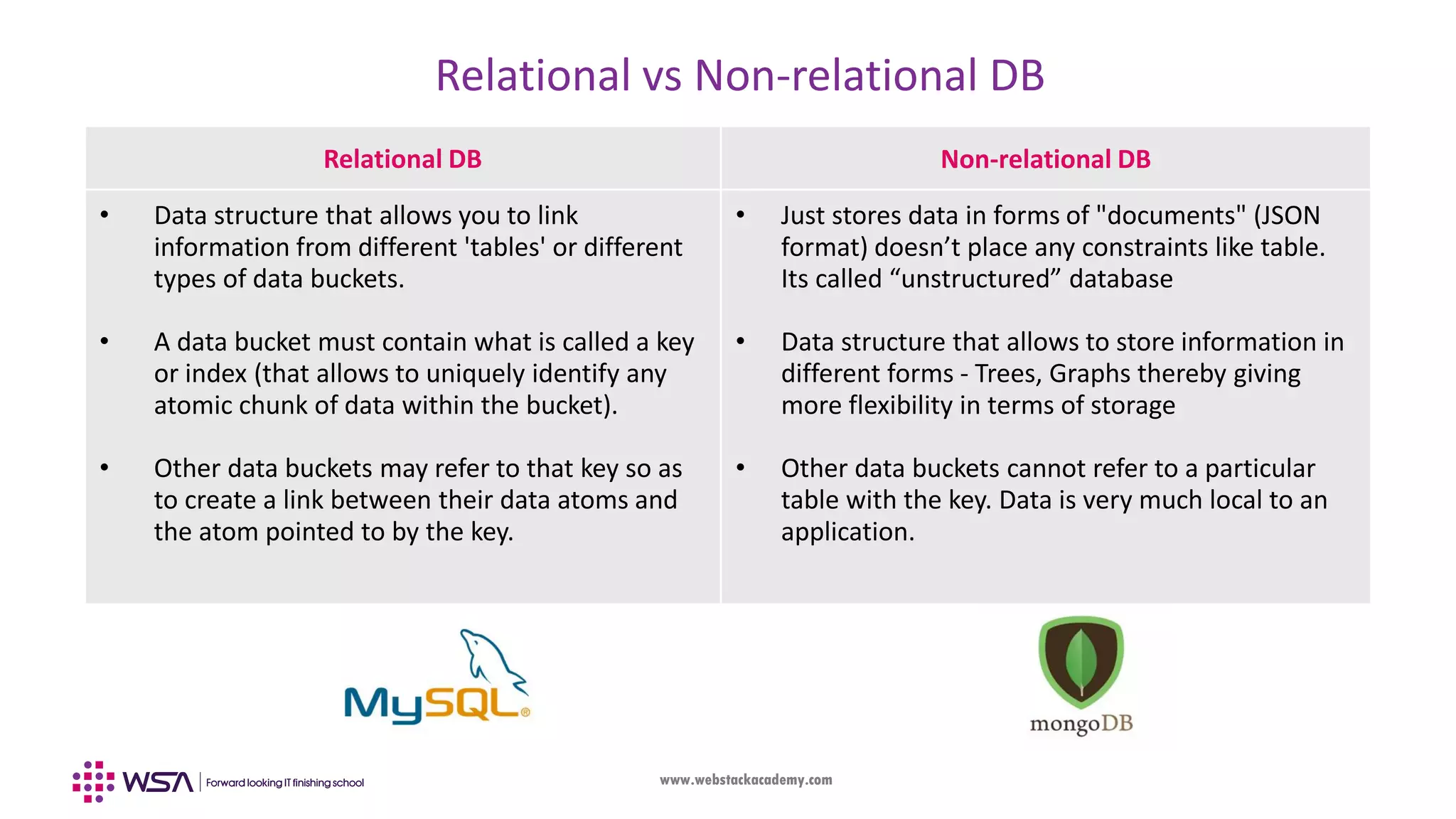
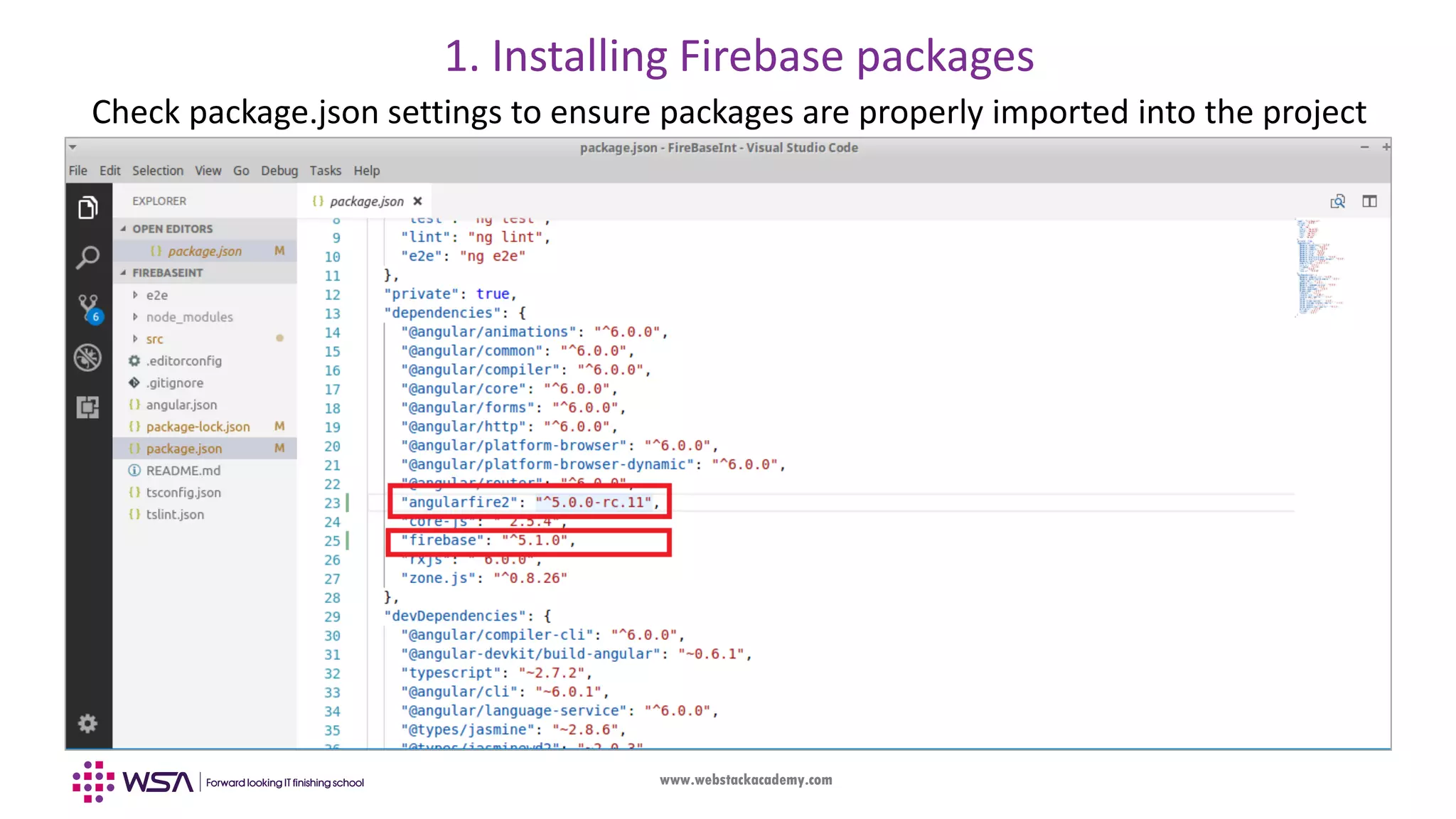
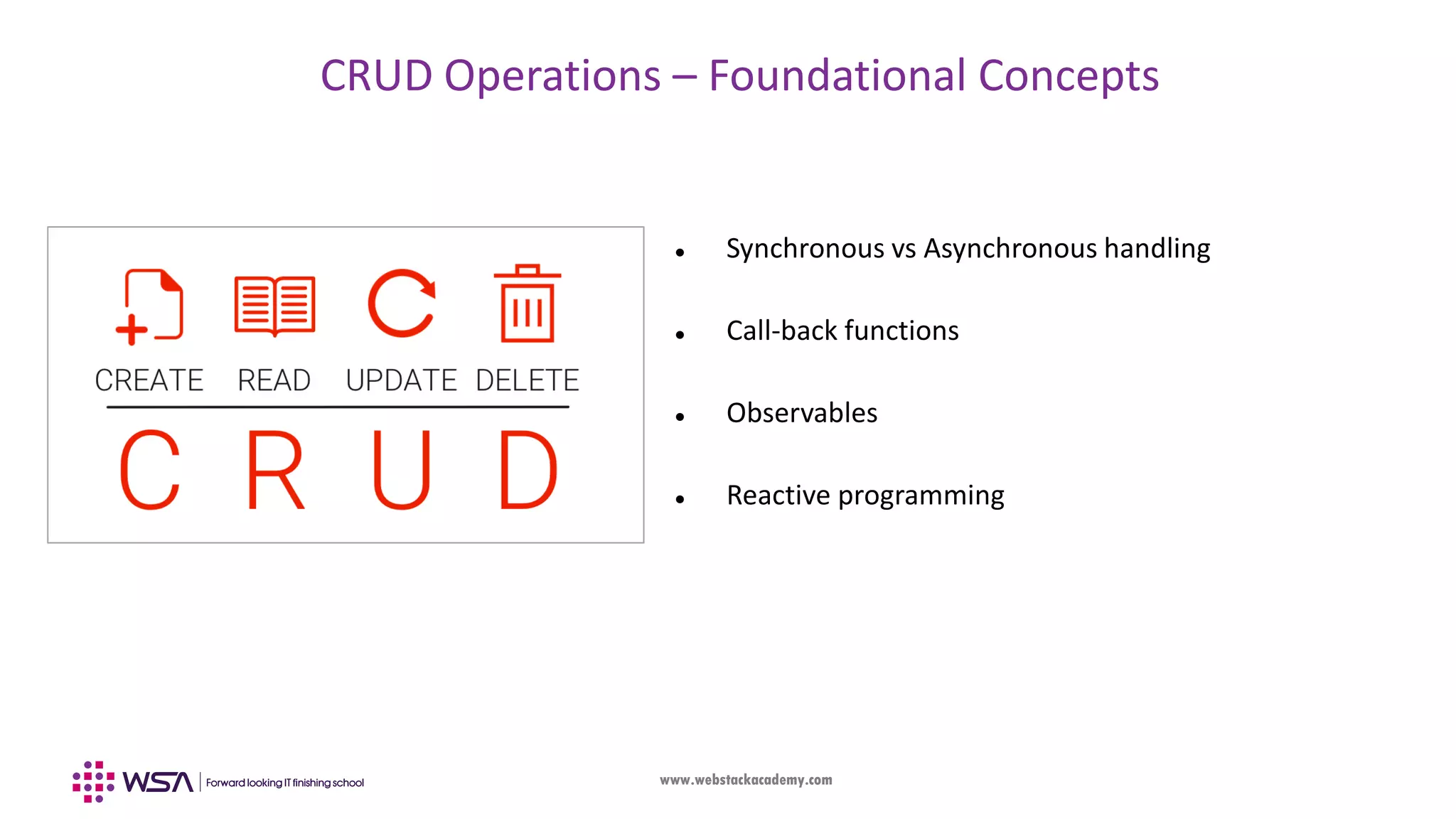
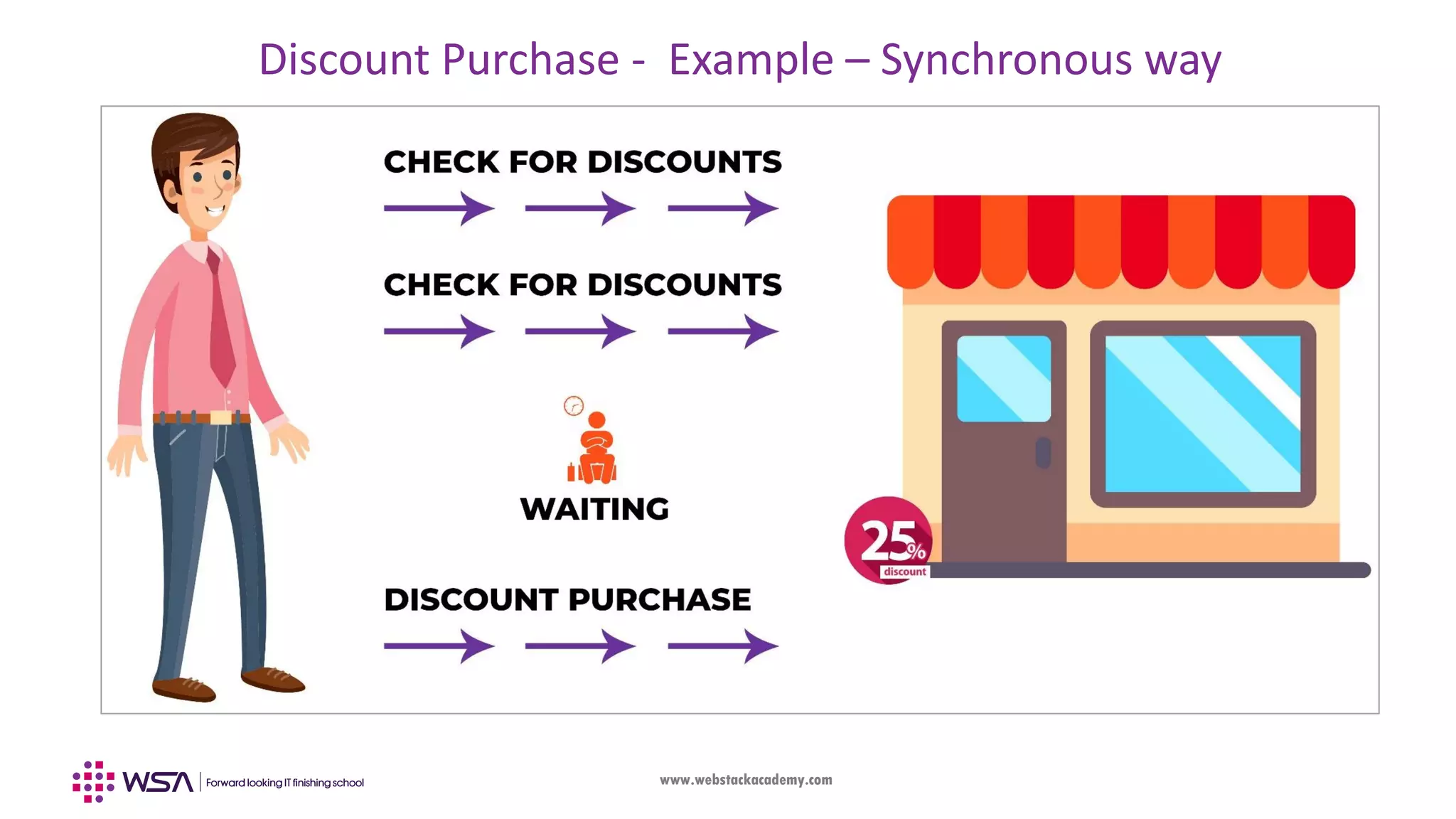
