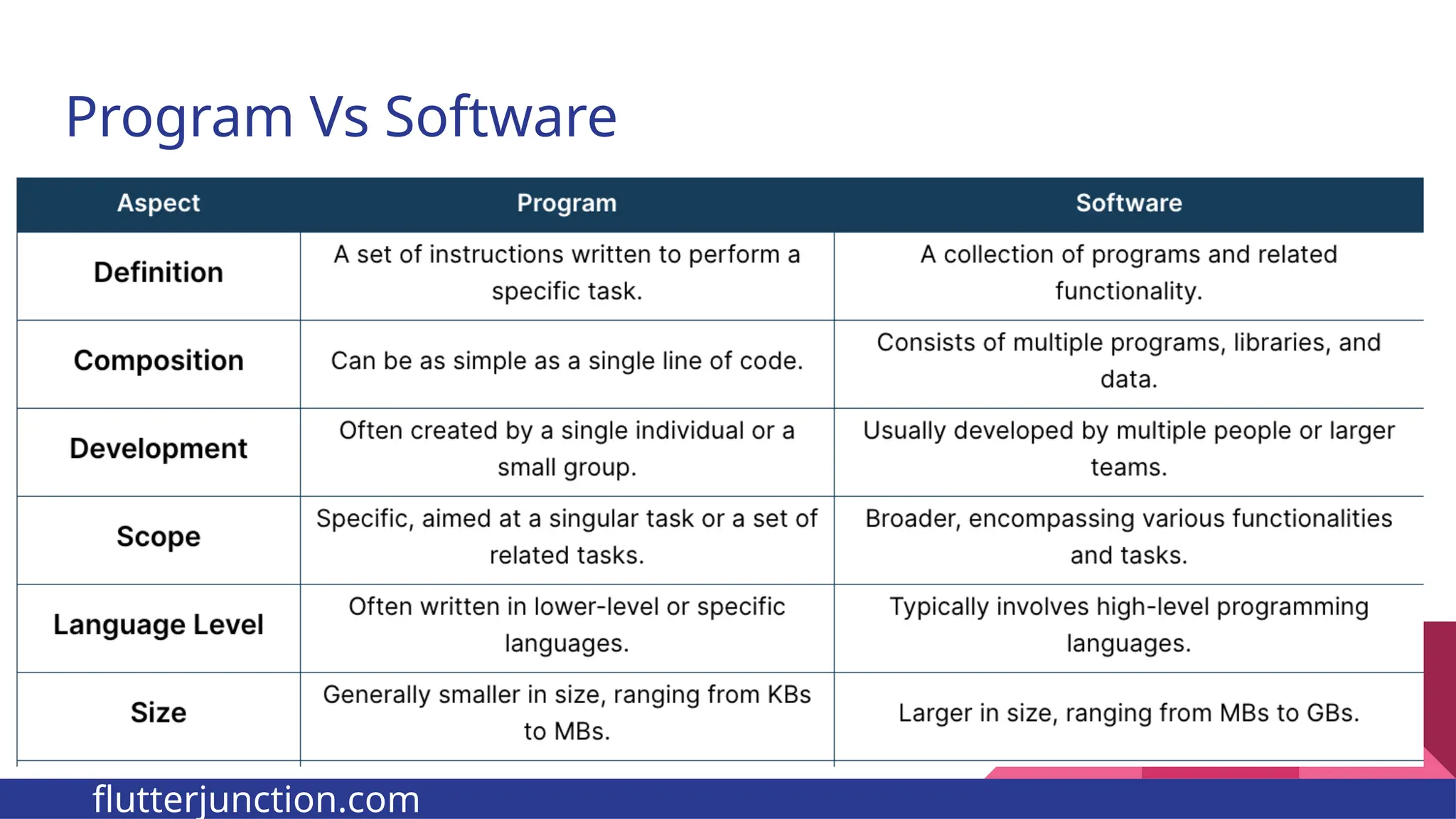
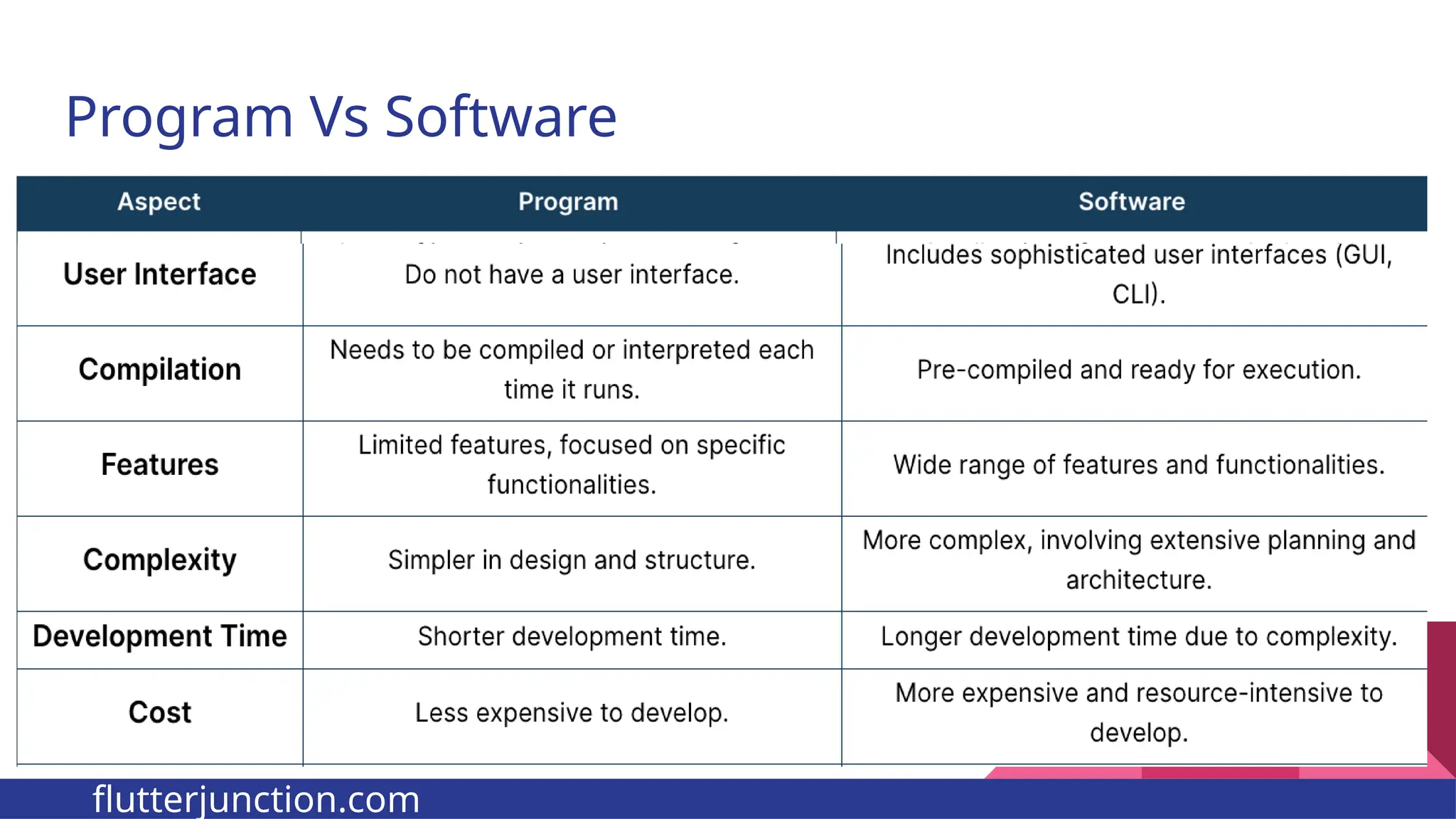
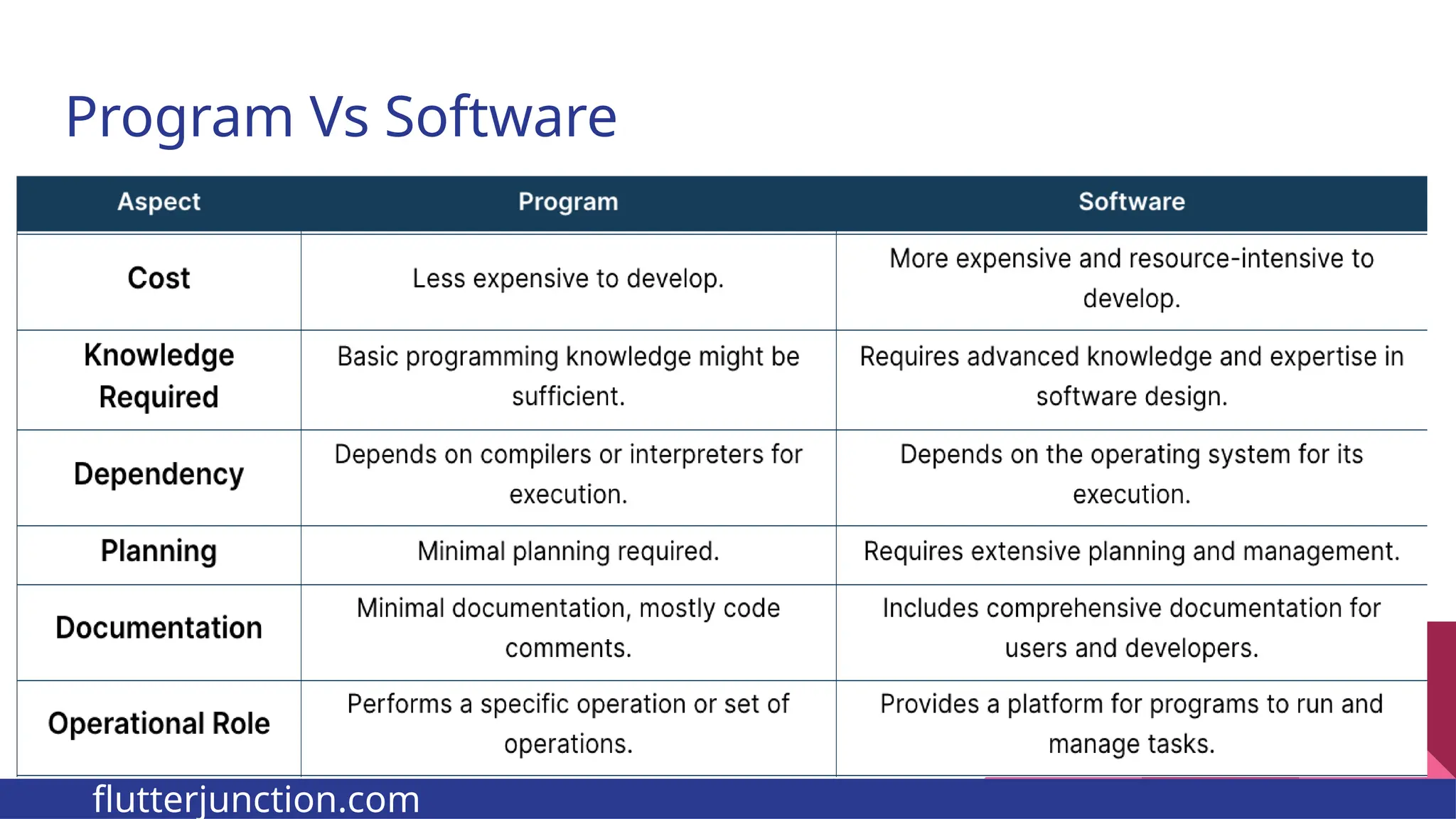
