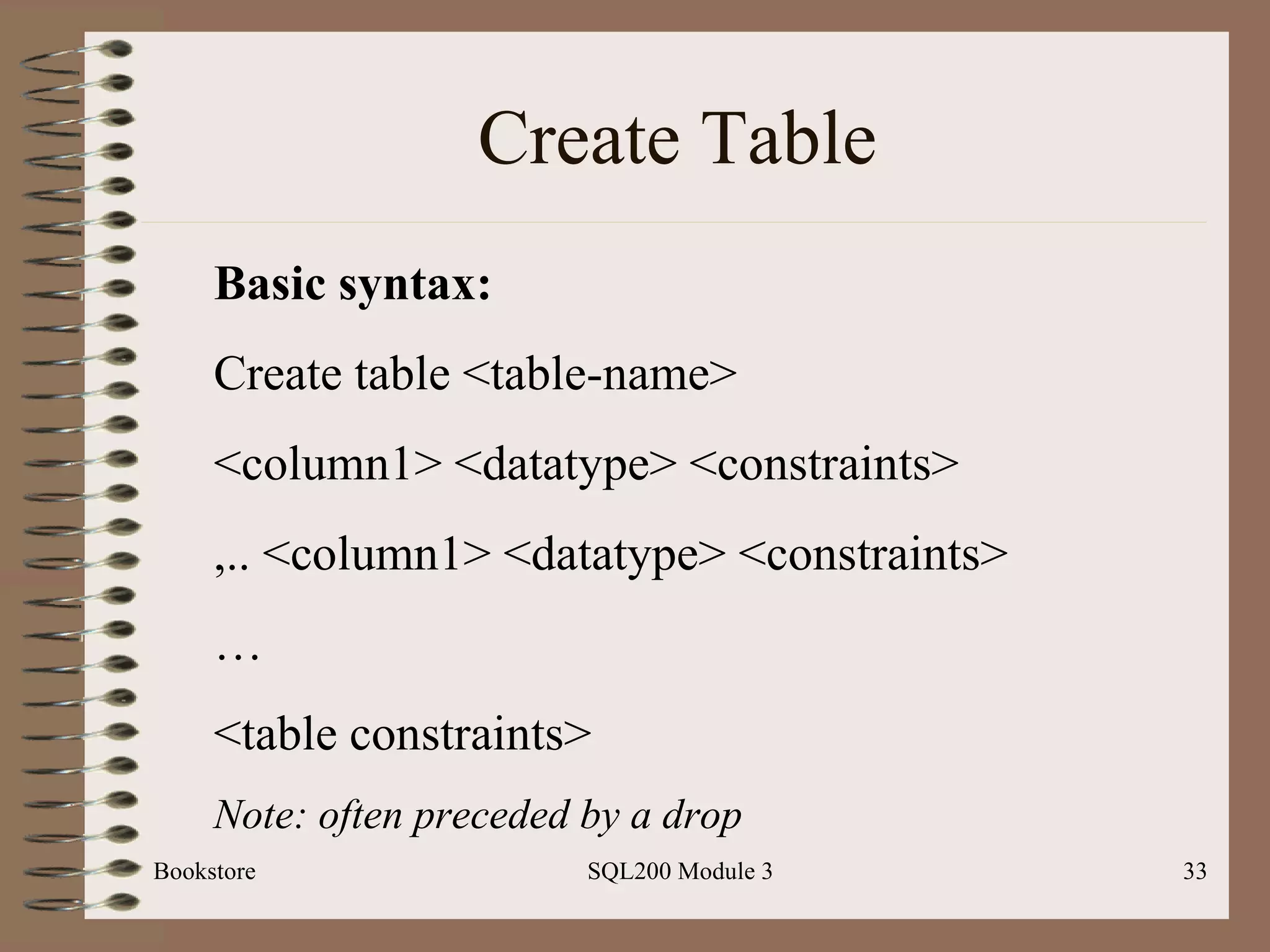
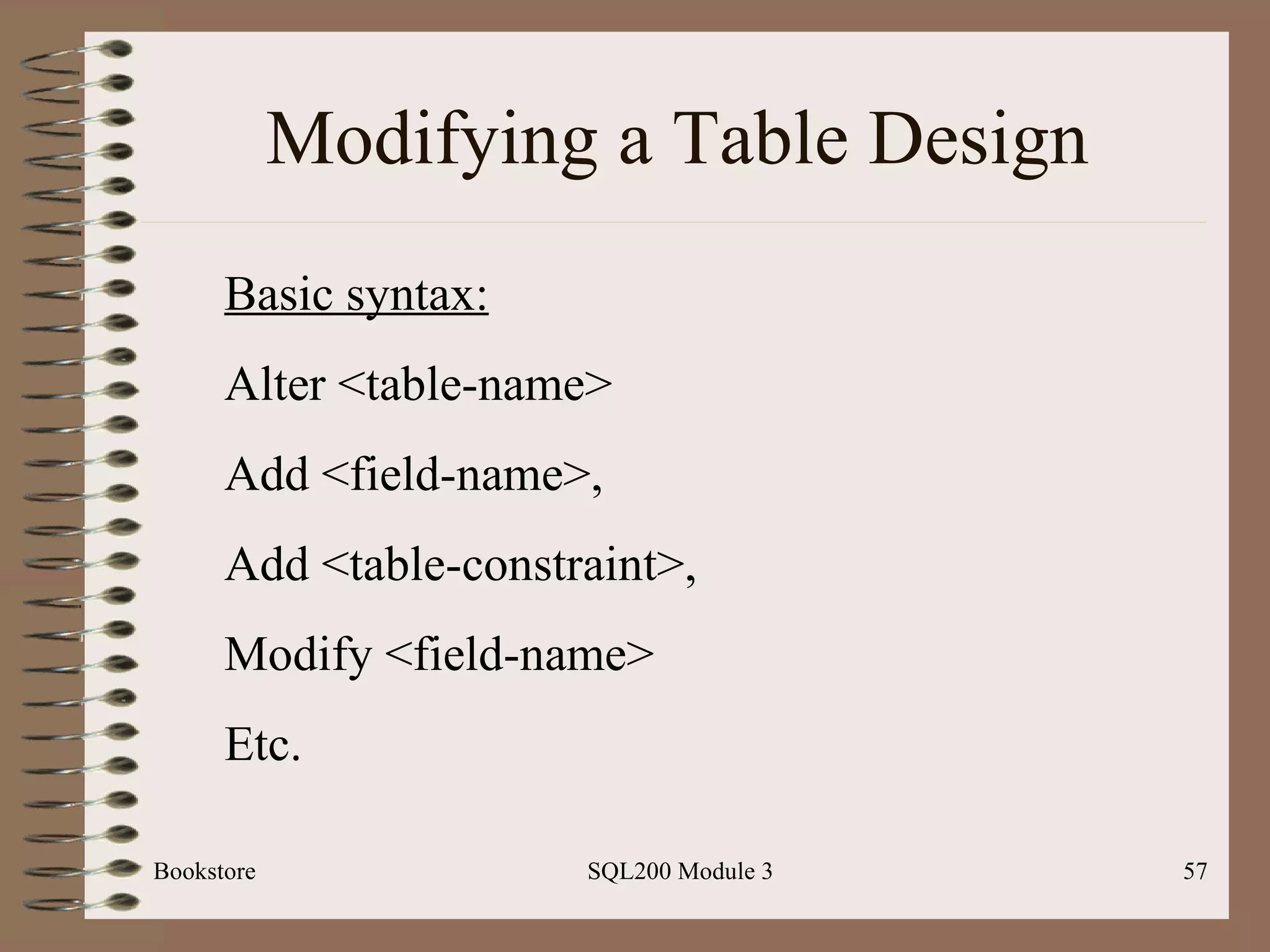
The document outlines a workshop on SQL programming, specifically focusing on modifying data and managing databases using Microsoft SQL Server. It covers essential concepts such as data modification statements, creating and altering tables, managing structures, and security considerations within databases. Additionally, it includes practical examples of SQL commands and best practices for database management.



