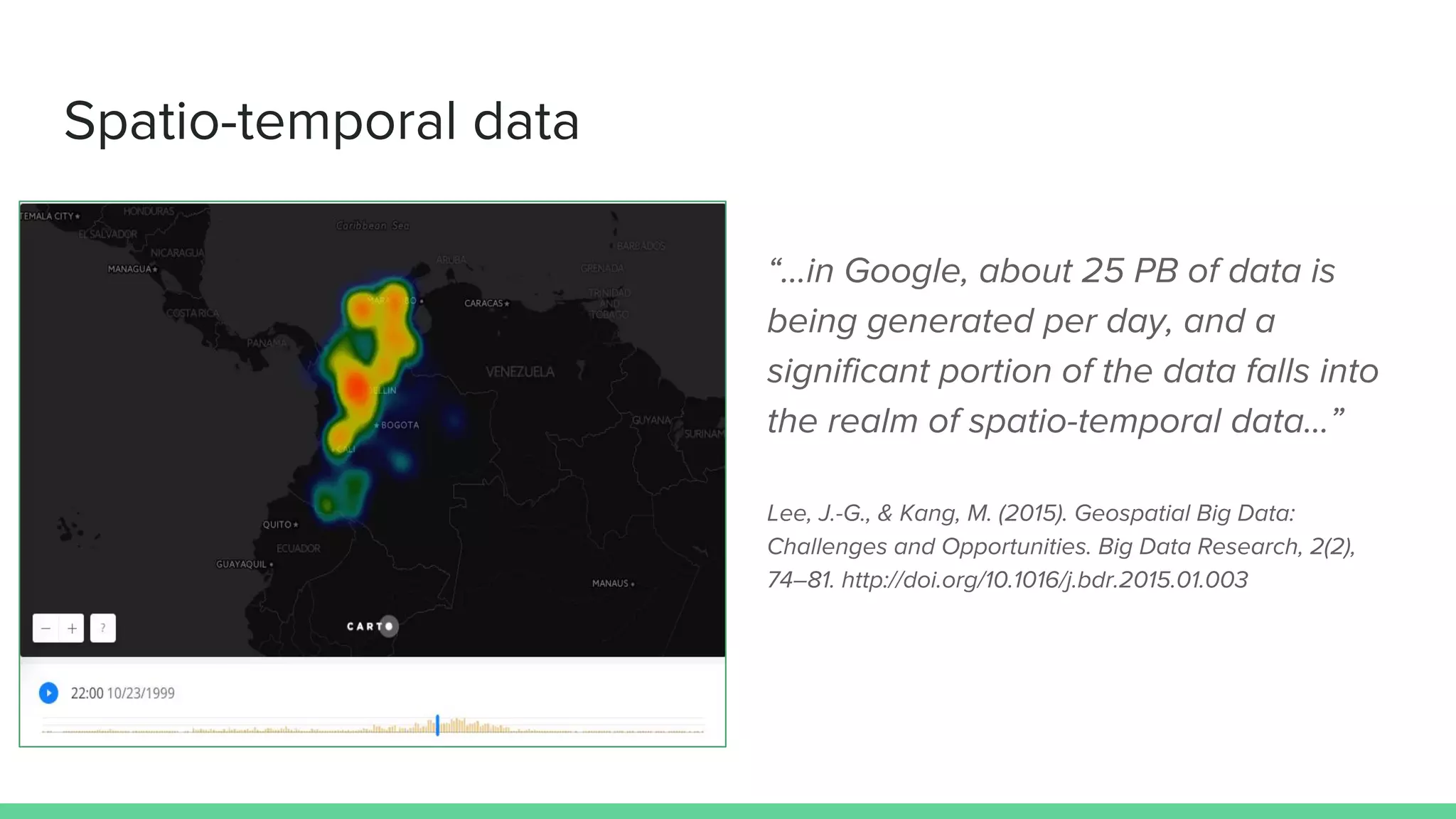
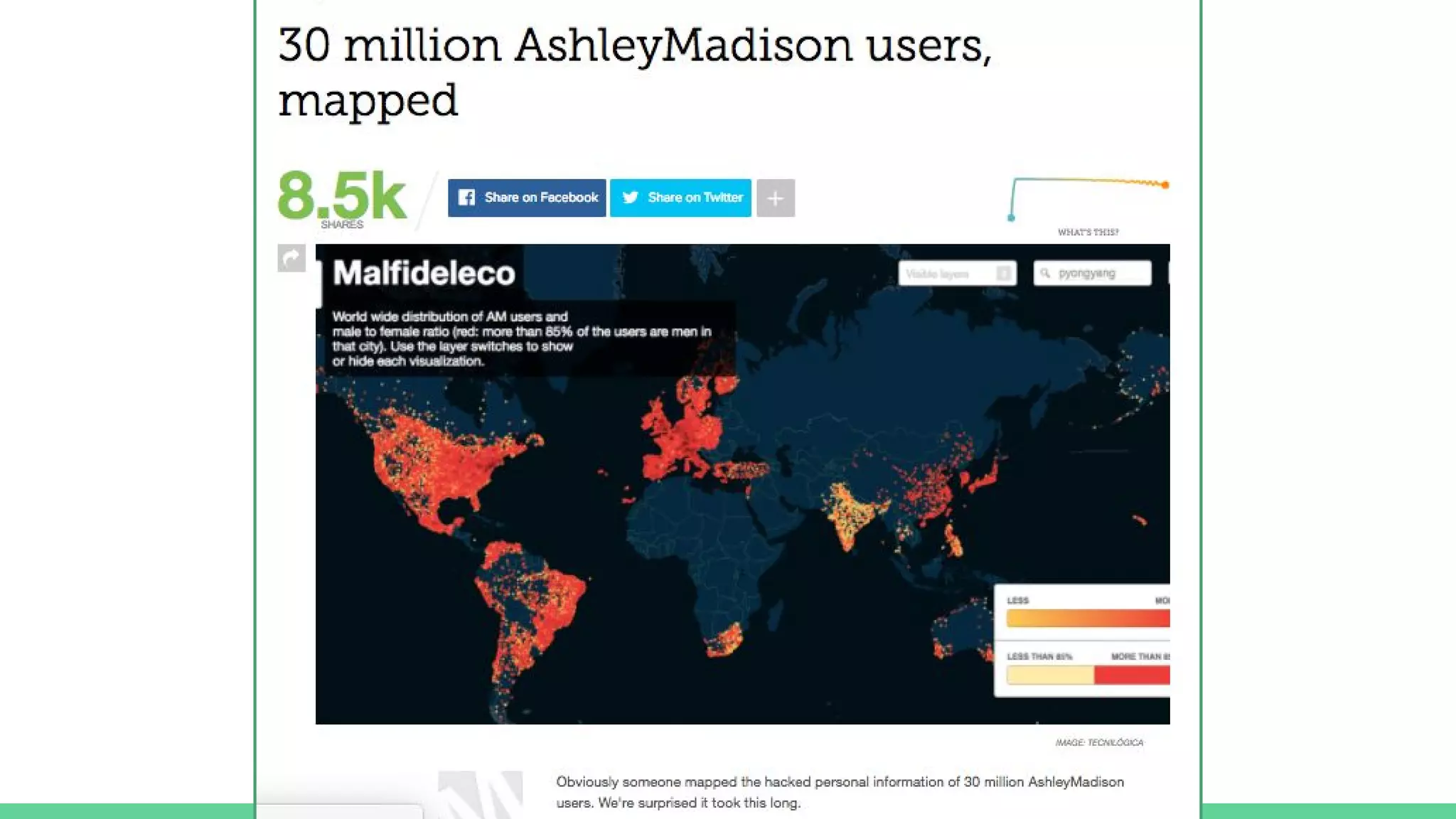
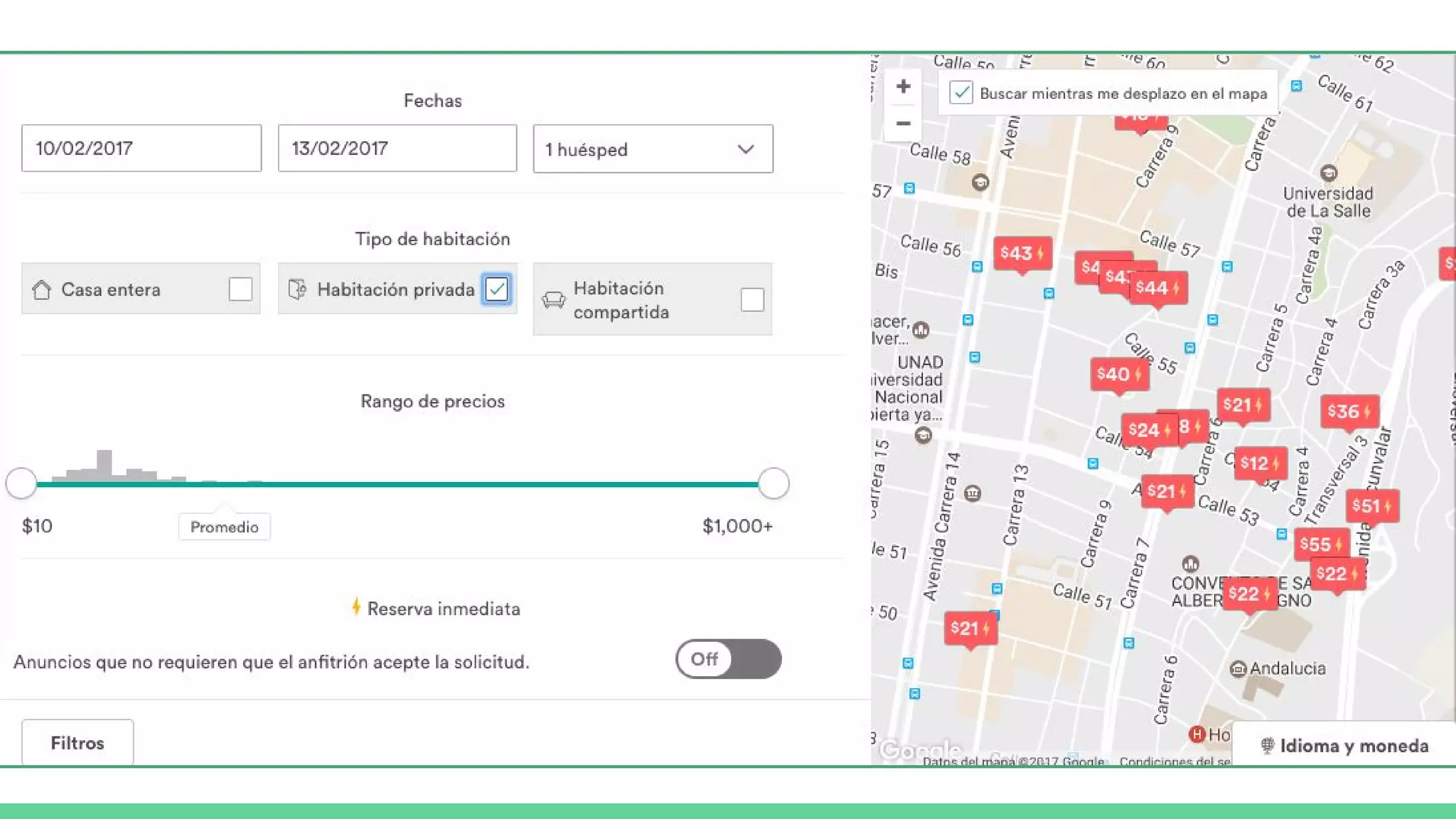
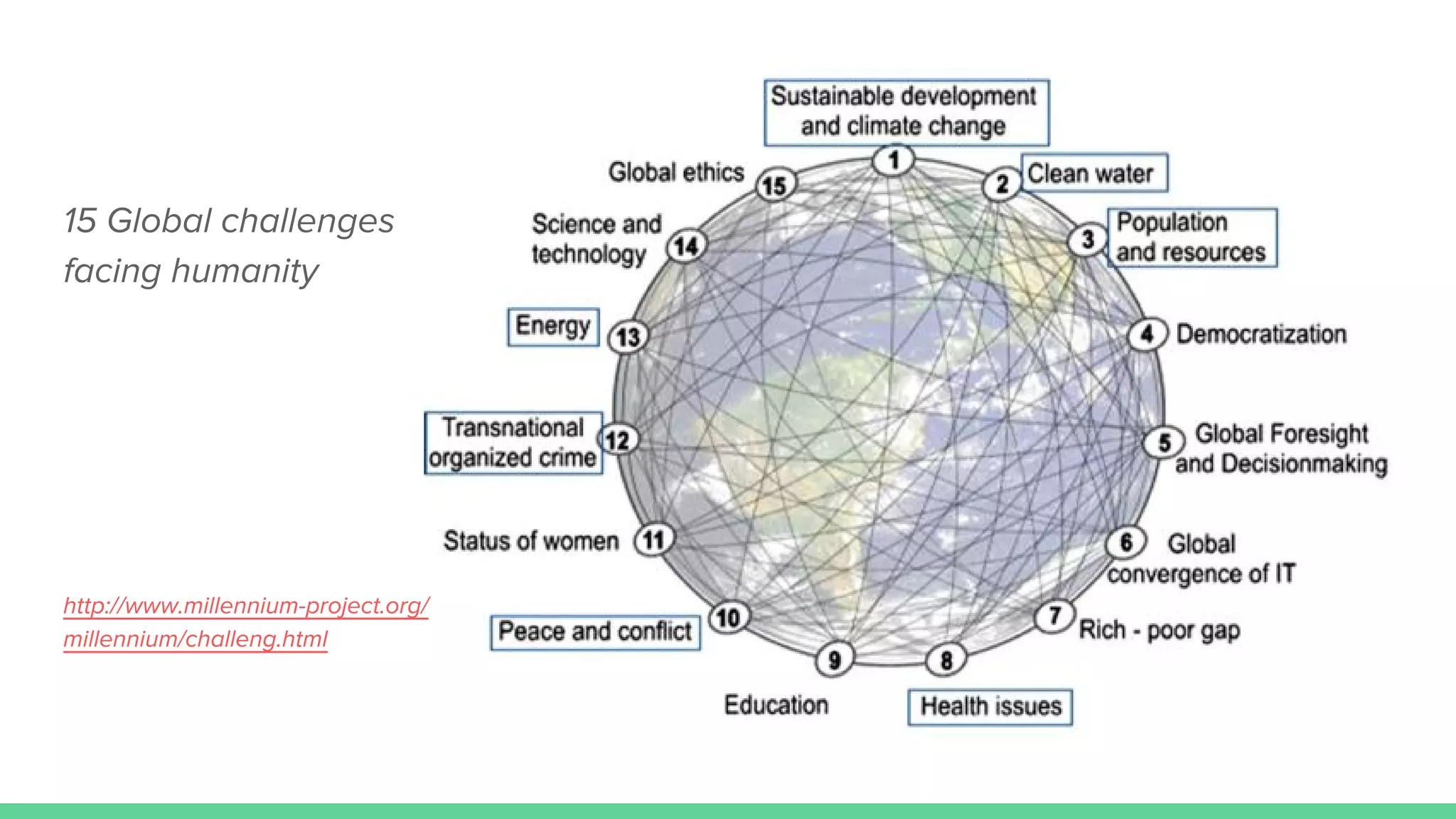
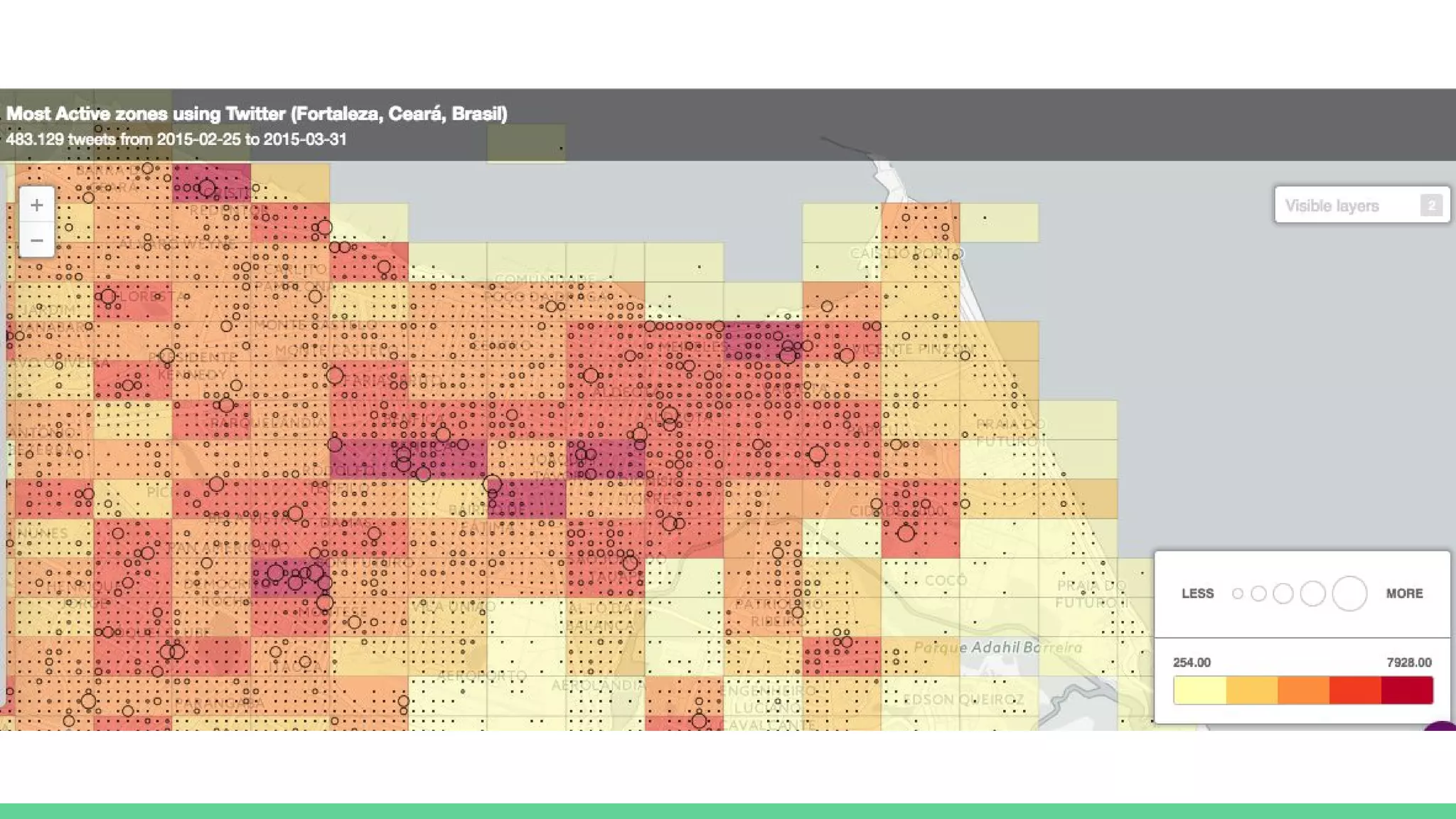