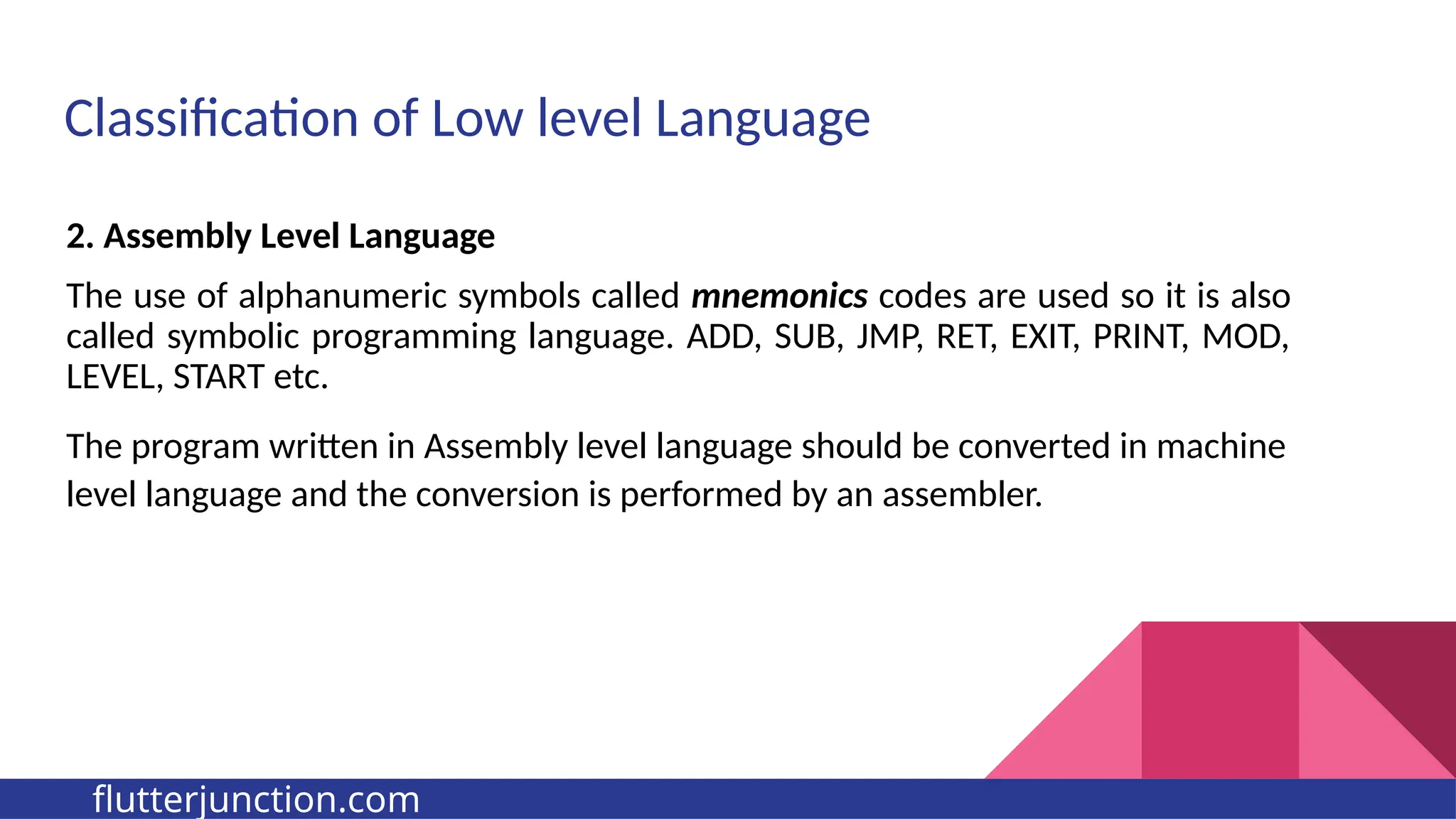
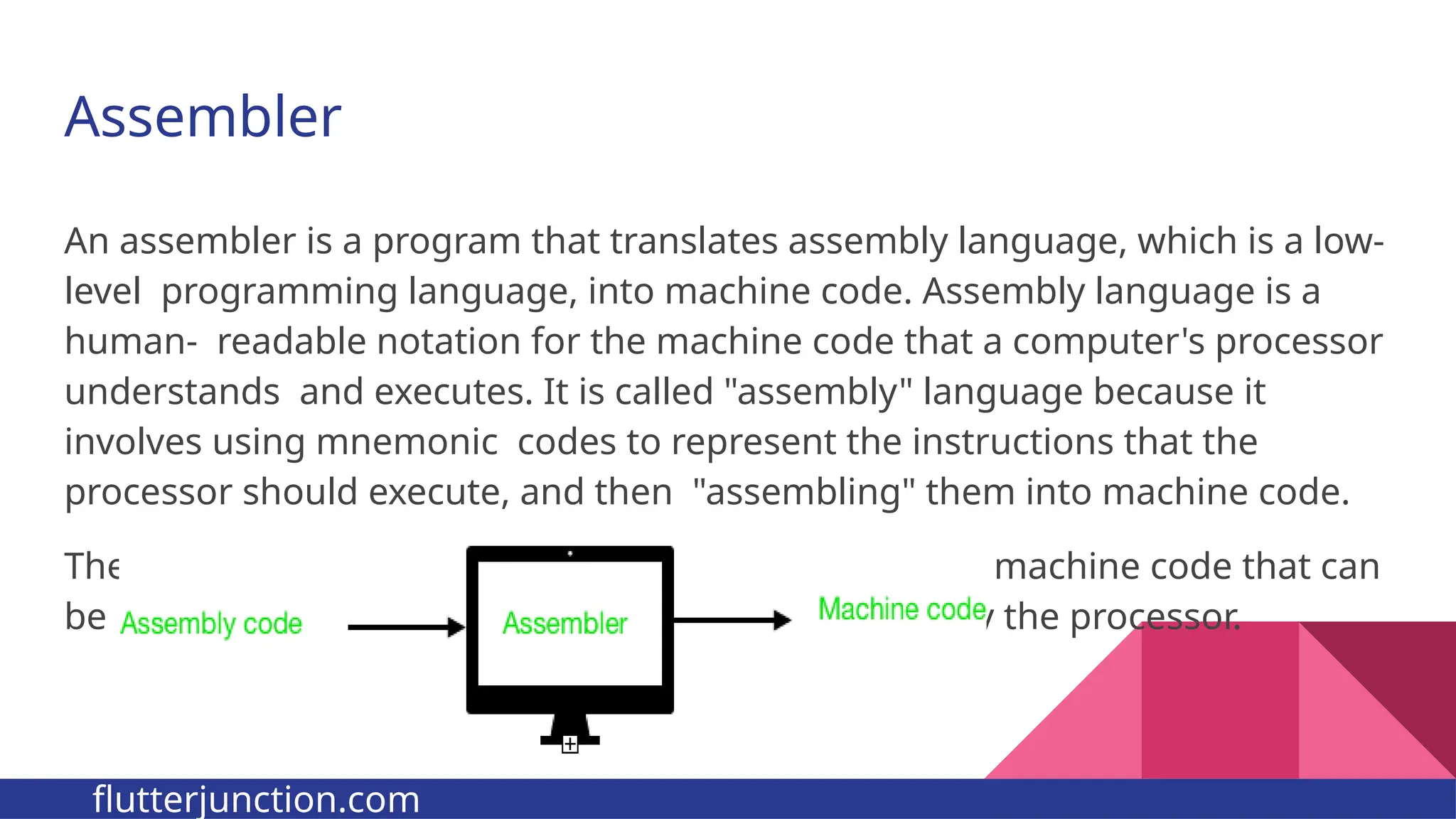
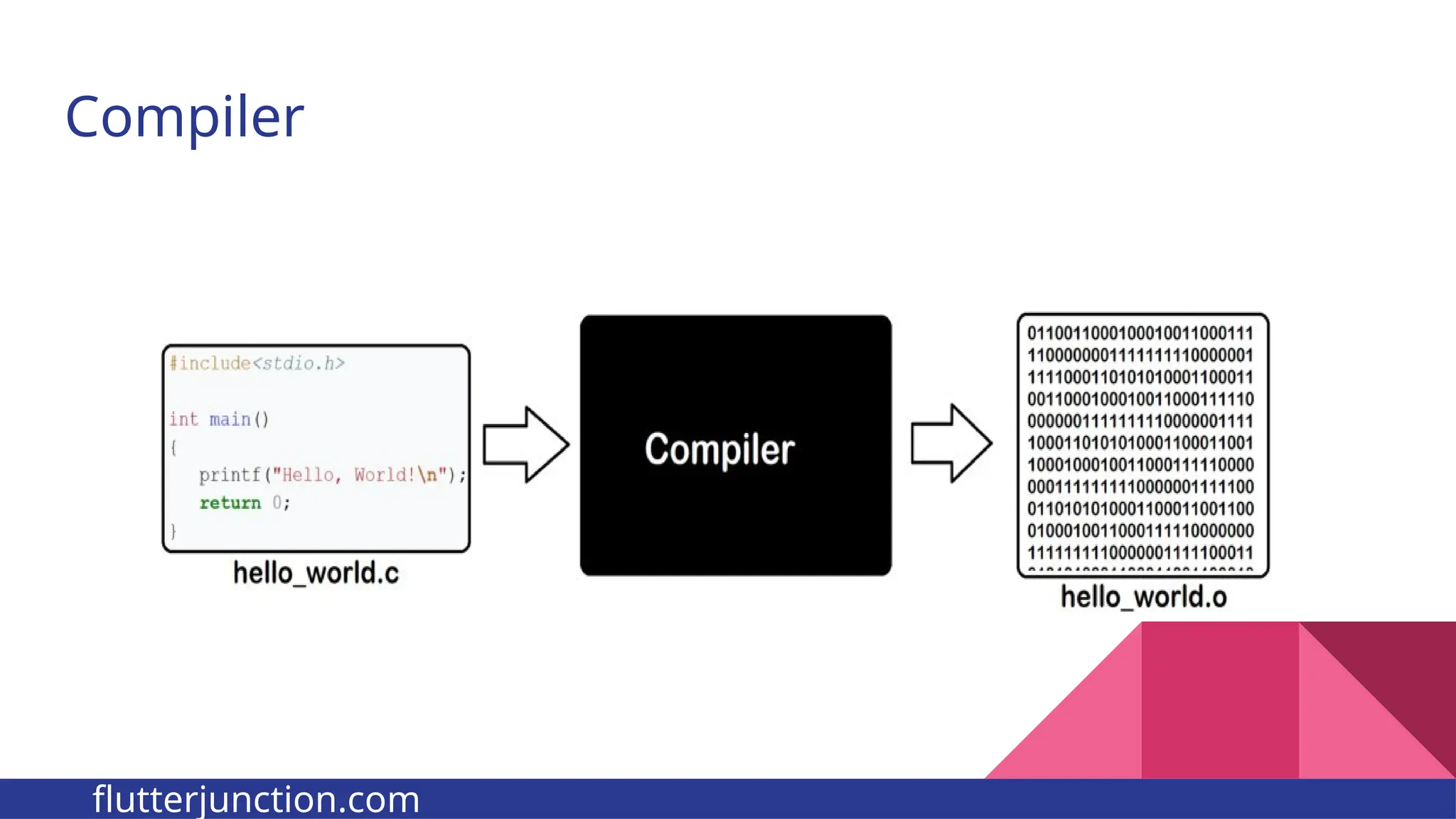
