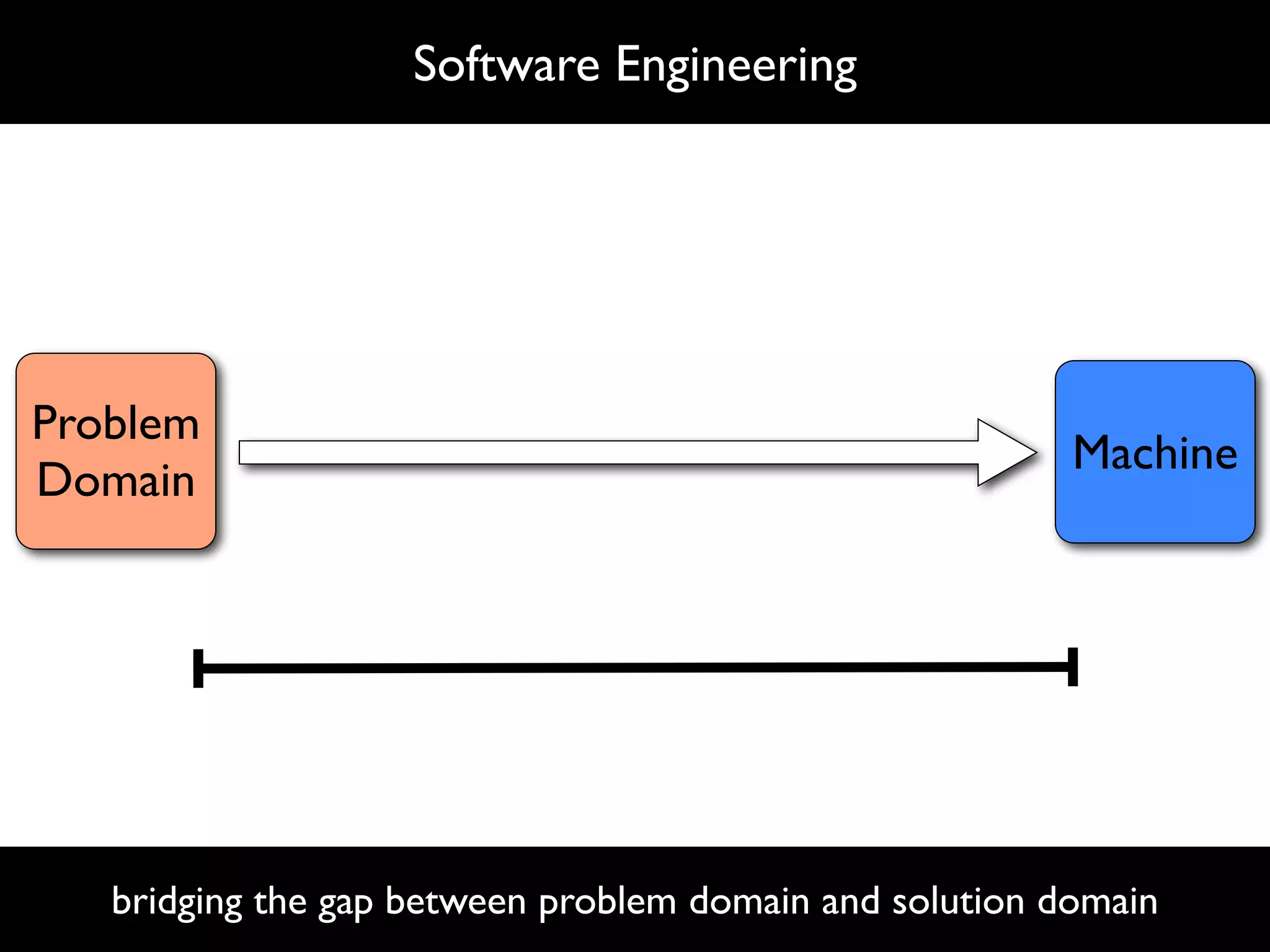
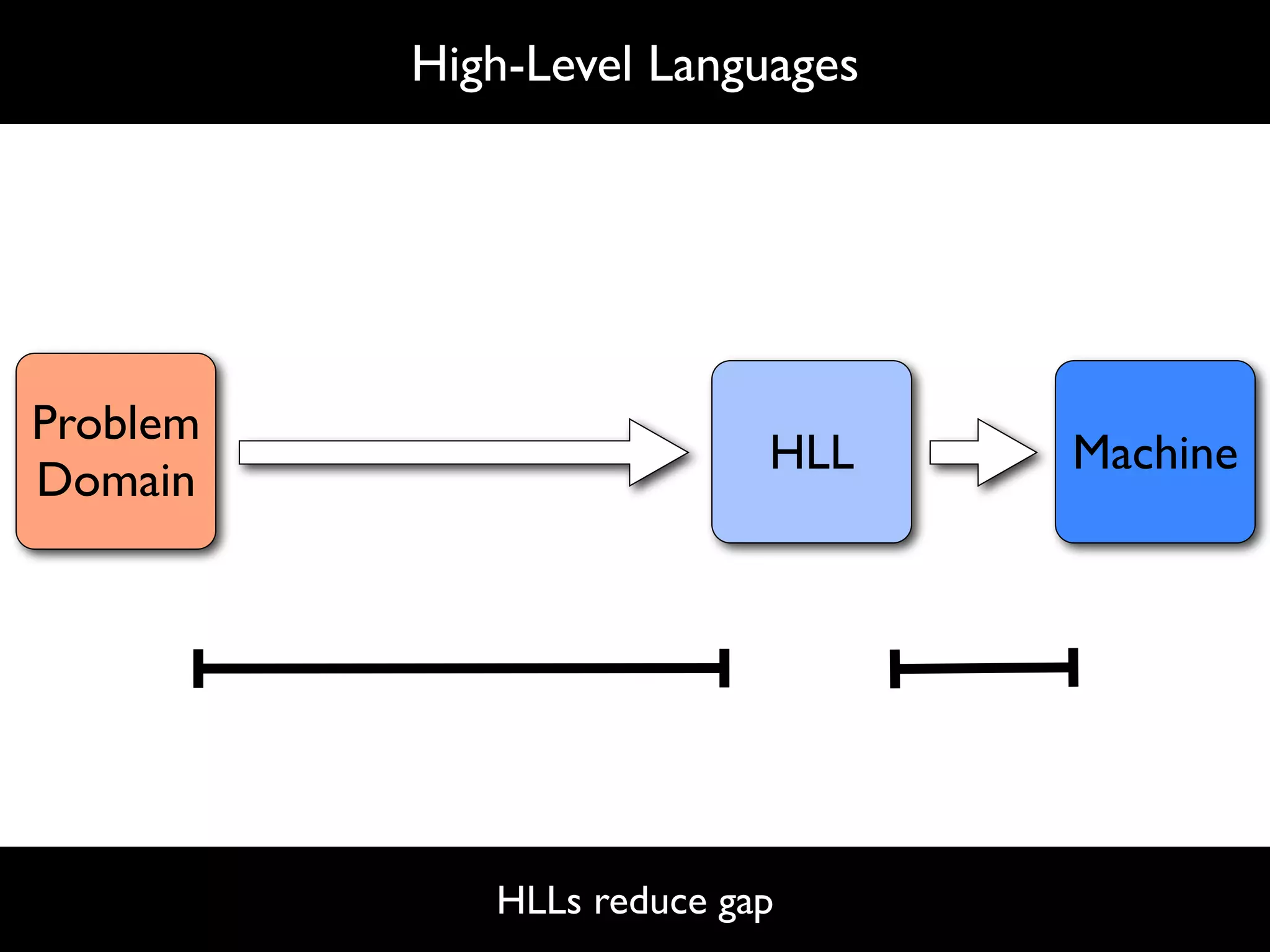
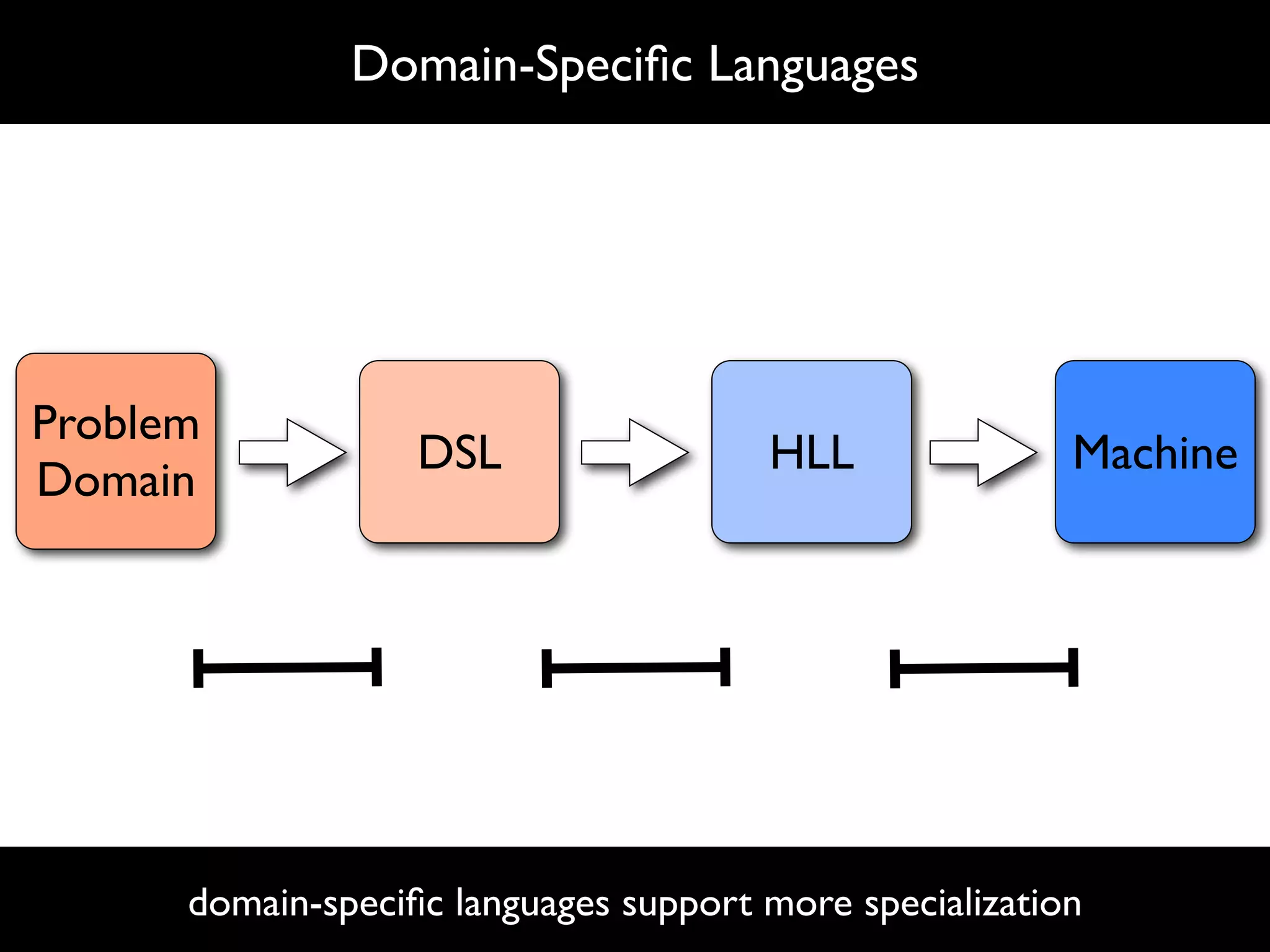
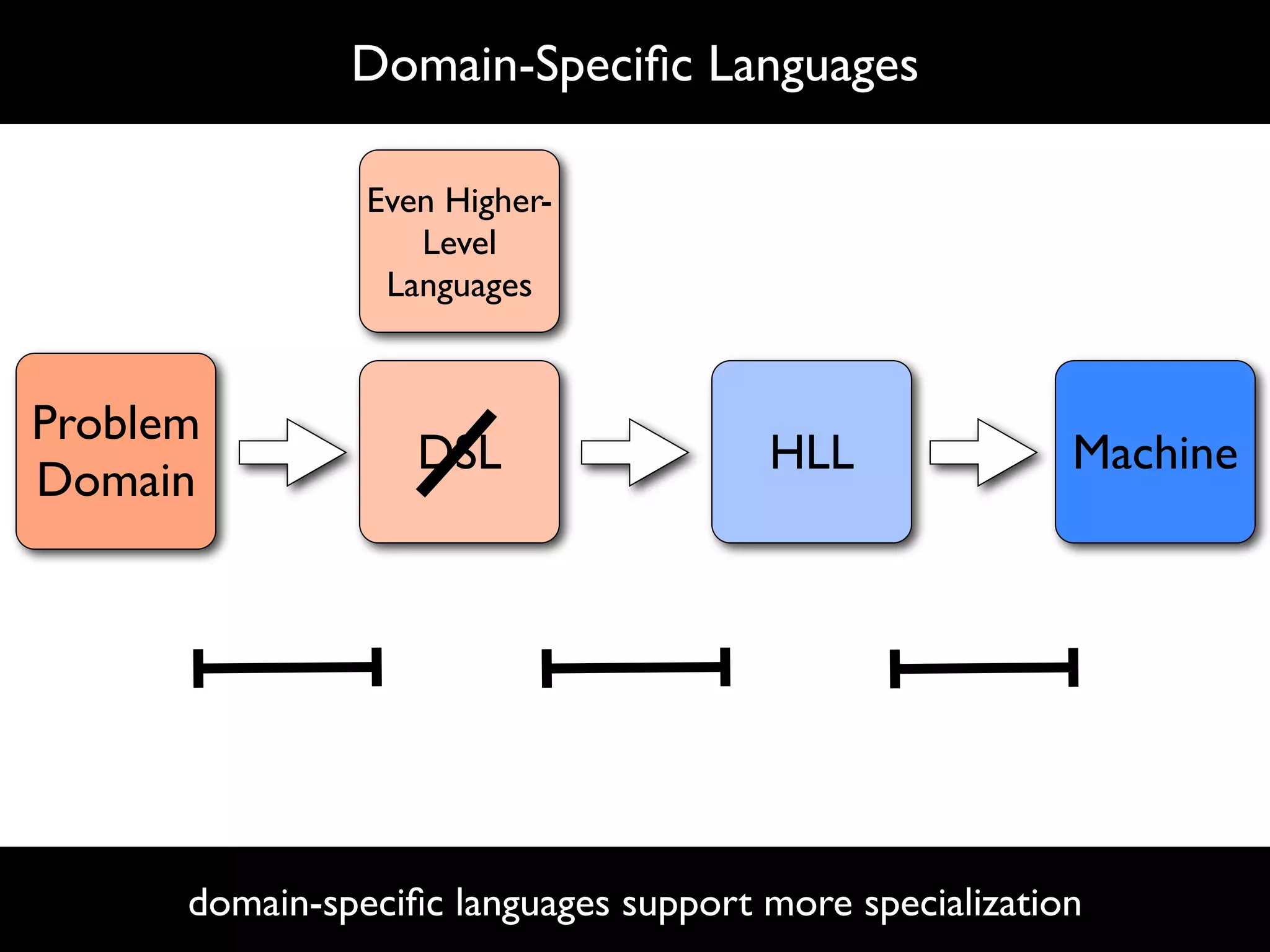
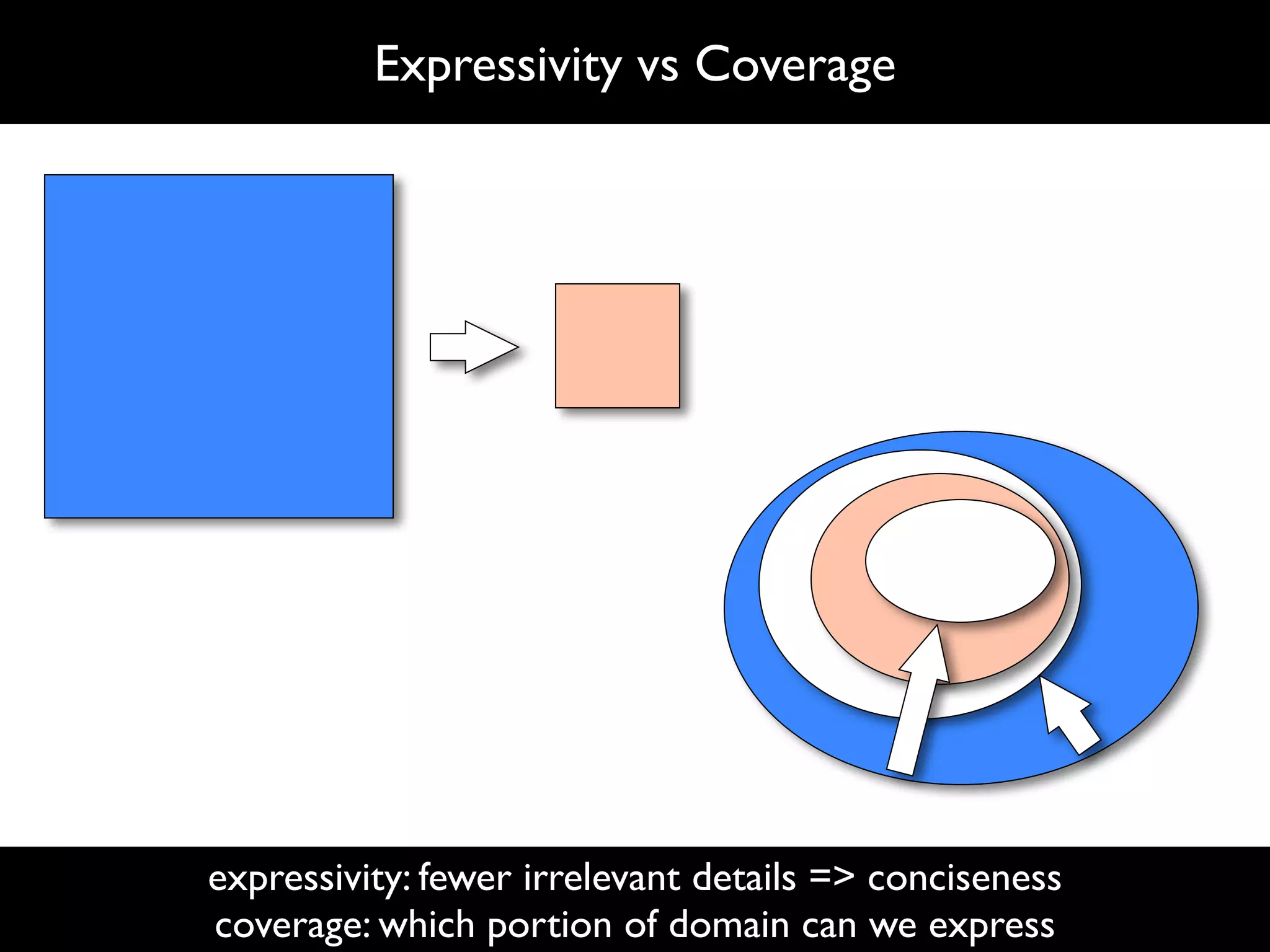
