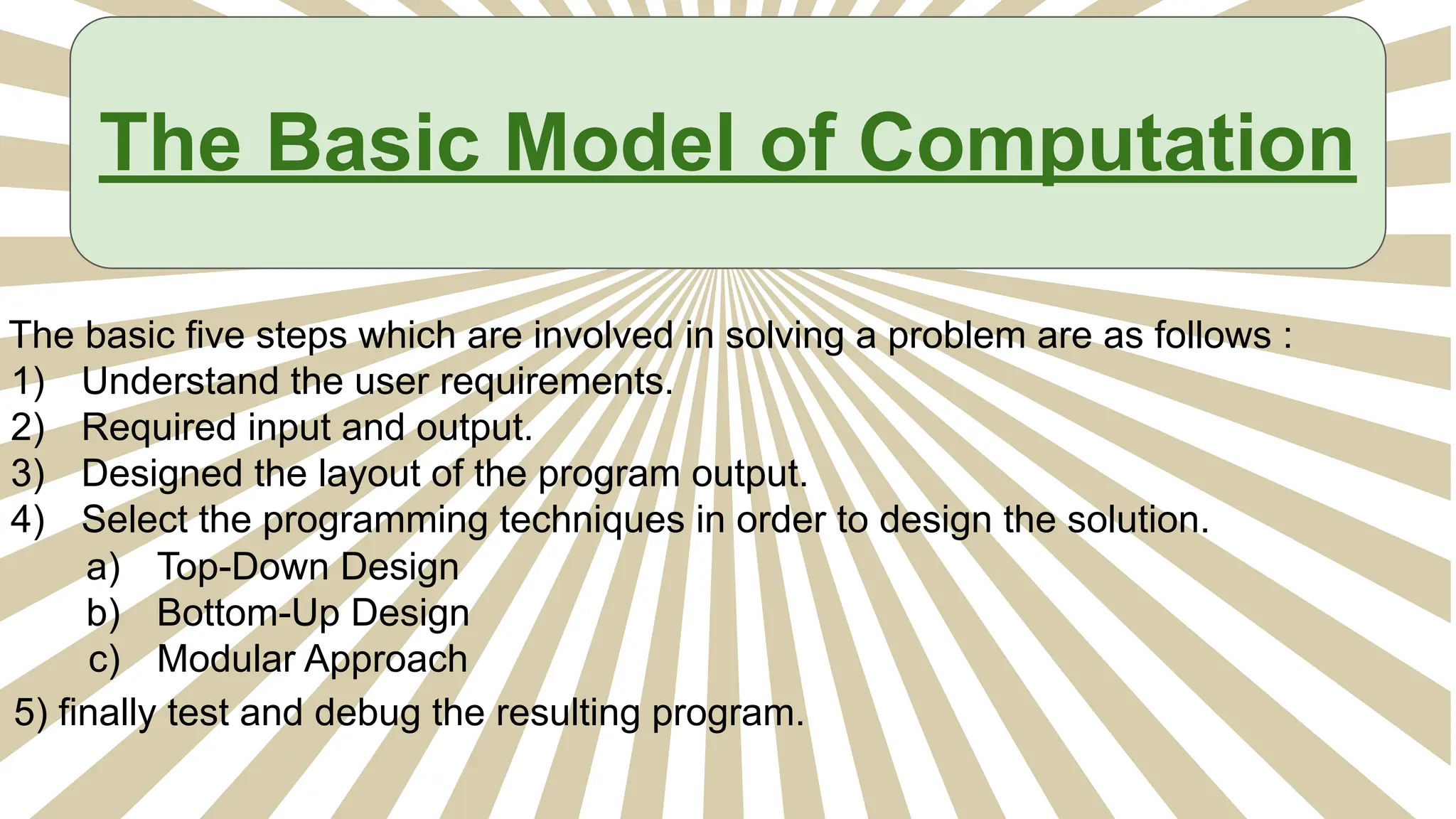
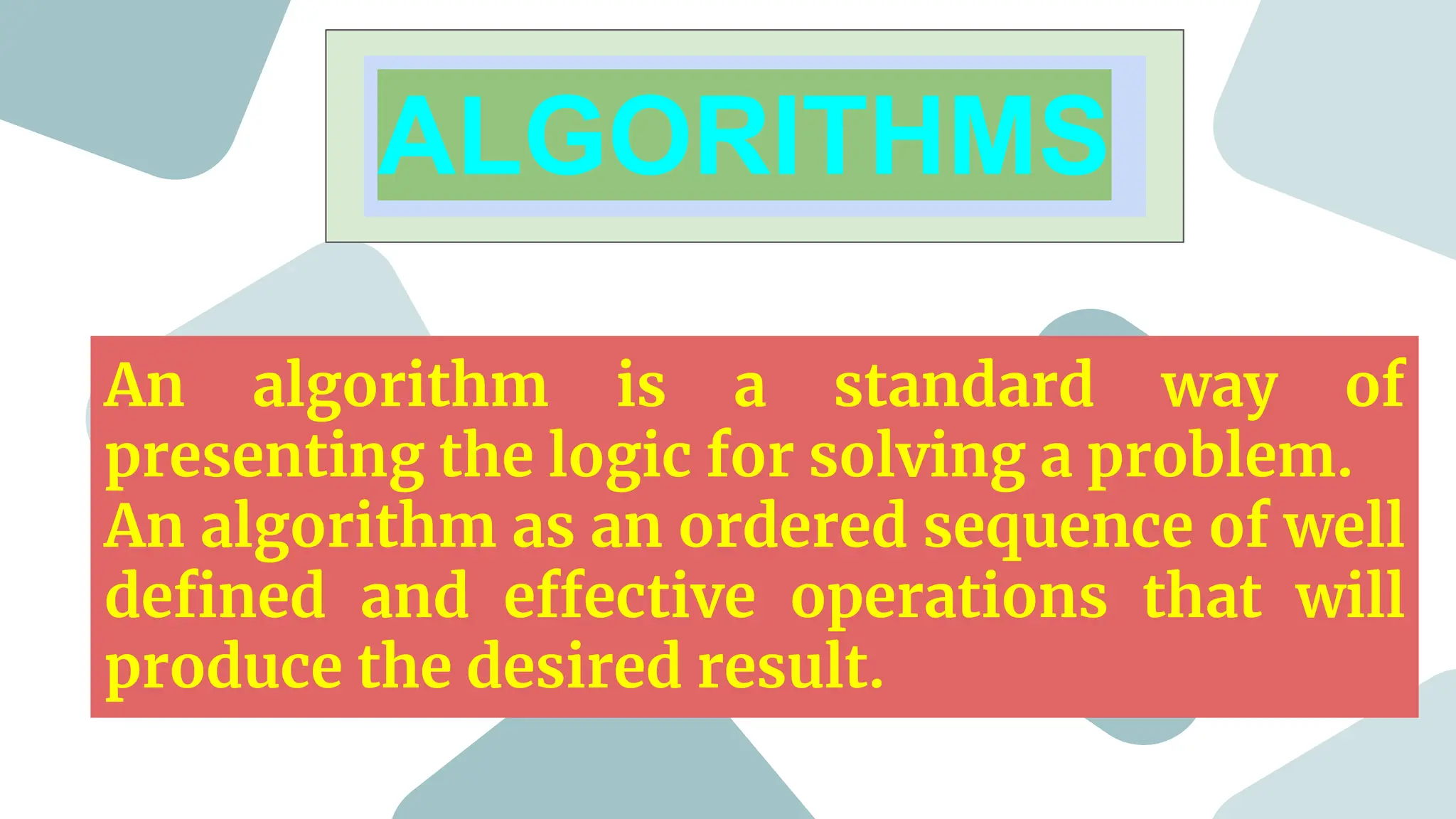
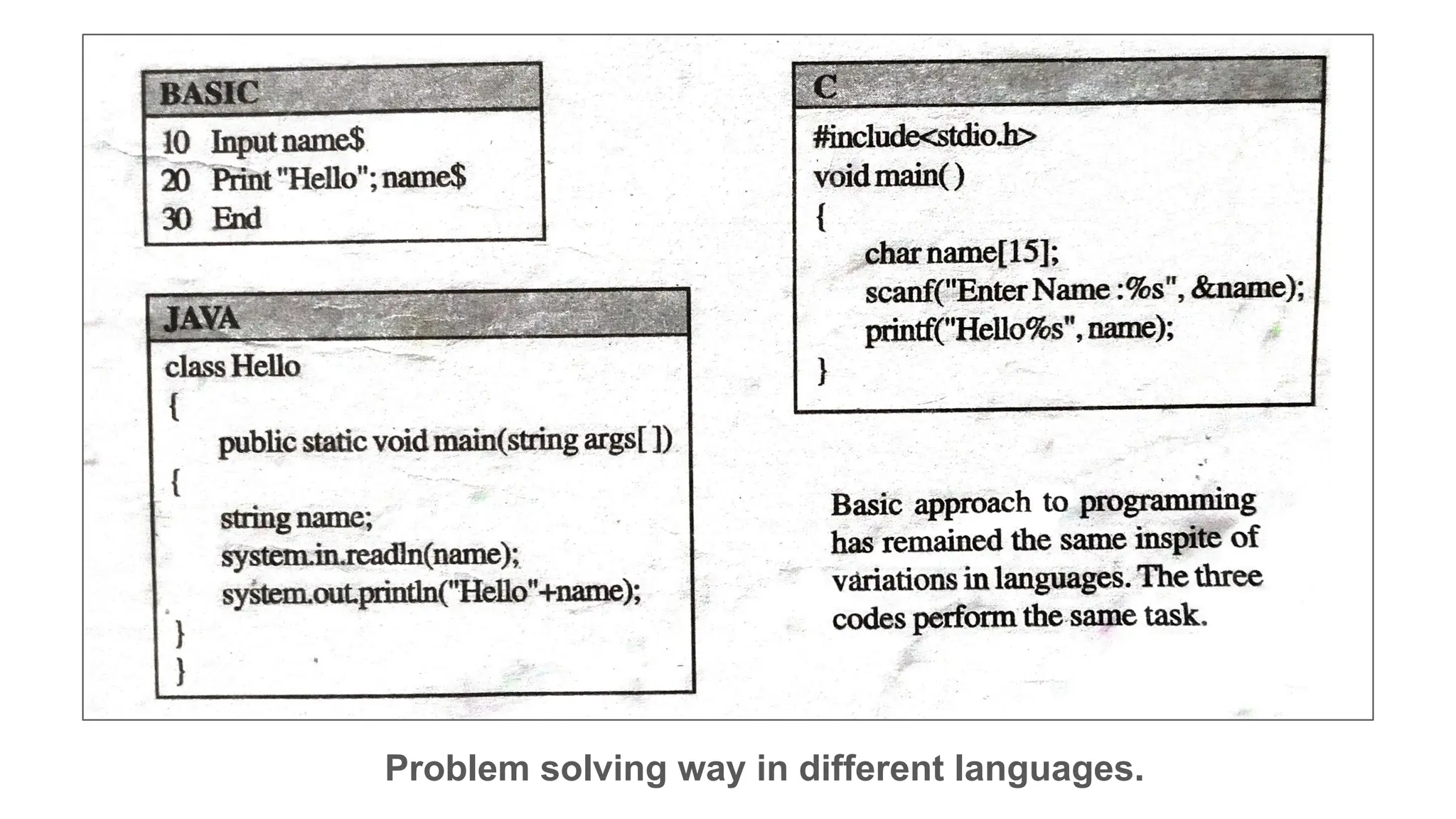
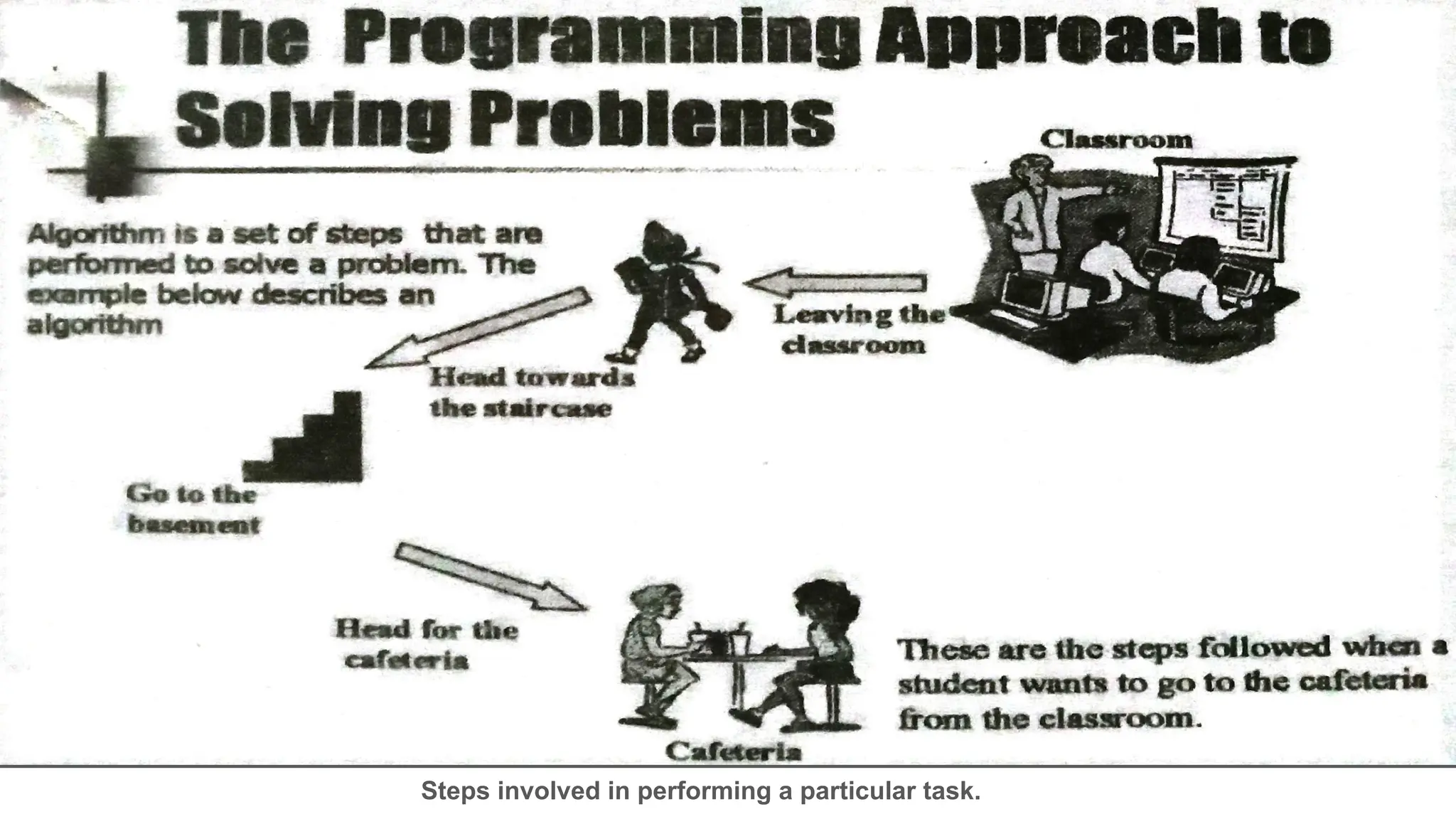