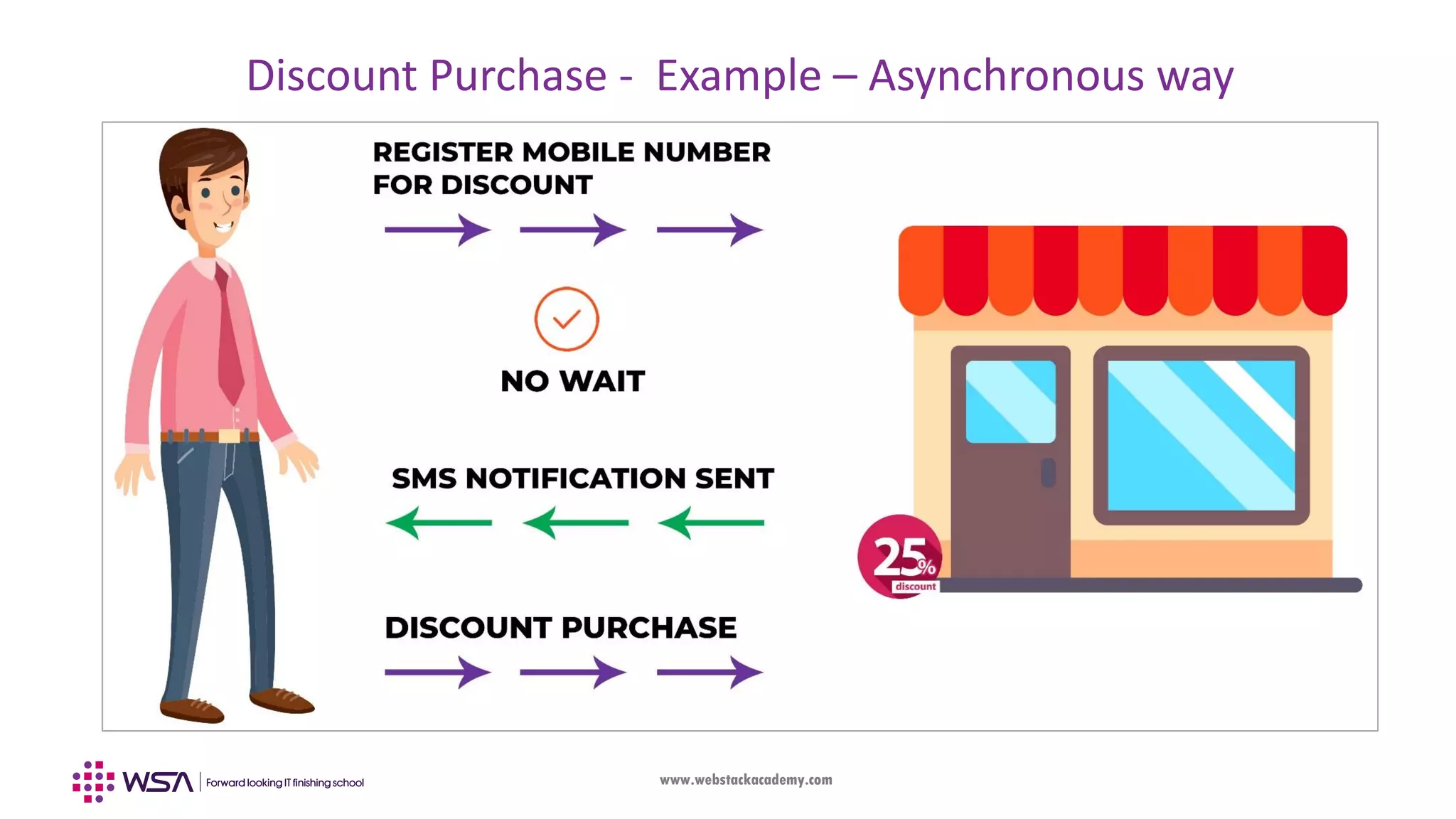
The document outlines the integration of Firebase with an Angular frontend application, covering concepts such as components, services, and CRUD operations. It emphasizes the differences between frontend and backend development, detailing the functionalities of Firebase as a backend platform. The content also includes step-by-step guidance on configuring Firebase and Angular integration, handling real-time data, and utilizing observables for asynchronous programming.


