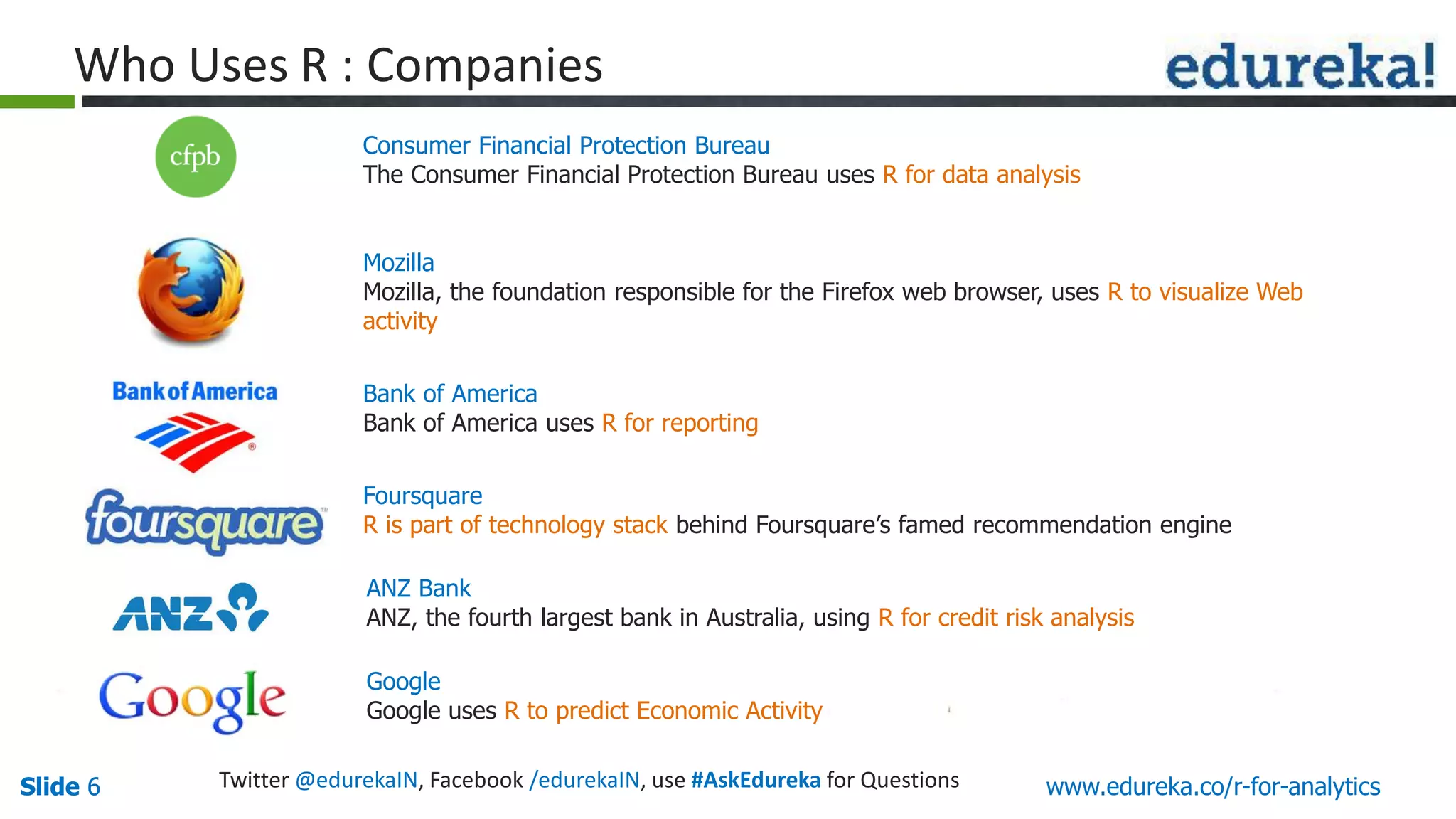
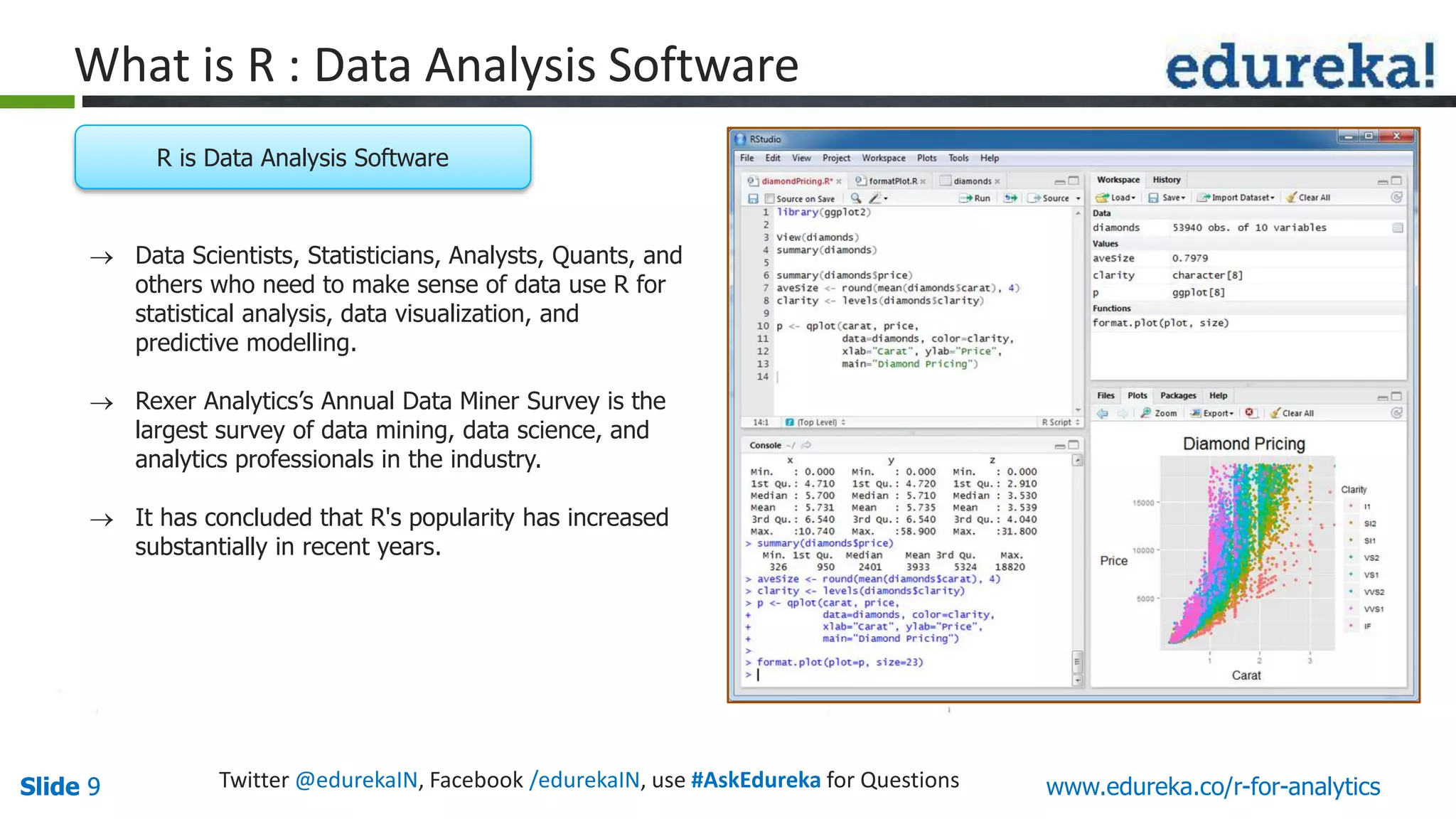
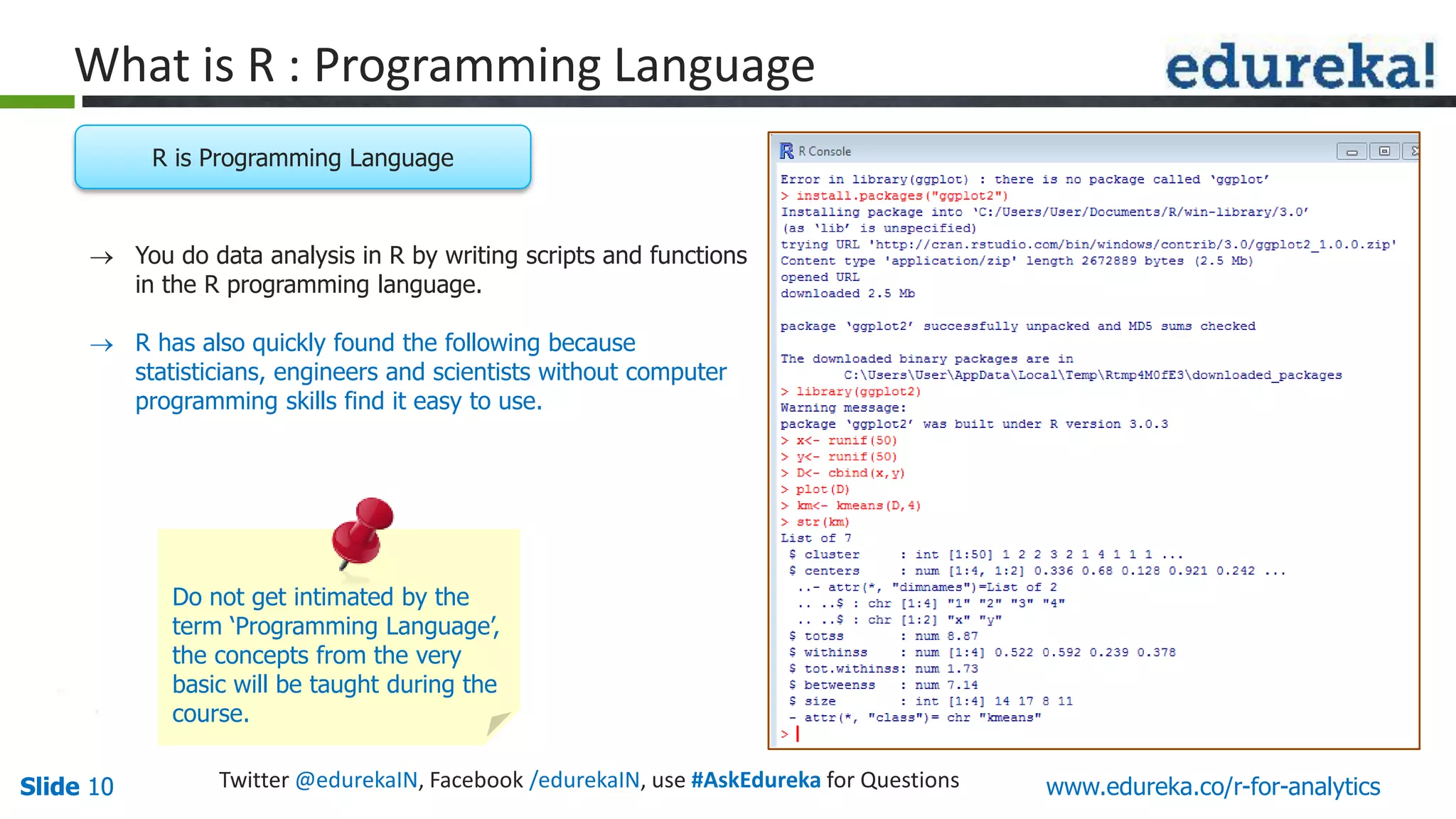
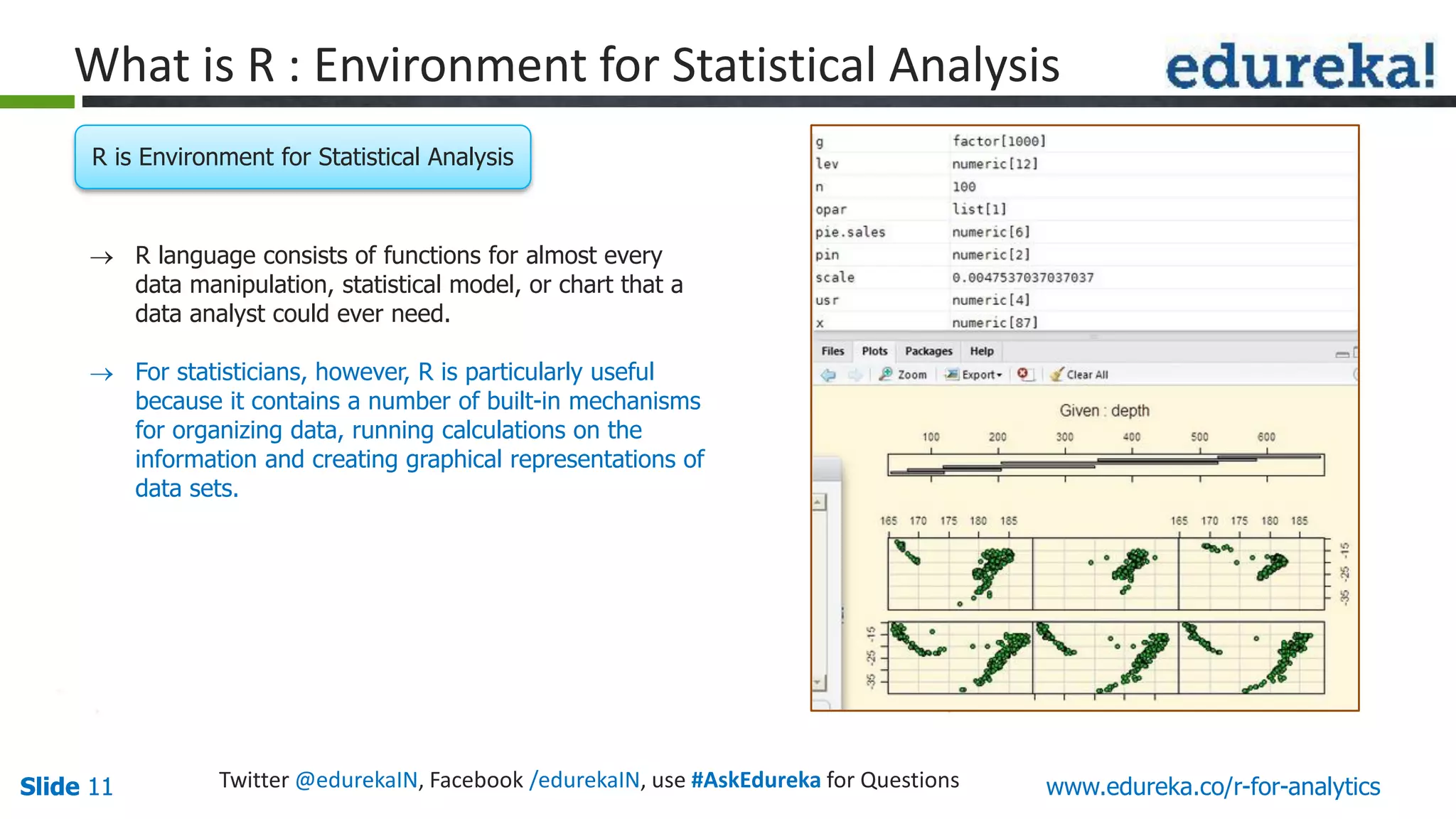
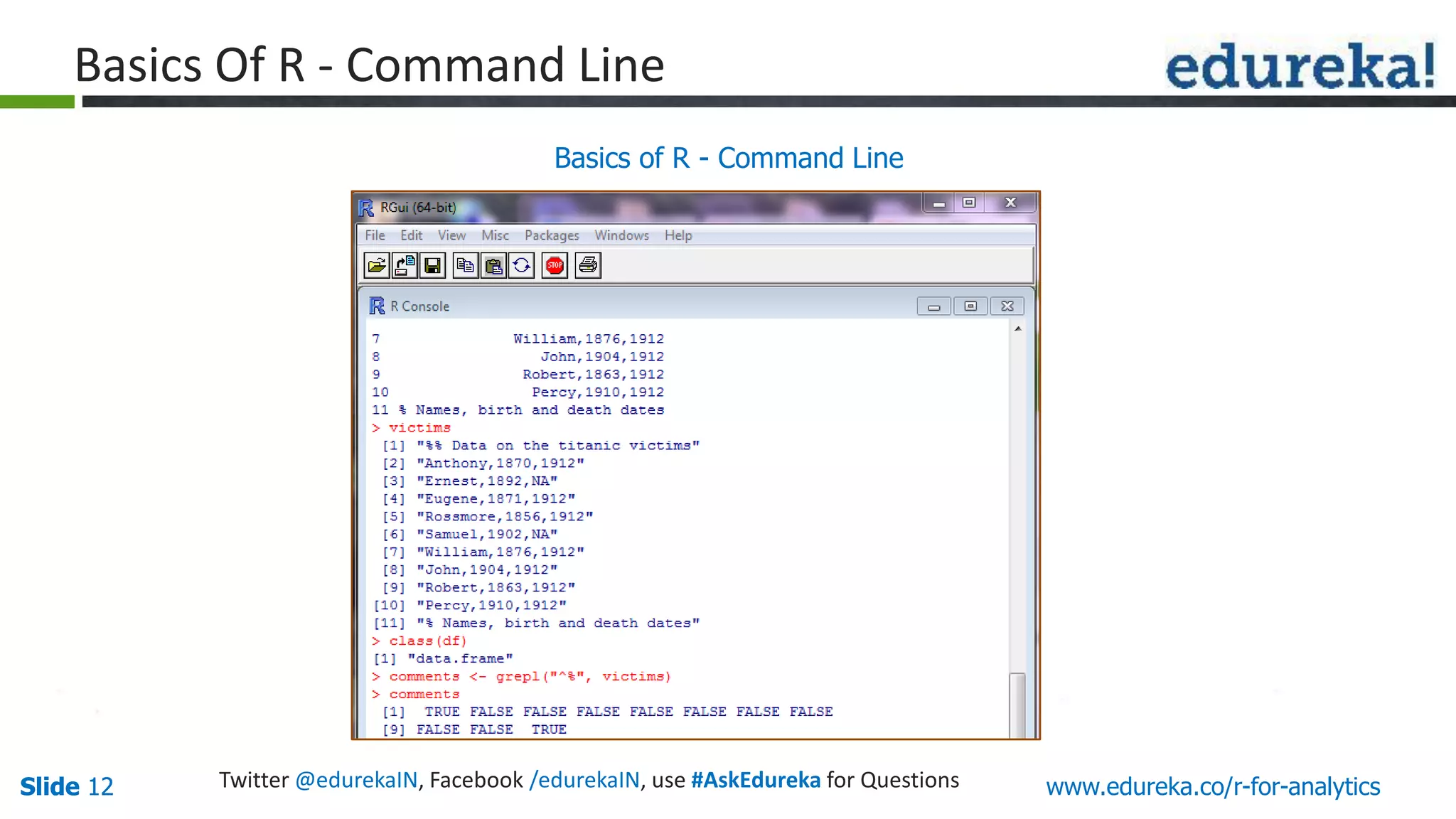