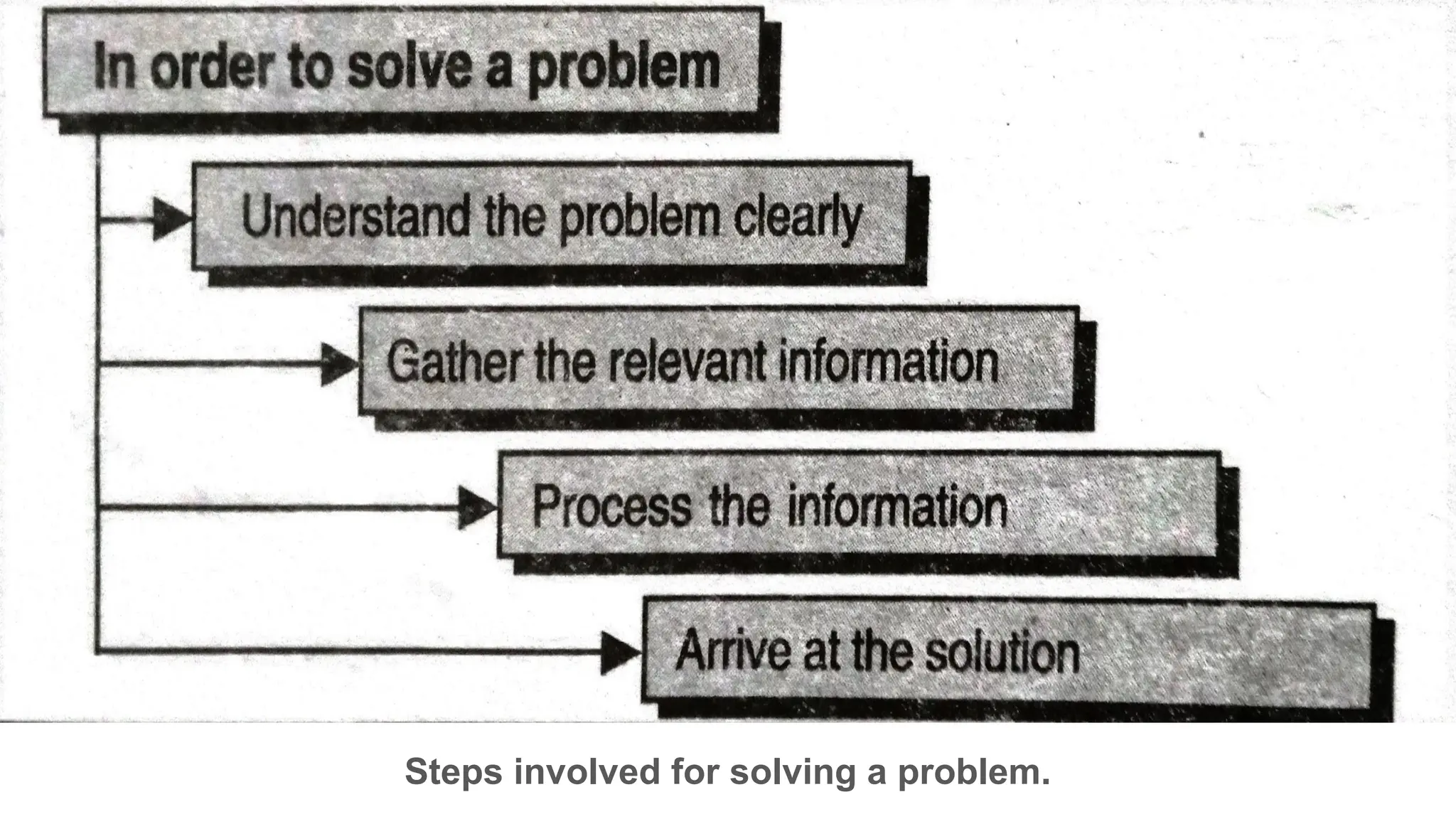
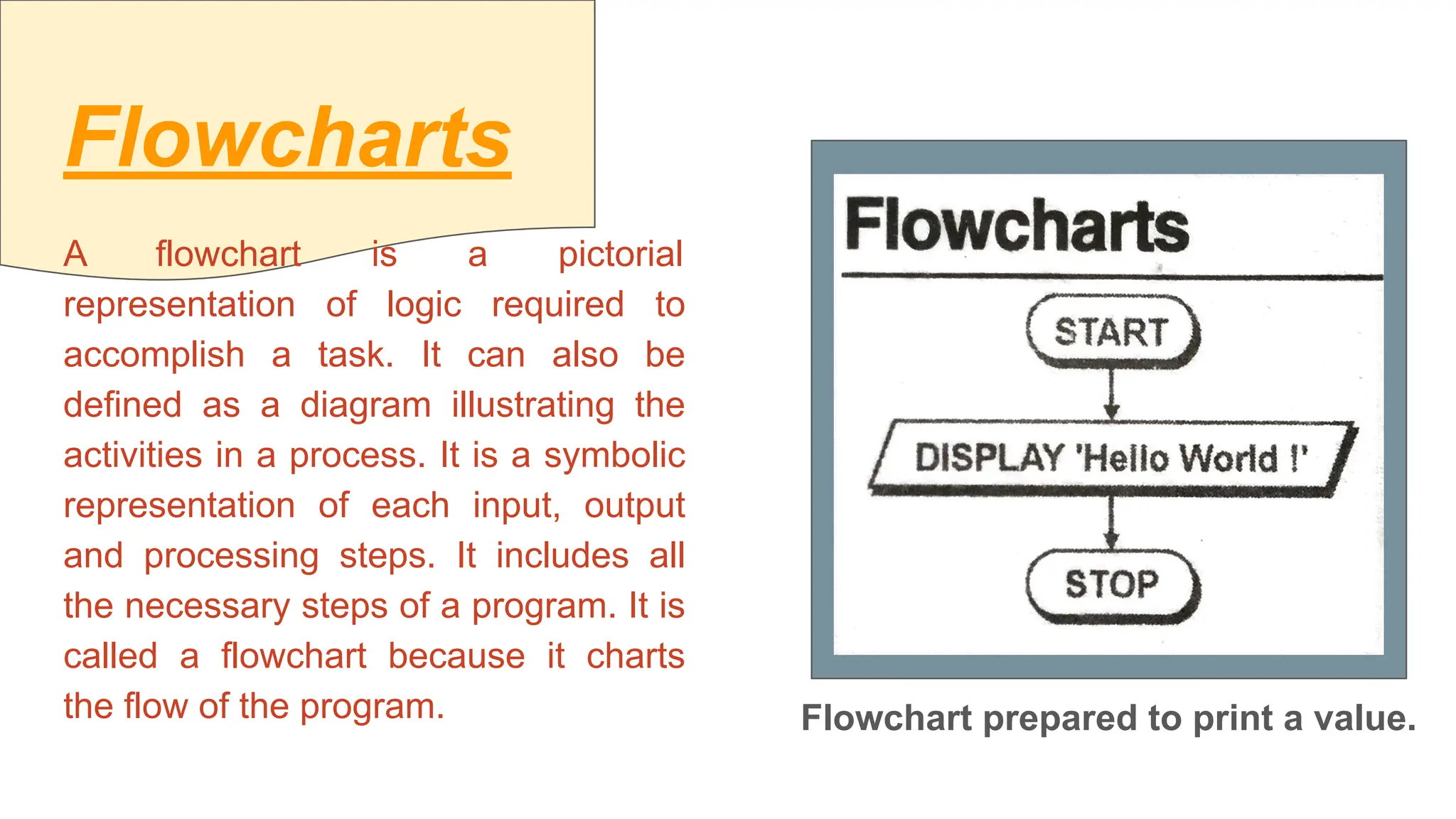
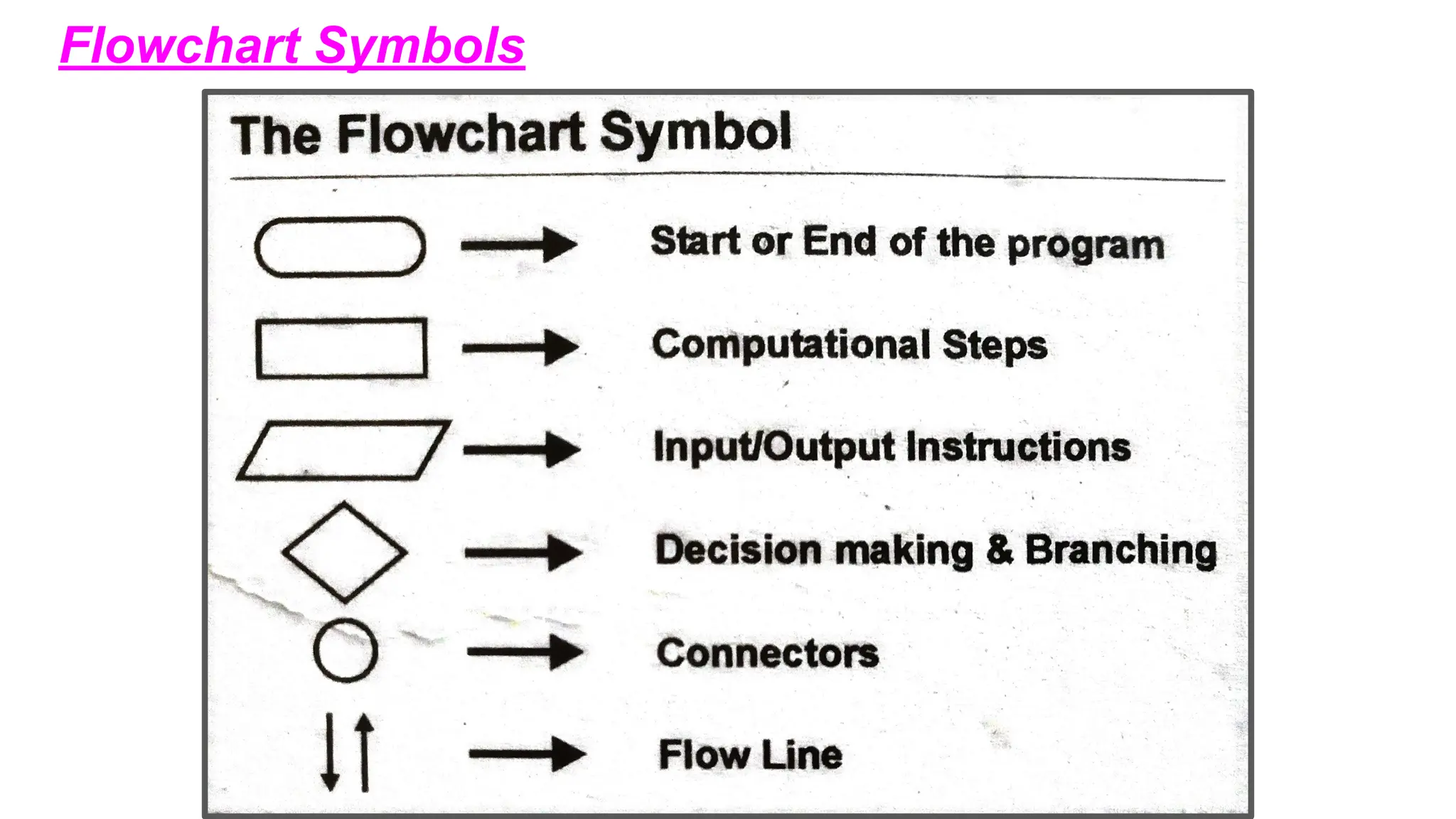
