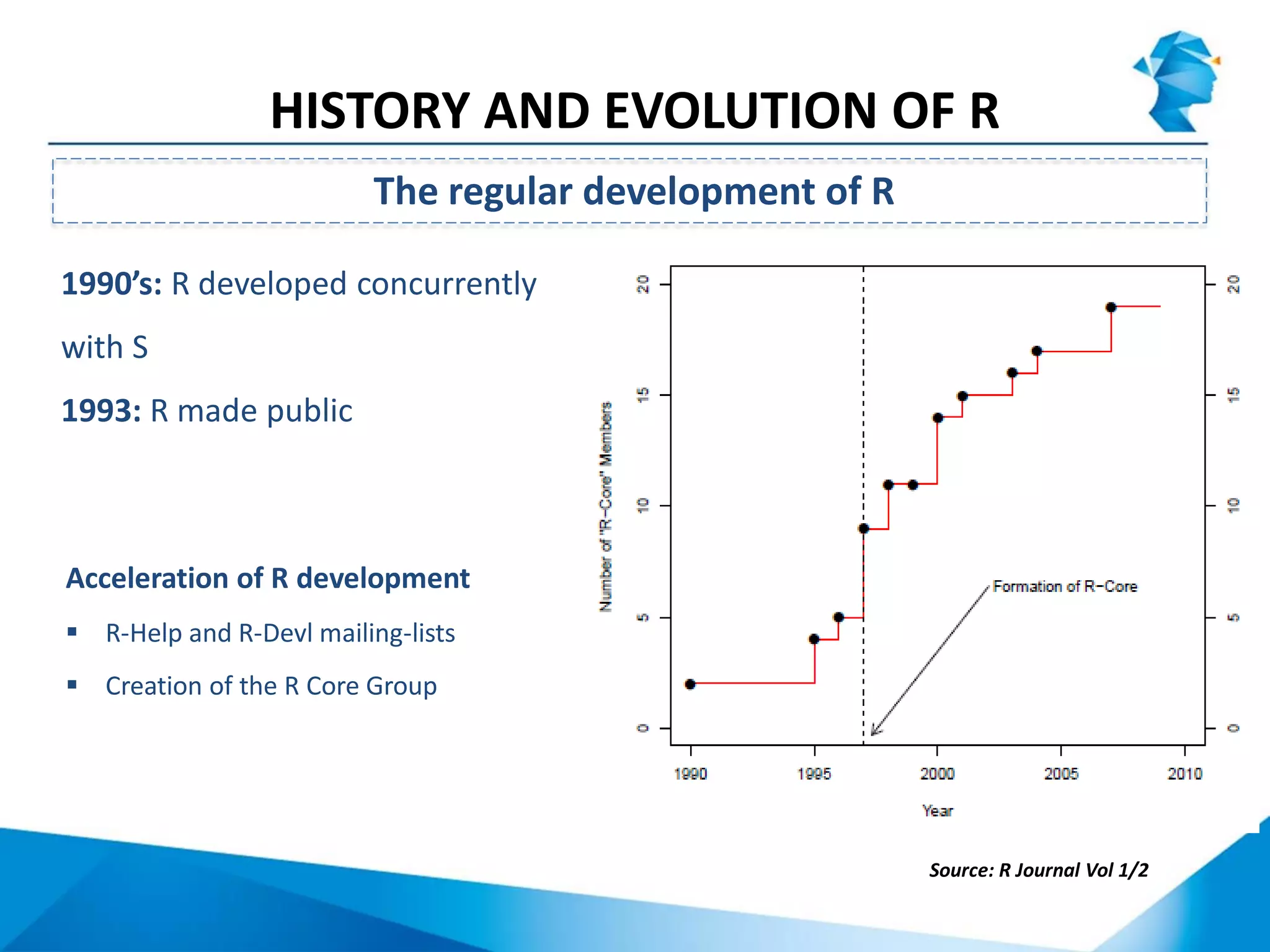
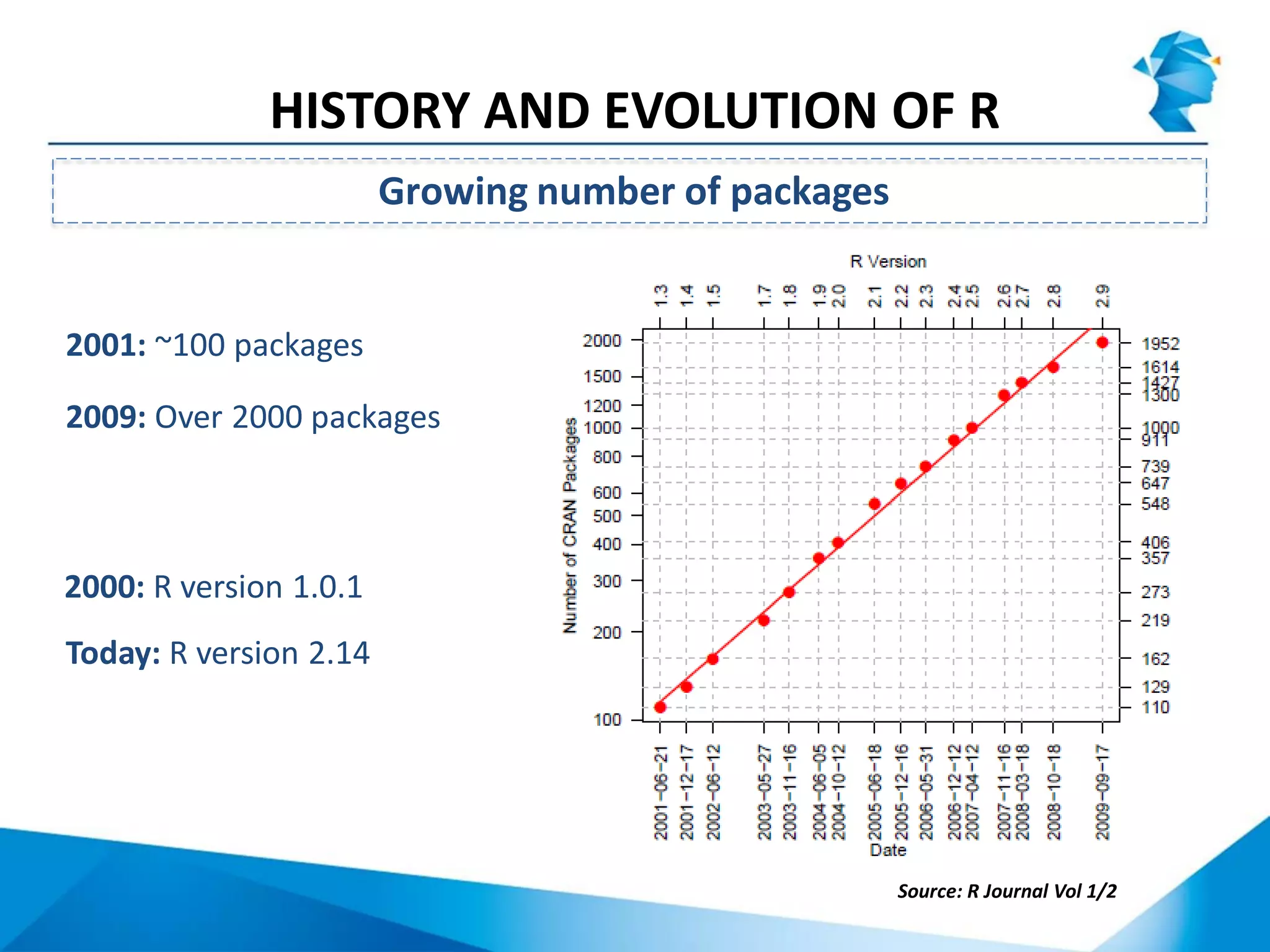
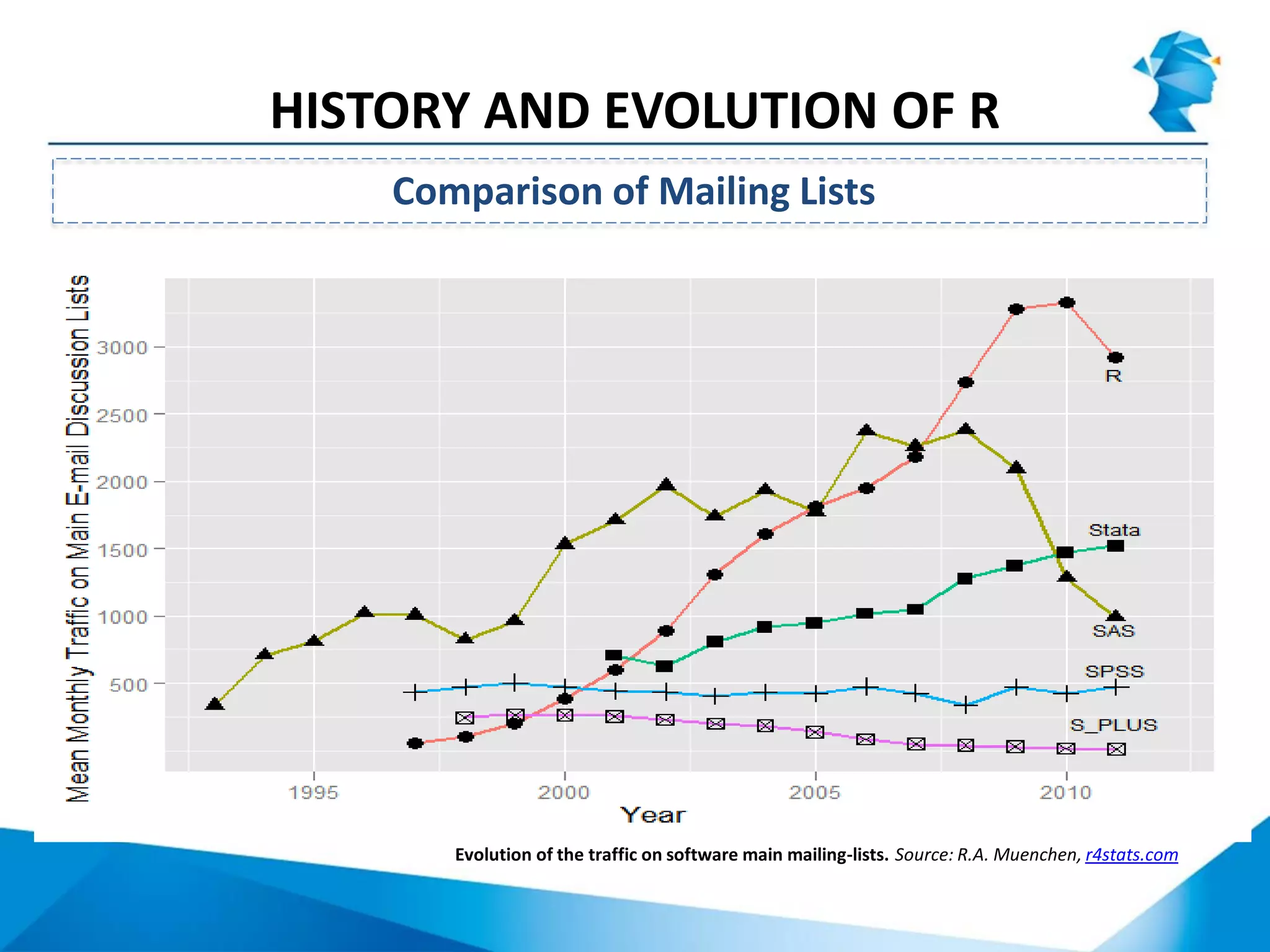
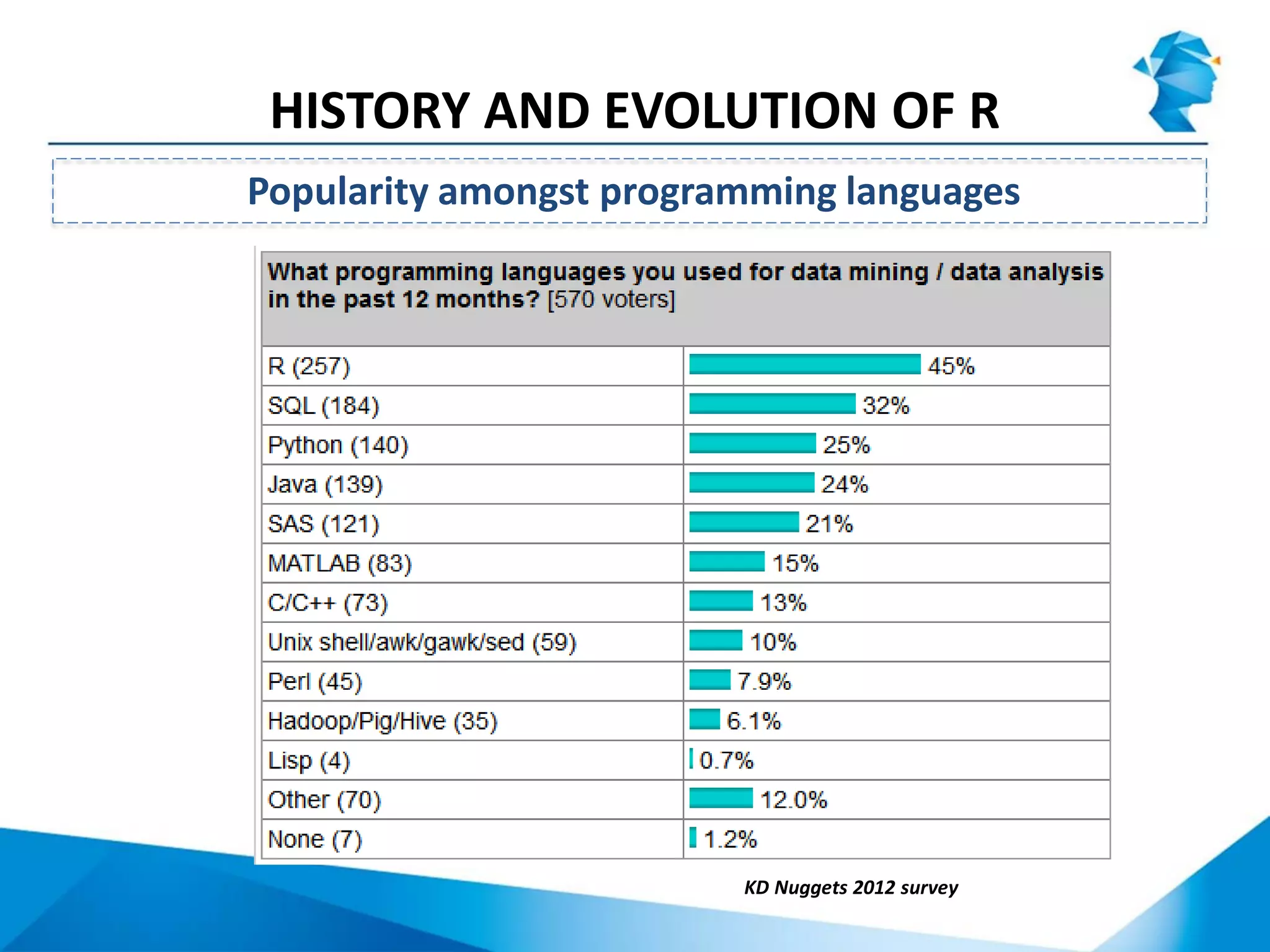