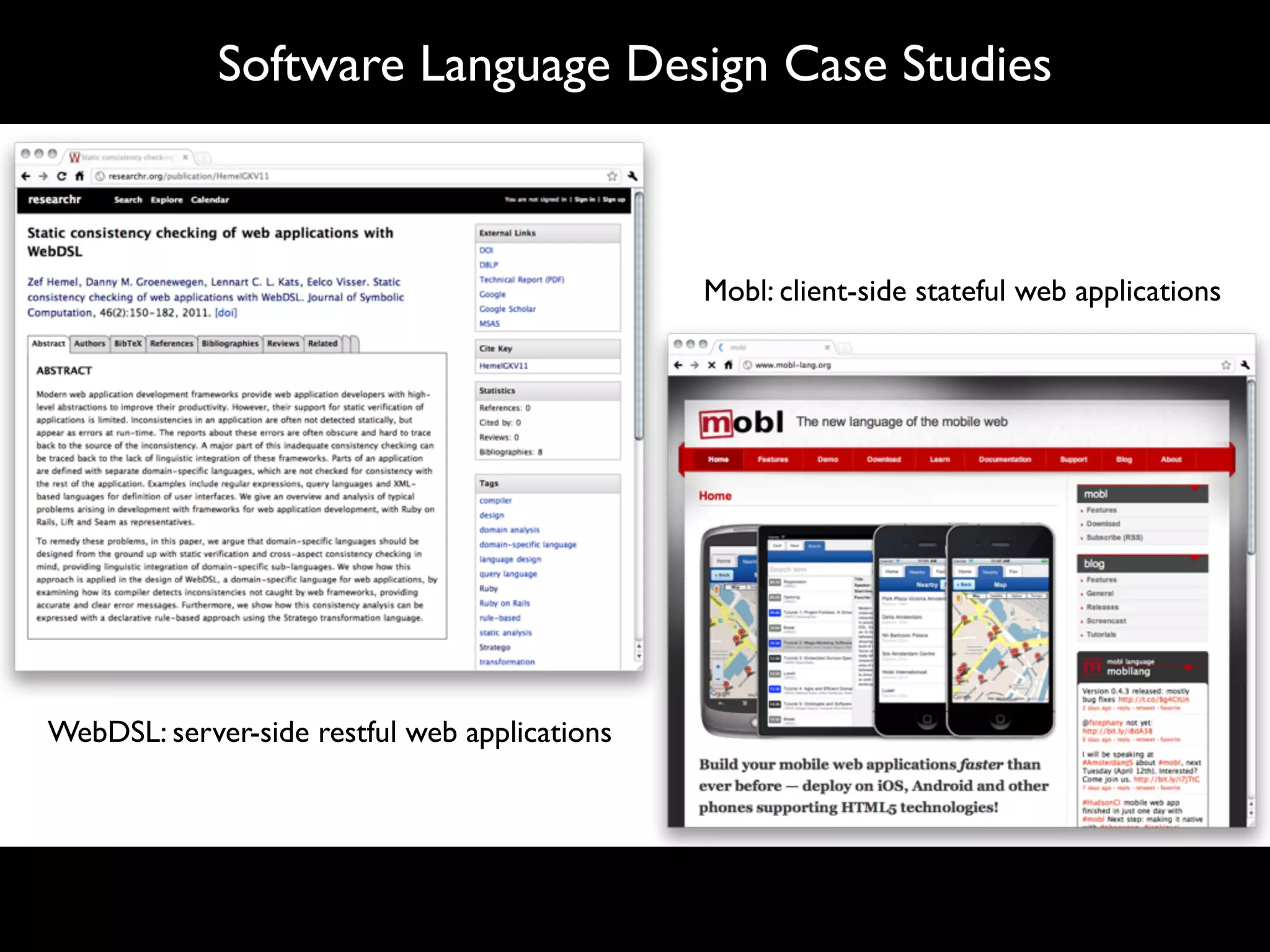
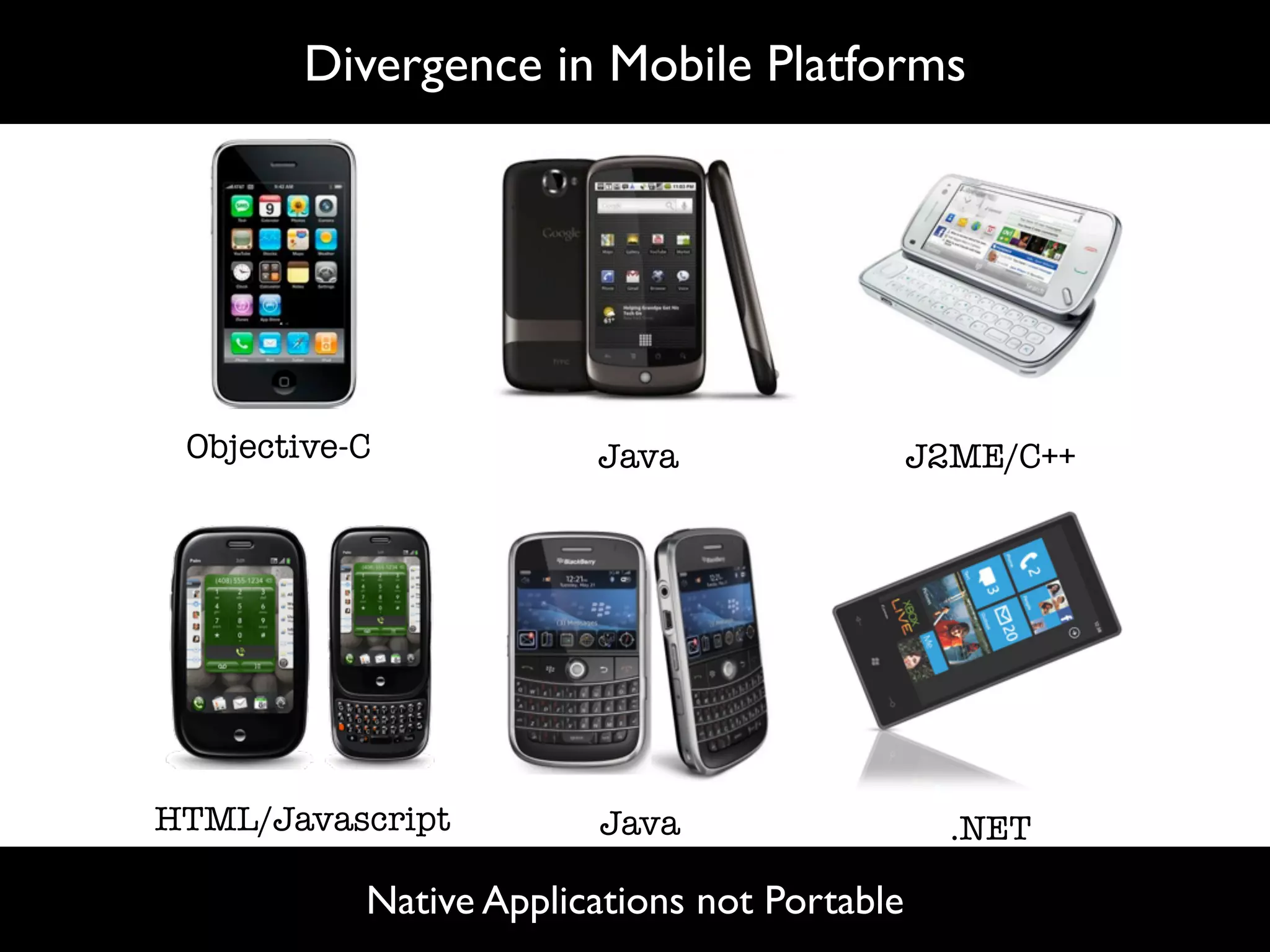
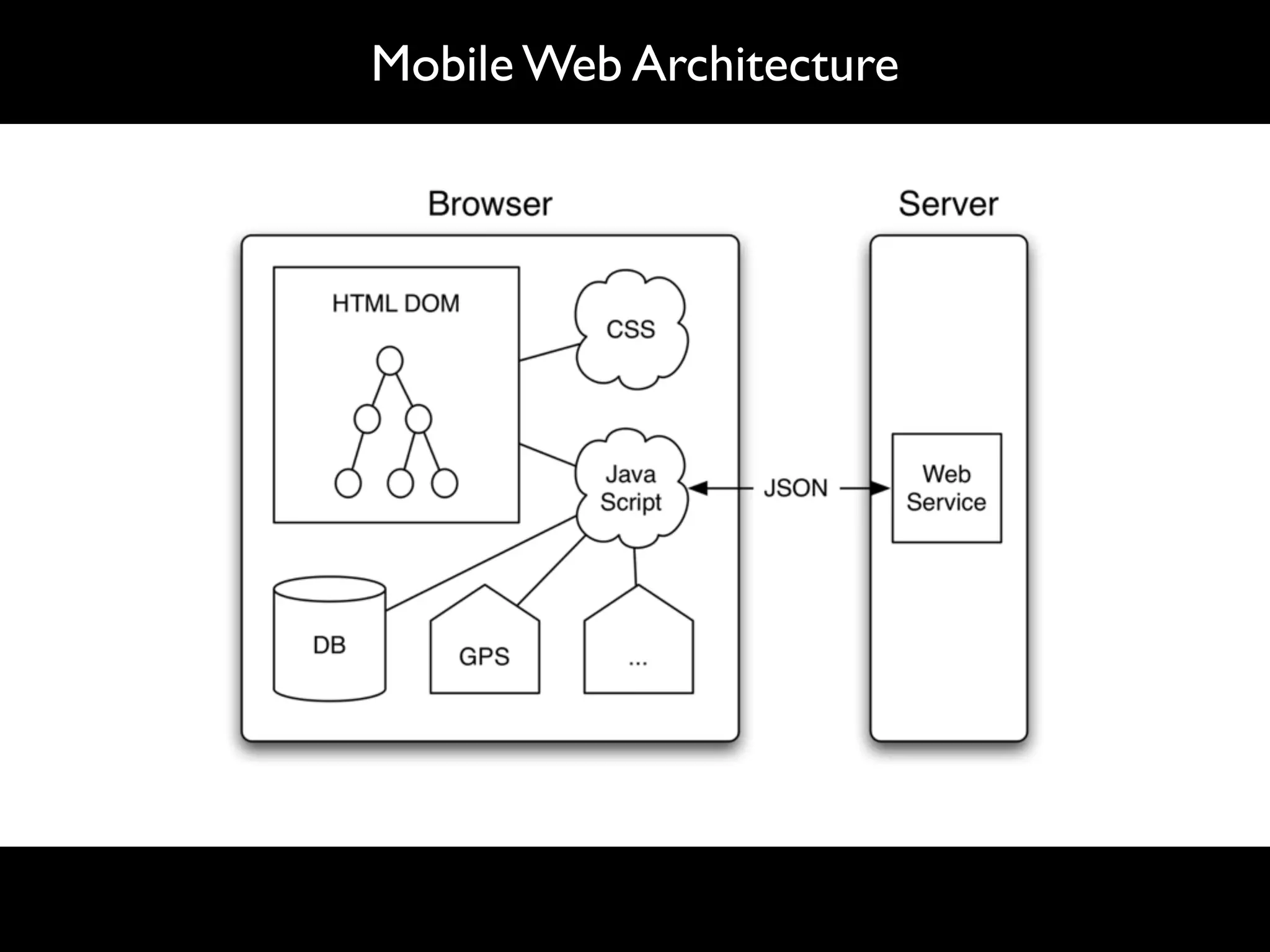
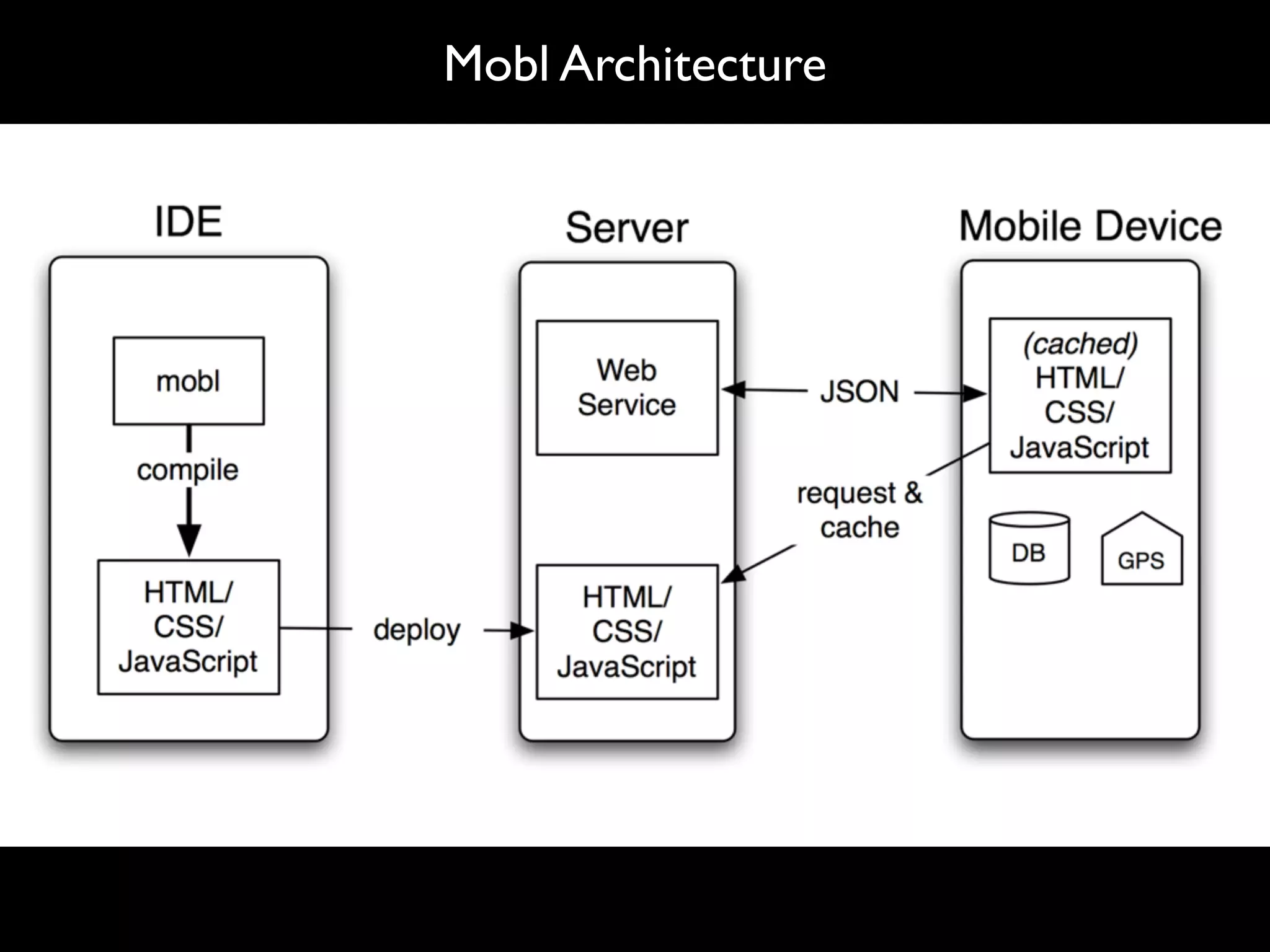
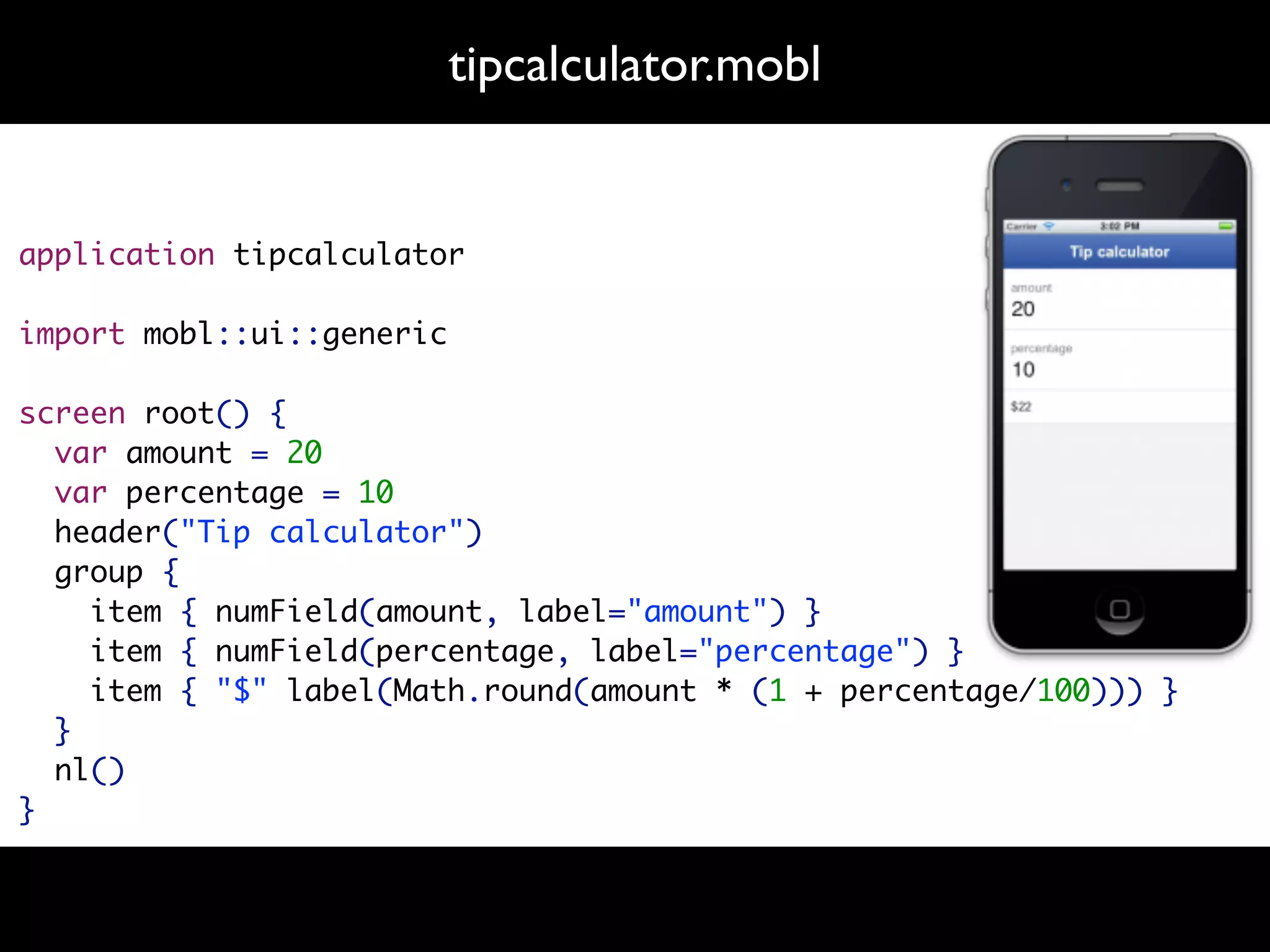
