This document summarizes a seminar on secure and efficient data transmission for cluster-based wireless sensor networks. It introduces wireless sensor networks and describes their centralized and hierarchical network architectures. It reviews previous work on the LEACH clustering protocol and its pros and cons. It then proposes two new secure transmission protocols called SET-IBS and SET-IBOOS that use identity-based signatures and offline/online signatures respectively to authenticate data transmitted between sensor nodes and cluster heads. The document analyzes the performance and security of the proposed protocols and discusses their applications and potential for future work.




![LITERATURE SURVEY [1] S. Sharma and S.K. Jena, “Secure Hierarchical Routing Protocols in Wireless Sensor Networks,” Proc. Int’l Conf. Comm., Computing & Security (ICCCS), pp. 146-151, 2011.[2] Hierarchical or cluster-base routing protocol for WSNs is the most energy- efficient among other routing protocols. [2] A.A. Abbasi and M. Younis, “A Survey on Clustering Algorithms for Wireless Sensor Networks,”Computer Comm., vol. 30, nos. 14/ 15, pp. 2826-2841, 2007[3] Clustering is introduced to WSNs because it has proven to be an effective approach to provide better data aggregation and scalability for large WSNs. [3] A. Shamir, “Identity-Based Cryptosystems and Signature Schemes,” Proc. Advances in Cryptology (CRYPTO), pp. 47- 53,[4] The scheme assumes the existence of trusted key generation centres , whose sole purpose is t o give each user a personalized smart card when he first join the network.