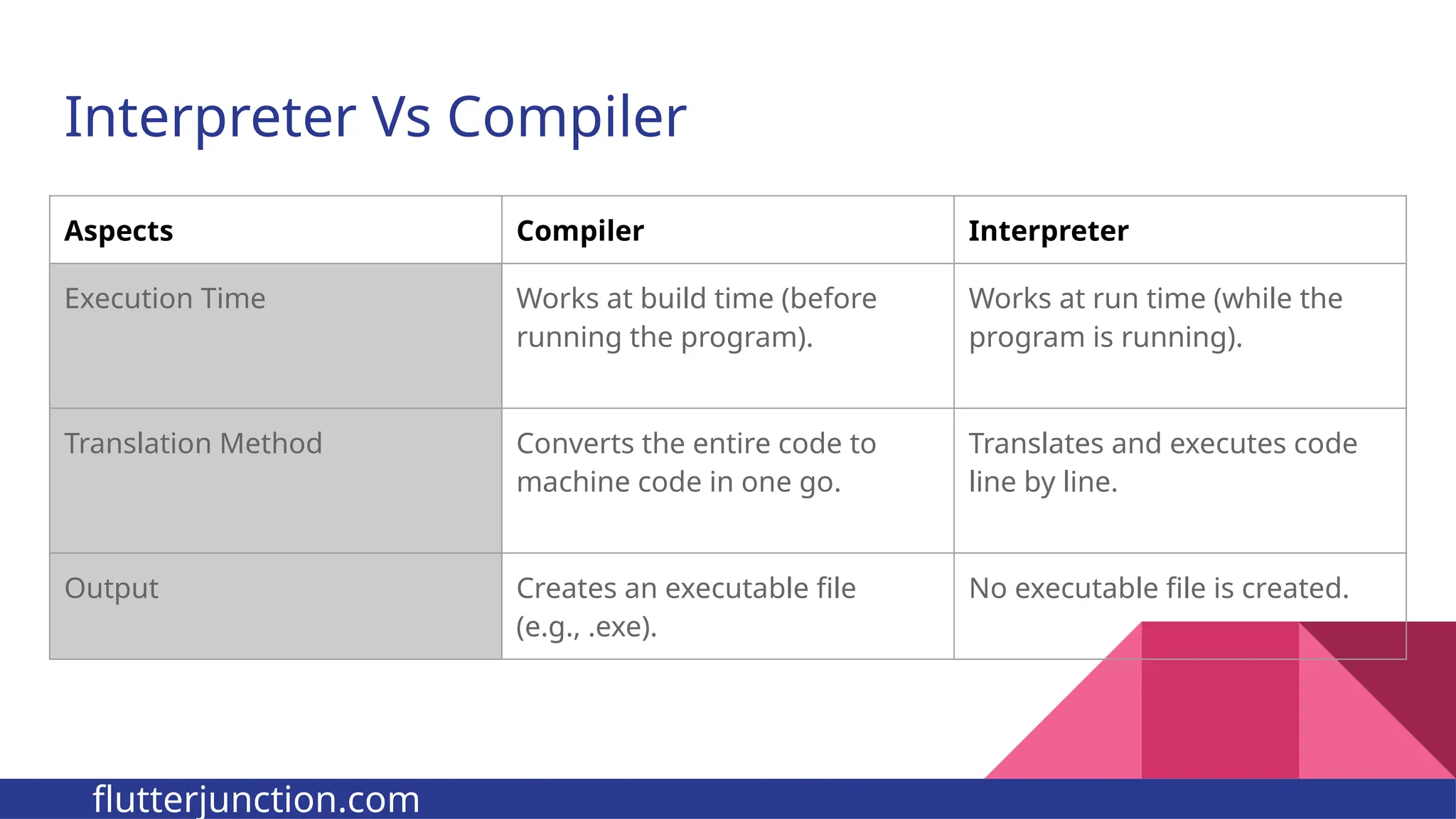
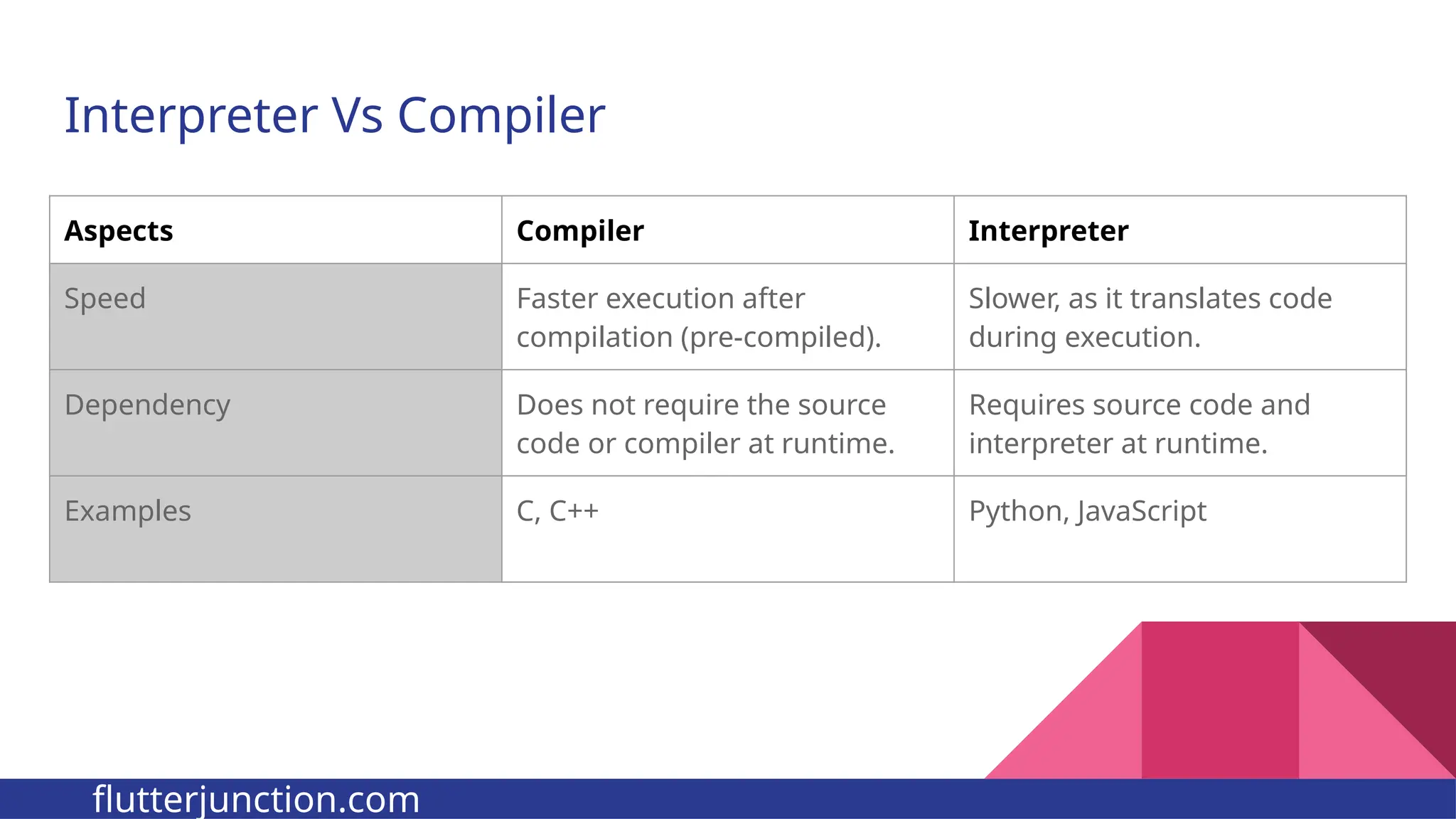
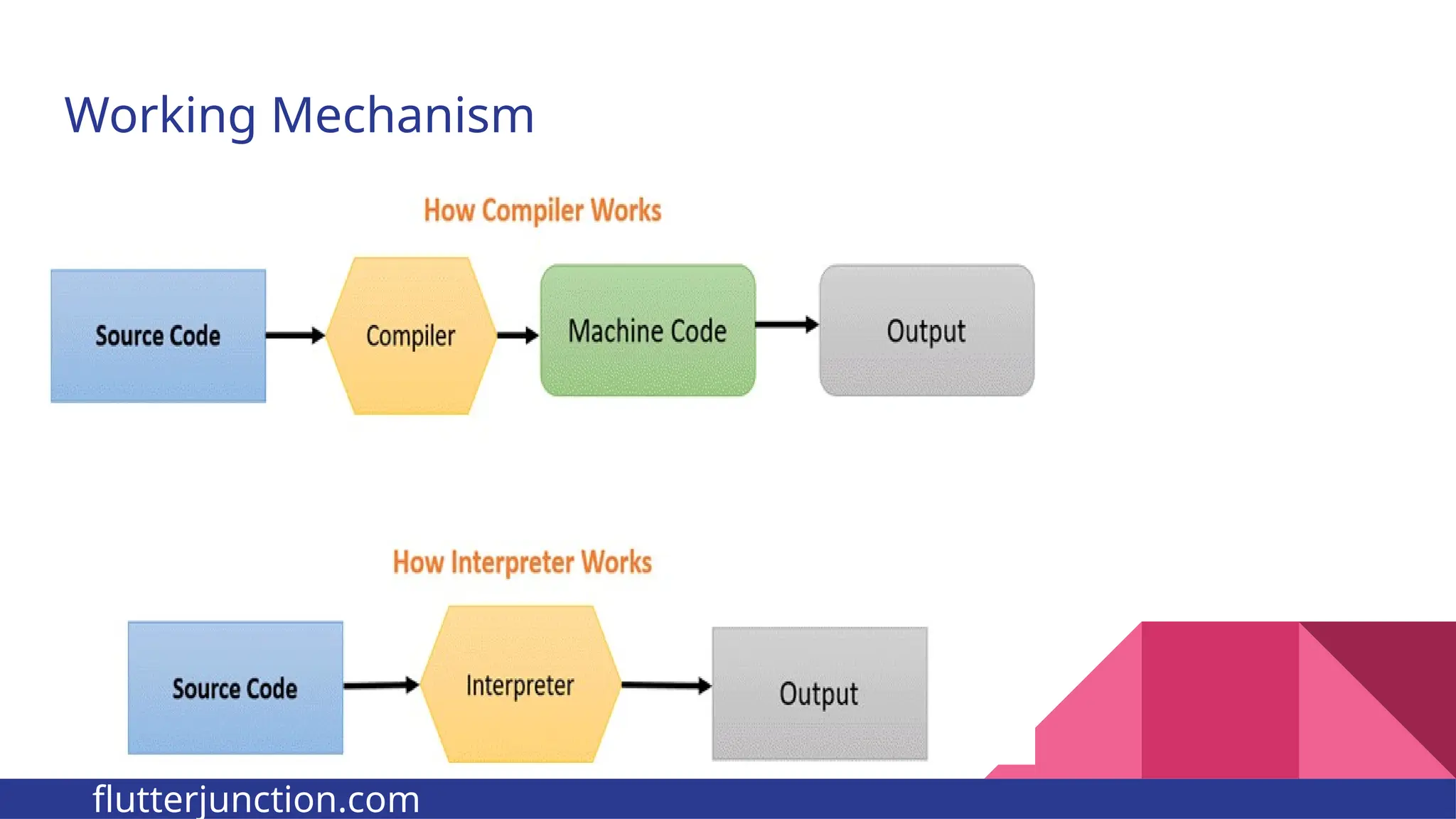
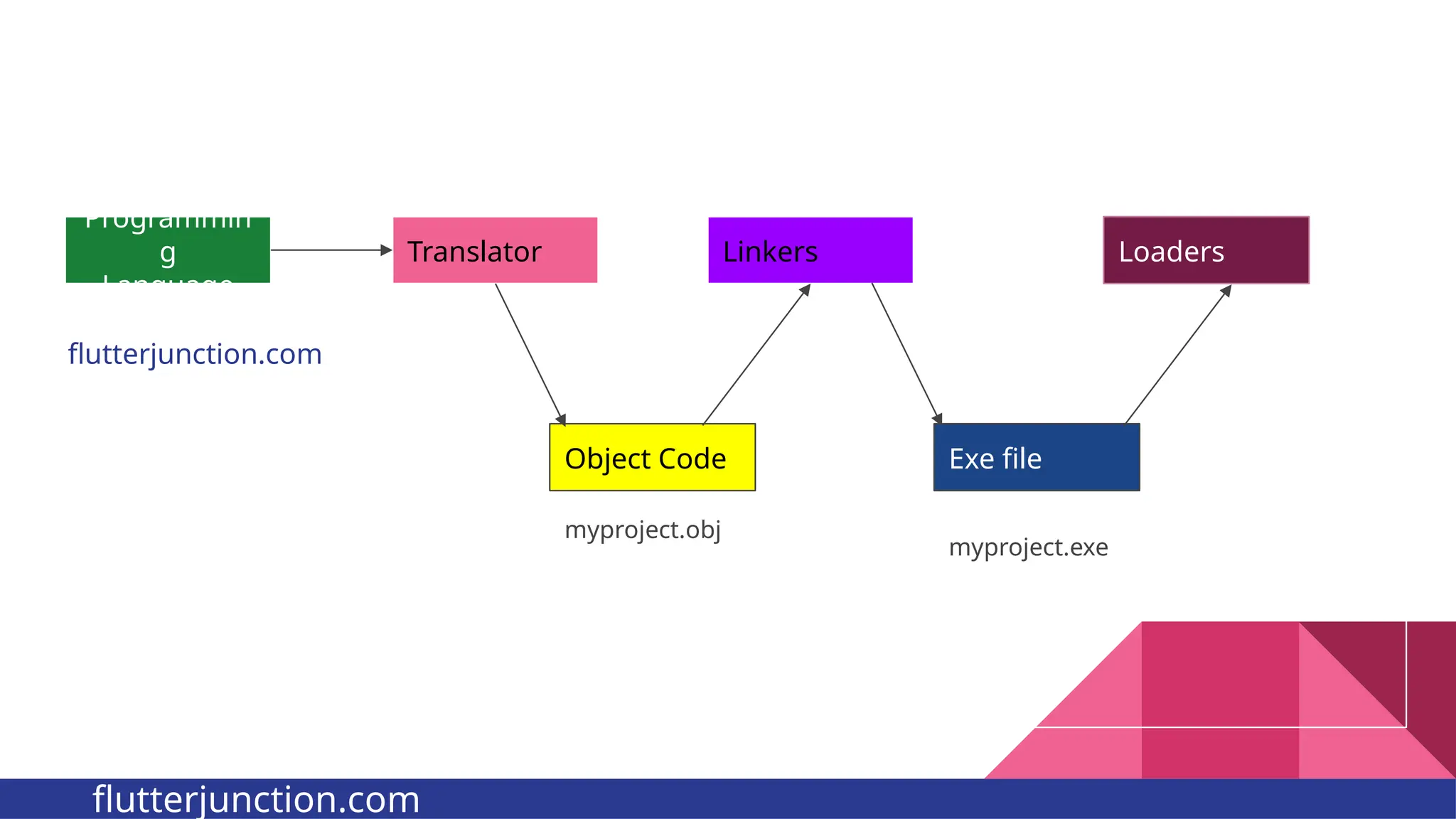