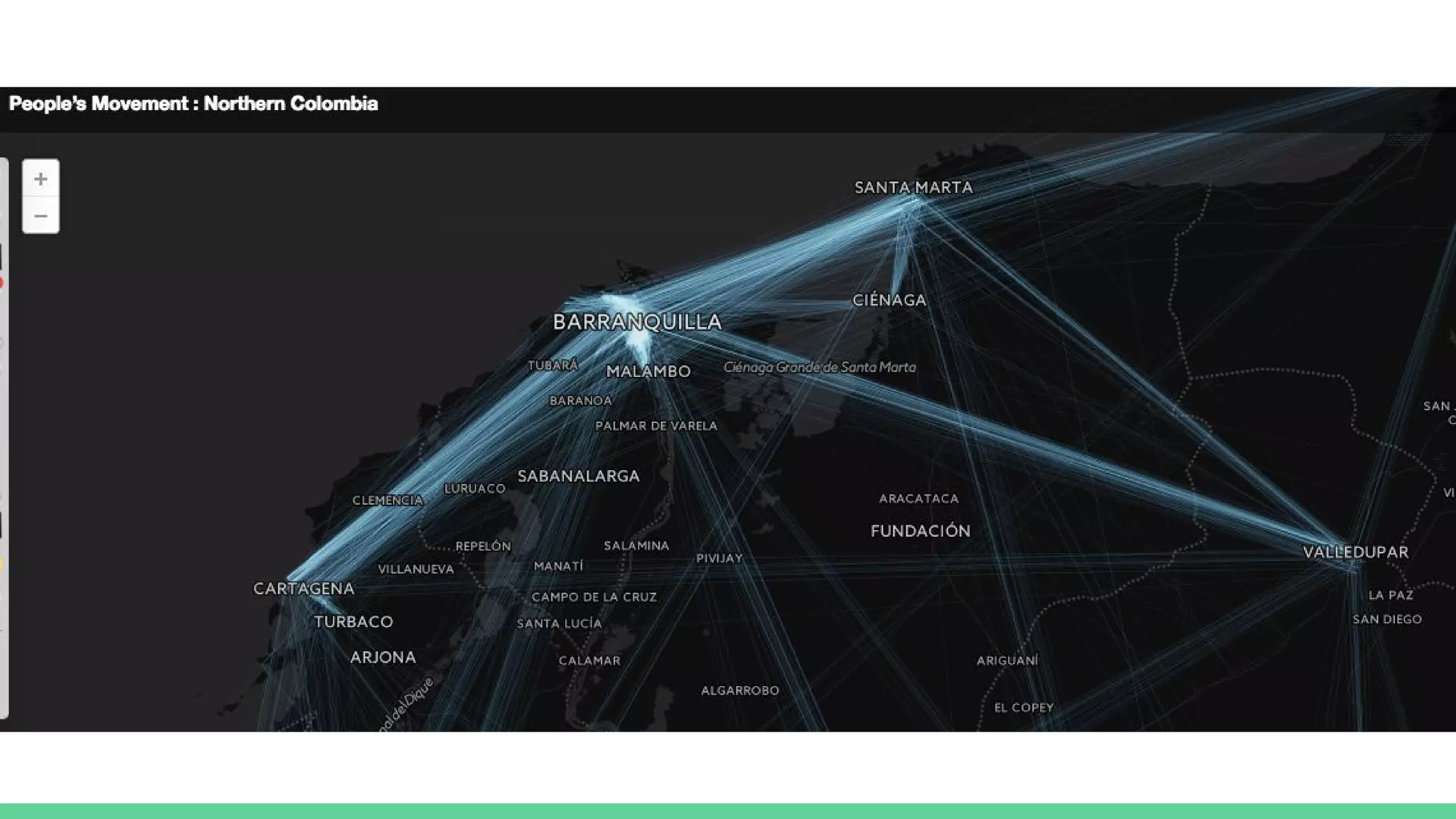
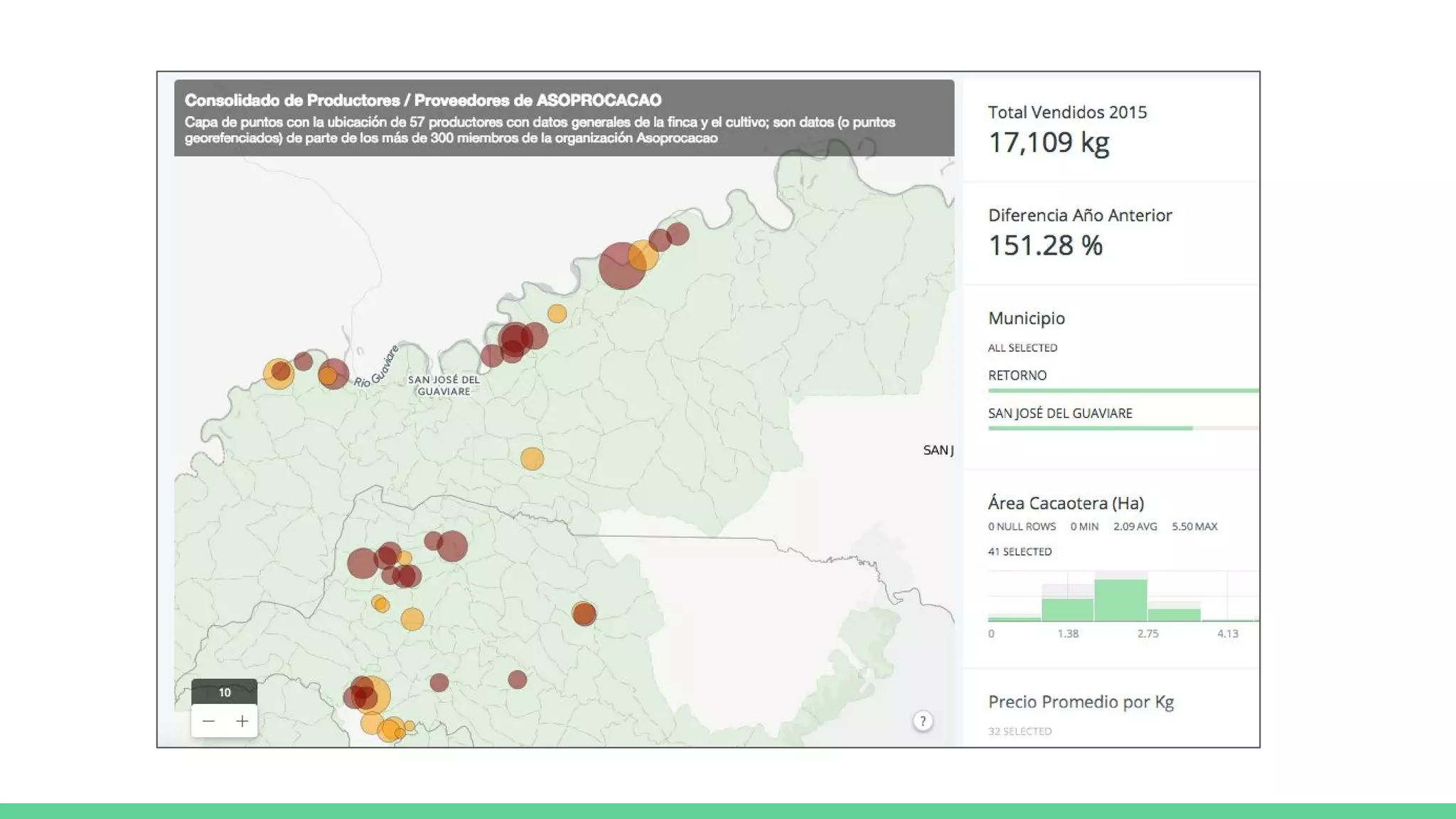
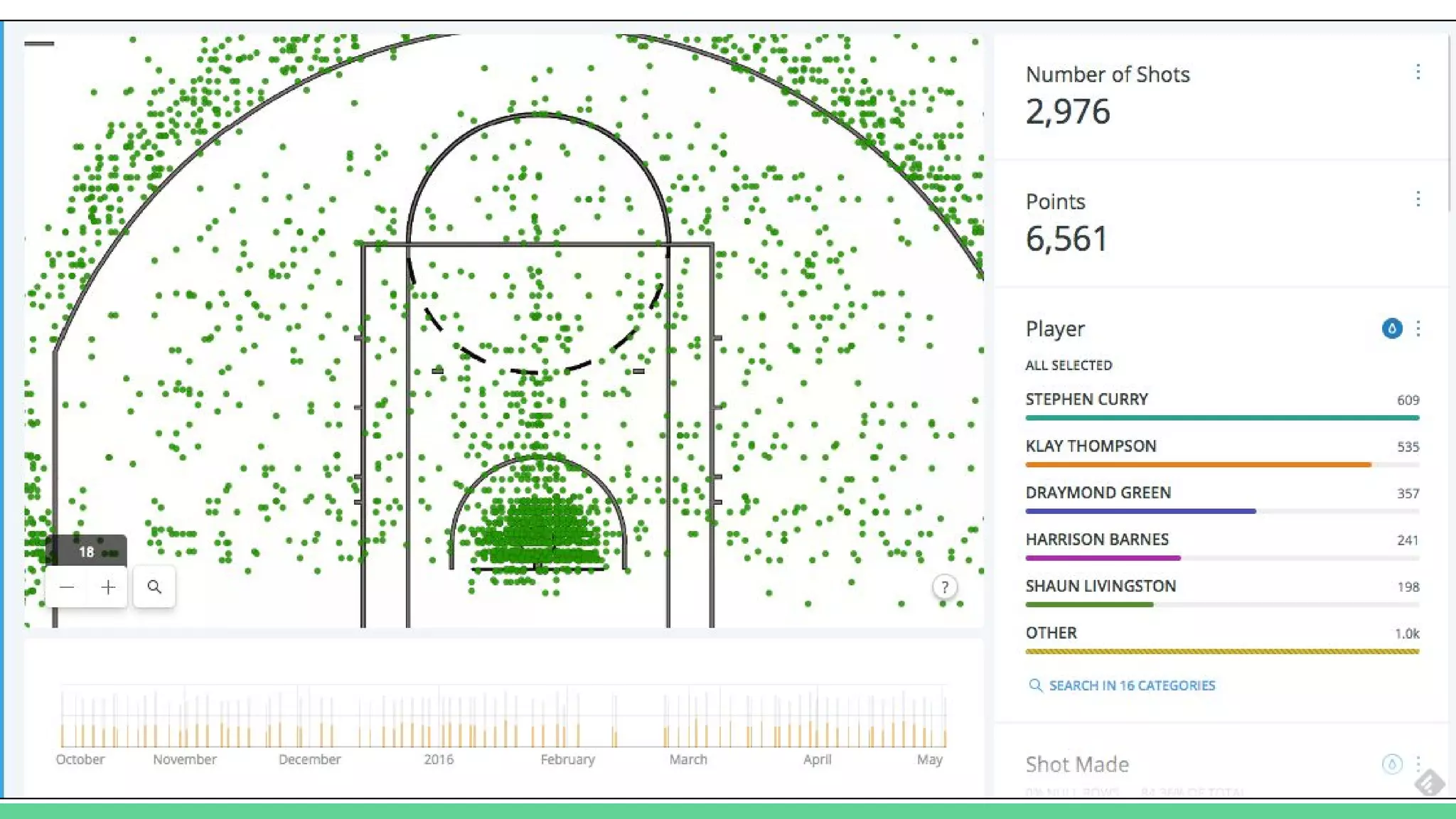
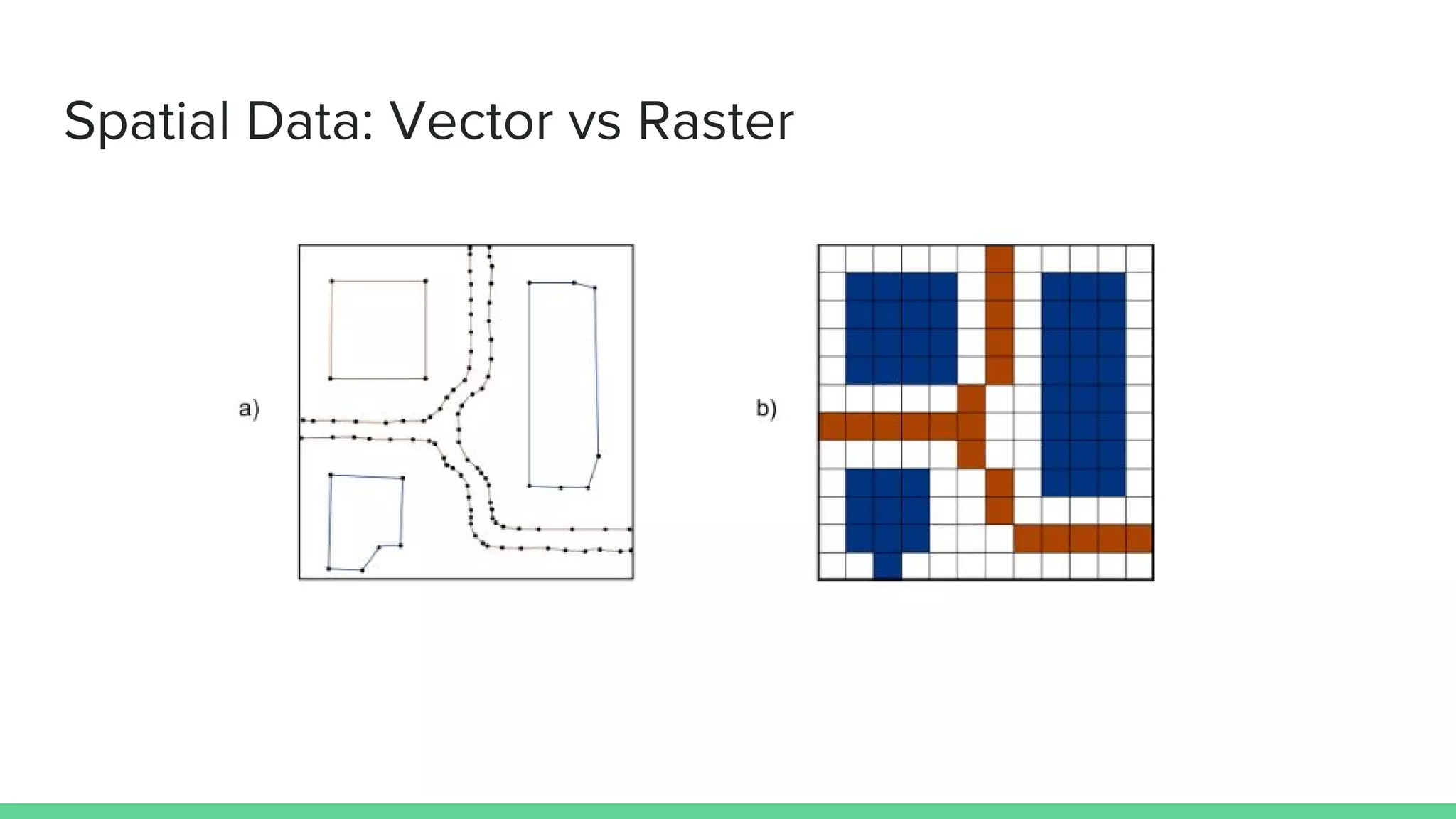
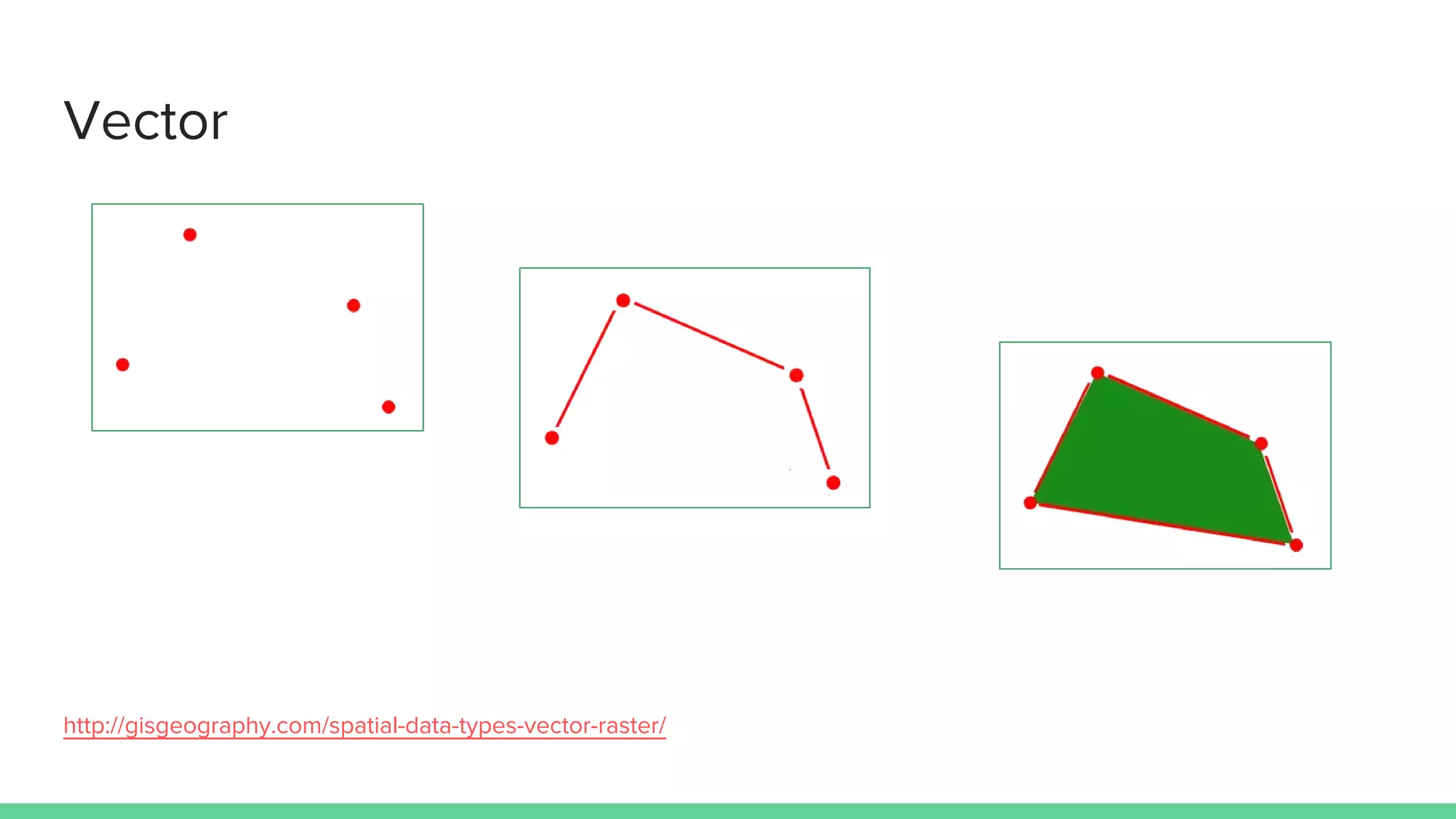
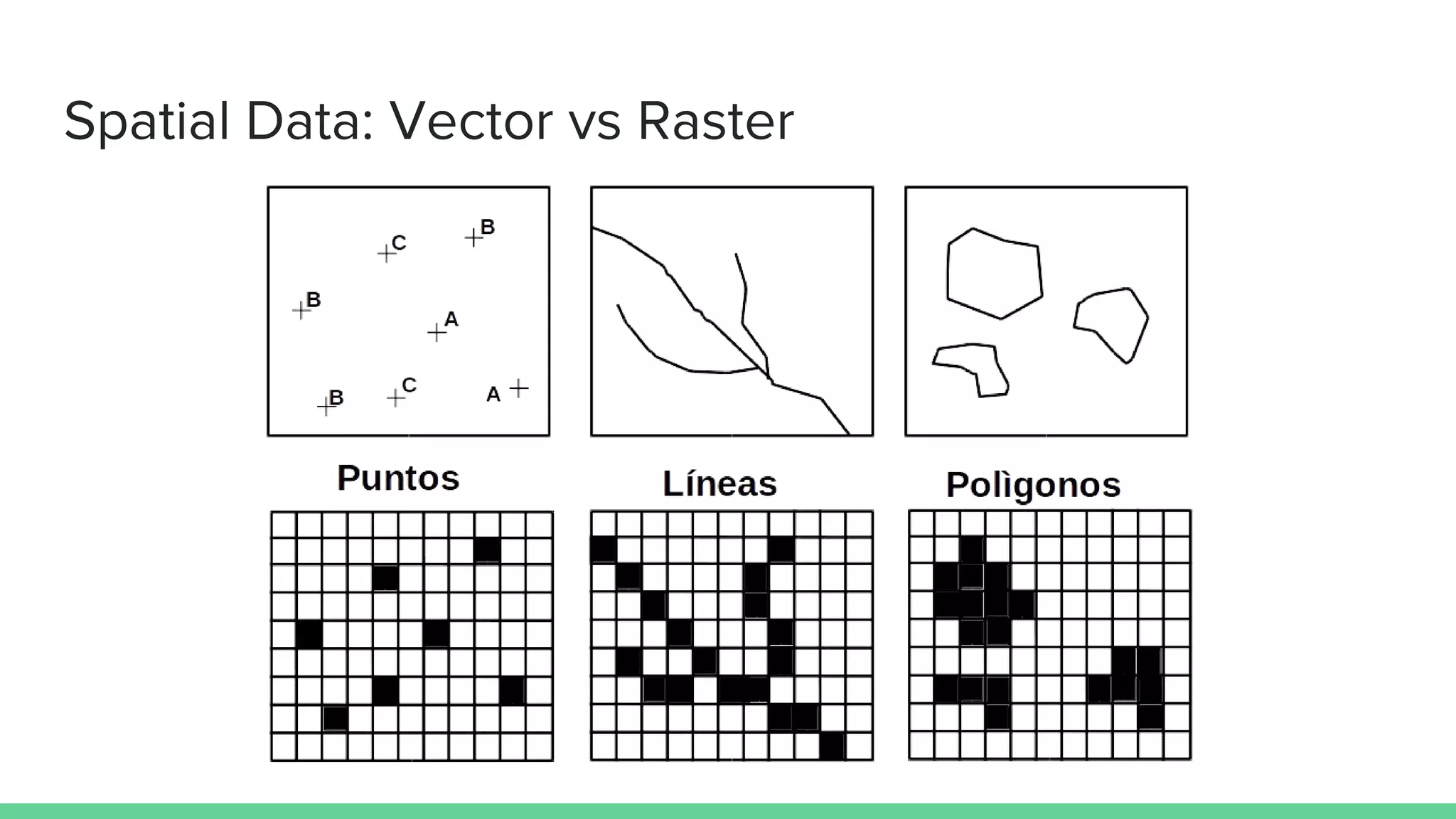