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar-160425171517/75/Secure-and-Efficient-Data-Transmission-for-Cluster-Based-Wireless-Sensor-Networks-8-2048.jpg)
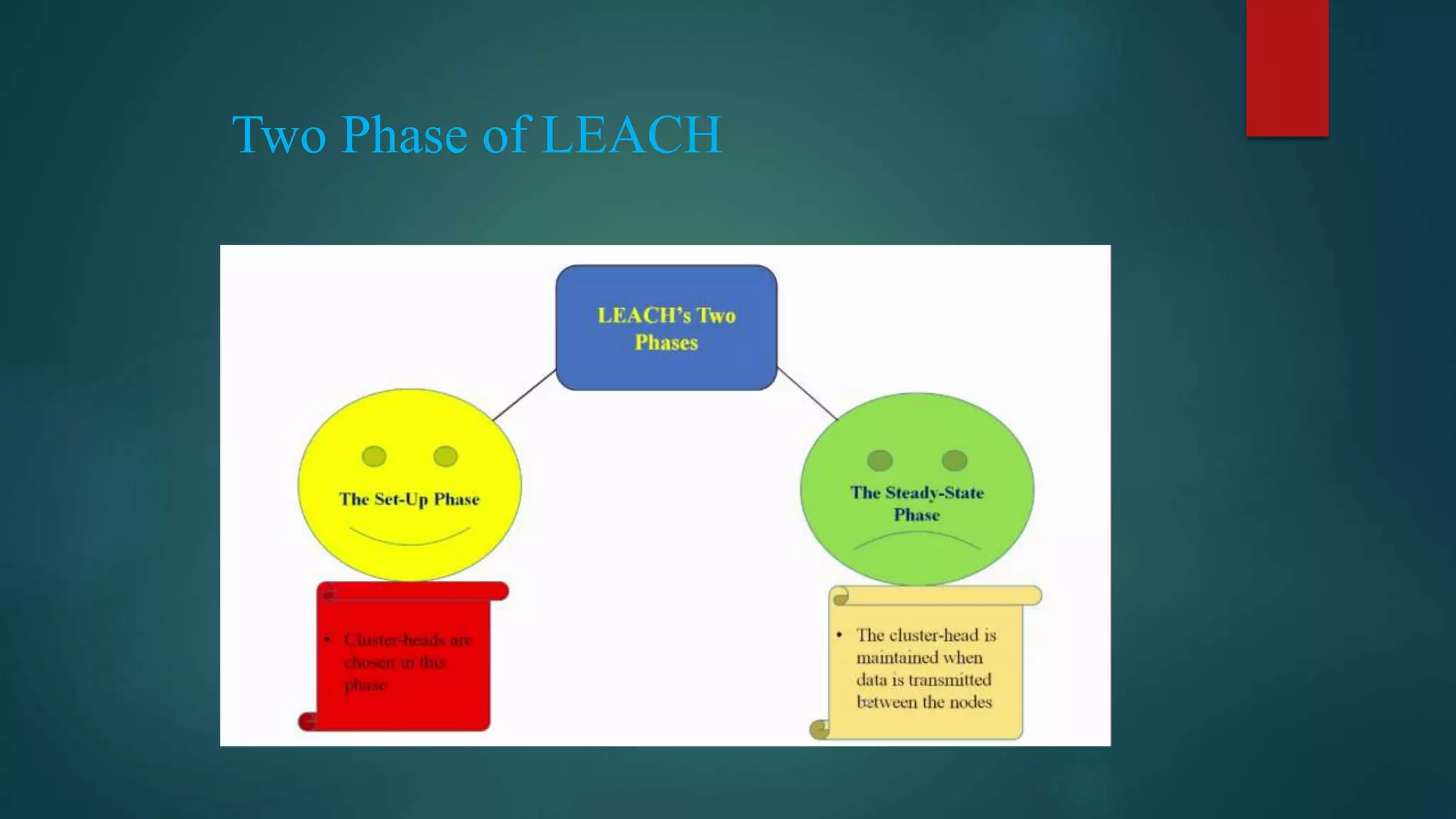
![Previous Work LEACH Protocol [6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar-160425171517/75/Secure-and-Efficient-Data-Transmission-for-Cluster-Based-Wireless-Sensor-Networks-9-2048.jpg)
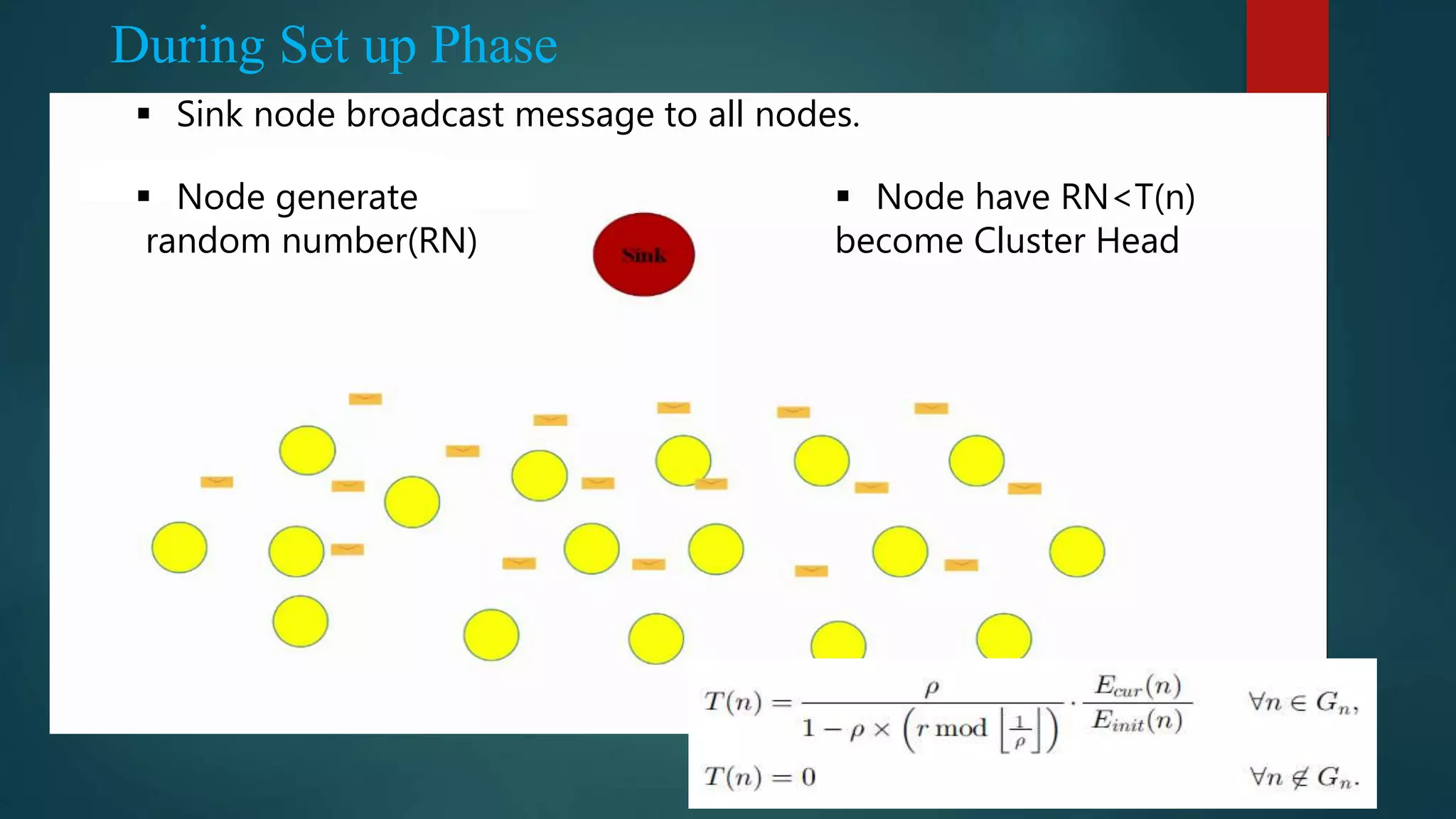
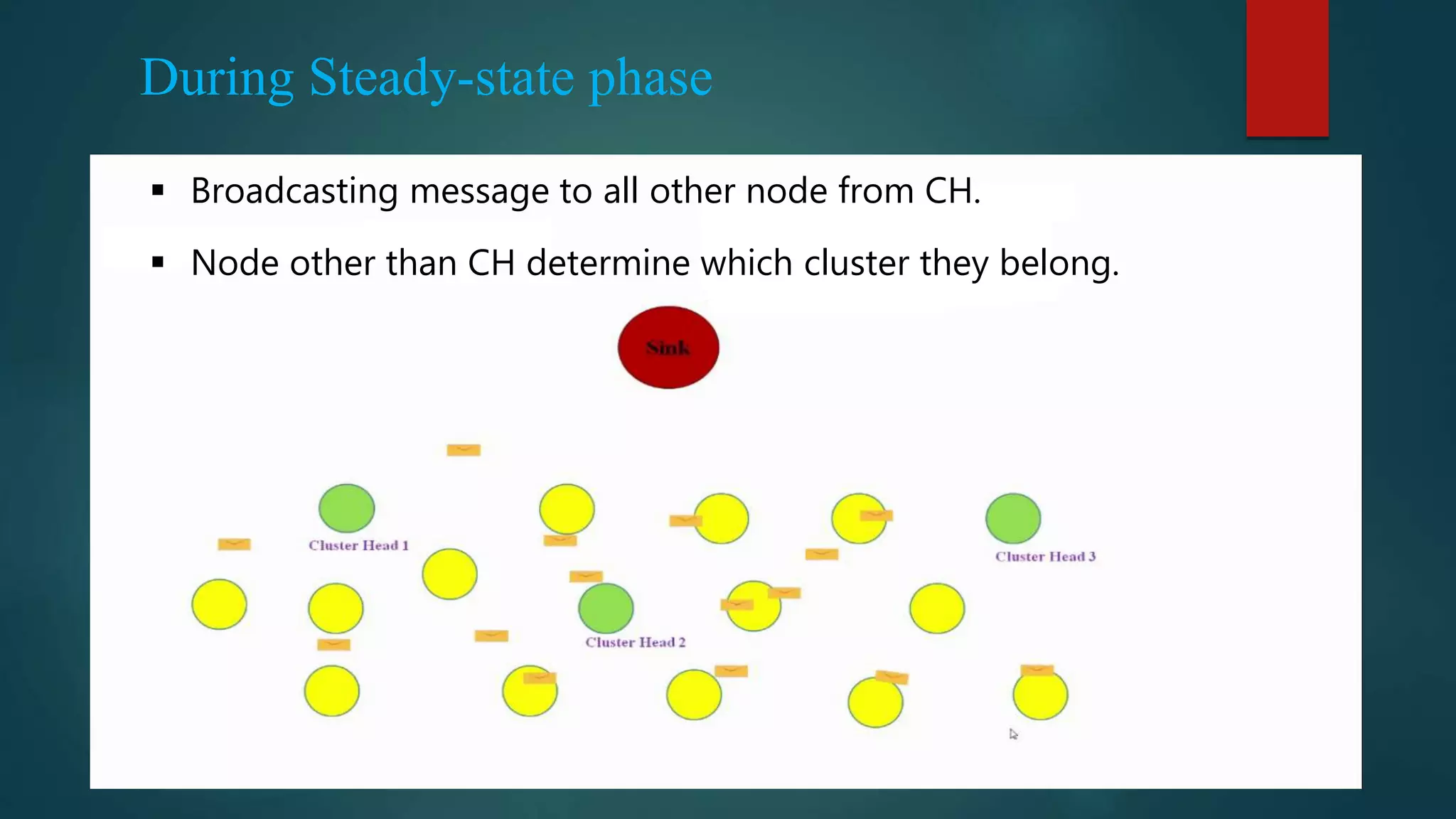
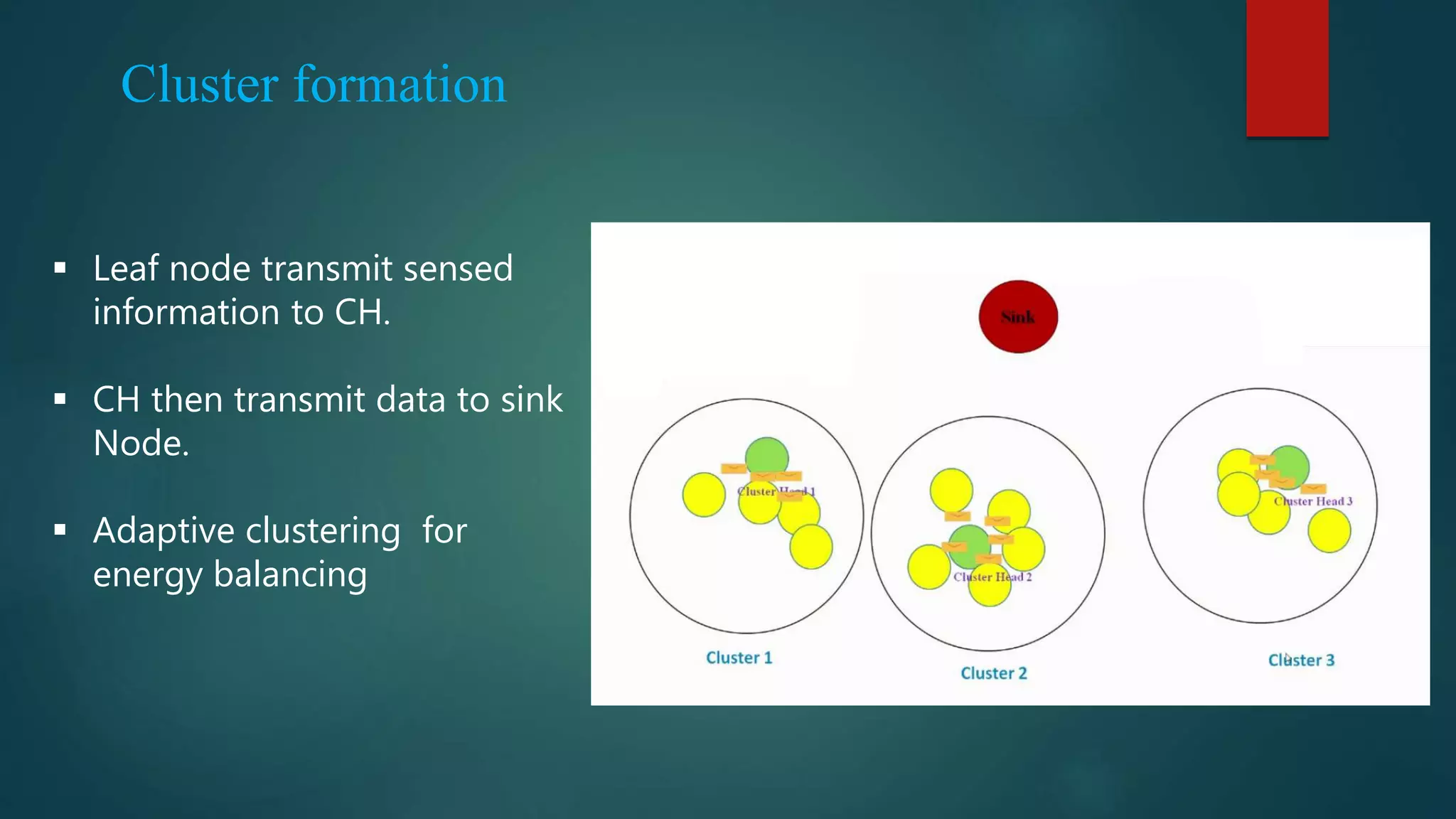






![ Use the additively homomorphic encryption scheme in [5] to encrypt the plaintext of sensed data This scheme allows efficient aggregation of encrypted data at the CHs