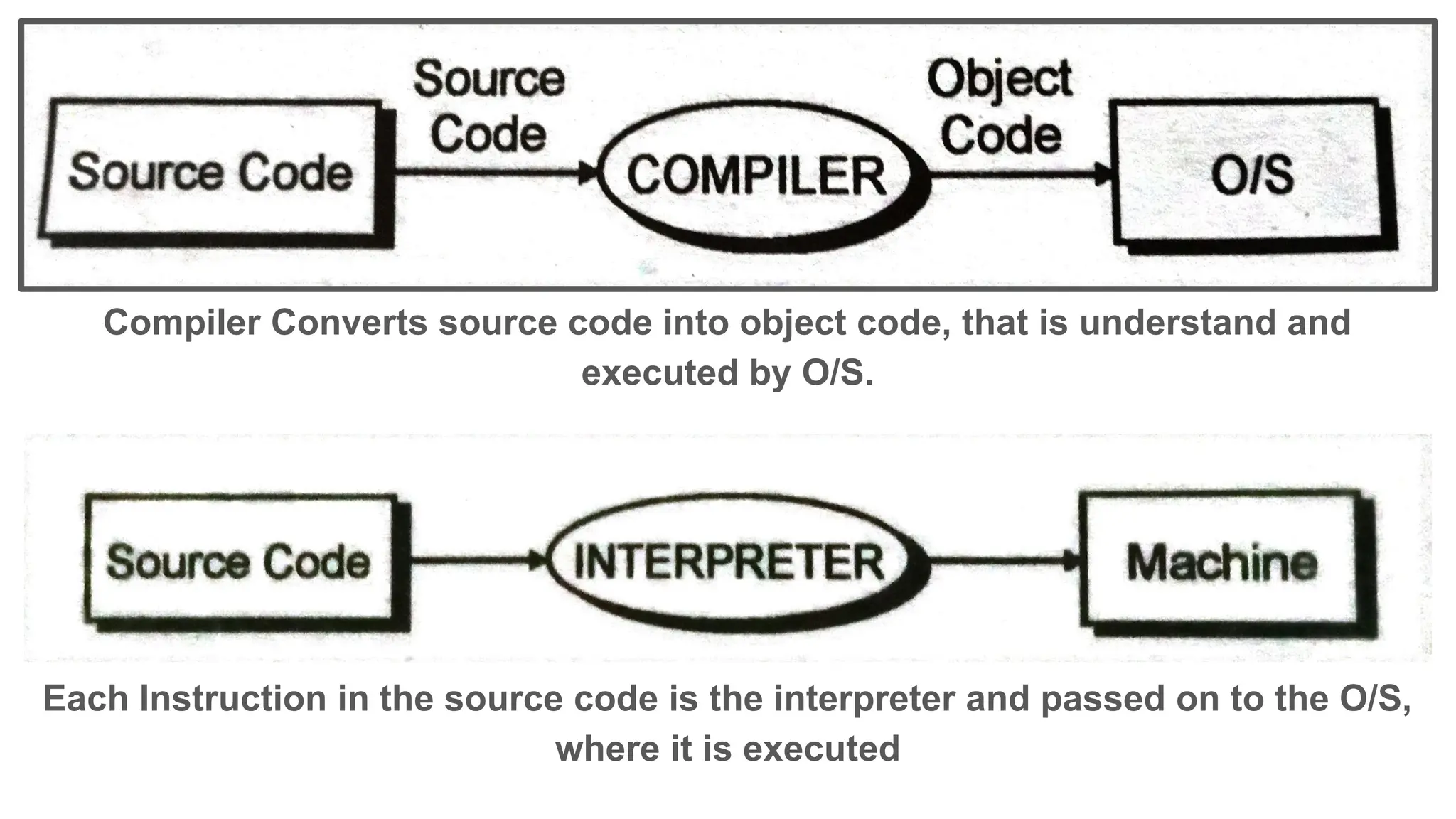
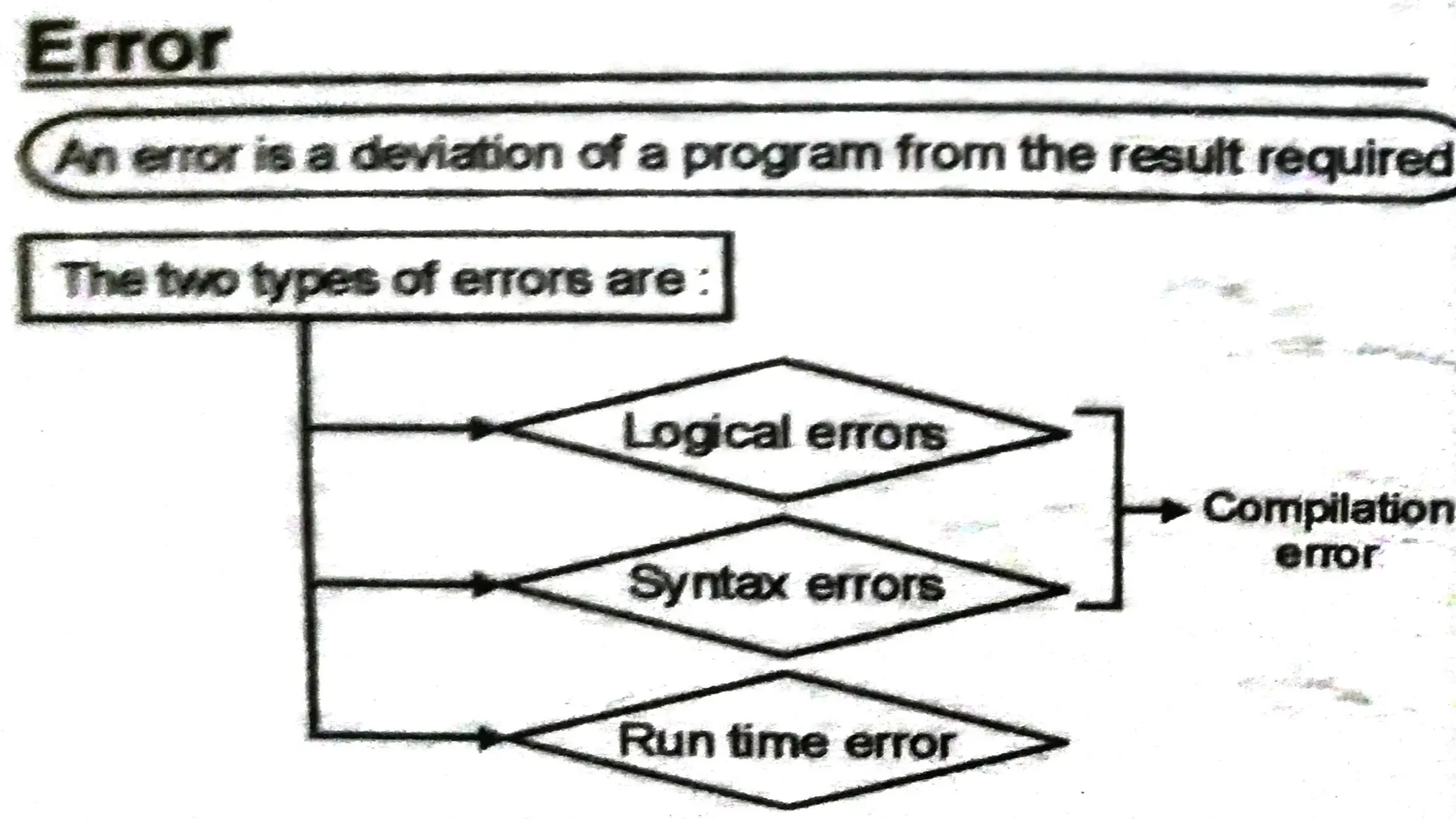
This document provides an introduction to programming topics including algorithms, pseudocode, flowcharts, programming languages, compilers, interpreters, testing, debugging and documentation. It discusses the basic model of computation involving understanding requirements, inputs/outputs, designing program layout and output, selecting techniques, and testing. Algorithms are defined as ordered sequences of operations to solve a problem. Pseudocode and flowcharts are used to represent program logic without real syntax. Programming languages are categorized as low-level (machine code) or high-level, with compilers and interpreters used to translate high-level languages. Testing and debugging involve inputting data to find and fix errors. Documentation records the development process for users.