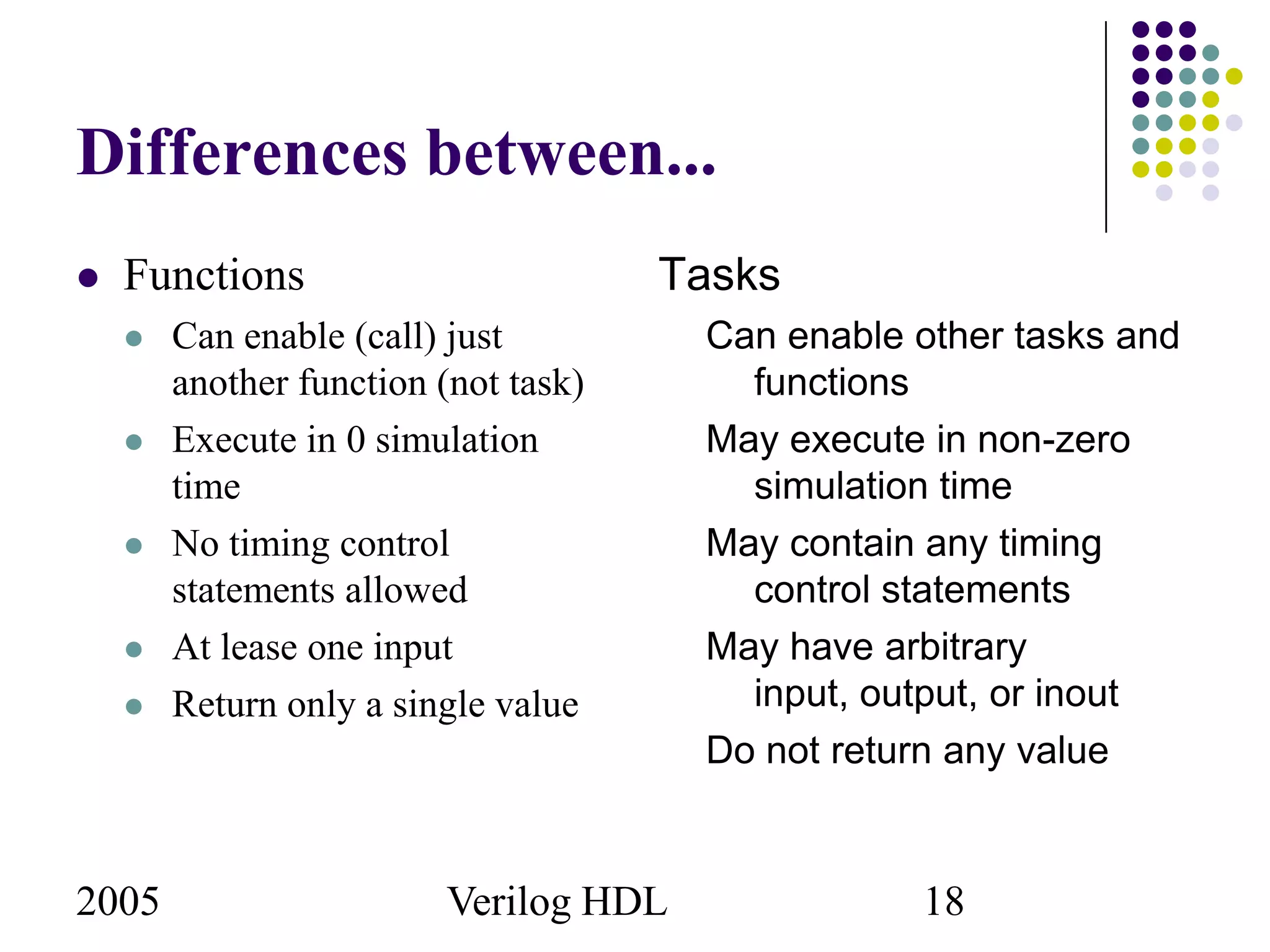
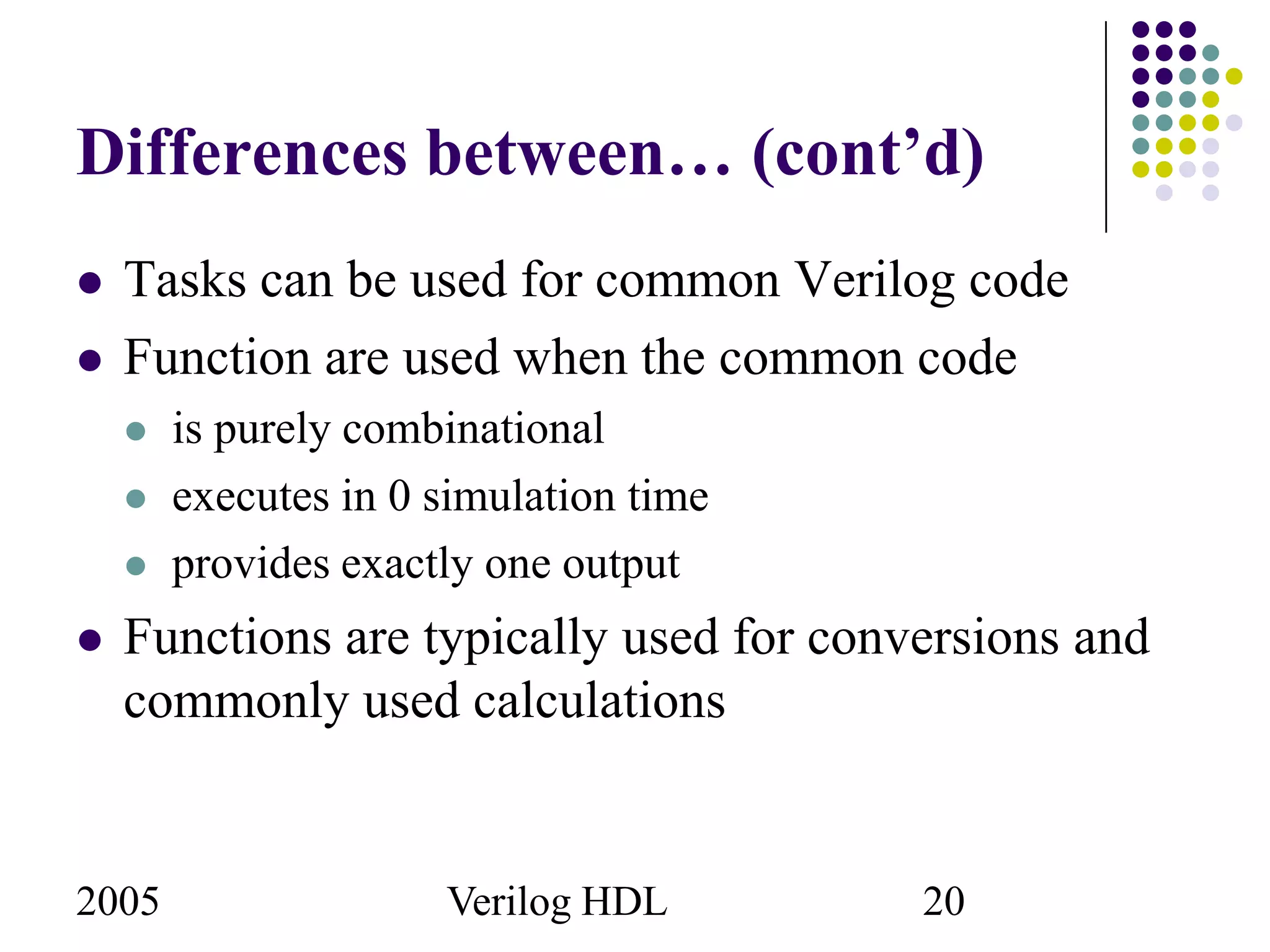
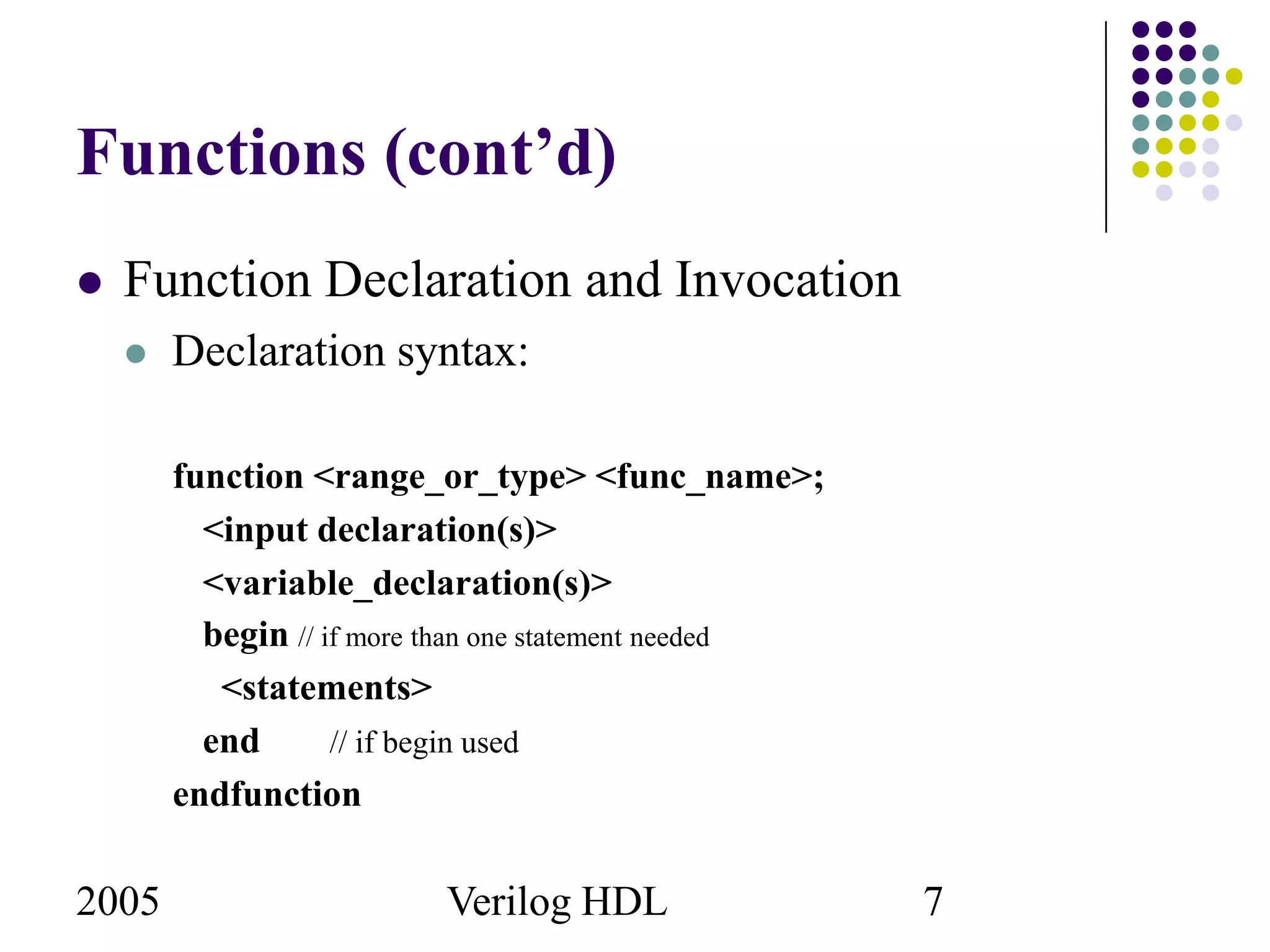
The document outlines the use of tasks and functions in Verilog HDL, emphasizing their purpose in behavioral modeling and code reuse. Functions return a single value without timing control, while tasks can have timing controls and multiple input/output arguments. Key differences and examples of their declaration and invocation are also provided.






![2005 Verilog HDL 10 Function Examples Parity Generator module parity; reg [31:0] addr; reg parity; initial begin … end always @(addr) begin parity = calc_parity(addr); $display("Parity calculated = %b", calc_parity(addr) ); end function calc_parity; input [31:0] address; begin calc_parity = ^address; end endfunction endmodule](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tasksandfunctions-140407012157-phpapp01/75/Verilog-Tasks-and-functions-10-2048.jpg)




![2005 Verilog HDL 16 module operation; parameter delay = 10; reg [15:0] A, B; reg [15:0] AB_AND, AB_OR, AB_XOR; initial $monitor( …); initial begin … end always @(A or B) begin bitwise_oper(AB_AND, AB_OR, AB_XOR, A, B); end task bitwise_oper; output [15:0] ab_and, ab_or, ab_xor; input [15:0] a, b; begin #delay ab_and = a & b; ab_or = a | b; ab_xor = a ^ b; end endtask endmodule Task Examples Use of input and output arguments](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tasksandfunctions-140407012157-phpapp01/75/Verilog-Tasks-and-functions-16-2048.jpg)