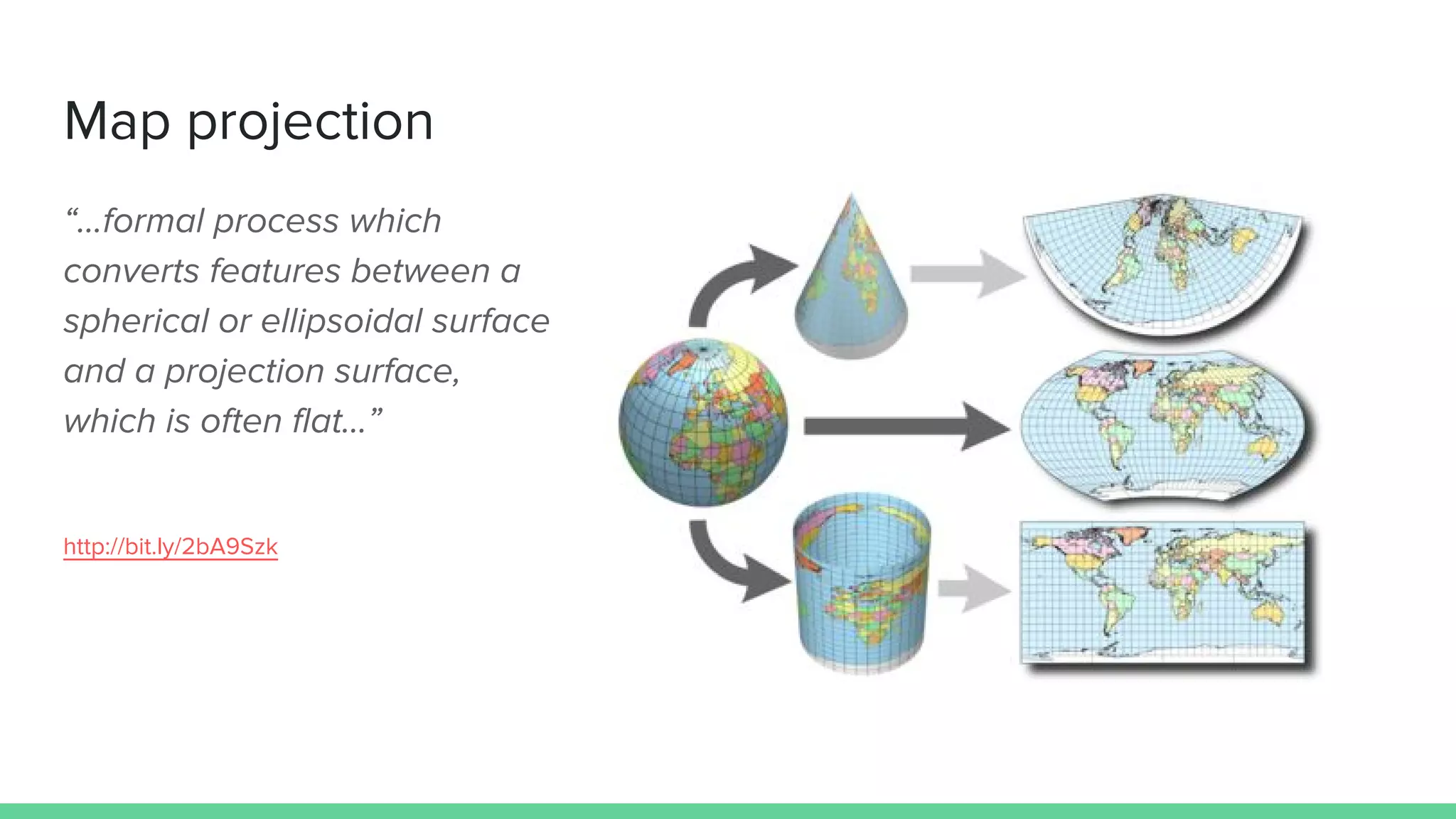
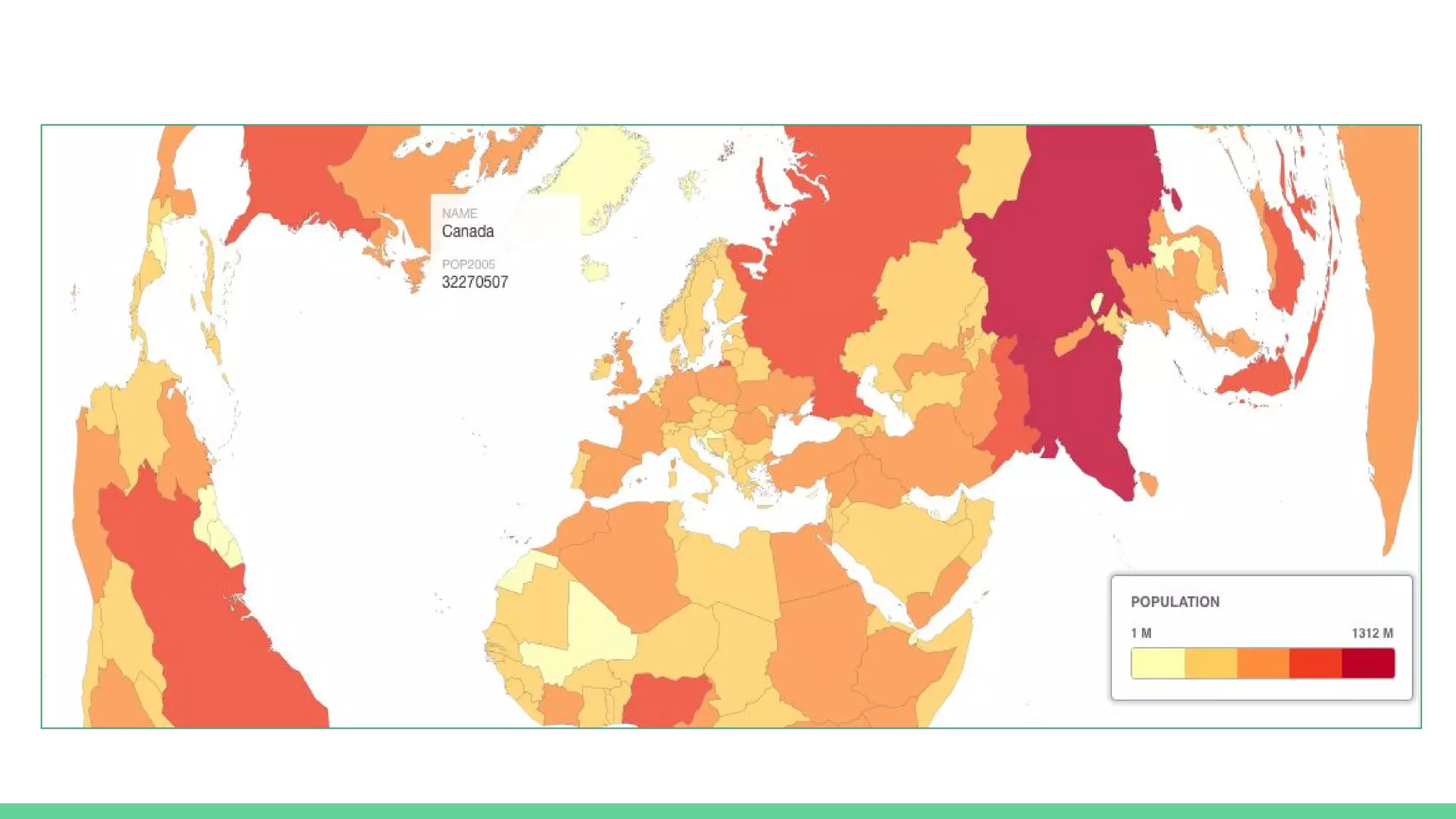
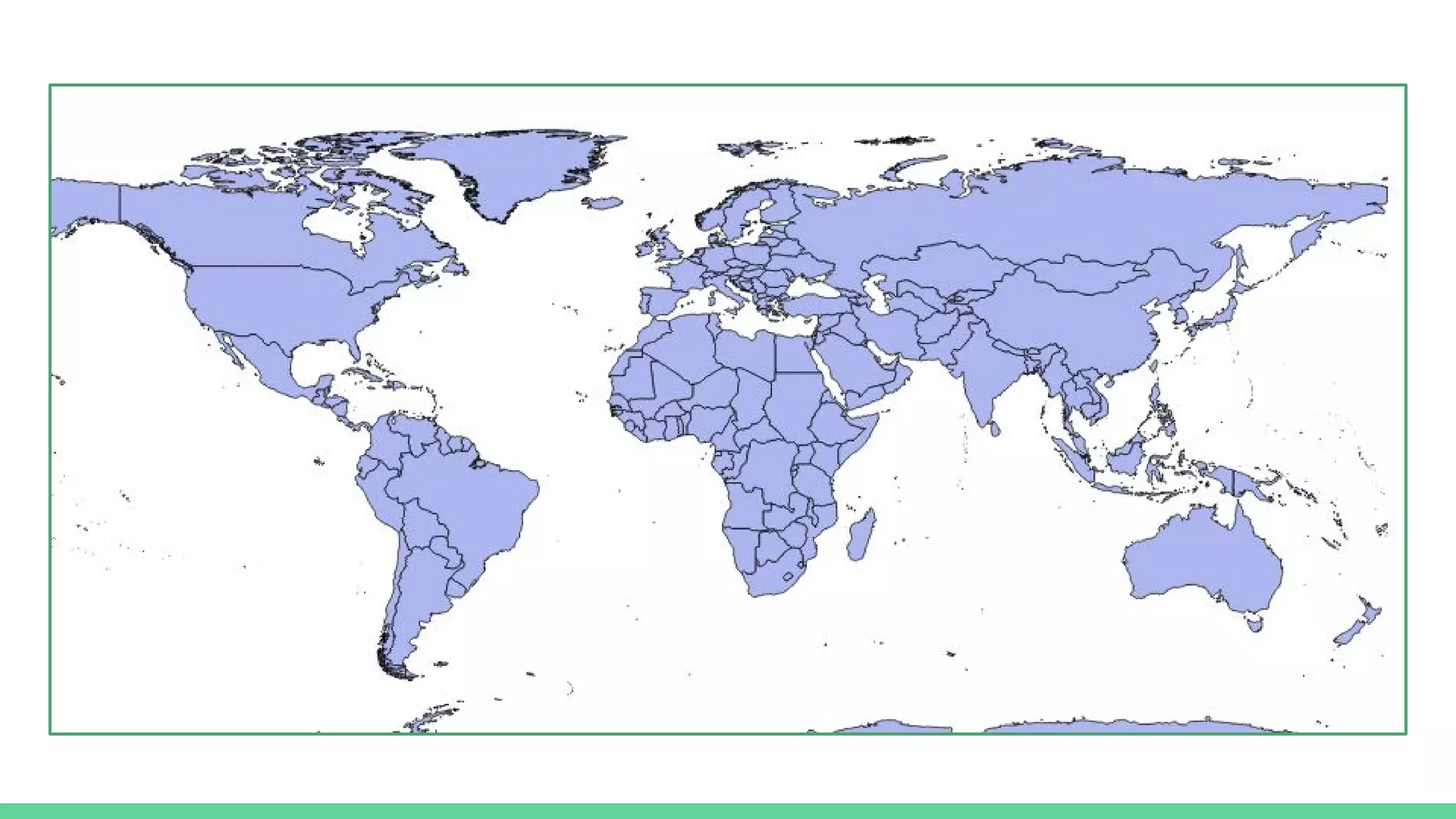
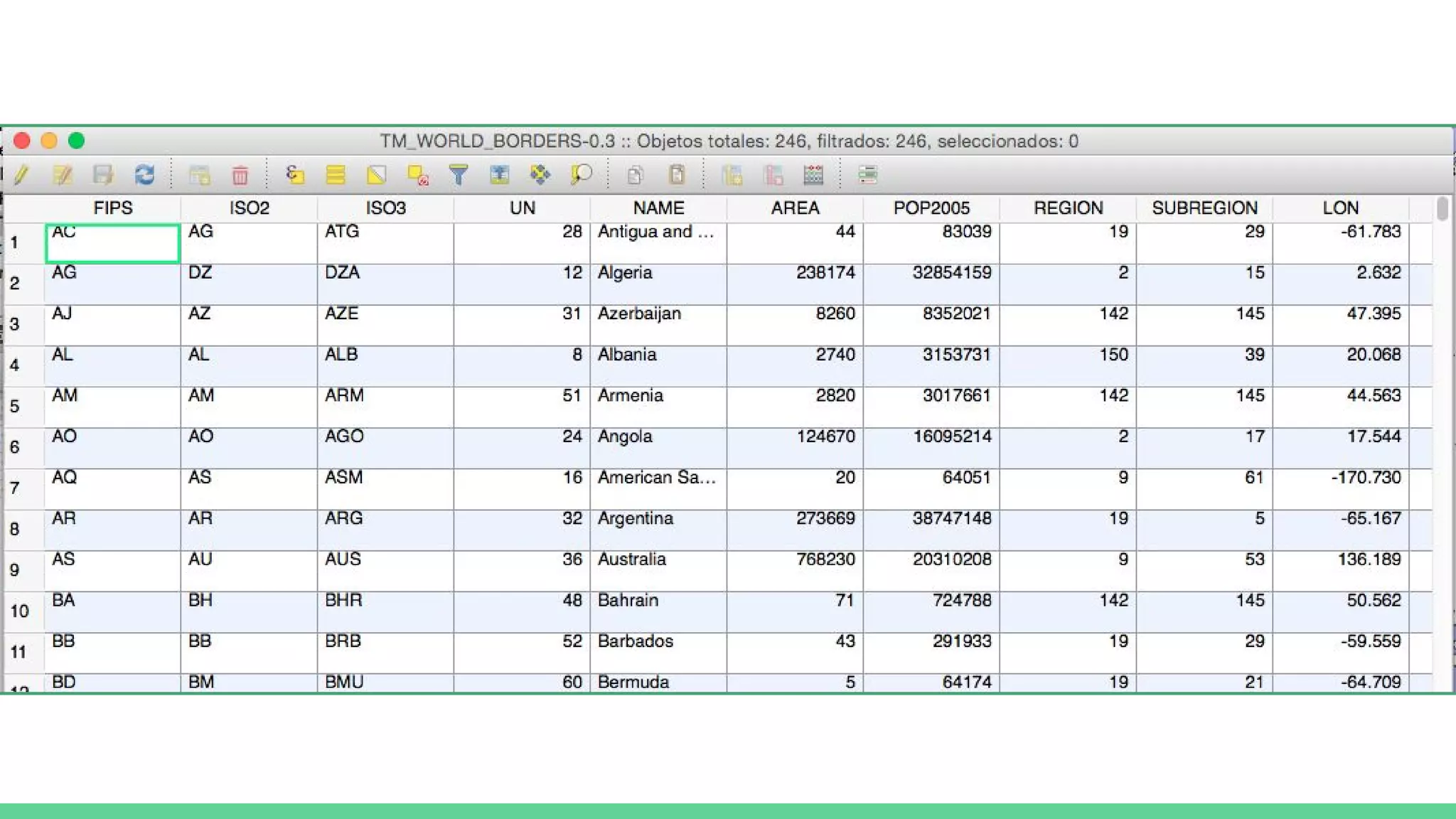
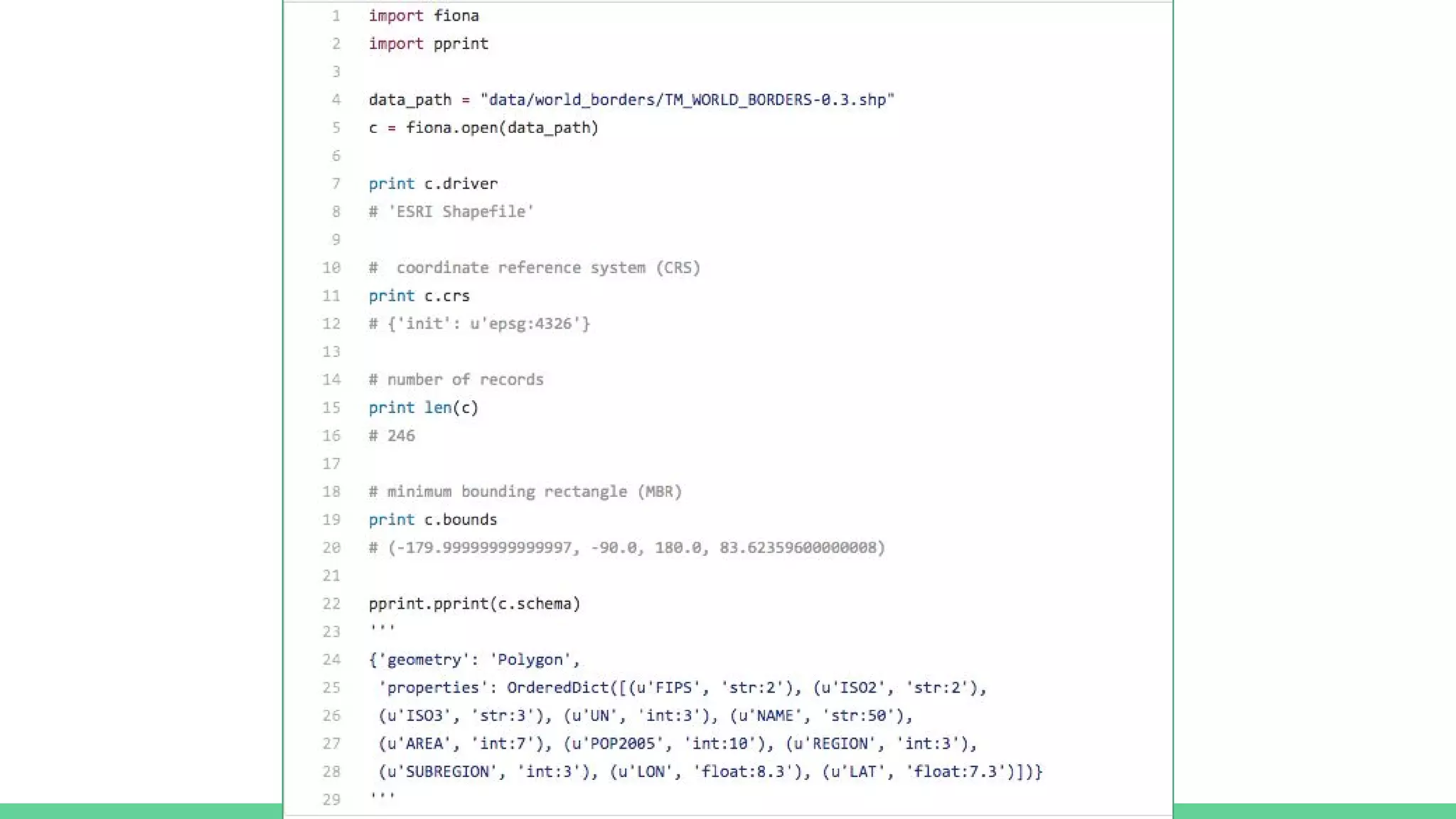