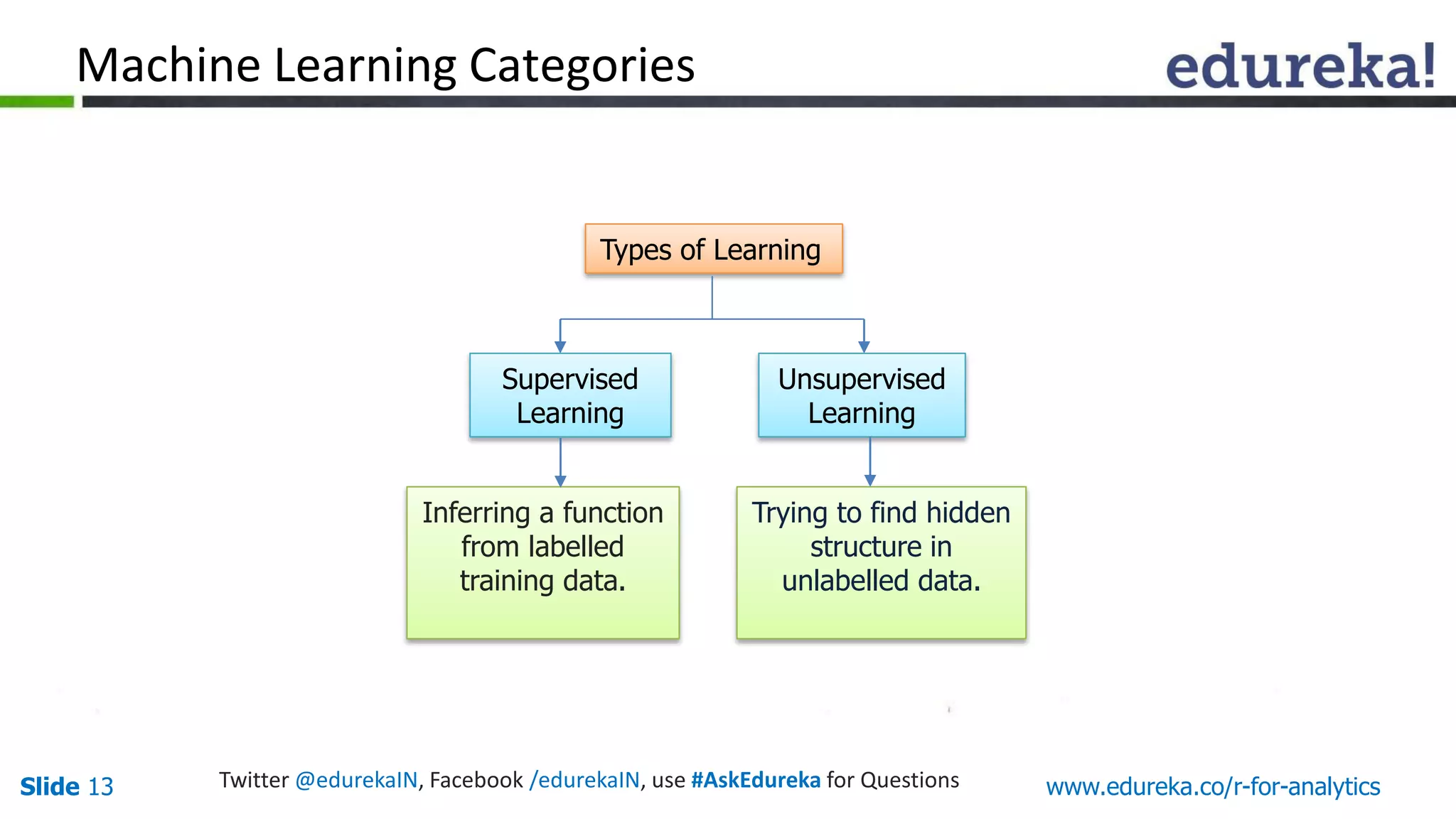
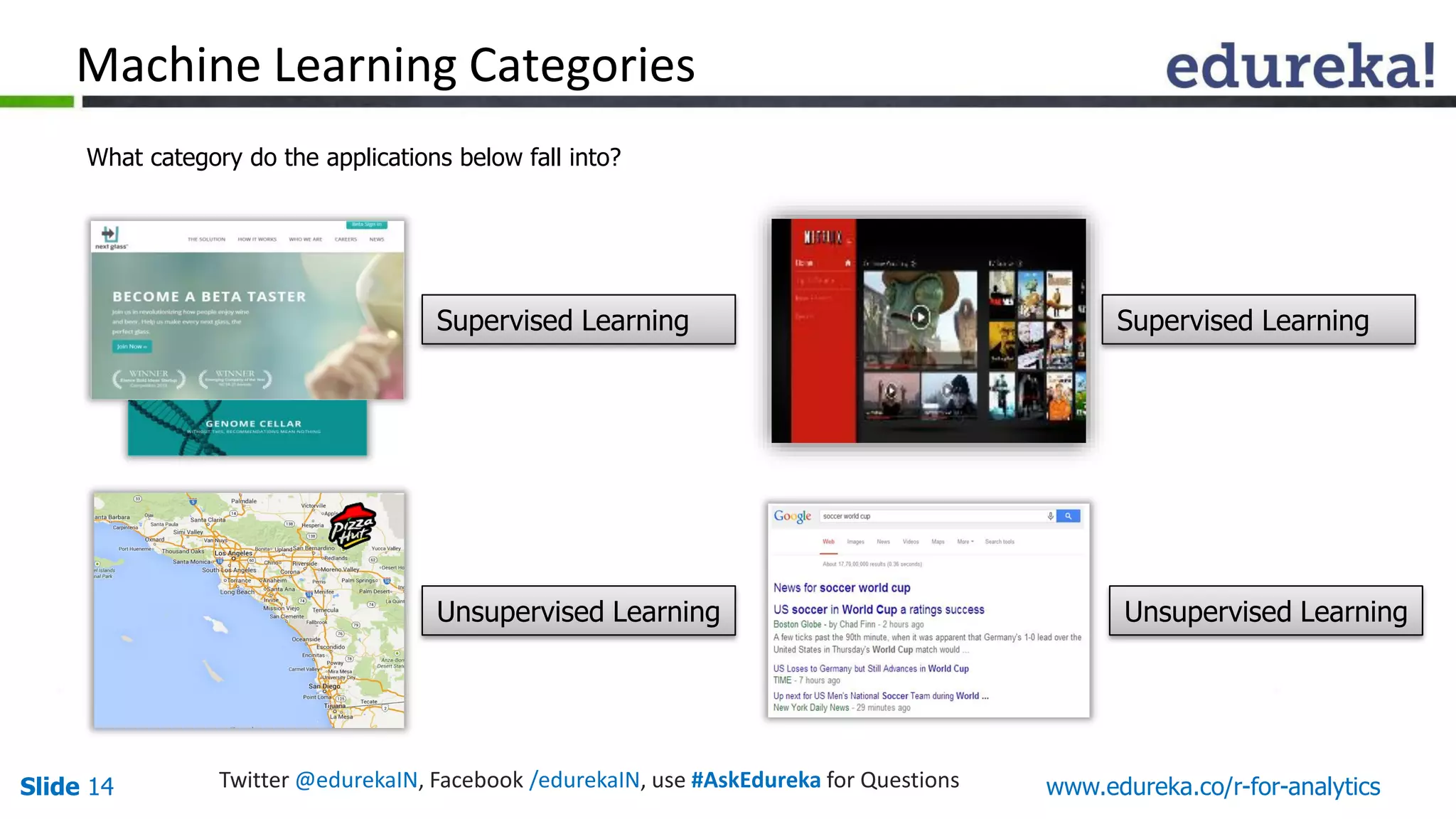
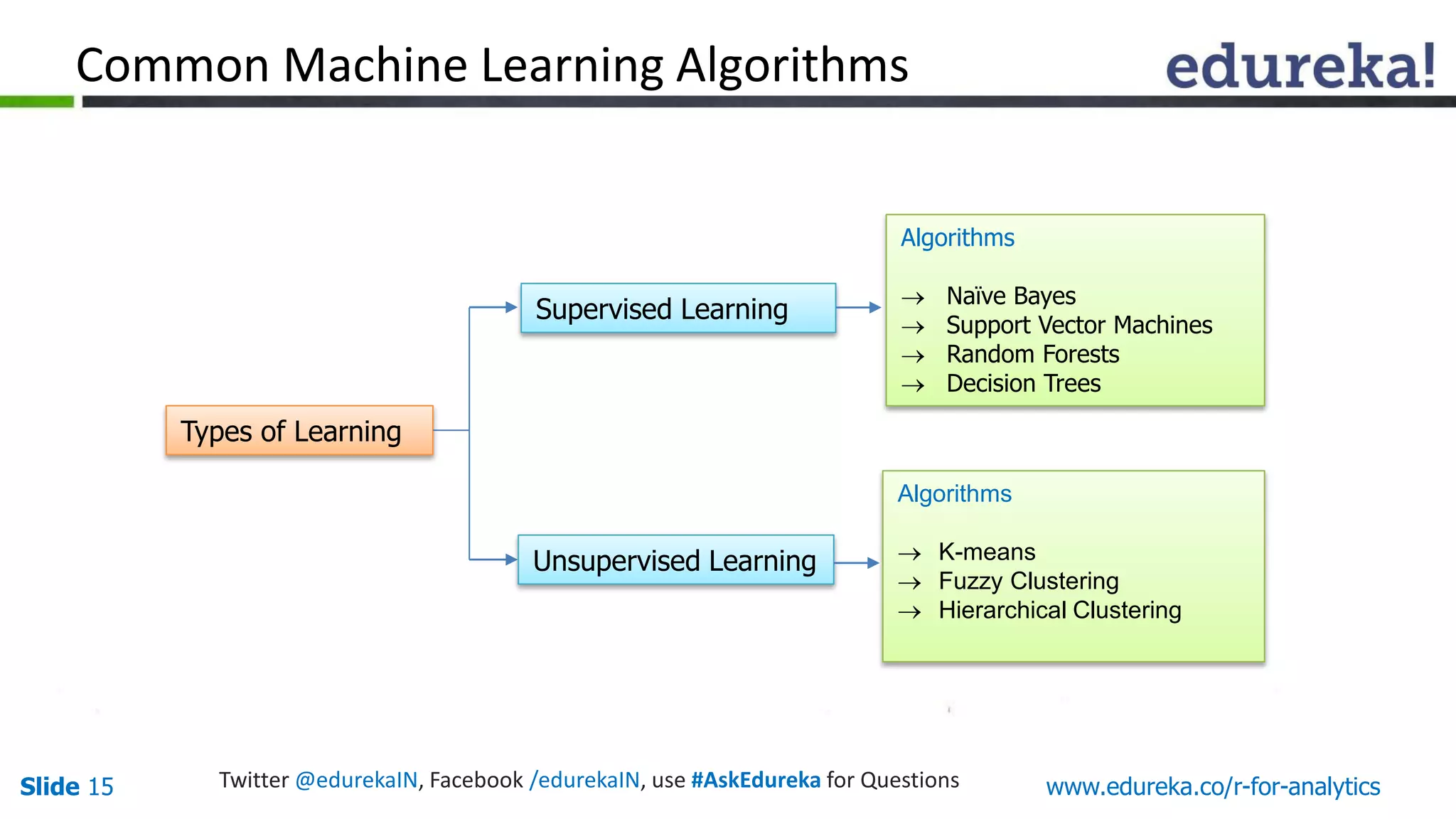
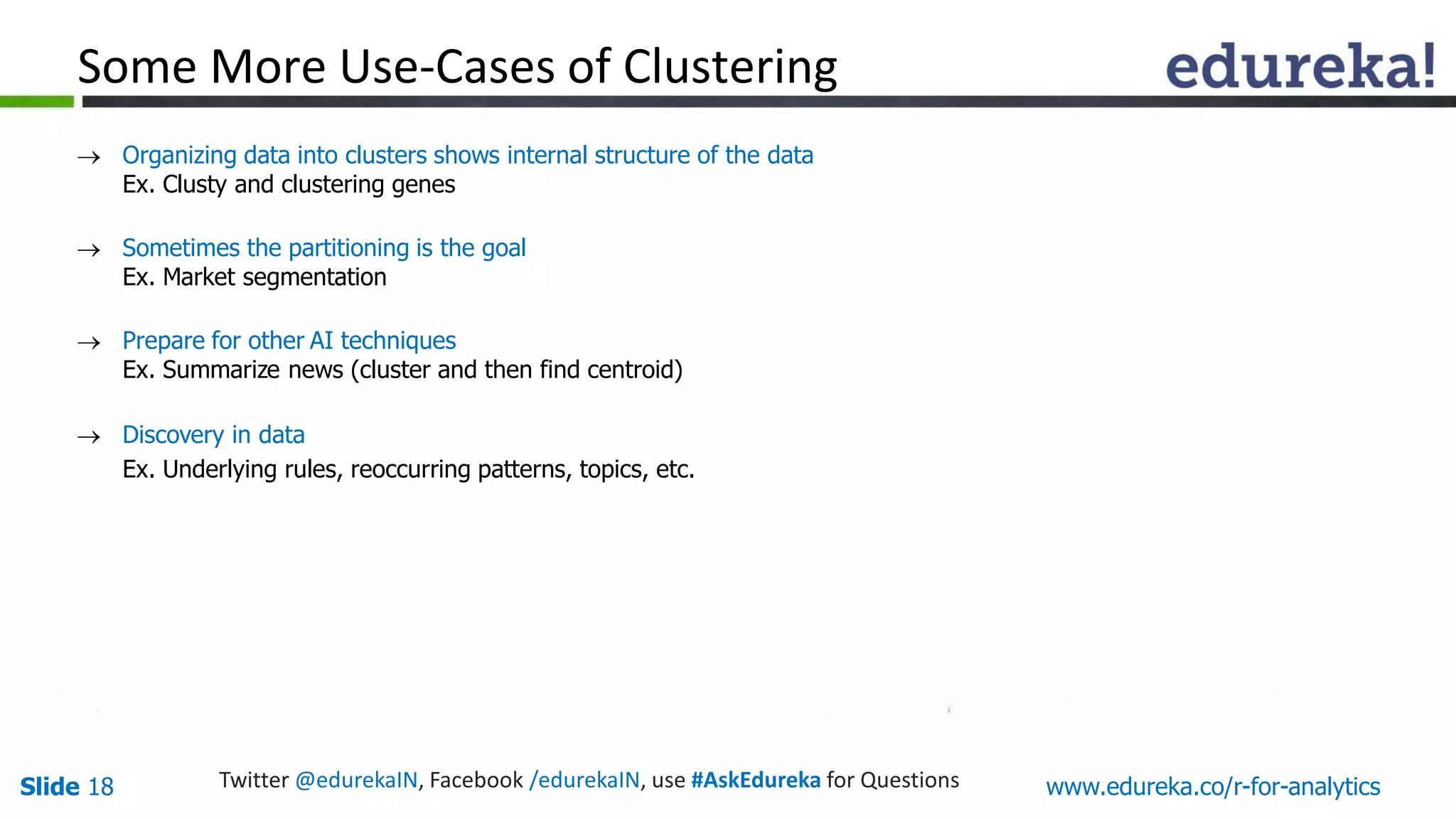
