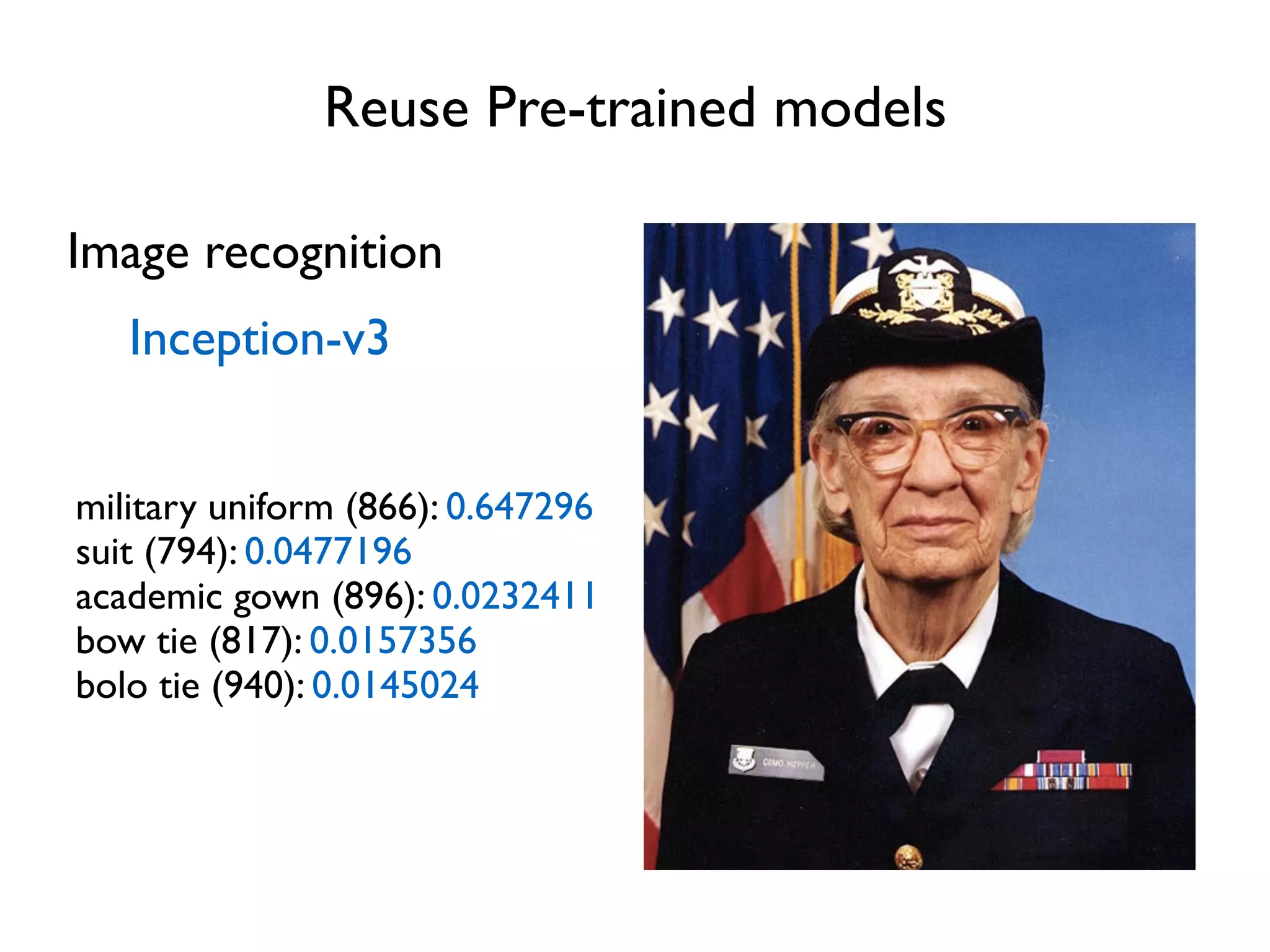
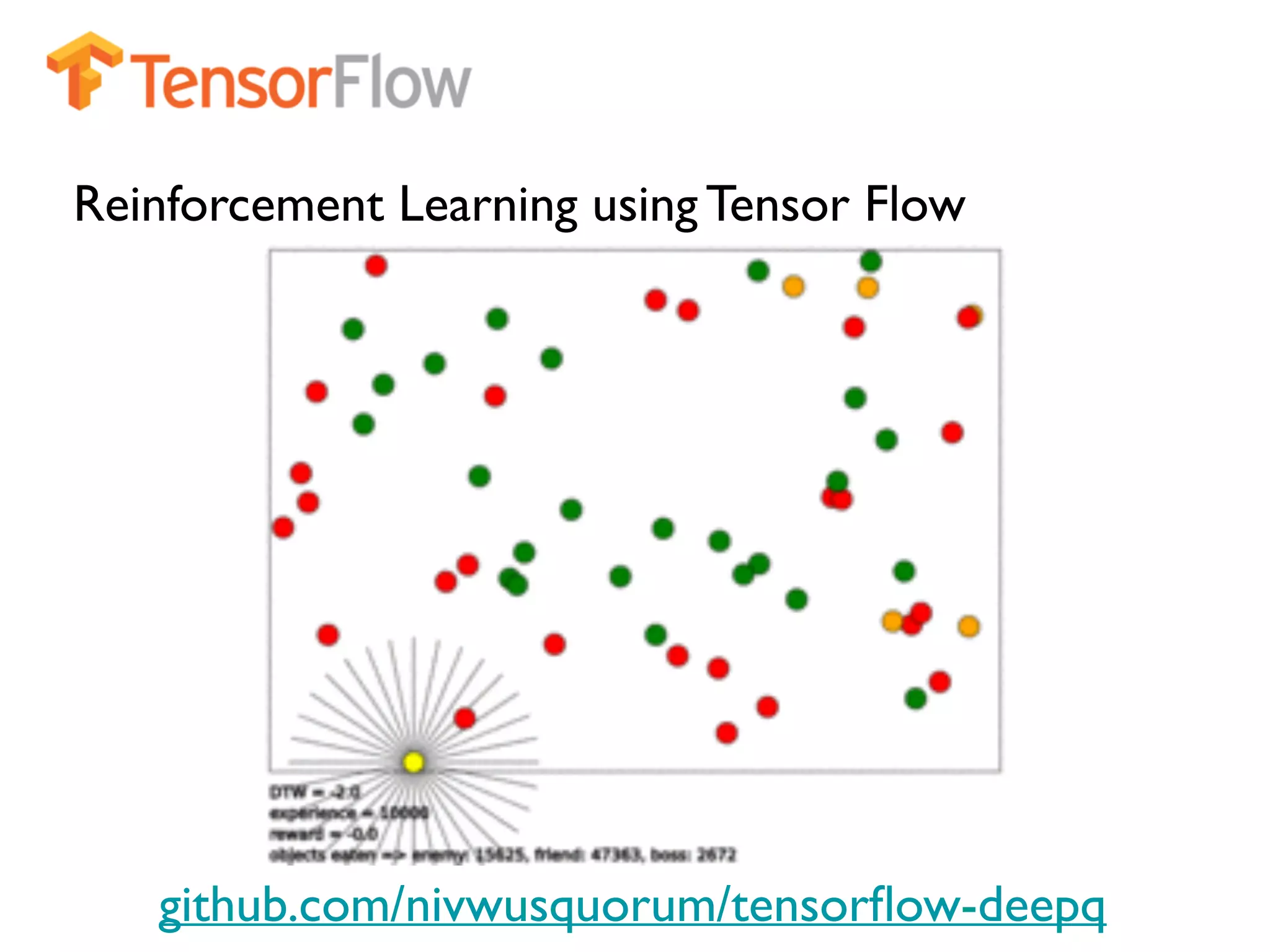
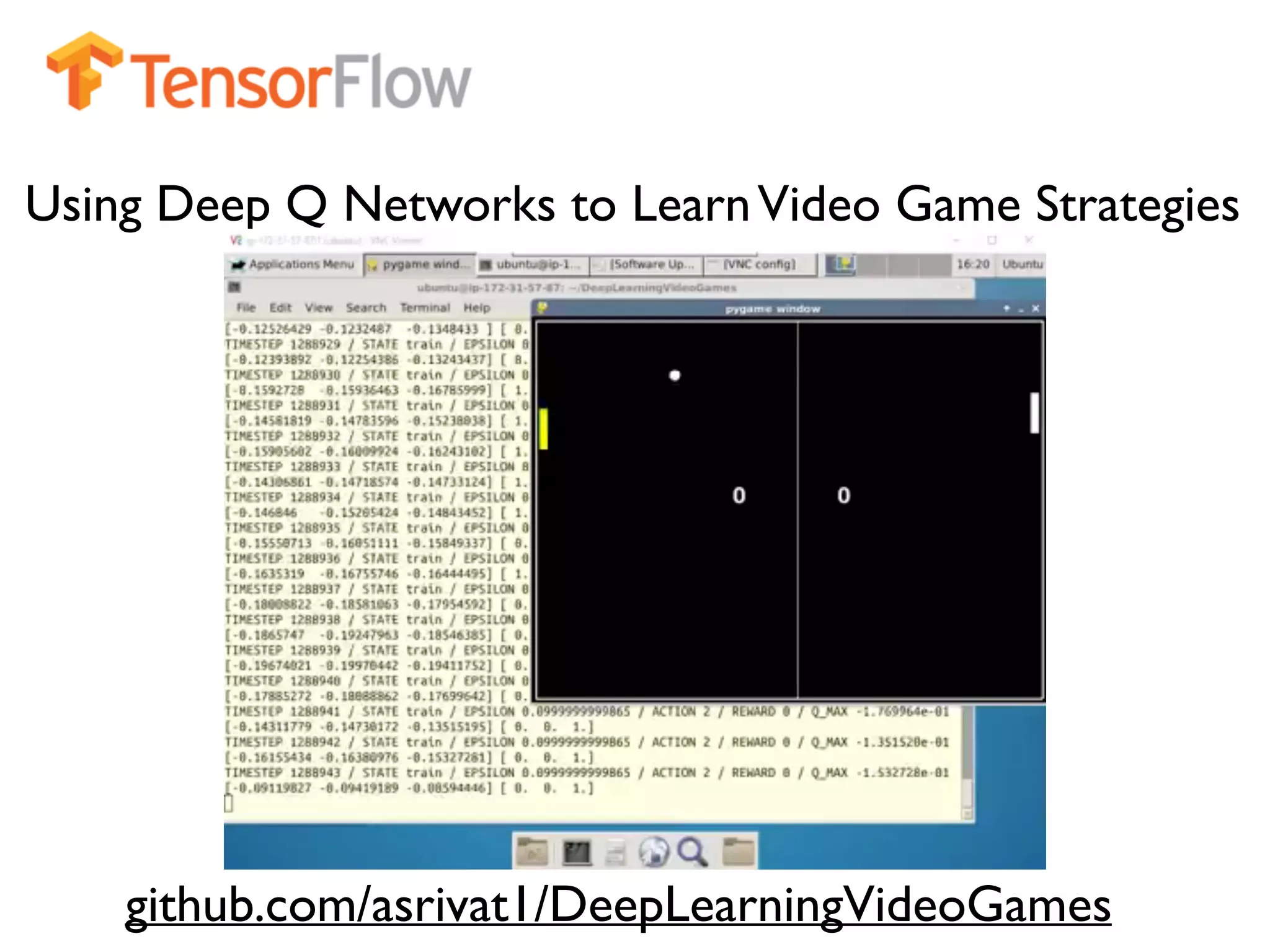
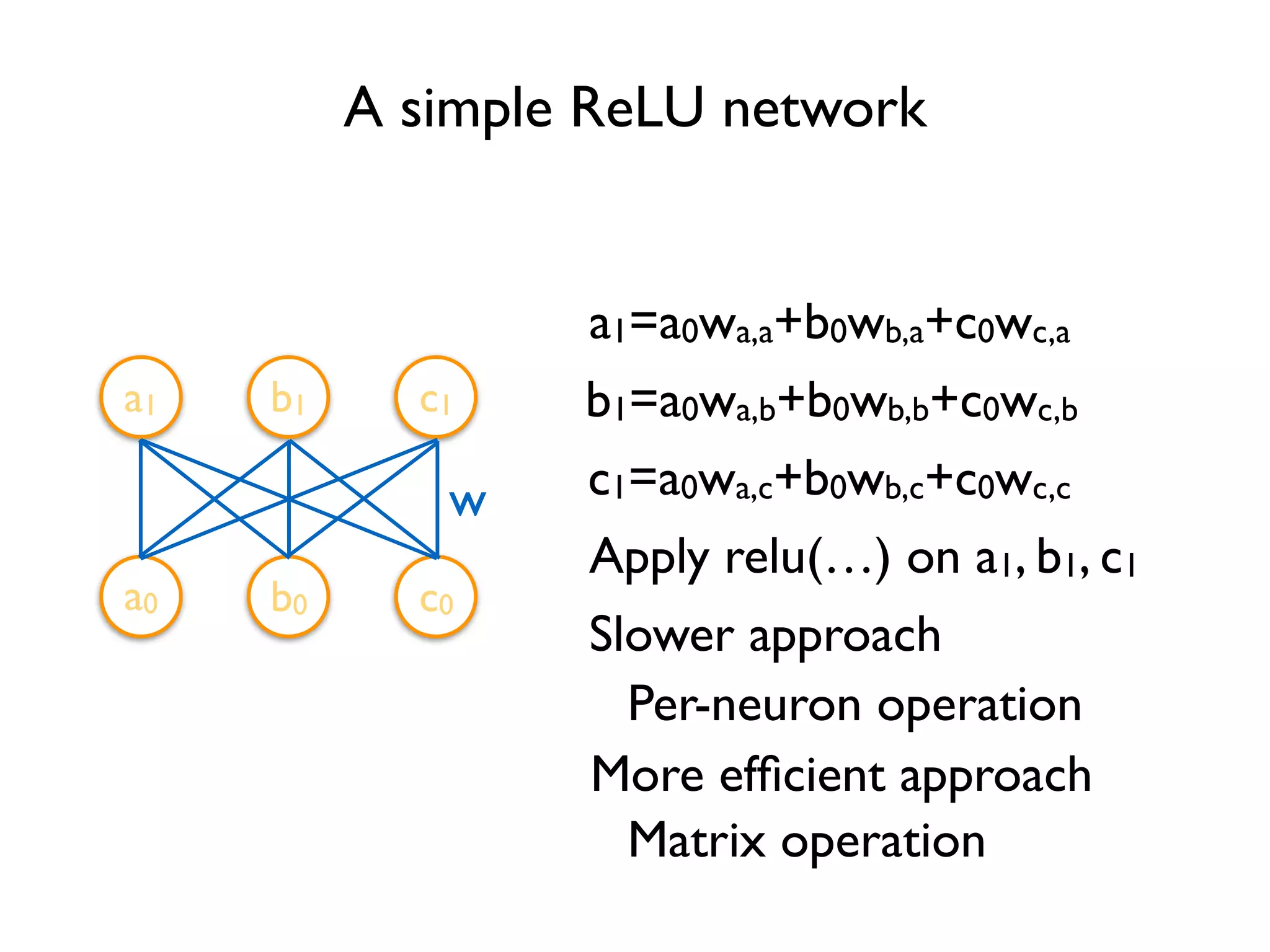
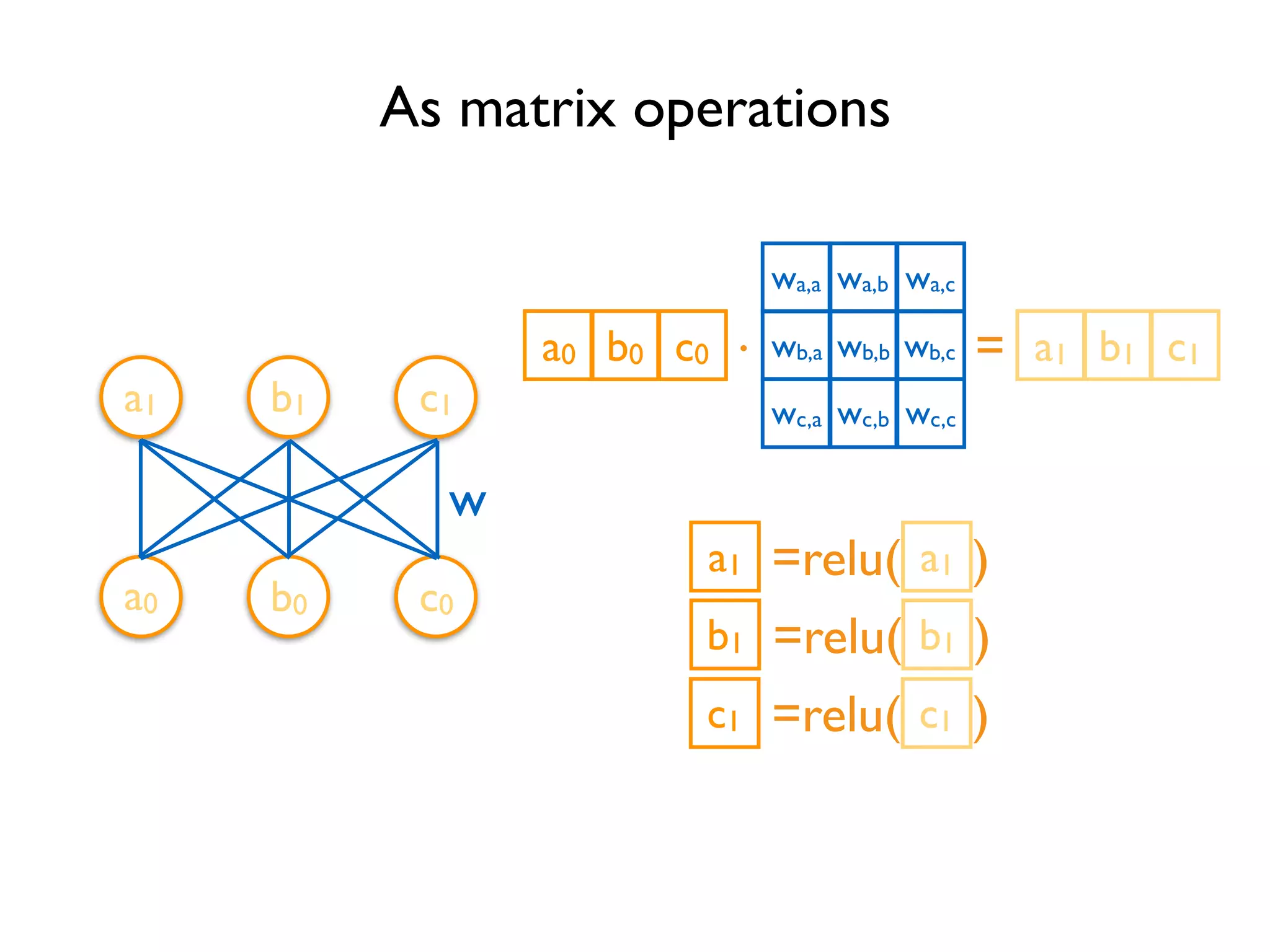
The document provides an extensive overview of using TensorFlow for deep learning, explaining concepts such as tensors, matrix operations, ReLU activation functions, and the data flow graph architecture. It also covers session management, variable initialization, placeholders, loss functions, optimization techniques, and model training processes, alongside practical examples. Additionally, the document touches on advanced topics like convolutional layers, LSTM cells, and applications related to image recognition and reinforcement learning.
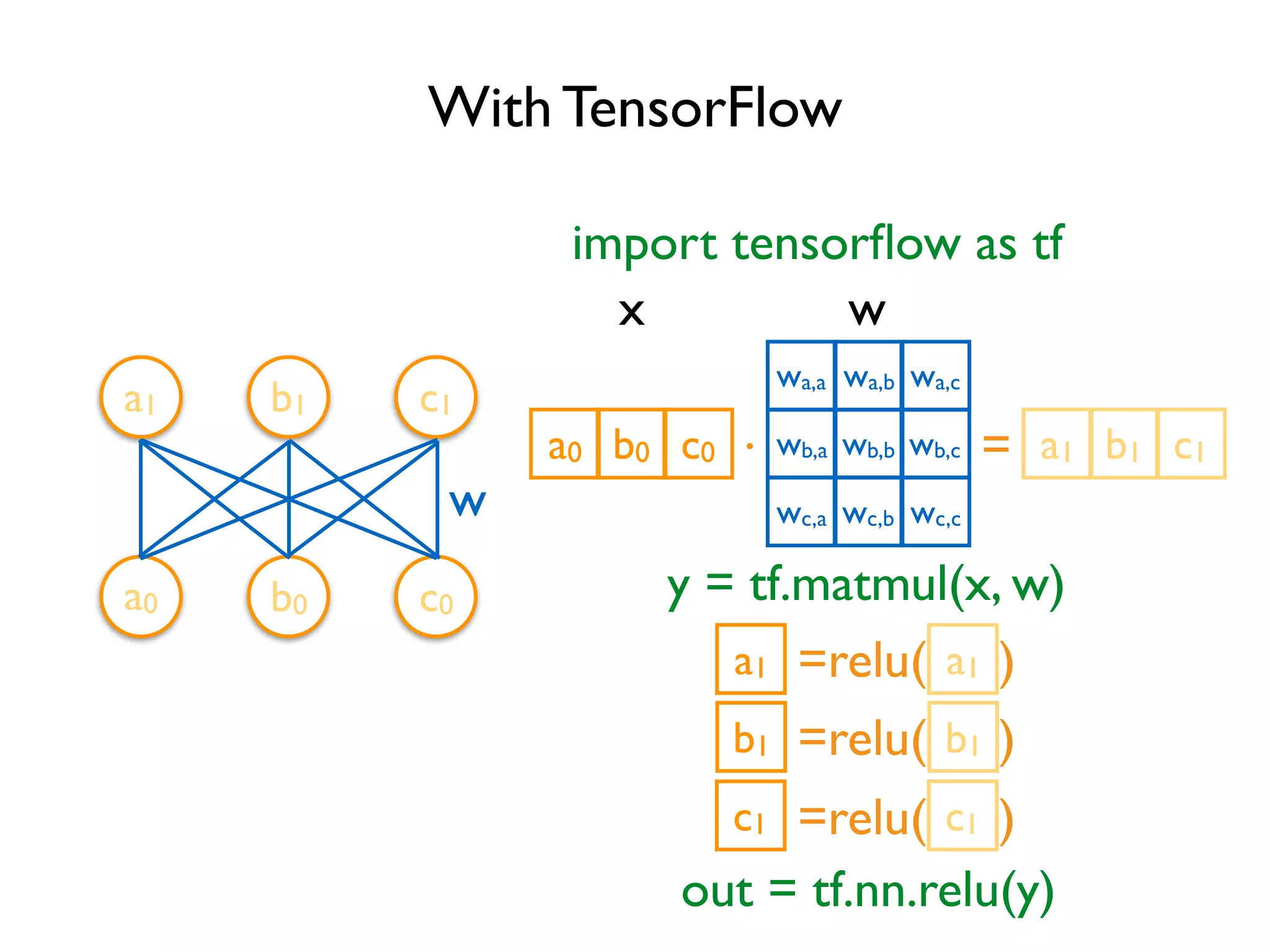
![Define Tensors xa,a xb,a xc,a xa,b xb,b xc,b xa,c xb,c xc,c w Variable(<initial-value>, name=<optional-name>) w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3]), name='w') import tensorflow as tf y = tf.matmul(x, w) relu_out = tf.nn.relu(y) Variable stores the state of current execution Others are operations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iispublic-160102031649/75/Google-TensorFlow-Tutorial-5-2048.jpg)