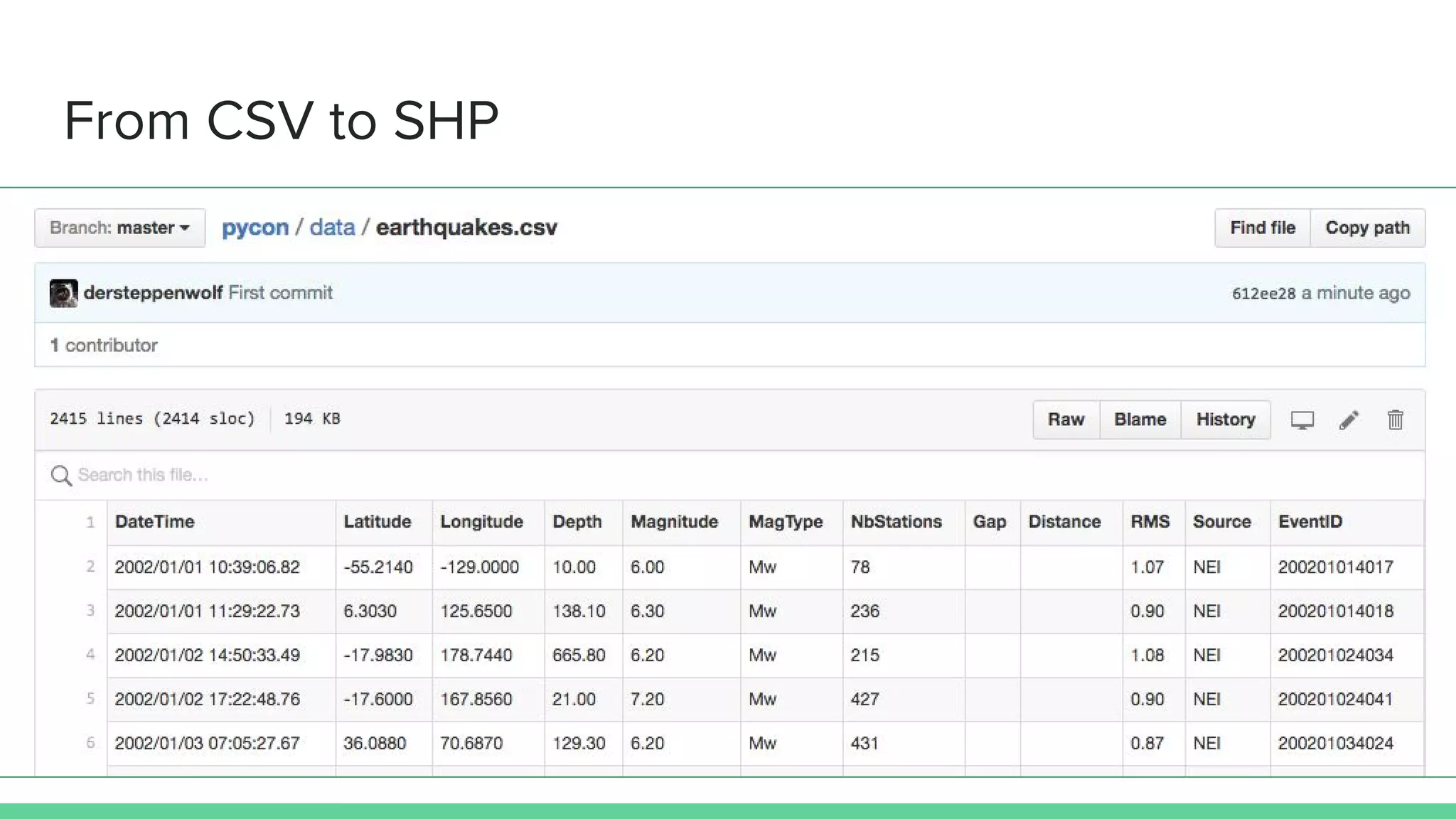
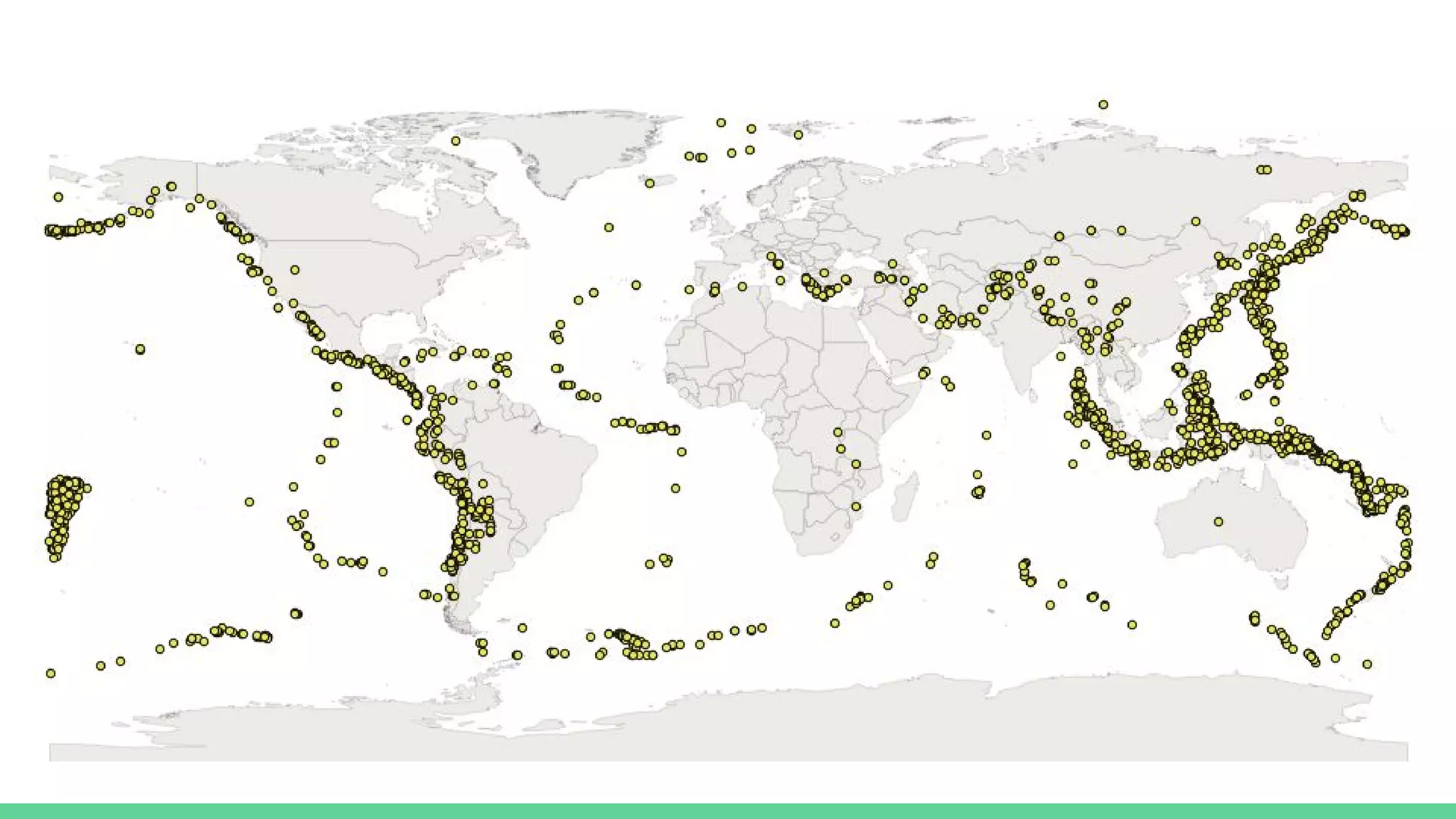
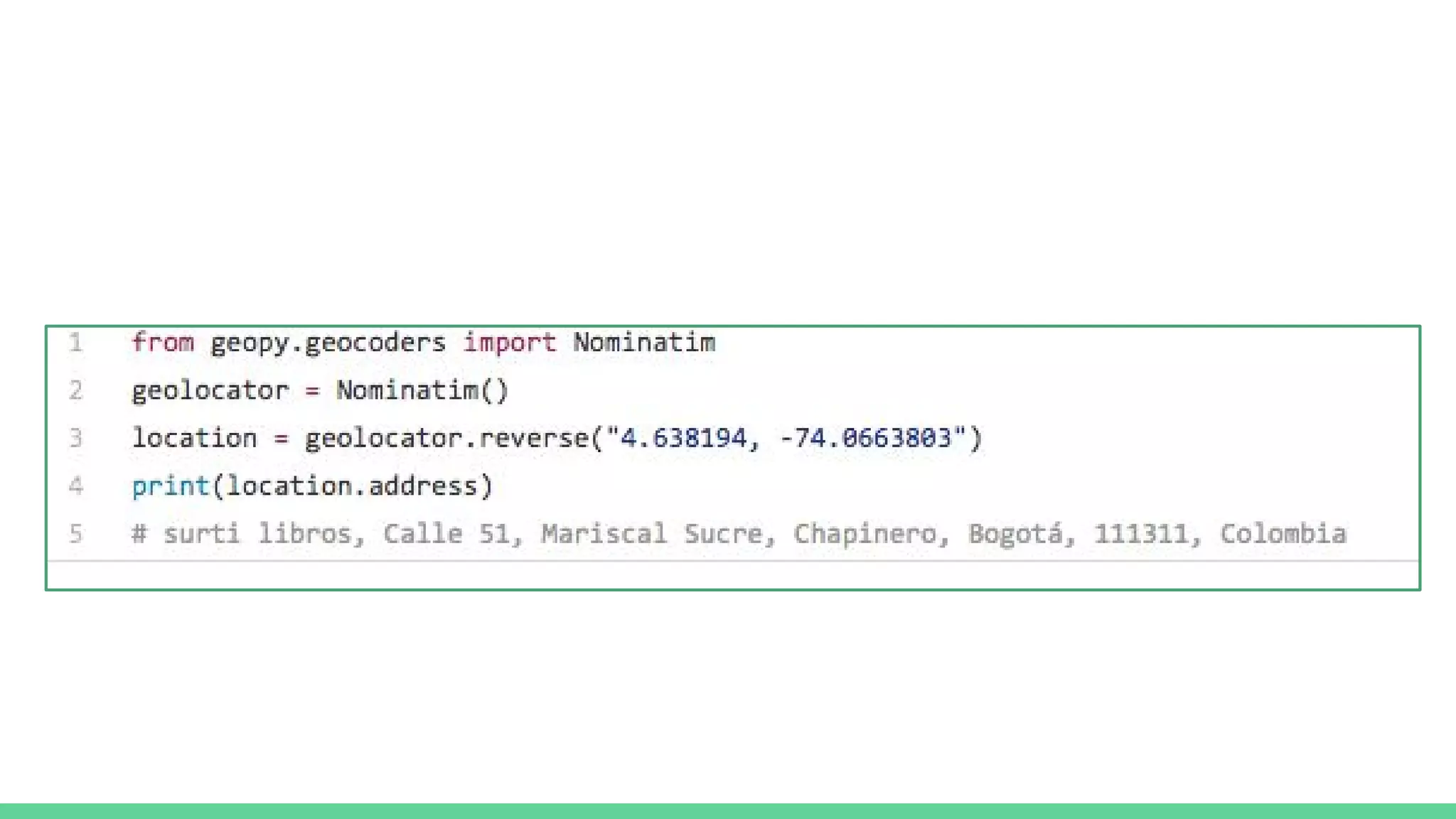
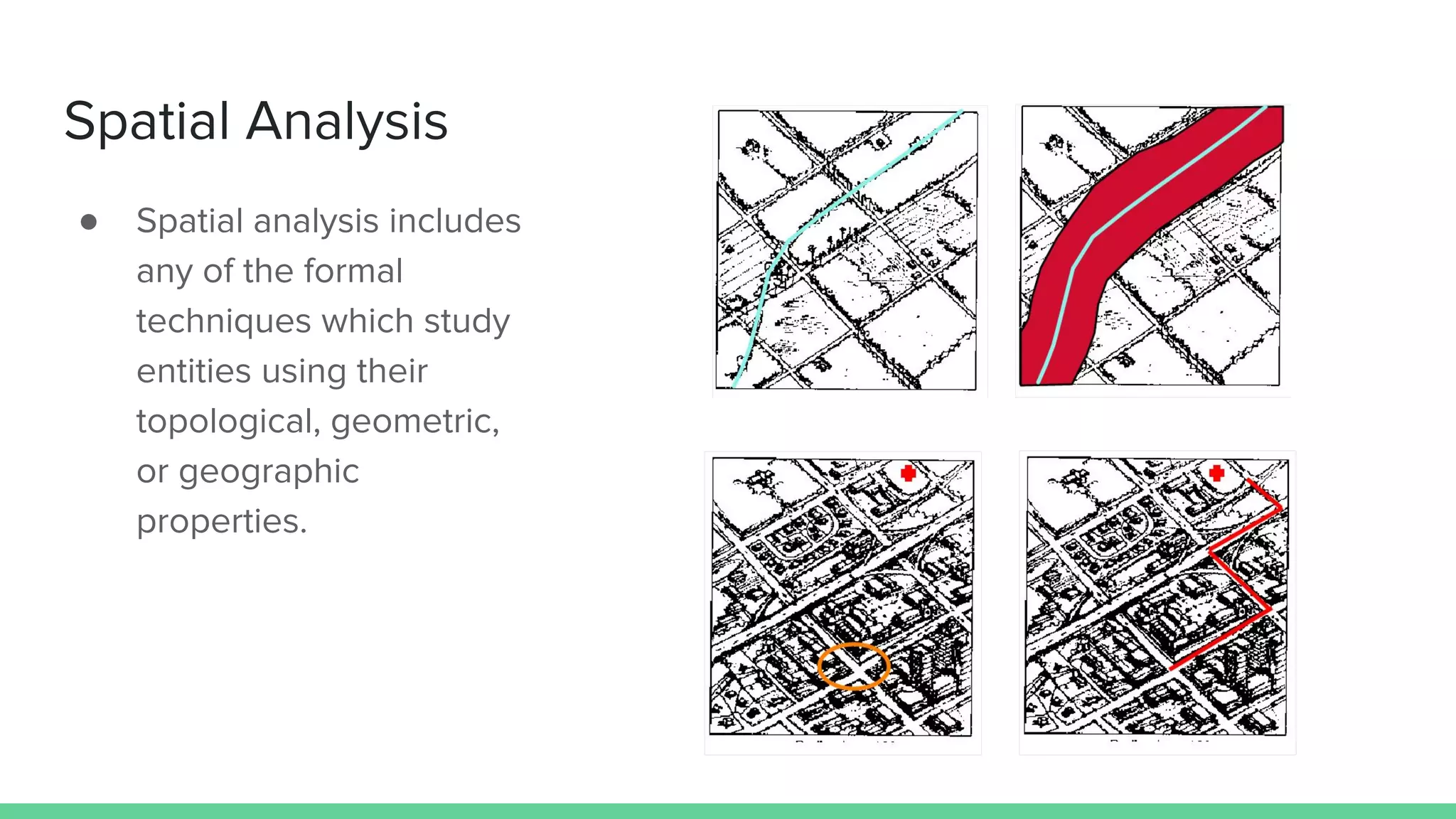
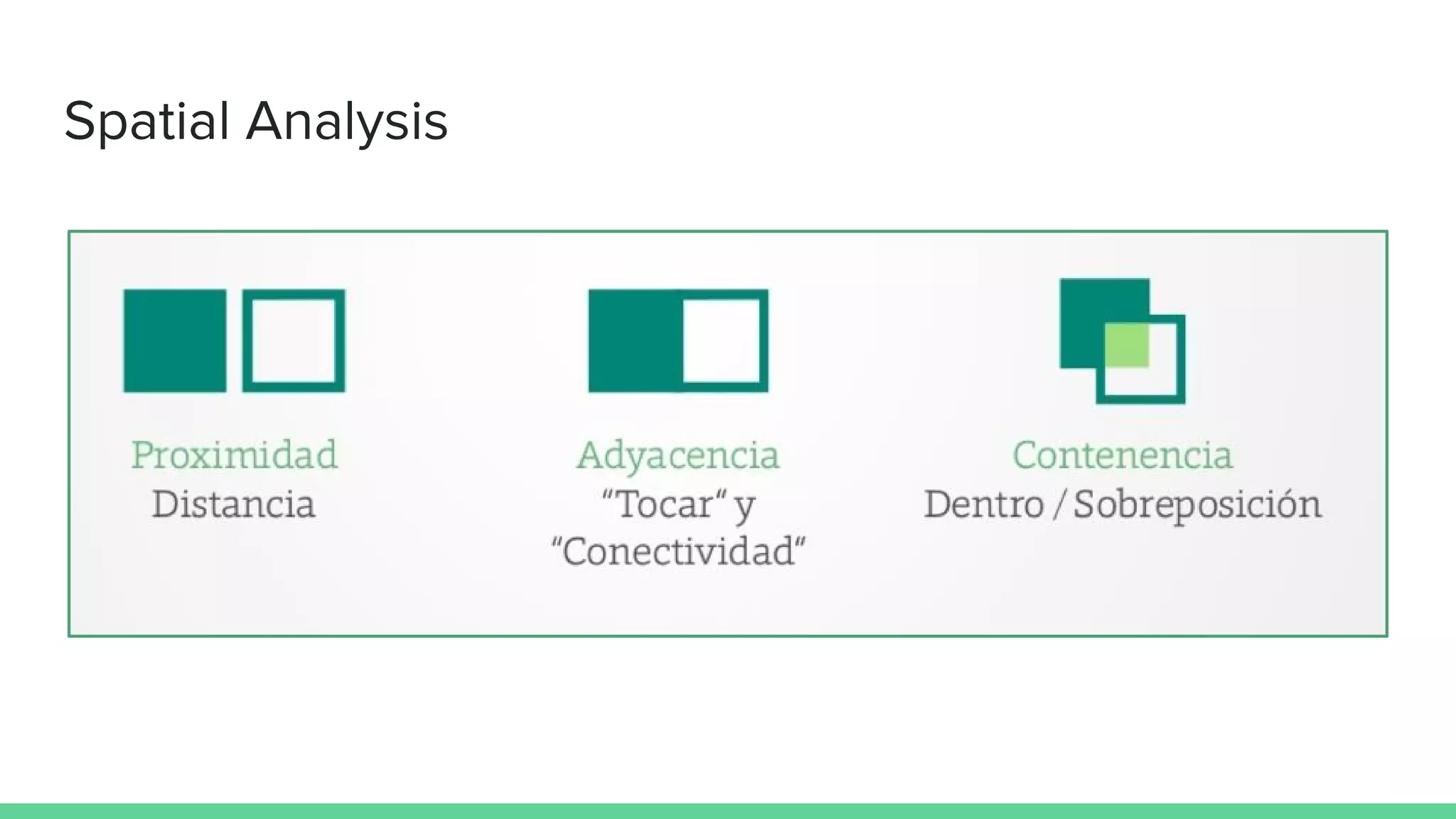
