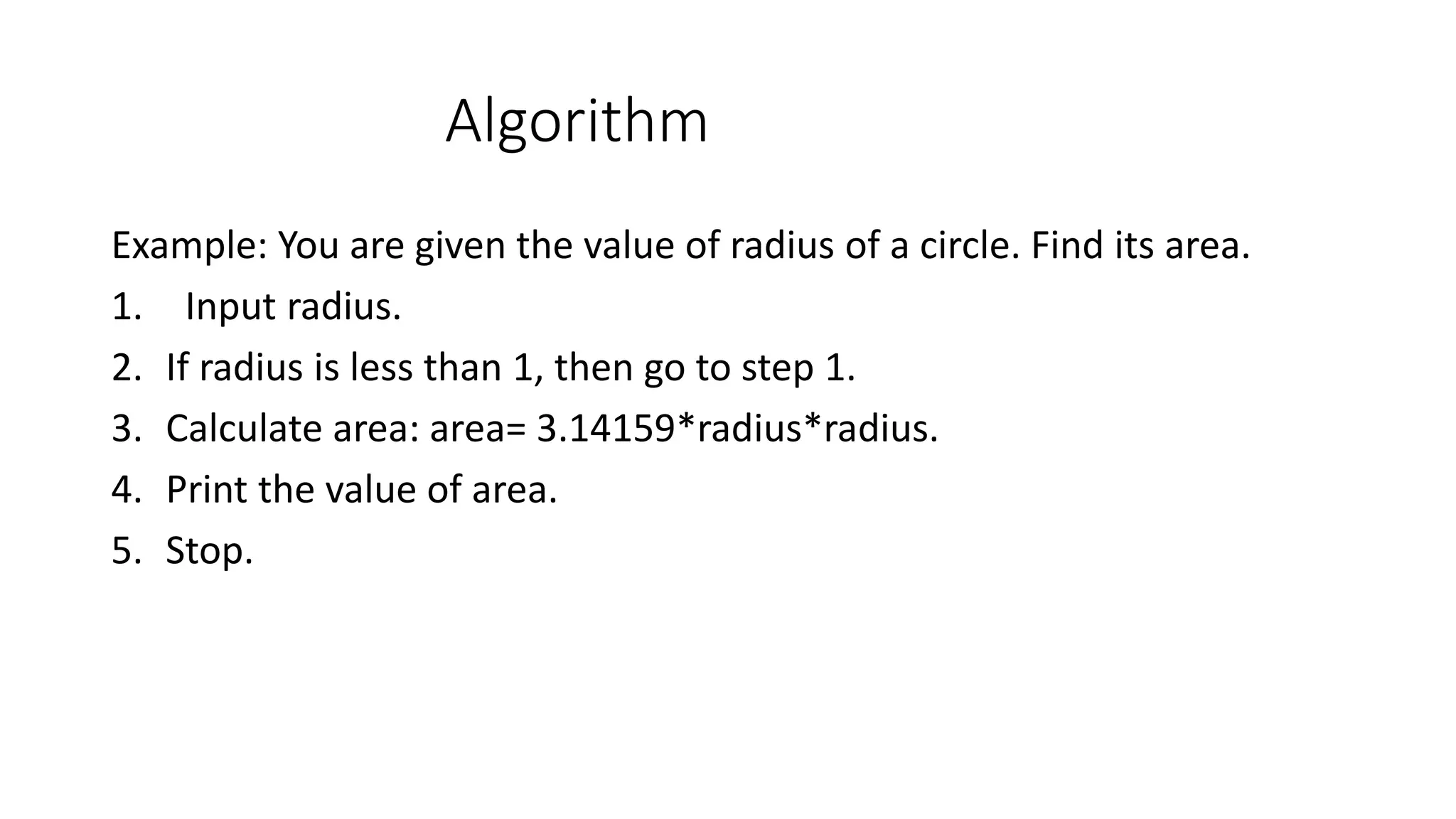
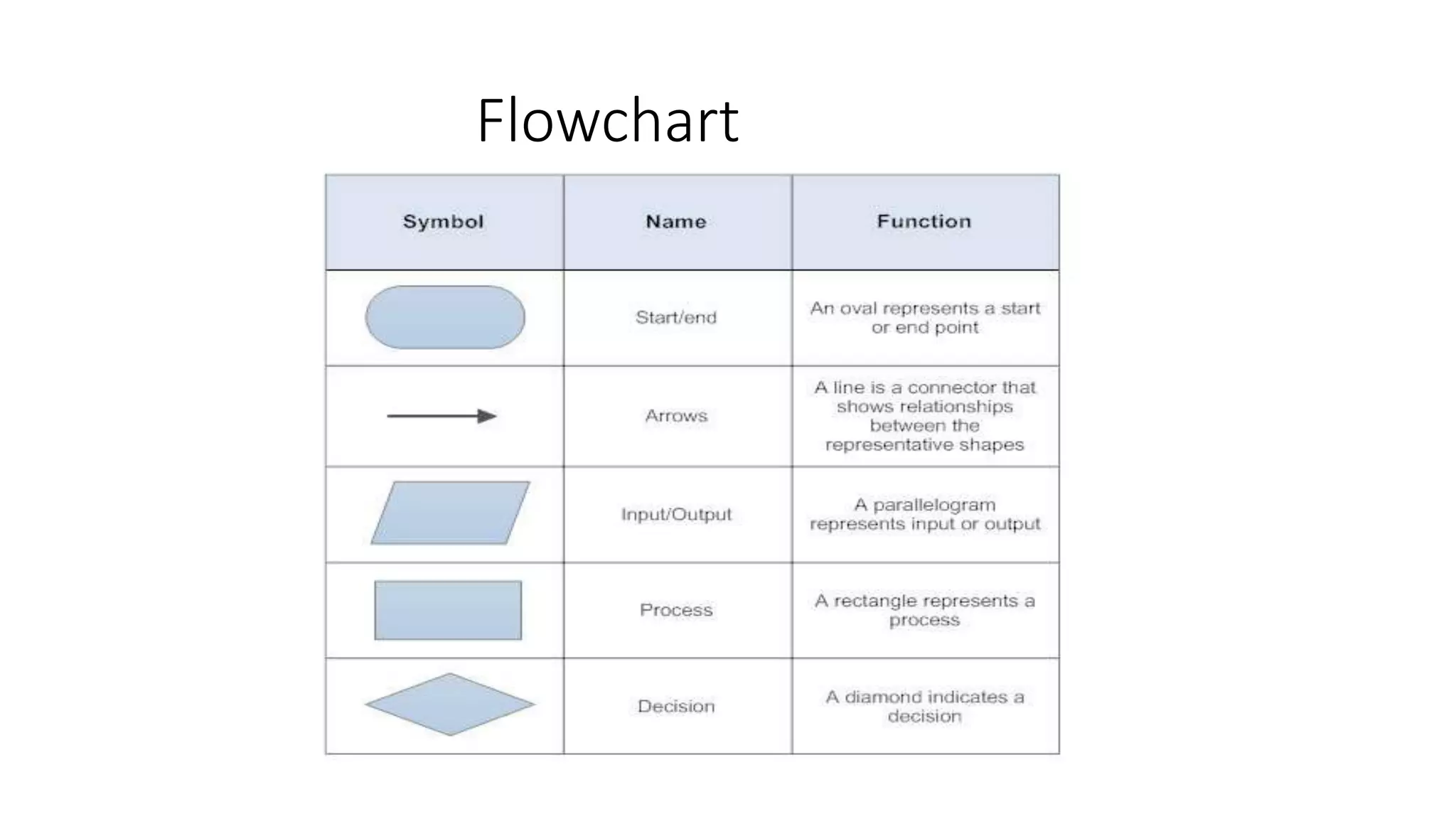
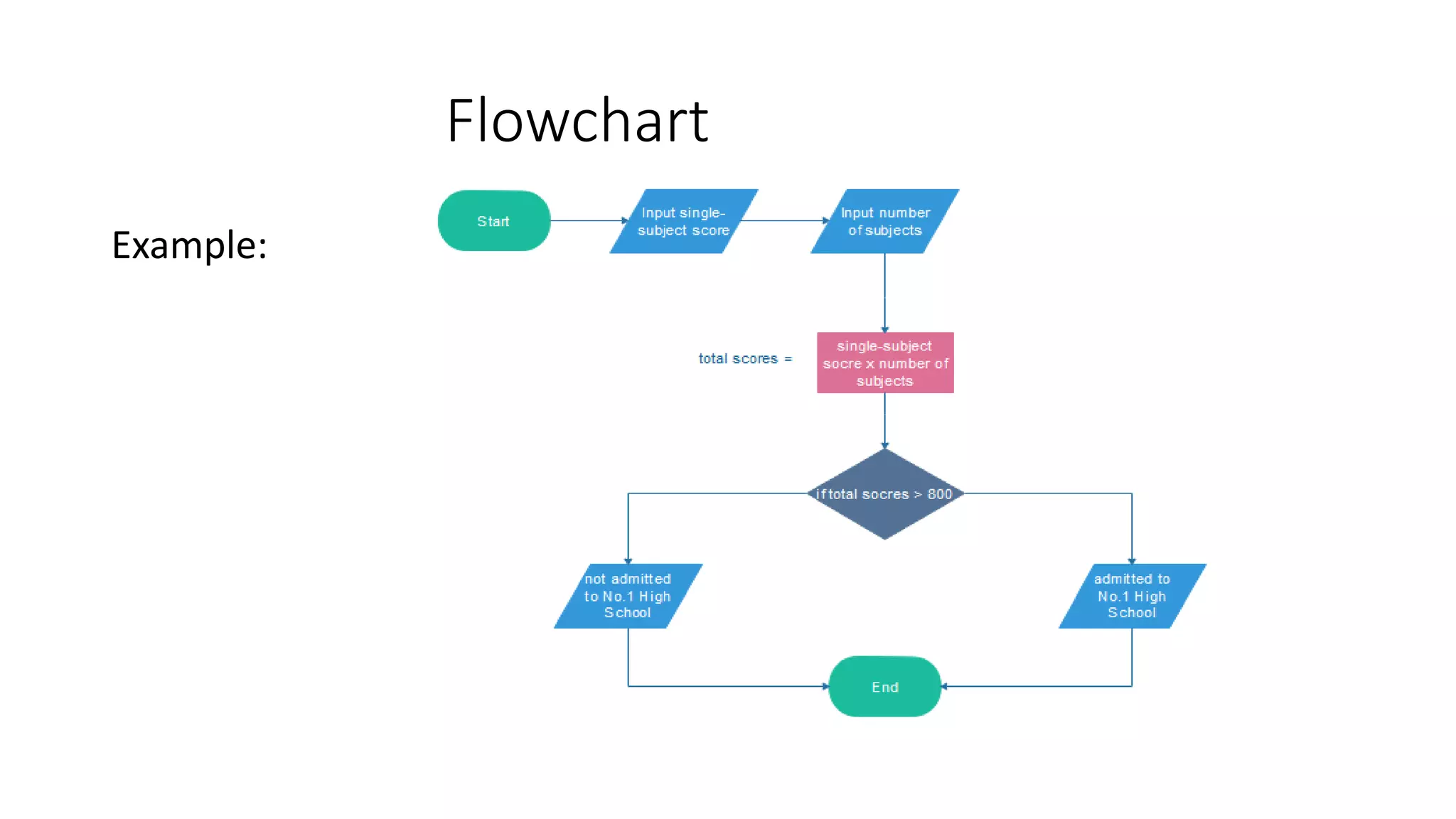
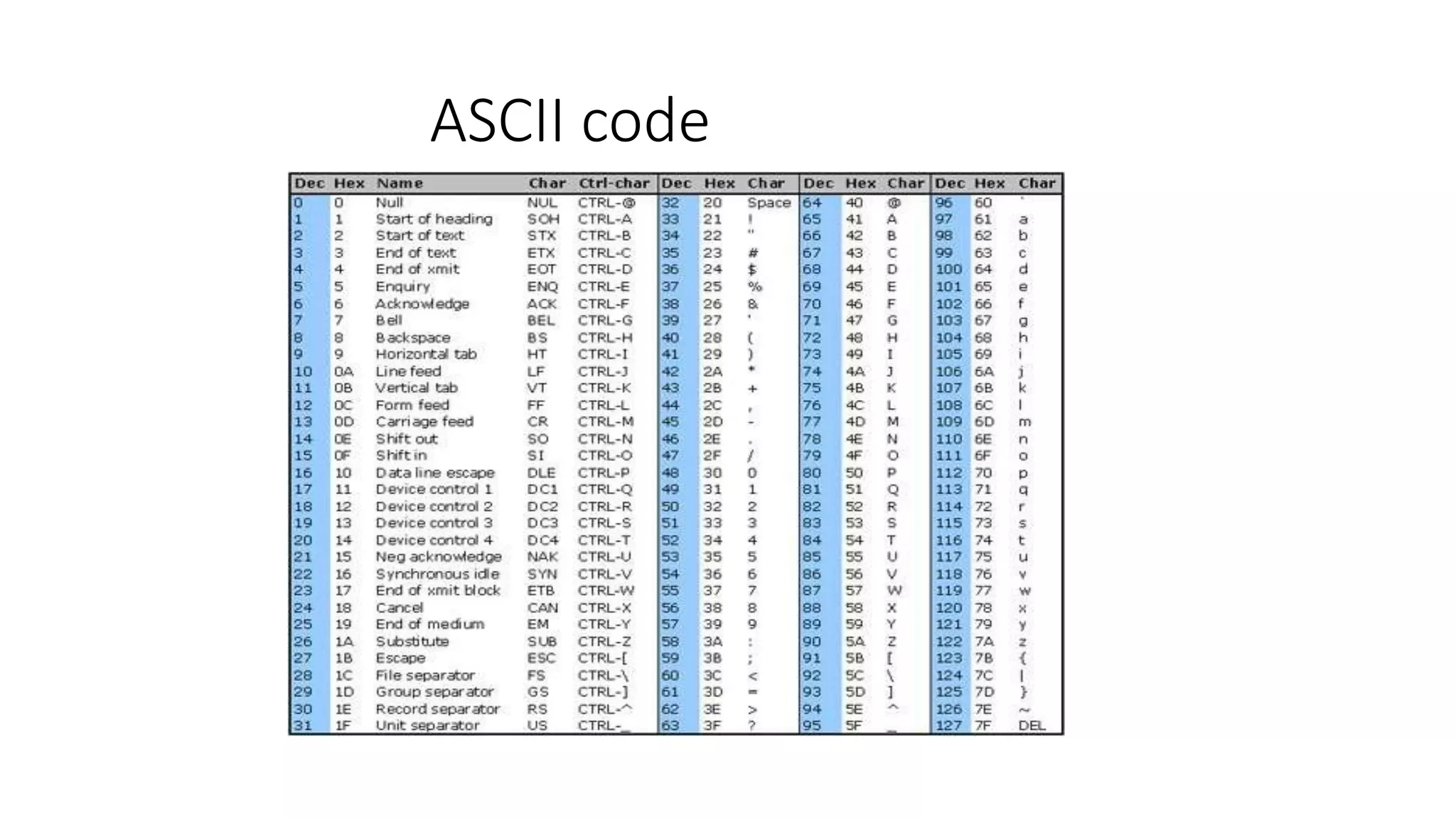
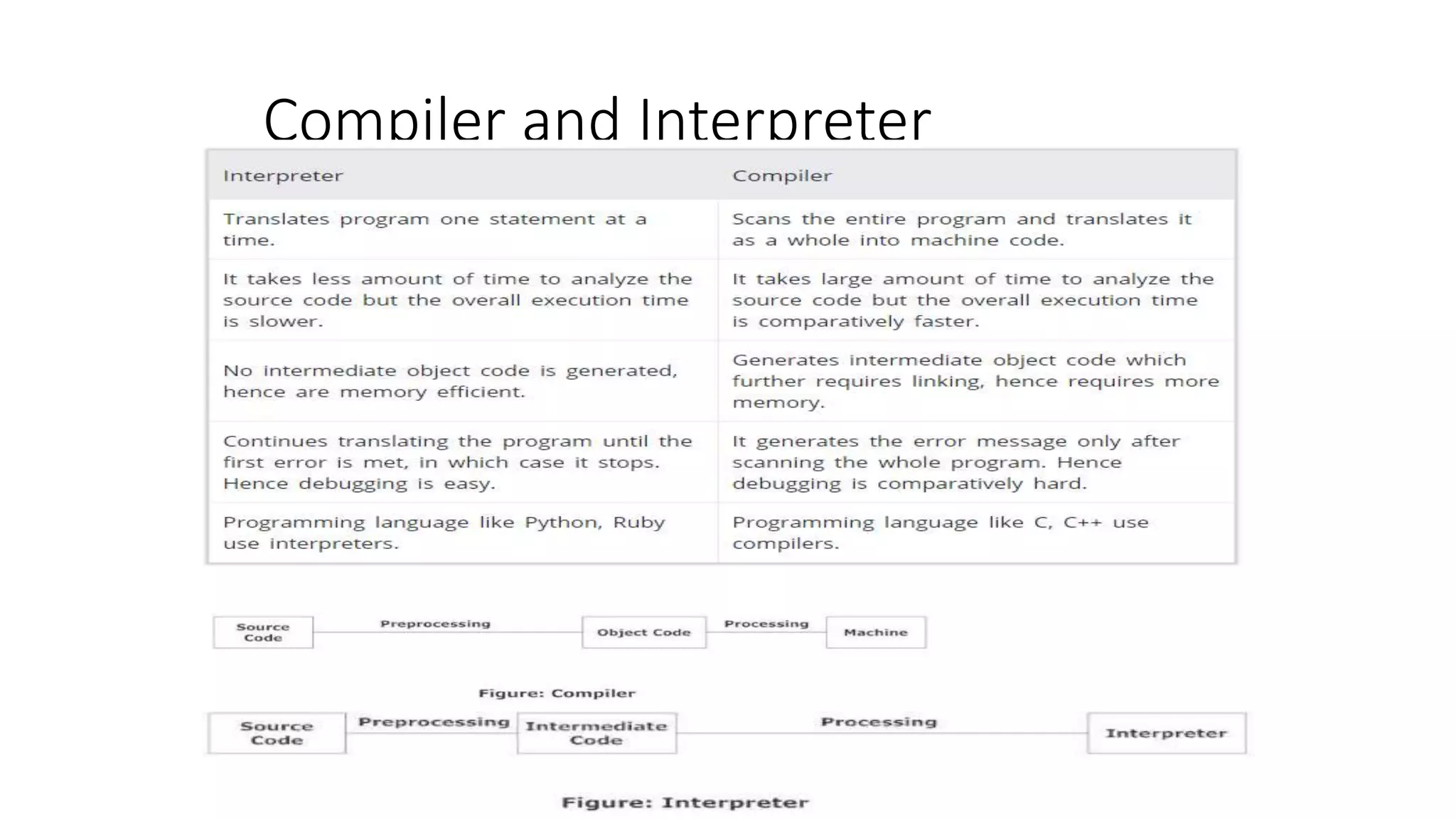
This document provides an introduction to the C programming language. It discusses the evolution of C from earlier languages like BCPL and B. C is described as a mid-level, structured programming language that is widely used and gives good machine efficiency while also being understandable by programmers. The document also defines key concepts like algorithms, flowcharts, pseudocode, ASCII/scan codes, and the differences between compilers and interpreters. It provides examples and questions to help learn about programming in C.









![Why Learn C • Compact, fast and powerful. (Compact- consisting of parts that are positioned together closely or in a tidy way, using very little space). Structured programming language – a disciplined approach to write programs that are clear and easily modified. “Mid-level” language. [High level language have been designed to give a better programming efficiency, where the low-level languages give good machine efficiency. C gives both. For this reason, C is often called a Middle-level language.] Standard for program development. Useful for all applications. C is the native language of UNIX. Friendly, reliable, simple and easy to use. Support Modular Programming style.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoprogrammingc-190414163357/75/Introduction-to-programming-c-10-2048.jpg)