and the BS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar-160425171517/75/Secure-and-Efficient-Data-Transmission-for-Cluster-Based-Wireless-Sensor-Networks-20-2048.jpg)


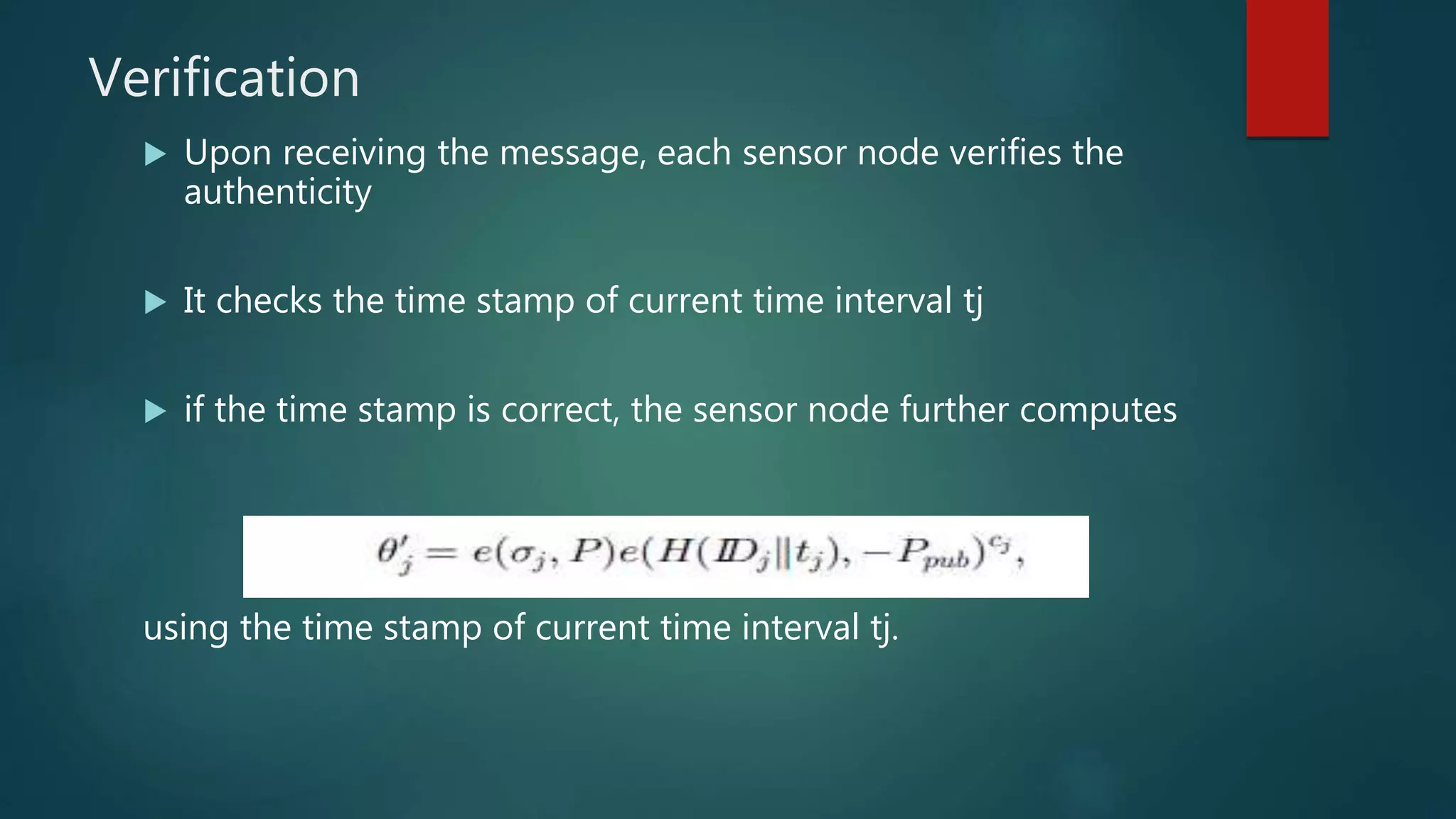
![Key Management leaf sensor node j transmits a message m to its CH i encrypts the data using the encryption key k from the additively homomorphic encryption scheme [5]. It contain three operation -Extraction -Signature signing -Verification](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar-160425171517/75/Secure-and-Efficient-Data-Transmission-for-Cluster-Based-Wireless-Sensor-Networks-23-2048.jpg)








![Solutions to Attacks Passive Attacks - The sensed data are encrypted by the homomorphic encryption scheme from [5], which deals with eavesdropping. Active Attack - attackers do not have valid digital signature.