![SQL200 Contact Information Bookstore SQL200 Module 3 P.O. Box 6142 Laguna Niguel, CA 92607 949-489-1472 http://www.d2associates.com [email_address] Copyright 2001-2011. All rights reserved.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql200-s3-bk-120110132749-phpapp01/75/SQL202-3-Accelerated-Introduction-to-SQL-Using-SQL-Server-Module-3-4-2048.jpg)
![SQL200 Resources Bookstore database scripts found on box.net at http://tinyurl.com/SQLScripts Slides can be viewed on SlideShare… http://www.slideshare.net/OCDatabases Follow up questions? [email_address] Bookstore SQL212 Module 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql200-s3-bk-120110132749-phpapp01/75/SQL202-3-Accelerated-Introduction-to-SQL-Using-SQL-Server-Module-3-5-2048.jpg)


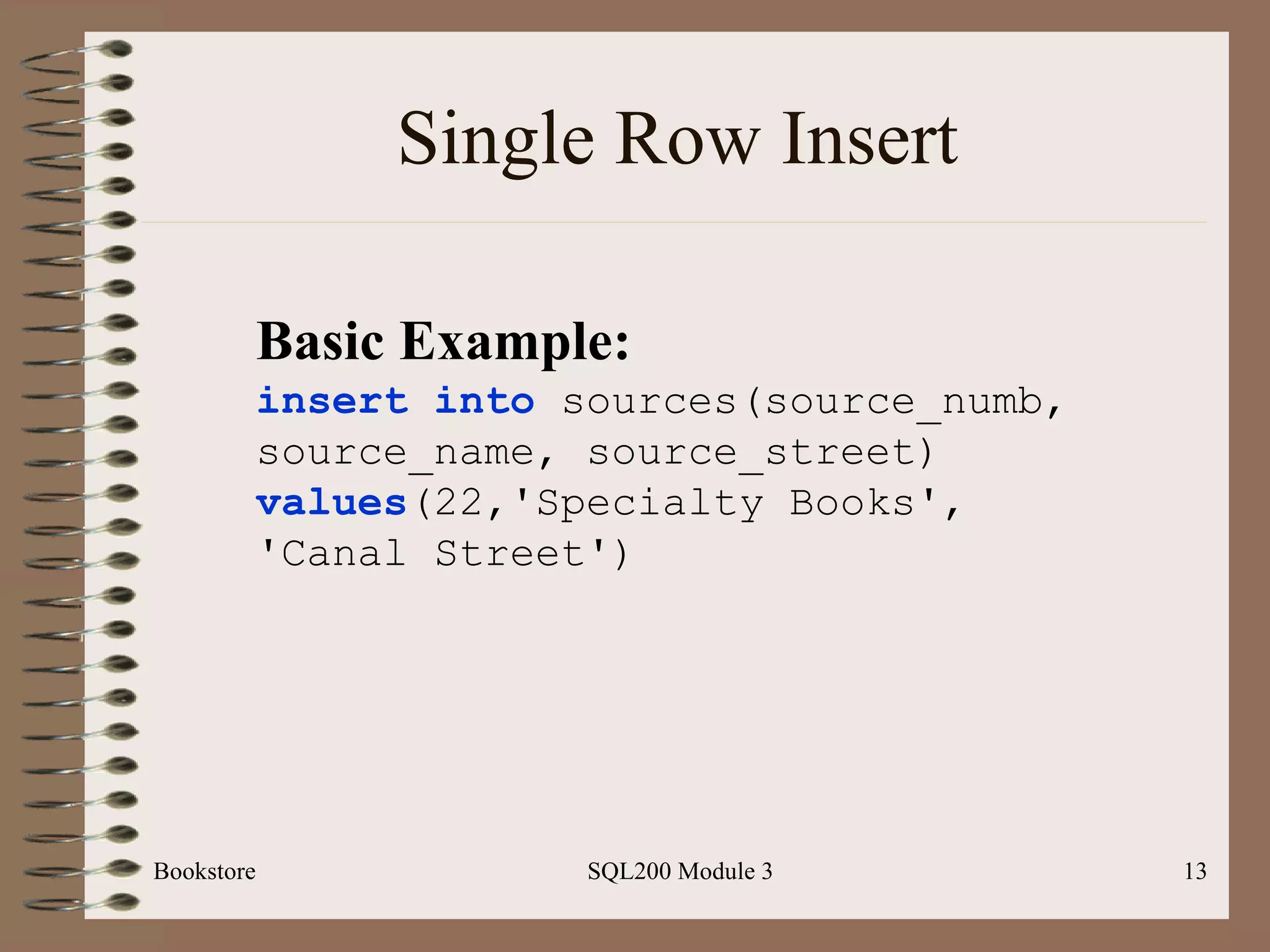
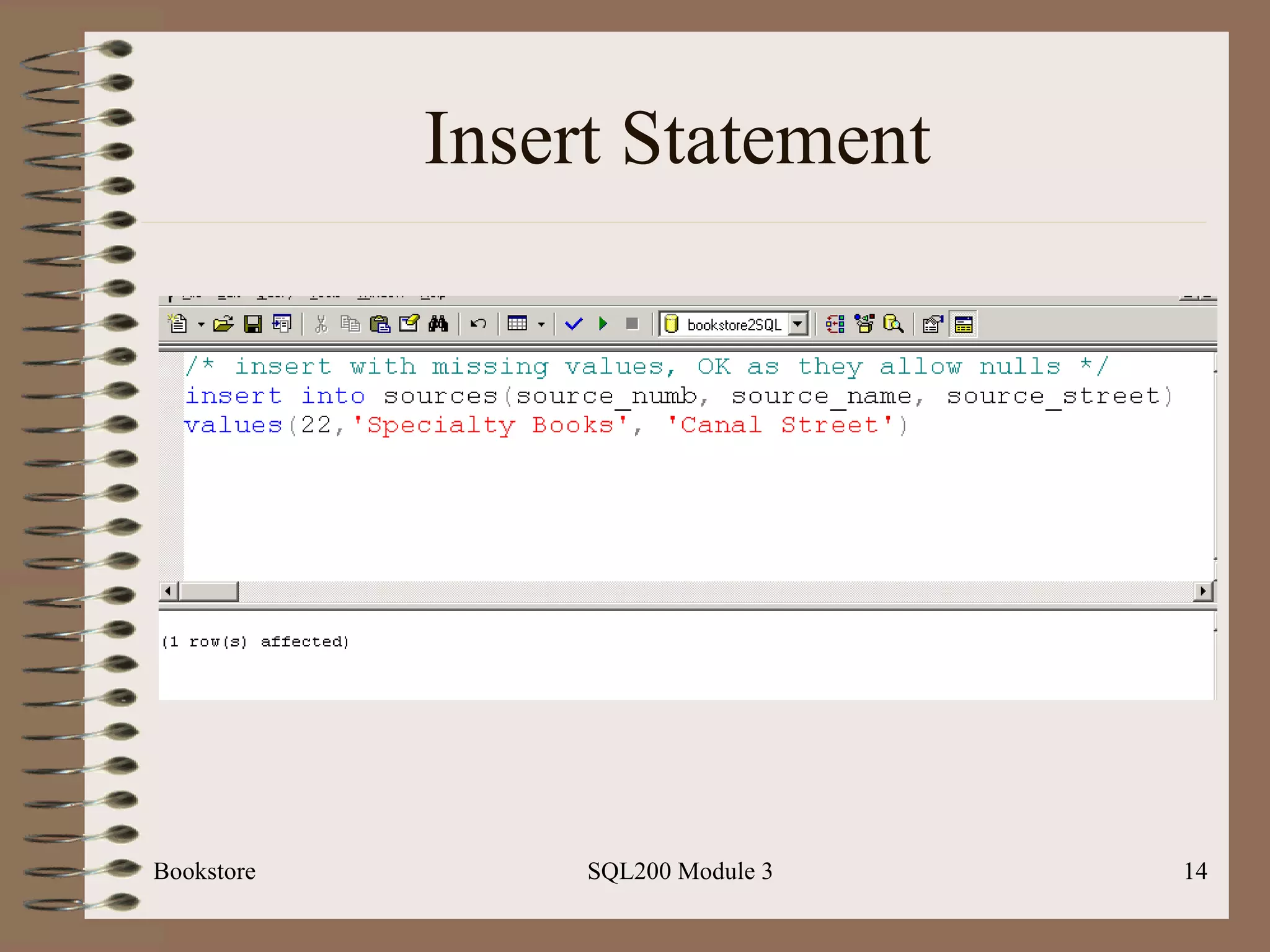
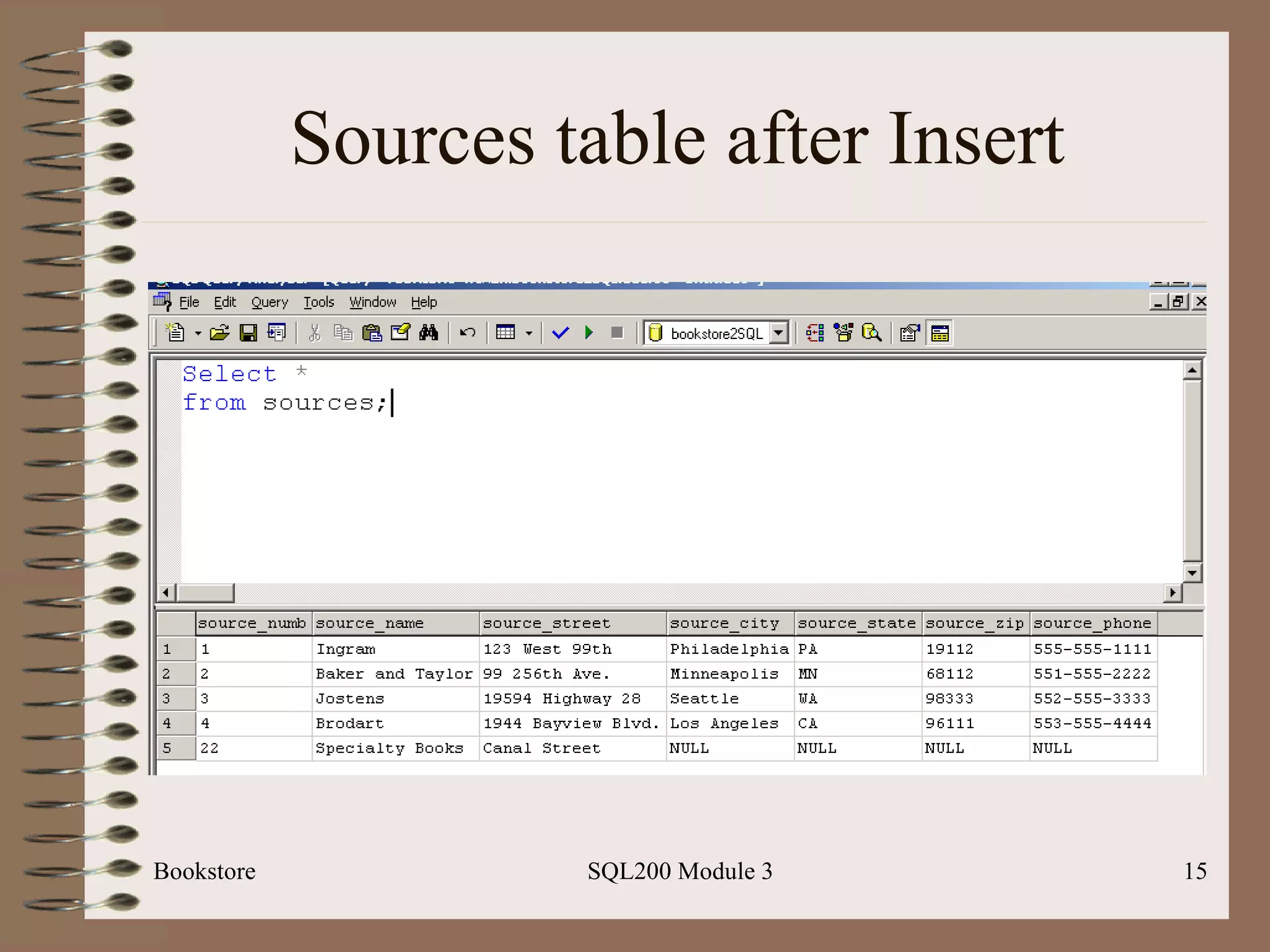
![Single Row Insert Bookstore SQL200 Module 3 Basic Syntax: Insert [into] <table-name> Values (<value-list>)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql200-s3-bk-120110132749-phpapp01/75/SQL202-3-Accelerated-Introduction-to-SQL-Using-SQL-Server-Module-3-12-2048.jpg)
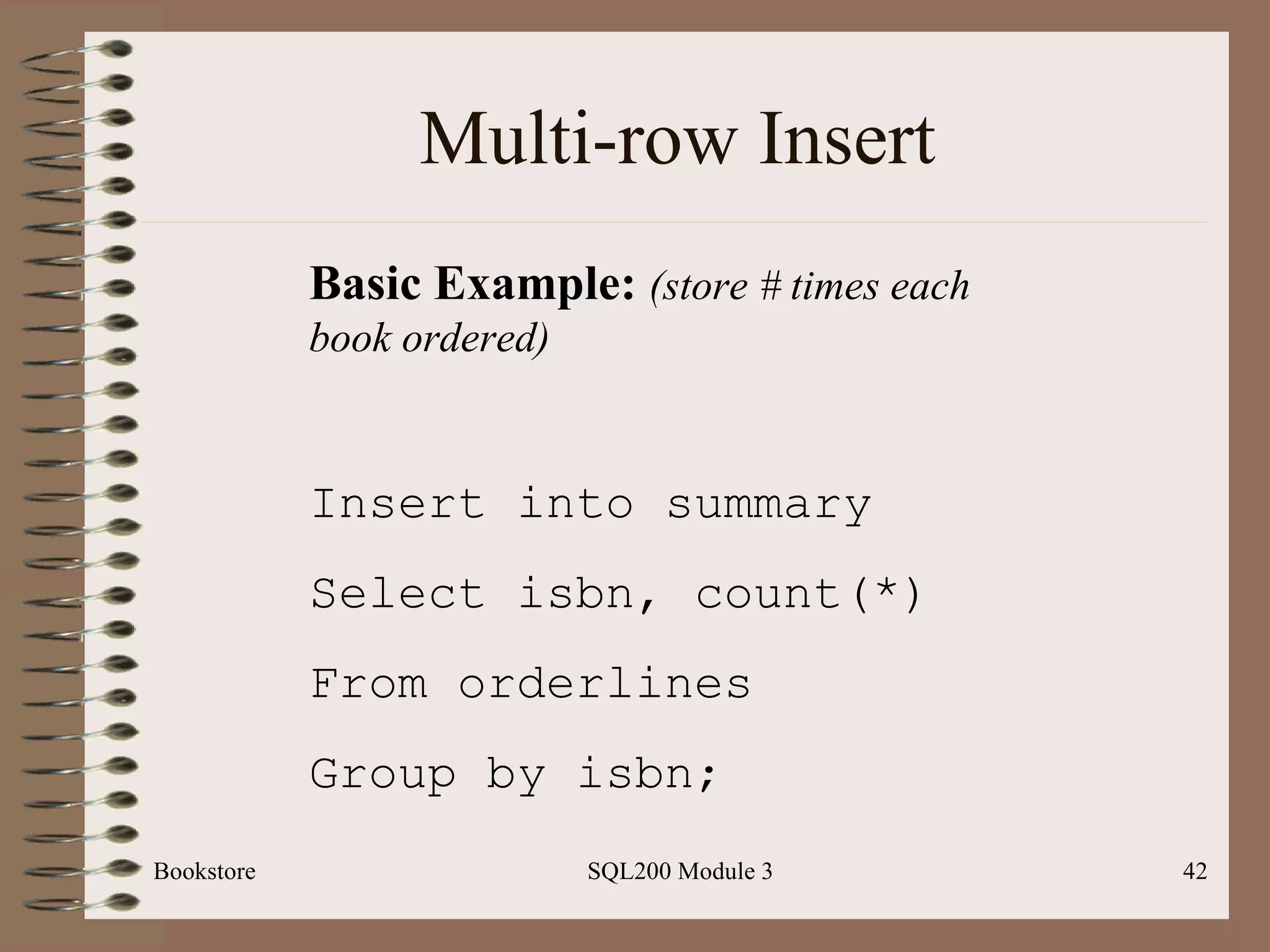
![Multi-row Insert Bookstore SQL200 Module 3 Basic Syntax: Insert [into] <table-name> Select <select-statement> We will do this after creating a new table later in this module](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql200-s3-bk-120110132749-phpapp01/75/SQL202-3-Accelerated-Introduction-to-SQL-Using-SQL-Server-Module-3-16-2048.jpg)