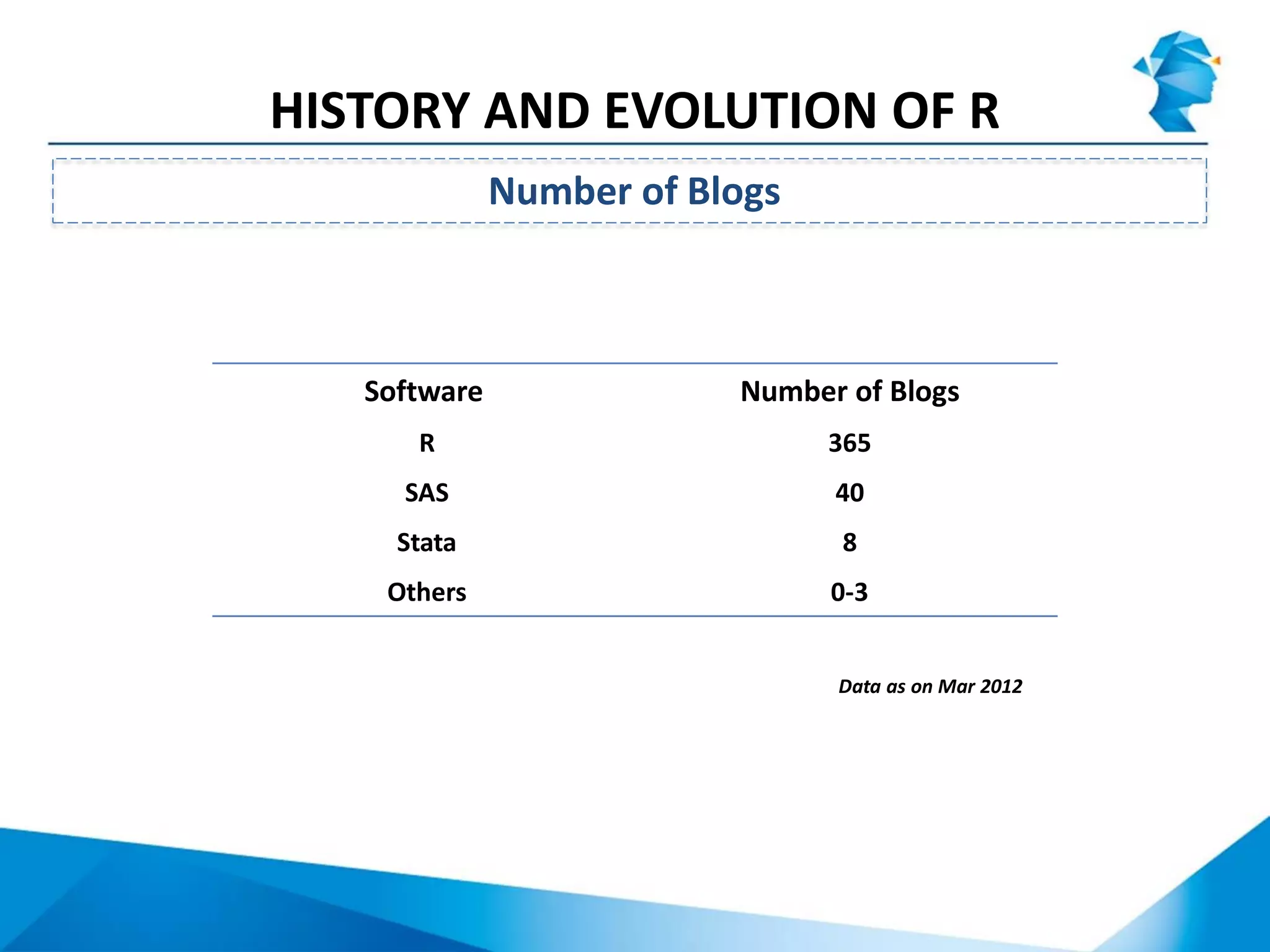
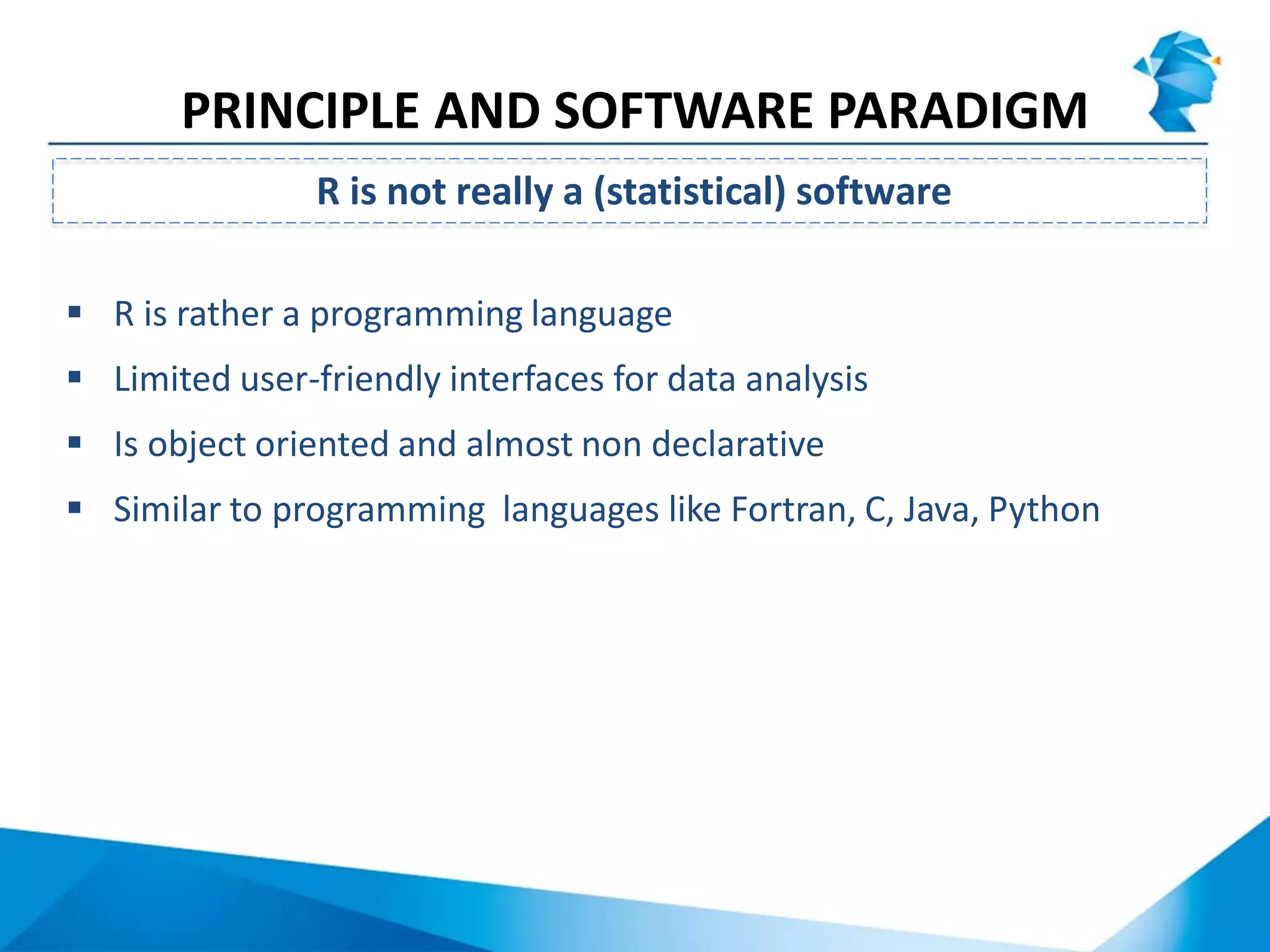
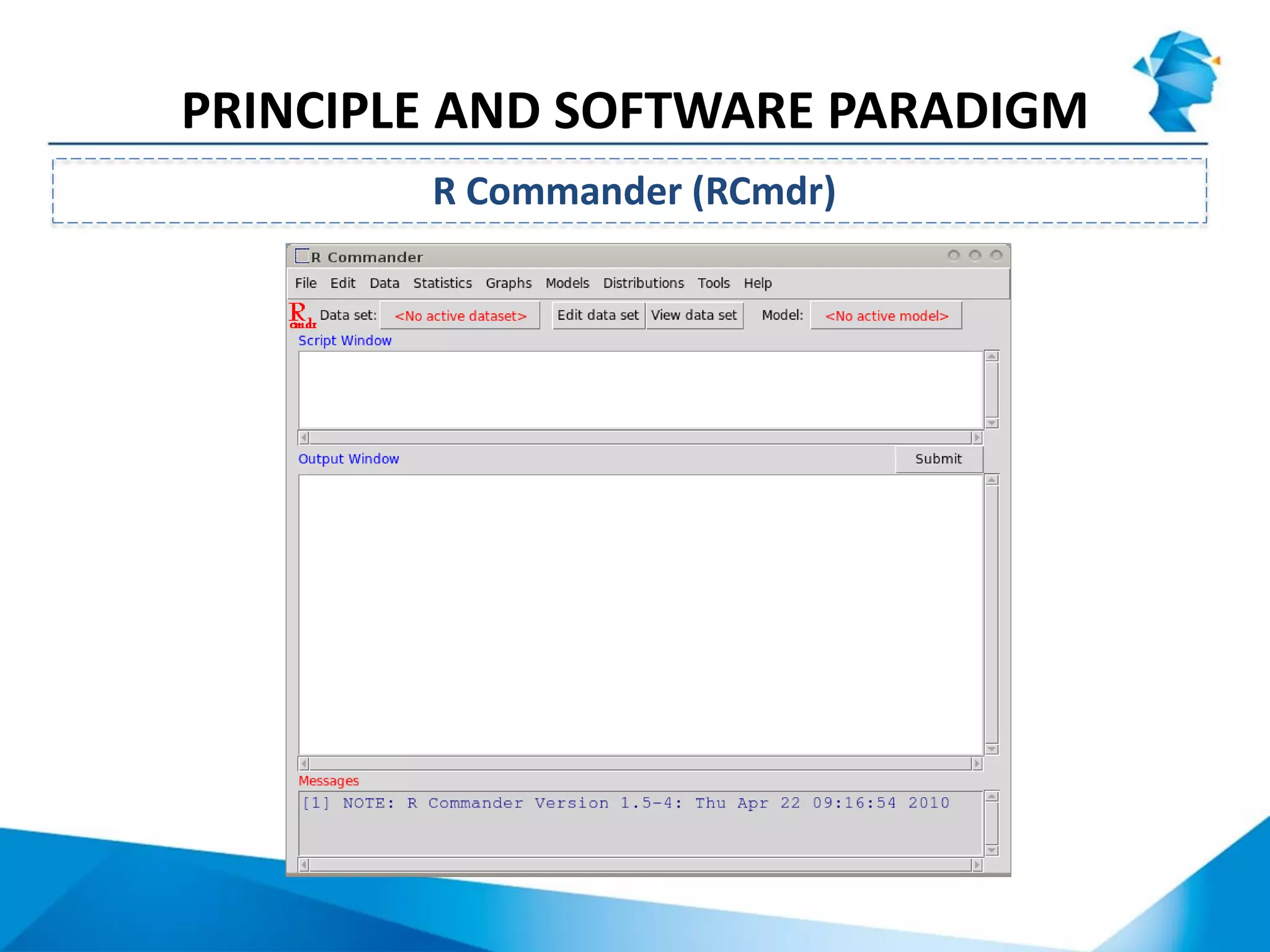
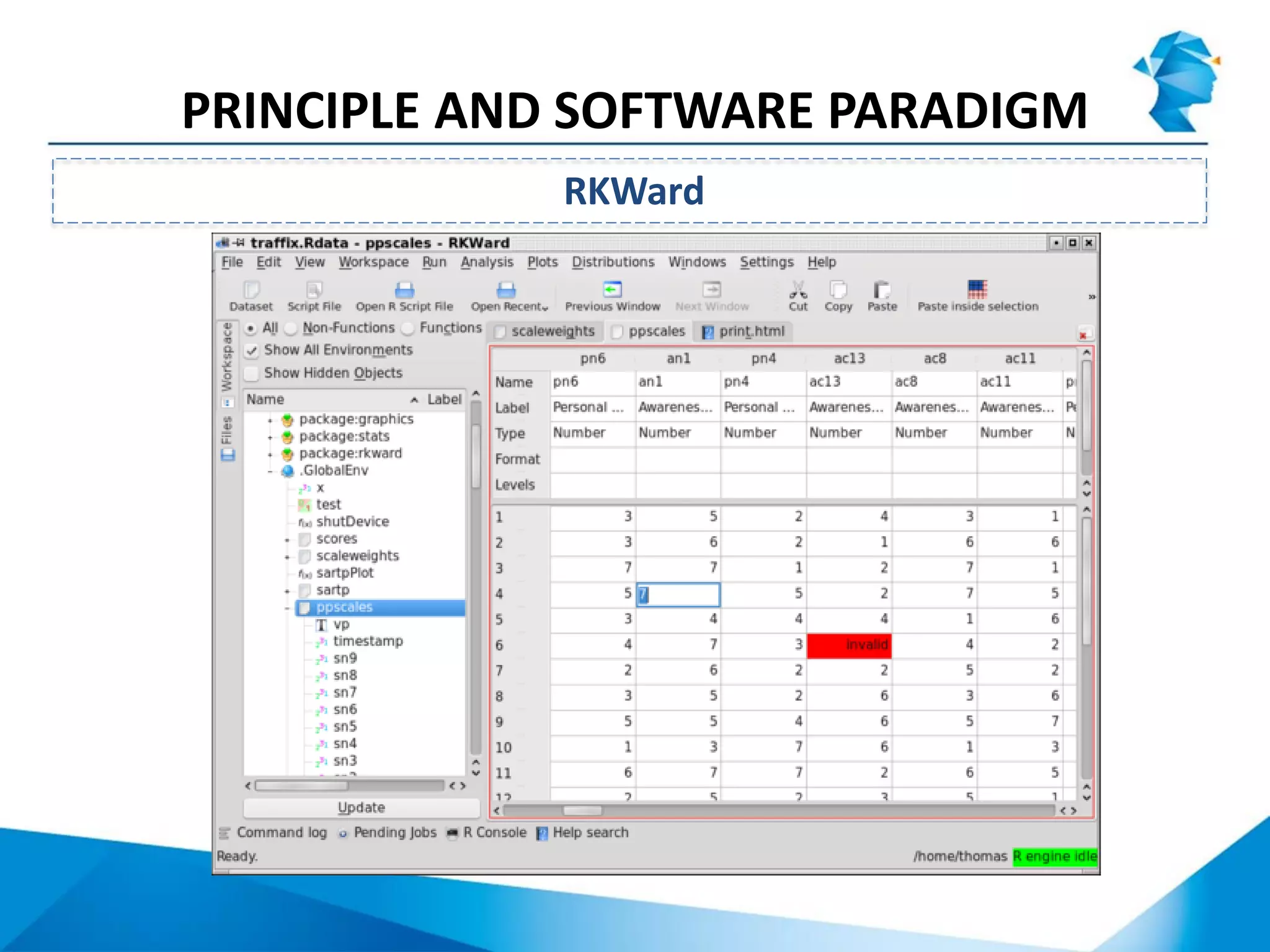