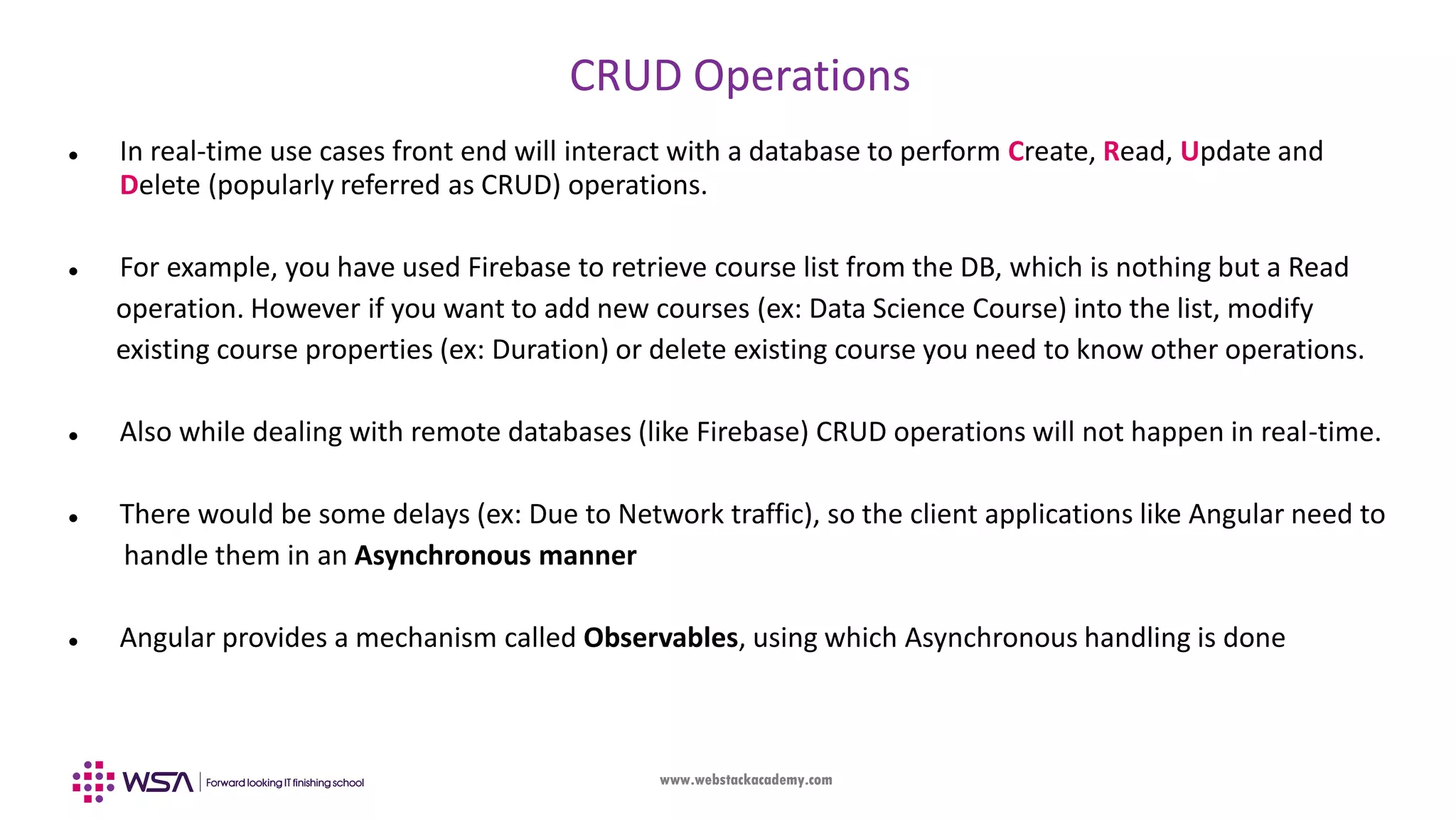
![www.webstackacademy.com What we have done so far? – Static / Compiled data • When we access any data in the business logic, local variables are used within the class so far (ex: courses = ["Fullstack", "Frontend", "Backend", "Java"]). This information is obtained in the view in form of interpolation {{ course }} mechanism • We also understood how to use event (Using () mechanism), data (Using [] mechanism) and two way binding - "Banana in a Box" (Using [()] mechanism) • Any time we wanted to demonstrate change in the data, we have edited the code changed some items and re-launched the angular application (using ng serve --open) • However in real time application data will be