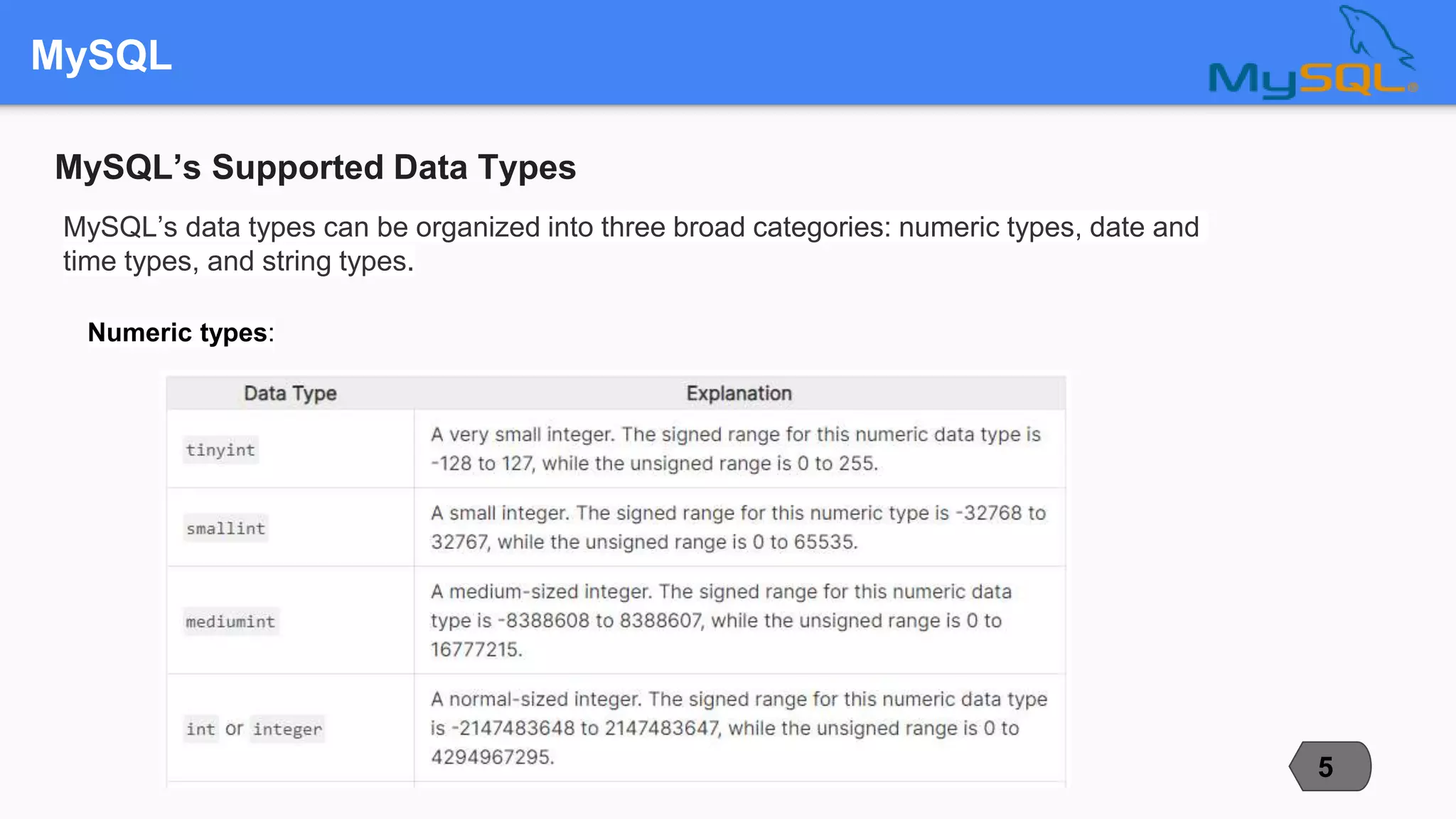
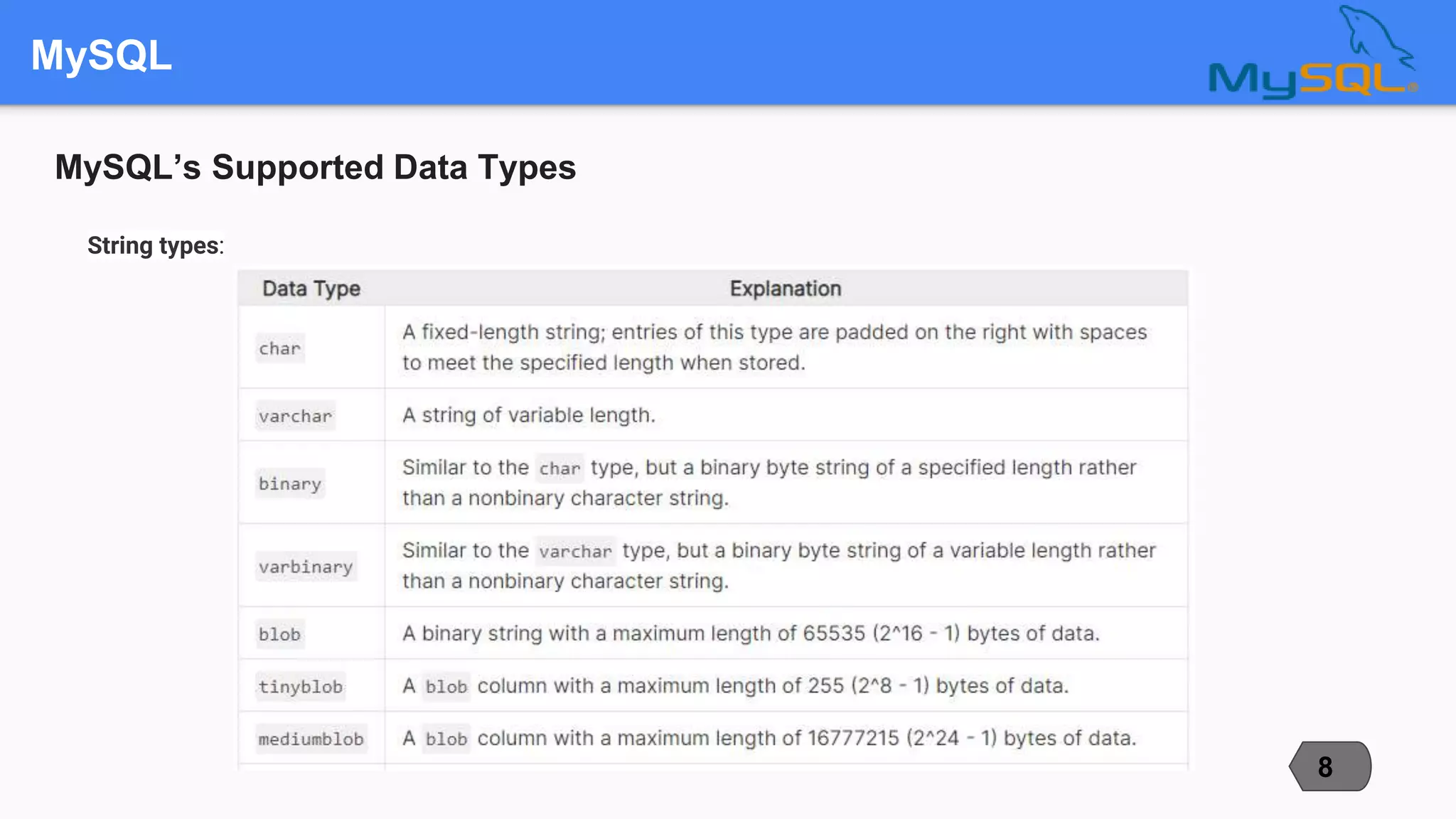
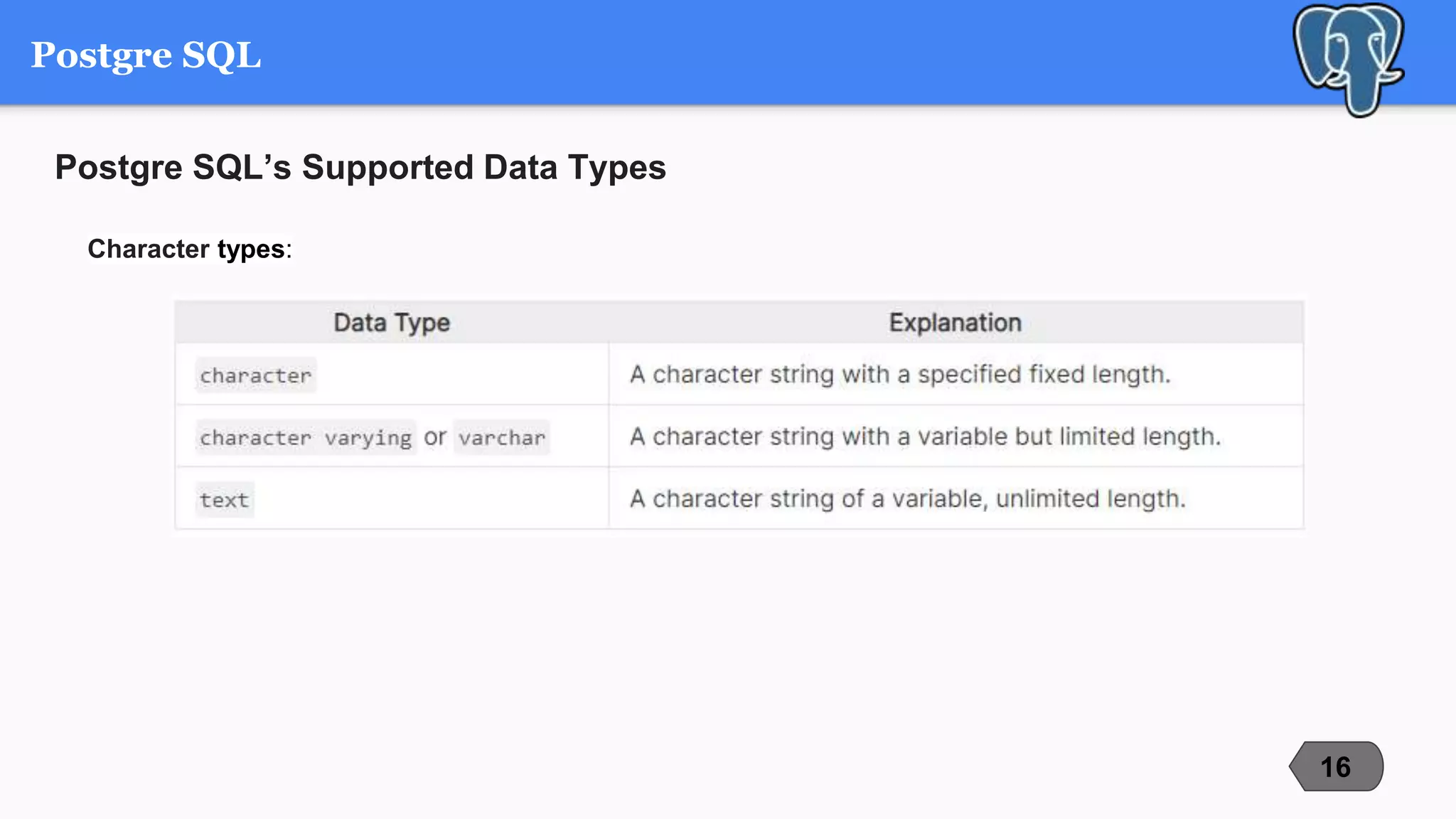