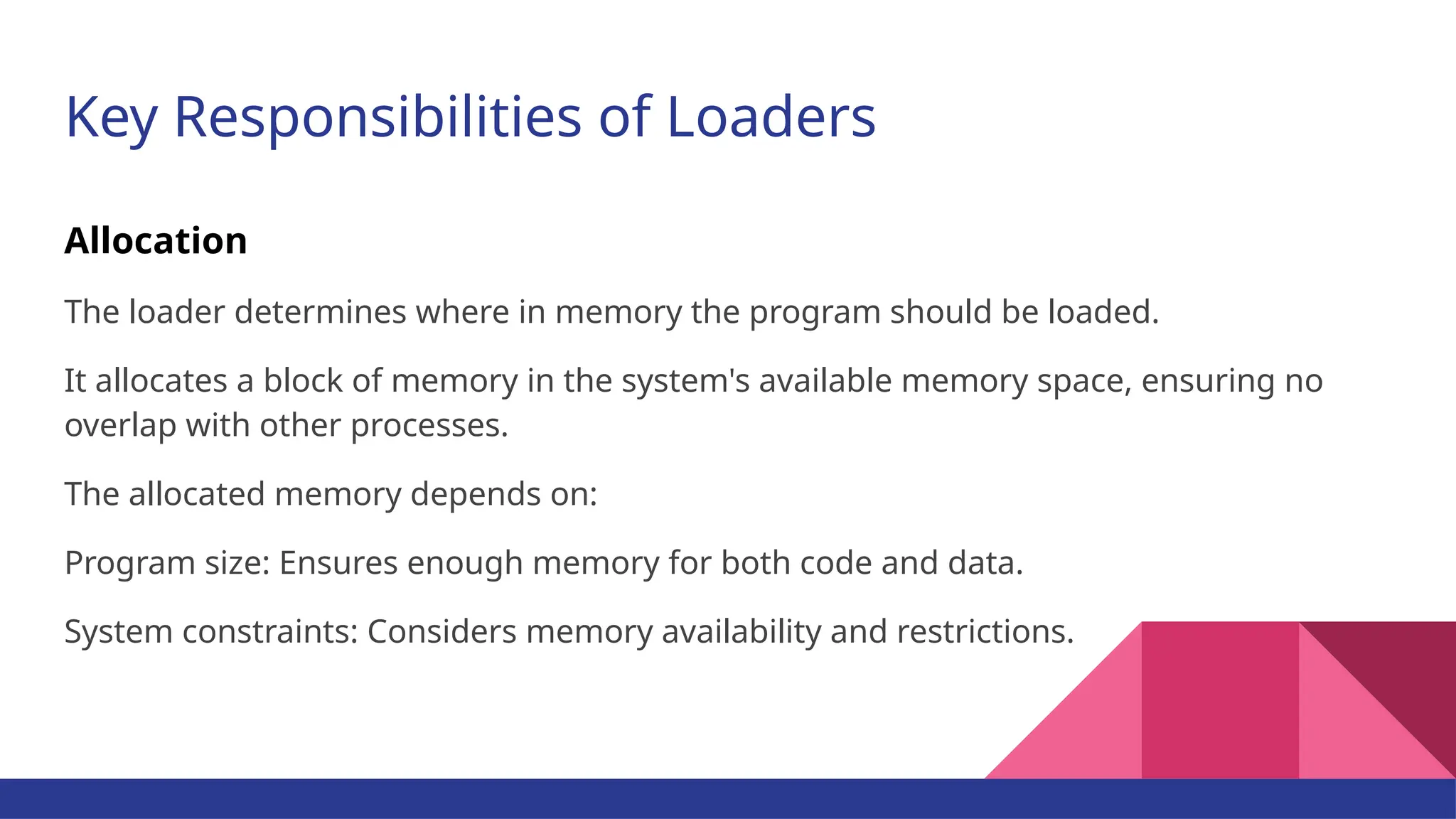
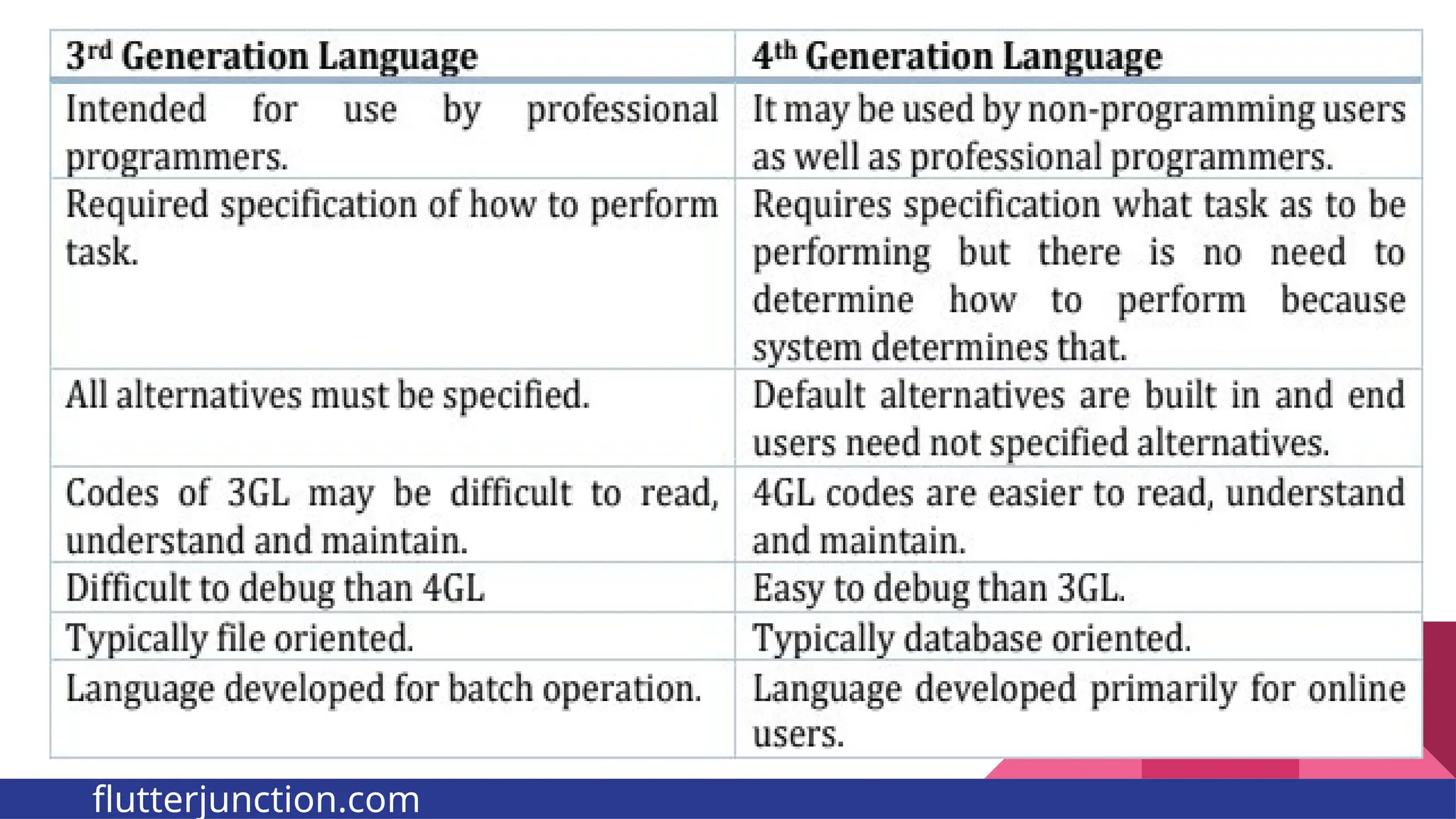
The document provides a comprehensive overview of programming languages, contrasting low-level and high-level languages, and discusses their characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. It also explains the role of programming language translators, including assemblers, compilers, and interpreters, as well as linkers and loaders in the software development process. Additionally, the document classifies computer languages into generations, highlighting the evolution towards higher-level programming for ease of use and portability.