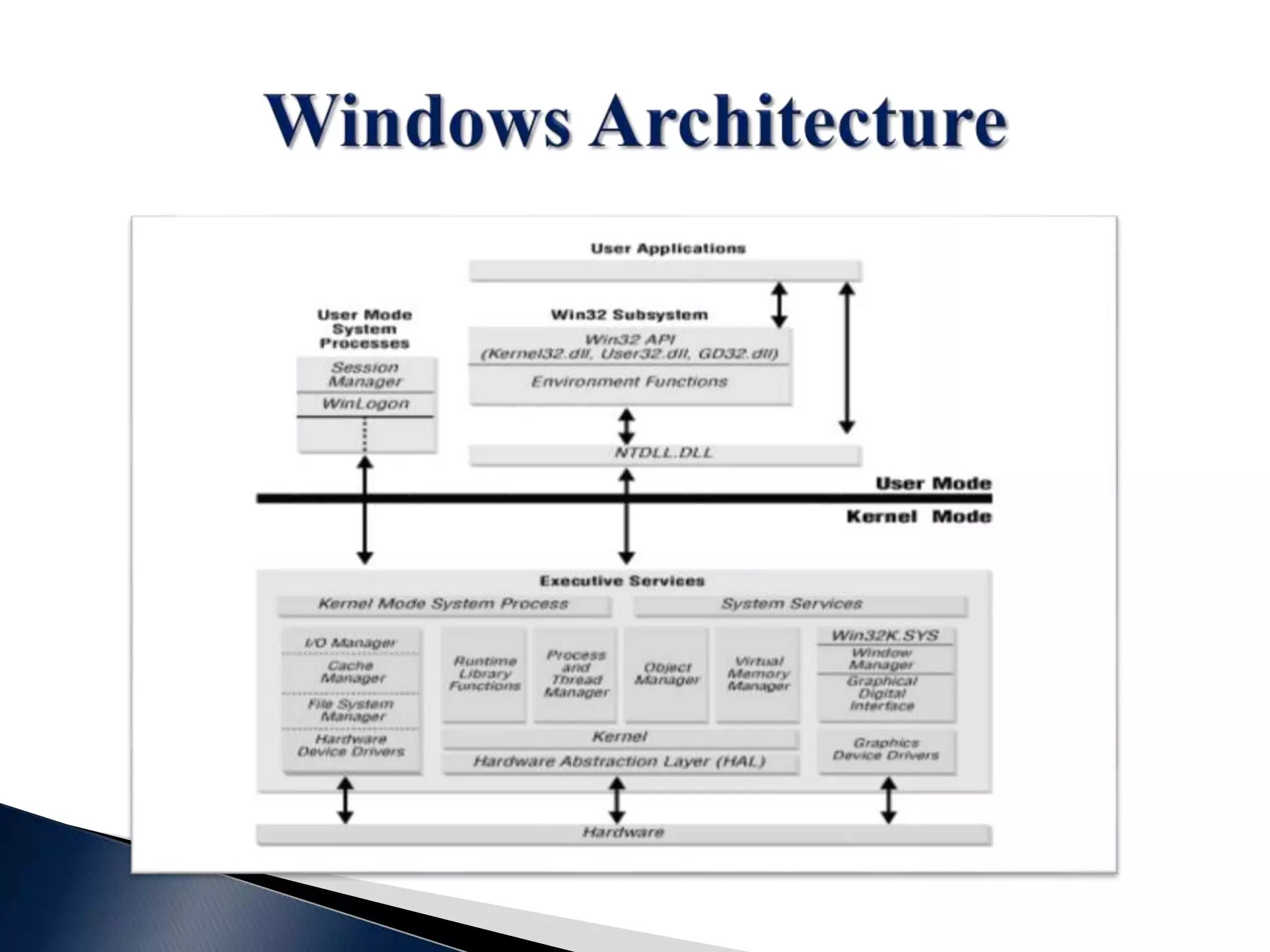
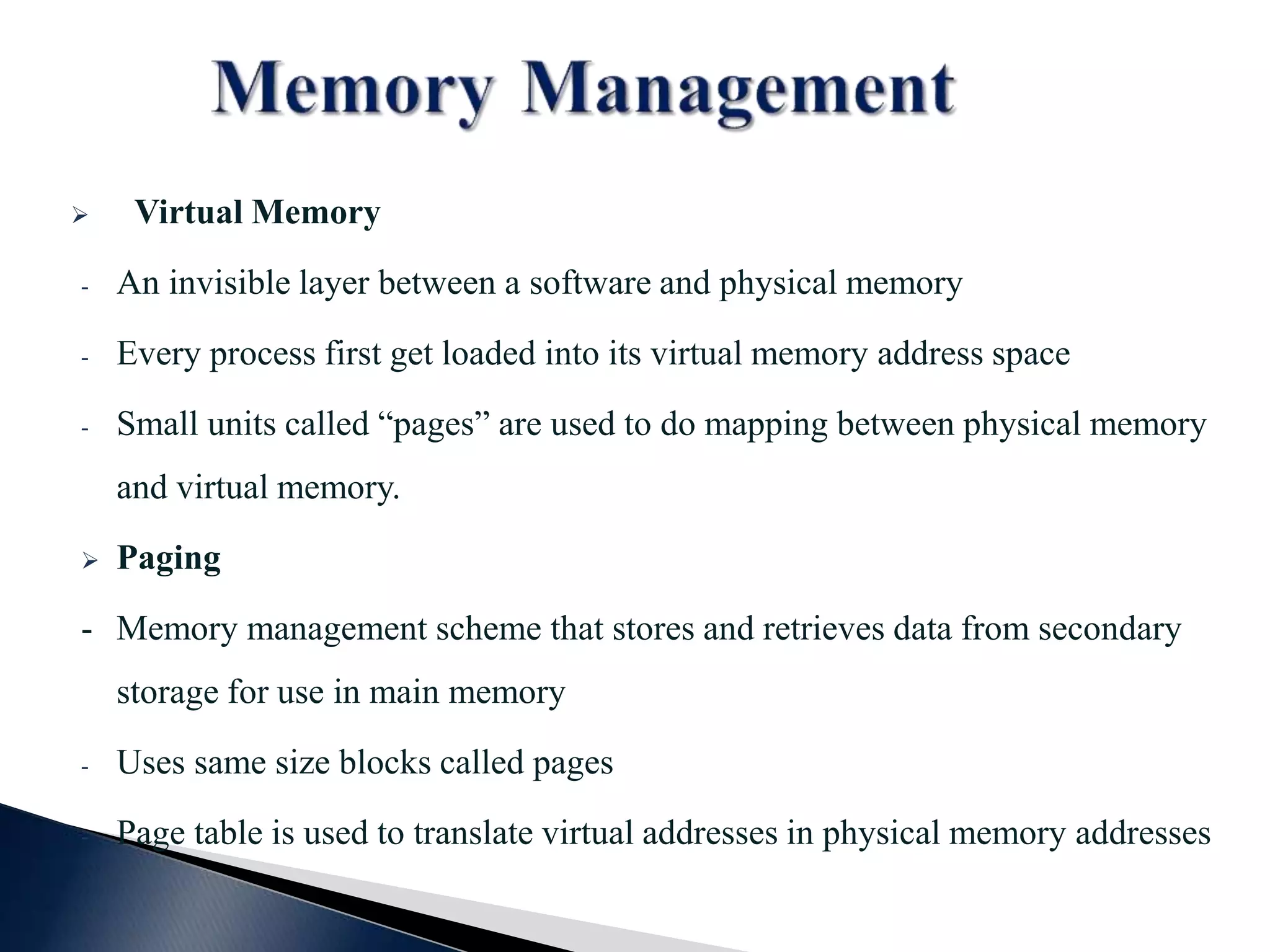