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar-160425171517/75/Secure-and-Efficient-Data-Transmission-for-Cluster-Based-Wireless-Sensor-Networks-35-2048.jpg)

![Refrences [1] “Secure and Efficient Data Transmission for Cluster-Based Wireless Sensor Networks” H. Lu; J. Li; M. Guizani IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems. [2] S. Sharma and S.K. Jena, “A Survey on Secure Hierarchical Routing Protocols in Wireless Sensor Networks,” Proc. Int’l Conf.Comm., Computing & Security (ICCCS), pp. 146-151, 2011. [3] A.A. Abbasi and M. Younis, “A Survey on Clustering Algorithms for Wireless Sensor Networks,”Computer Comm., vol. 30, nos. 14/ 15, pp. 2826-2841, 2007 [4] A. Shamir, “Identity-Based Cryptosystems and Signature Schemes,” Proc. Advances in Cryptology (CRYPTO), pp. 47-53, [5] C. Castelluccia, E. Mykletun, and G. Tsudik, “Efficient Aggregation of Encrypted Data in Wireless Sensor Networks,” Proc. Second Ann. Int’l Conf. Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Networking and Services (MobiQuitous), pp. 109-117, 2005. [6] Wireless Sensor Network Remote Triggered Virtual Labs At AMRITA UNIVERSITY (Wireless Remote Sensing, Experimentation, Monitoring and Administration Lab) http://vlab.amrita.edu/index.php?sub=78&brch=256&sim=1558&cnt=1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar-160425171517/75/Secure-and-Efficient-Data-Transmission-for-Cluster-Based-Wireless-Sensor-Networks-39-2048.jpg)