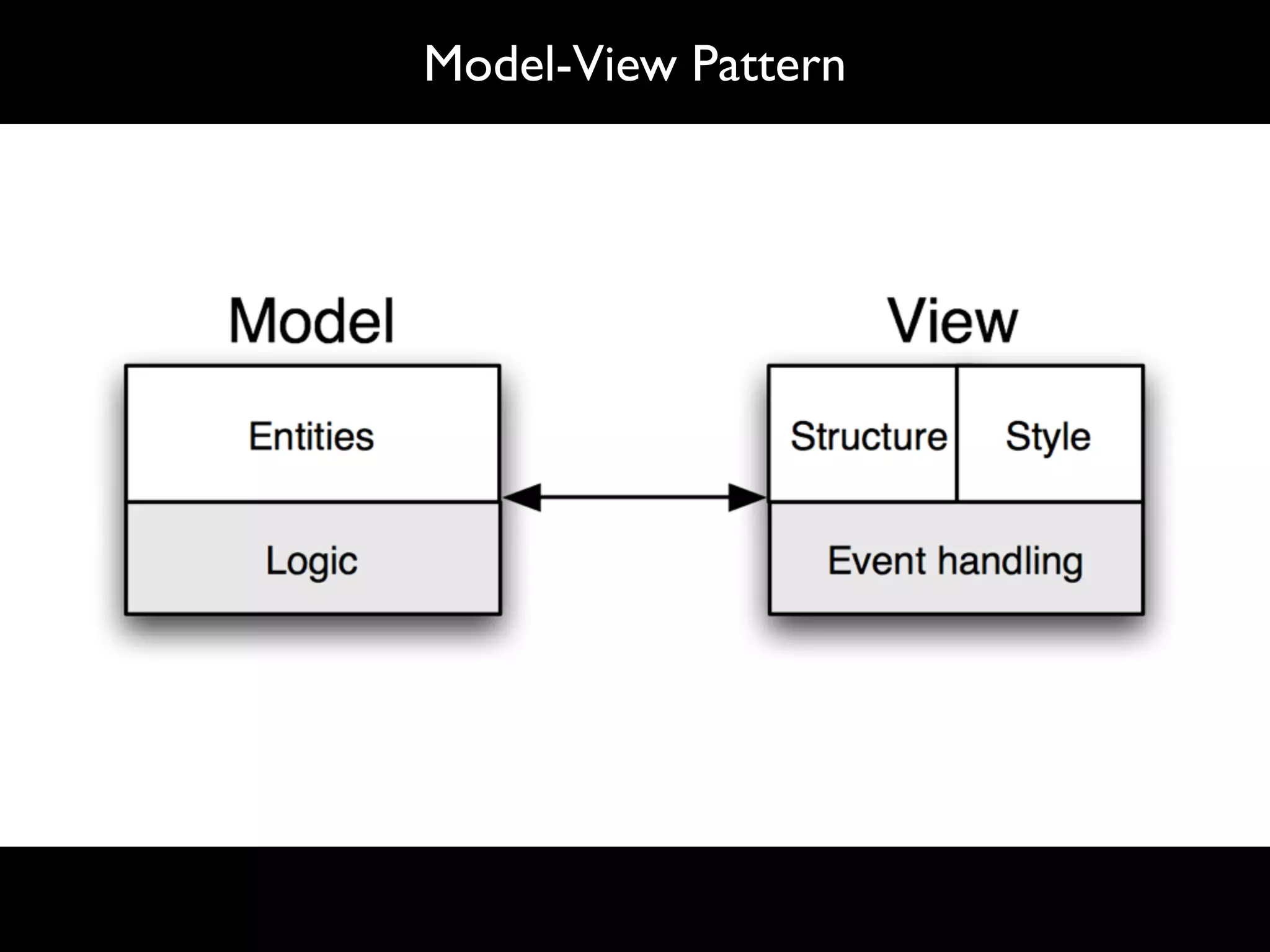
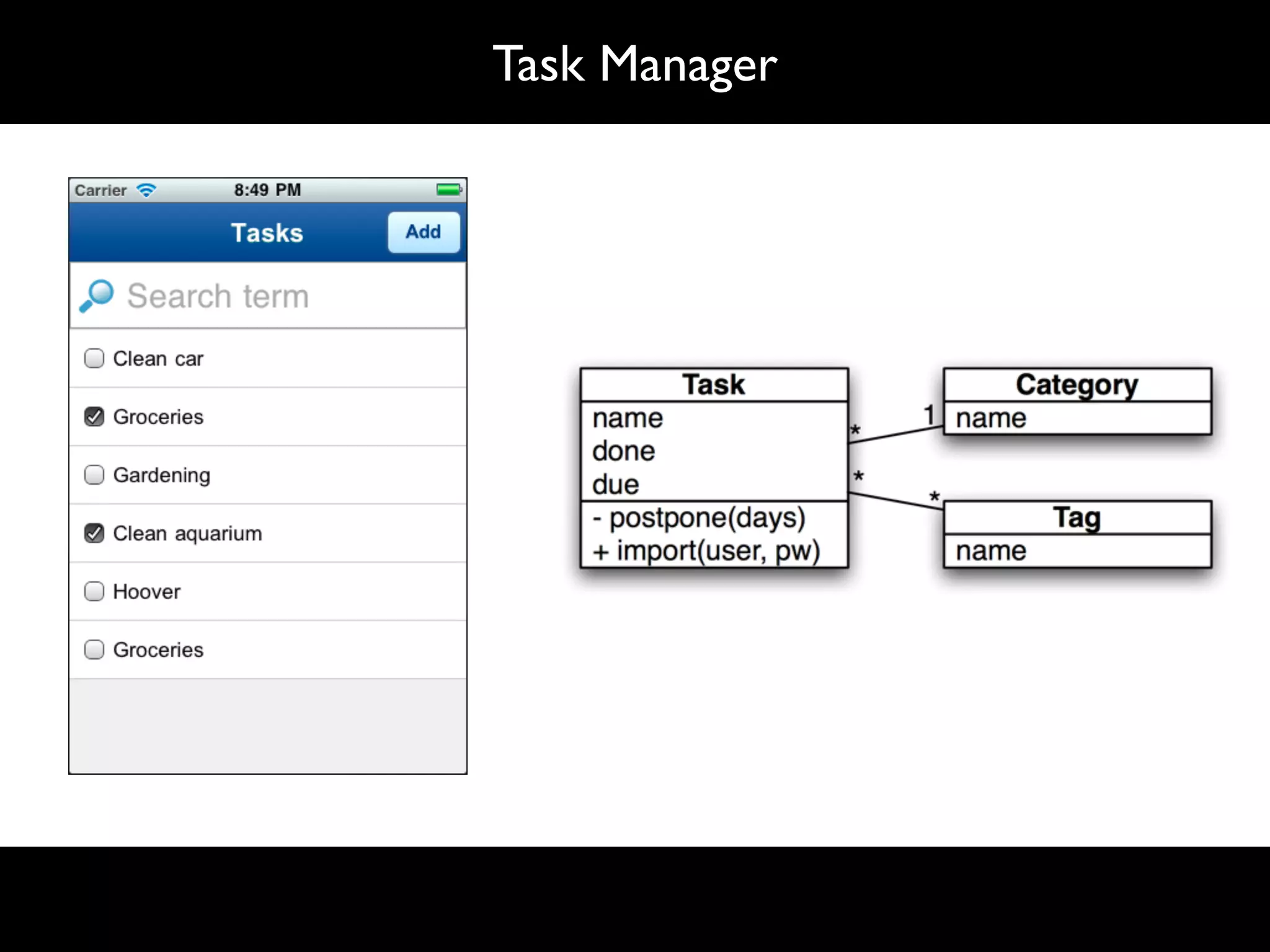
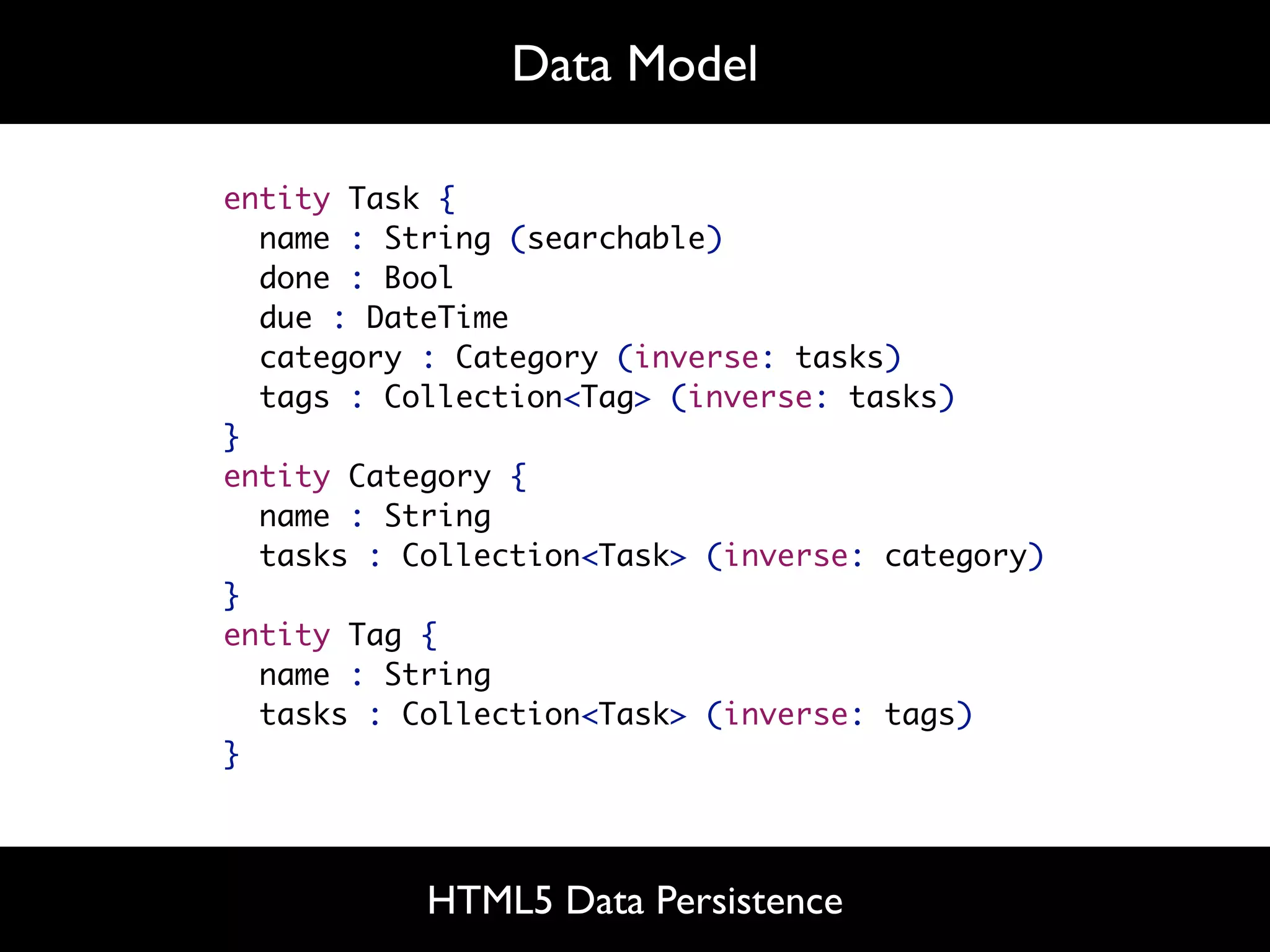
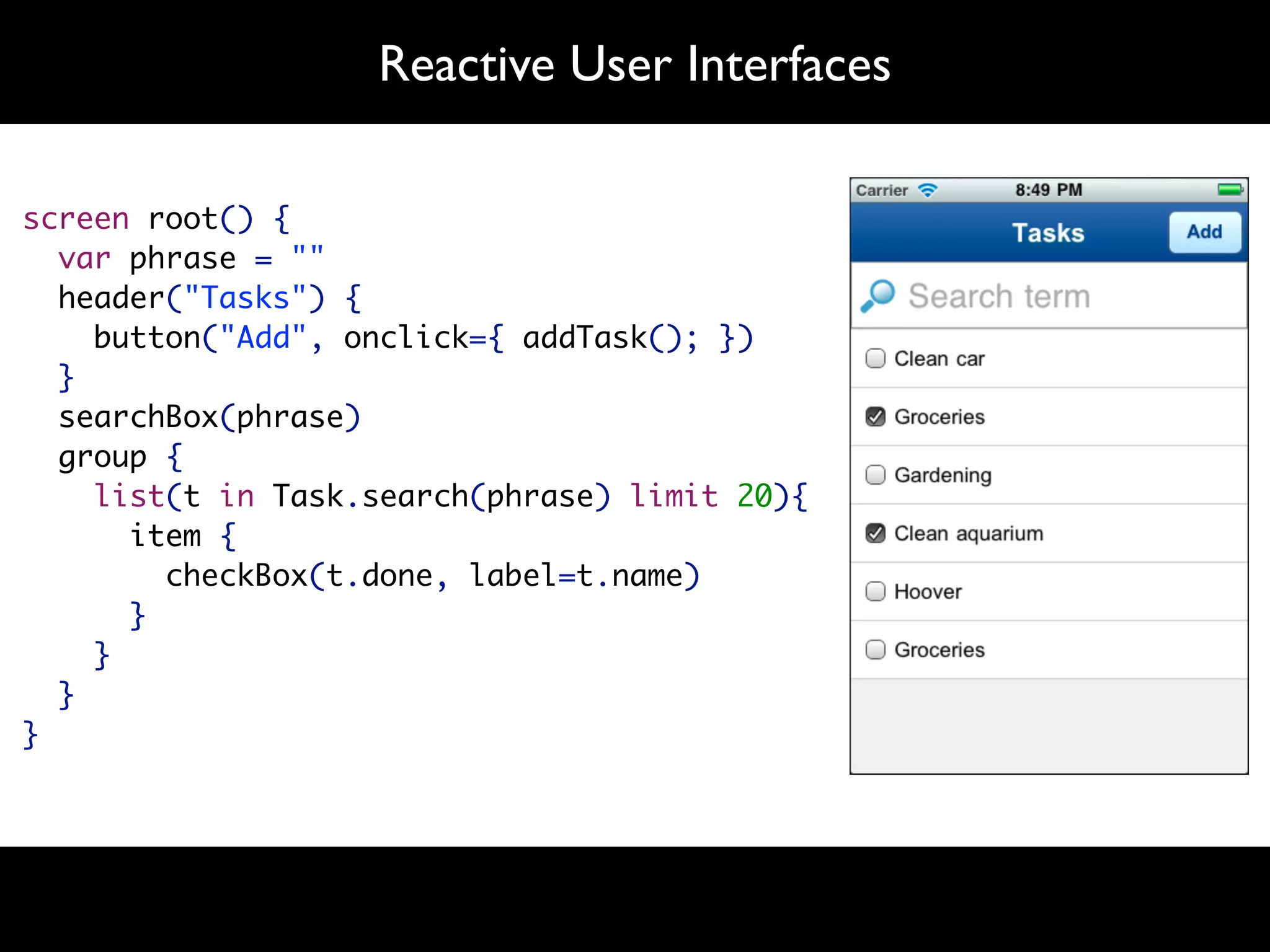
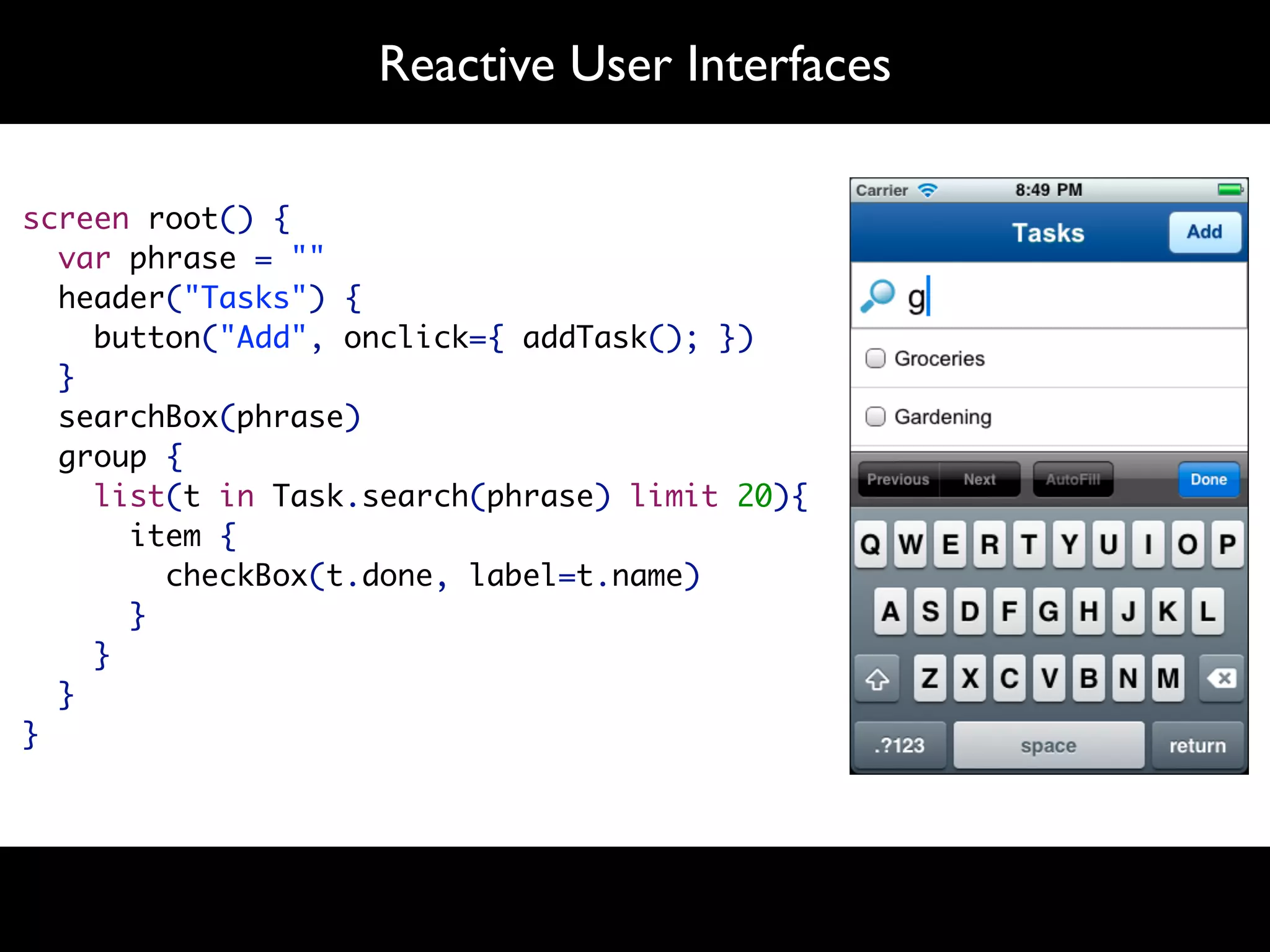