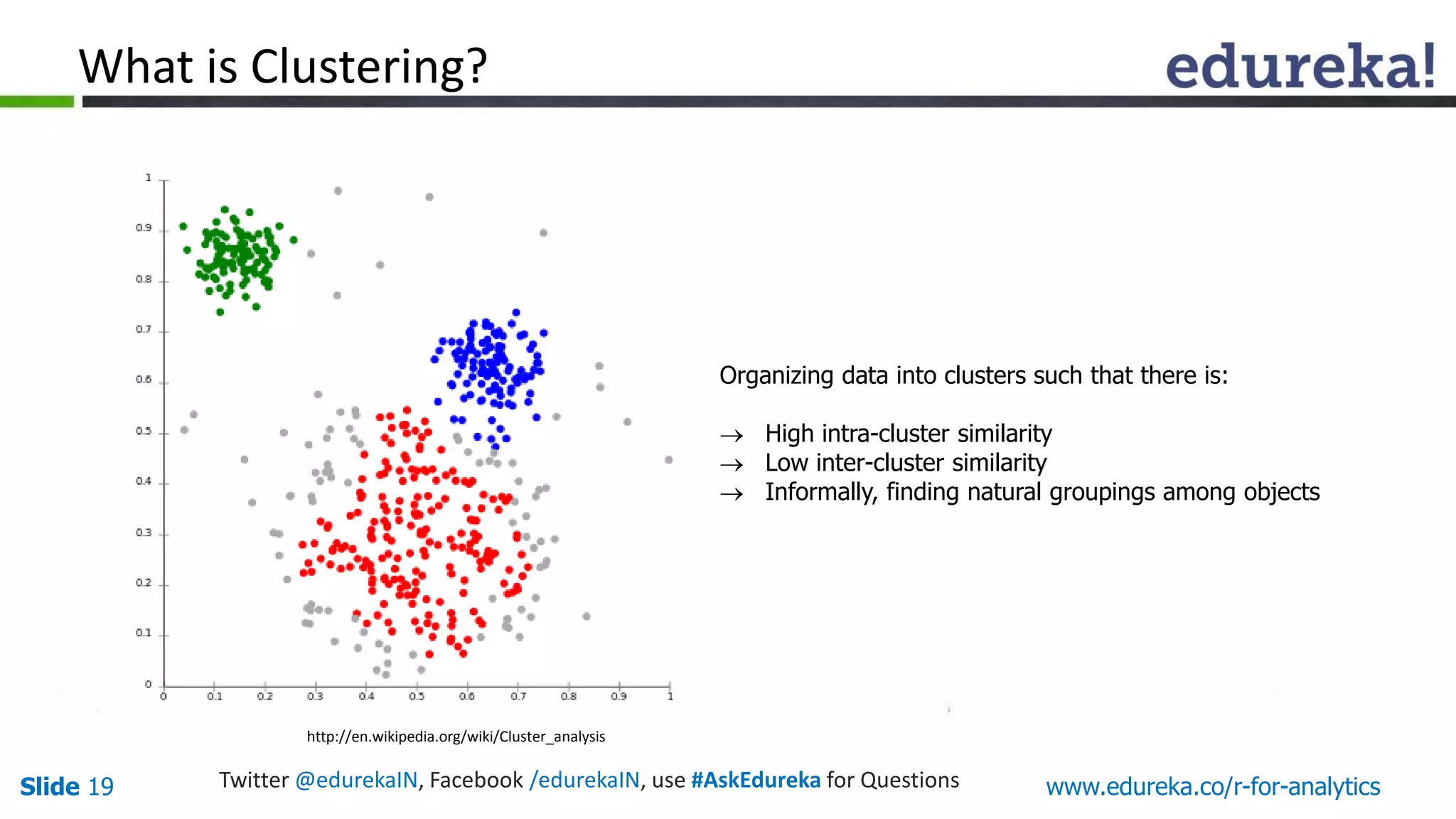
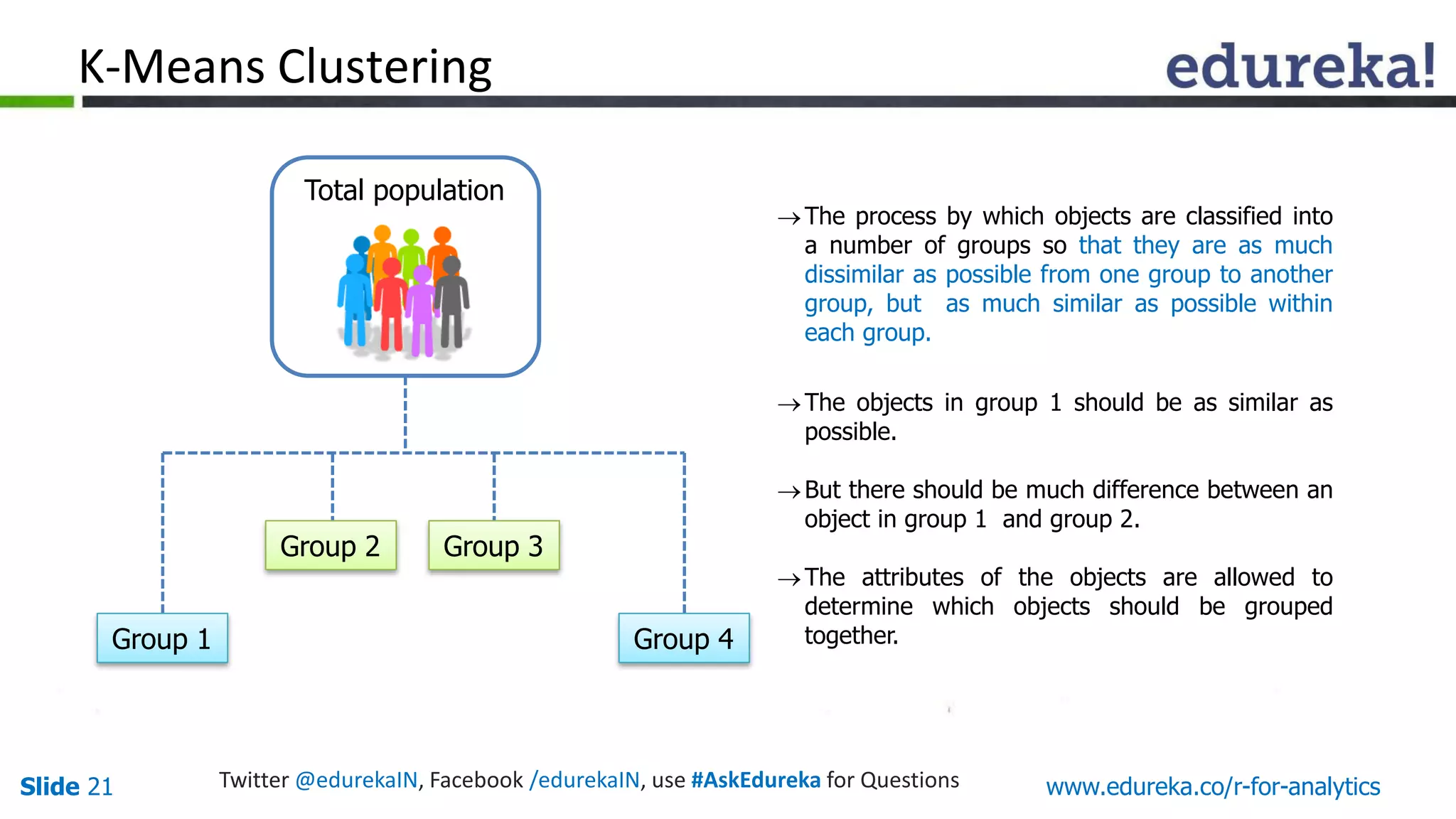
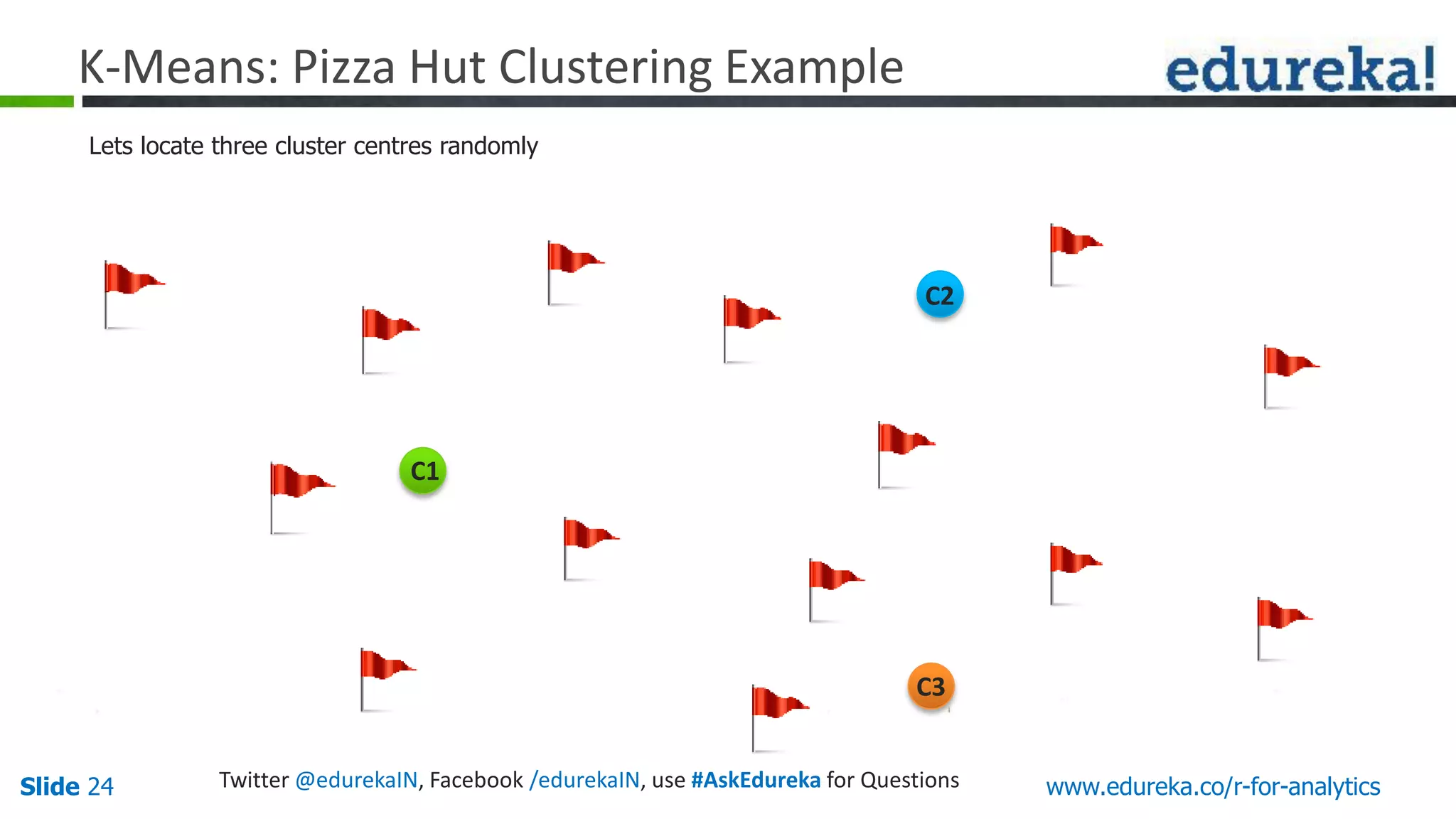
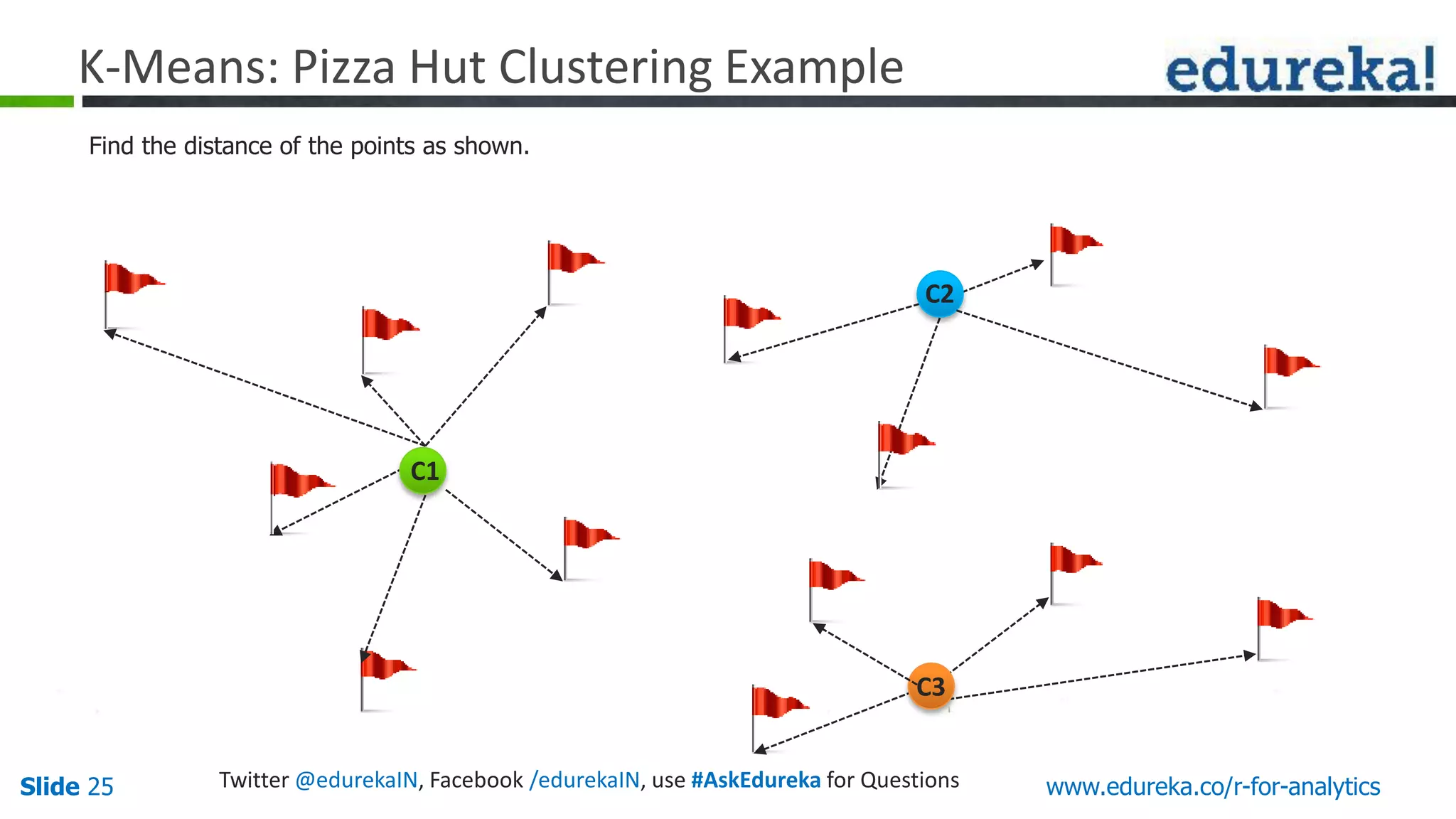
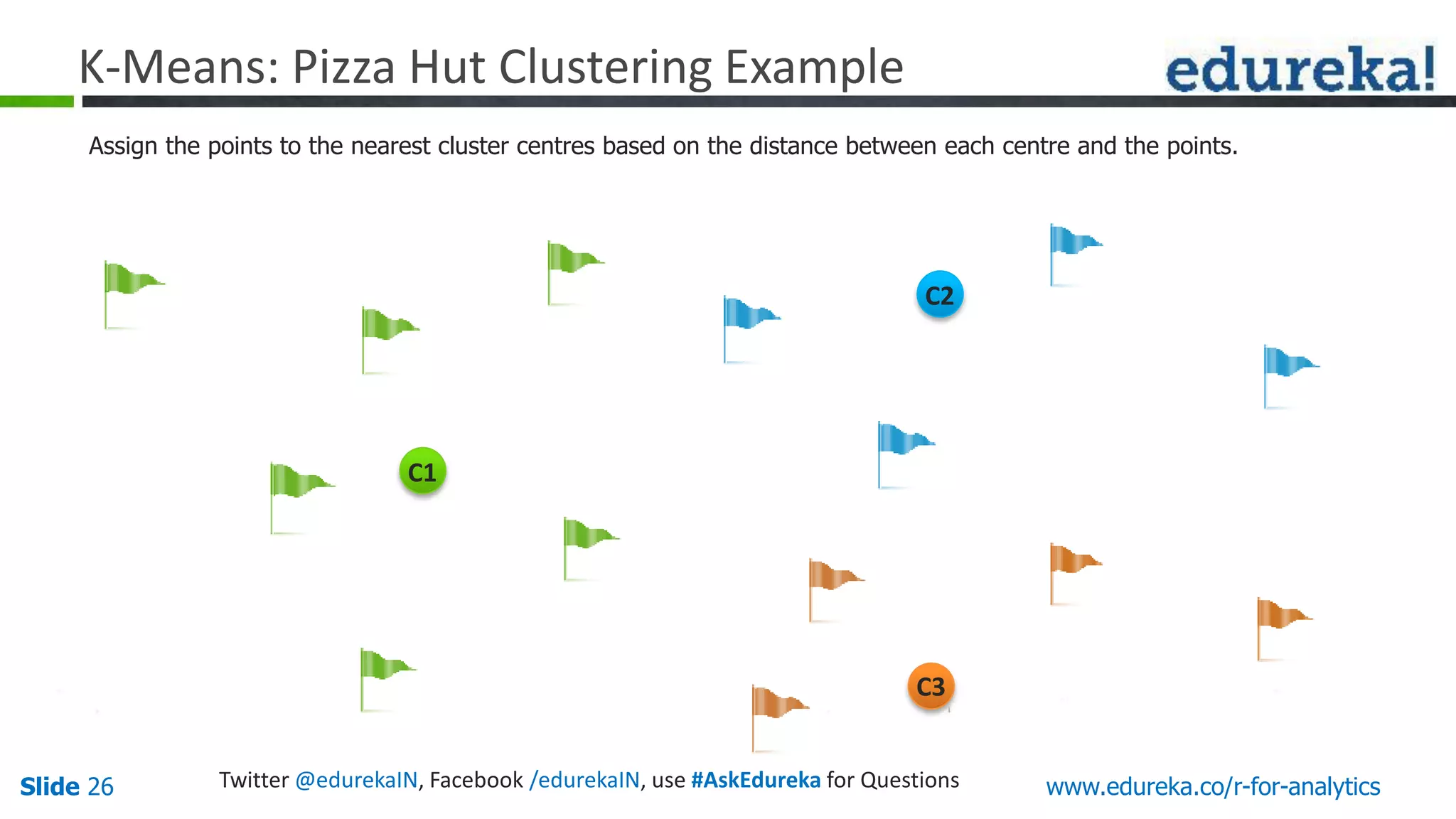
