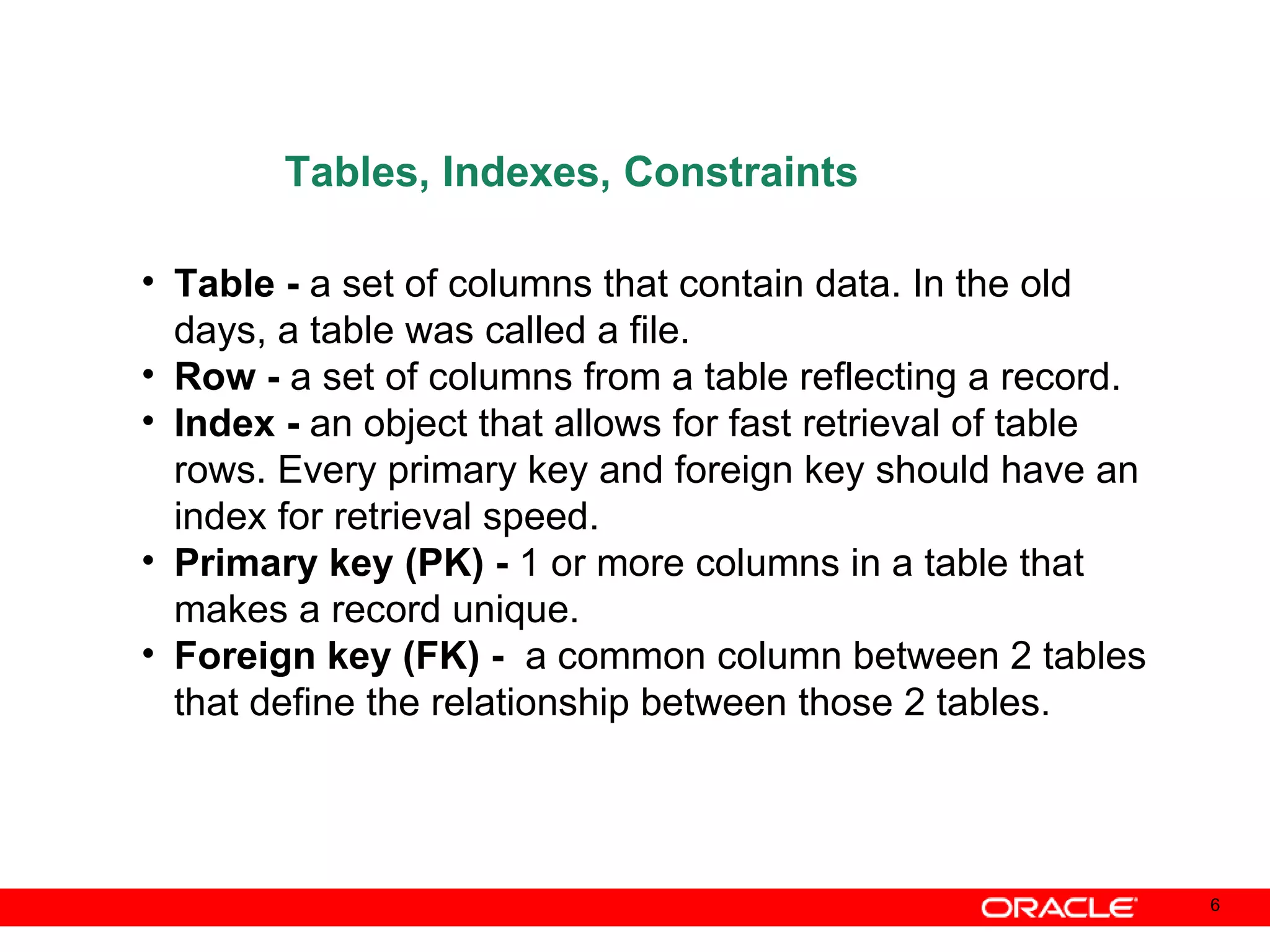
