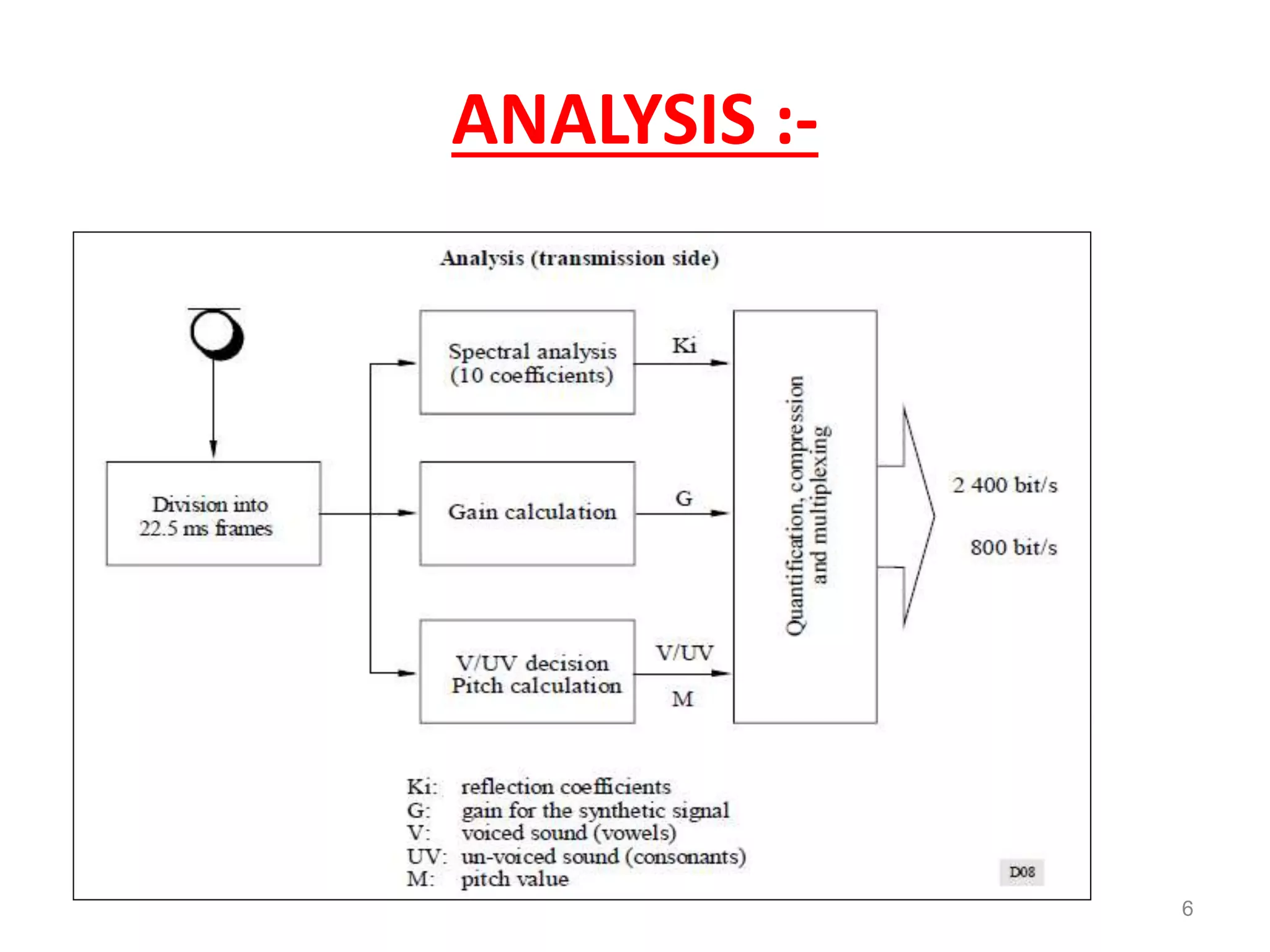
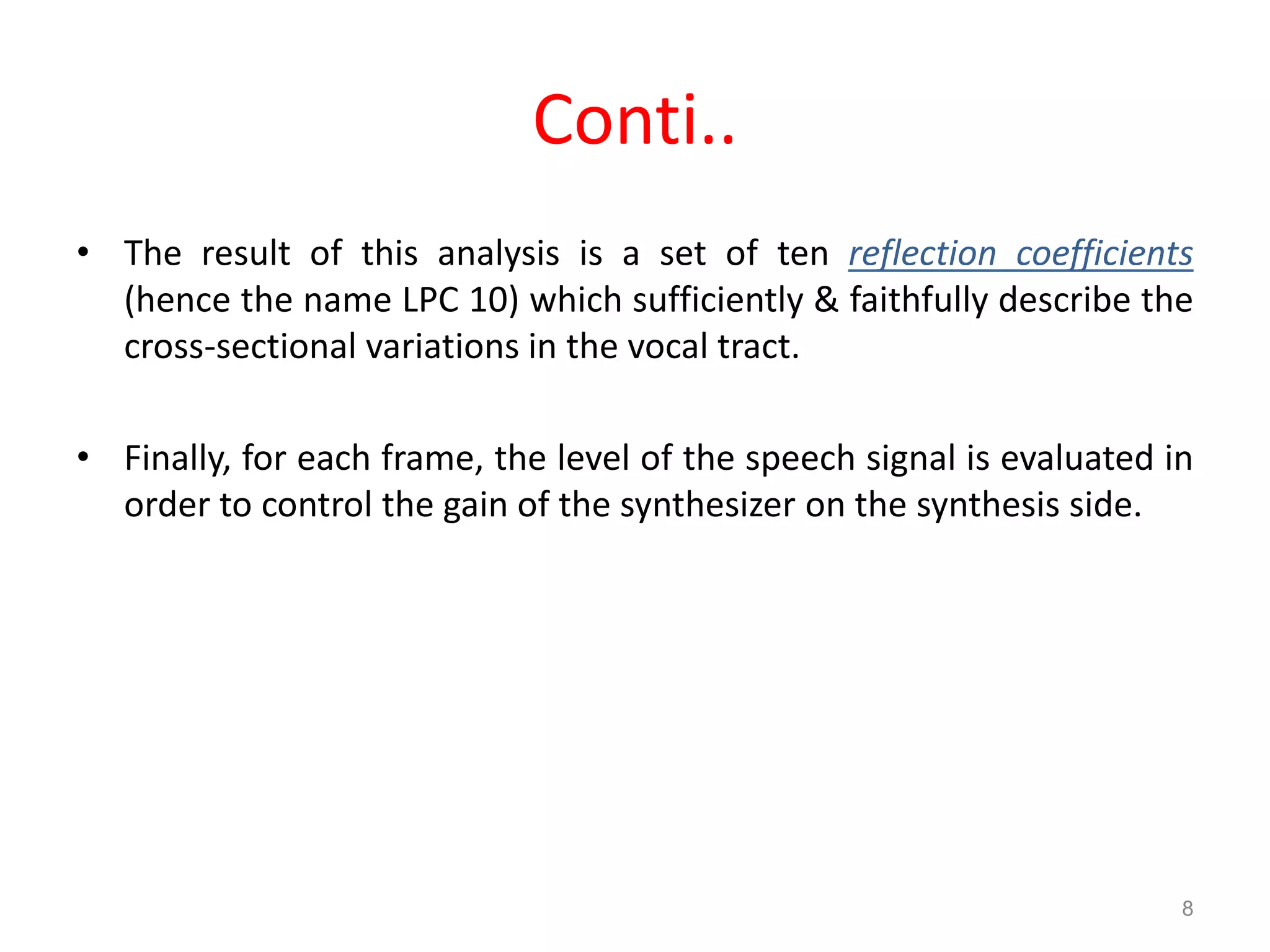
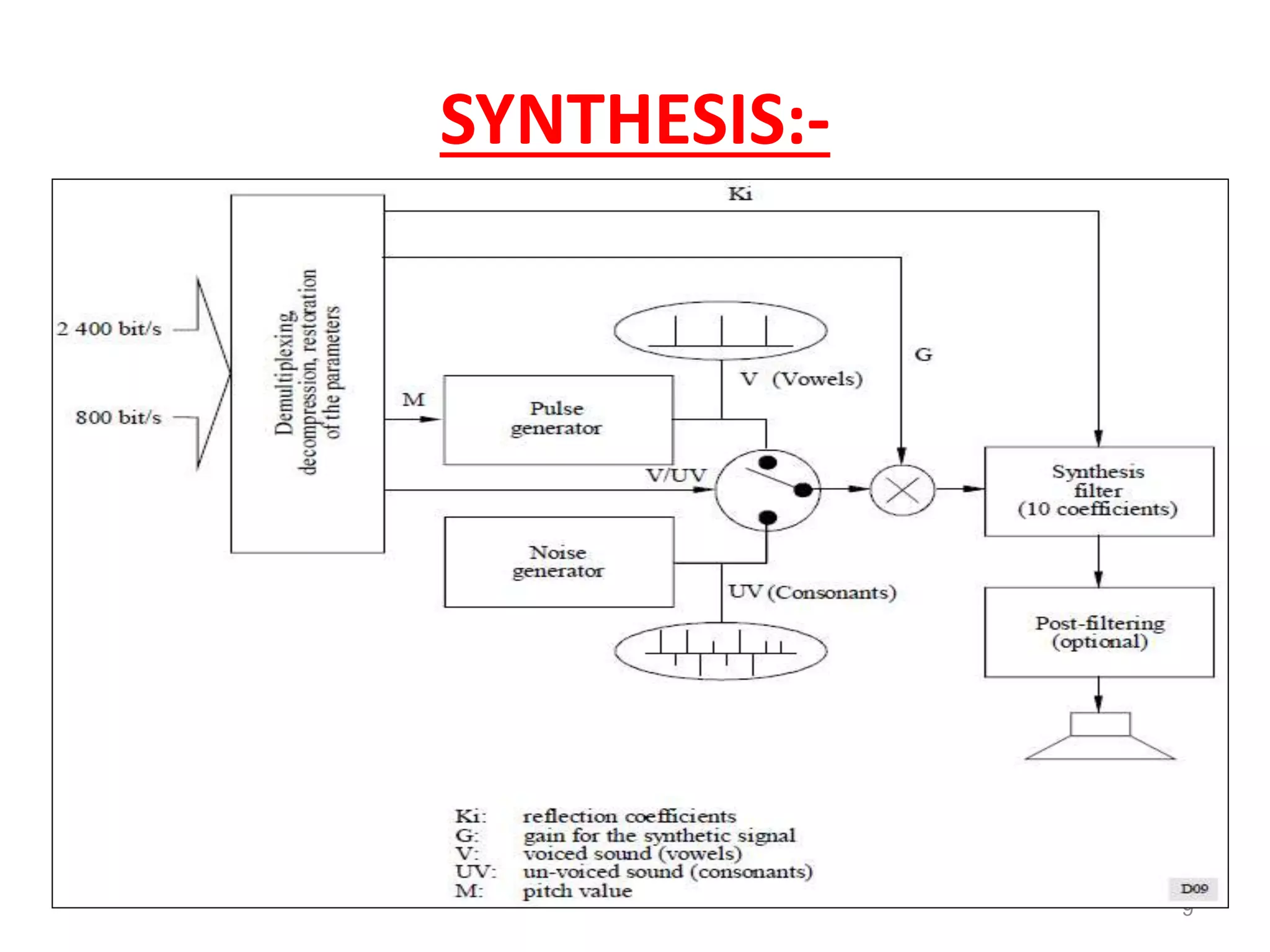
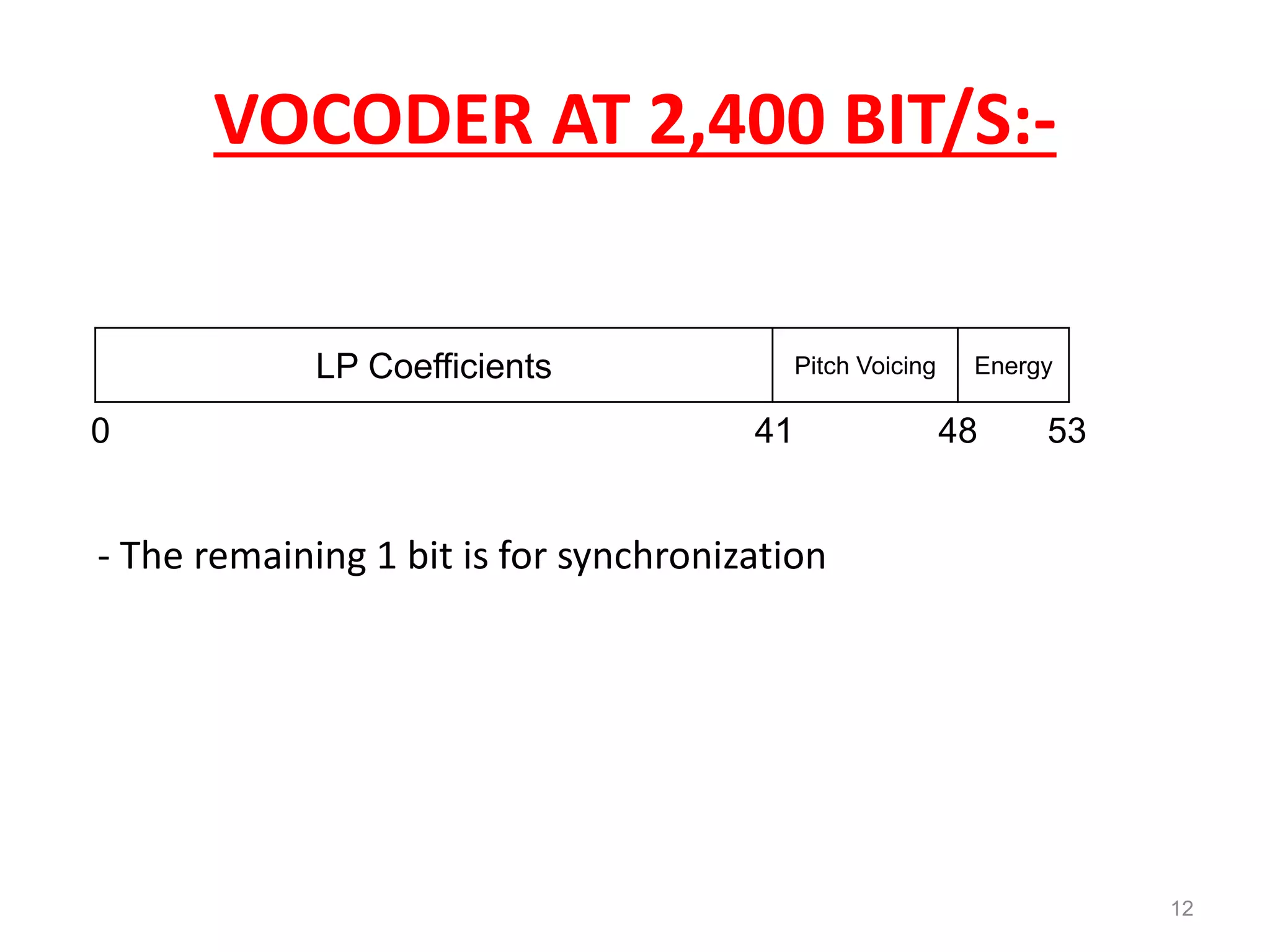