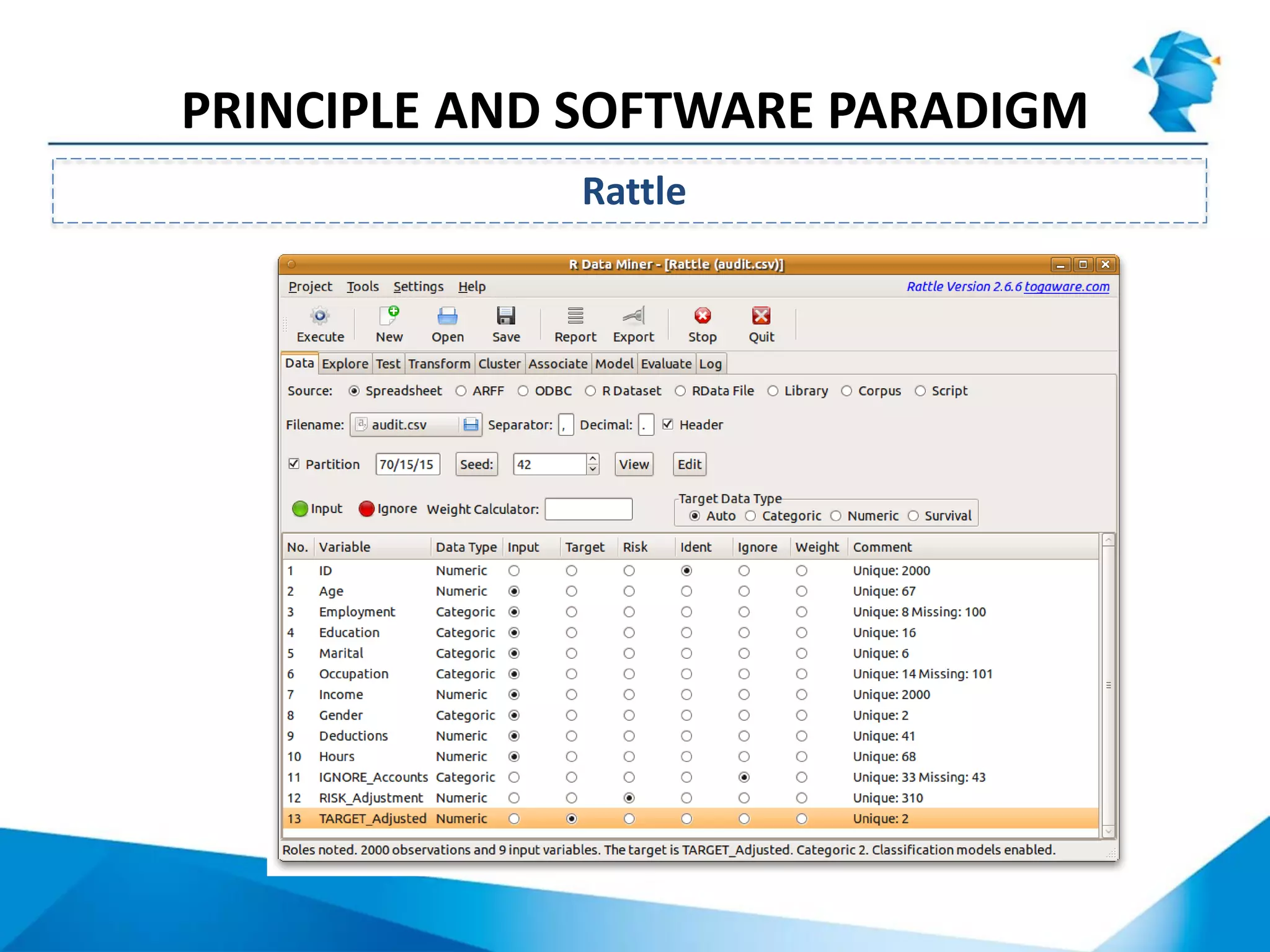
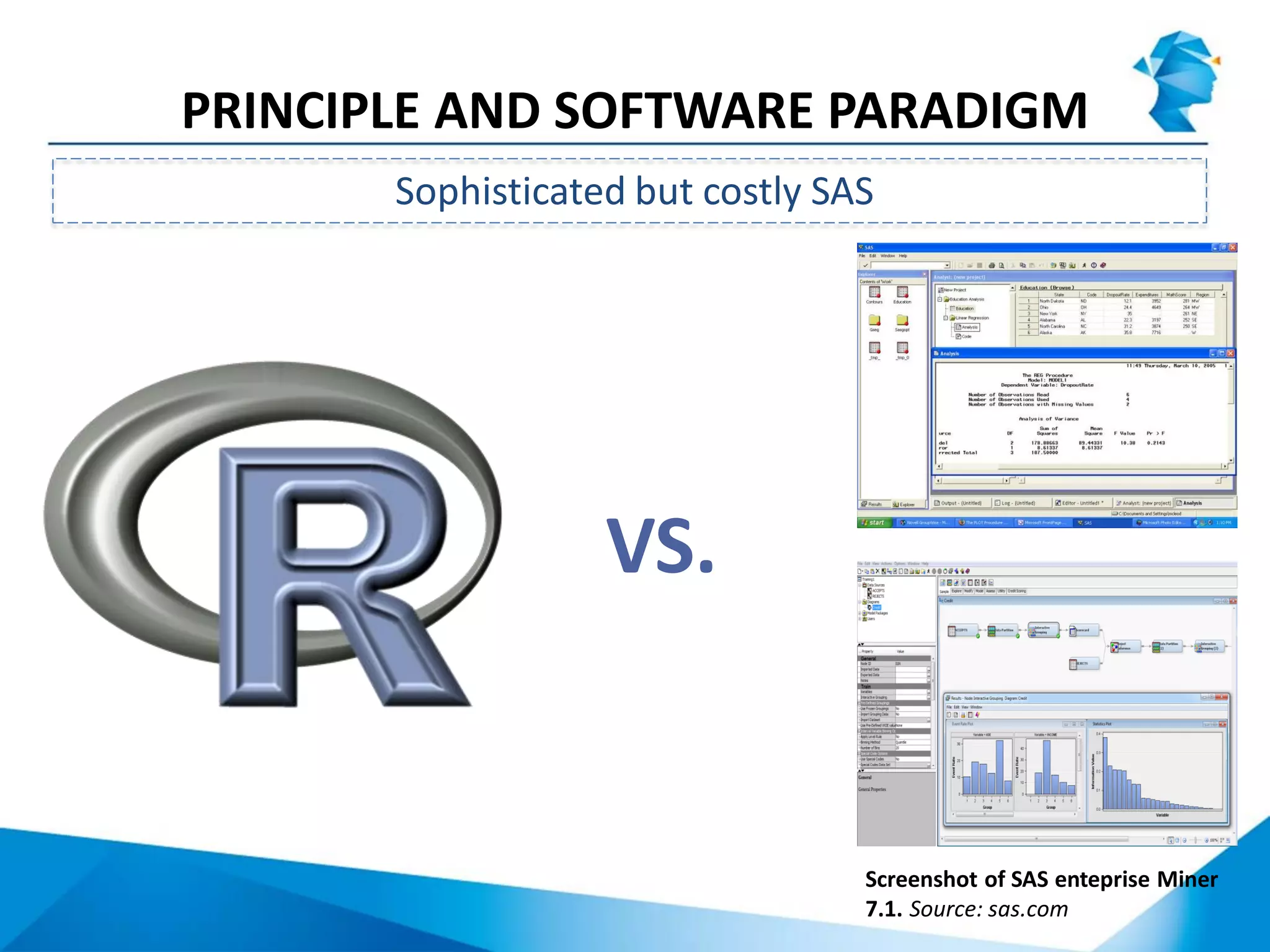
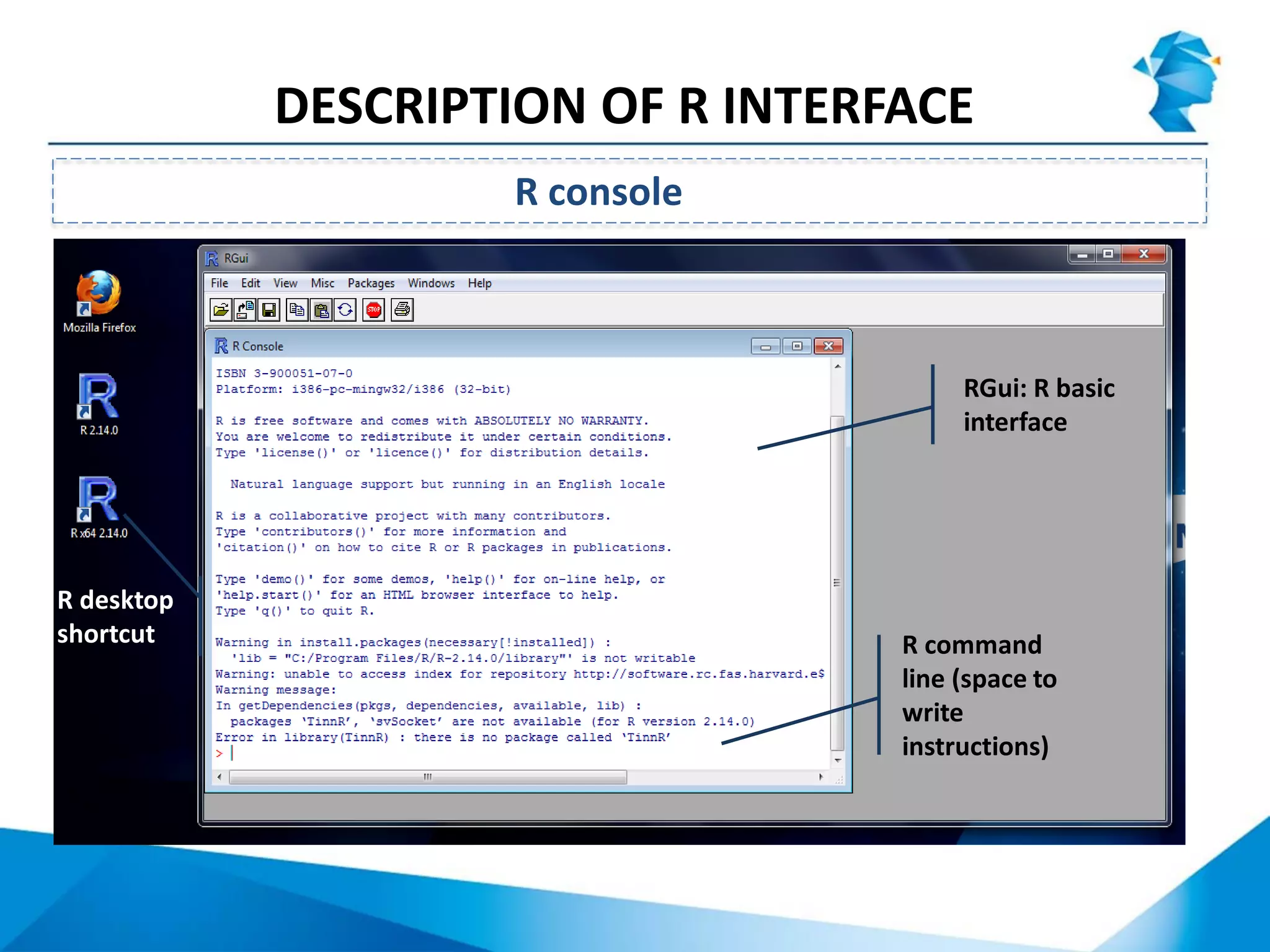
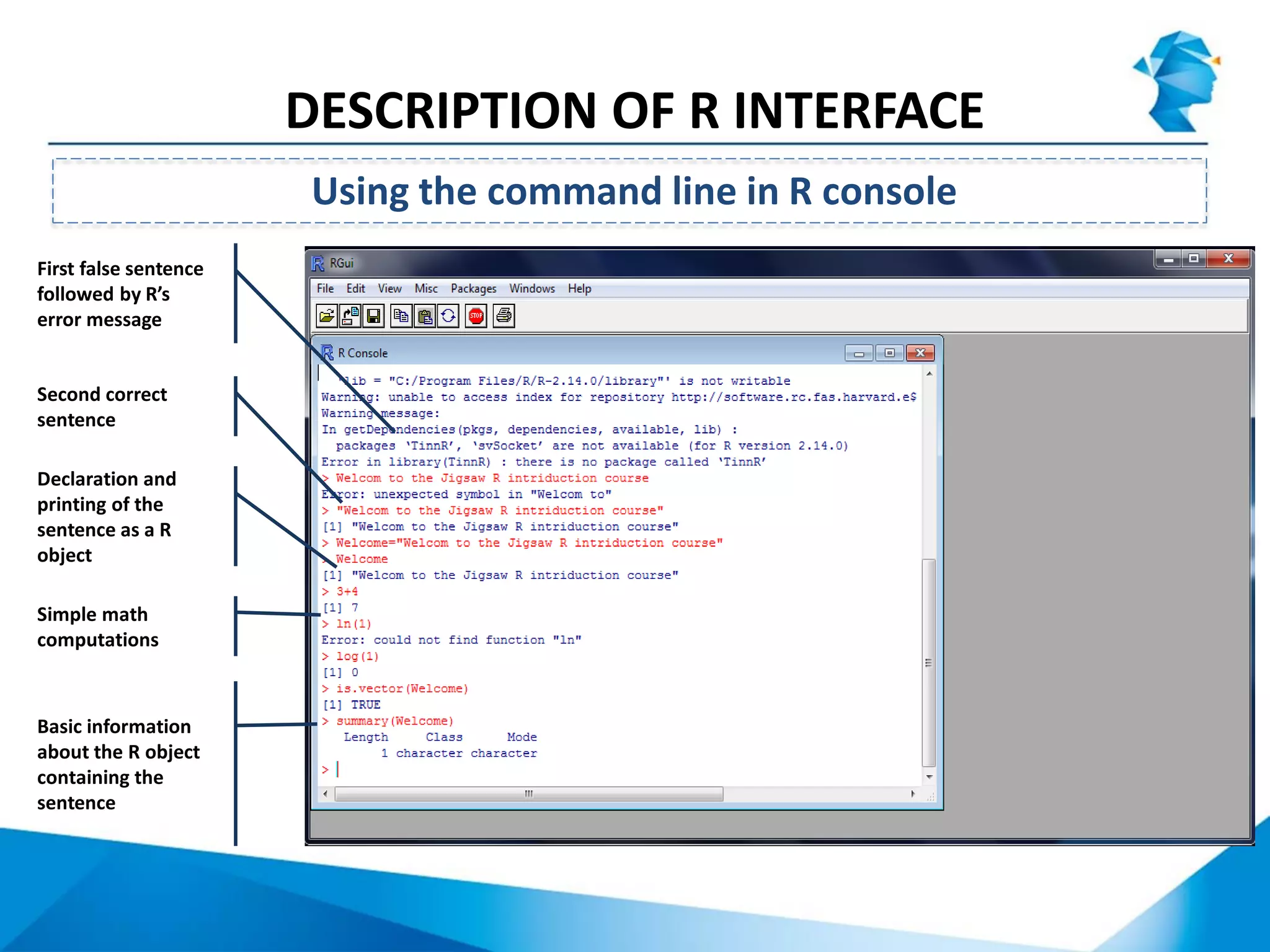
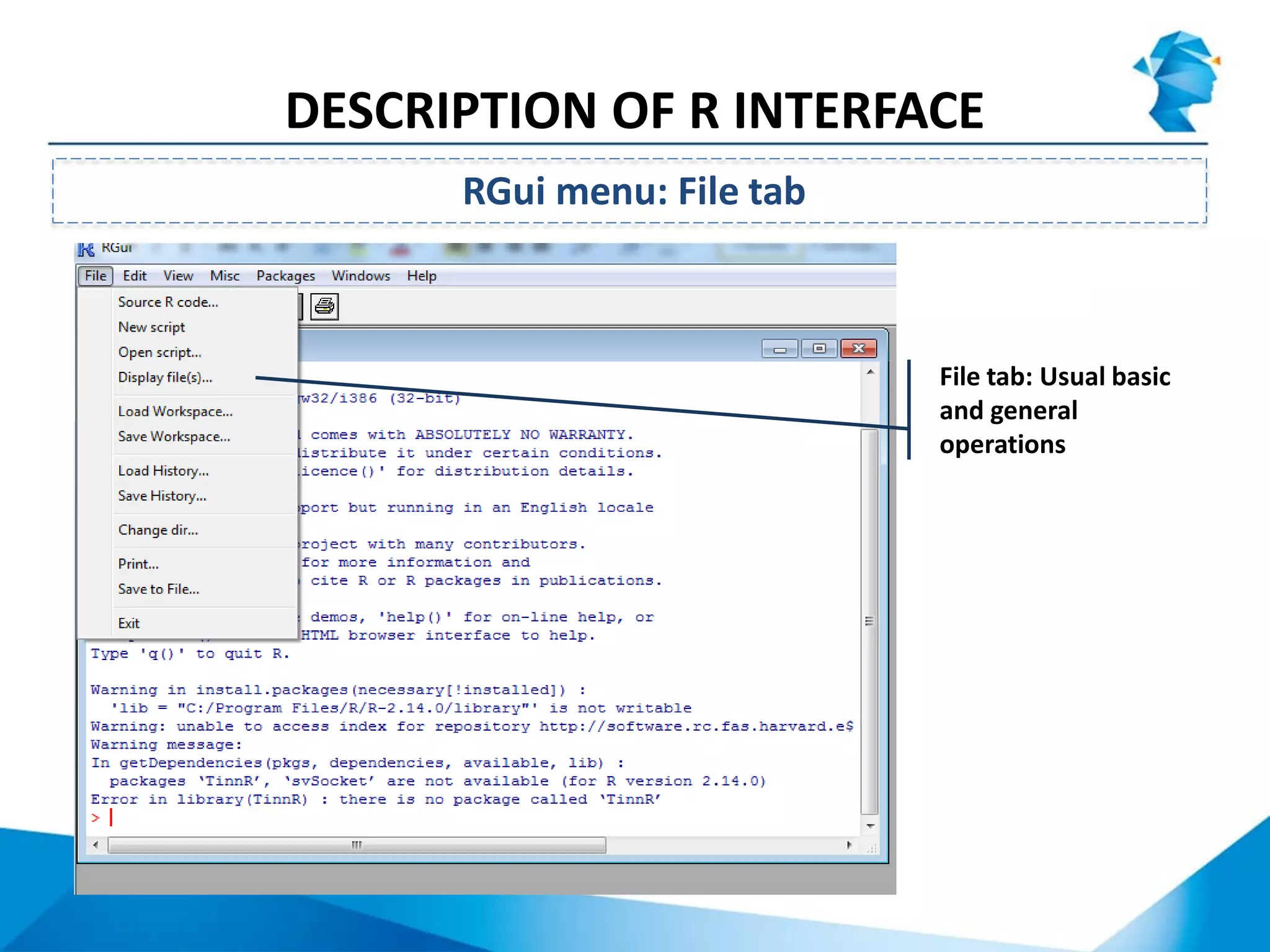