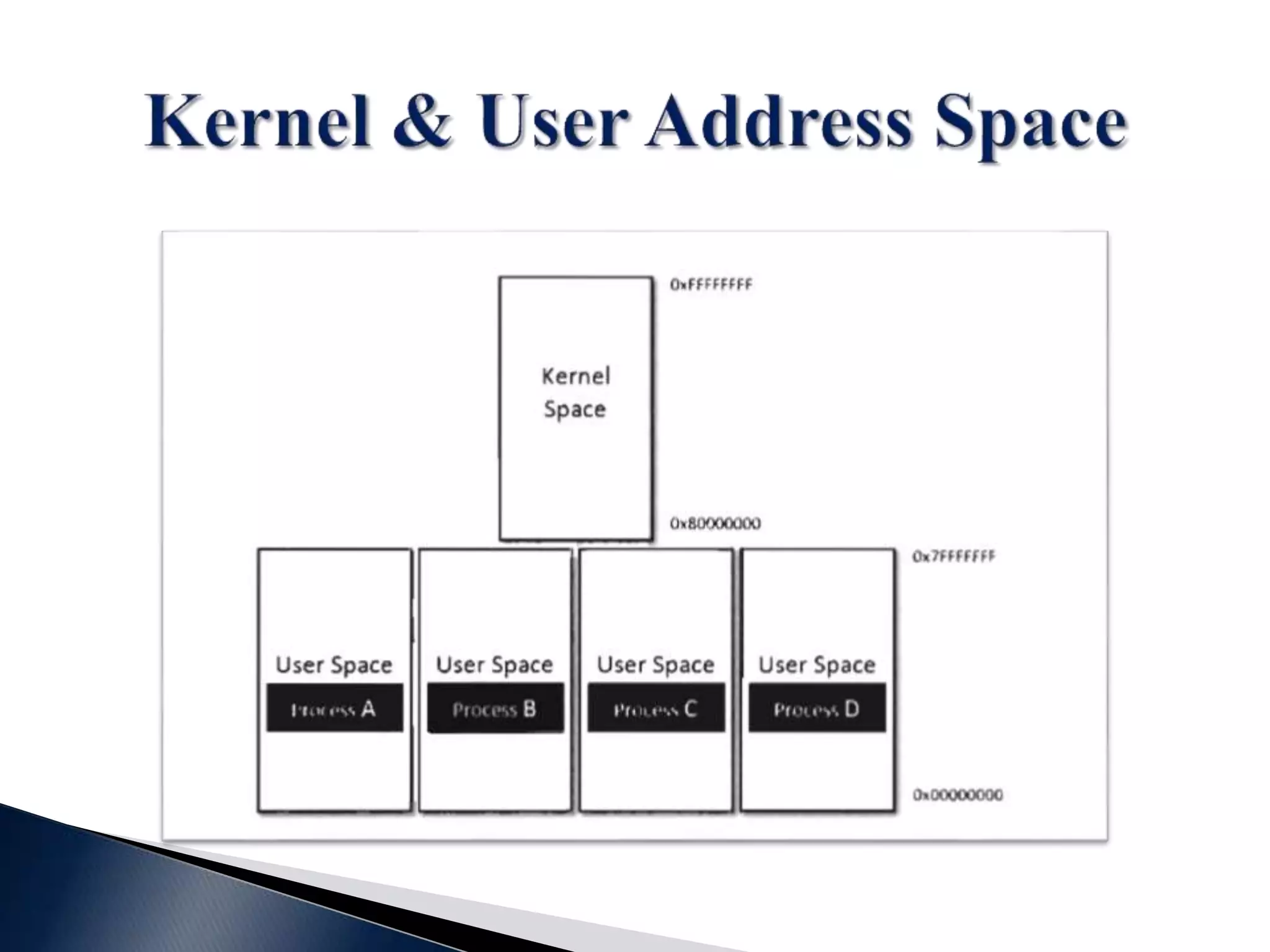
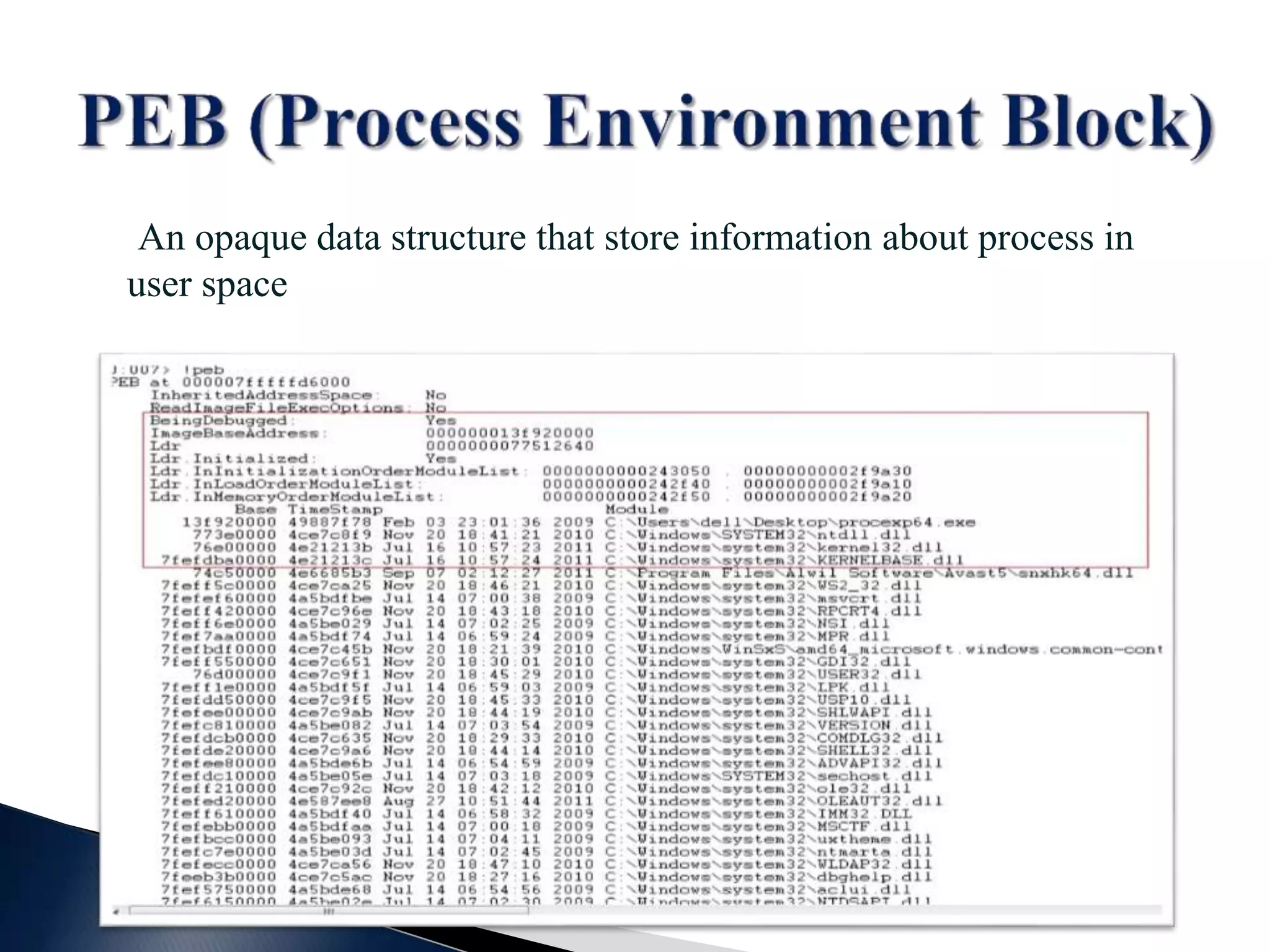
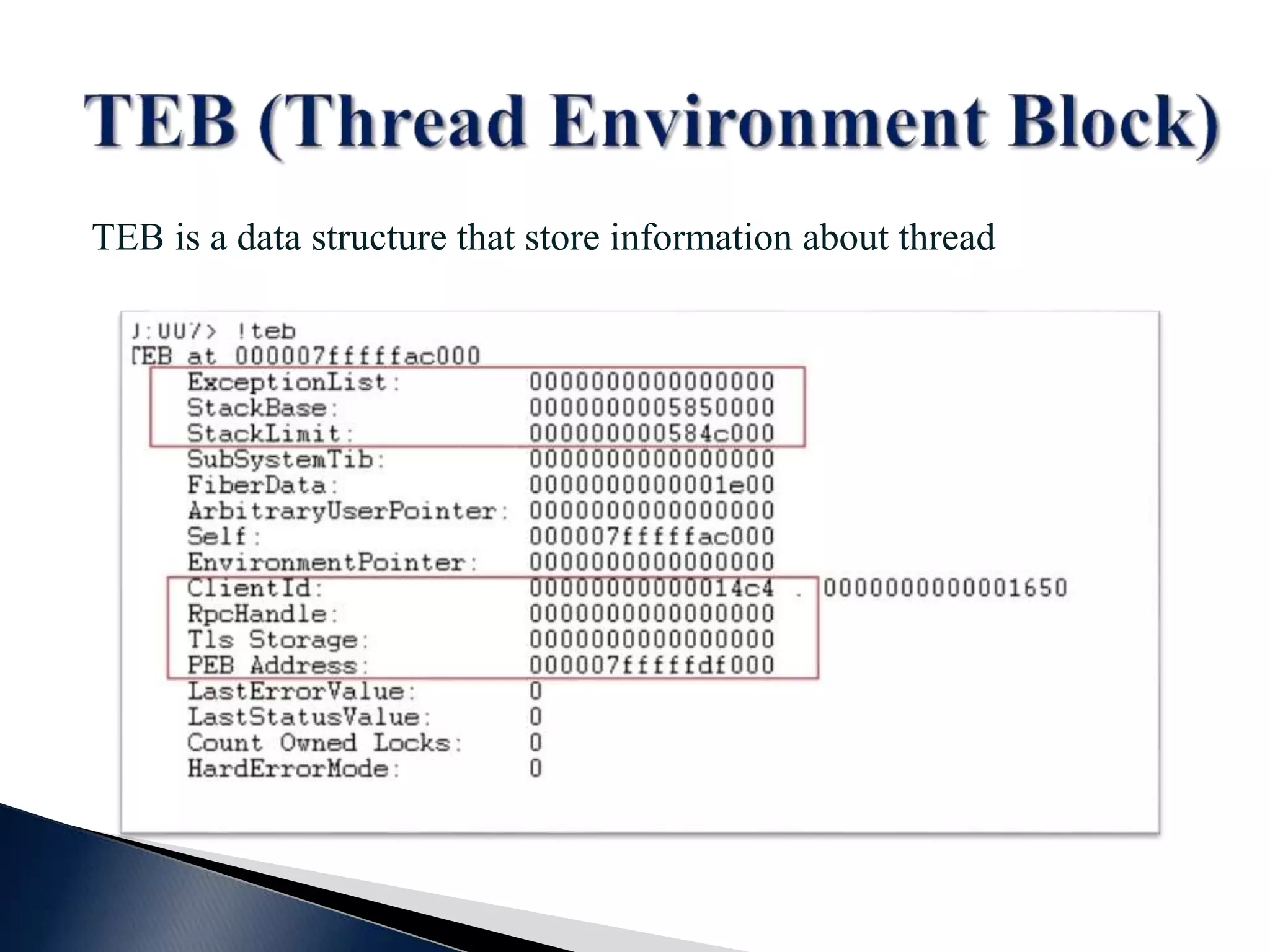
