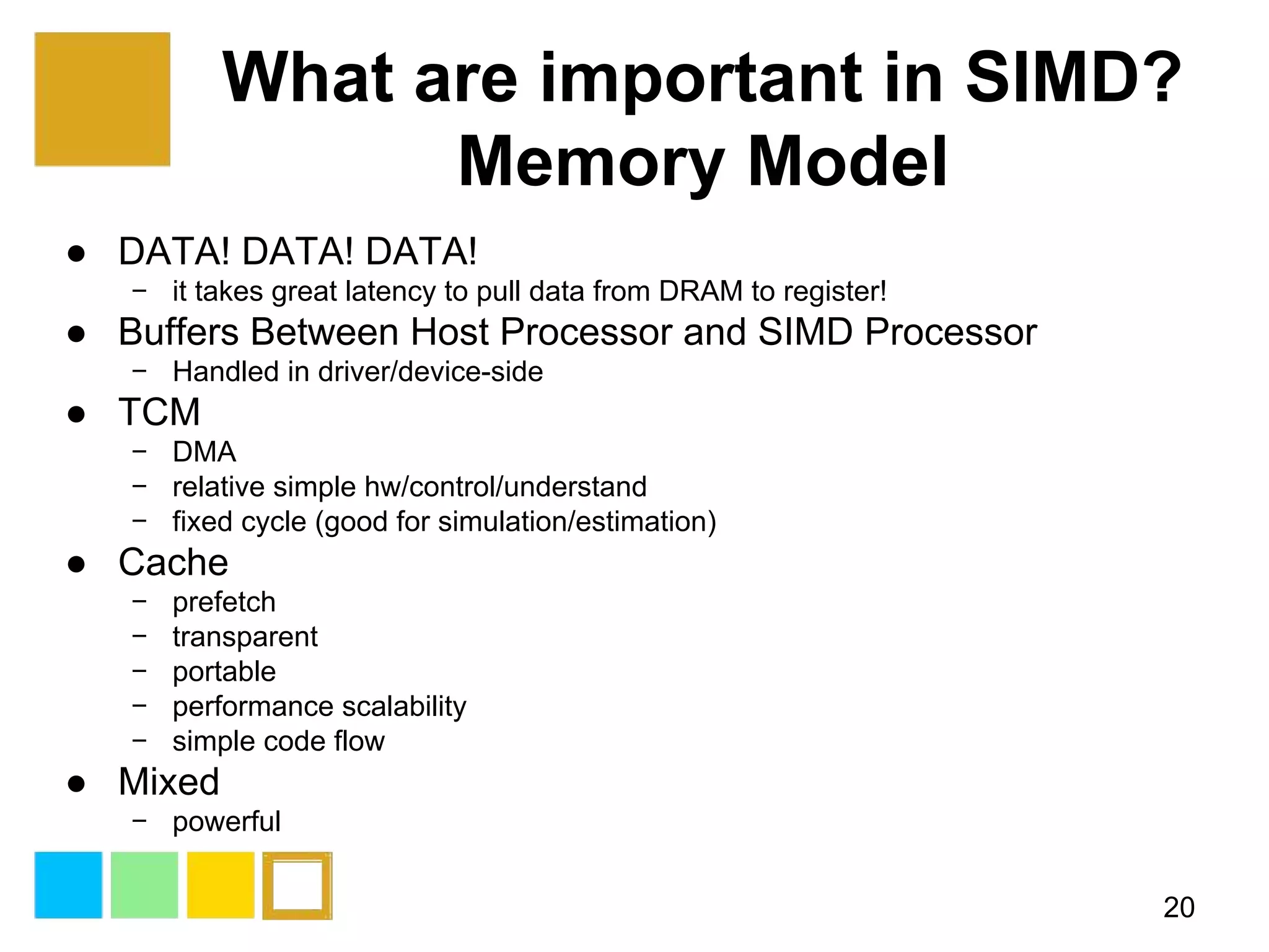
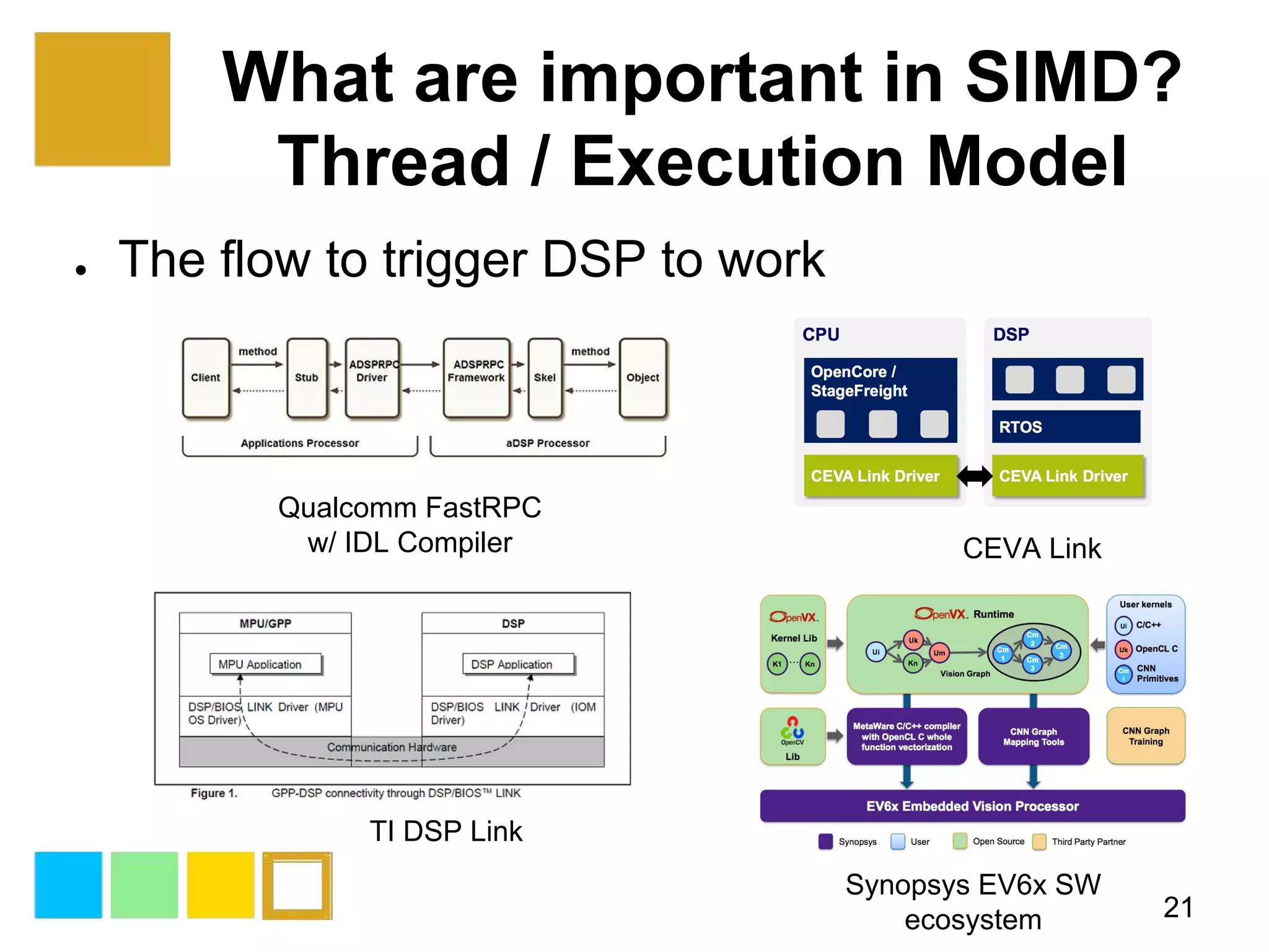
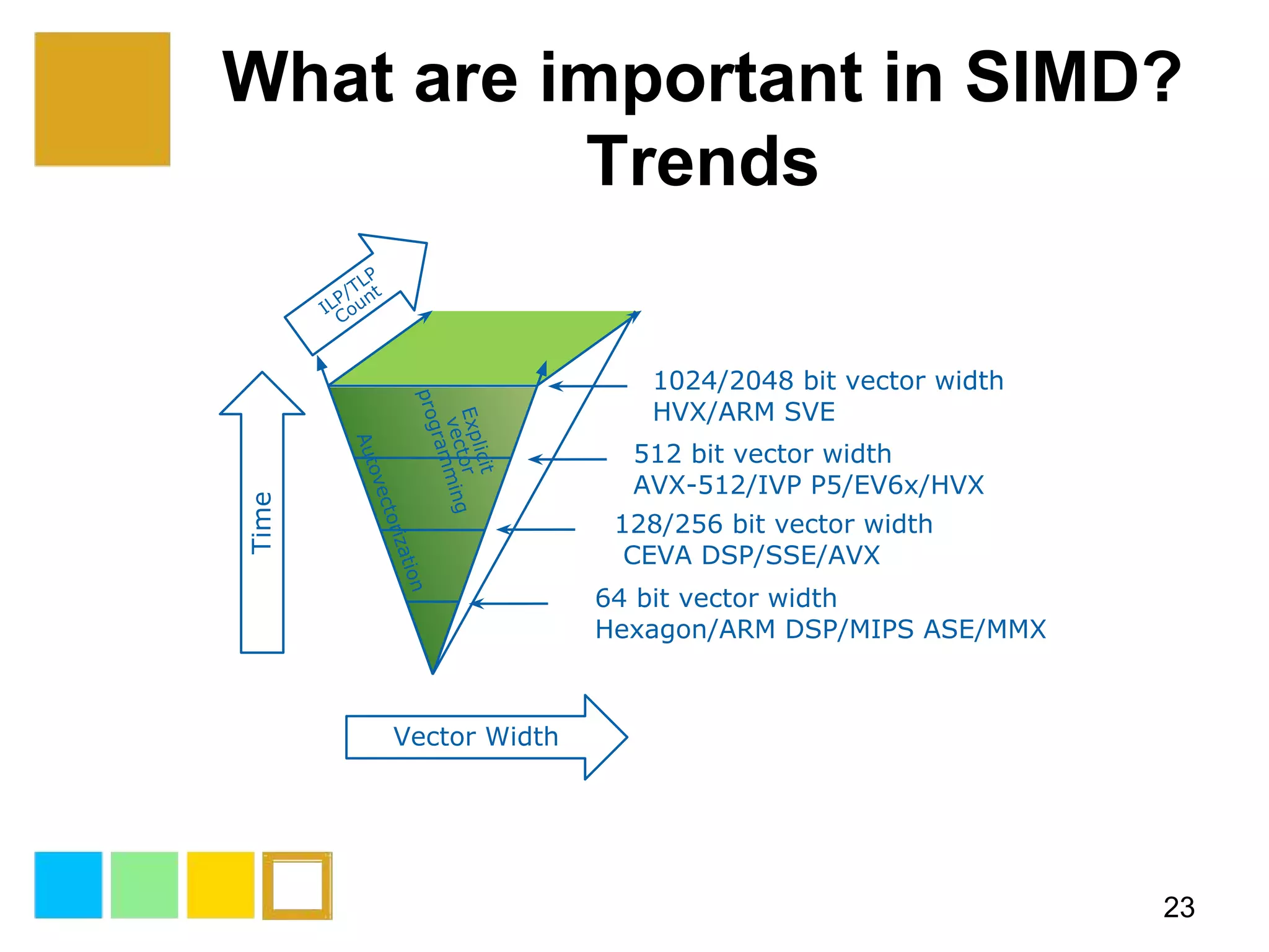
This document provides an introduction to SIMD (Single Instruction Multiple Data) programming. It discusses what SIMD is and why it is useful for software optimization. It then covers SIMD support in different processors like CPUs, GPUs, and DSPs. The document discusses different techniques for SIMD optimization including using auto-vectorization, compiler intrinsics, specific frameworks, and assembly coding. It notes some difficult aspects of SIMD programming and concludes by discussing important considerations like ISA design, memory model, execution model, scalability, and trends in SIMD.