fetched dynamically from an external source (ex: Firebase or your own custom backend application) which will not only ensure we get rid of using static local variables but also the data takes care of Asynchronous updates • Primarily data updates include Create, Read, Update and Delete which is popularly known as CRUD operations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/006angularfirebase-190503102852/75/Angular-Chapter-6-Firebase-Integration-4-2048.jpg)








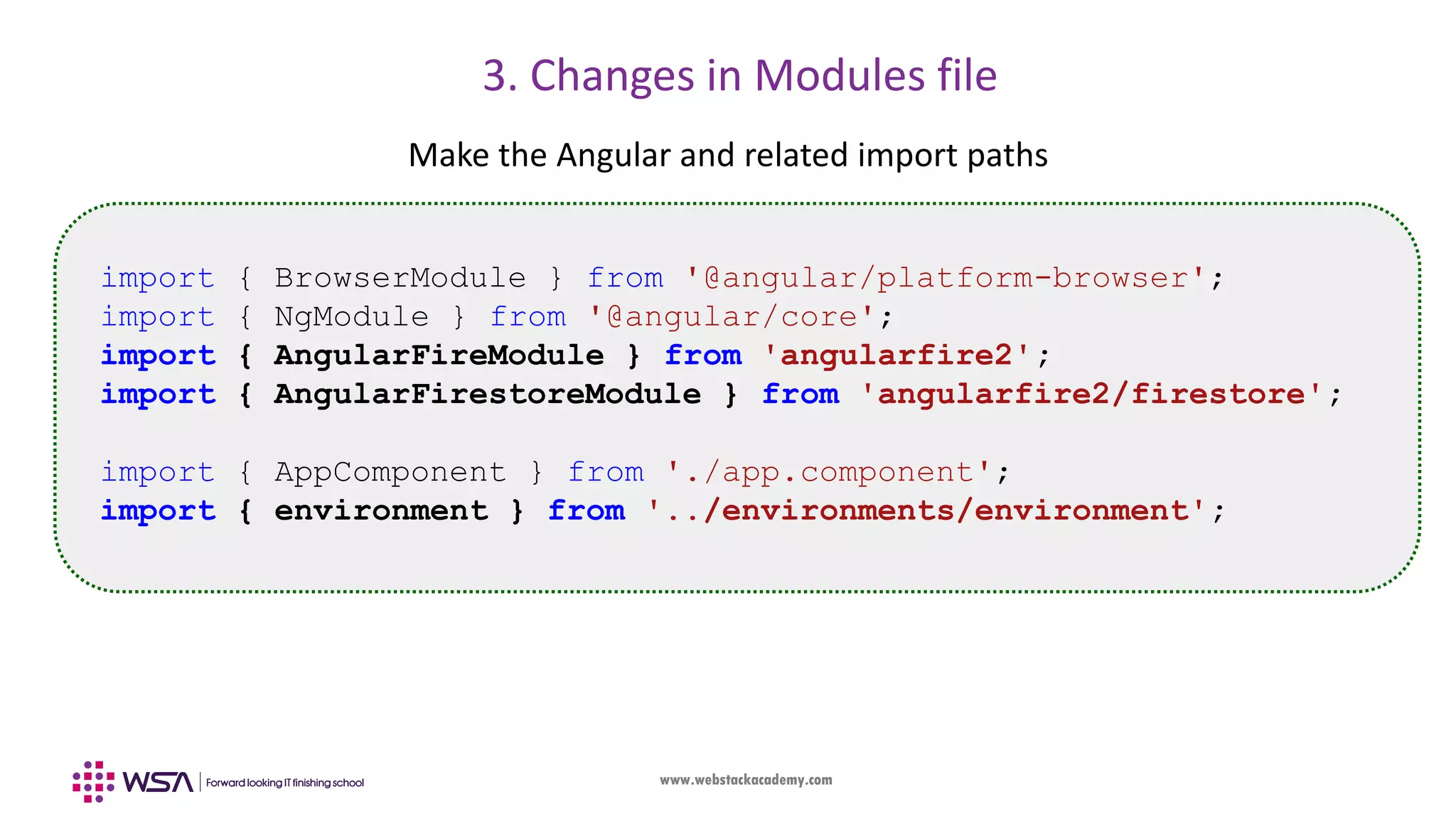
![www.webstackacademy.com 3. Changes in Modules file Add them into import section as well @NgModule({ declarations: [ AppComponent, ], imports: [ BrowserModule, AngularFireModule.initializeApp(environment.firebase,'angularfs'), AngularFirestoreModule ], providers: [], bootstrap: [AppComponent] }) export class AppModule { }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/006angularfirebase-190503102852/75/Angular-Chapter-6-Firebase-Integration-25-2048.jpg)
![www.webstackacademy.com 4. Changes in Component files Component Imports and constructor import { AngularFirestore } from 'angularfire2/firestore'; import { Observable } from 'rxjs'; // Observable and other function details in next section items: Observable<Item[]>; constructor(public db: AngularFirestore) { this.items = this.db.collection('courses').valueChanges(); this.items.subscribe(items => { console.log(items); }); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/006angularfirebase-190503102852/75/Angular-Chapter-6-Firebase-Integration-26-2048.jpg)
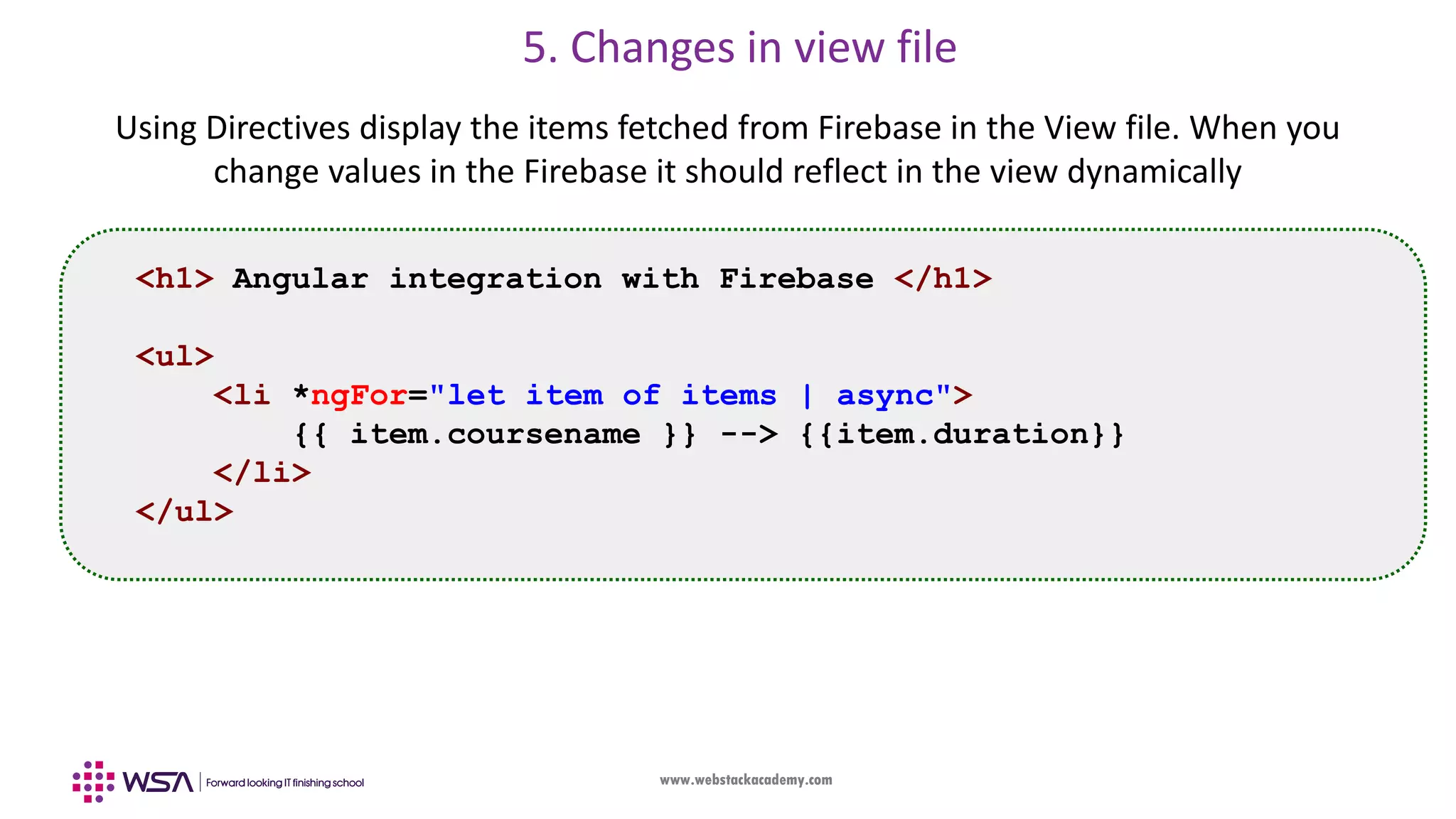



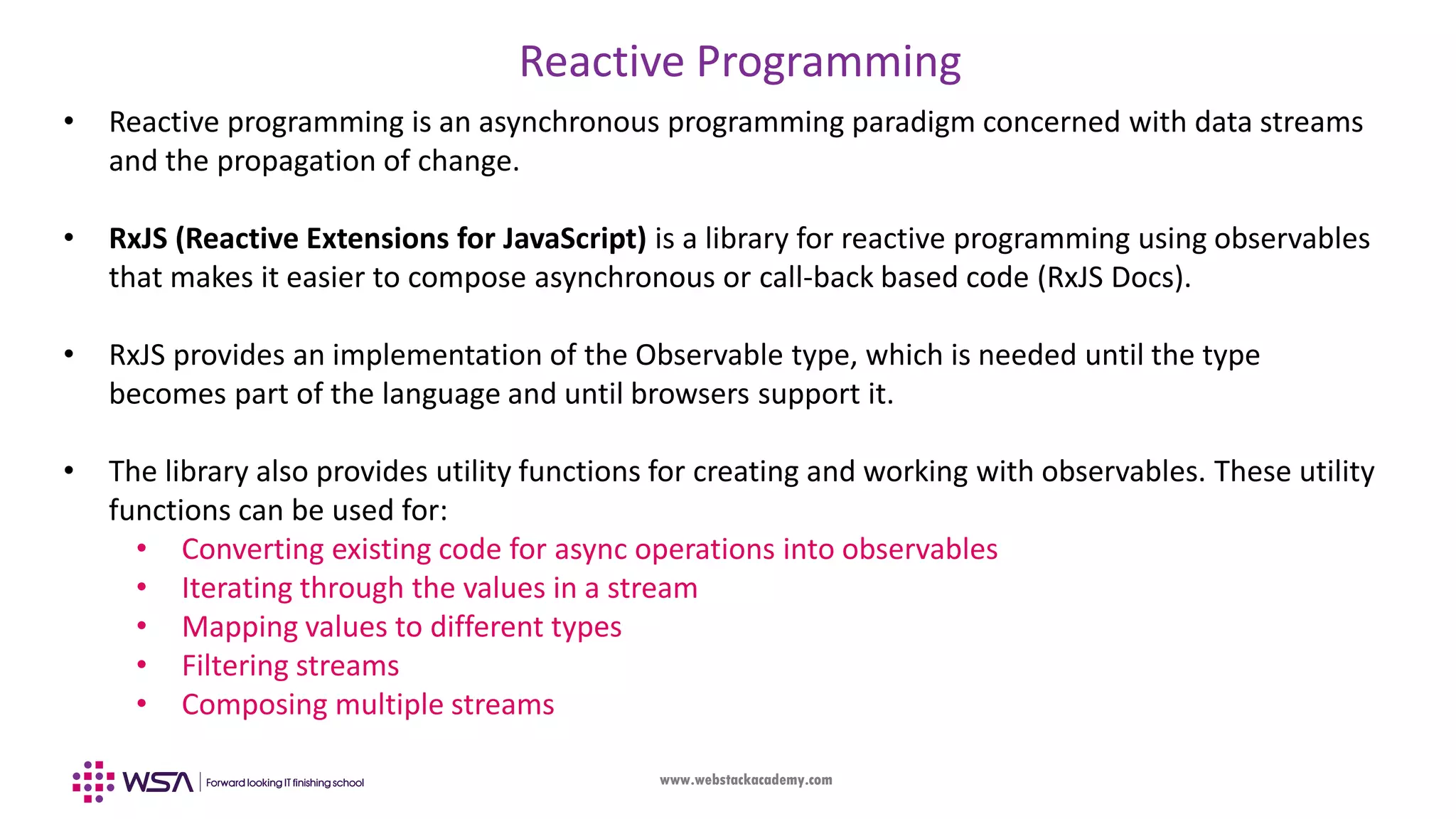

![www.webstackacademy.com And Finally….to back to our same source code…. import { AngularFirestore } from 'angularfire2/firestore'; import { Observable } from 'rxjs'; items: Observable<Item[]>; constructor(public db: AngularFirestore) { // Monitor changes this.items = this.db.collection('courses').valueChanges(); // Asynchronously retrieve changed values this.items.subscribe(myValues => { console.log(myValues); }); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/006angularfirebase-190503102852/75/Angular-Chapter-6-Firebase-Integration-38-2048.jpg)