The document outlines an SQL programming course, emphasizing foundational skills and basic retrieval operations using relational databases like MS Access, MySQL, Oracle, and SQL Server. It provides essential information on SQL syntax and commands, database evolution, and important features such as querying with conditions, sorting, and distinct selection. The course aims to develop proficiency in managing and manipulating databases, focusing on the SQL language for various applications.


![SQL200 Contact Information Bookstore2 SQL200 Module 2 P.O. Box 6142 Laguna Niguel, CA 92607 949-489-1472 http://www.d2associates.com [email_address] Copyright 2001-2011. All rights reserved.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql200-s1-bk-120110123708-phpapp02/75/SQL202-1-Accelerated-Introduction-to-SQL-Using-SQL-Server-Module-1-4-2048.jpg)
![SQL200 Resources Bookstore database scripts found on box.net at http://tinyurl.com/SQLScripts Slides can be viewed on SlideShare… http://www.slideshare.net/OCDatabases Follow up questions? [email_address] Bookstore SQL212 Module 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql200-s1-bk-120110123708-phpapp02/75/SQL202-1-Accelerated-Introduction-to-SQL-Using-SQL-Server-Module-1-5-2048.jpg)






















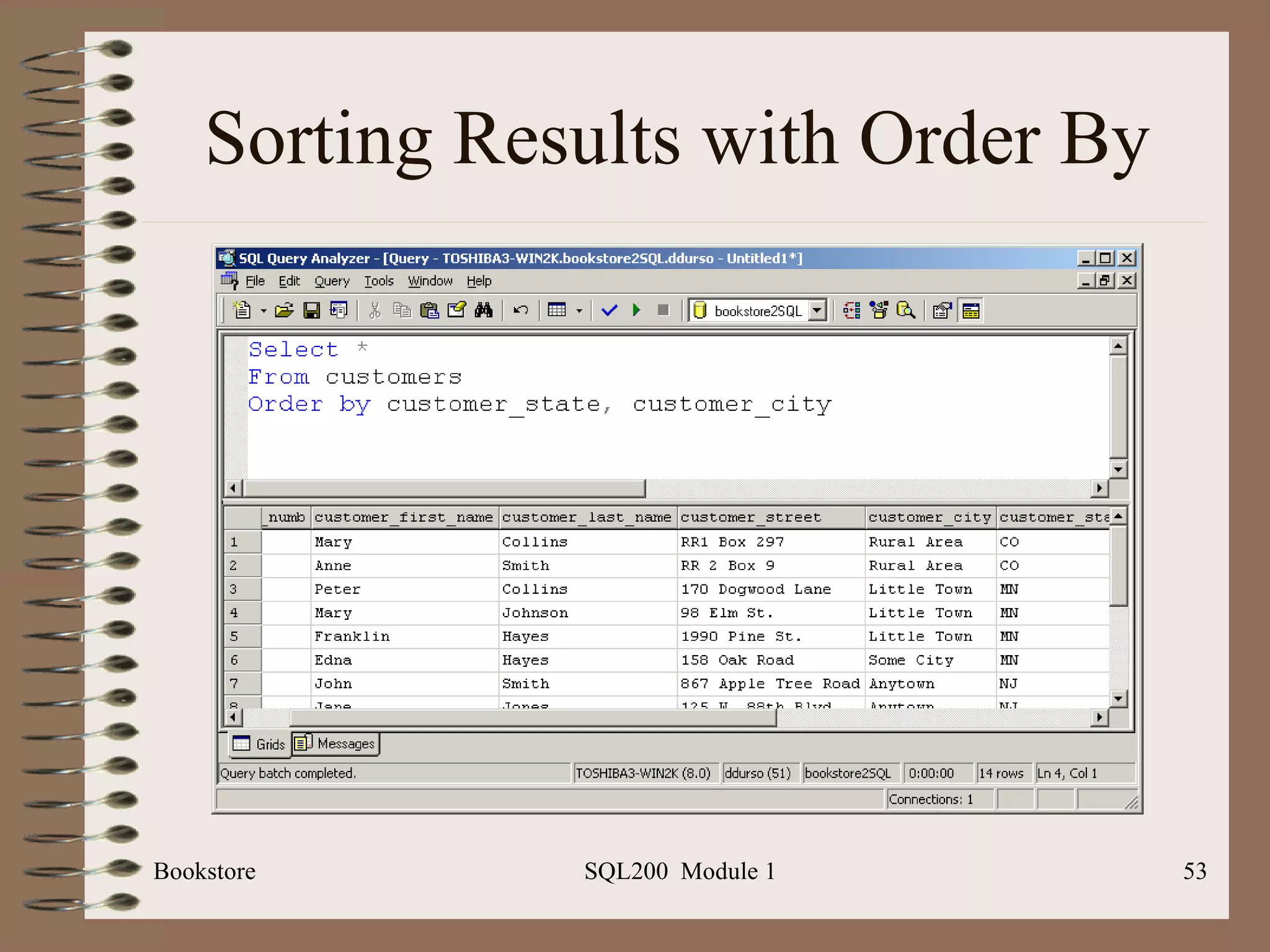
![Sorting – ORDER BY Bookstore SQL200 Module 1 DESC will sort in descending order Basic syntax : Select <column list> From <table list> Where <selection criteria> Order by <column list> [DESC]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql200-s1-bk-120110123708-phpapp02/75/SQL202-1-Accelerated-Introduction-to-SQL-Using-SQL-Server-Module-1-51-2048.jpg)


![SQL Exercises List all books whose publisher name begins with “H” or “T”; sort by title [hint: use LIKE] List all customers whose last name ends with “S”; sort by state, city, last name Find the order numbers of orders with order dates in 1999; sort by order #. [Hint: use BETWEEN] Find the order numbers and order dates of all orders with a “2” in column 2 of the credit card #; sort by order date descending Bookstore SQL200 Module 1 [end module]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql200-s1-bk-120110123708-phpapp02/75/SQL202-1-Accelerated-Introduction-to-SQL-Using-SQL-Server-Module-1-55-2048.jpg)