![What is SIMD (Single Instruction Multiple Data) 3 for(y = 0; y < height; y++){ for(x = 0; x < width; x+=8){ //process 8 point simutaneously uin16x8_t va, vb, vout; va = vld1q_u16(a+x); vb = vld1q_u16(b+x); vout = vaddq_u16(va, vb); vst1q_u16(out, vout); } a+=width; b+=width; out+=width; } for(y = 0; y < height; y++){ for(x = 0; x < width; x++){ //process 1 point out[x] = a[x]+b[x]; } a+=width; b+=width; out+=width; } one lane](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/simdprogrammingintroduction-161010040931/75/Simd-programming-introduction-3-2048.jpg)
![SIMD Optimization – Auto/SemiAuto 11 ● compiler − auto-vectorization optimization options − #pragma − IR optimization ● CilkPlus/OpenMP/OpenACC Serial Code for(i = 0; i < N; i++){ A[i] = B[i] + C[i]; } #pragma omp simd for(i = 0; i < N; i++){ A[i] = B[i] + C[i]; } SIMD Pragma https://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/performance-essentials-with-openmp-40-vectorization](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/simdprogrammingintroduction-161010040931/75/Simd-programming-introduction-11-2048.jpg)
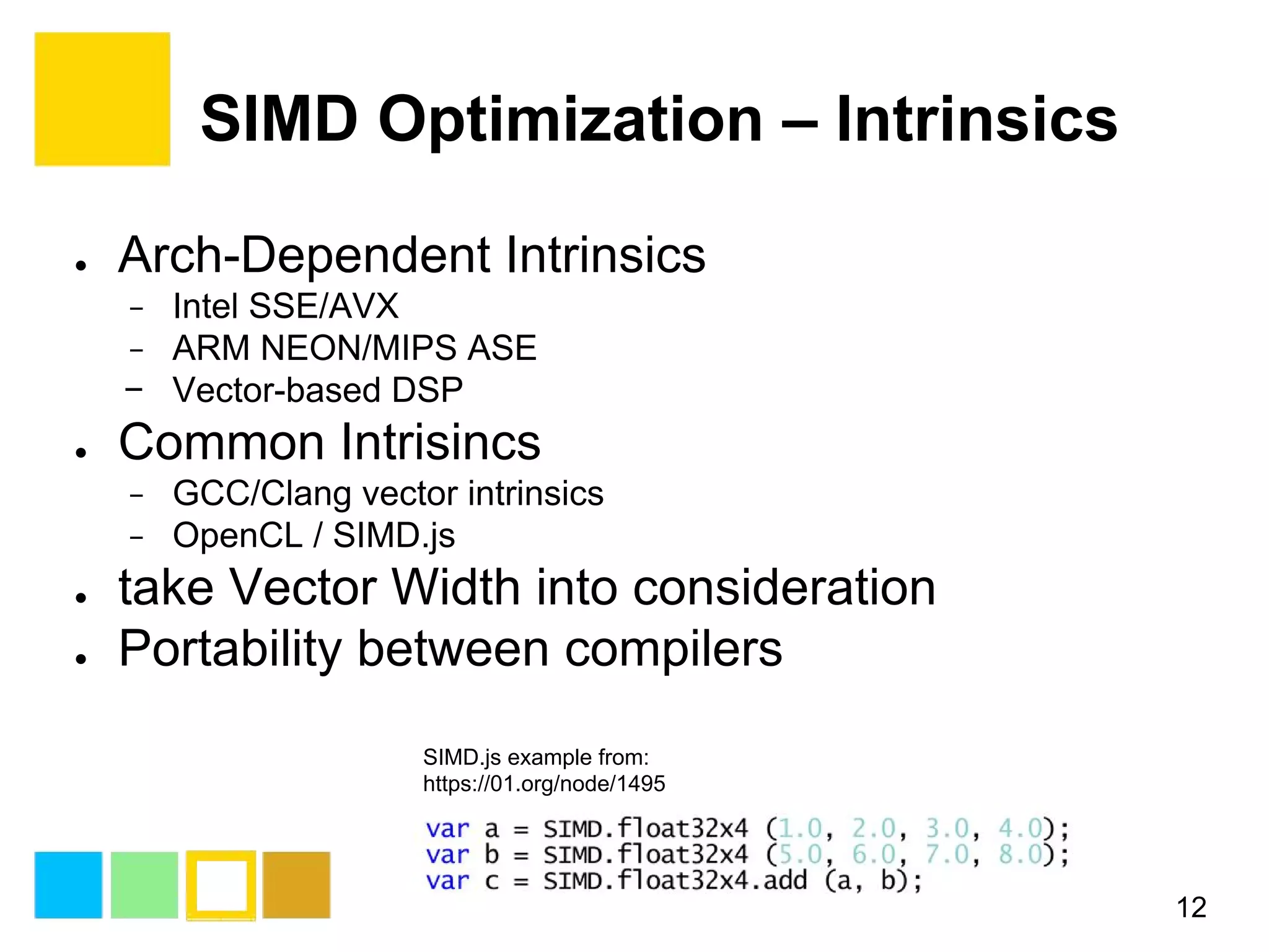
![SIMD Optimization – Intrinsics 13 4x4 Matrix Multiplication ARM NEON Example http://www.fixstars.com/en/news/?p=125 //... //Load matrixB into four vectors uint16x4_t vectorB1, vectorB2, vectorB3, vectorB4; vectorB1 = vld1_u16 (B[0]); vectorB2 = vld1_u16 (B[1]); vectorB3 = vld1_u16 (B[2]); vectorB4 = vld1_u16 (B[3]); //Temporary vectors to use with calculating the dotproduct uint16x4_t vectorT1, vectorT2, vectorT3, vectorT4; // For each row in A... for (i=0; i<4; i++){ //Multiply the rows in B by each value in A's row vectorT1 = vmul_n_u16(vectorB1, A[i][0]); vectorT2 = vmul_n_u16(vectorB2, A[i][1]); vectorT3 = vmul_n_u16(vectorB3, A[i][2]); vectorT4 = vmul_n_u16(vectorB4, A[i][3]); //Add them together vectorT1 = vadd_u16(vectorT1, vectorT2); vectorT1 = vadd_u16(vectorT1, vectorT3); vectorT1 = vadd_u16(vectorT1, vectorT4); //Output the dotproduct vst1_u16 (C[i], vectorT1); } //... A B C A B C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/simdprogrammingintroduction-161010040931/75/Simd-programming-introduction-13-2048.jpg)