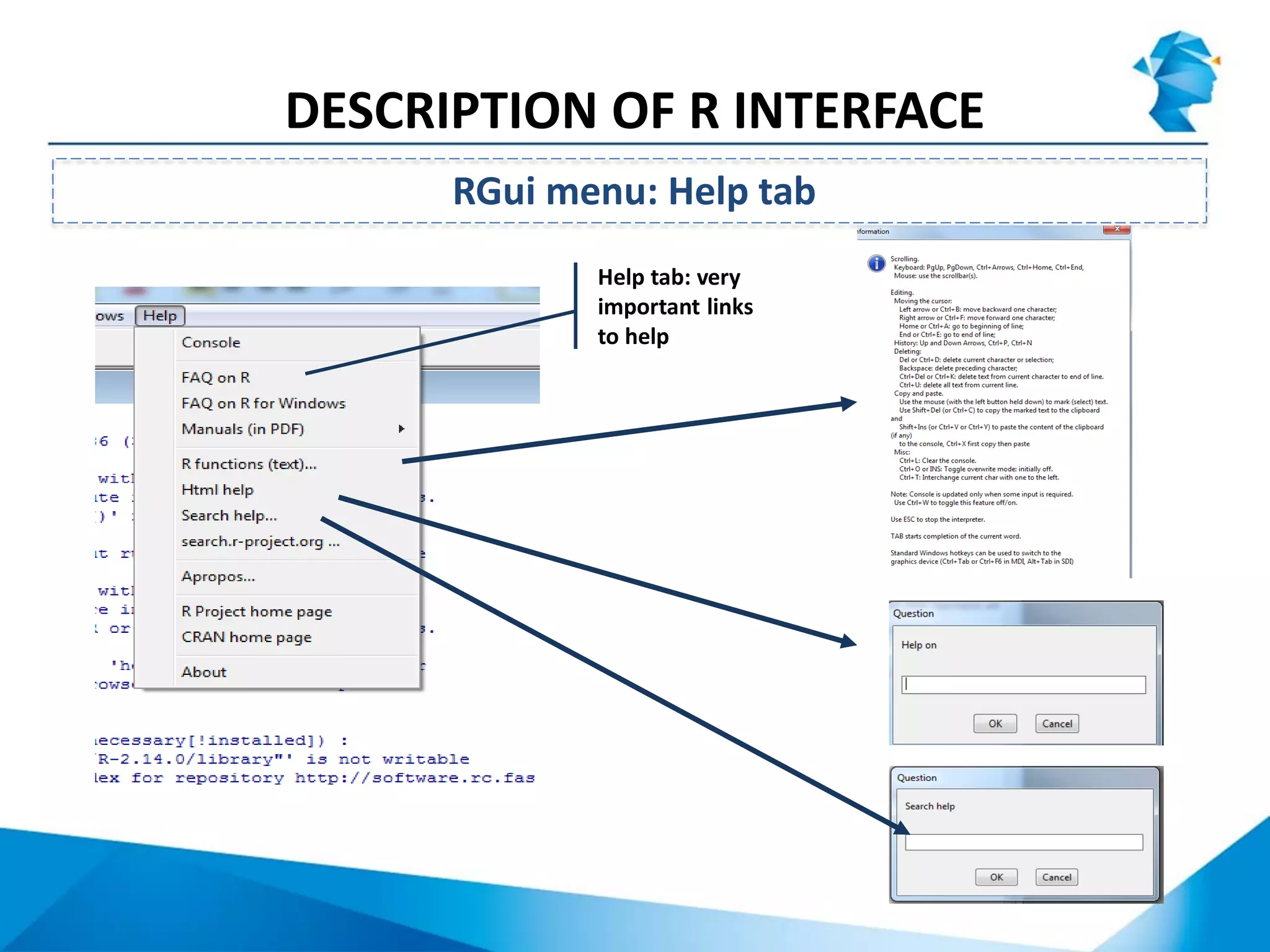
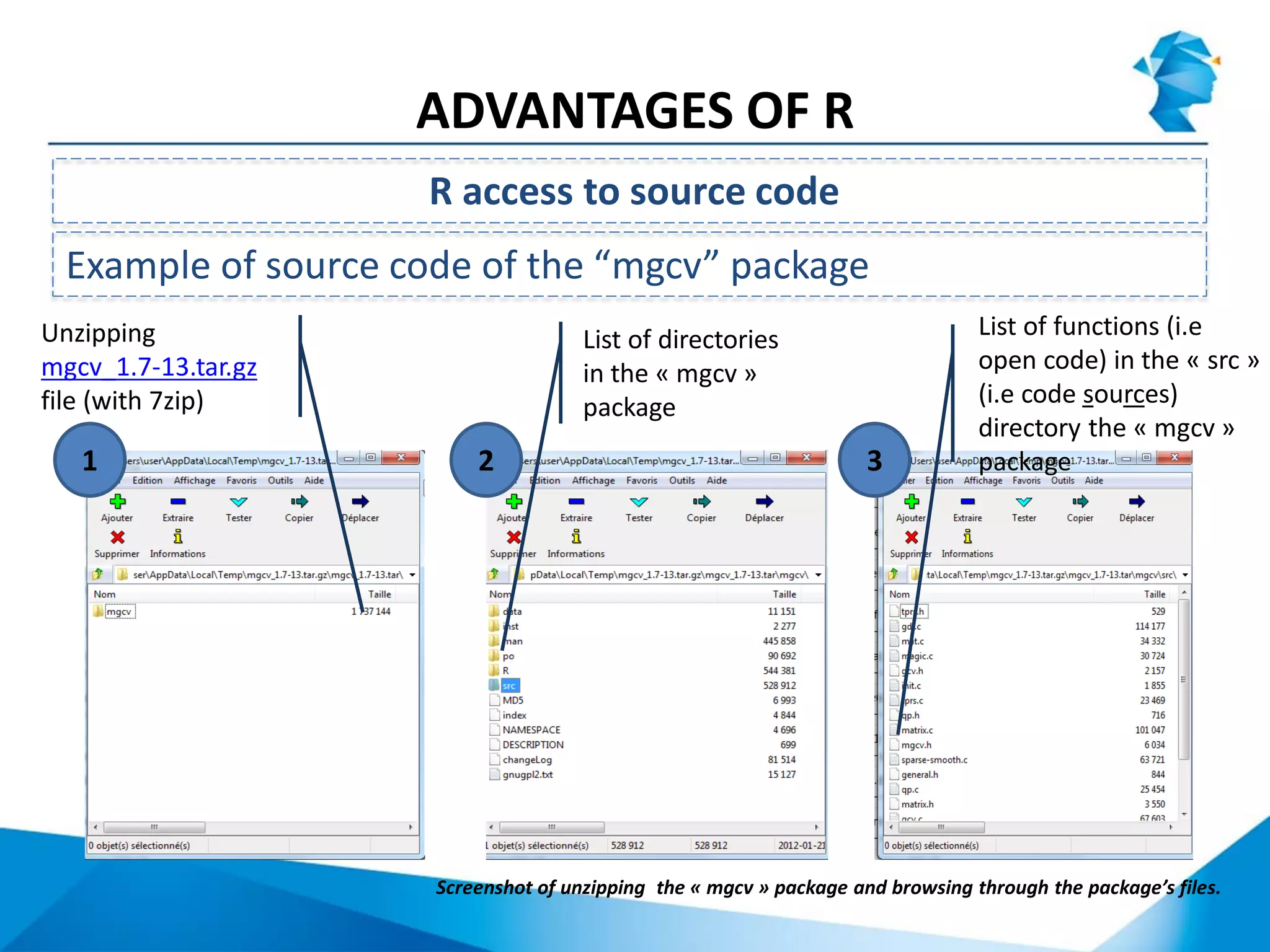
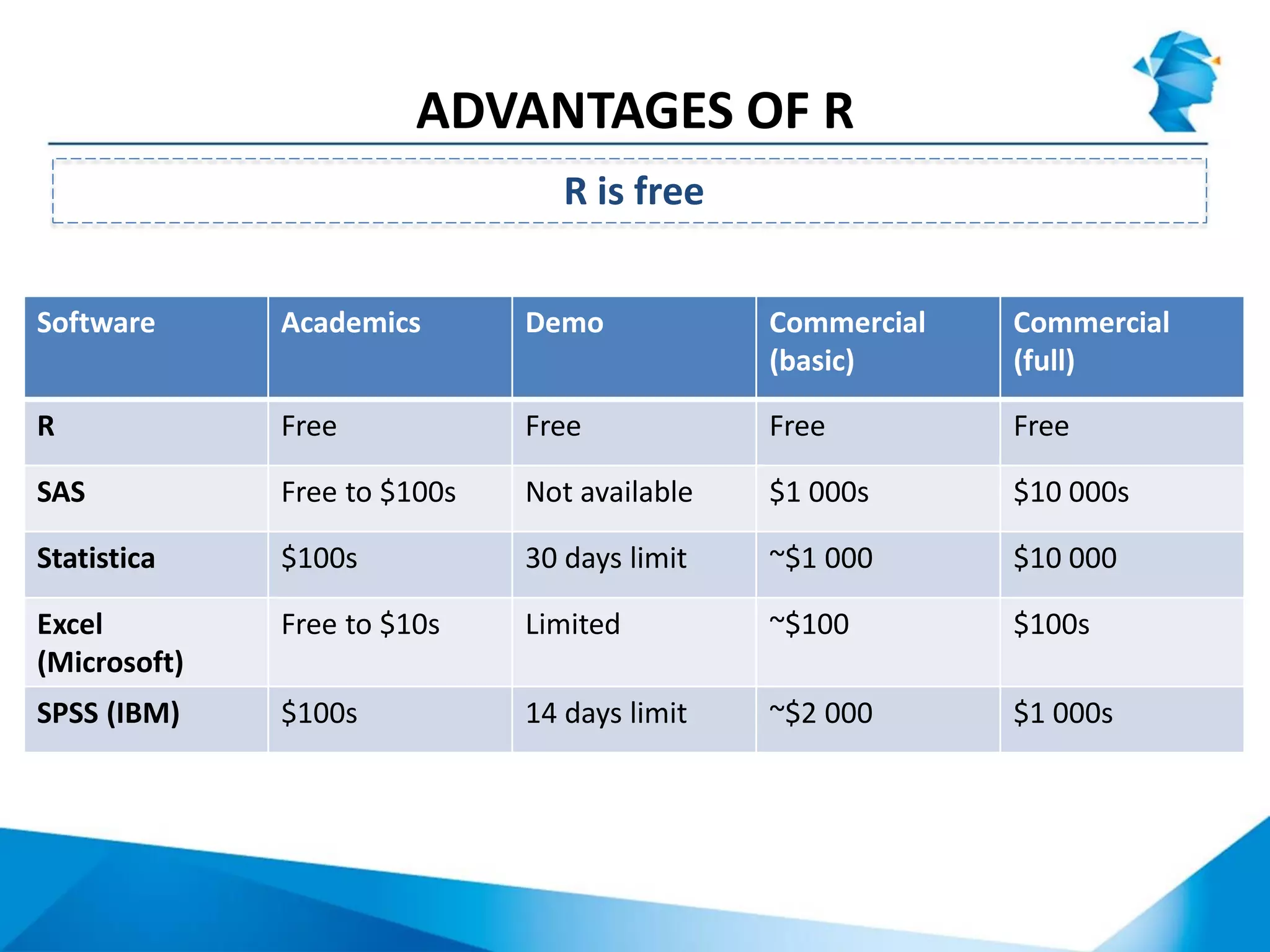
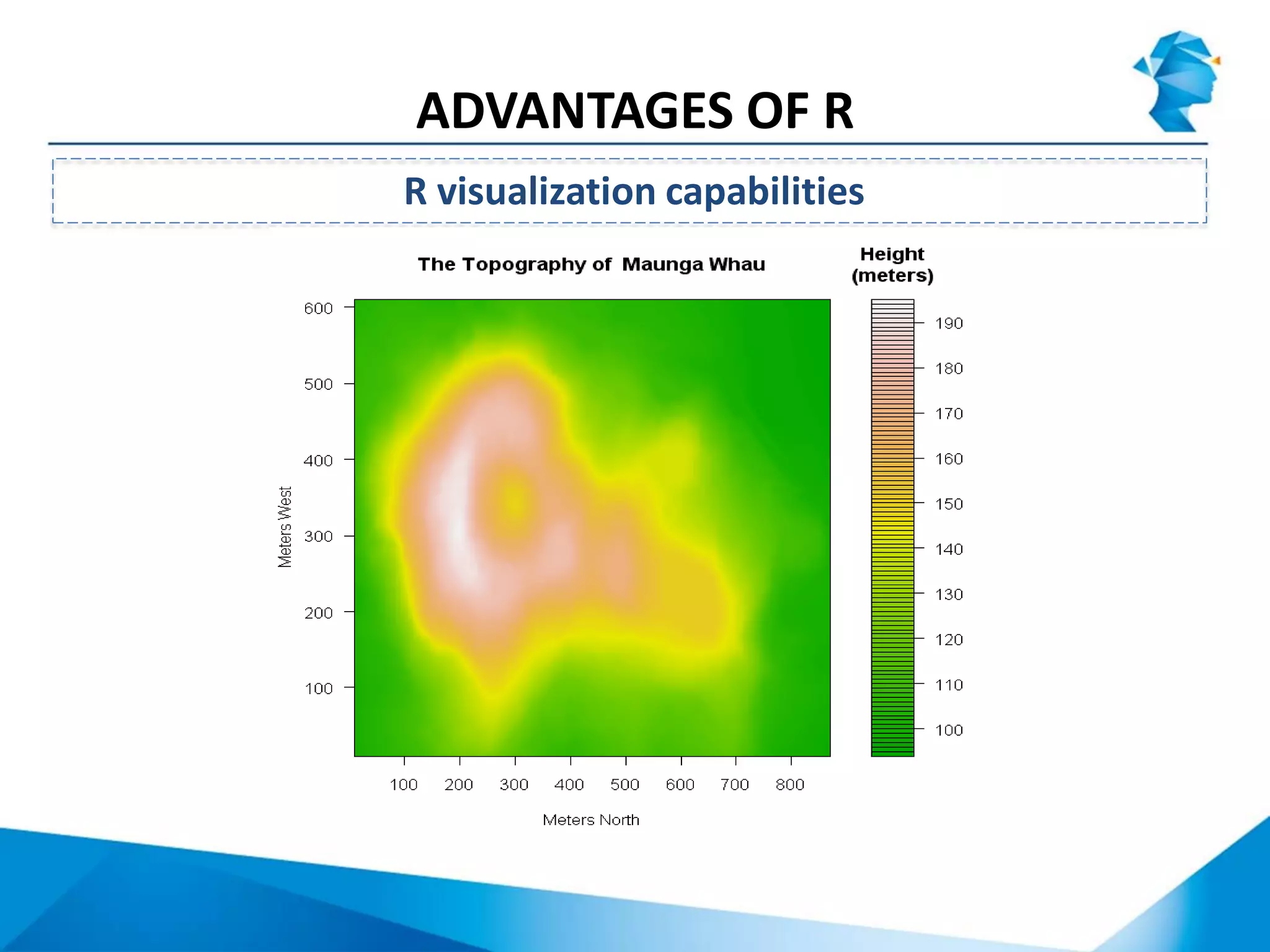