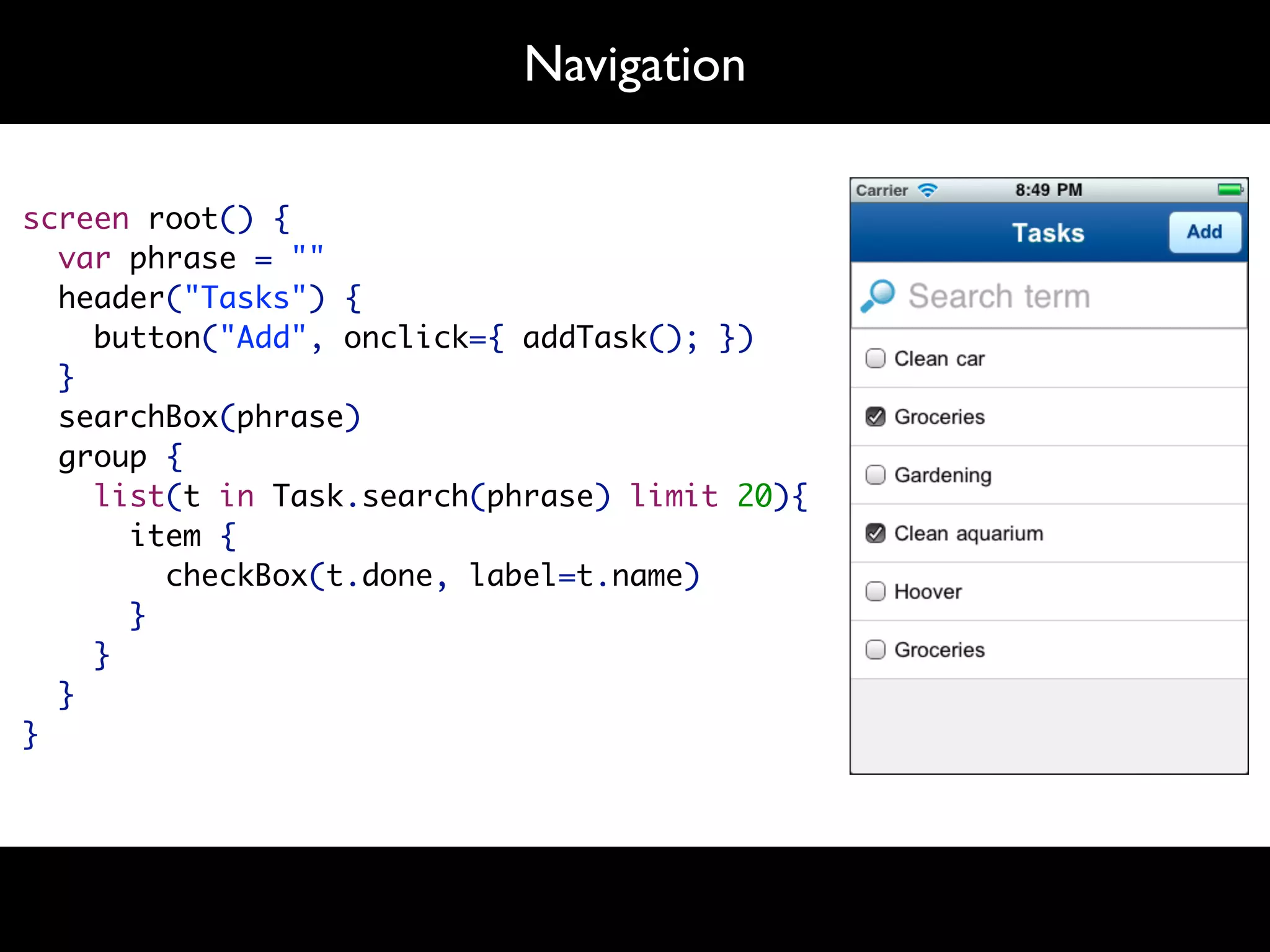
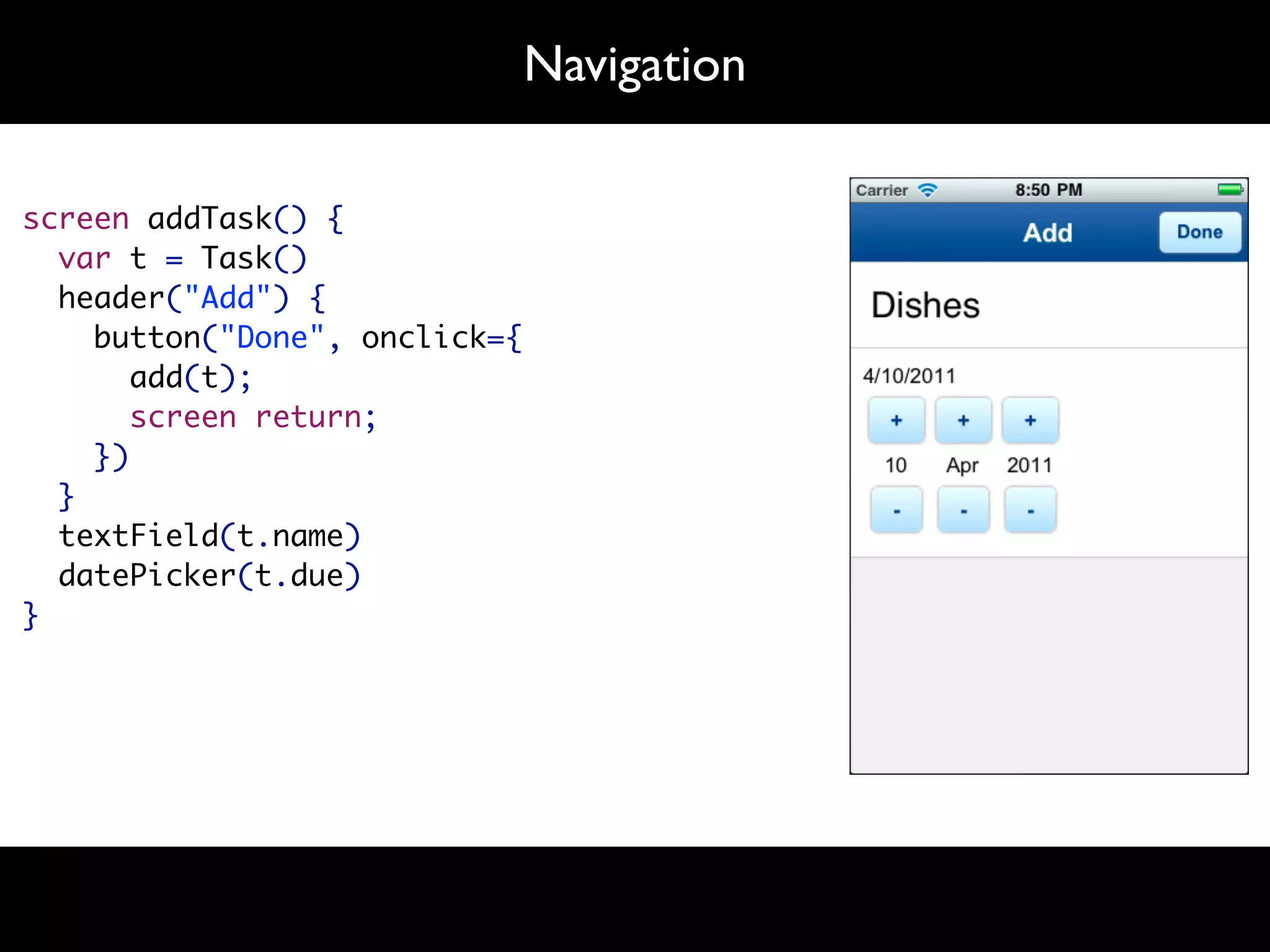
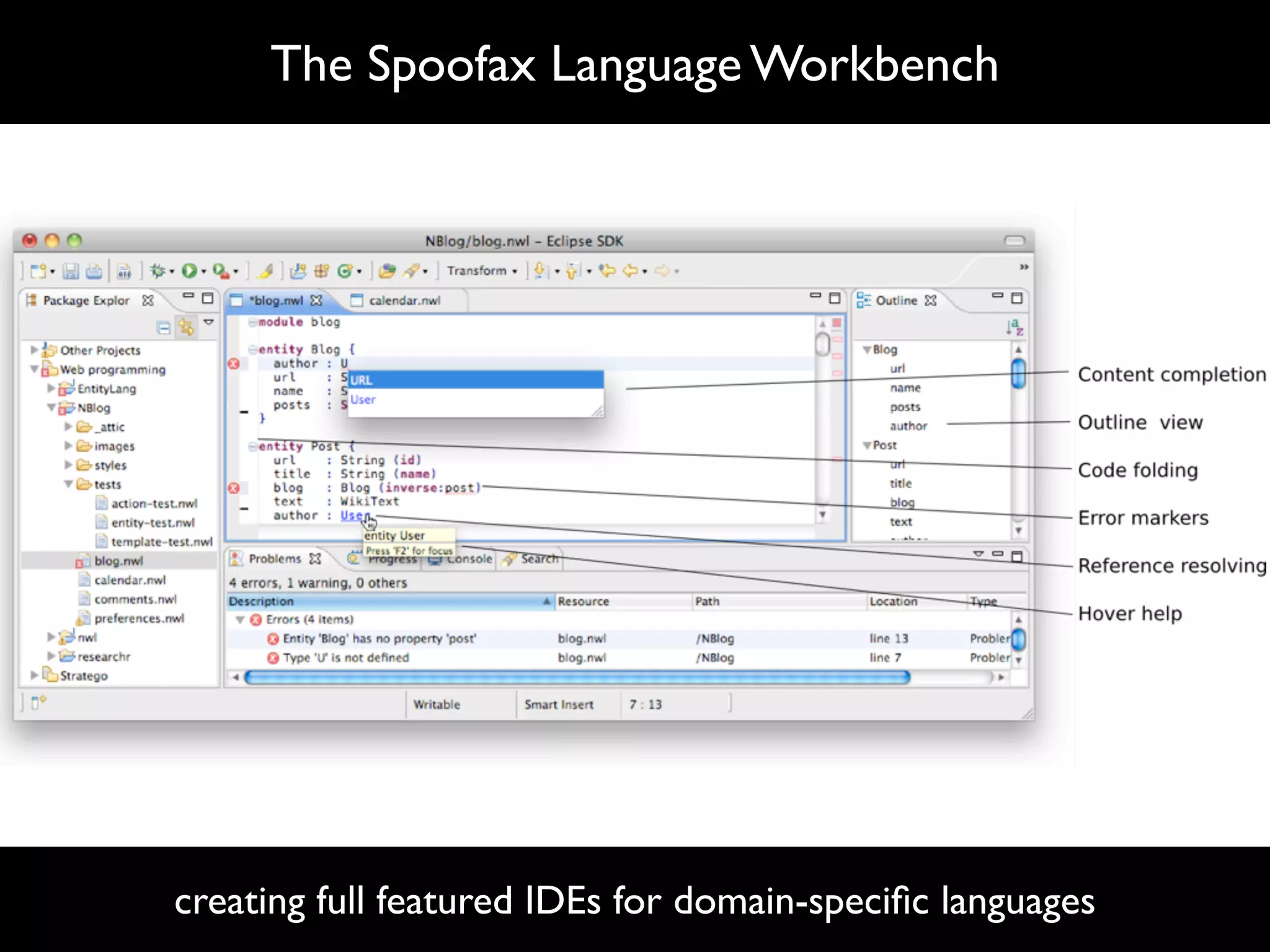
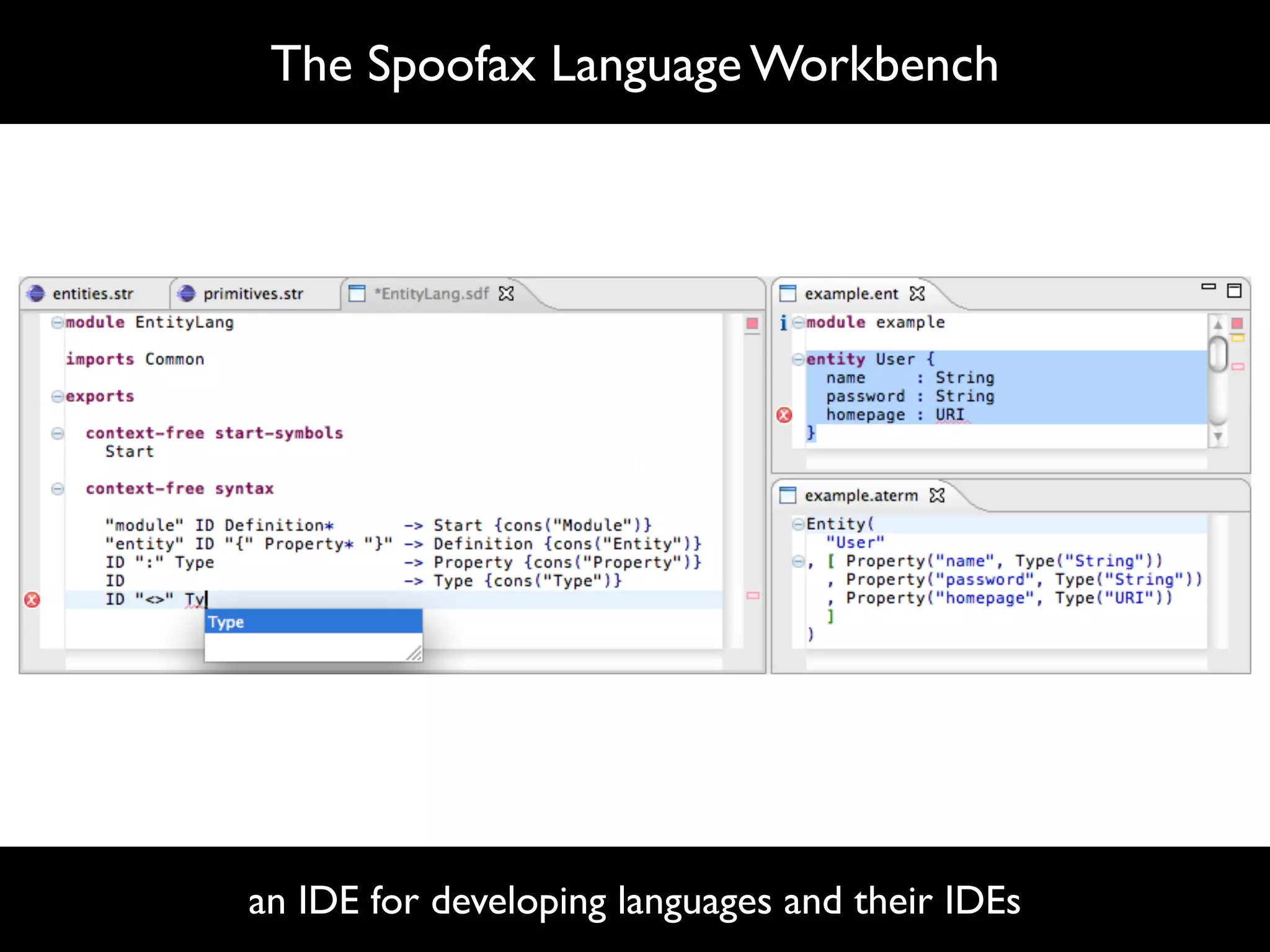
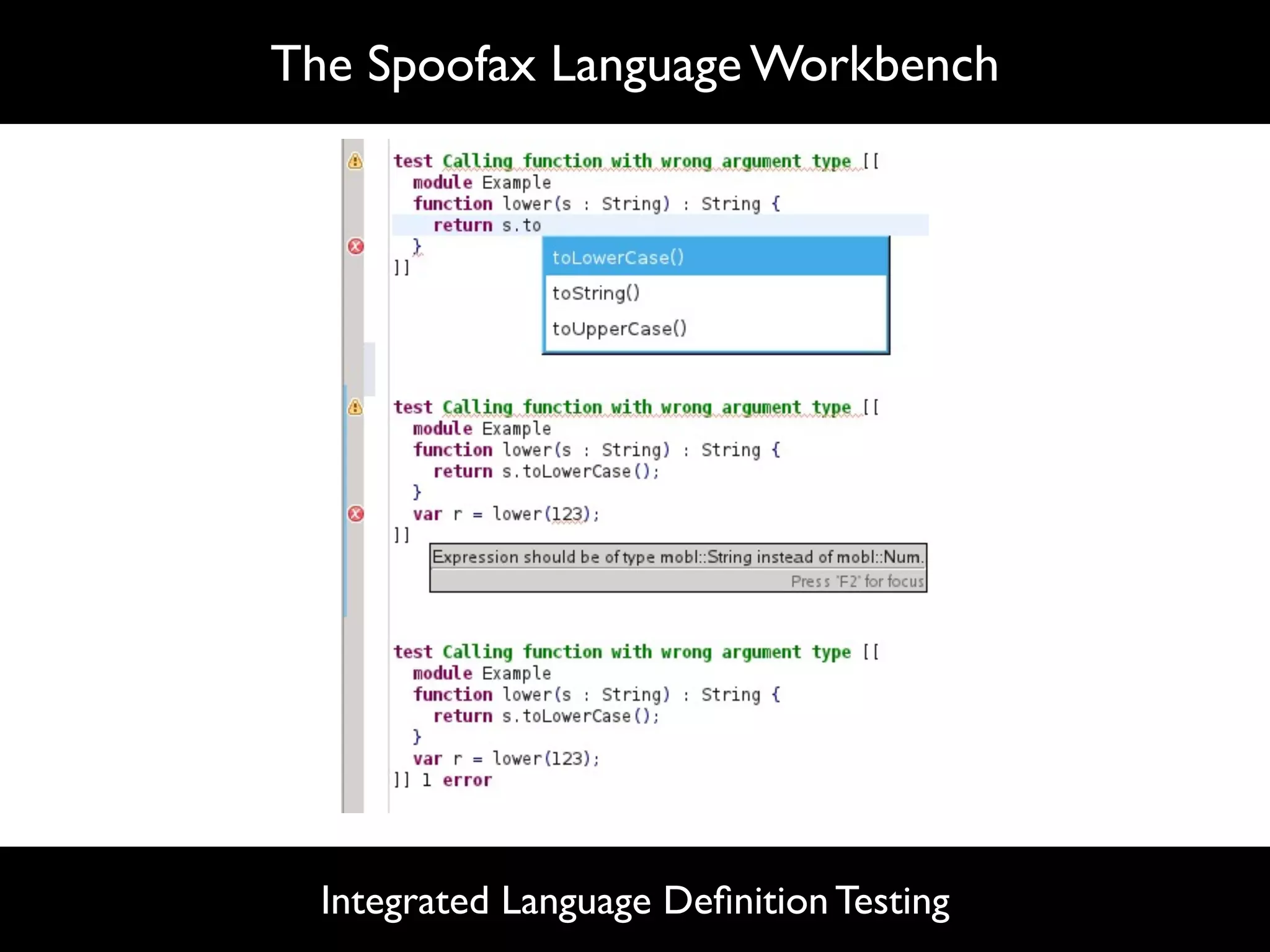
The document discusses software language design and engineering, emphasizing the importance of bridging the gap between problem domains and solution domains through high-level and domain-specific languages (DSLs). It outlines methodologies for systematically designing DSLs with a focus on expressivity, completeness, and maintainability, illustrated with case studies like 'mobl' for mobile applications and 'webdsl' for web applications. Additionally, it covers challenges in mobile platform divergence and convergence, and the development of IDEs using the Spoofax language workbench.