![TensorFlow Code so far defines a data flow graph MatMul ReLU Variable x w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3]), name='w') import tensorflow as tf y = tf.matmul(x, w) relu_out = tf.nn.relu(y) Each variable corresponds to a node in the graph, not the result Can be confusing at the beginning](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iispublic-160102031649/75/Google-TensorFlow-Tutorial-6-2048.jpg)
![TensorFlow Code so far defines a data flow graph Needs to specify how we want to execute the graph MatMul ReLU Variable x Session Manage resource for graph execution w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3]), name='w') sess = tf.Session() y = tf.matmul(x, w) relu_out = tf.nn.relu(y) import tensorflow as tf result = sess.run(relu_out)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iispublic-160102031649/75/Google-TensorFlow-Tutorial-7-2048.jpg)
![Graph Fetch Retrieve content from a node w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3]), name='w') sess = tf.Session() y = tf.matmul(x, w) relu_out = tf.nn.relu(y) import tensorflow as tf print sess.run(relu_out) MatMul ReLU Variable x Fetch We have assembled the pipes Fetch the liquid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iispublic-160102031649/75/Google-TensorFlow-Tutorial-8-2048.jpg)
![Graph sess = tf.Session() y = tf.matmul(x, w) relu_out = tf.nn.relu(y) import tensorflow as tf print sess.run(relu_out) sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3]), name='w') InitializeVariable Variable is an empty node MatMul ReLU Variable x Fetch Fill in the content of a Variable node](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iispublic-160102031649/75/Google-TensorFlow-Tutorial-9-2048.jpg)
![Graph sess = tf.Session() y = tf.matmul(x, w) relu_out = tf.nn.relu(y) import tensorflow as tf print sess.run(relu_out) sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3]), name='w') x = tf.placeholder("float", [1, 3]) Placeholder How about x? MatMul ReLU Variable x Fetch placeholder(<data type>, shape=<optional-shape>, name=<optional-name>) Its content will be fed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iispublic-160102031649/75/Google-TensorFlow-Tutorial-10-2048.jpg)
![Graph import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf sess = tf.Session() x = tf.placeholder("float", [1, 3]) w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3]), name='w') y = tf.matmul(x, w) relu_out = tf.nn.relu(y) sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) print sess.run(relu_out, feed_dict={x:np.array([[1.0, 2.0, 3.0]])}) Feed MatMul ReLU Variable x FetchPump liquid into the pipe Feed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iispublic-160102031649/75/Google-TensorFlow-Tutorial-11-2048.jpg)