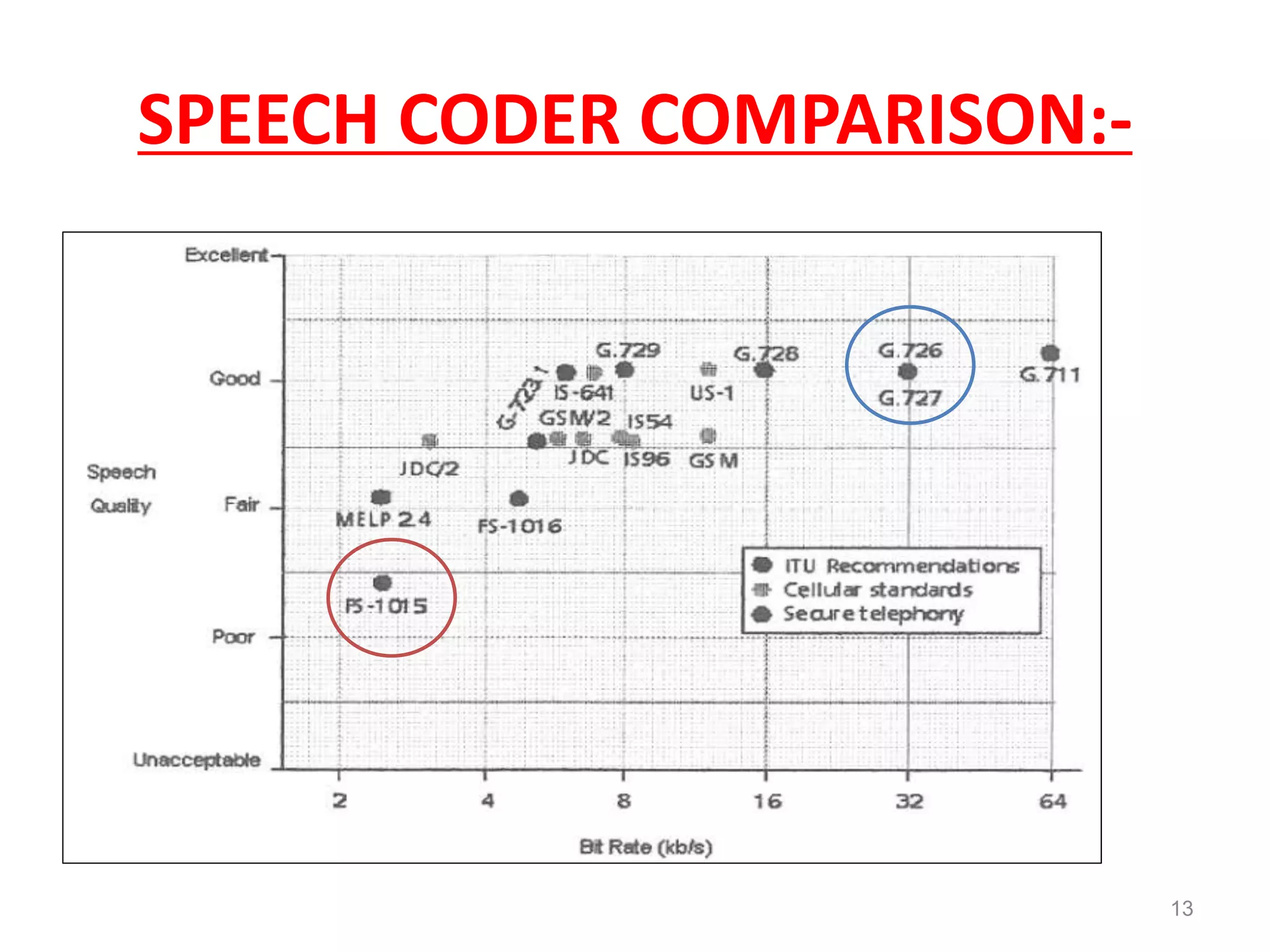
Speech coding is used to efficiently transmit speech through digital channels by retaining only the information useful to listeners. The LPC-10 standard uses linear predictive coding with 10 coefficients to analyze and synthesize speech. During analysis, it extracts parameters like voicing and pitch from the speech signal. The synthesis process uses these parameters to generate noise or periodic excitation, apply an LPC filter, and control gain. LPC-10 transmits speech at 2.4kbps by coding the 10 LPC coefficients, pitch, voicing, and energy into 54 bits per frame. It enables understandable but unnatural sounding speech and is used for secure voice transmissions.