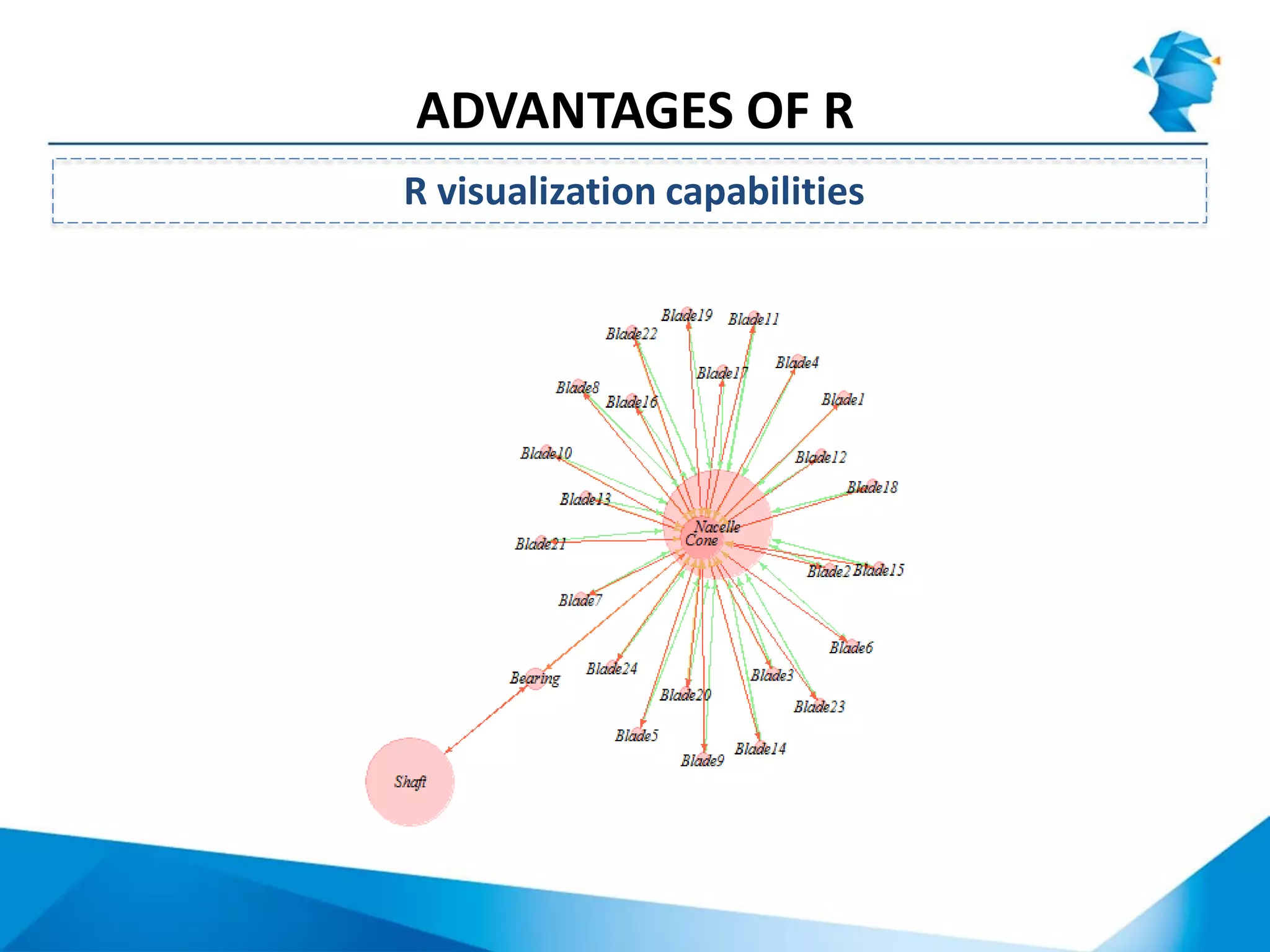
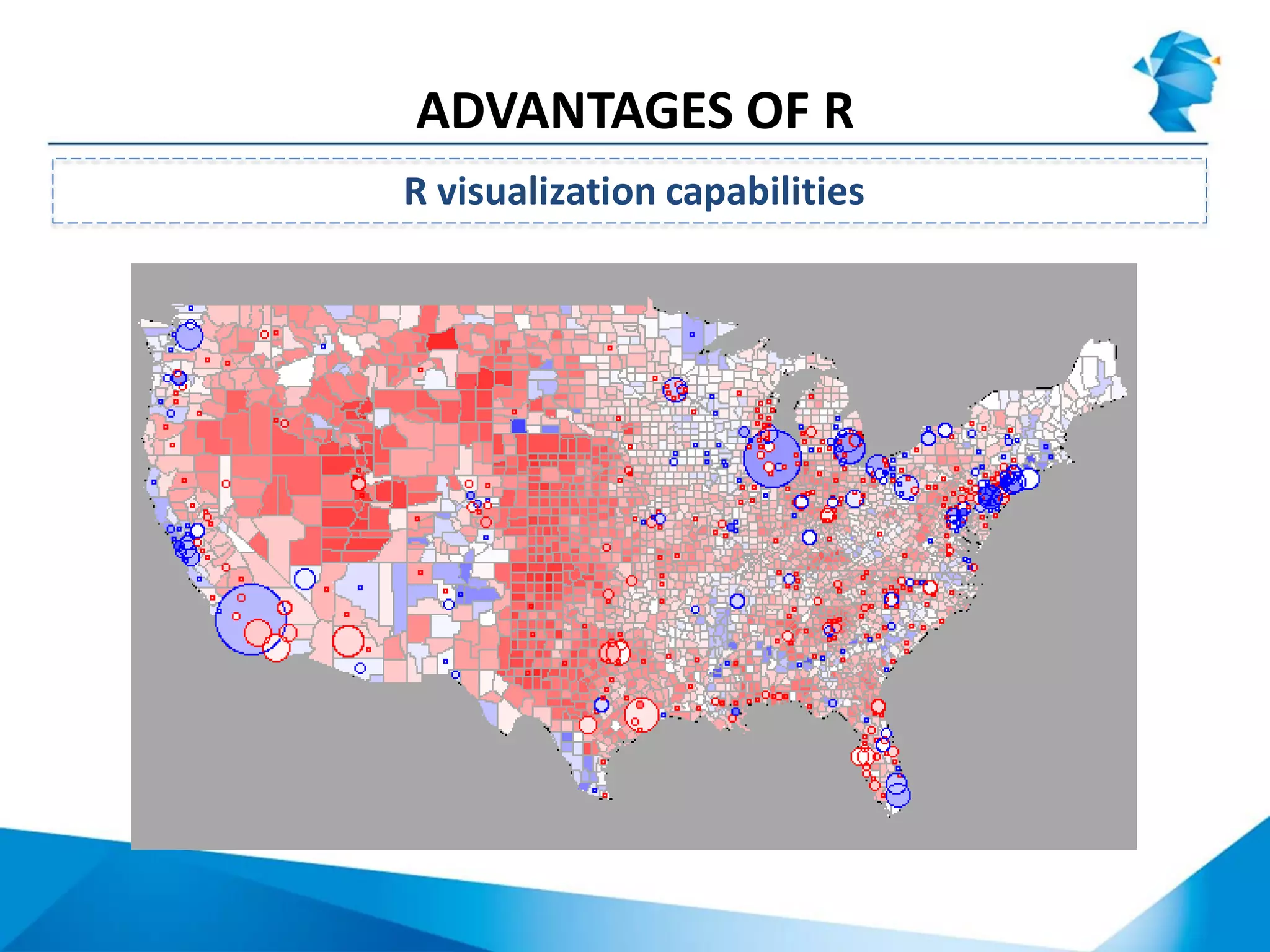
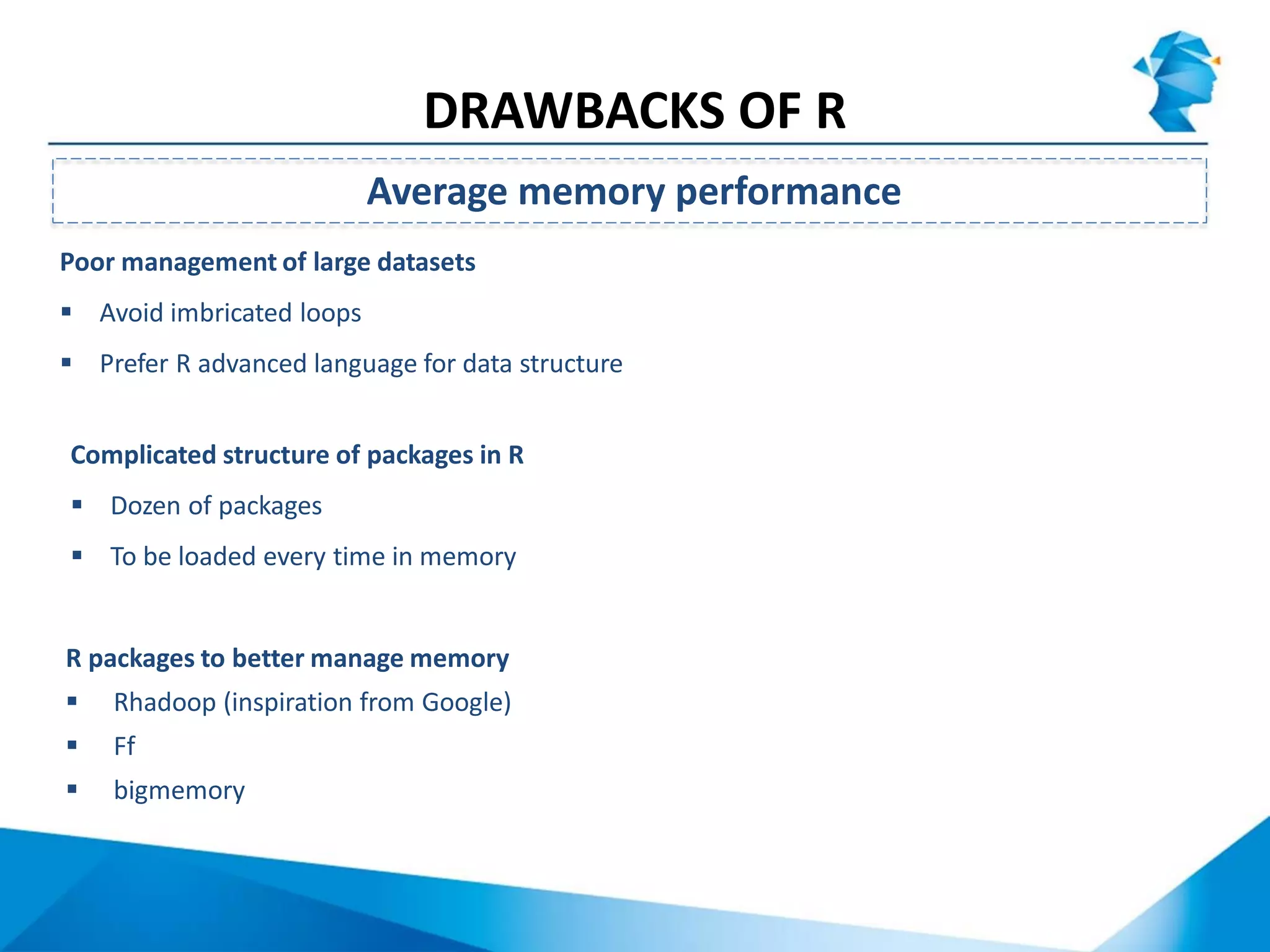
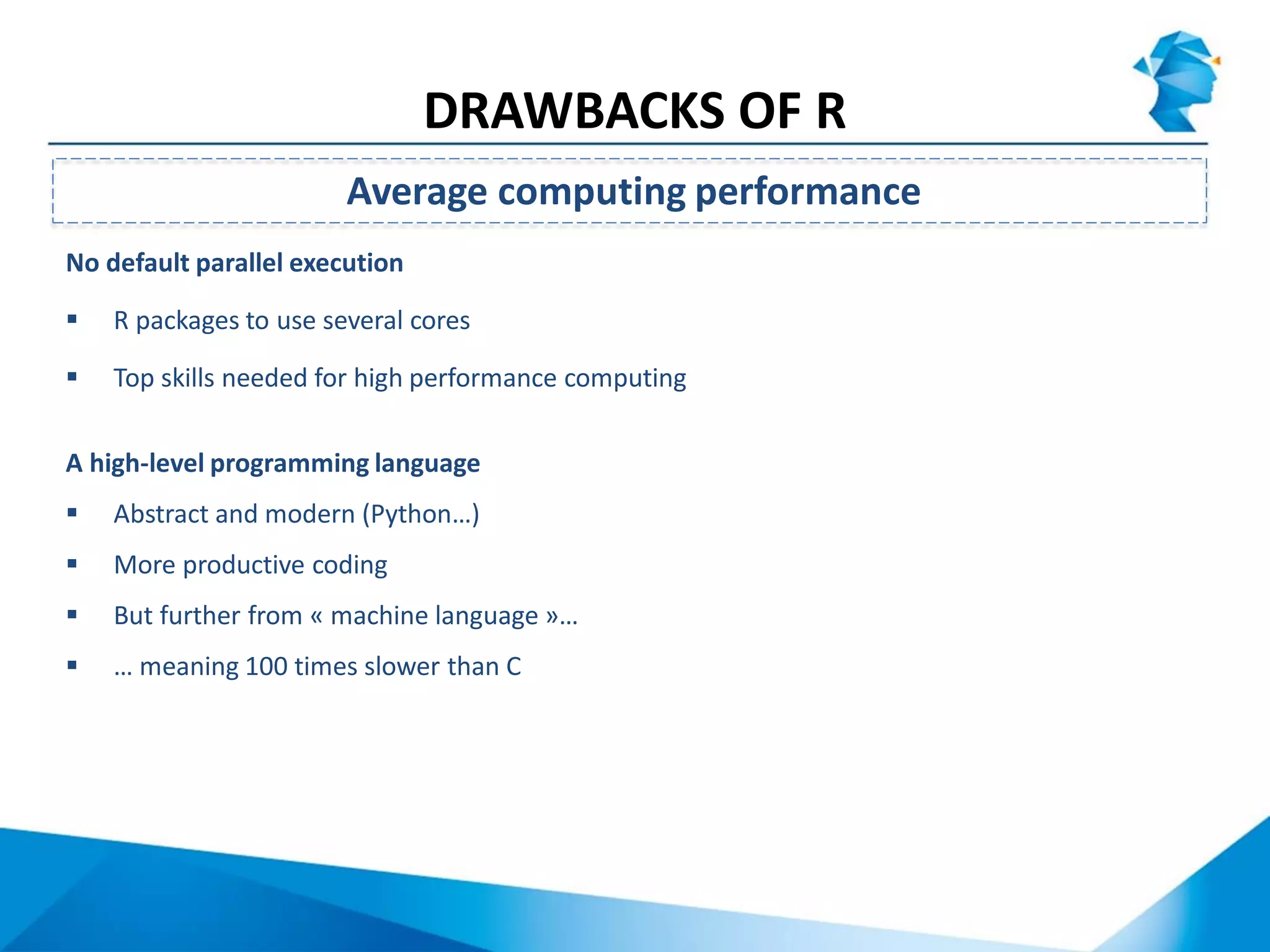
