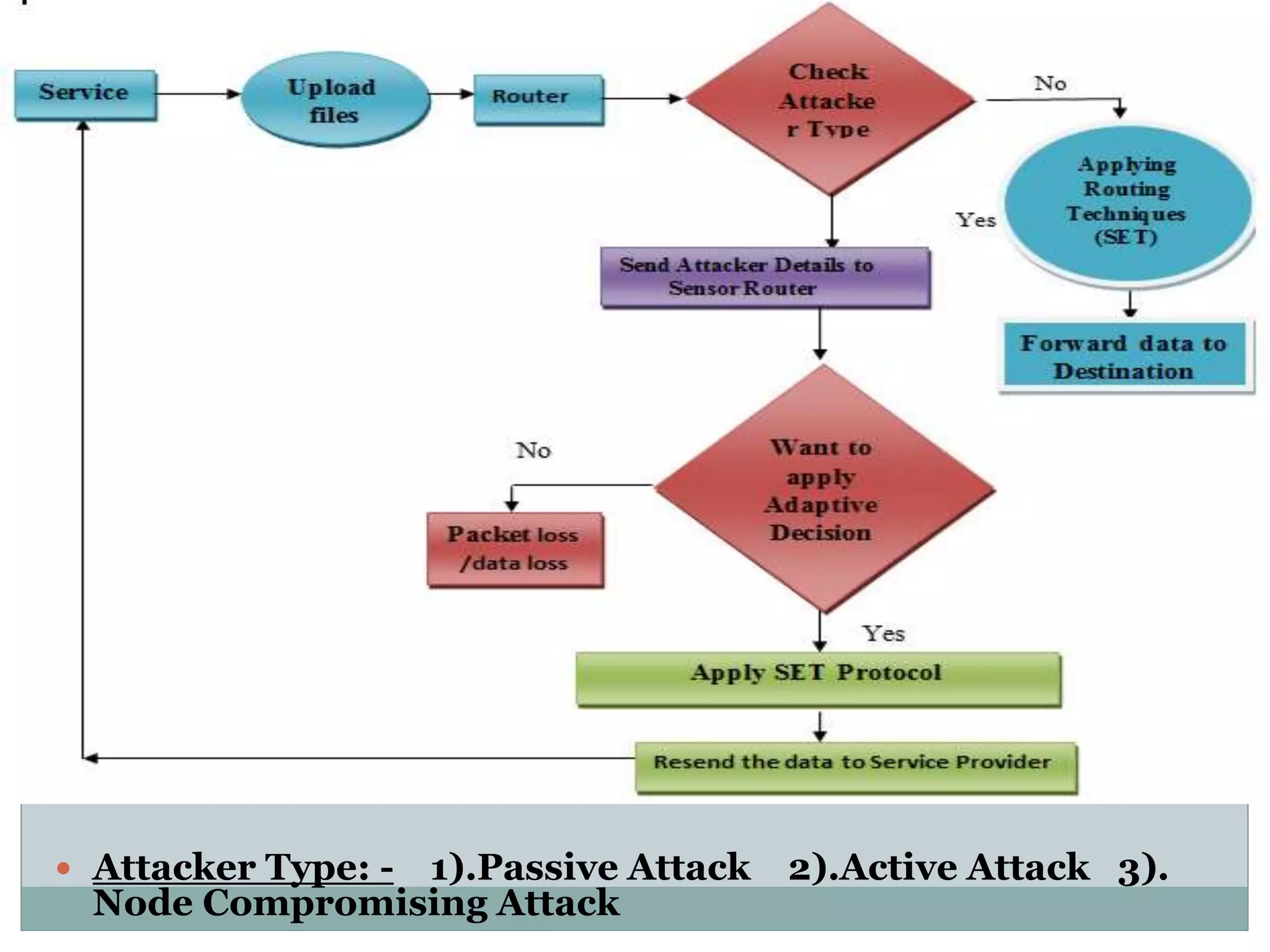
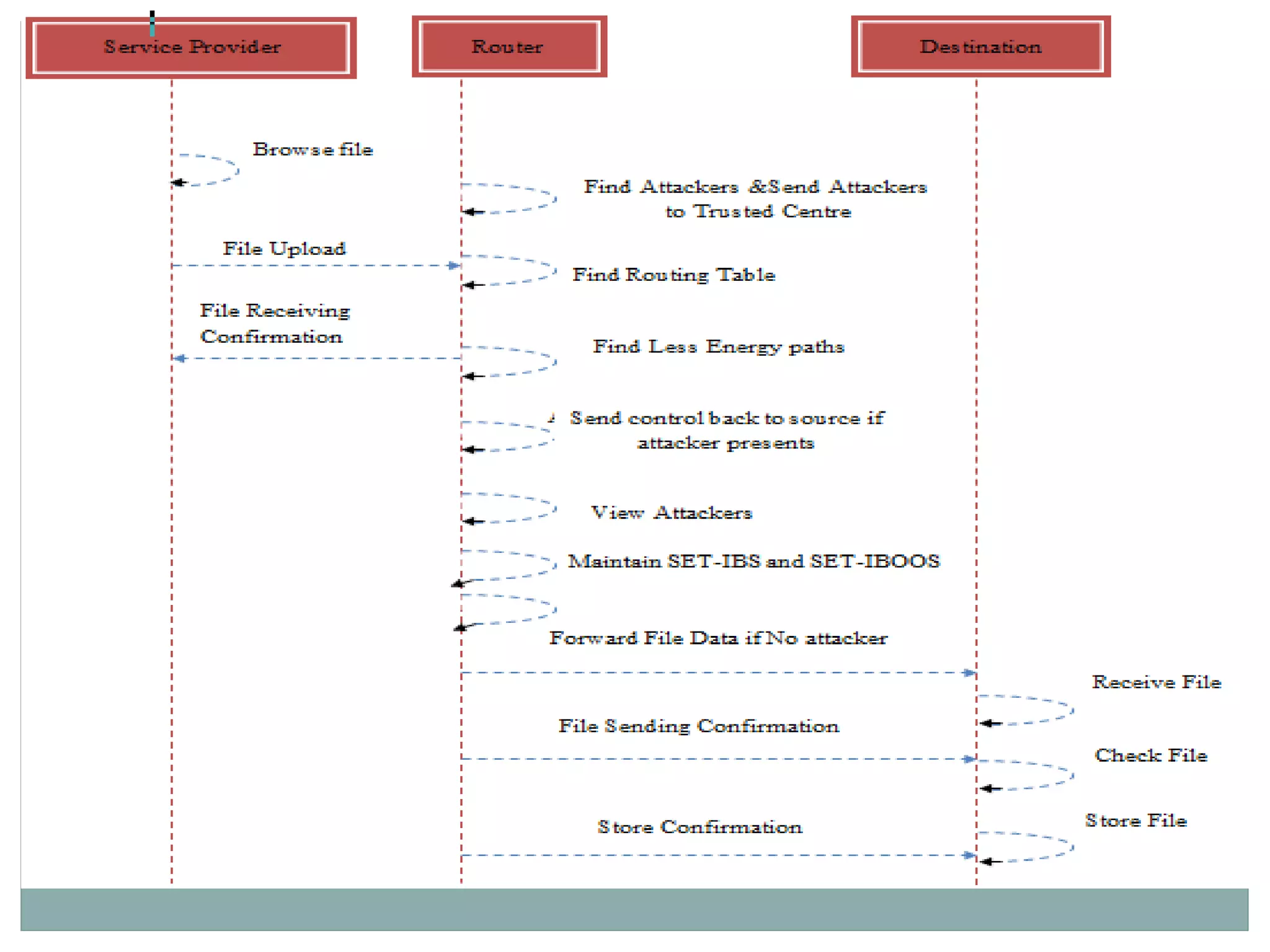
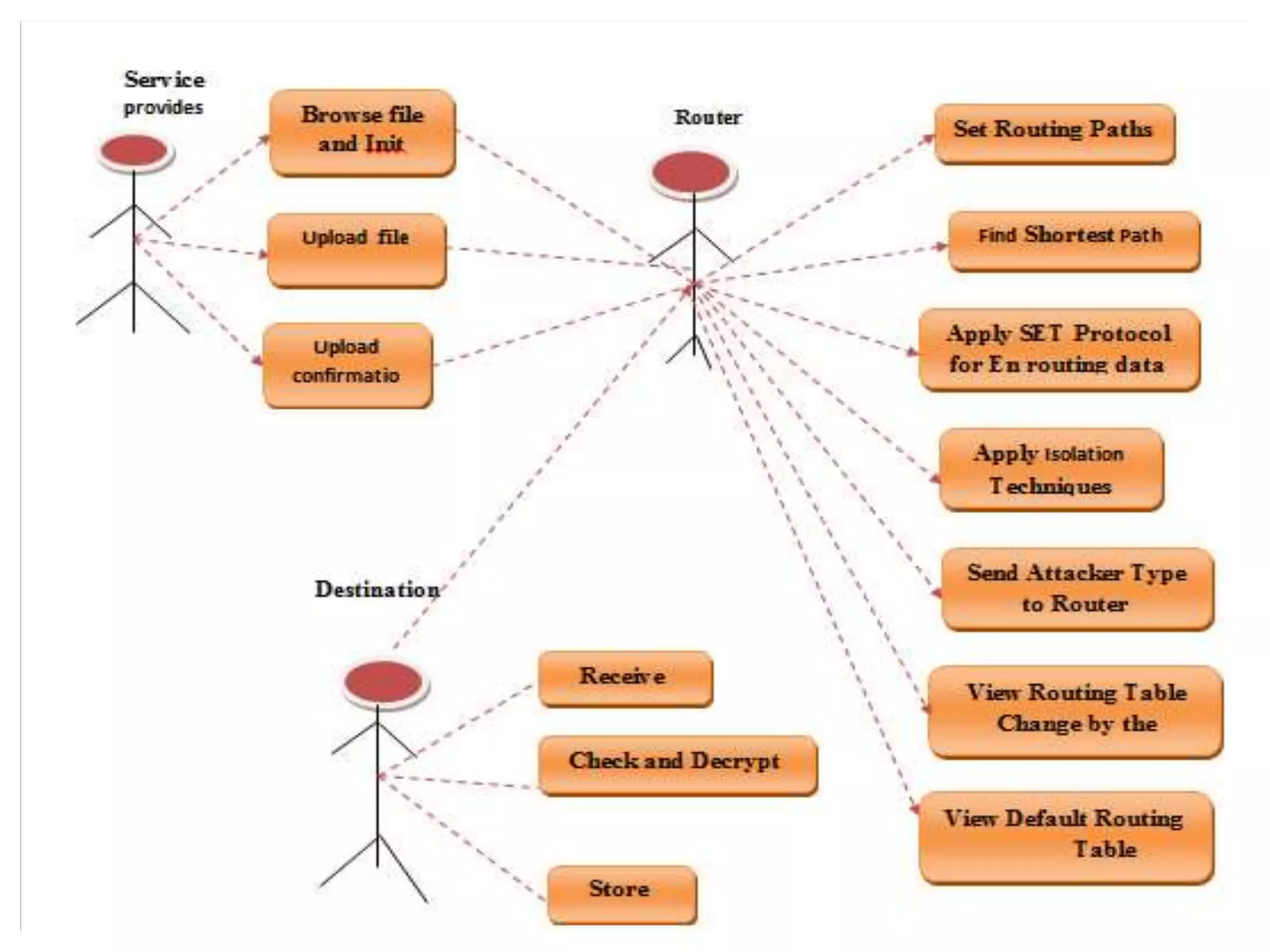
The document discusses secure and efficient data transmission in cluster-based wireless sensor networks (WSNs), highlighting two protocols: SET-IBS and SET-IBOOS, which utilize identity-based digital signatures for enhanced security. It reviews relevant literature and identifies the objectives, system analysis, and design specifications aimed at improving data transmission between nodes and base stations while minimizing energy consumption. The proposed system addresses computational and communication overhead through innovative algorithms aimed at maintaining energy efficiency and security.













