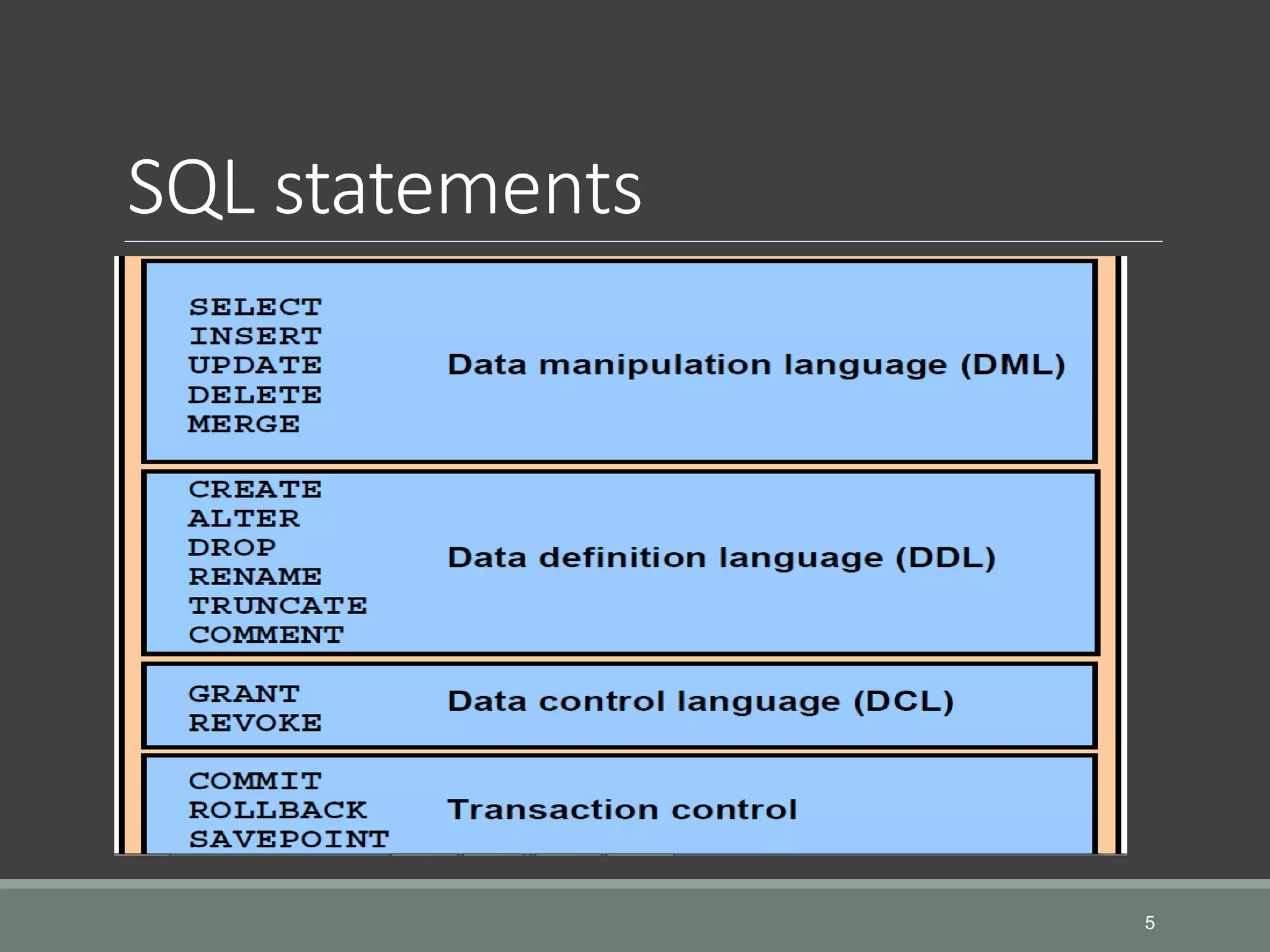
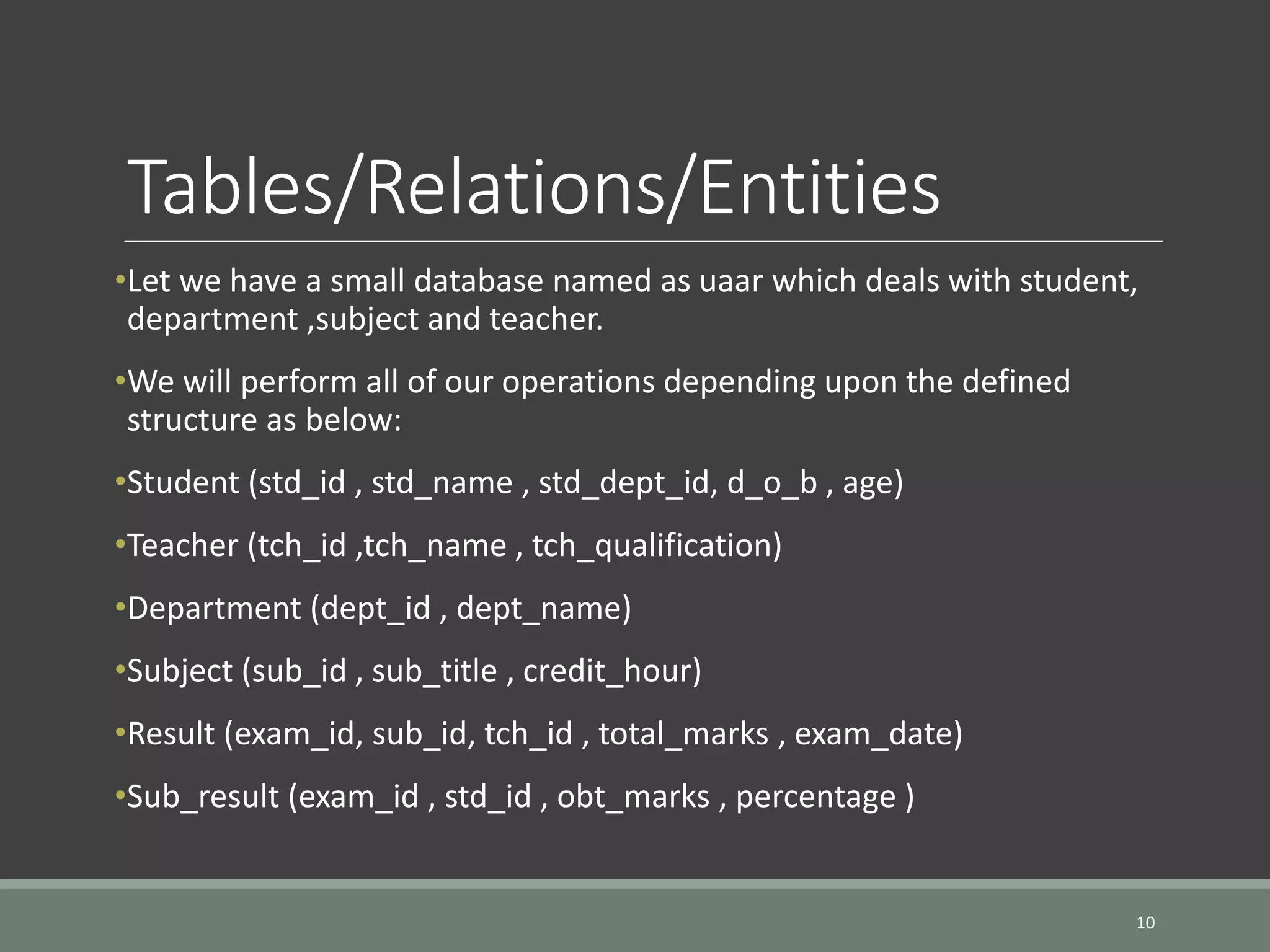
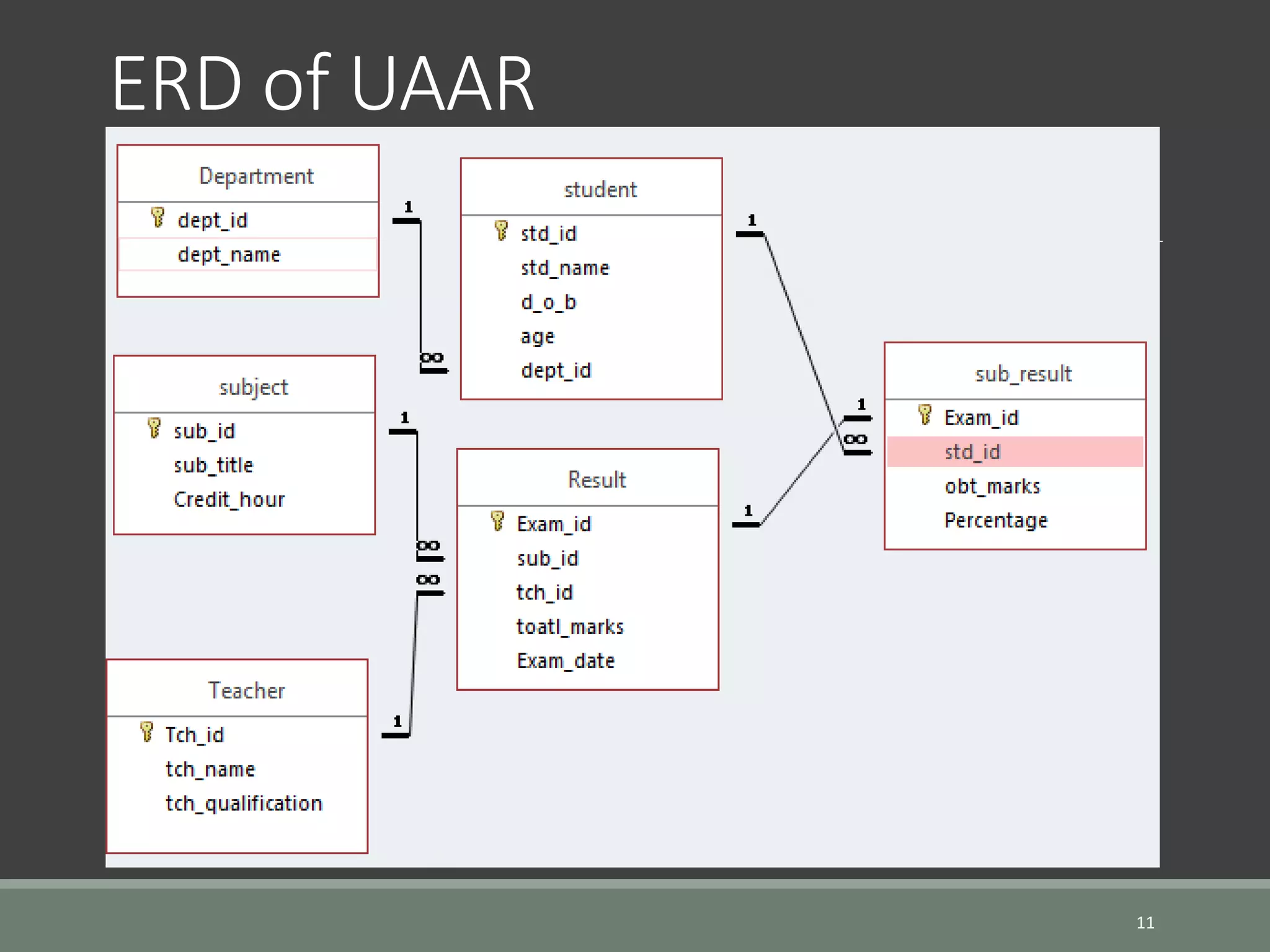
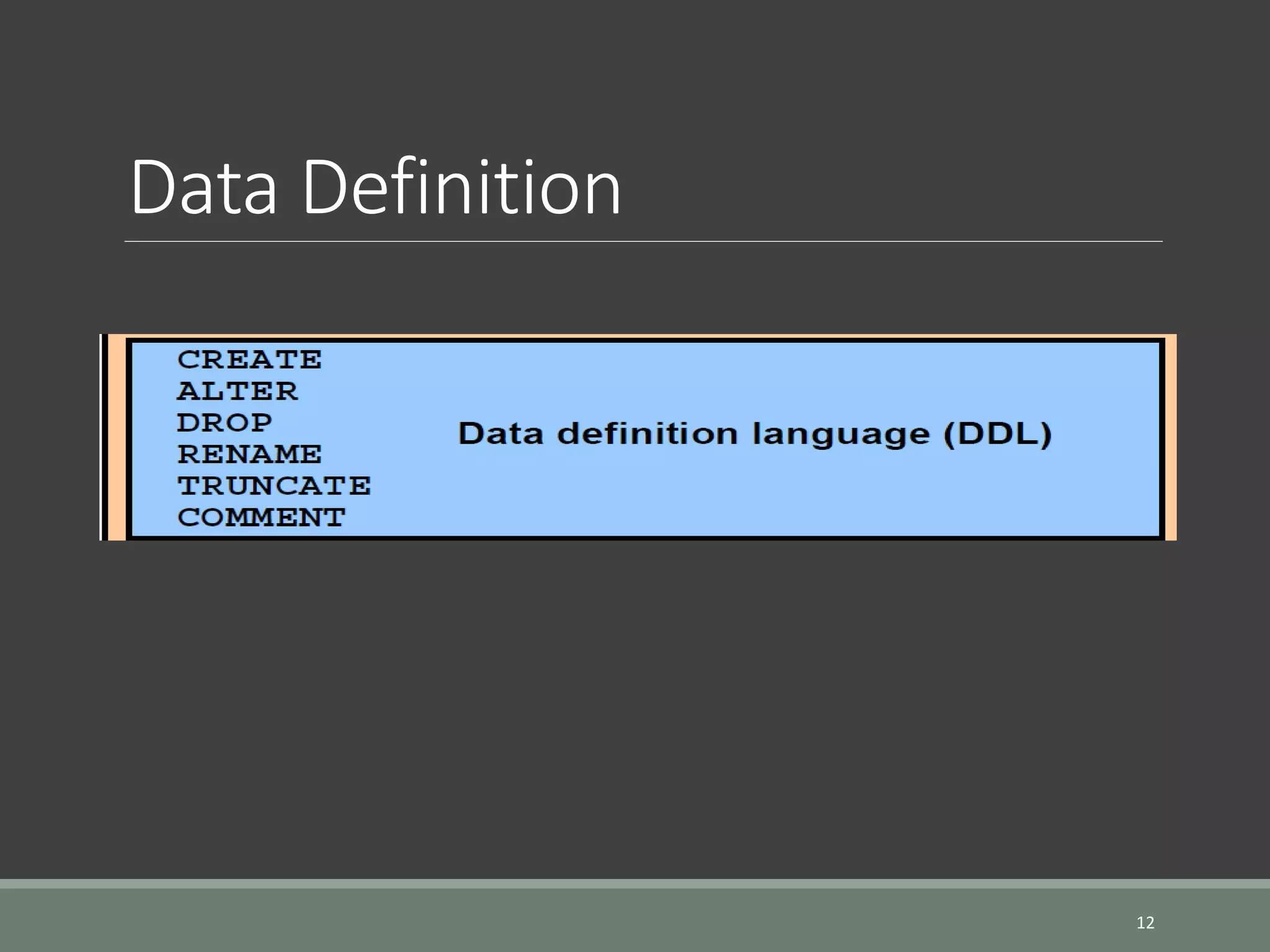
SQL is a language for operating databases and is used to perform operations like inserting, searching, updating, and deleting records from databases. The document discusses SQL fundamentals including SQL statements, database users, creating and managing tables, and adding comments. Key points covered are how to connect to a database, create users and tables, alter and drop tables, and add comments to tables and columns. Various SQL statements and syntax are provided for these operations.