![User Interface Idiom: Tab control tab1() { header("Tab 1") label("This is tab 1") } control tab2() { header("Tab 2") label("This is tab 2") } screen root() { tabSet([("One", tab1), ("Two", tab2)], defaultTab="One") }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slde-google-110512080643-phpapp01/75/Software-Language-Design-Engineering-33-2048.jpg)
![Tab Set: Higher-Order Control control tabSet(tabs : [(String,Control)], activeTab : String) { list((tabName, tabControl) in tabs) { block(onclick={ activeTab = tabName; }, style=activeTab==tabName ? activeTabButton : inactiveTabButton) { label(tabName) } } list((tabName, tabControl) in tabs) { block(activeTab==tabName ? visibleTab : invisibleTab) { tabControl() } } } increase coverage: developers can create abstractions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slde-google-110512080643-phpapp01/75/Software-Language-Design-Engineering-34-2048.jpg)


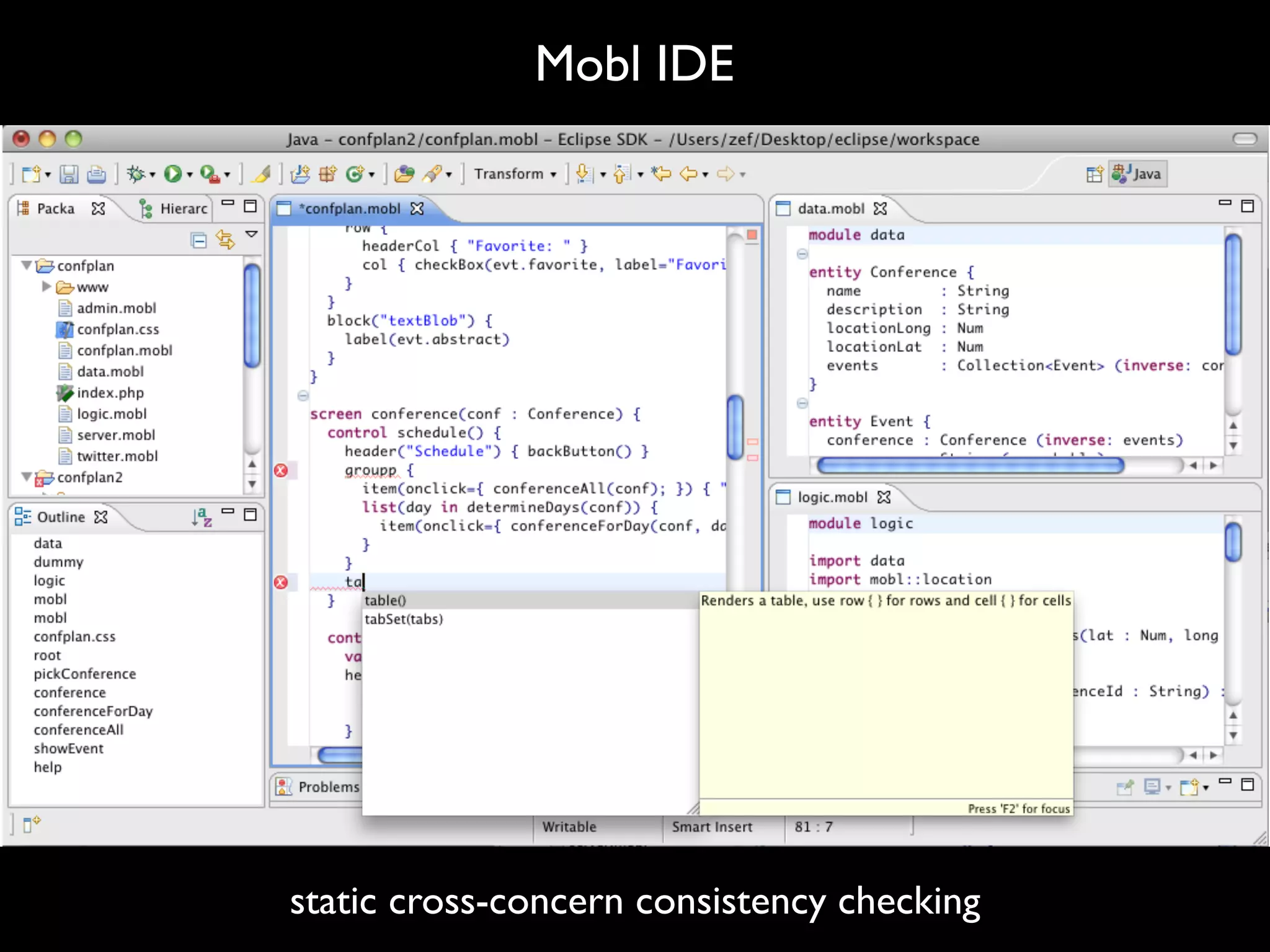

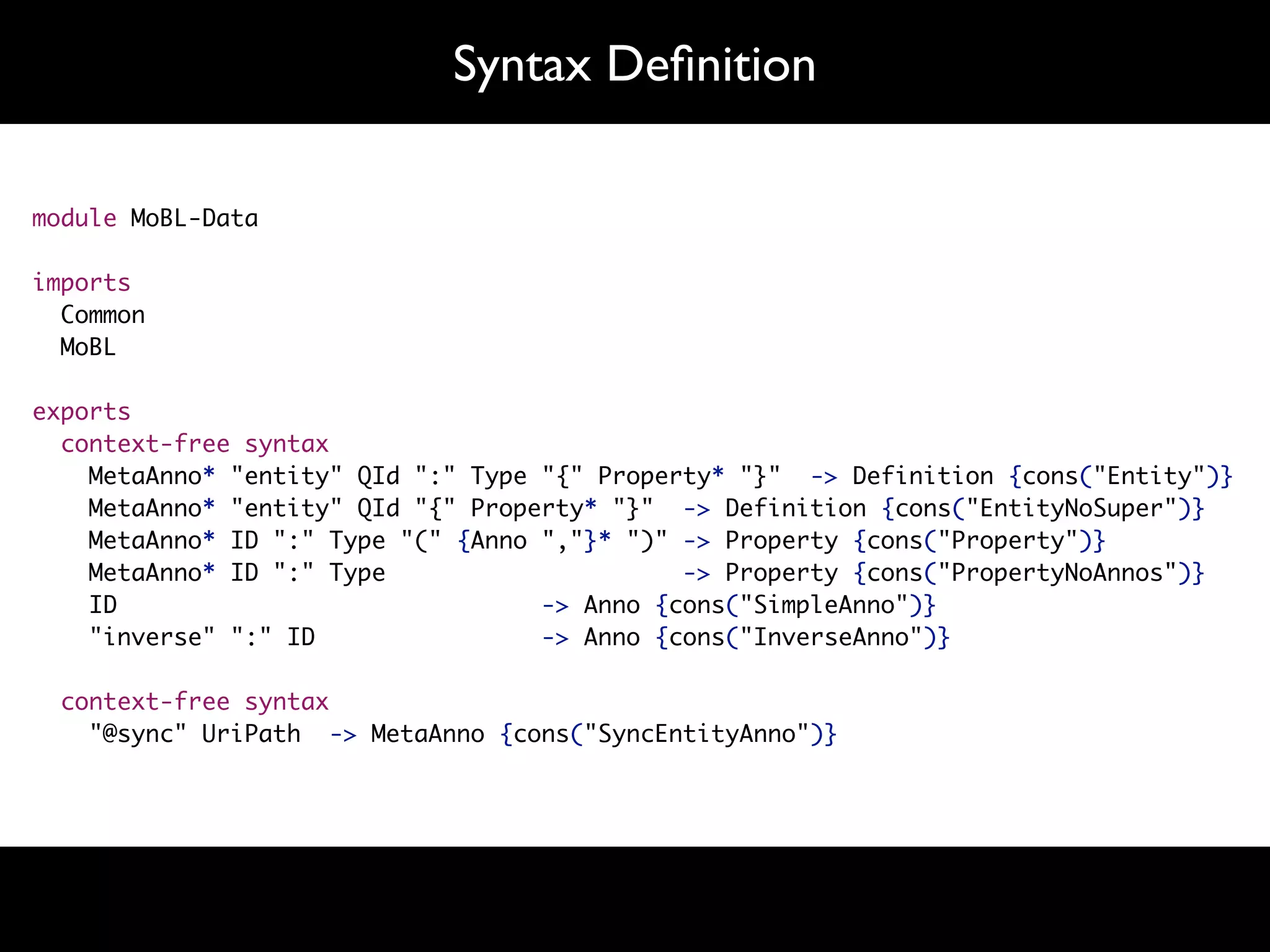
![Type Checking rules constraint-error : t@SimpleType(_) -> (t, $[Type is not defined: [<pp-mobl-type> t]]) where not(<lookup-type> t) constraint-error : t@FieldAccess(e, x) -> (t, $[Property [x] not defined]) where <type-of> e where not(type-of)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slde-google-110512080643-phpapp01/75/Software-Language-Design-Engineering-48-2048.jpg)
![Code Generation rules property-to-js(|ent) : Property(_, x, t@SimpleType(_), anno*) -> $['[x]': '[sqlType]'] where not(<is-entity-type> t) with sqlType := <sql-type> t ; if [_] := <filter(?SimpleAnno("searchable"))> anno* then rules ( SearchableProperties :+= (ent, x) ) end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slde-google-110512080643-phpapp01/75/Software-Language-Design-Engineering-49-2048.jpg)
