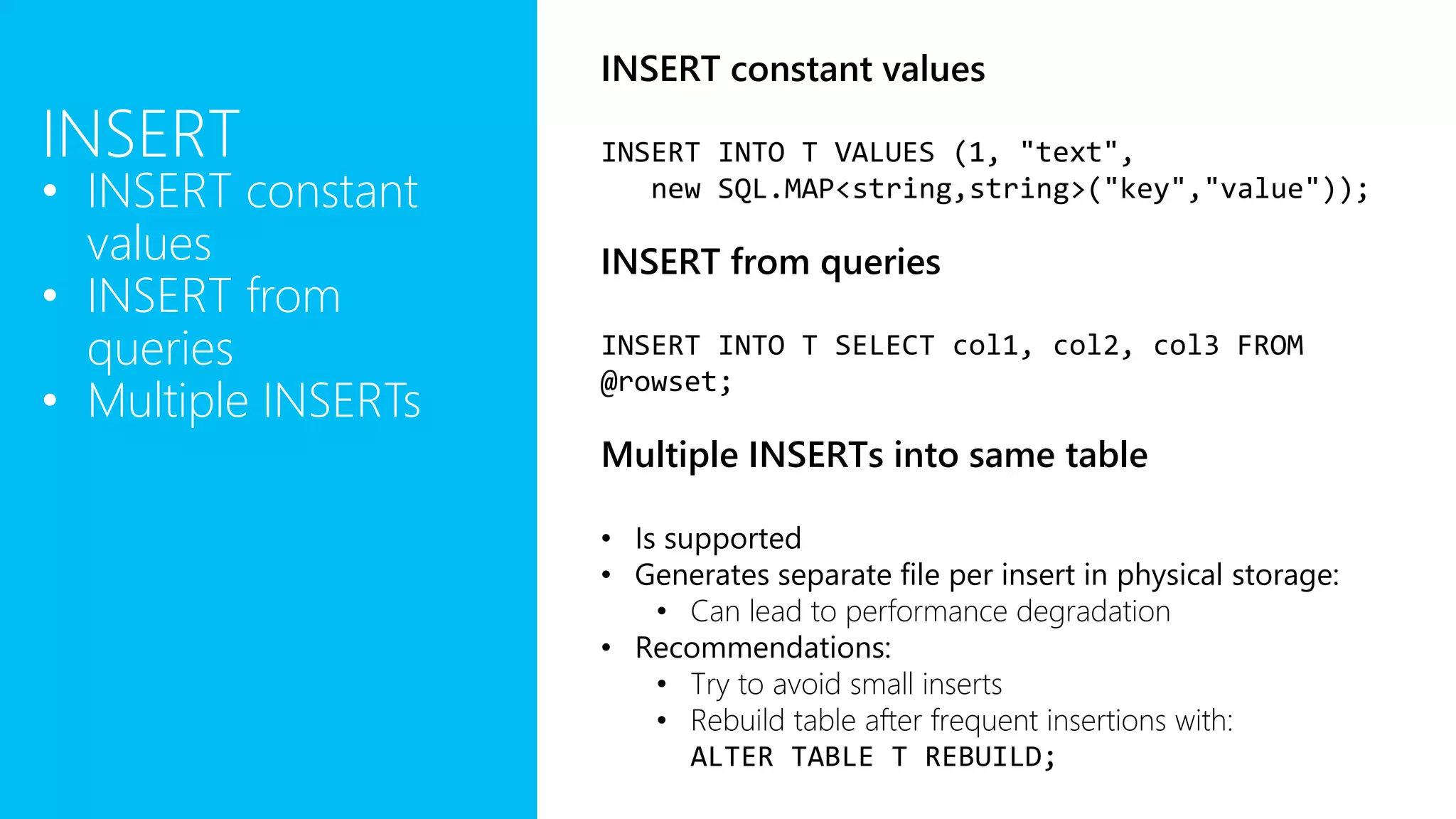
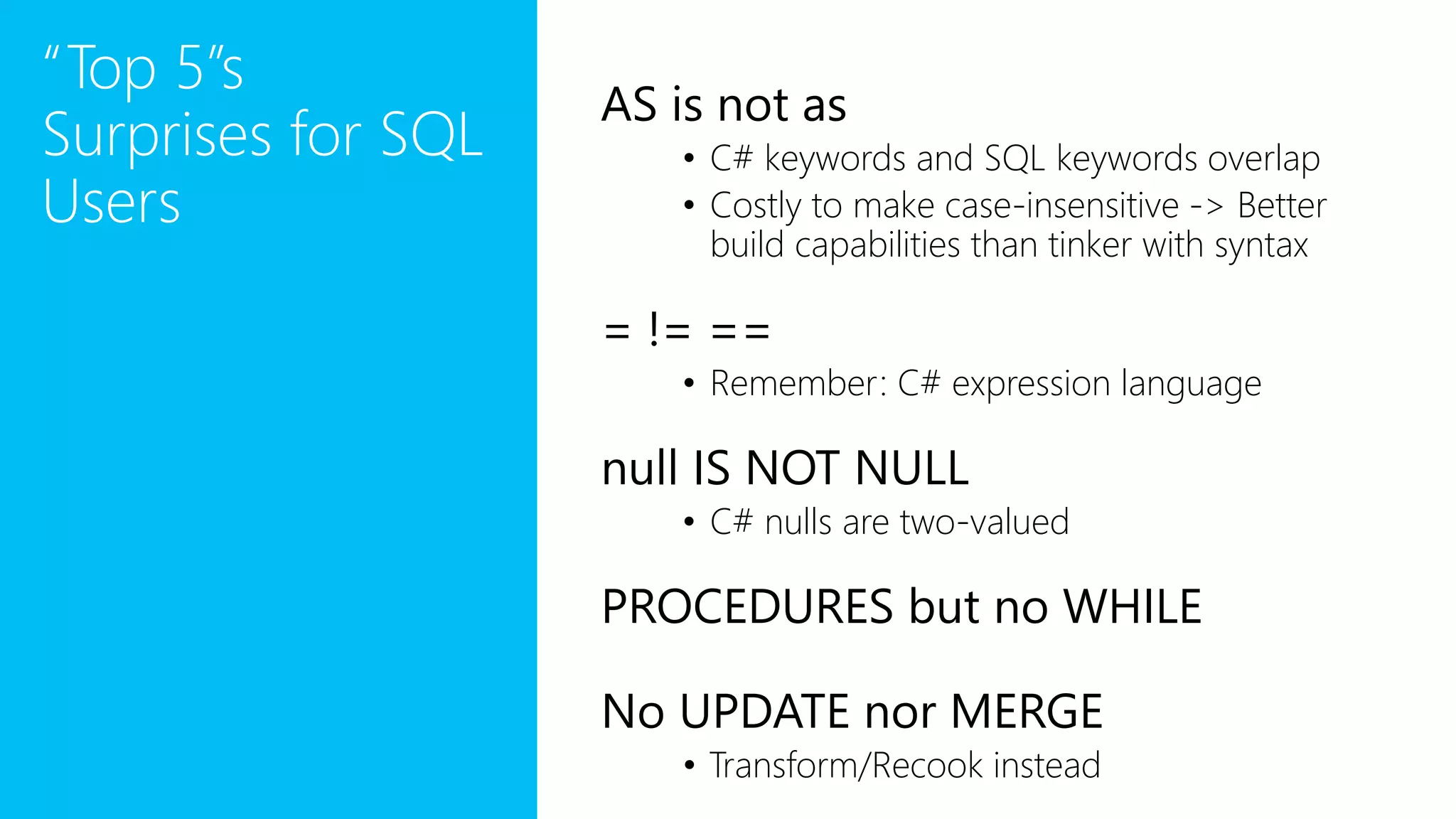
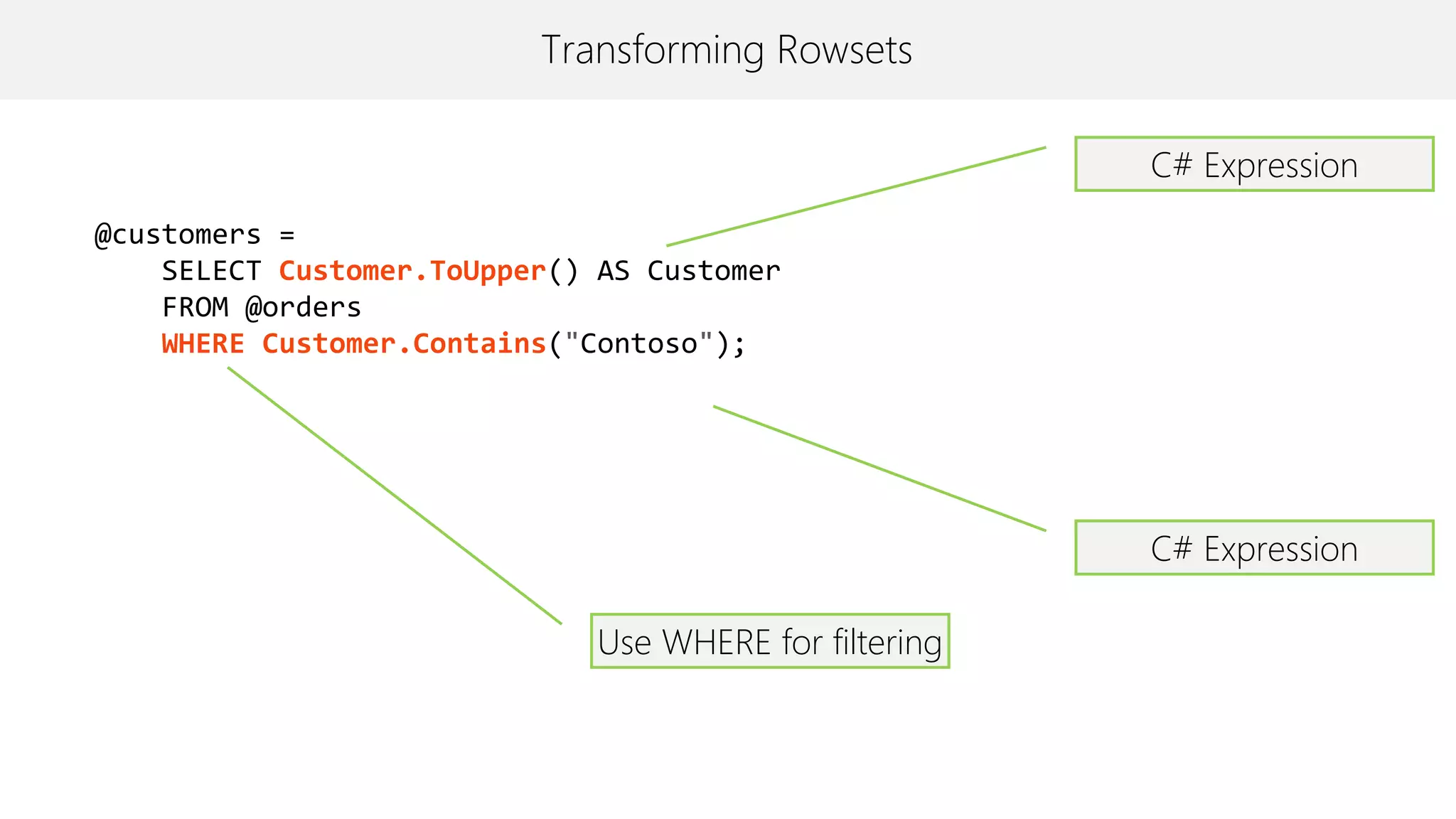
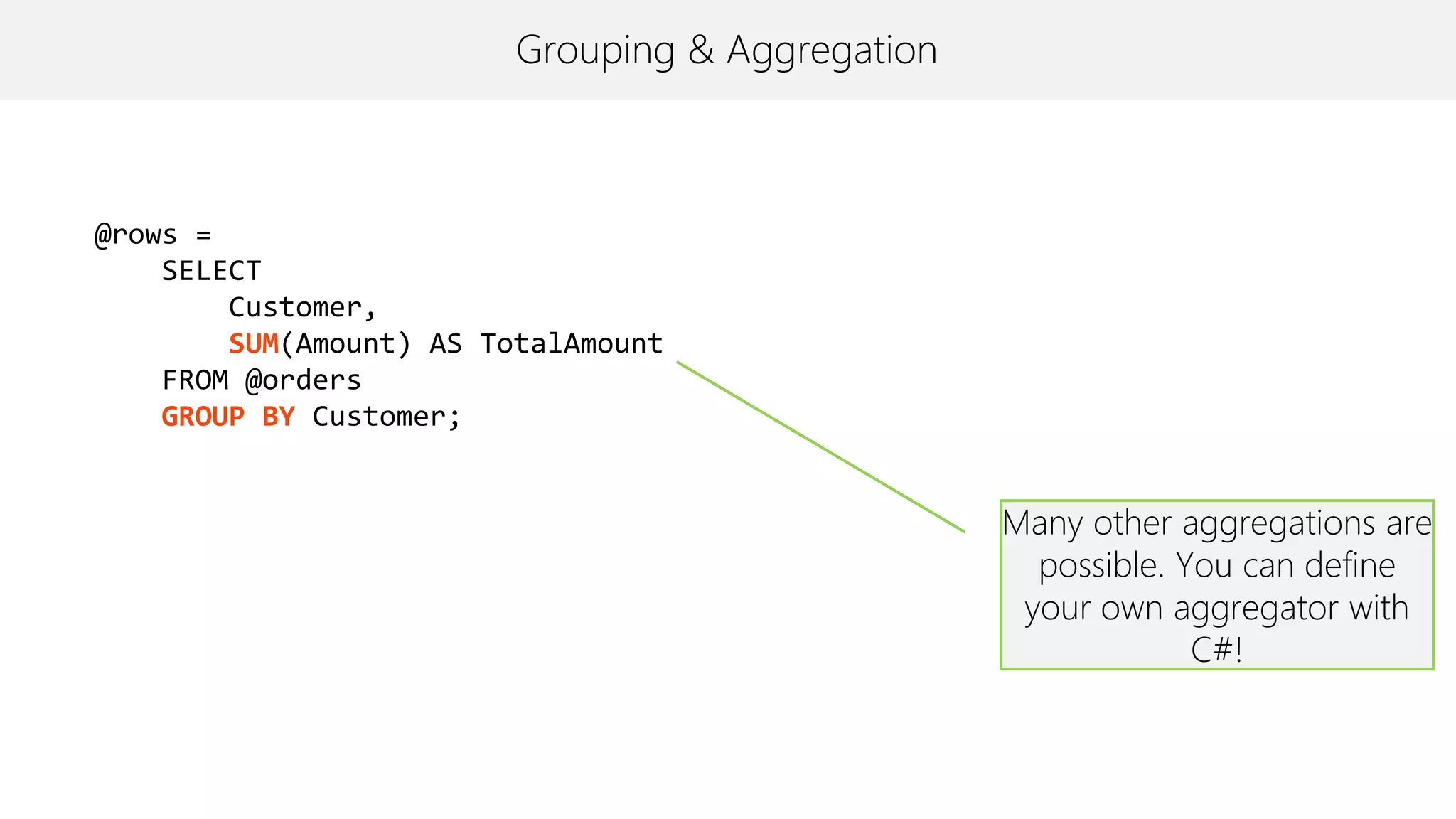
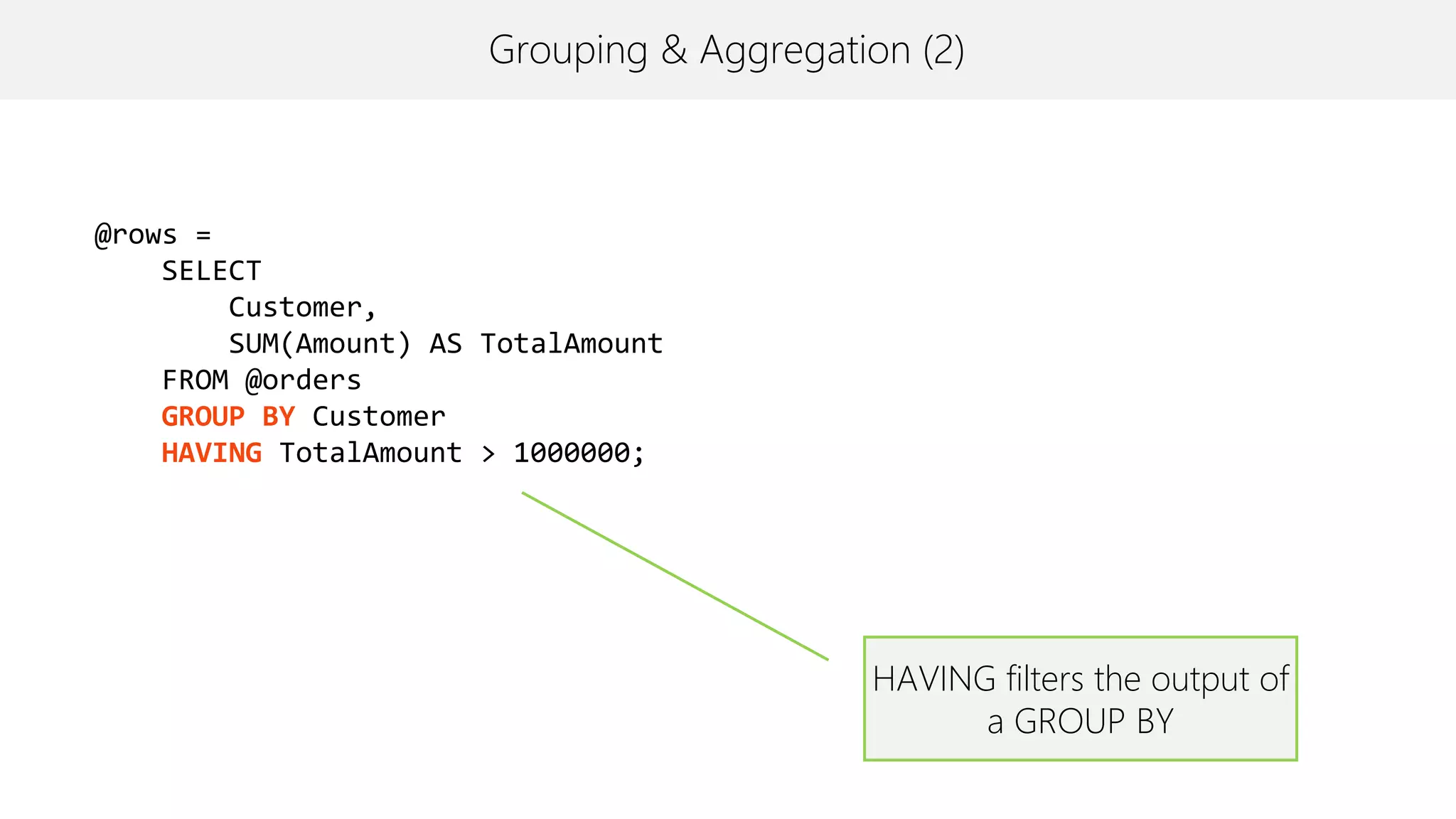