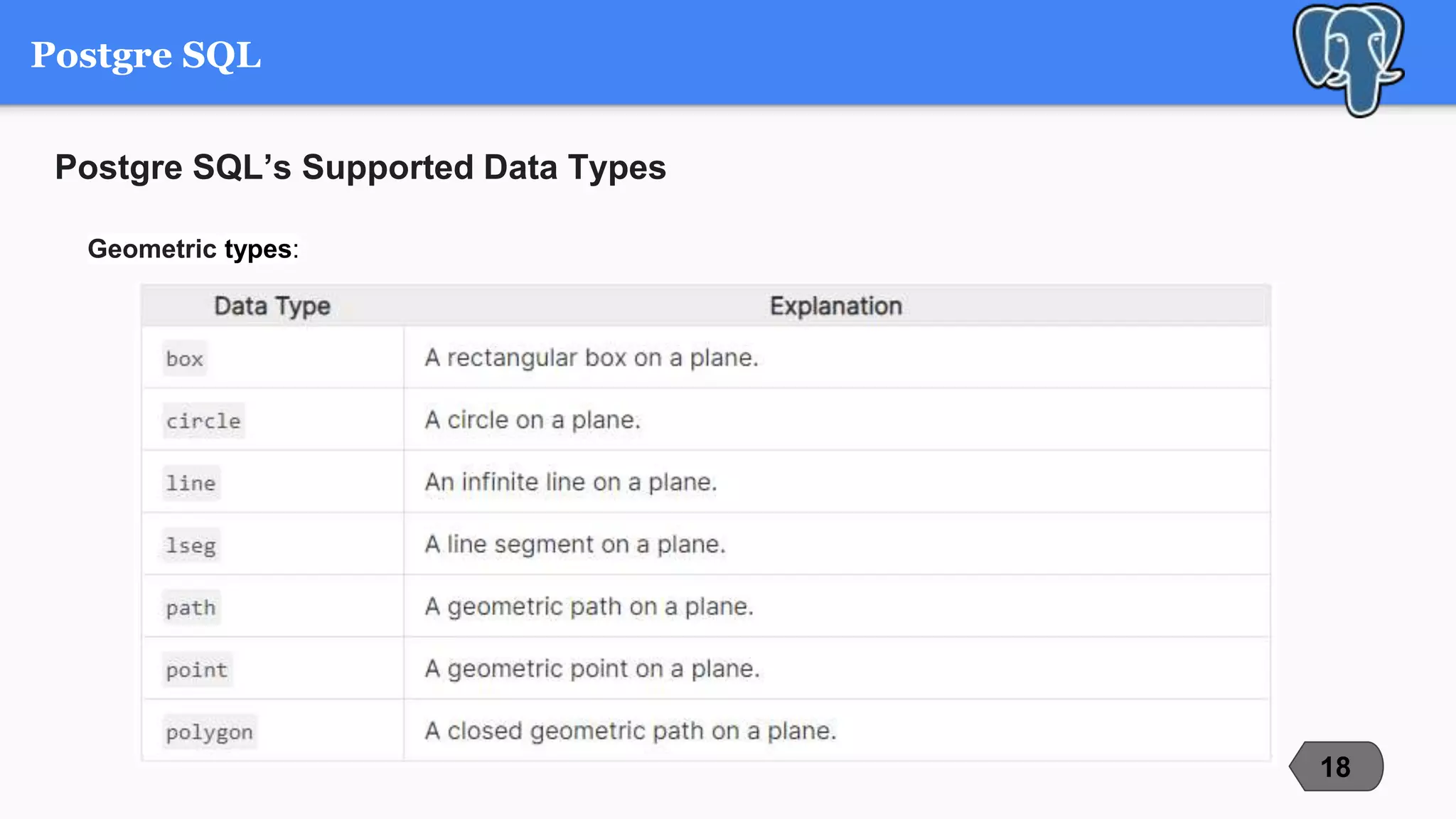
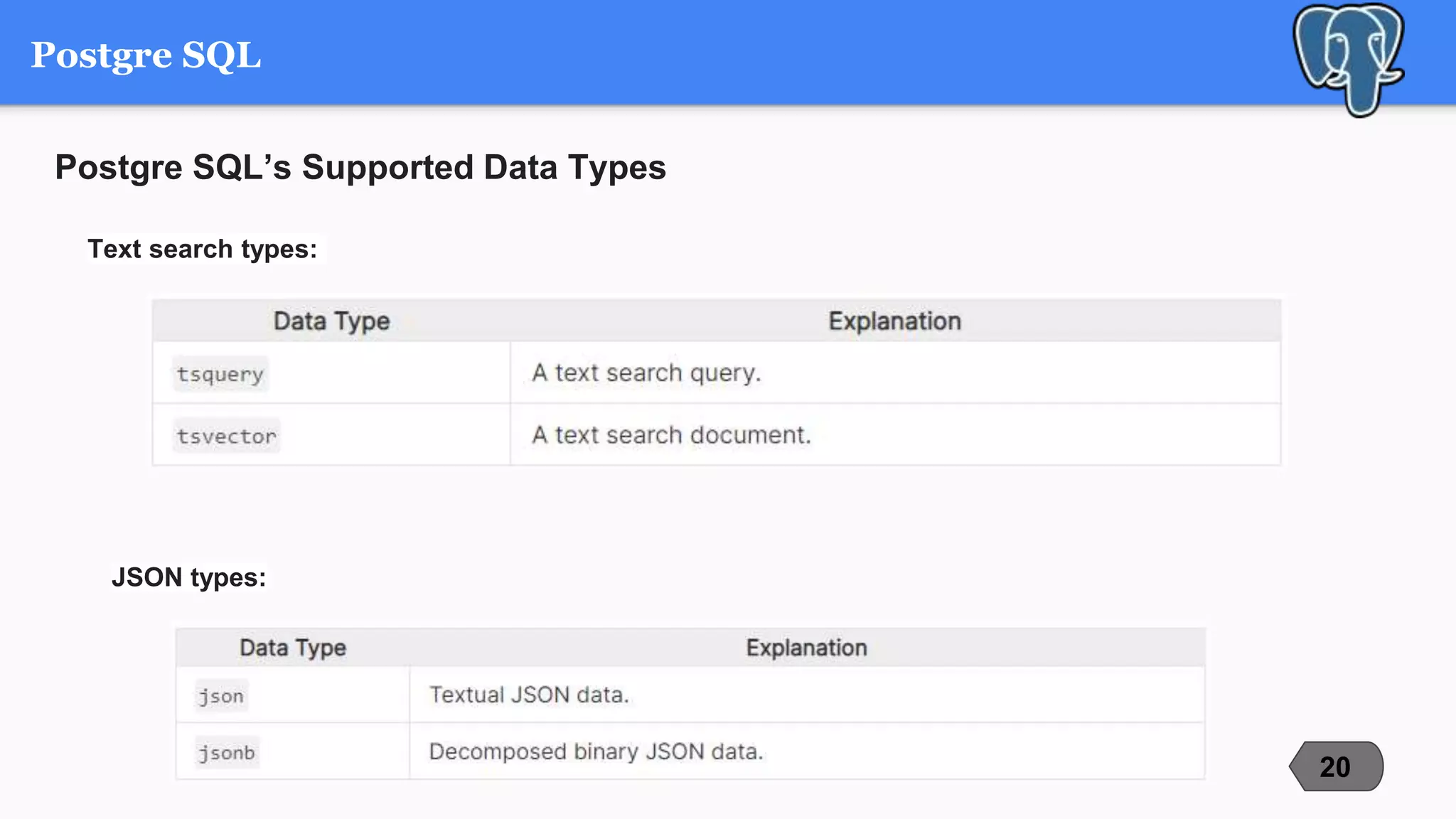
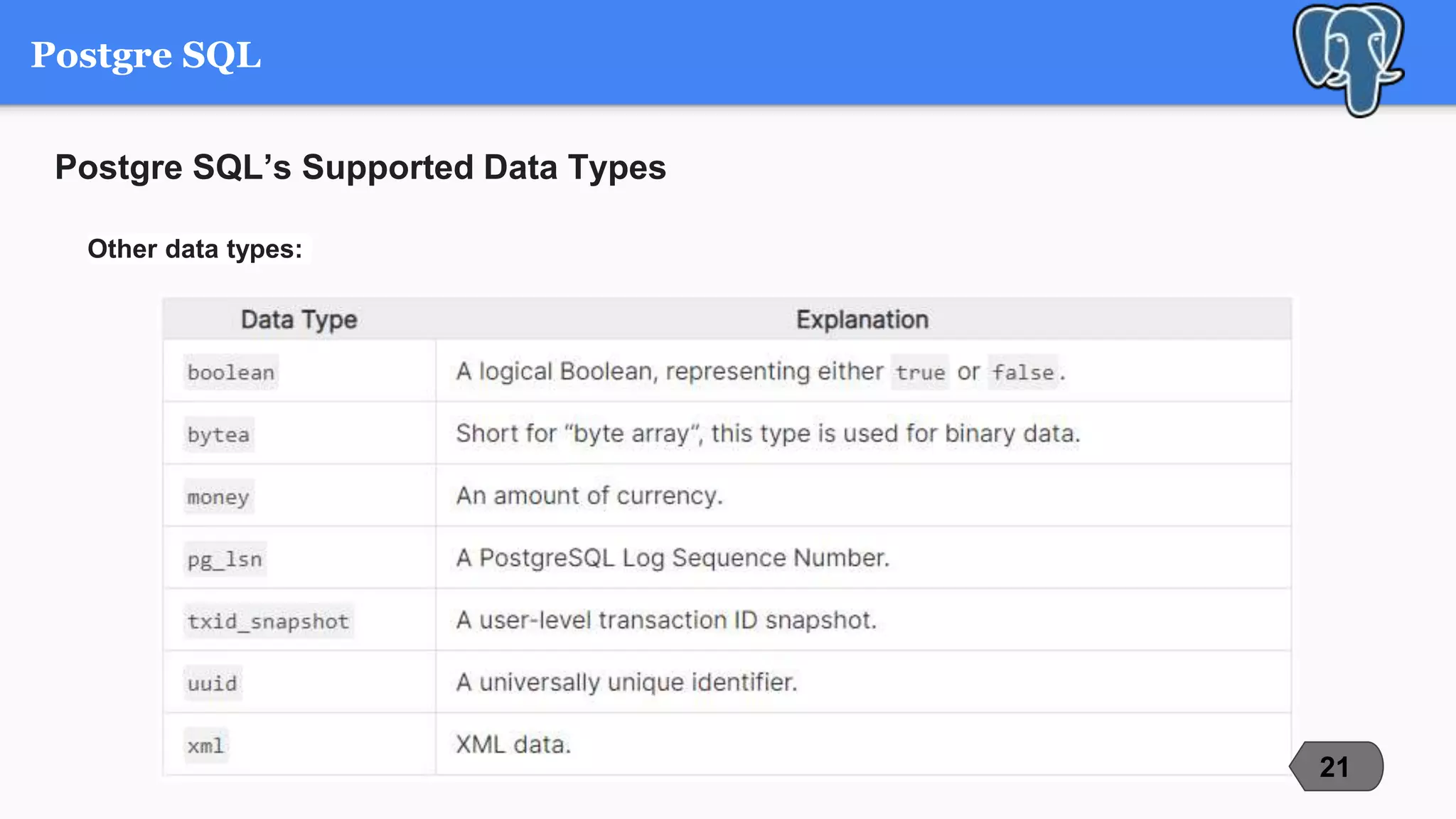