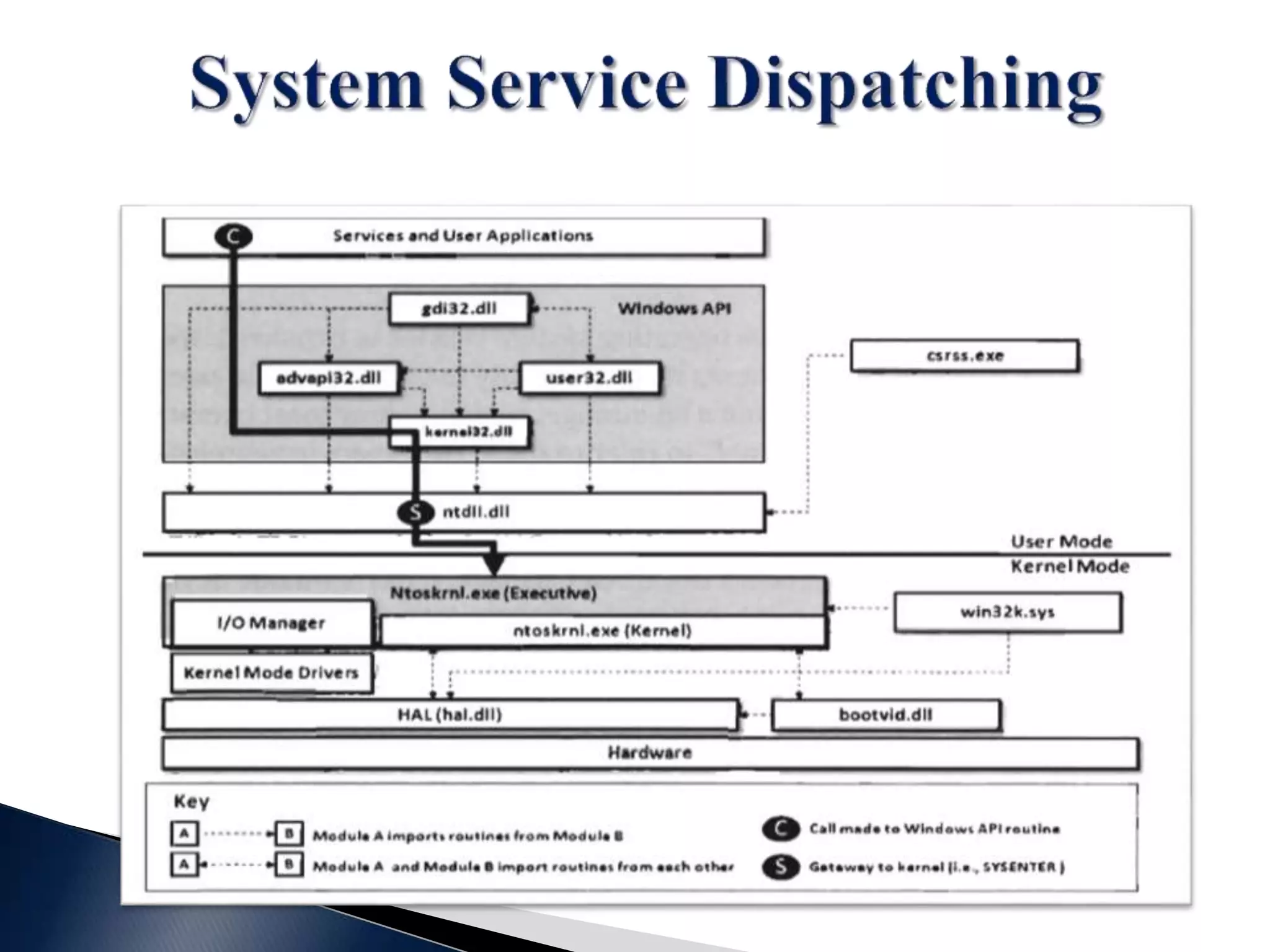
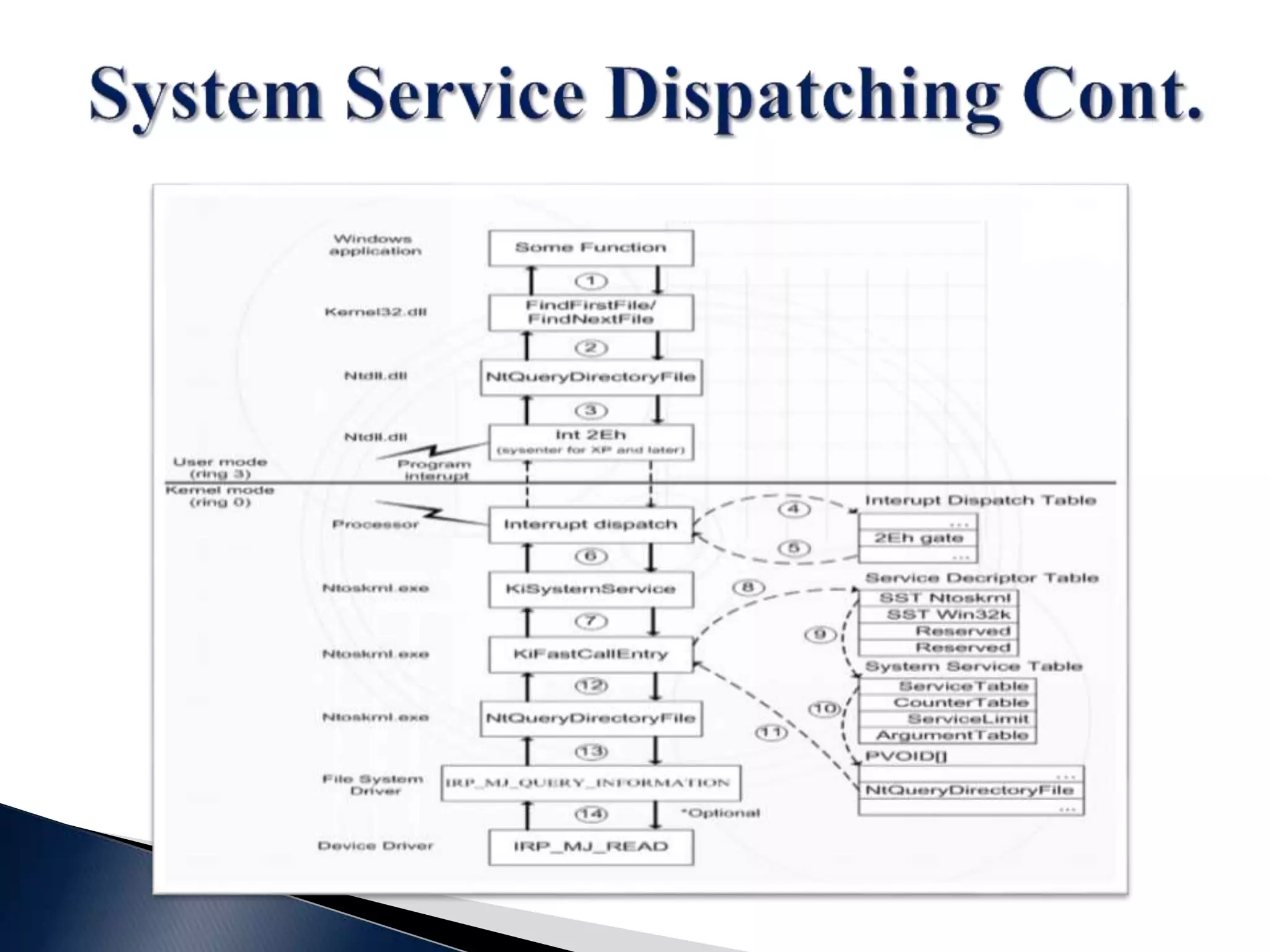
This document contains a disclaimer stating that the content is provided as-is without warranty. It also acknowledges those who have supported the training program. The document introduces the presenters and states that the reversing and malware analysis training is currently only offered locally for free. It provides some key information about processes, threads, virtual memory, paging, and common Windows APIs.