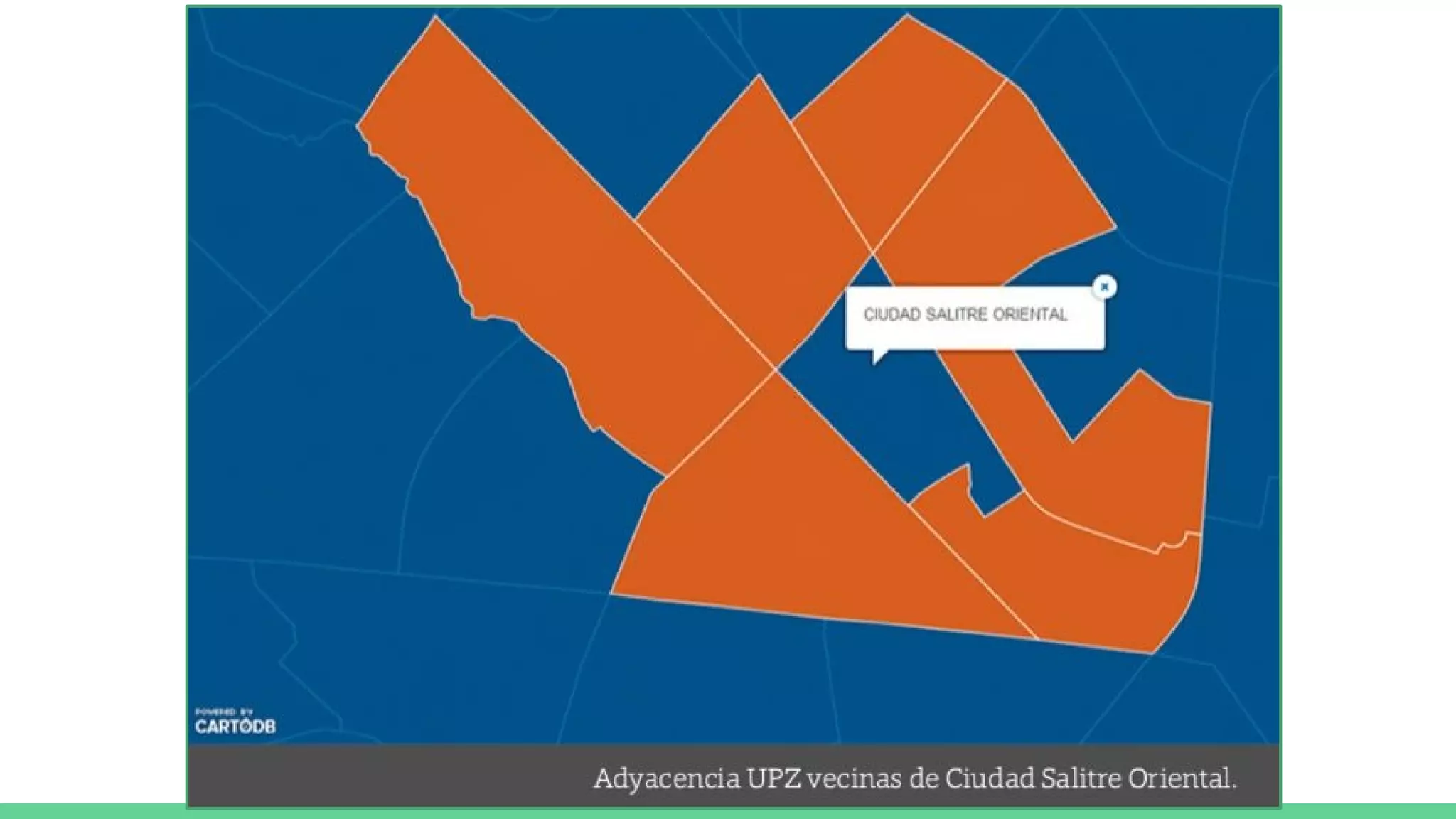
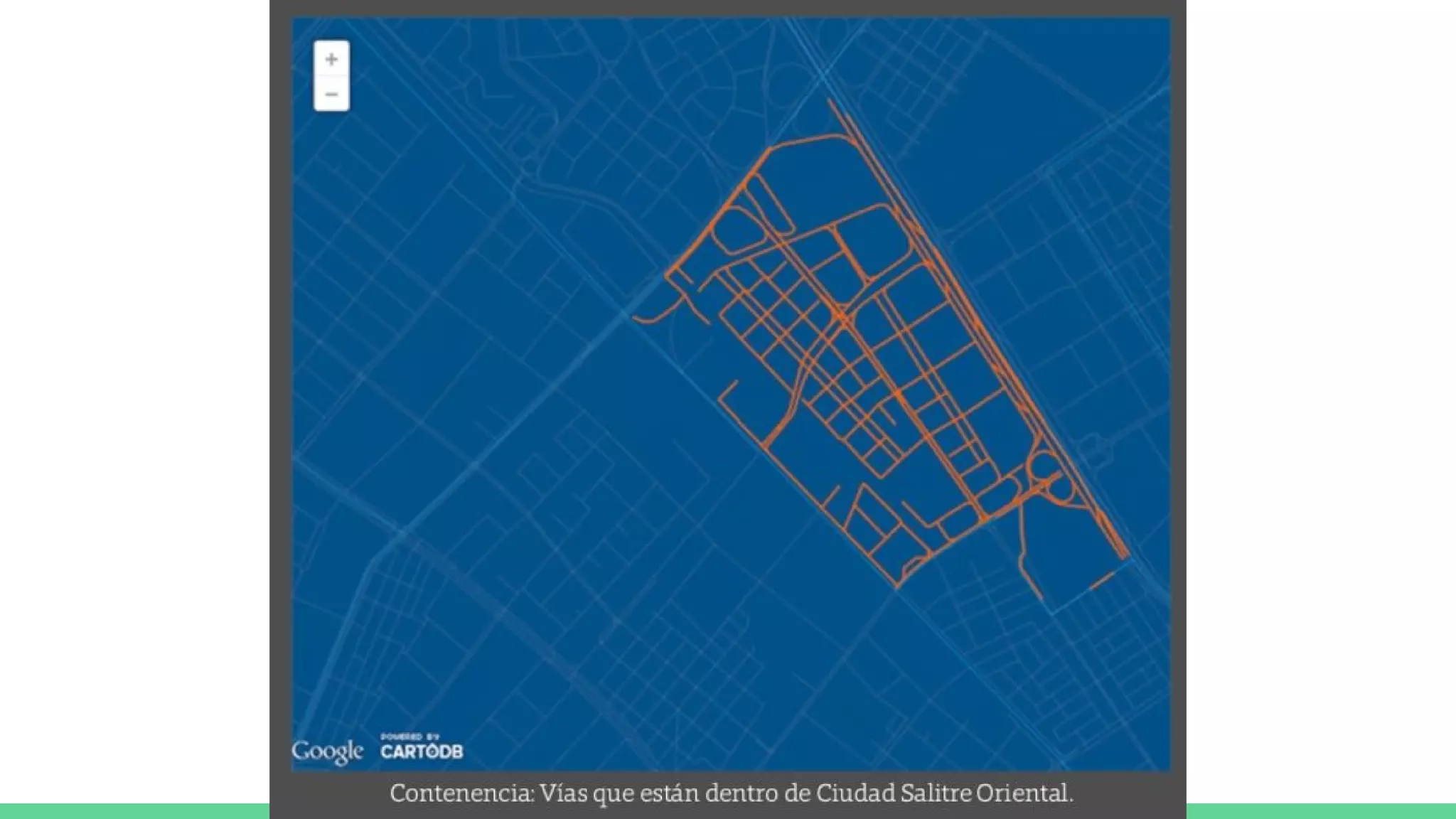
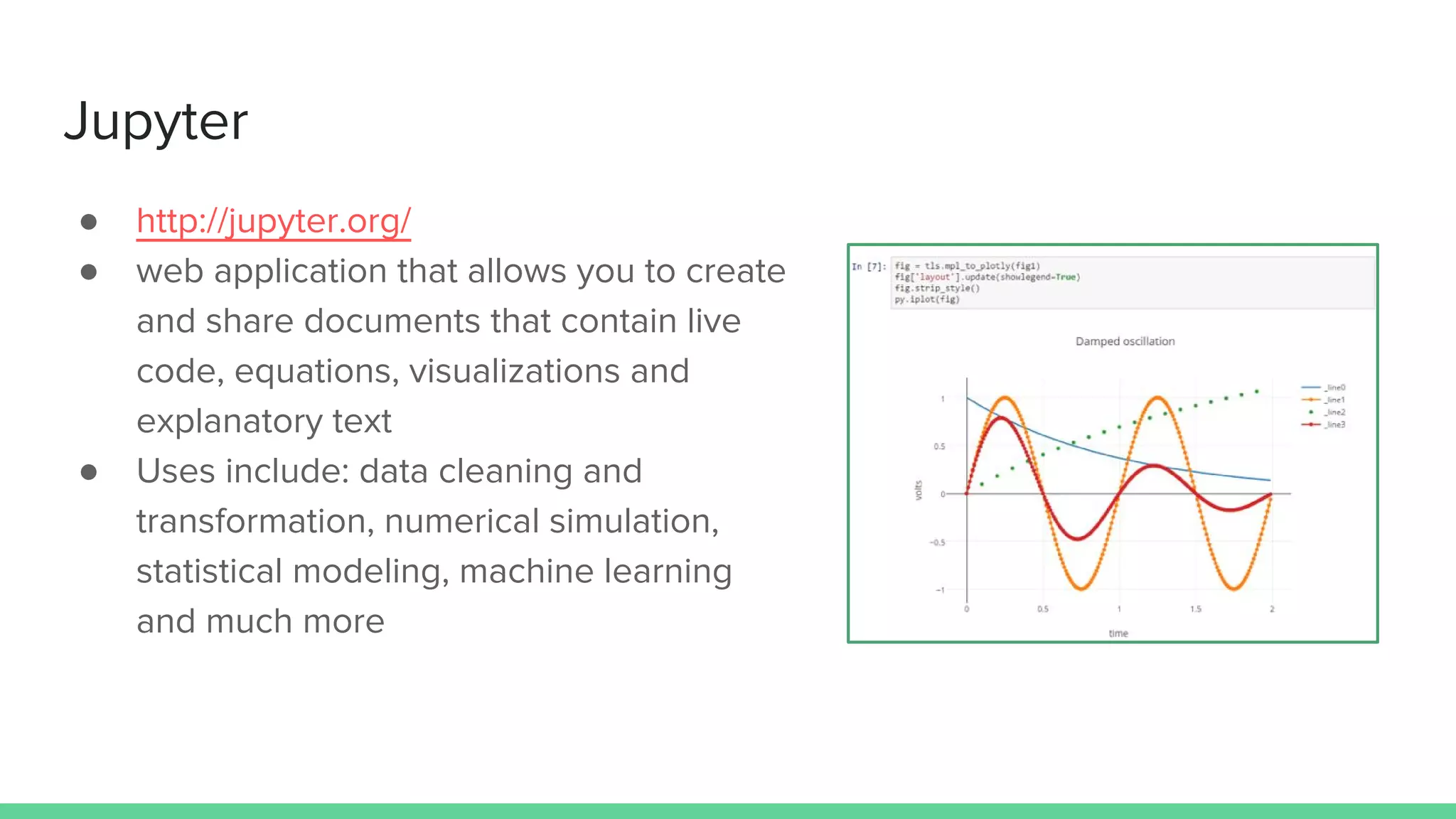
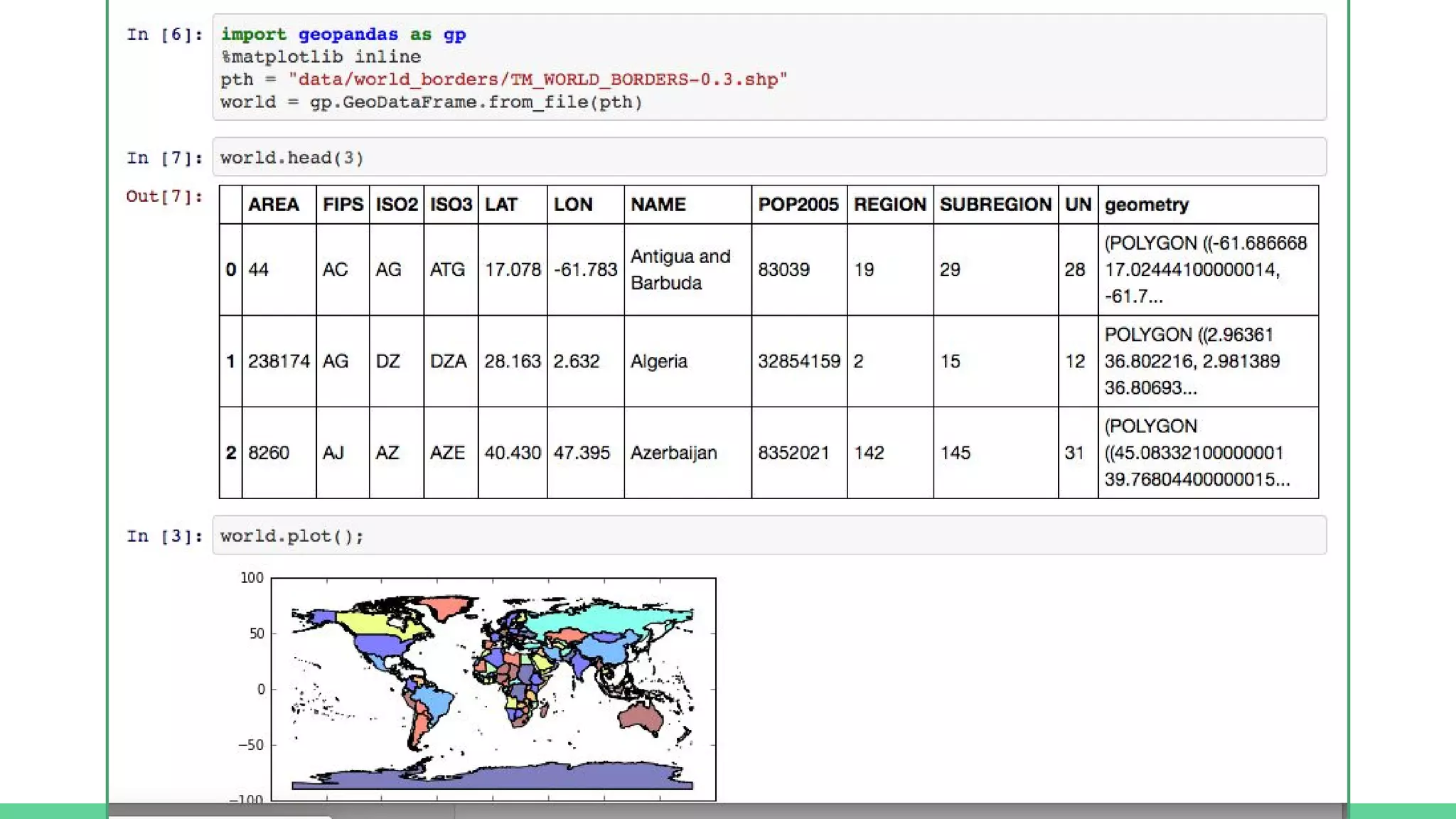
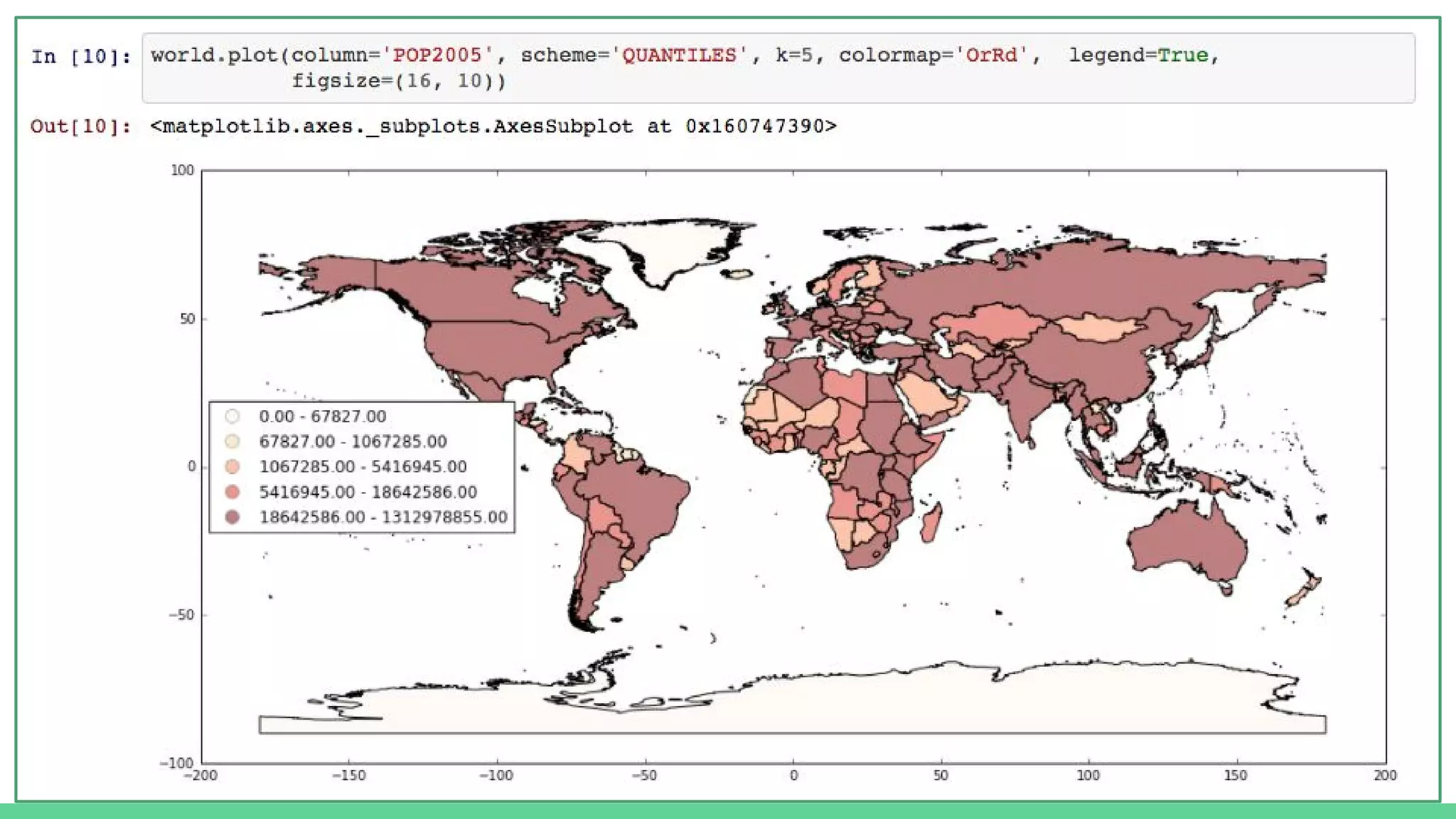
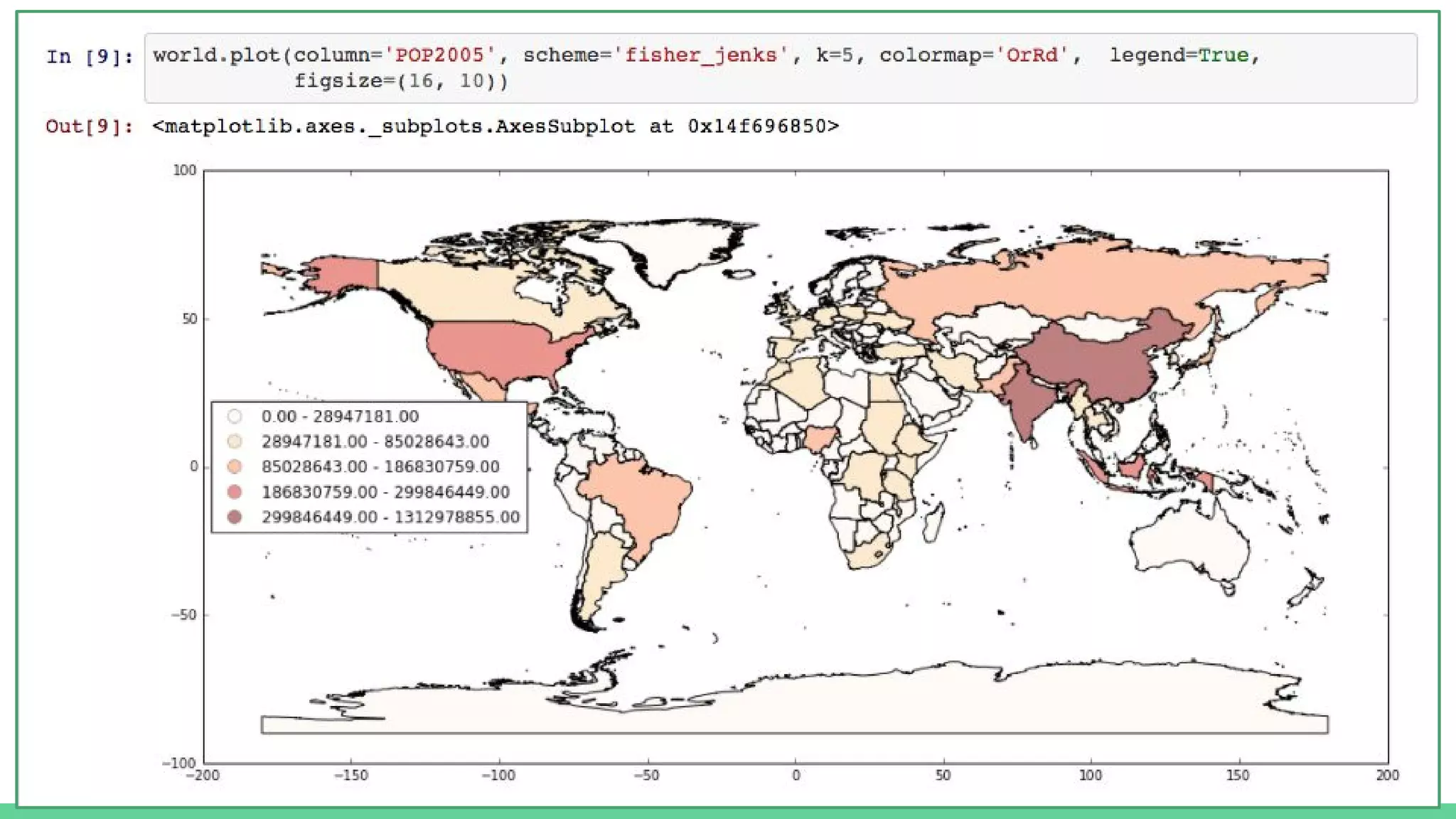