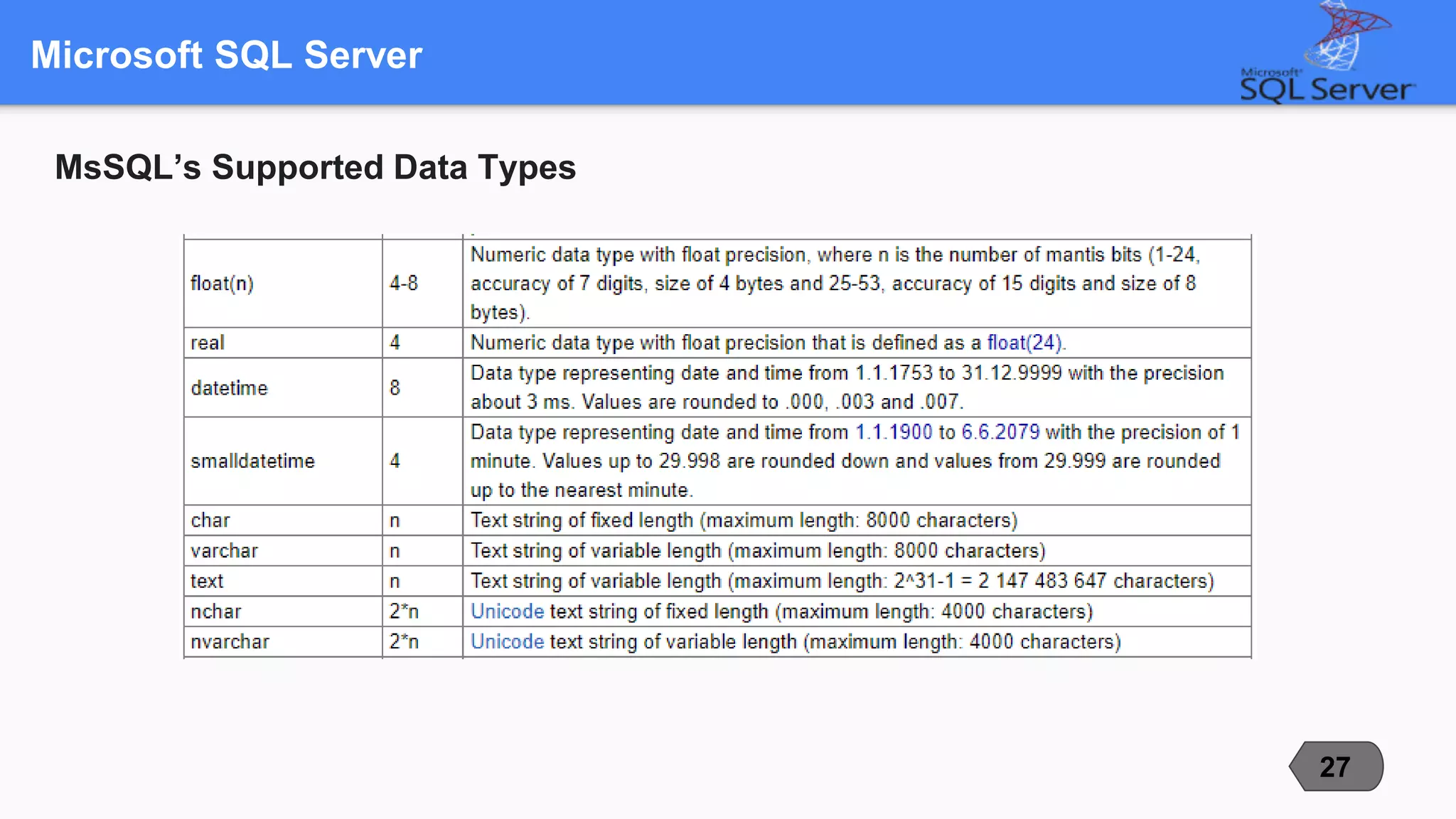
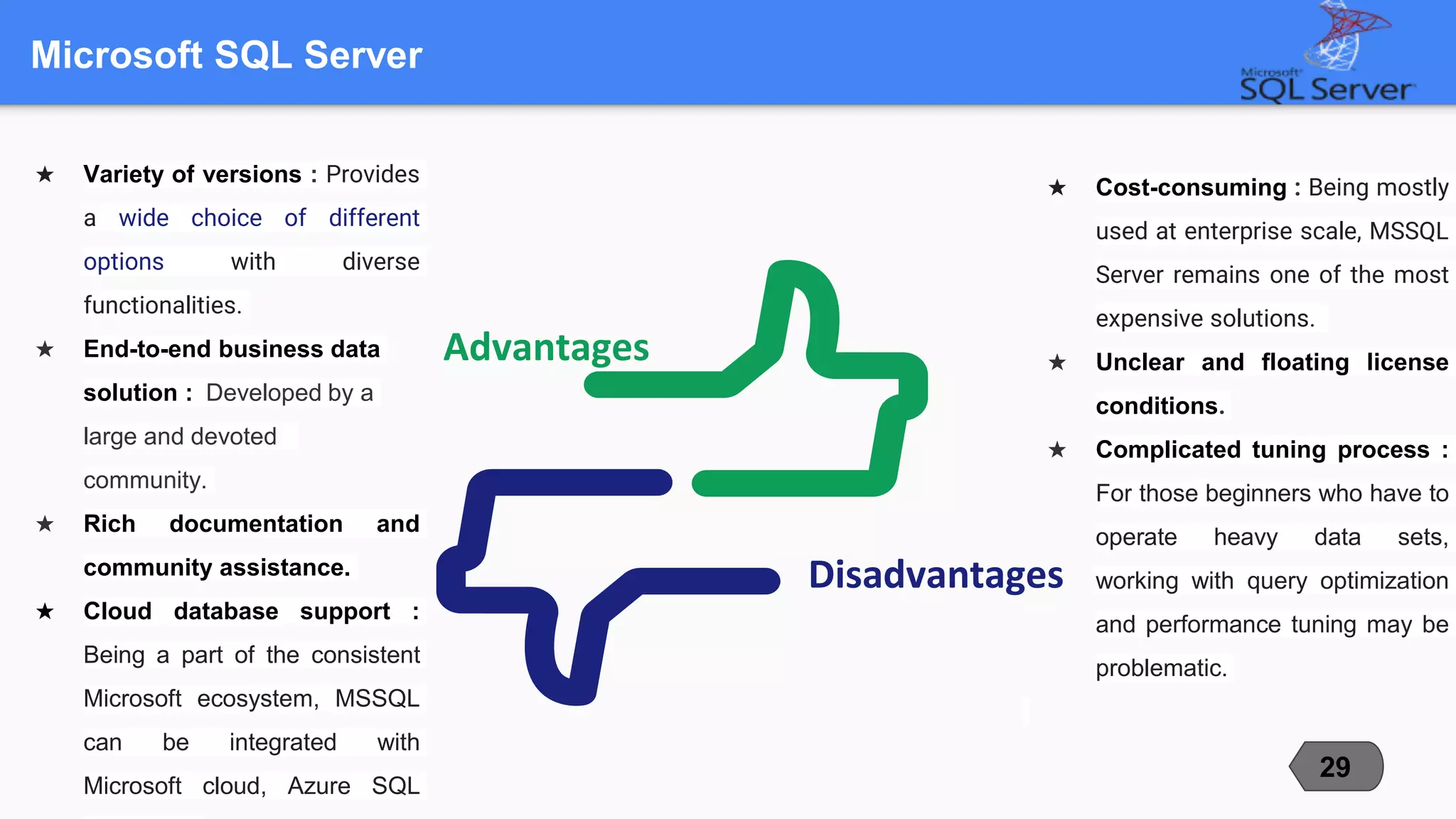
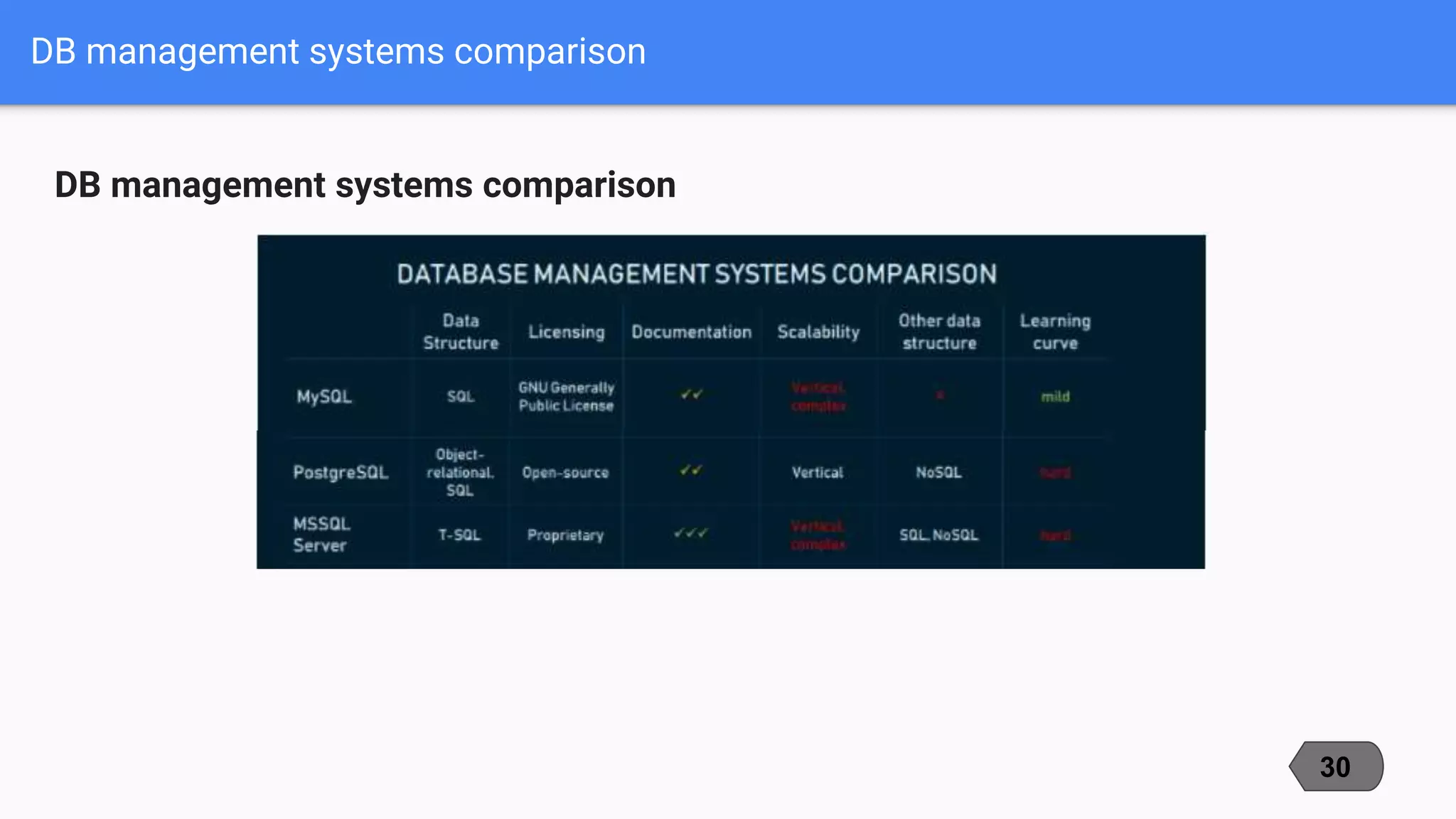
This document compares and contrasts three popular open-source relational database management systems (RDBMS): MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Microsoft SQL Server. It discusses each RDBMS's supported data types, advantages, disadvantages, and best use cases. MySQL is noted as the most popular with strengths in speed and ease of use, while PostgreSQL focuses on compliance and extensibility. SQL Server is suited for large enterprise systems but has higher costs. The document provides an overview of key factors to consider when selecting an RDBMS.