![Prediction import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf with tf.Session() as sess: x = tf.placeholder("float", [1, 3]) w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3]), name='w') relu_out = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(x, w)) softmax = tf.nn.softmax(relu_out) sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) print sess.run(softmax, feed_dict={x:np.array([[1.0, 2.0, 3.0]])}) Softmax Make predictions for n targets that sum to 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iispublic-160102031649/75/Google-TensorFlow-Tutorial-13-2048.jpg)
![Prediction Difference import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf with tf.Session() as sess: x = tf.placeholder("float", [1, 3]) w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3]), name='w') relu_out = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(x, w)) softmax = tf.nn.softmax(relu_out) sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) answer = np.array([[0.0, 1.0, 0.0]]) print answer - sess.run(softmax, feed_dict={x:np.array([[1.0, 2.0, 3.0]])})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iispublic-160102031649/75/Google-TensorFlow-Tutorial-14-2048.jpg)
![Learn parameters: Loss Define loss function Loss function for softmax softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits( logits, labels, name=<optional-name>) labels = tf.placeholder("float", [1, 3]) cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits( relu_out, labels, name='xentropy')](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iispublic-160102031649/75/Google-TensorFlow-Tutorial-15-2048.jpg)
![Learn parameters: Optimization Gradient descent class GradientDescentOptimizer GradientDescentOptimizer(learning rate) labels = tf.placeholder("float", [1, 3]) cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits( relu_out, labels, name='xentropy') optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1) train_op = optimizer.minimize(cross_entropy) sess.run(train_op, feed_dict= {x:np.array([[1.0, 2.0, 3.0]]), labels:answer}) learning rate = 0.1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iispublic-160102031649/75/Google-TensorFlow-Tutorial-16-2048.jpg)
![Iterative update labels = tf.placeholder("float", [1, 3]) cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits( relu_out, labels, name=‘xentropy') optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1) train_op = optimizer.minimize(cross_entropy) for step in range(10): sess.run(train_op, feed_dict= {x:np.array([[1.0, 2.0, 3.0]]), labels:answer}) Gradient descent usually needs more than one step Run multiple times](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iispublic-160102031649/75/Google-TensorFlow-Tutorial-17-2048.jpg)