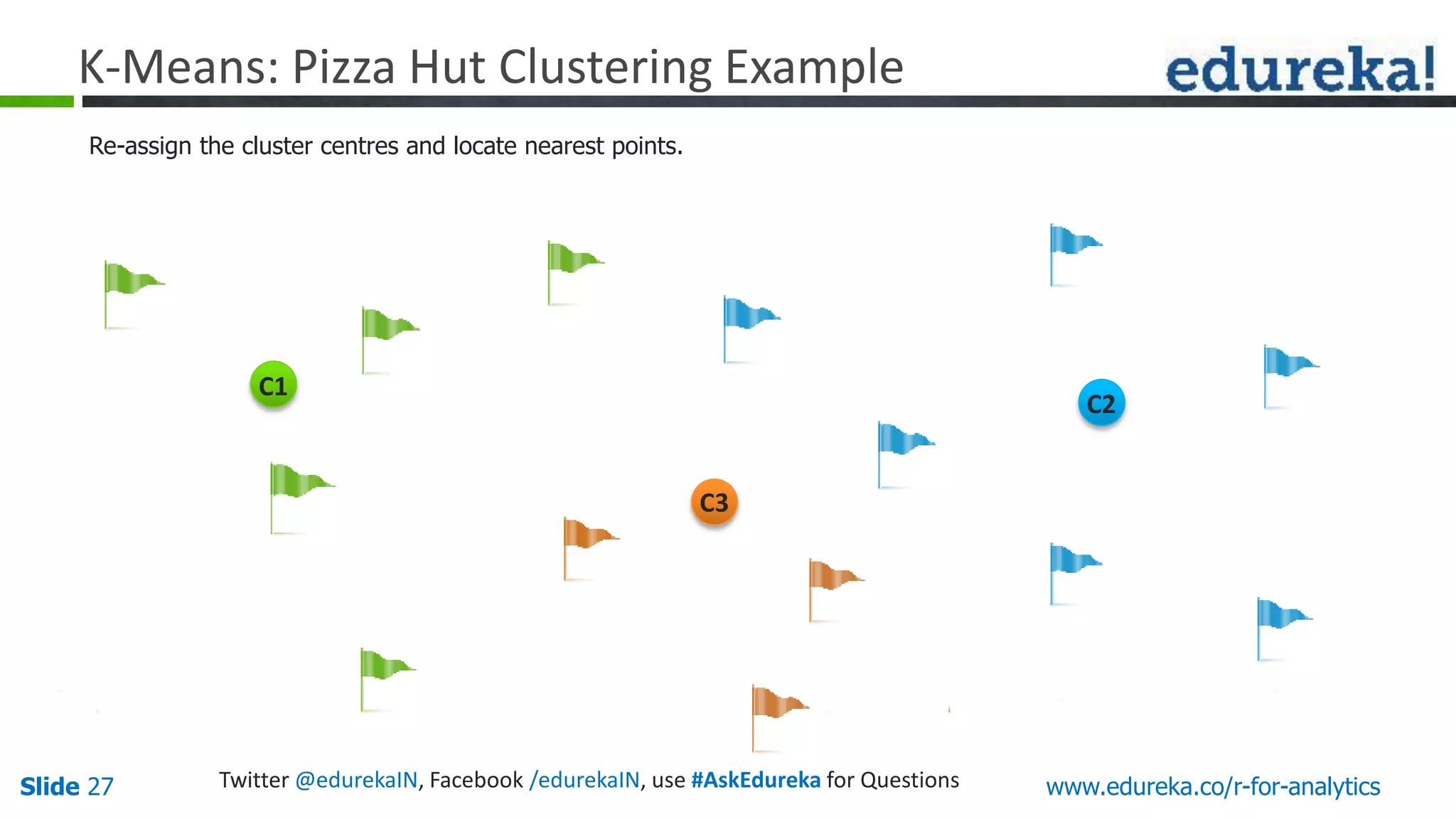
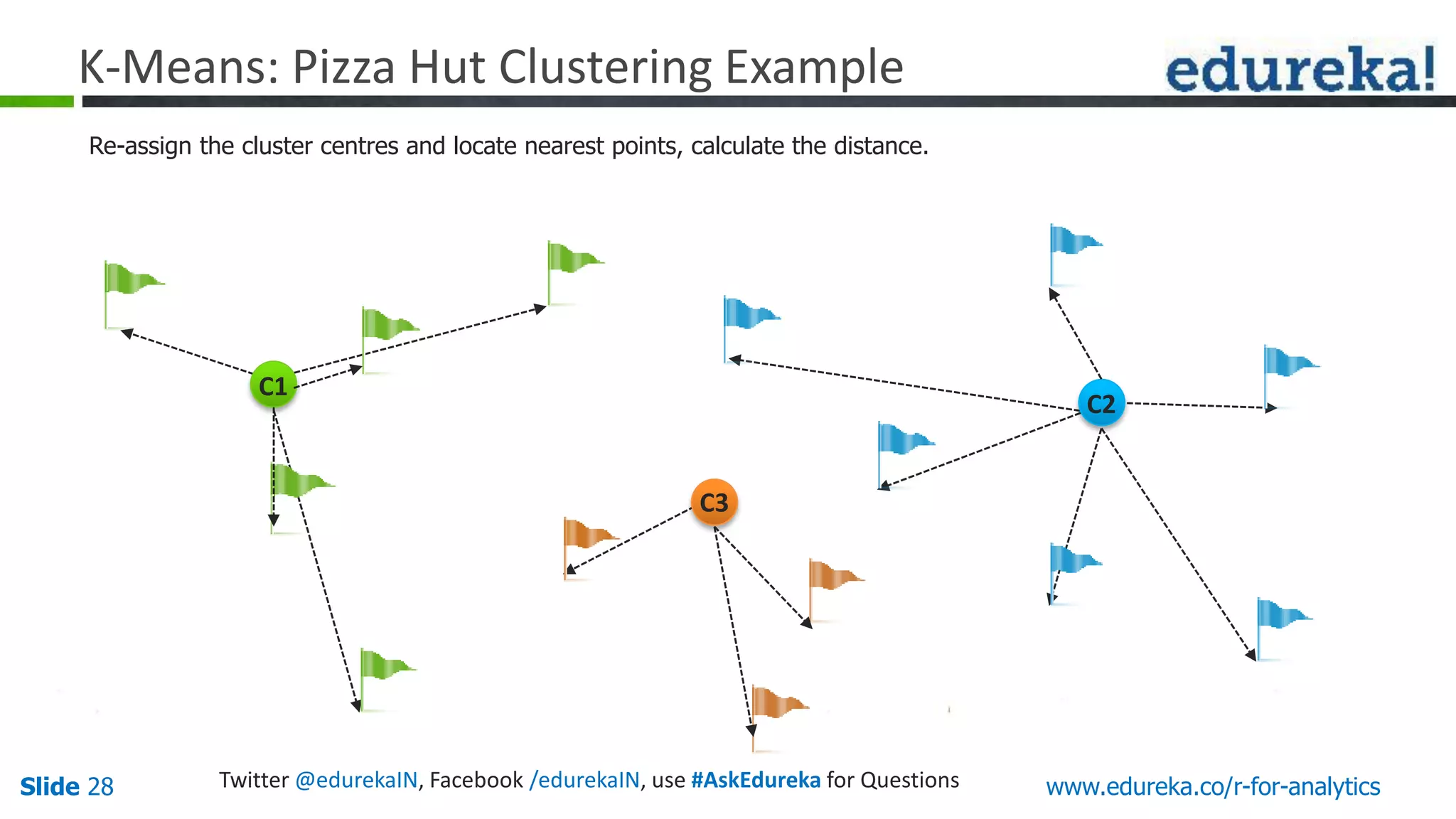
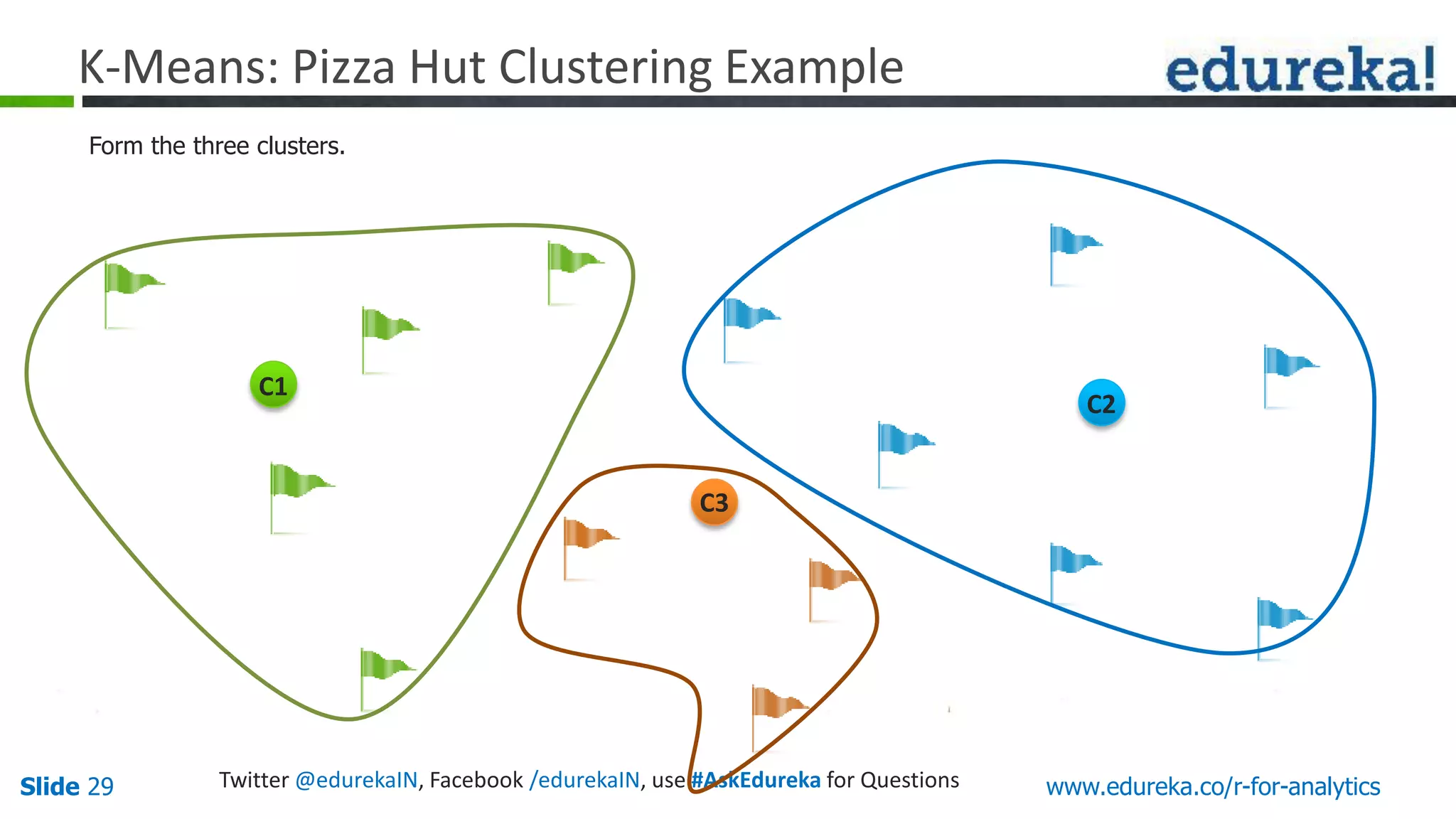
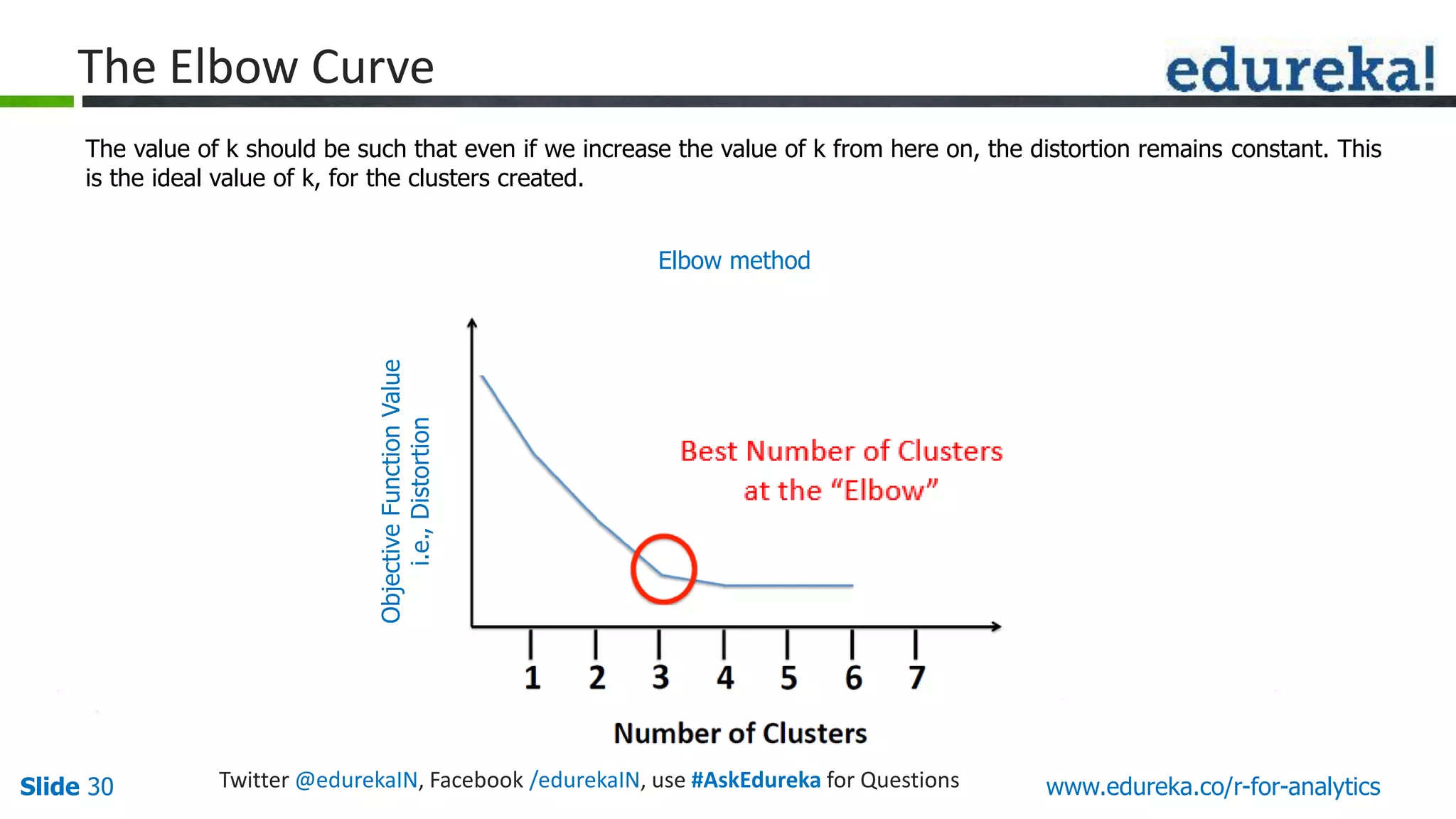
