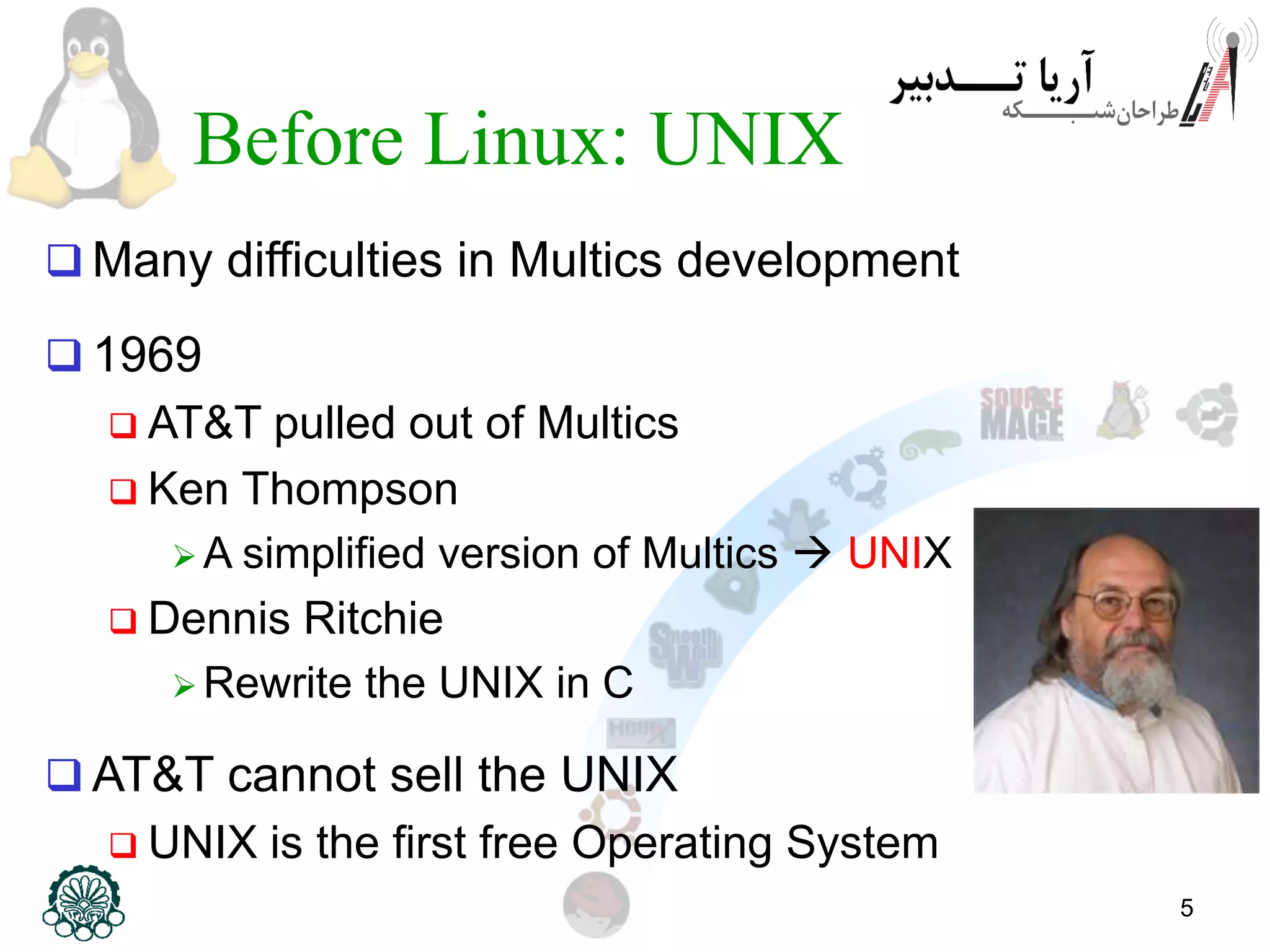
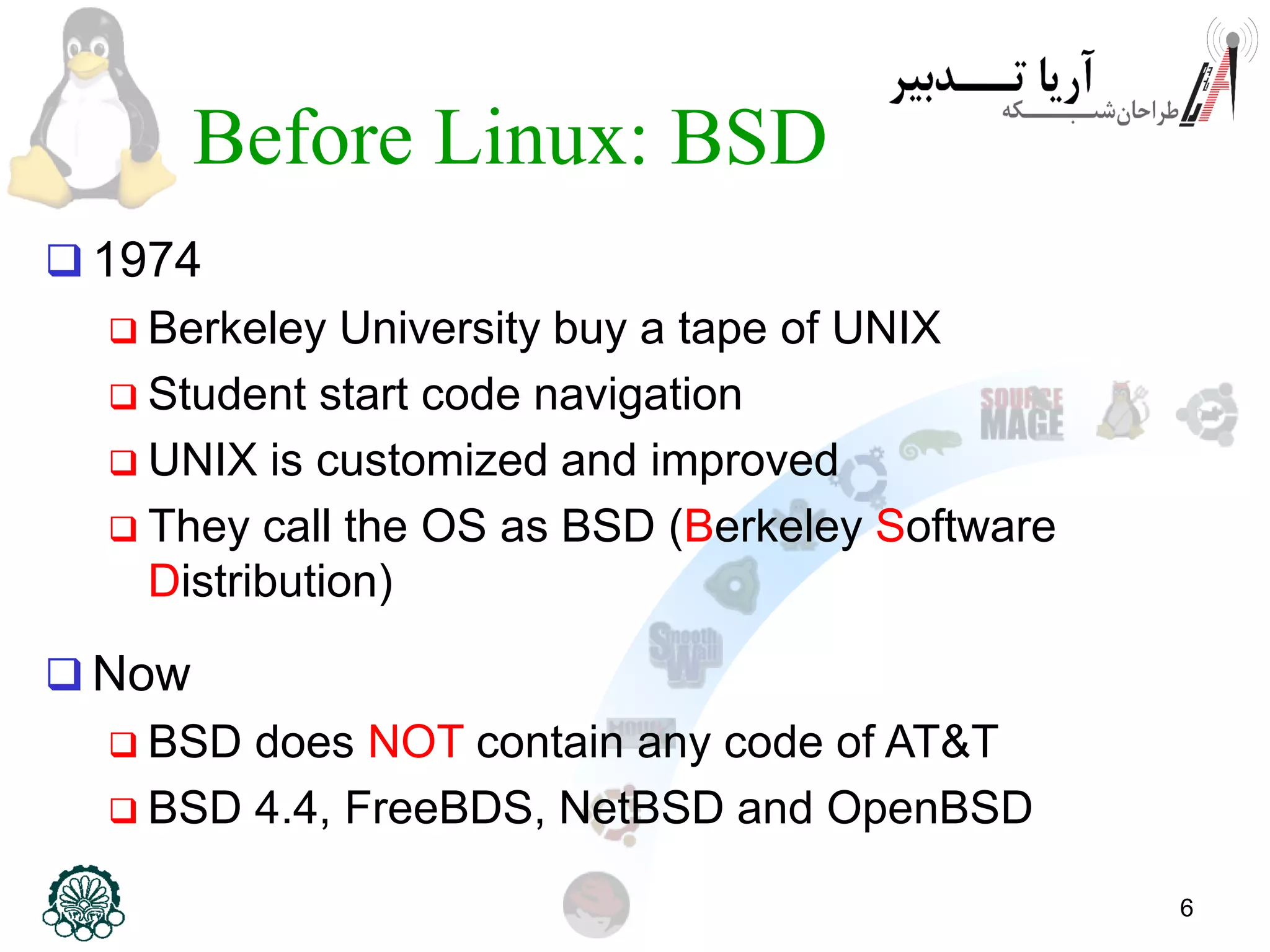
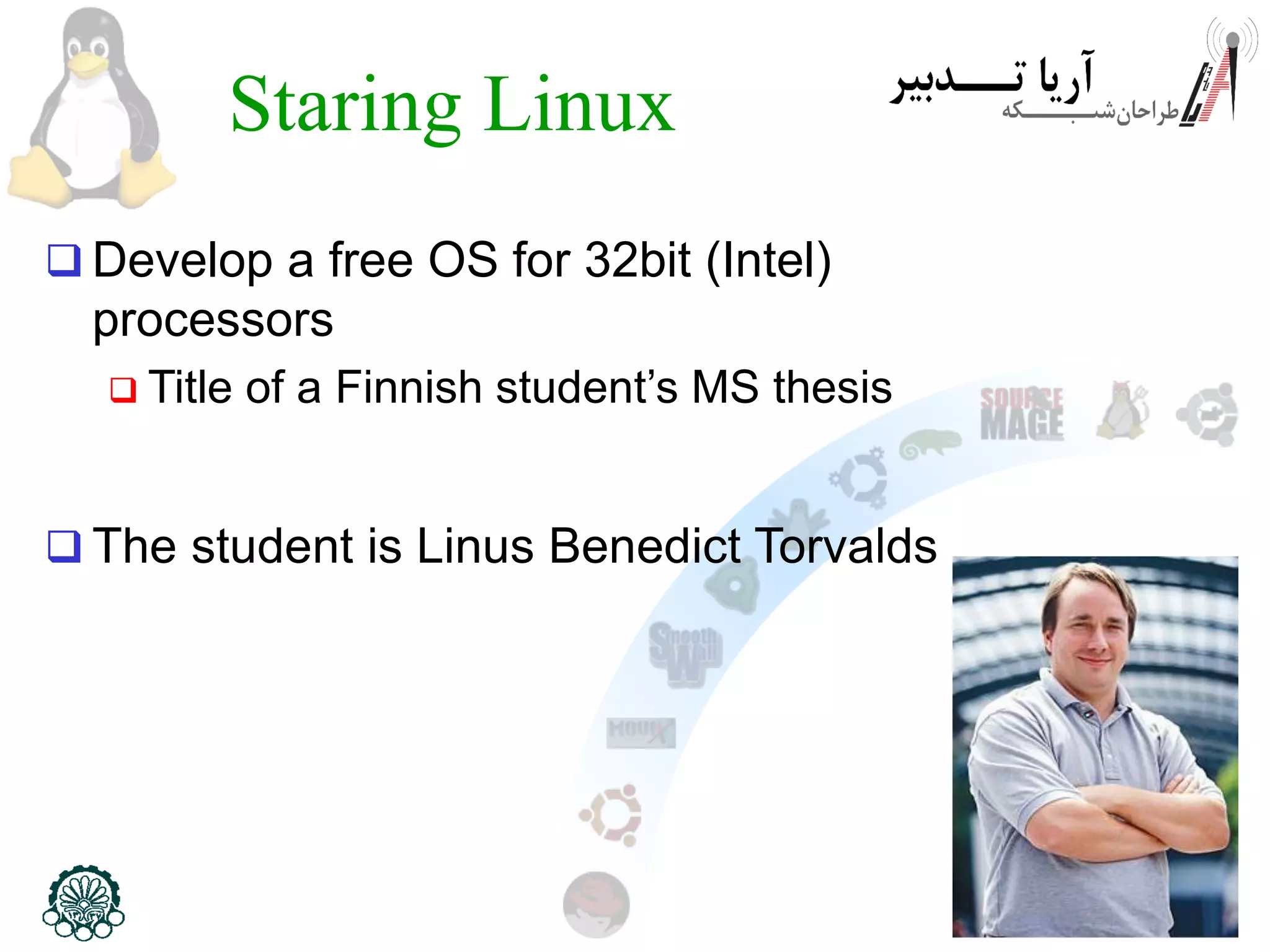
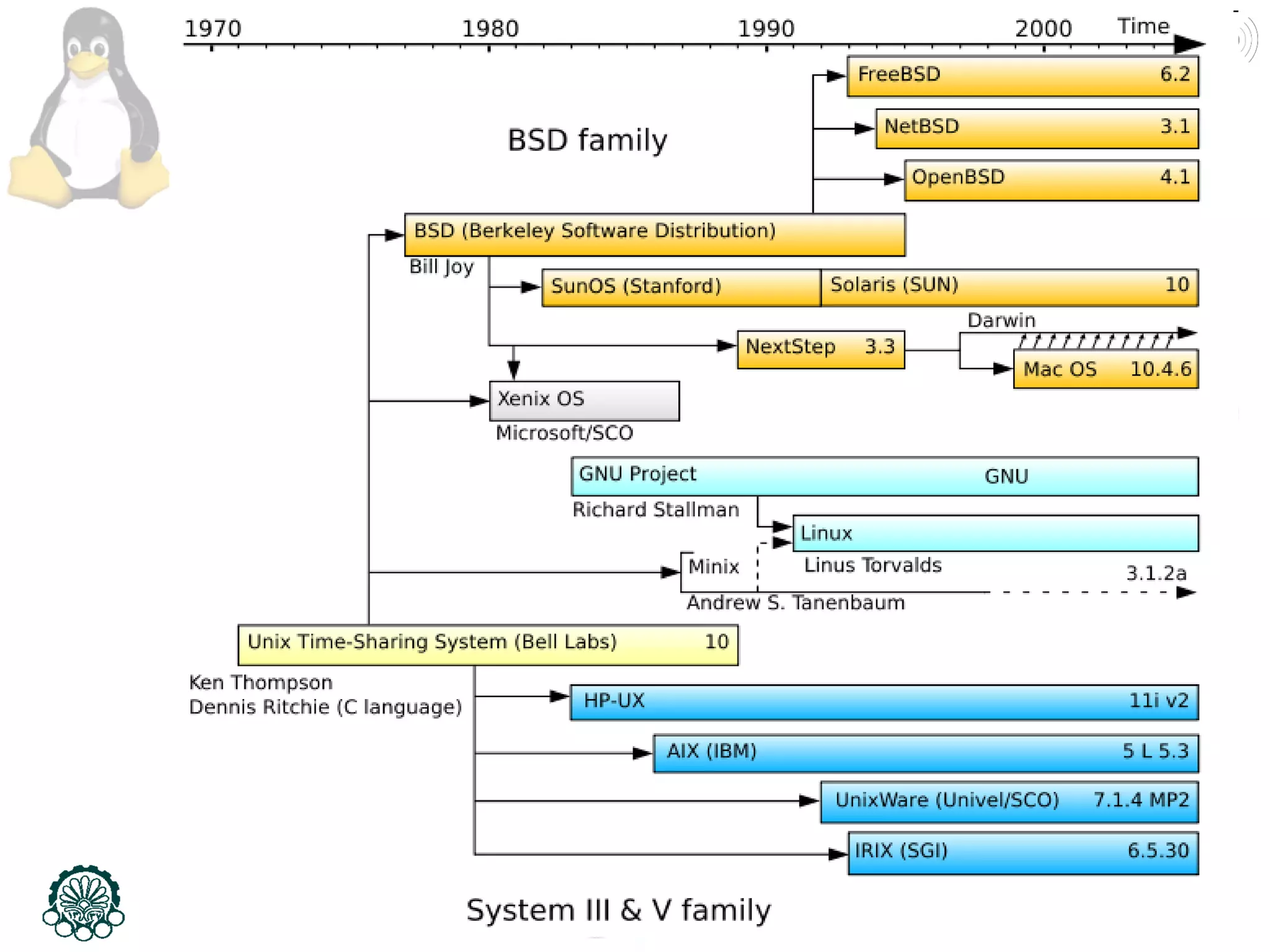