![Temporary Tables Bookstore SQL200 Module 3 Basic syntax (SQL standard): Create [global] temporary table <table-name> <rest of statement as for normal create> Note: SQL Server uses a different syntax. Just put a #in front of the table name as in #mytable.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql200-s3-bk-120110132749-phpapp01/75/SQL202-3-Accelerated-Introduction-to-SQL-Using-SQL-Server-Module-3-34-2048.jpg)




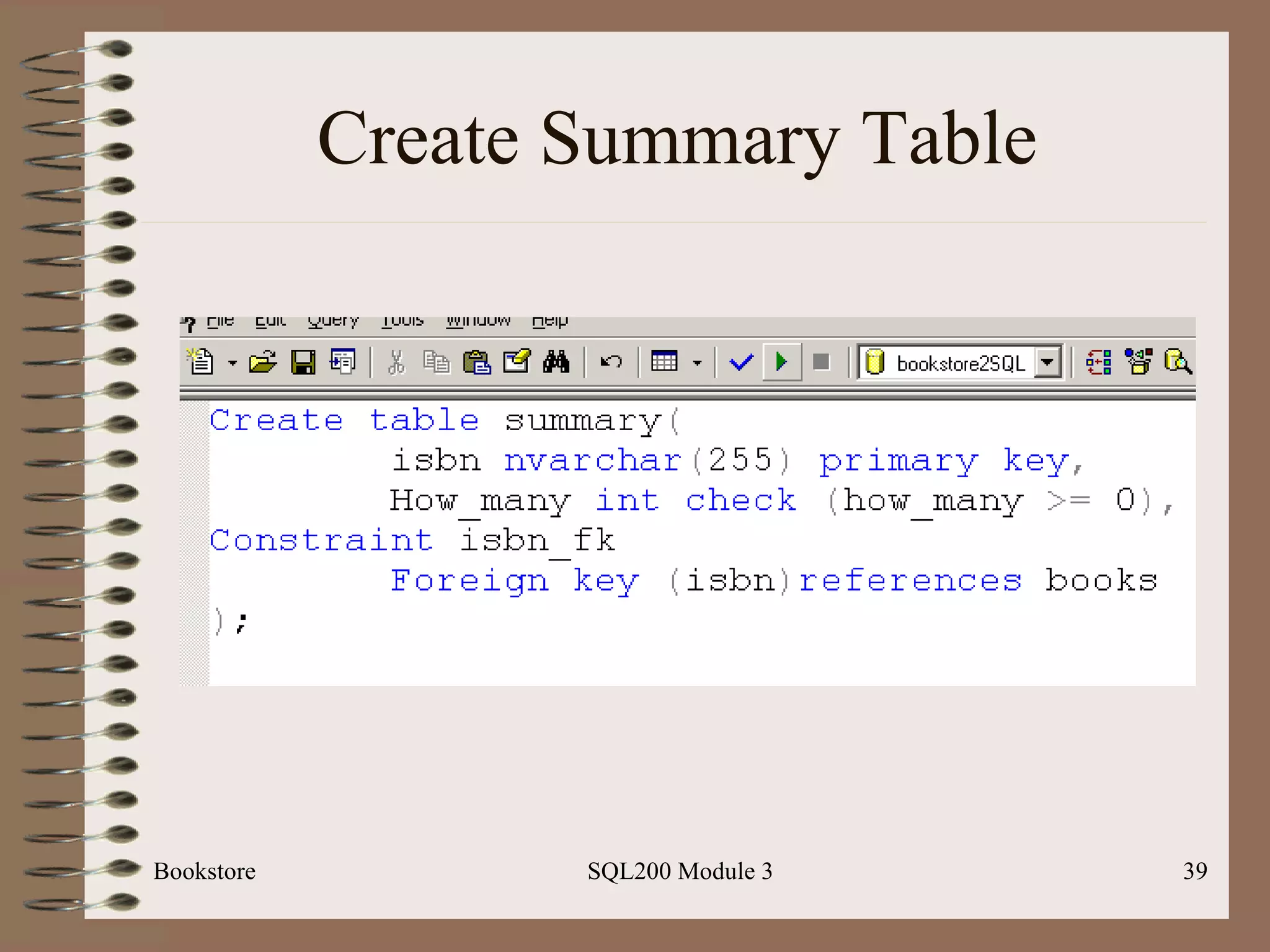
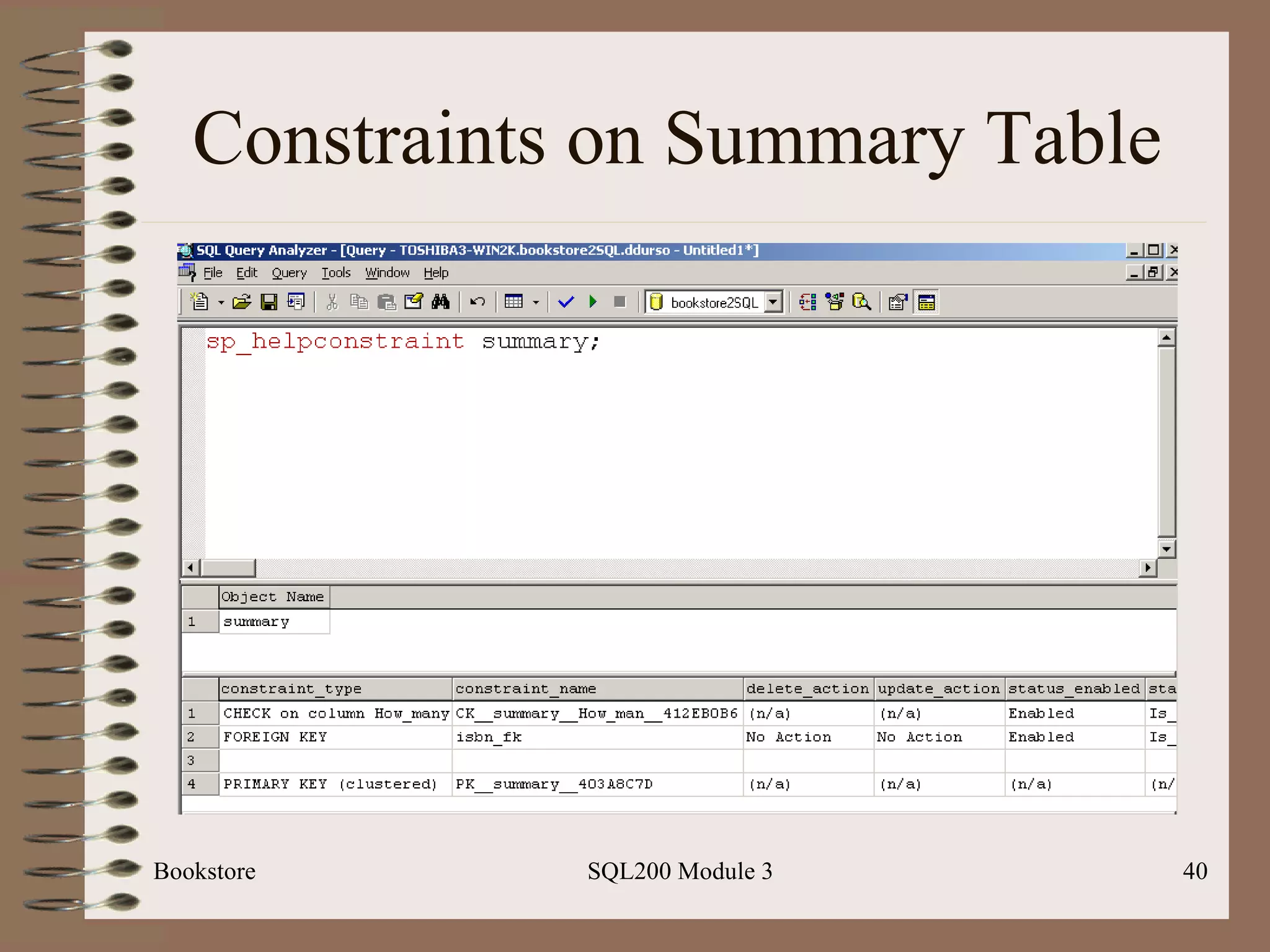