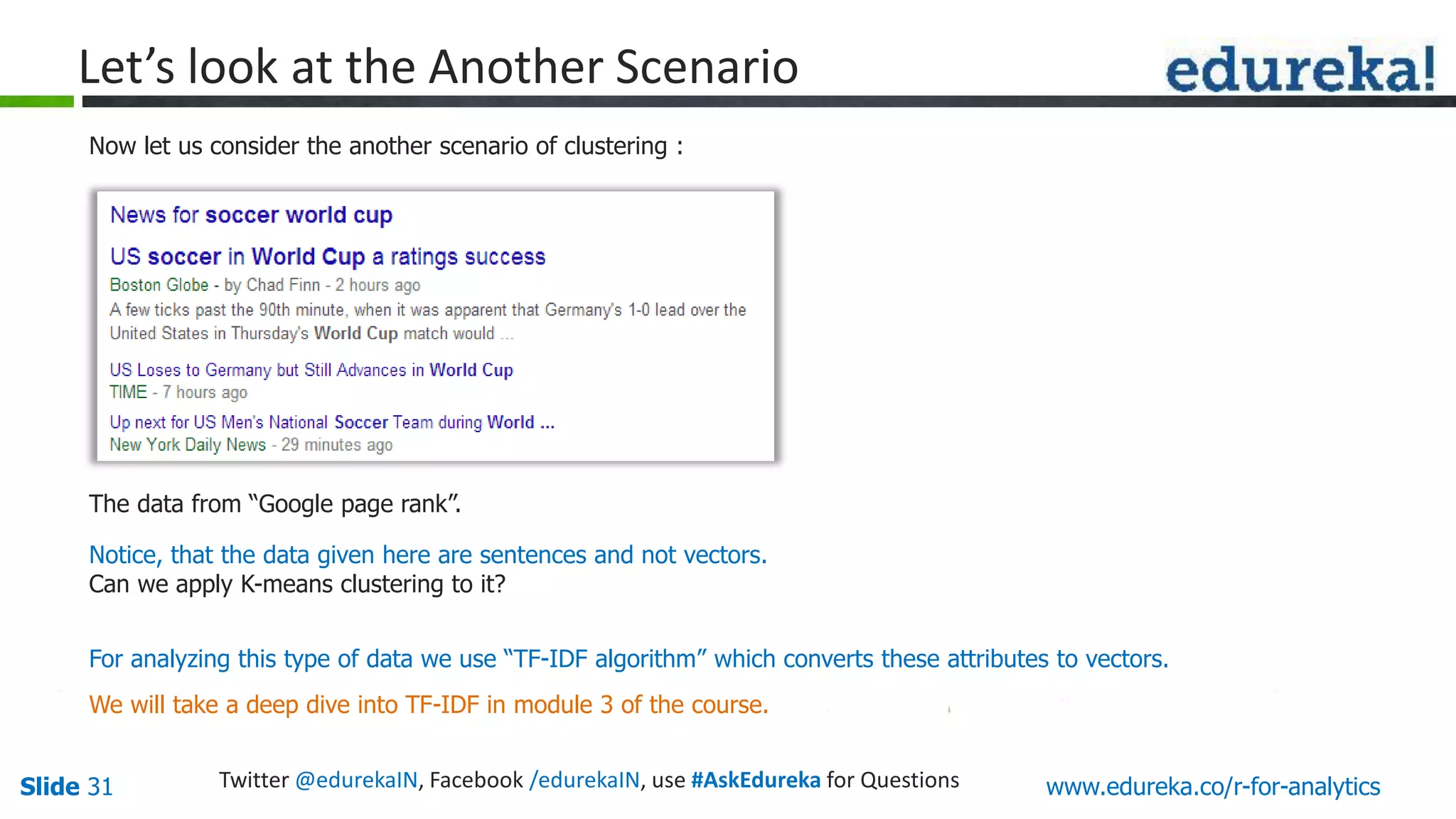
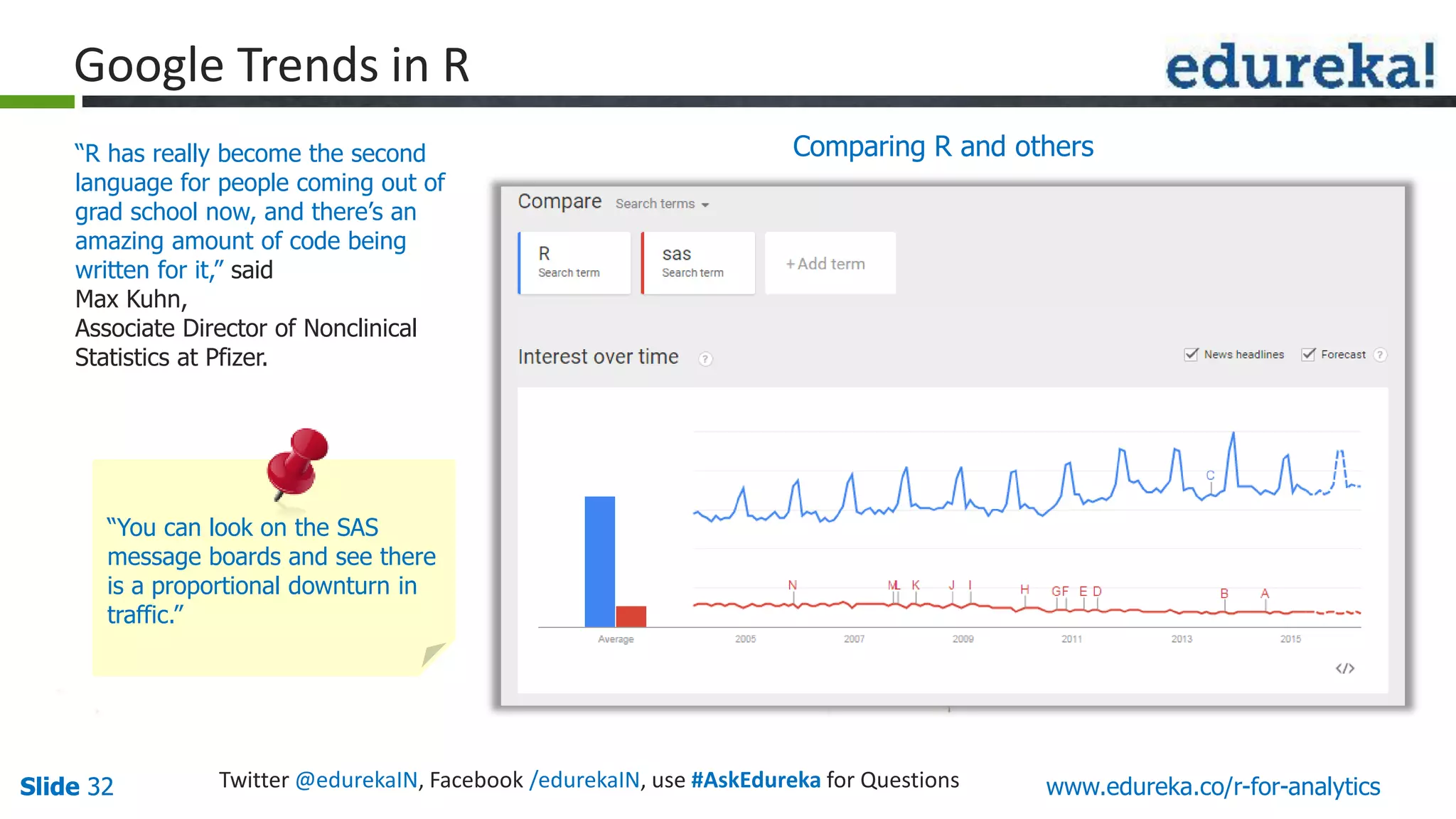
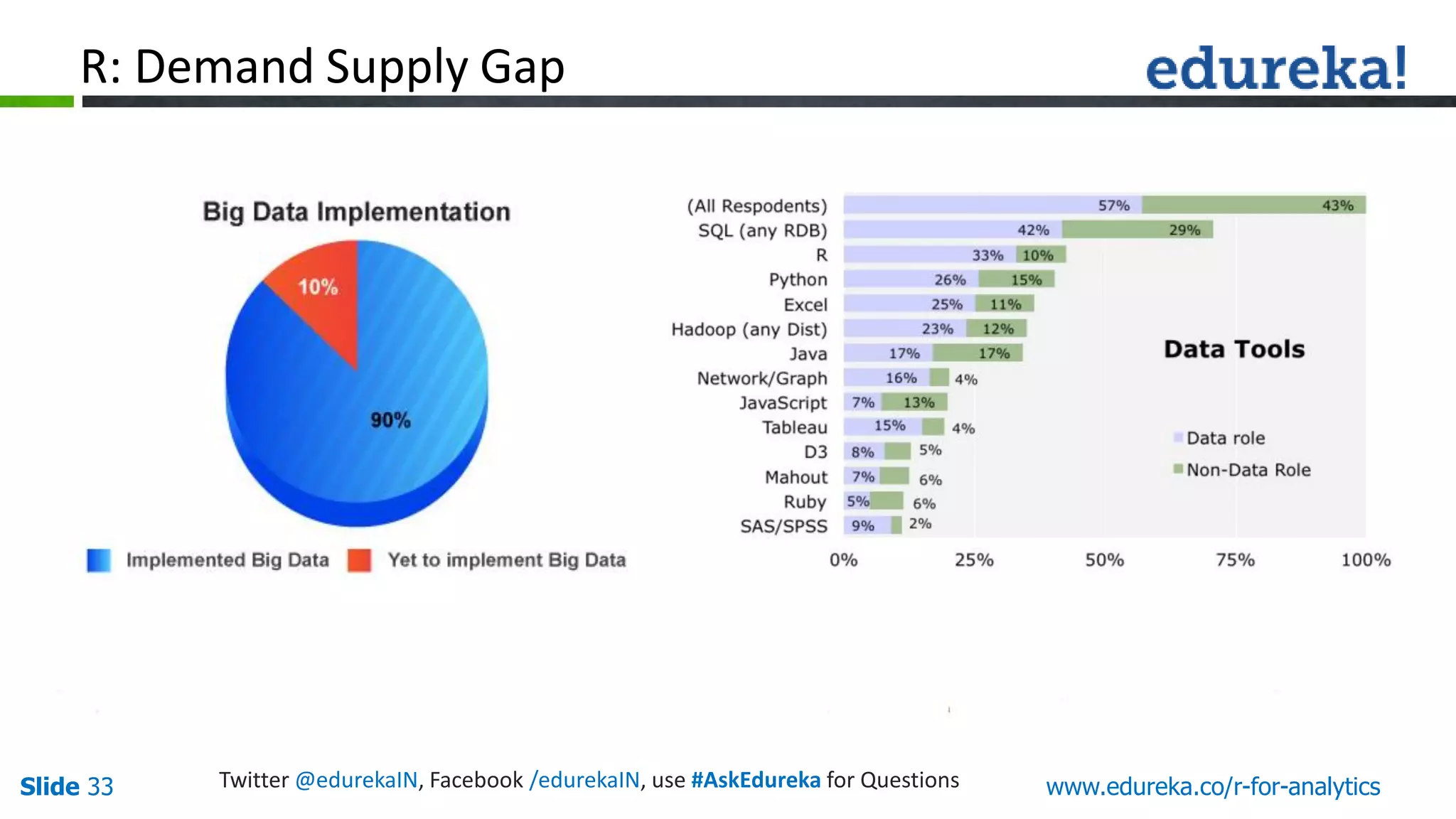
The document is a slide presentation on Business Analytics with R from Edureka. It discusses: - The objectives of learning R and an overview of machine learning concepts like supervised vs. unsupervised learning. - How R is used widely in various domains and companies for tasks like data analysis, visualization, and predictive modeling. - An introduction to clustering and k-means clustering algorithms along with examples. - How to implement k-means clustering in R and evaluate the results. - The course topics that will be covered related to data manipulation, visualization, regression, and data mining techniques in R.