![REFERENCES [1] Y. Wang, G. Attebury, and B. Ramamurthy, “A Survey of Security Issues in Wireless Sensor Networks,” IEEE Comm. Surveys & Tutorials, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 2-23, Second Quarter 2006. [2] A.A. Abbasi and M. Younis, “A Survey on Clustering Algorithms for Wireless Sensor Networks,” Computer Comm., vol. 30, nos. 14/ 15, pp. 2826-2841, 2007. [3] W. Heinzelman, A. Chandrakasan, and H. Balakrishnan, “An Application-Specific Protocol Architecture for Wireless Microsensor Networks,” IEEE Trans. Wireless Comm., vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 660-670, Oct. 2002.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/secureandefficientdatatransmissions-150519030127-lva1-app6892/75/Secure-and-efficient-data-transmission-for-cluster-based-wireless-sensor-network-23-2048.jpg)
![CONTINUED… [4] A. Manjeshwar, Q.-A. Zeng, and D.P. Agrawal, “An Analytical Model for Information Retrieval in Wireless Sensor Networks Using Enhanced APTEEN Protocol,” IEEE Trans. Parallel & Distributed Systems, vol. 13, no. 12, pp. 1290-1302, Dec. 2002. [5] S. Yi et al., “PEACH: Power-Efficient and Adaptive Clustering Hierarchy Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks,” Computer Comm., vol. 30, nos. 14/15, pp. 2842-2852, 2007.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/secureandefficientdatatransmissions-150519030127-lva1-app6892/75/Secure-and-efficient-data-transmission-for-cluster-based-wireless-sensor-network-24-2048.jpg)