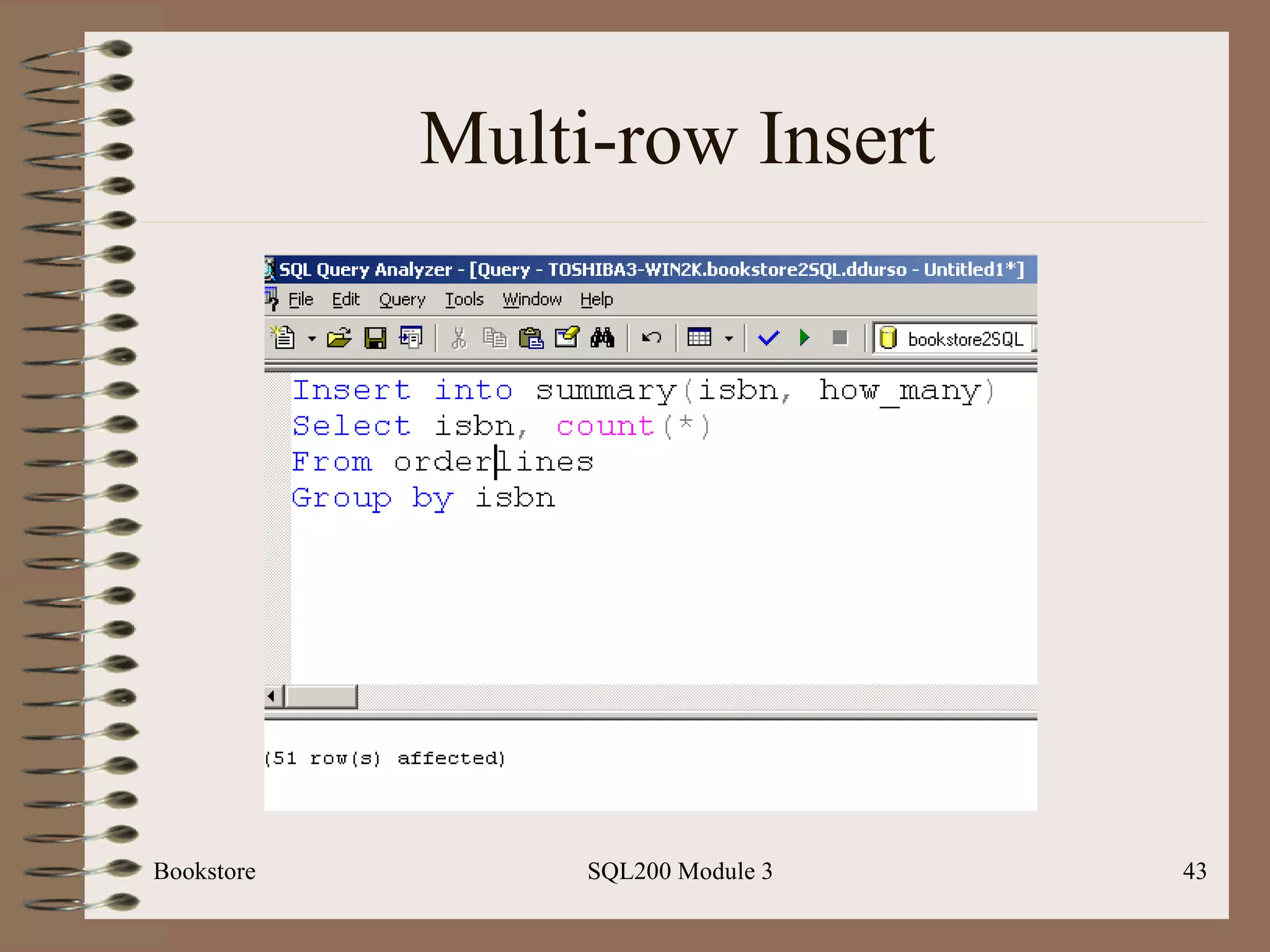
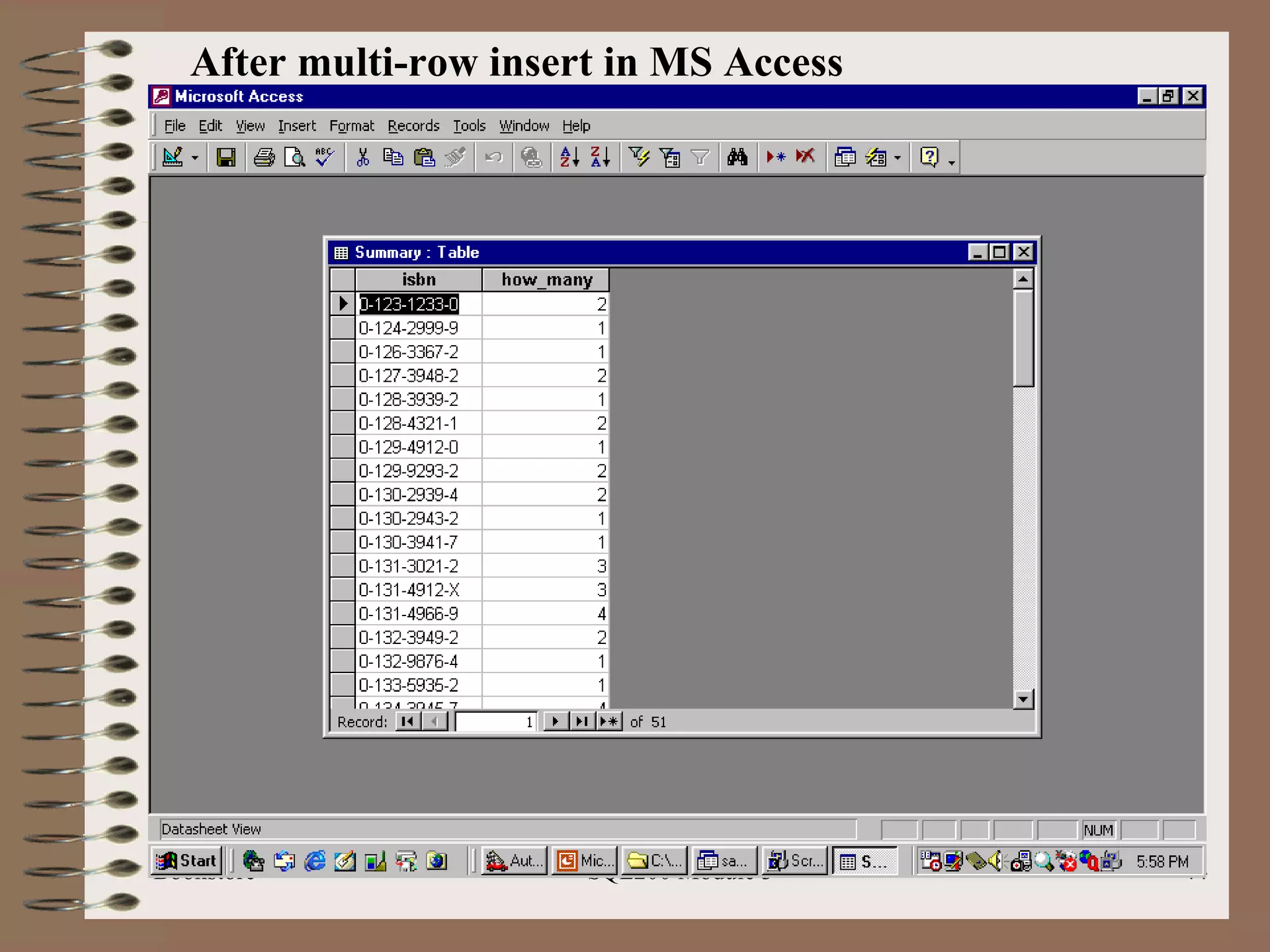
![Multi-row Insert Bookstore SQL200 Module 3 Basic Syntax: Insert [into] <table-name> [(<column list>)] Select <select-statement>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql200-s3-bk-120110132749-phpapp01/75/SQL202-3-Accelerated-Introduction-to-SQL-Using-SQL-Server-Module-3-41-2048.jpg)


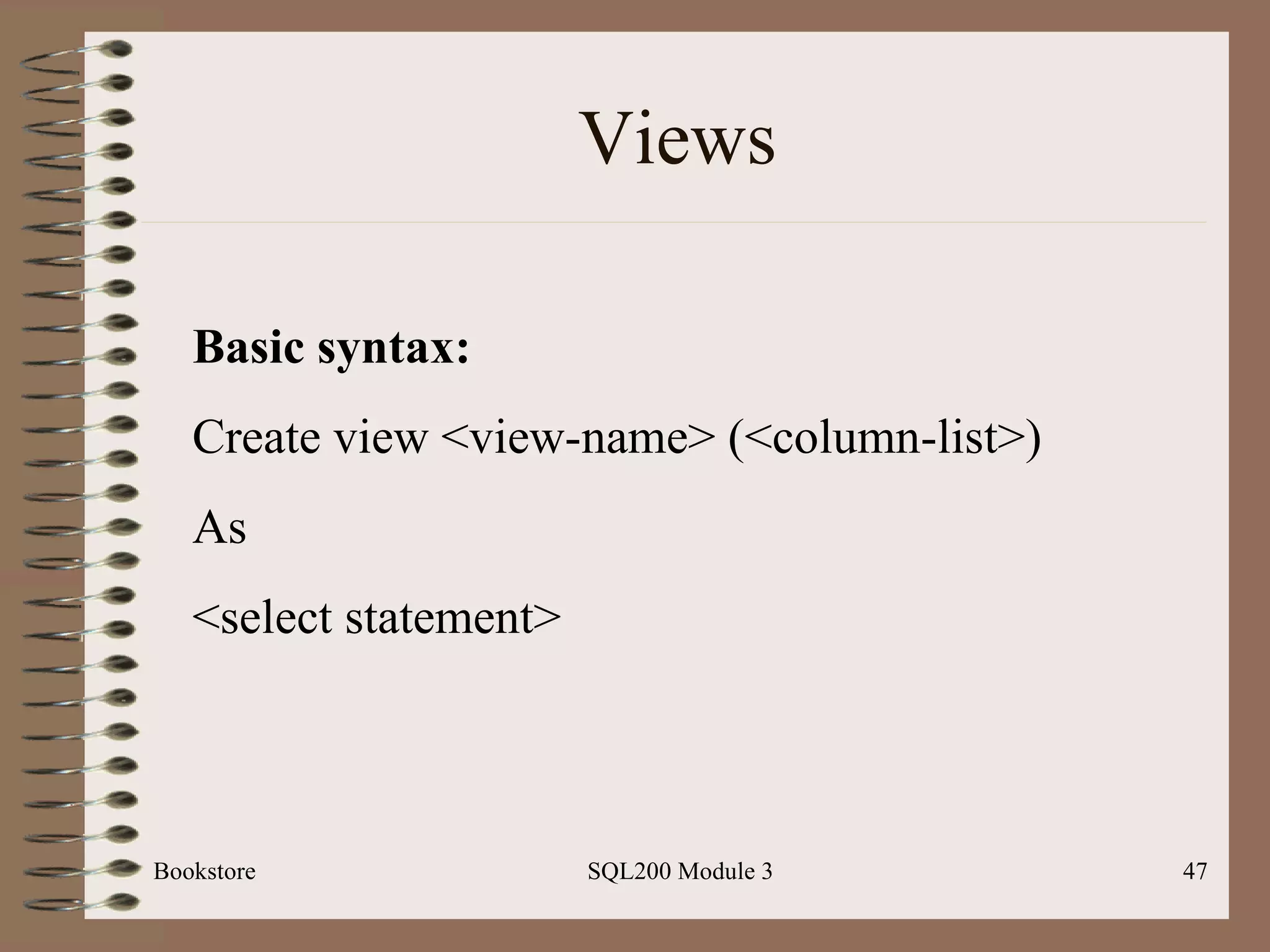
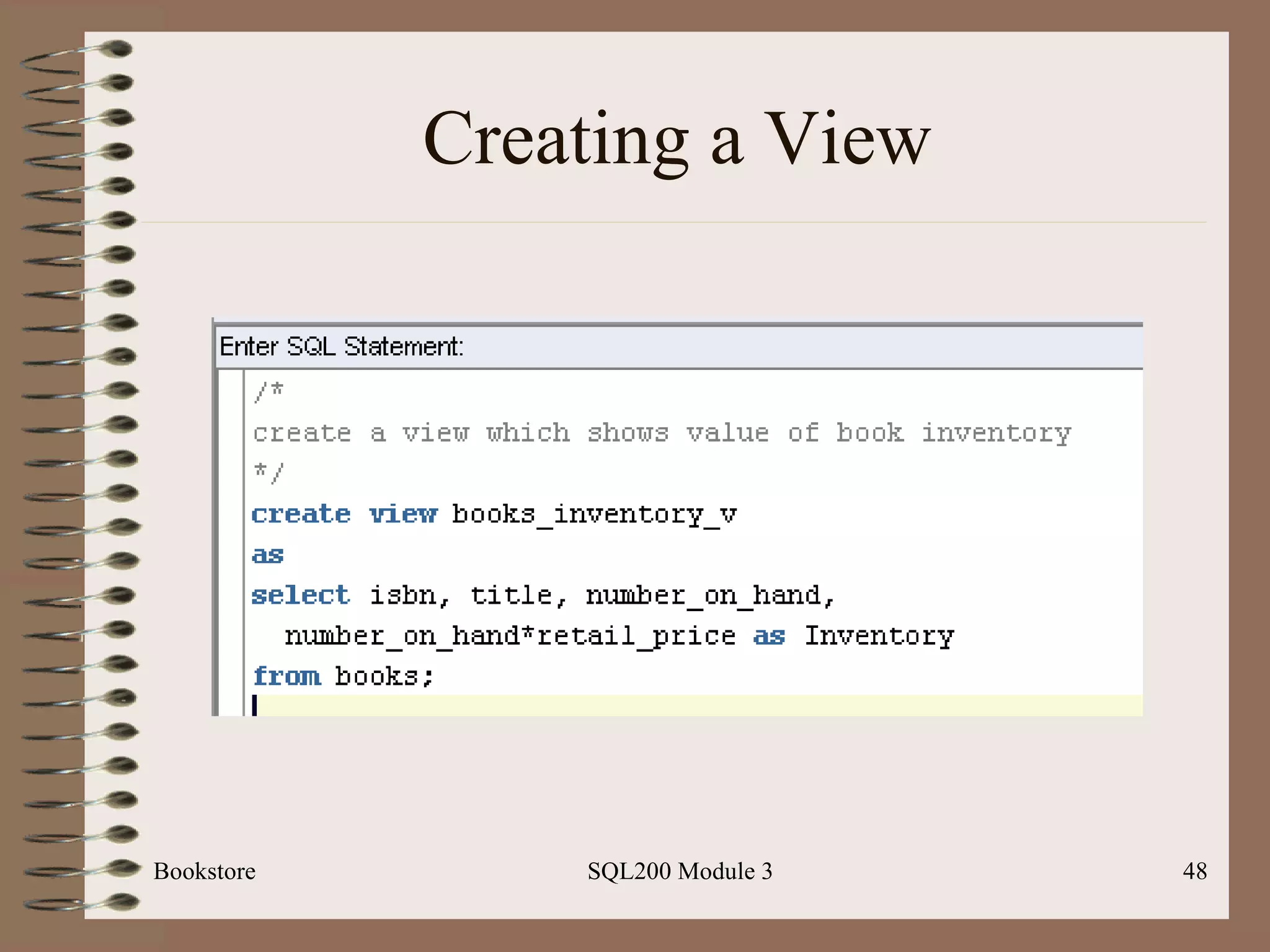



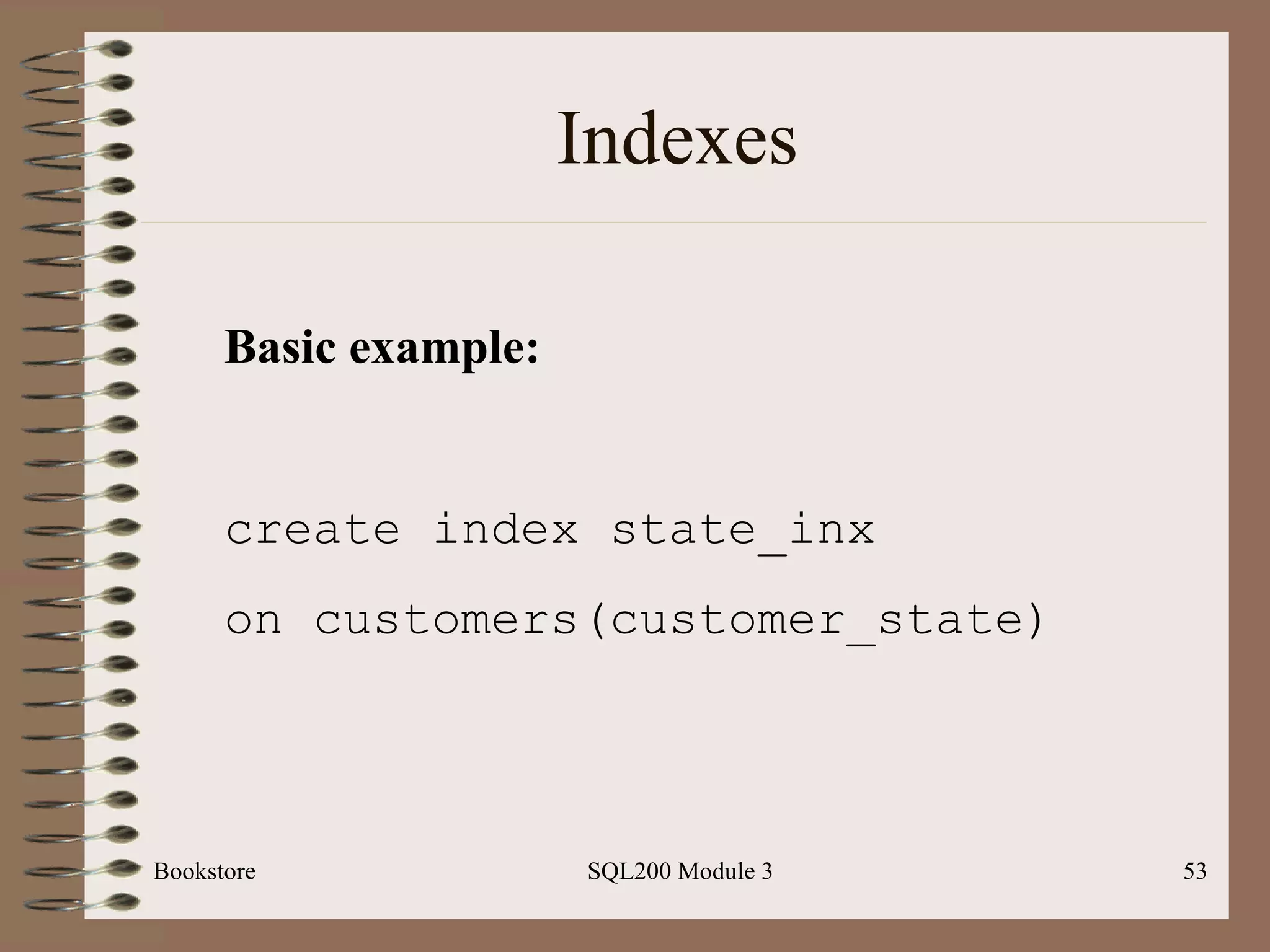