![Add parameters for Softmax … softmax_w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3])) logit = tf.matmul(relu_out, softmax_w) softmax = tf.nn.softmax(logit) … cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits( logit, labels, name=‘xentropy') … Do not want to use only non-negative input Softmax layer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iispublic-160102031649/75/Google-TensorFlow-Tutorial-18-2048.jpg)
![Add biases … w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3])) b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, 3])) relu_out = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(x, w) + b) softmax_w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3])) softmax_b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, 3])) logit = tf.matmul(relu_out, softmax_w) + softmax_b softmax = tf.nn.softmax(logit) … Biases initialized to zero](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iispublic-160102031649/75/Google-TensorFlow-Tutorial-19-2048.jpg)
![Make it deep … x = tf.placeholder("float", [1, 3]) relu_out = x num_layers = 2 for layer in range(num_layers): w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3])) b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, 3])) relu_out = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(relu_out, w) + b) … Add layers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iispublic-160102031649/75/Google-TensorFlow-Tutorial-20-2048.jpg)
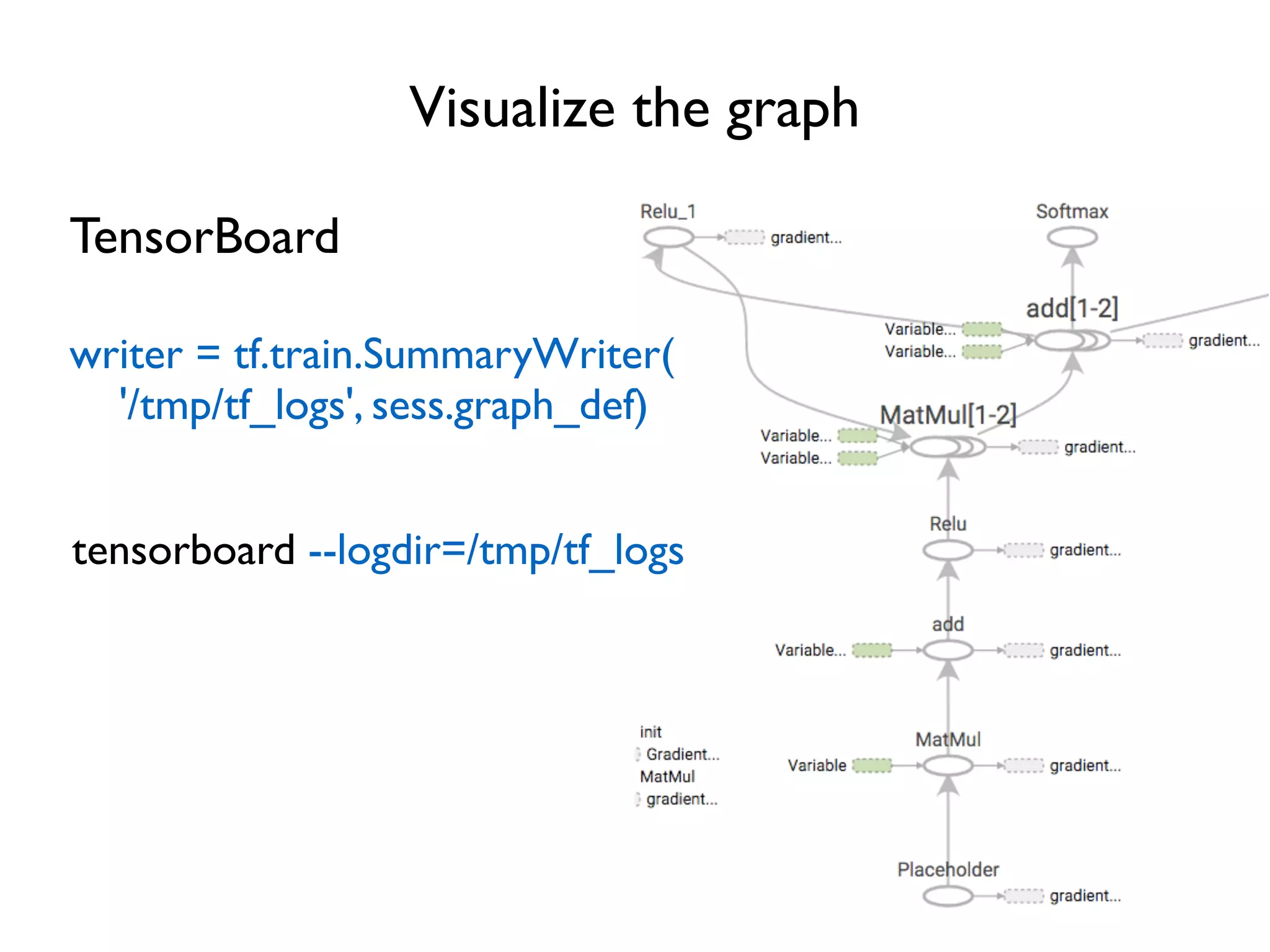
![Improve naming, improve visualization name_scope(name) Help specify hierarchical names … for layer in range(num_layers): with tf.name_scope('relu'): w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3])) b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, 3])) relu_out = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(relu_out, w) + b) … Will help visualizer to better understand hierarchical relation Move to outside the loop?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iispublic-160102031649/75/Google-TensorFlow-Tutorial-22-2048.jpg)
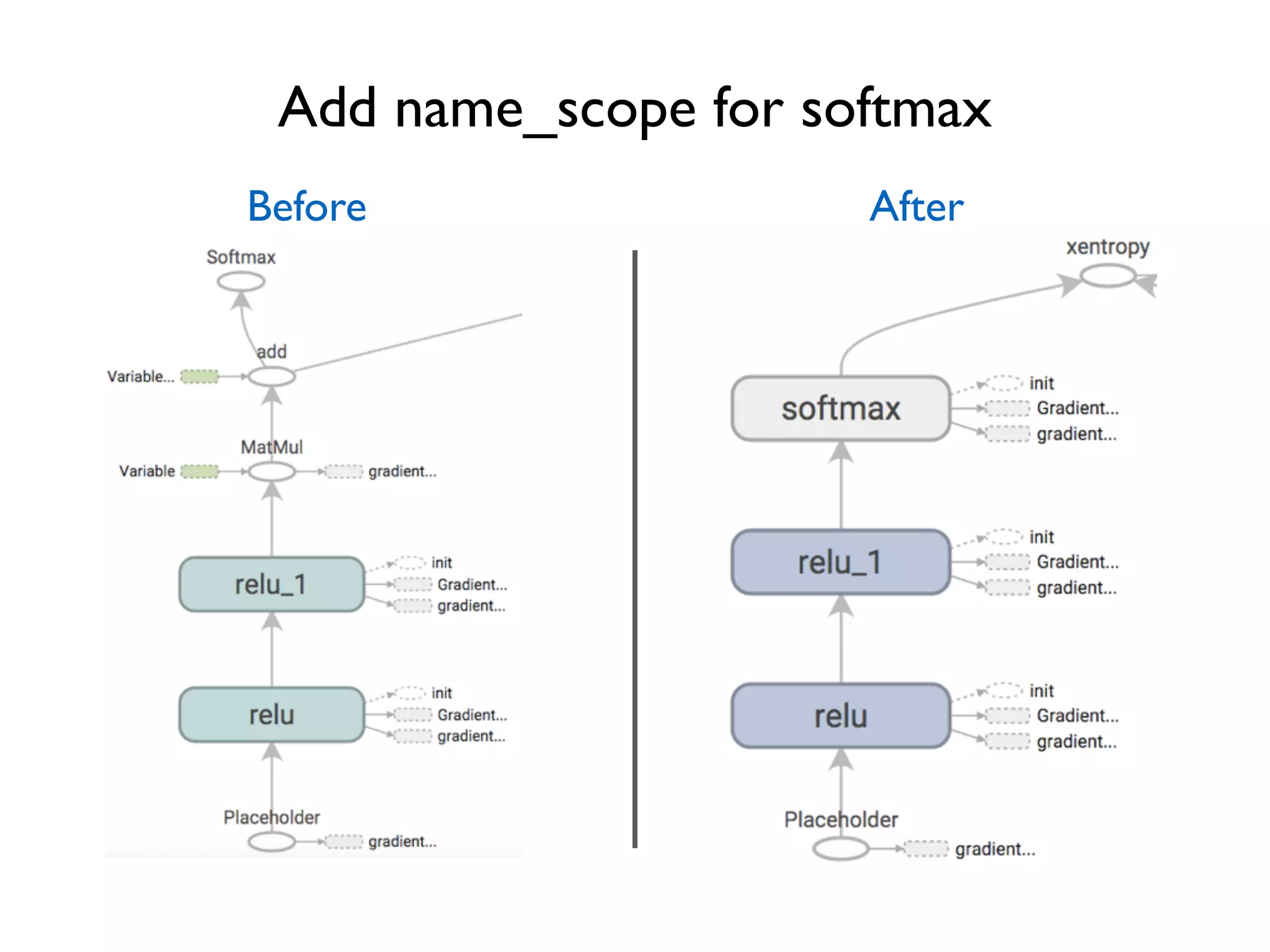

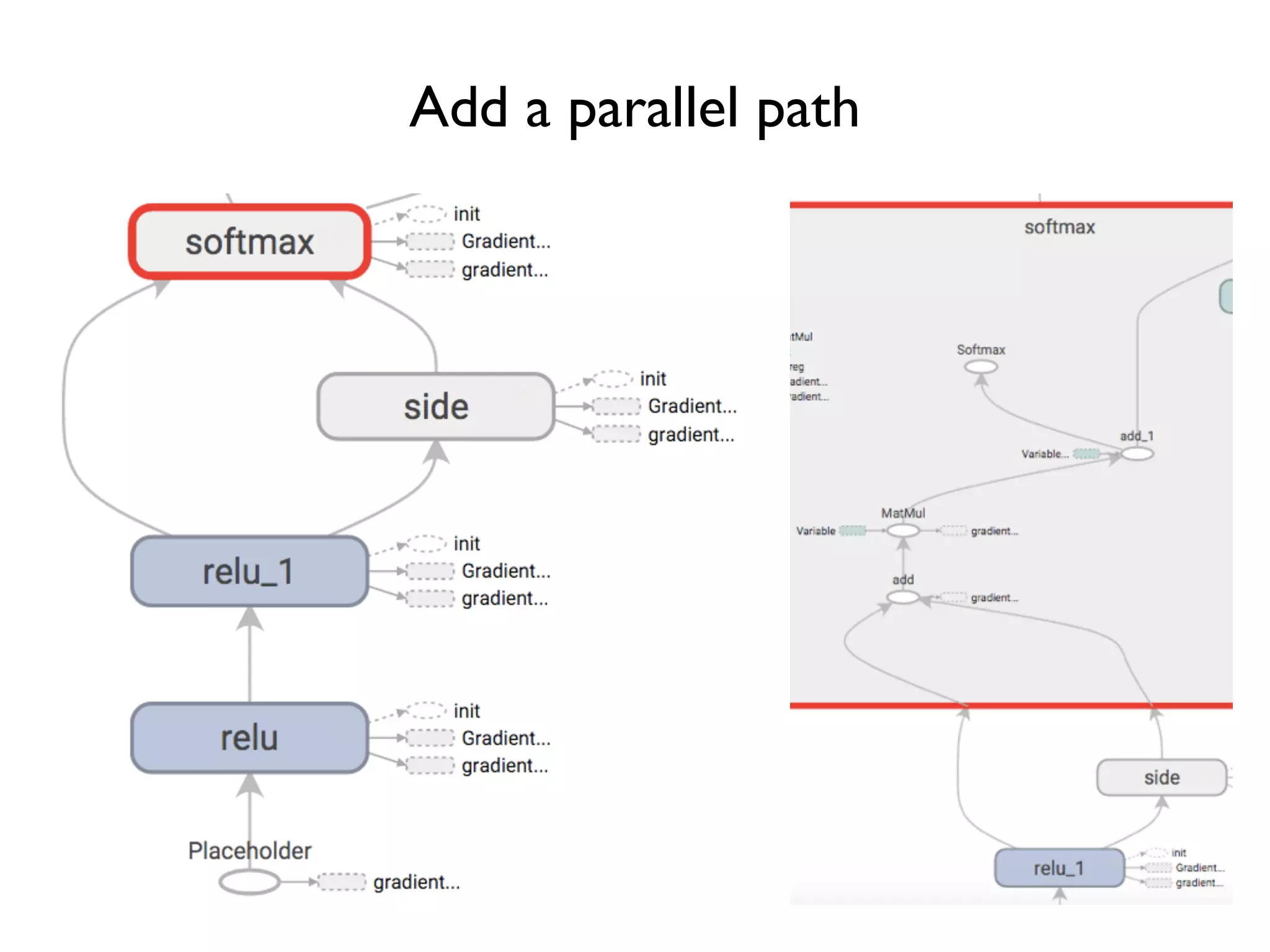
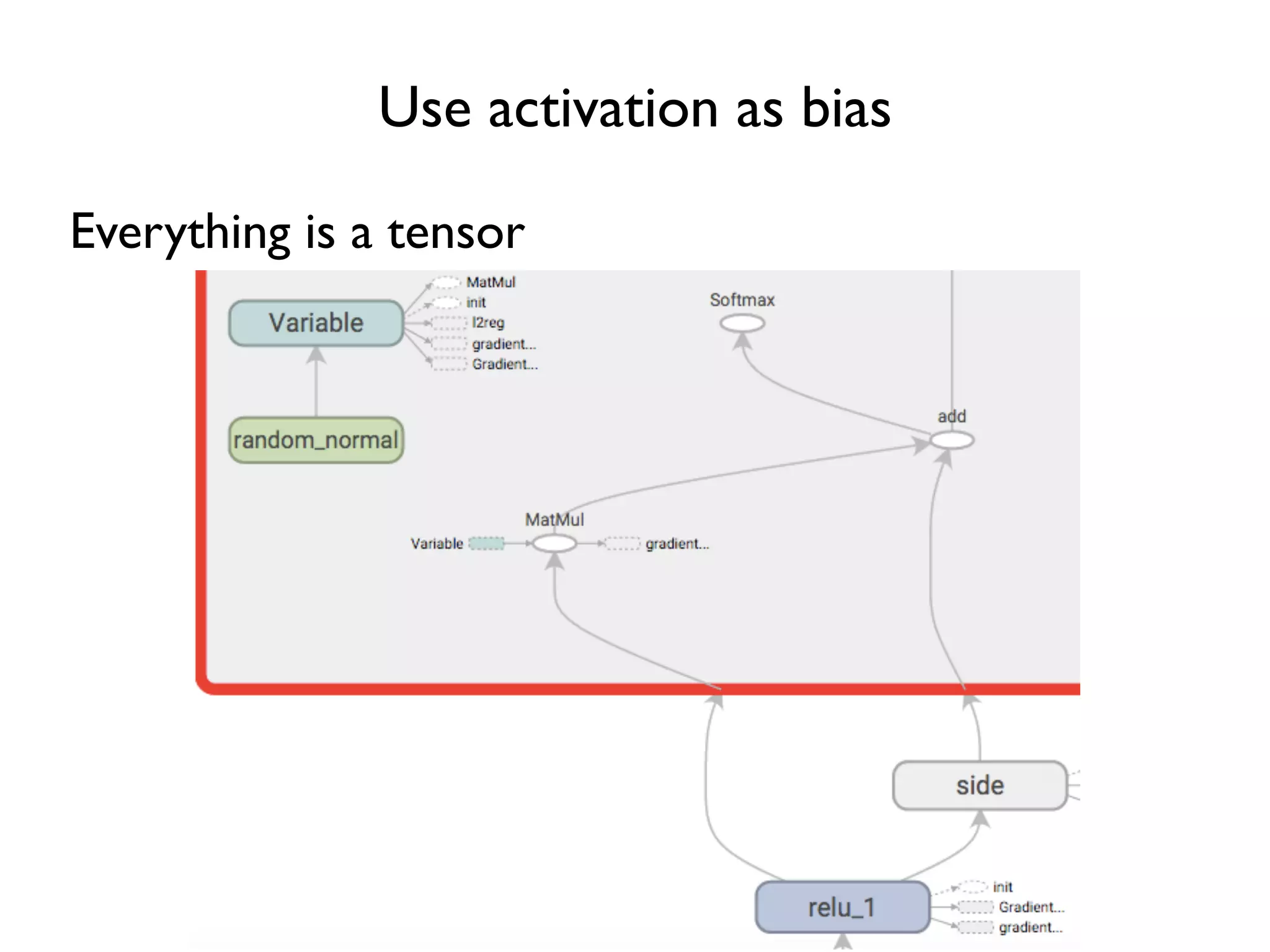
![Visualize states Add summaries scalar_summary histogram_summary merged_summaries = tf.merge_all_summaries() results = sess.run([train_op, merged_summaries], feed_dict=…) writer.add_summary(results[1], step)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iispublic-160102031649/75/Google-TensorFlow-Tutorial-28-2048.jpg)