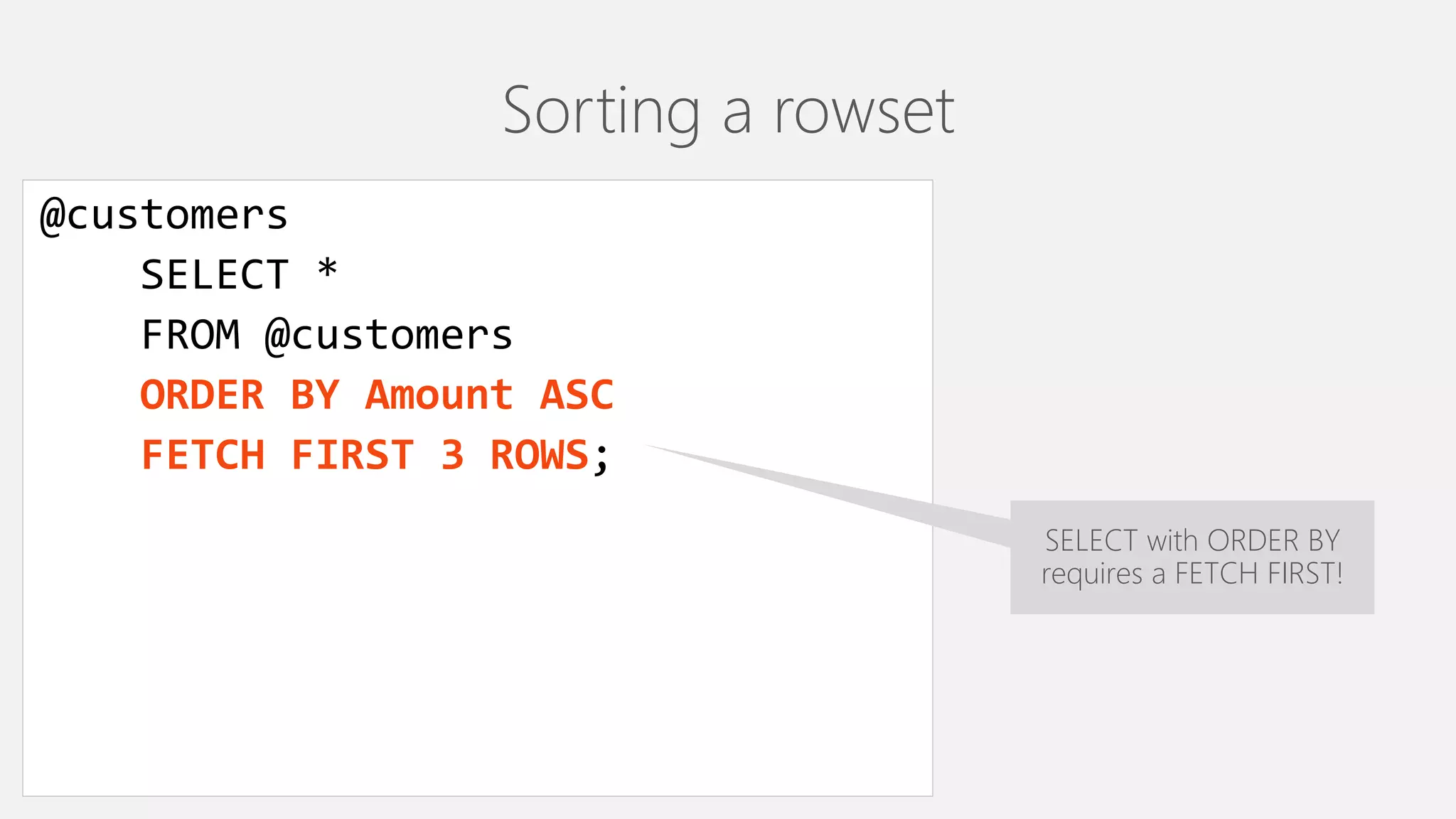
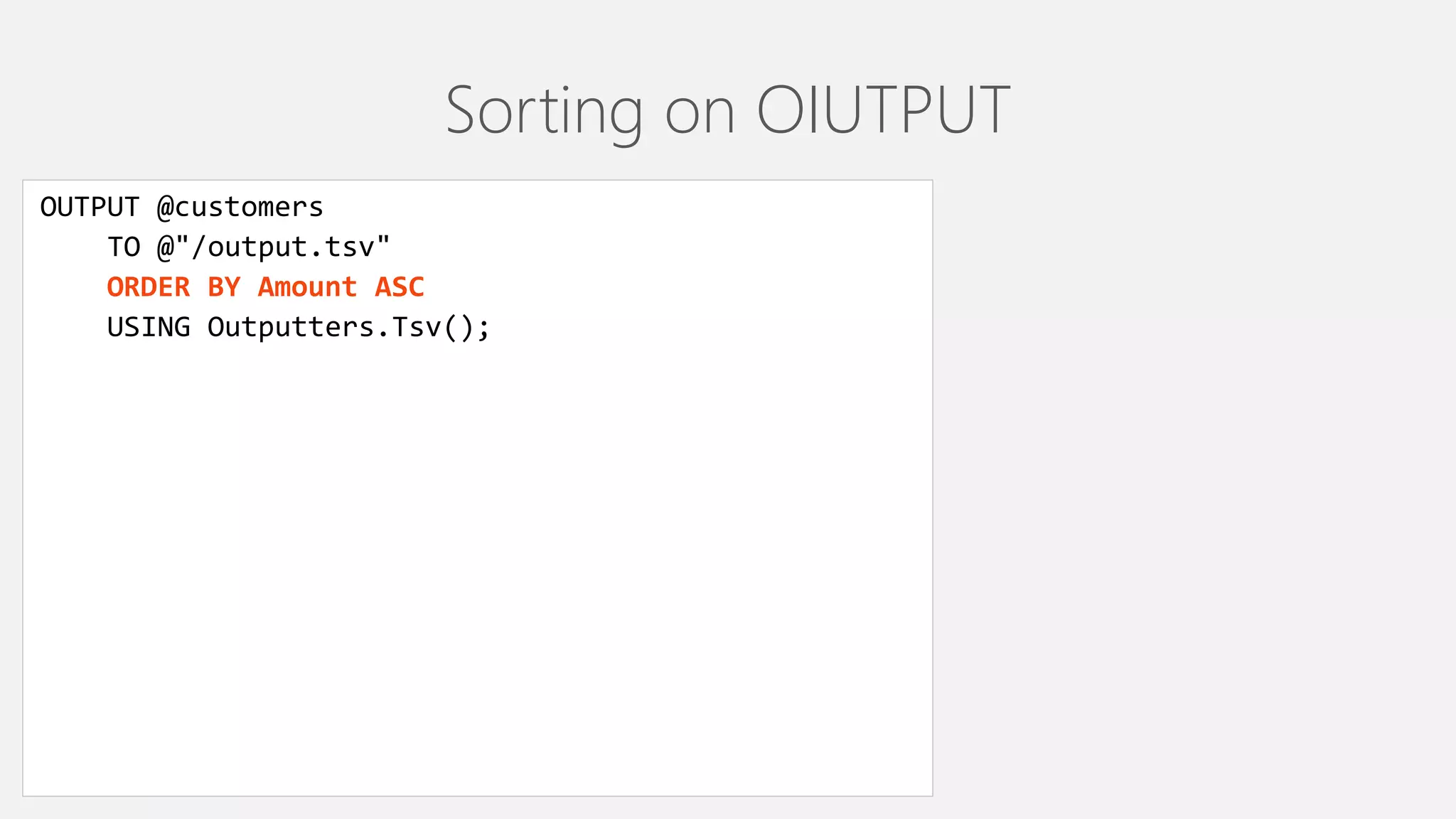
The document provides an overview of U-SQL, highlighting some differences from traditional SQL like C# keywords overlapping with SQL keywords, the ability to write C# expressions for data transformations, and supporting windowing functions, joins, and analytics capabilities. It also briefly covers topics like sorting, constant rowsets, inserts, and additional resources for learning more about U-SQL.




![U-SQL Analytics Windowing Expression Window_Function_Call 'OVER' '(' [ Over_Partition_By_Clause ] [ Order_By_Clause ] [ Row _Clause ] ')'. Window_Function_Call := Aggregate_Function_Call | Analytic_Function_Call | Ranking_Function_Call. Windowing Aggregate Functions ANY_VALUE, AVG, COUNT, MAX, MIN, SUM, STDEV, STDEVP, VAR, VARP Analytics Functions CUME_DIST, FIRST_VALUE, LAST_VALUE, PERCENTILE_CONT, PERCENTILE_DISC, PERCENT_RANK; soon: LEAD/LAG Ranking Functions DENSE_RANK, NTILE, RANK, ROW_NUMBER](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-sqlbits-usqlsql-160505125908/75/U-SQL-Does-SQL-SQLBits-2016-12-2048.jpg)