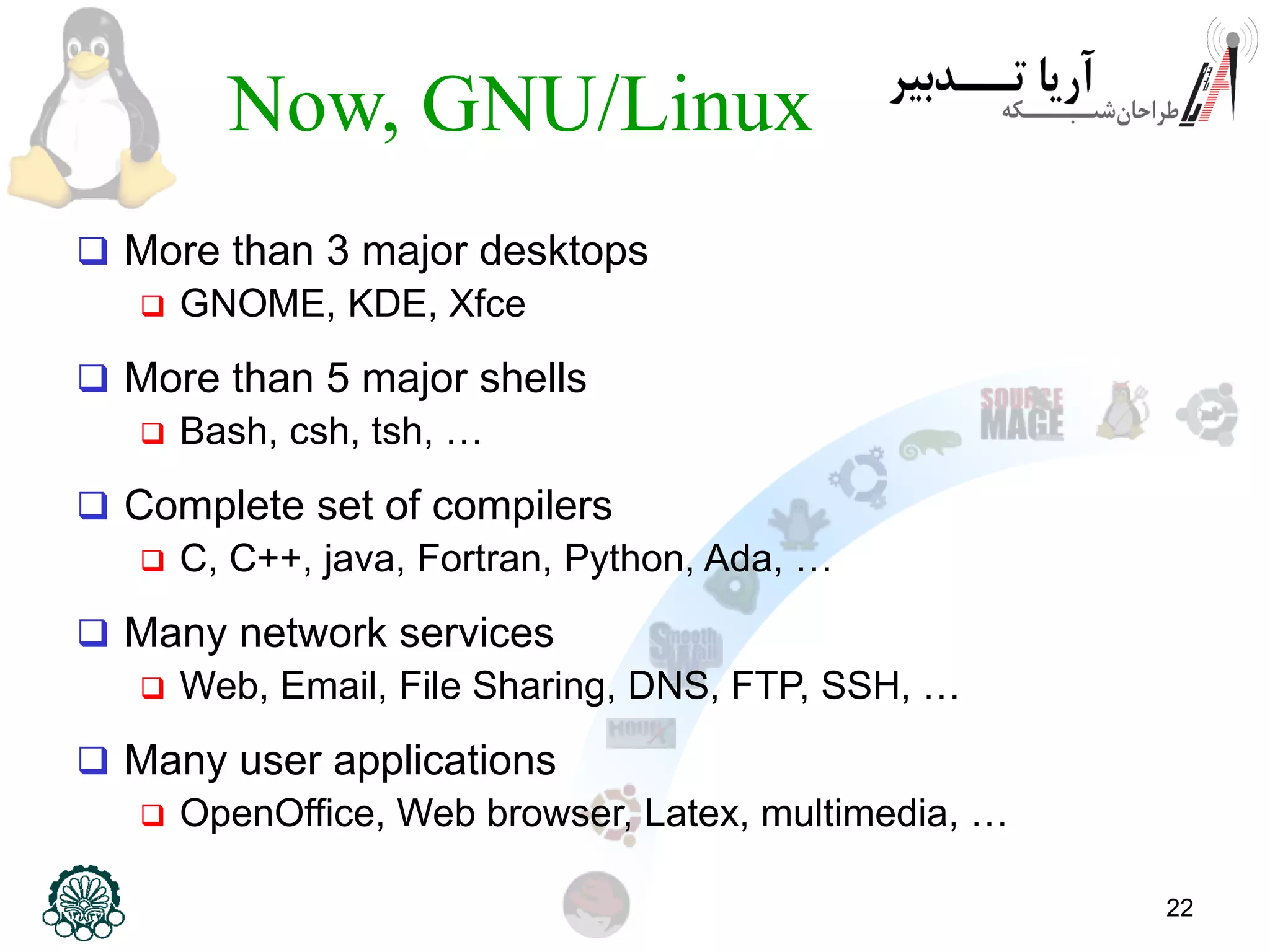
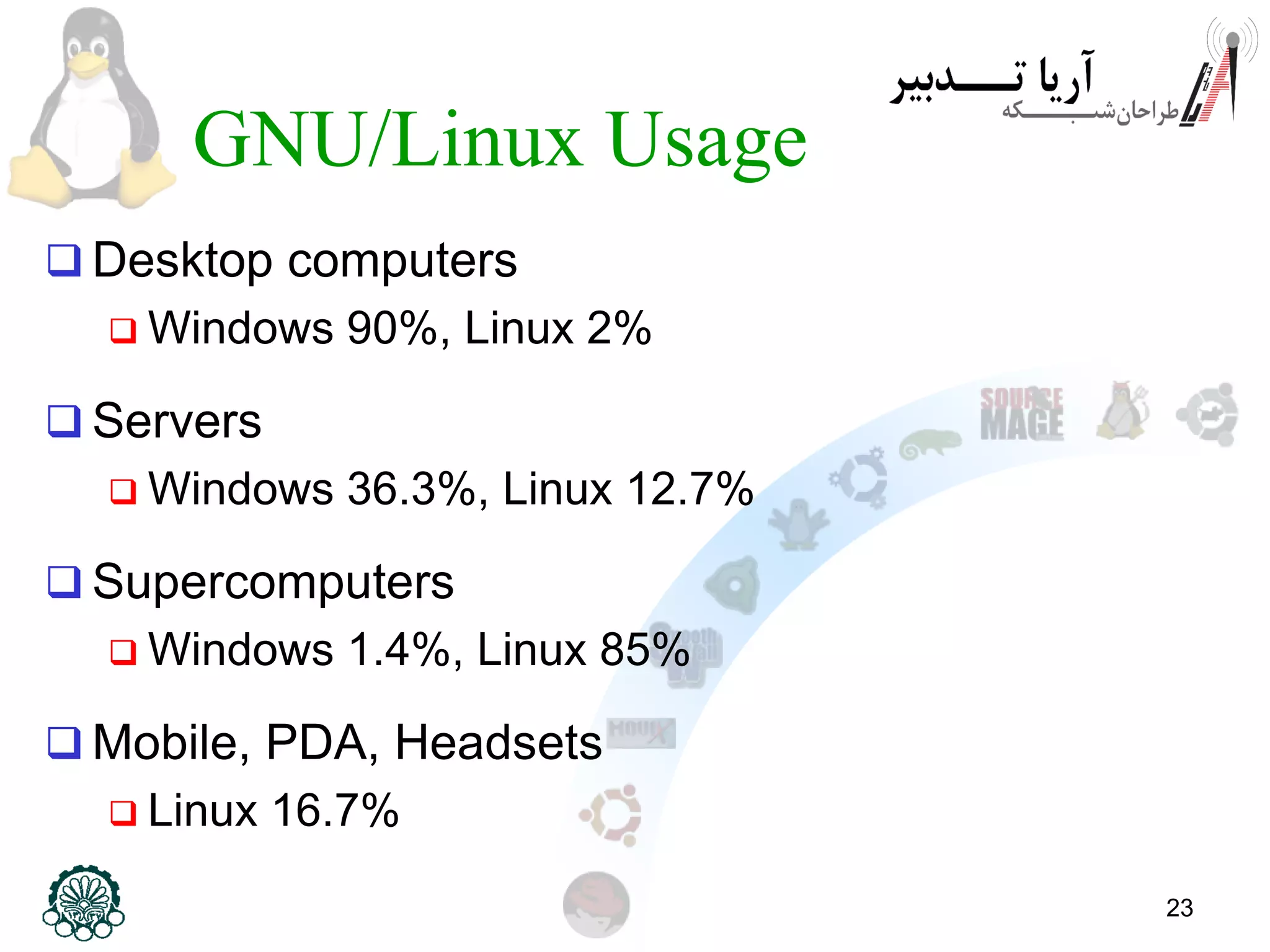
This document provides an introduction to the Linux operating system, including its history and development. It discusses early operating systems like Multics and UNIX that influenced Linux. It describes the development of Linux by Linus Torvalds in 1991 to create a free operating system for Intel processors. It explains that Linux is an operating system kernel that requires additional software like the GNU project to function as a full operating system, called GNU/Linux. The document outlines some advantages of GNU/Linux like stability, security, and free access, as well as some disadvantages like a learning curve and limited application support. It encourages computer engineers to learn Linux due to its importance in technical fields.