![LSTM # Parameters of gates are concatenated into one multiply for efficiency. c, h = array_ops.split(1, 2, state) concat = linear([inputs, h], 4 * self._num_units,True) # i = input_gate, j = new_input, f = forget_gate, o = output_gate i, j, f, o = array_ops.split(1, 4, concat) new_c = c * sigmoid(f + self._forget_bias) + sigmoid(i) * tanh(j) new_h = tanh(new_c) * sigmoid(o) BasicLSTMCell](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iispublic-160102031649/75/Google-TensorFlow-Tutorial-31-2048.jpg)
![Word2Vec with TensorFlow # Look up embeddings for inputs. embeddings = tf.Variable( tf.random_uniform([vocabulary_size, embedding_size], -1.0, 1.0)) embed = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embeddings, train_inputs) # Construct the variables for the NCE loss nce_weights = tf.Variable( tf.truncated_normal([vocabulary_size, embedding_size], stddev=1.0 / math.sqrt(embedding_size))) nce_biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([vocabulary_size])) # Compute the average NCE loss for the batch. # tf.nce_loss automatically draws a new sample of the negative labels each # time we evaluate the loss. loss = tf.reduce_mean( tf.nn.nce_loss(nce_weights, nce_biases, embed, train_labels, num_sampled, vocabulary_size))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iispublic-160102031649/75/Google-TensorFlow-Tutorial-32-2048.jpg)