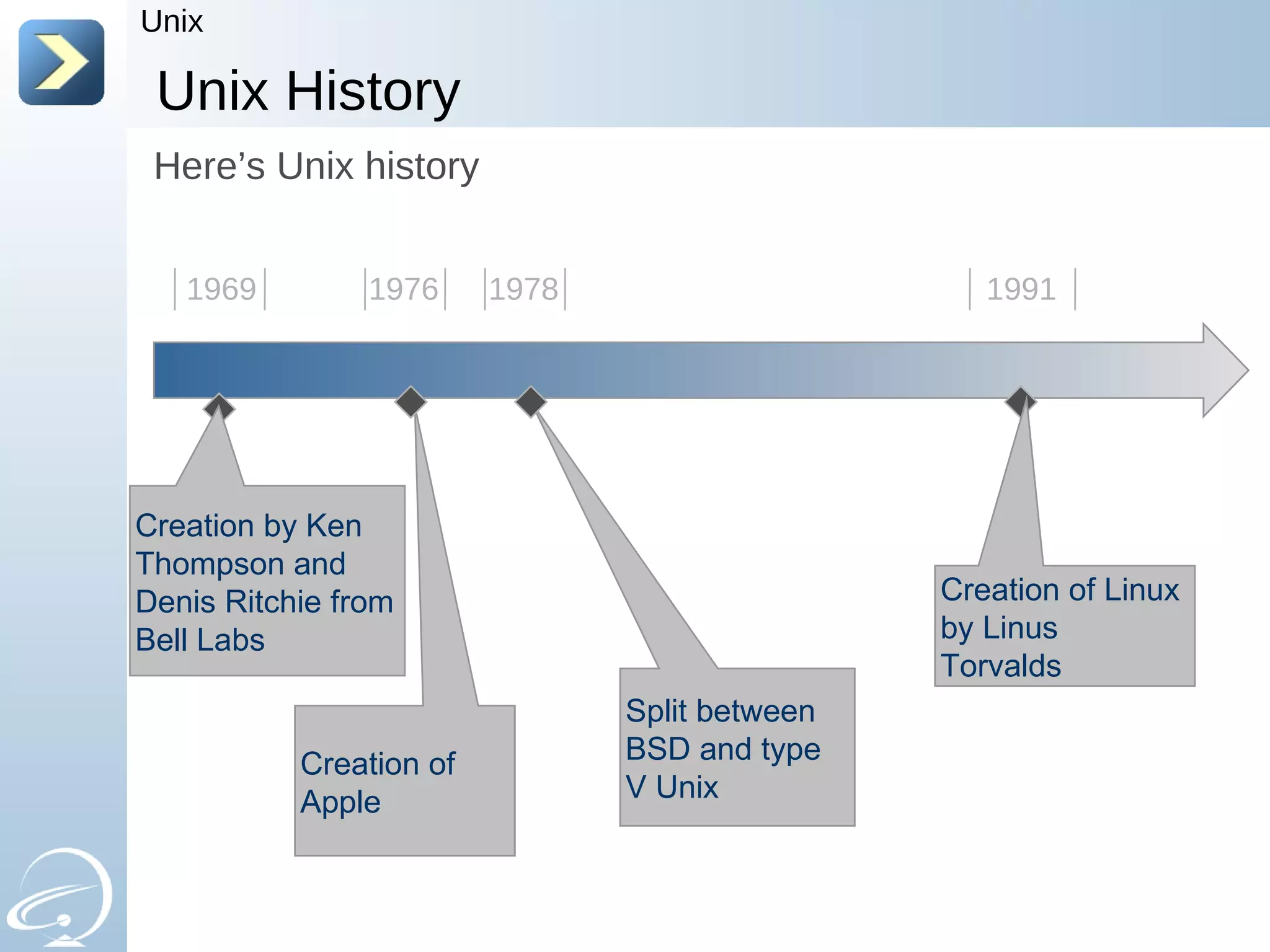
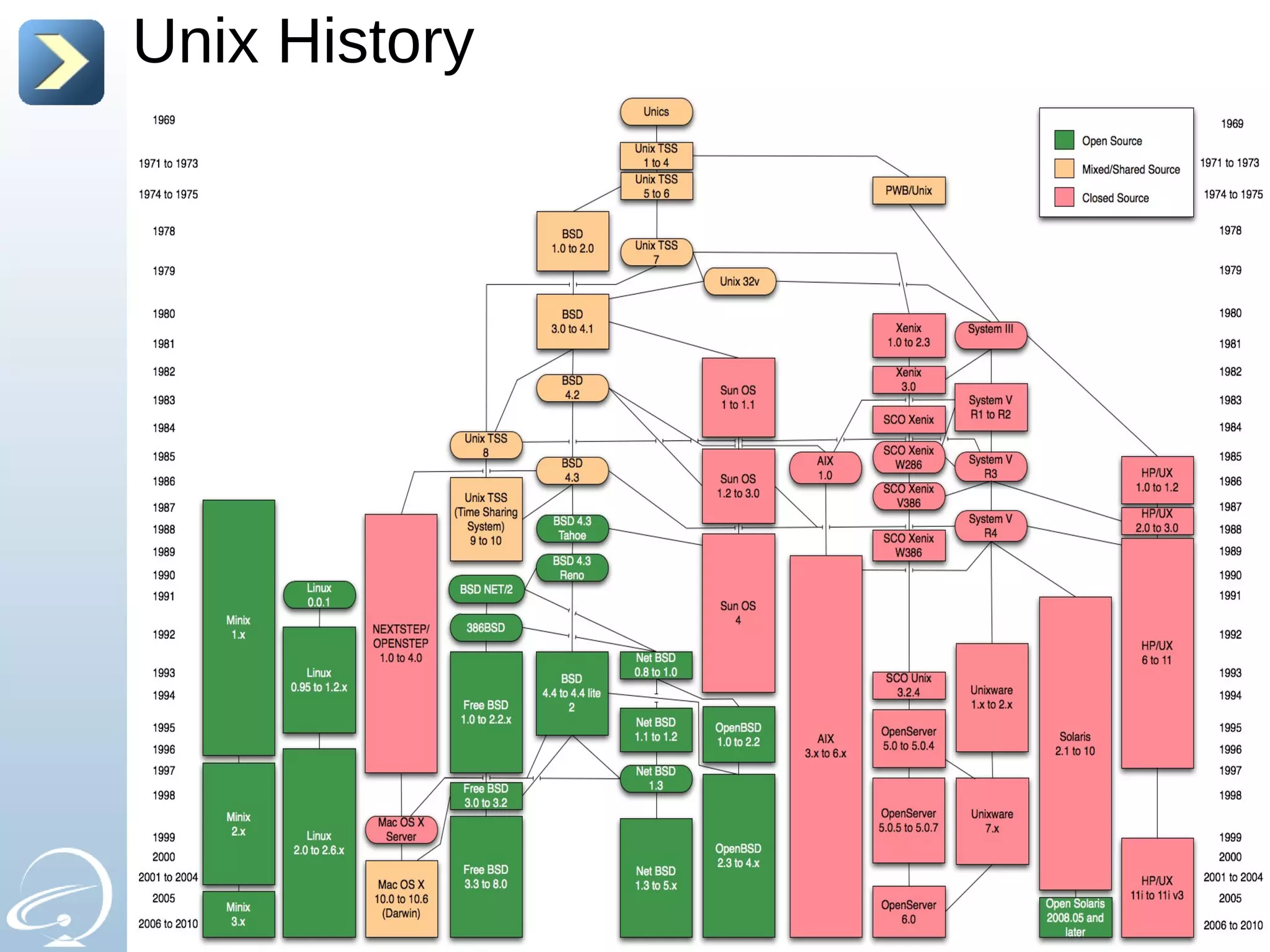
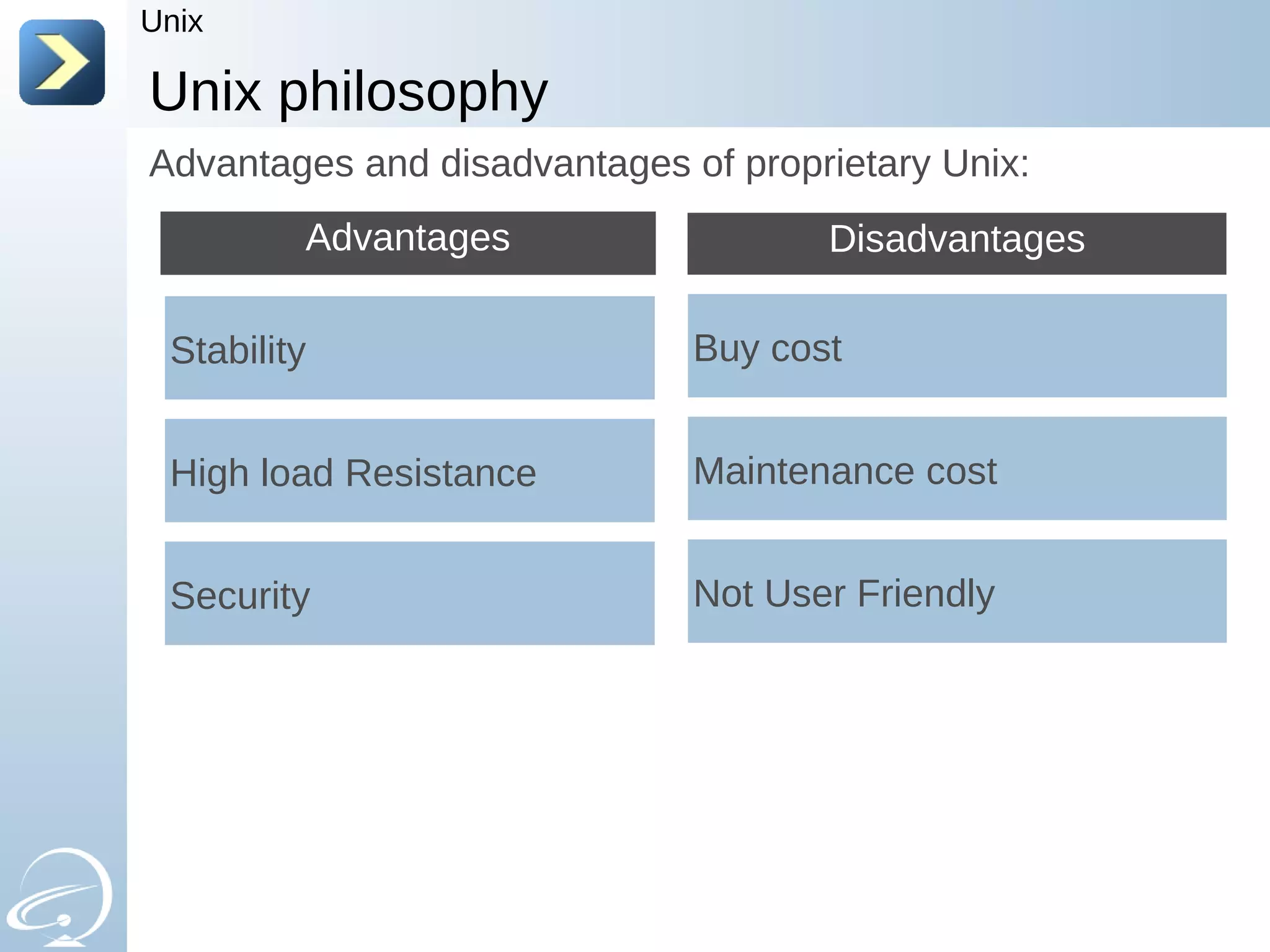
The document provides an introduction to UNIX and the history of UNIX and Linux. It discusses the following key points: - UNIX was created in 1969 at Bell Labs to be multi-tasking and multi-user to help scientists with their calculations. It has a philosophy of everything being treated as a file. - Over time, UNIX split between proprietary UNIX variants from companies like Sun and IBM and non-proprietary variants like BSD and Linux. - The GNU project was launched in 1984 to create a free UNIX-like operating system. Linux was created in 1991 by Linus Torvalds as a kernel based on UNIX concepts. - When the GNU software was combined with the Linux kernel, it