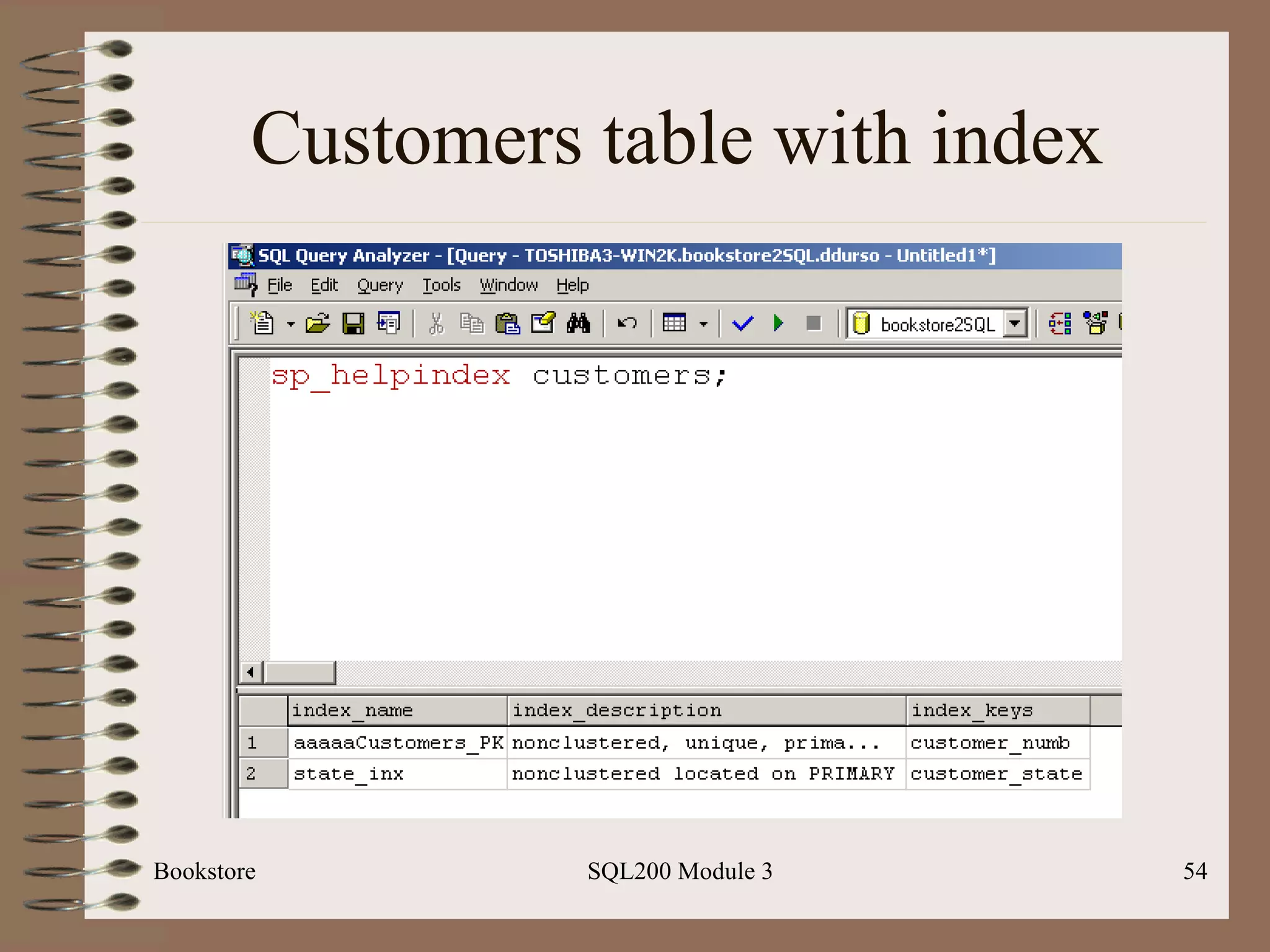
![Indexes Bookstore SQL200 Module 3 Basic syntax: Create [unique] index <index-name> On <table-name> (field-name> [desc]) Note: can place index on a composite key; ex: state and city](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql200-s3-bk-120110132749-phpapp01/75/SQL202-3-Accelerated-Introduction-to-SQL-Using-SQL-Server-Module-3-52-2048.jpg)




![Grant Bookstore SQL200 Module 3 Syntax: Grant <access-right> [with grant option] On <object> to <user> Note: by default only tables owners and admins can access a table. Others must be granted the relevant rights.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql200-s3-bk-120110132749-phpapp01/75/SQL202-3-Accelerated-Introduction-to-SQL-Using-SQL-Server-Module-3-64-2048.jpg)


![Revoke Revokes the rights Syntax similar to grant Bookstore SQL200 Module 3 [end module]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql200-s3-bk-120110132749-phpapp01/75/SQL202-3-Accelerated-Introduction-to-SQL-Using-SQL-Server-Module-3-67-2048.jpg)
