This document proposes a method for remote data integrity checking with a third party auditor using an identity-based proxy server protocol (IDPP) in public clouds. The IDPP protocol uses identity-based cryptography and computational Diffie-Hellman problems to authorize a proxy to process and upload data to the cloud on behalf of an owner who may be restricted. It allows the owner to remotely check the integrity of their data stored in the public cloud. The proposed system uses key generation, encryption, labeling files with tags, and an interactive proof between the cloud and owner to verify integrity.

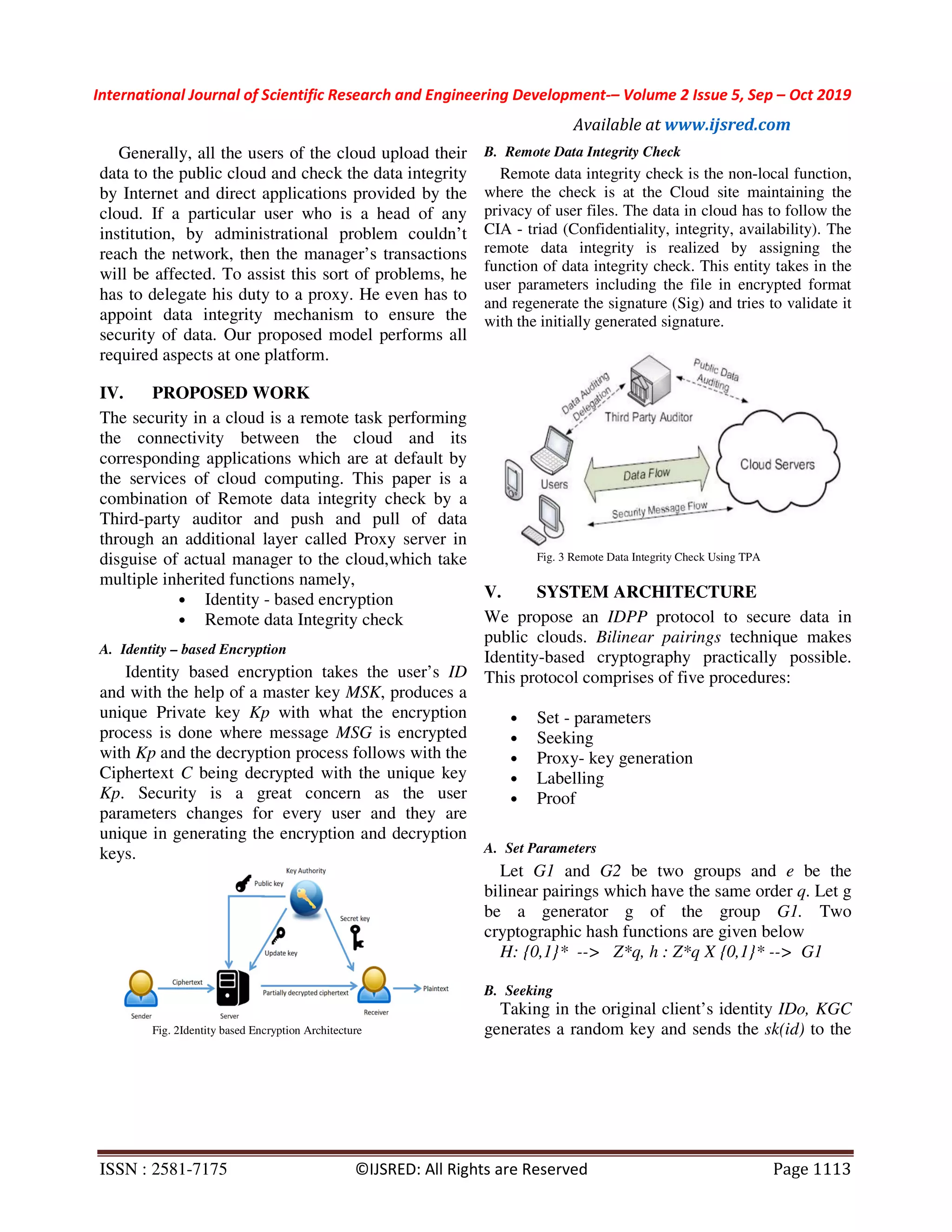
![International Journal of Scientific Research and Engineering Development-– Volume 2 Issue 5, Sep – Oct 2019 Available at www.ijsred.com ISSN : 2581-7175 ©IJSRED: All Rights are Reserved Page 1112 Cloud Computing has client infrastructure, Internet, application, services, Cloud runtime, Storage, Infrastructure, and security blocks in the architecture. Below figure shows the architecture of Cloud Computing Fig. 1Cloud Computing Architecture Security of the cloud refers to the data uploaded by the user in remote public cloud servers since the data stored is out of user’s reach in terms of confidentiality, integrity and availability of data and service. Remote data integrity checking is an essential task in convincing the users of the cloud that their data is kept safe. Some special cases the actual user may be restricted due to administrational problems, and the same is realized by the Identity based Proxy server Processing (IDPP). II. LITERATURE REVIEW WentingShen[1]proposed a new model for the integrity check on the cloud computing environment and the use of TPA (Third party auditor) and digital signaturetechnique for achieving the integrity over cloud computing. They also brought up a new method of encrypting a file with the concept of “Sanitization”. This is again broughtby[6] where the concept of “sanitizable signatures” was explained. The sanitizable signatures idea led to the development of sanitization. B.Wang[4] discussed the “public auditing for shared data for efficient user revocation in cloud services”. This analysed the concepts of users in cloud and their bound of access in a protected cloud environment. All the services that cloud provide, basic security but identifying the user based on the ID and auditing of data in cloud have the efficient method of data handling. BhalePradeepkumar[7] made the part of functional algorithms used in this paper in auditing and data integrity checking in cloud while all this is done by a third-party auditor. They used concepts like Third party auditor and MD5 algorithm in generating message block of 32-bit length key. J.Sun[3] showed the cross-domain distribution of files especially the electronic health records and relevant permission access to use them. This in return showcased the concepts that are used in WentingShen[1] that project on electronic health records and the partly encrypted files were pushed into the cloud using specified sanitization techniques. These both allowed us to think over the domain and area of research. In this paper the proposed algorithm is using the entire cloud service with a proxy, both uploading and downloading alongside the auditing and data integrity checking. These concepts were motivated by many earlier published papers and the core algorithm in generating the keys was designed in showing a concreteness in development. This uses IDPP protocol depending on the Diffie Hellman key algorithm keeping in mind the CDH (computational Diffie Hellman problem). III. MOTIVATION The earlier proposed WentingShen[1] showcased a challenging problem of partial encryption with “Sanitization” and advancing the cloud usage. Further study at this process of upload and usage of data is clear and struck with at problem of initial uploader, which is the motivation for this paper.