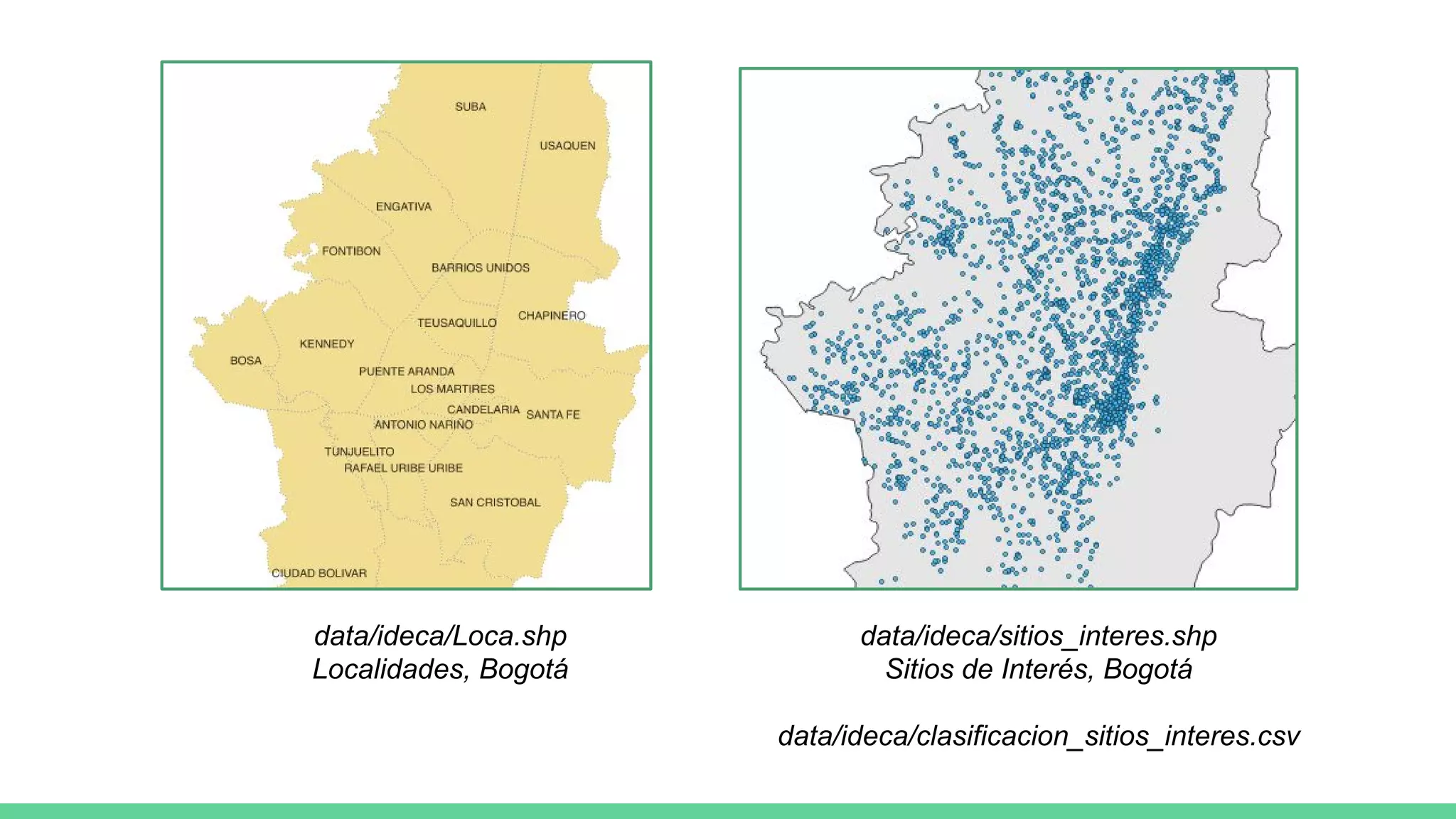
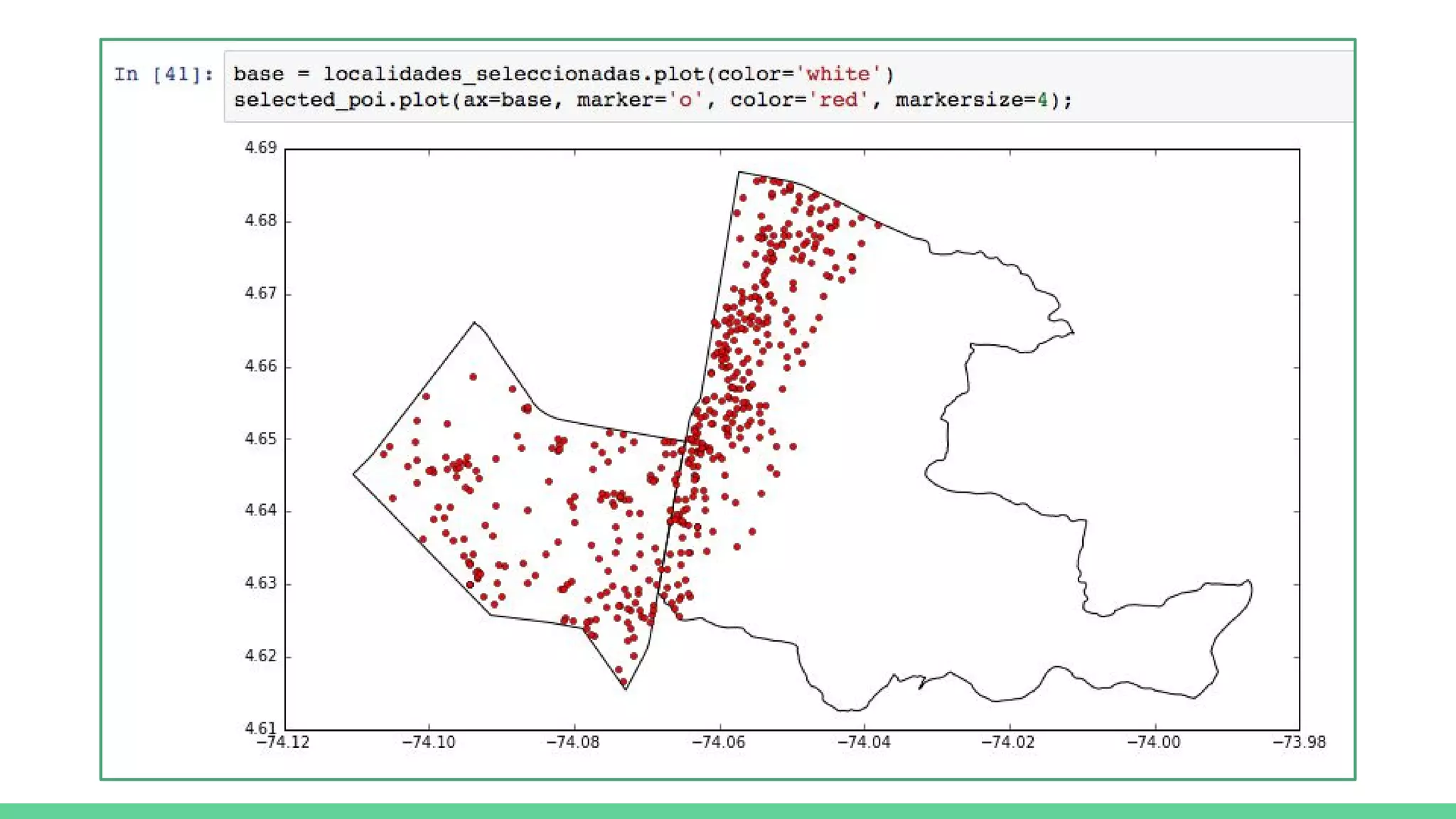
This document provides an overview and introduction to analyzing spatial data using Python. It discusses what spatial data is, popular Python libraries for working with spatial data like Fiona, Shapely, GeoPy, and Mapnik, and how to perform spatial analysis tasks in Python such as geocoding, data conversion and visualization. Jupyter notebooks are presented as an interactive environment for exploring spatial data and libraries like Geopandas and PySAL are introduced for performing spatial analysis. Examples analyze Colombian location and point of interest data.