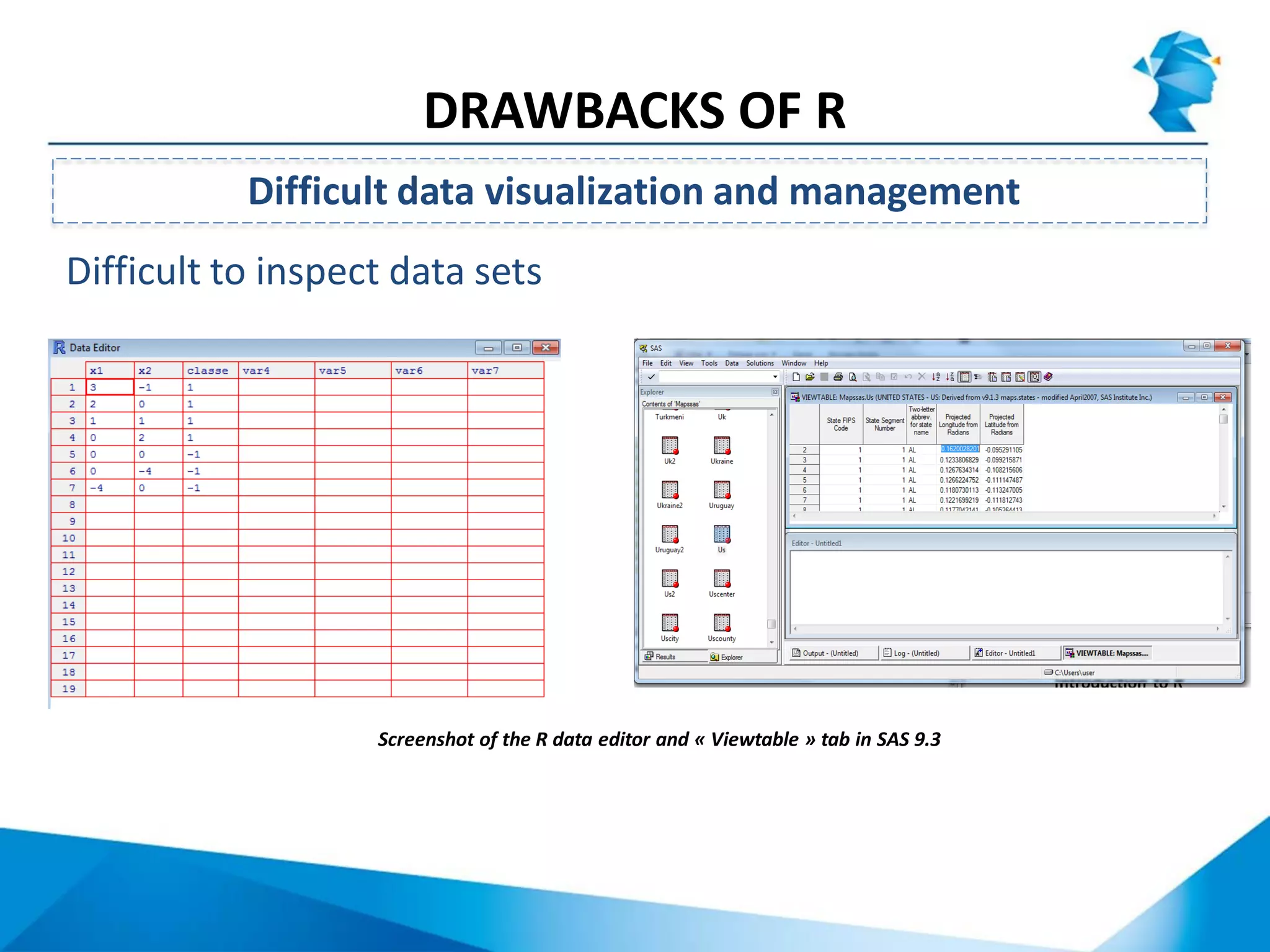
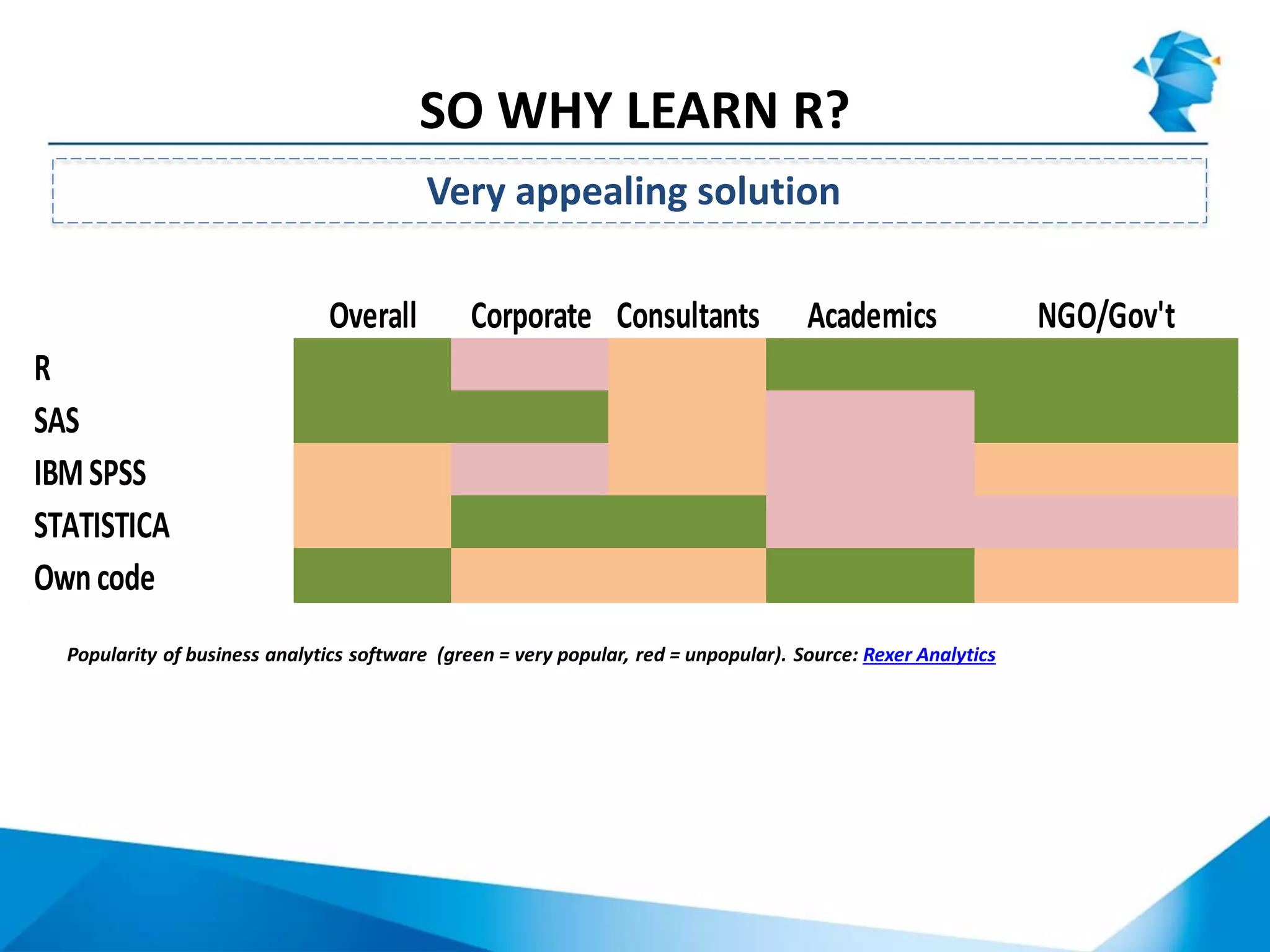
R originated in the 1970s at Bell Labs and has since evolved significantly. It is an open-source programming language used widely for statistical analysis and graphics. While powerful, R has some drawbacks like poor performance for large datasets and a steep learning curve. However, its key advantages including being free, having a large community of users, and extensive libraries have made it a popular tool, especially for academic research.