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ijsred-v2i5p111-200210181754/75/Remote-data-integrity-checking-with-a-third-party-auditor-in-public-cloud-using-a-proxy-server-2-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Scientific Research and Engineering Development-– Volume 2 Issue 5, Sep – Oct 2019 Available at www.ijsred.com ISSN : 2581-7175 ©IJSRED: All Rights are Reserved Page 1114 original client by the secure channel. Let sk(id) be the original client’s private key. C. Proxy-key Generation KGC generates its master key and is kept confidential by KGC. D. Labelling Taking in the file F and proxy-key, the proxy generates the corresponding tag for each file Fi. Then it uploads the block-tag pair to PCS. E. Proof Proof is an interactive system between Public Cloud and Original client. At the end of the interactive proof protocol, Original Client output a bit {0|1} denoting “success” or “failure” after the remote data integrity check is over. Fig 4 IDPP Protocol VI. SYSTEM MODEL IDPP protocol in the application generated consists of few entities each performing certain functions. There are four entities similar to them A. Client: This is an entity which uploads massive data to the PCS (Public Cloud Server), by the delegated proxy which can perform the data integrity checking. B. PCS (Public Cloud Server): This is maintained by the cloud service provider and has significant storage and computation capacity. User’s data is securely managed in the cloud. C. Proxy: This is delegated and authorized by the manager to process the Client’s data and upload them. This verifies the signature signed by the Client and processes it when the same is satisfied, otherwise it cannot perform the procedure. D. KGC (Key Generation Centre): This is an entity that generates the private key upon seeking the data and all inputs from the Client. This procedure provides the Client to interact directly with the PCS to check the remote data integrity. Thus, delivering the integrity check and securing the data in a specified design method. VII. CONCLUSION Motivated by the security needs, we proposed a novel security concept of IDPP implemented on public cloud. The concrete IDPP protocol is designed by using the bilinear pairings technique. This protocol is provably secure and efficient by using the formal security proof and efficiency analysis. This finally accomplishes the managerial tasks with updated security mechanisms. REFERENCES [1] Wenting Shen, Jing Qin, Jia Yu , Rong Hao, and Jiankun Hu, Enabling Identity Based Integrity Auditing And Data Sharing With Sensitive Information Hiding for Secure cloud Storages, IEEE transactions vol 14 , February 2019 [2] G. Ateniese et al., “Provable data possession at untrusted stores,” in Proc. 14th ACM Conf. Comput. Commun. Secur., 2007, pp. 598– 609. [3] J. Sun and Y. Fang, “Cross-domain data sharing in distributed electronichealth record systems,” IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst., vol. 21, no. 6,pp. 754–764, Jun. 2010 [4] B. Wang, B. Li, and H. Li, “Panda: Public auditing for shared data with efficient user revocation in the cloud,” IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput.,vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 92–106, Jan./Feb. 2015. [5] Y. Yu et al., “Identity-based remote data integrity checking with perfectdata privacy preserving for cloud storage,” IEEE Trans. Inf. ForensicsSecurity, vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 767–778, Apr. 2017. [6] G. Ateniese, D. H. Chou, B. de Medeiros, and G. Tsudik, “Sanitizable signatures,” in Proc. 10th Eur. Symp. Res. Comput. Secur. Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag, 2005, pp. 159–177. [7] Bhale Pradeepkumar Gajendra, Vinay kumar singh, More Sujeeth, “ Achieving cloud security using third party auditor, MD5 and Identity based encryption”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ijsred-v2i5p111-200210181754/75/Remote-data-integrity-checking-with-a-third-party-auditor-in-public-cloud-using-a-proxy-server-4-2048.jpg)