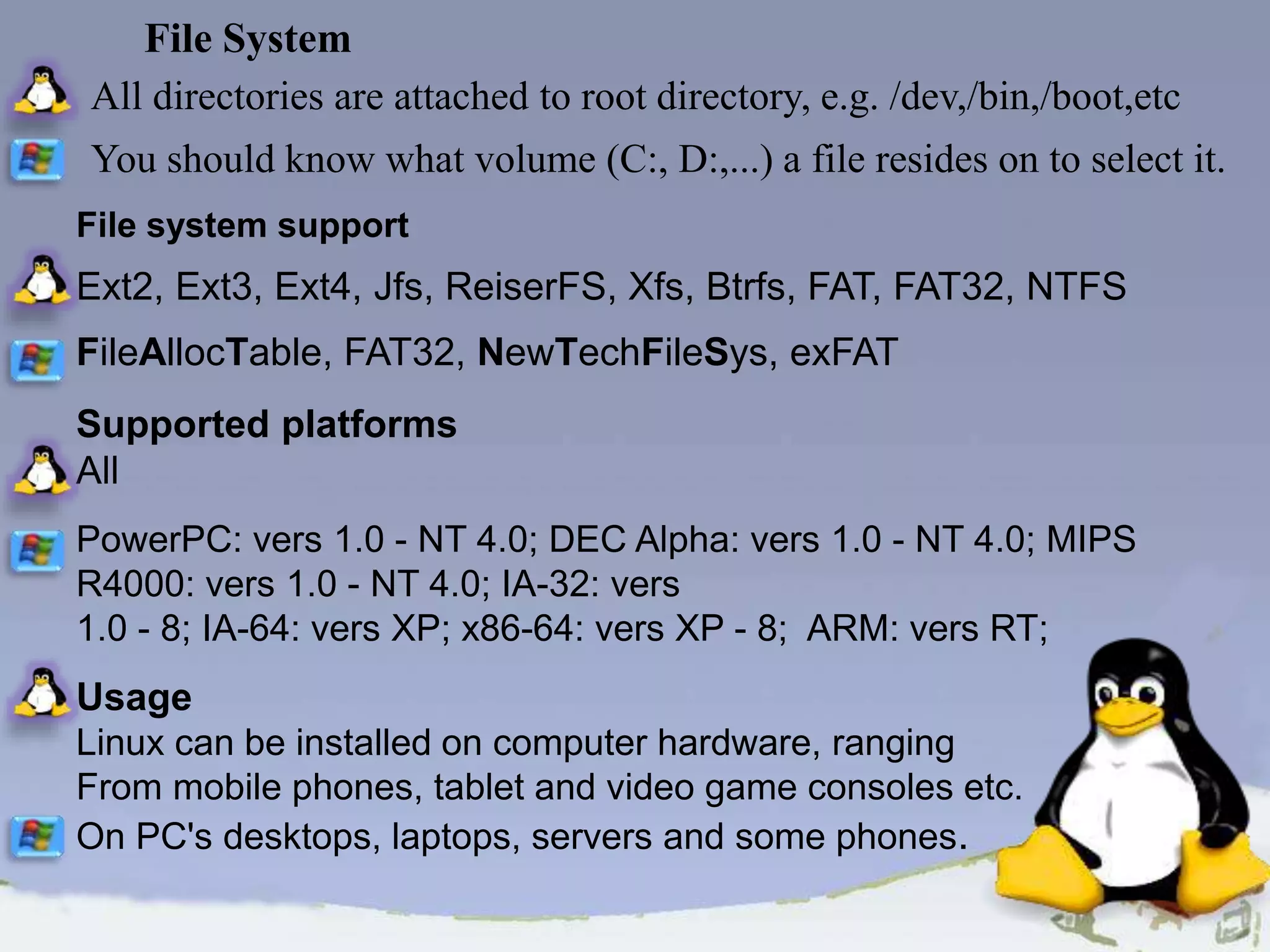
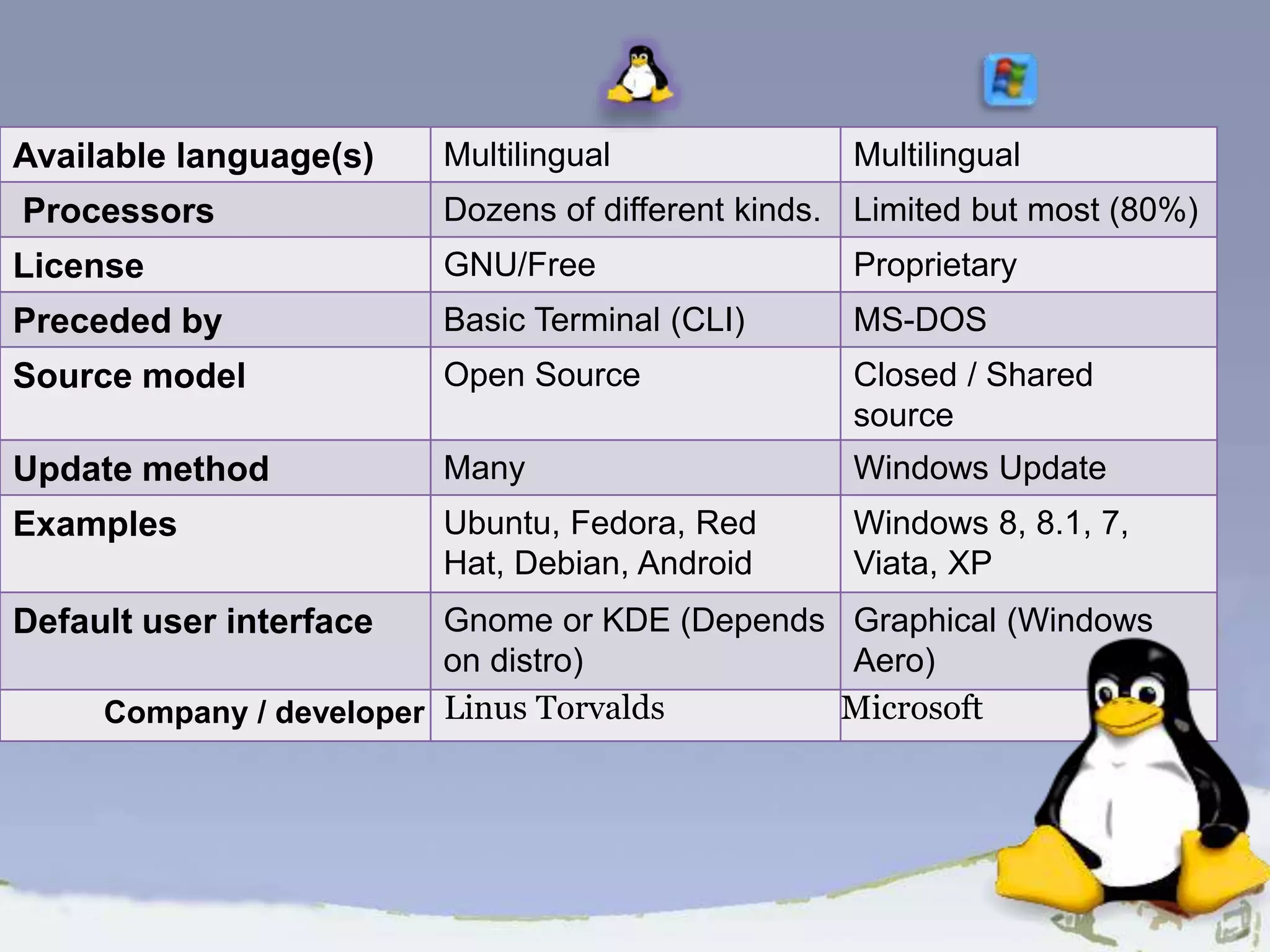
The document discusses the history, definition, and characteristics of Linux, an open-source operating system created by Linus Torvalds. It compares Linux with other operating systems like Windows and highlights its advantages, such as lower cost, customization, and security. Additionally, it emphasizes the collaborative nature of Linux development and the significance of community contributions to its evolution.