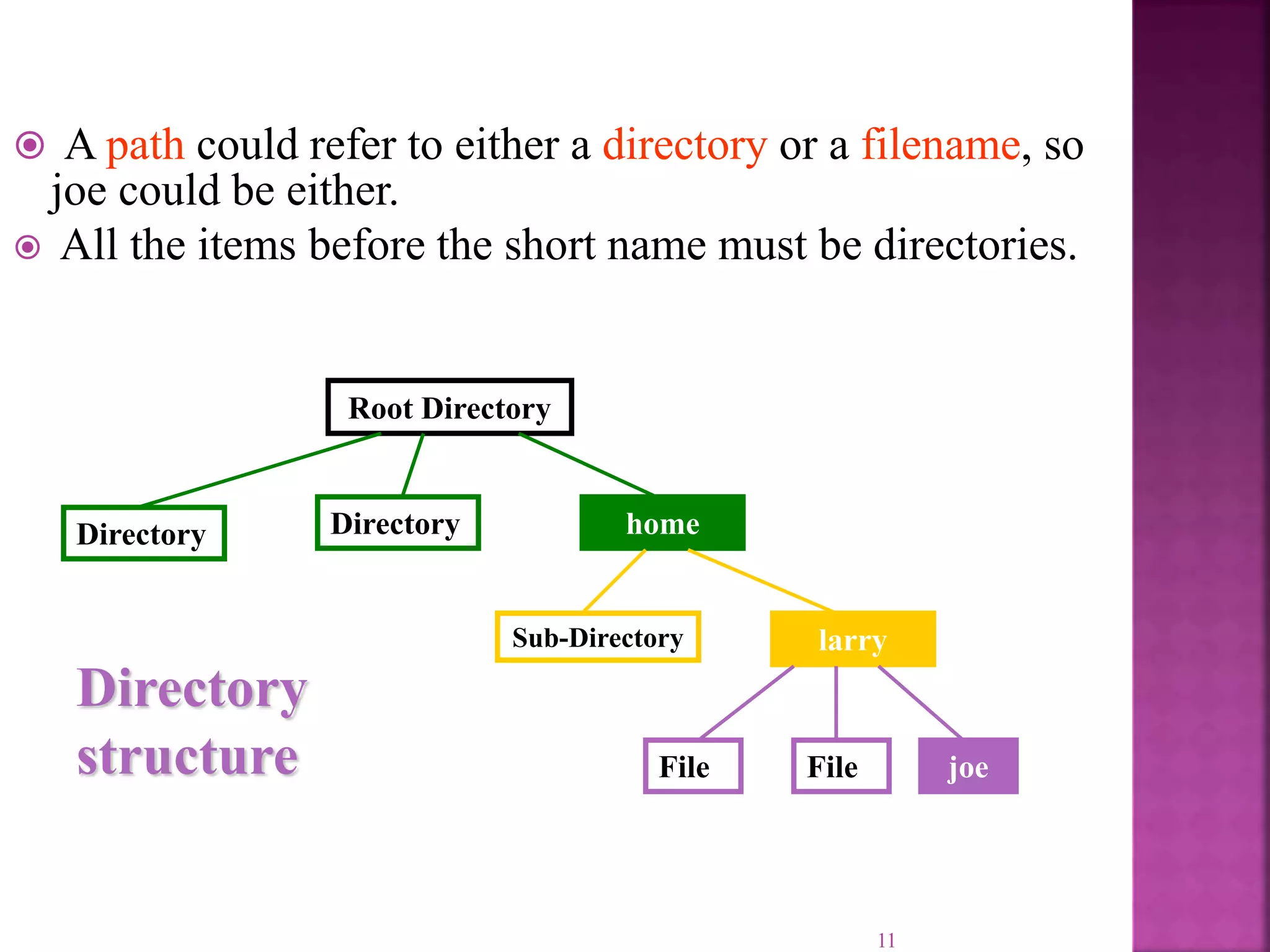
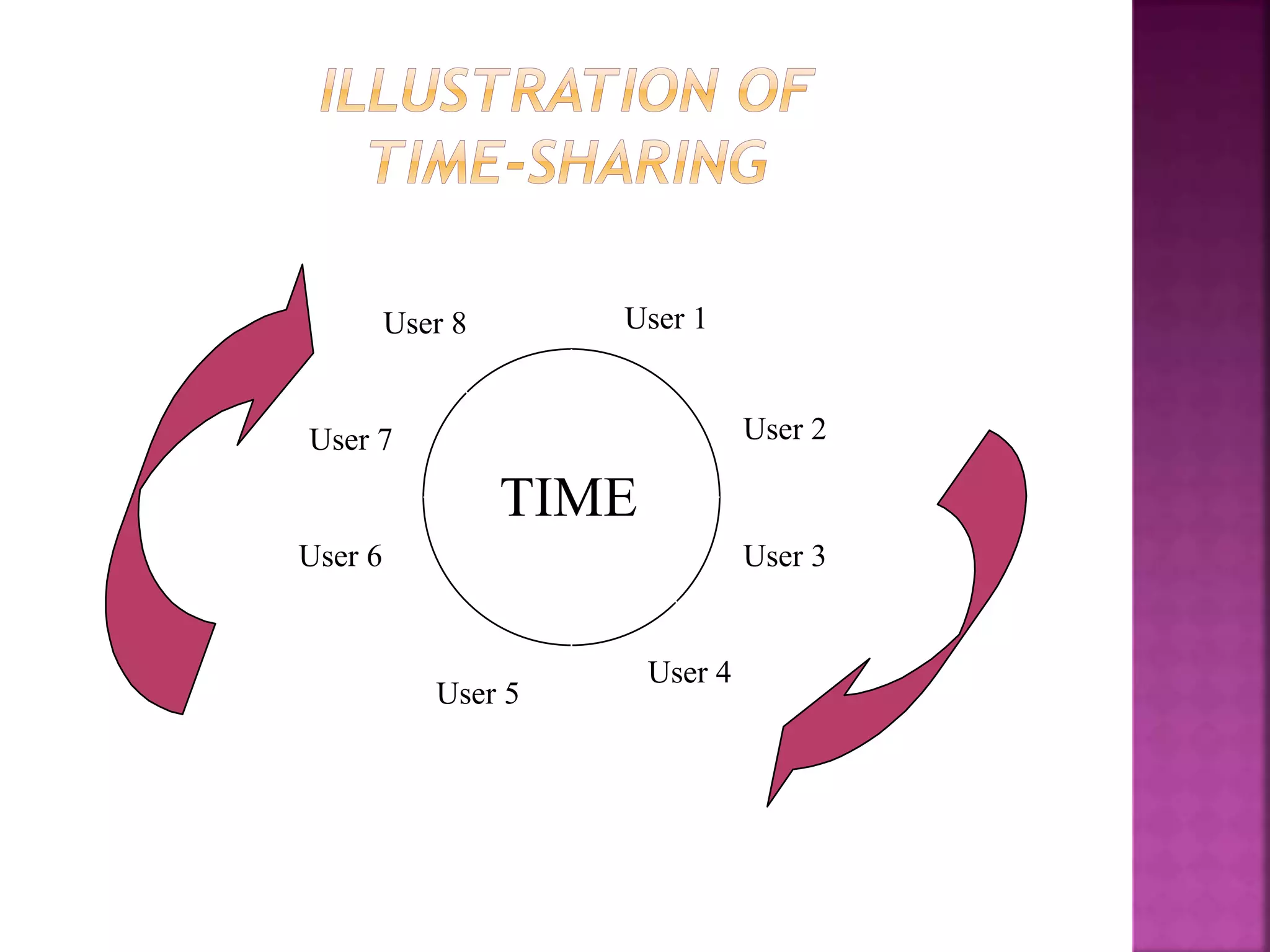
The document discusses the UNIX operating system. It describes UNIX as a stable, multi-user operating system developed in the 1960s for servers, desktops, and laptops. The UNIX operating system consists of three main parts: the kernel, the shell, and programs. The kernel allocates resources and handles processes and communications, while the shell acts as an interface between the user and kernel. There are various versions of UNIX that share common features.