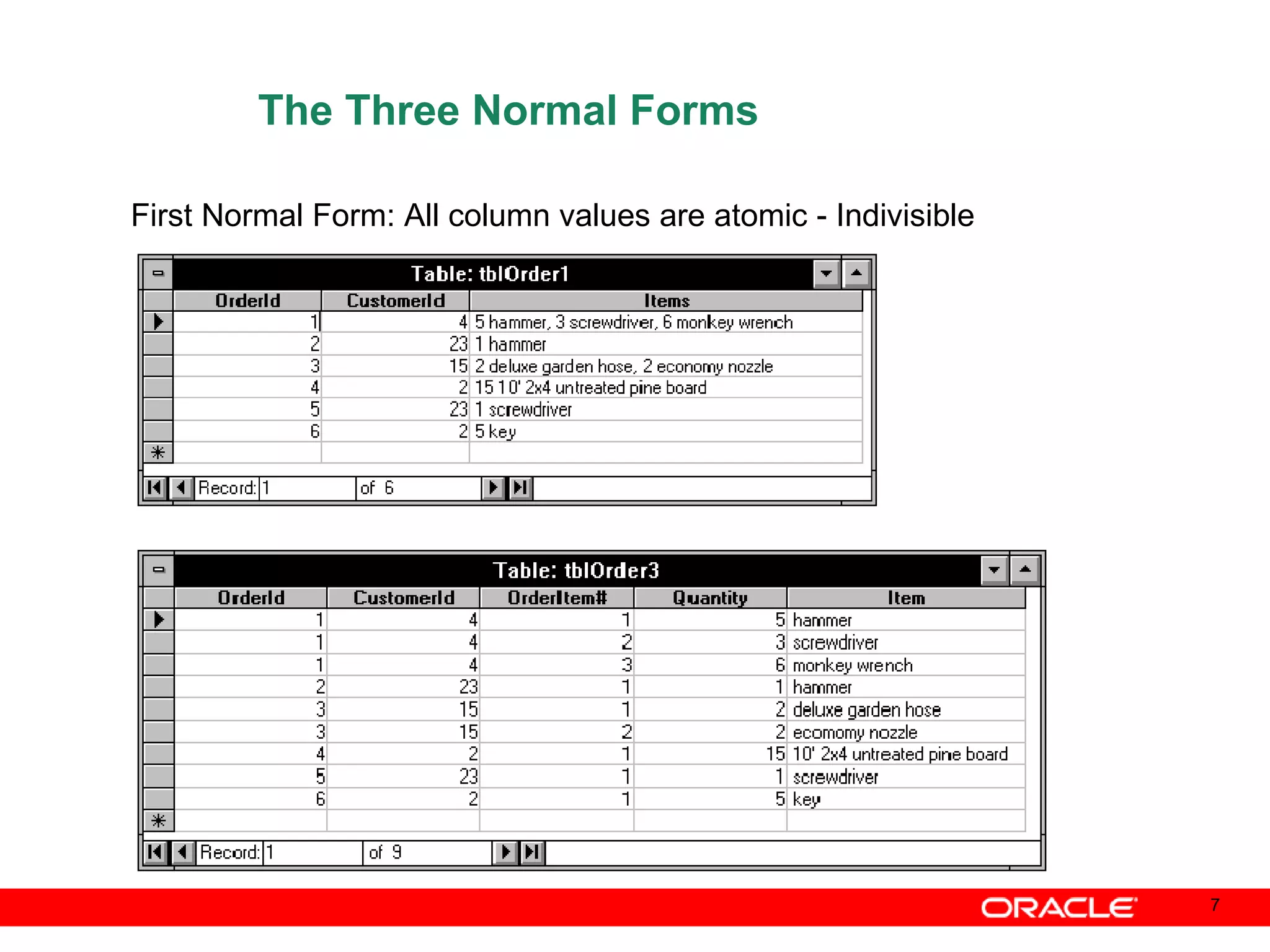
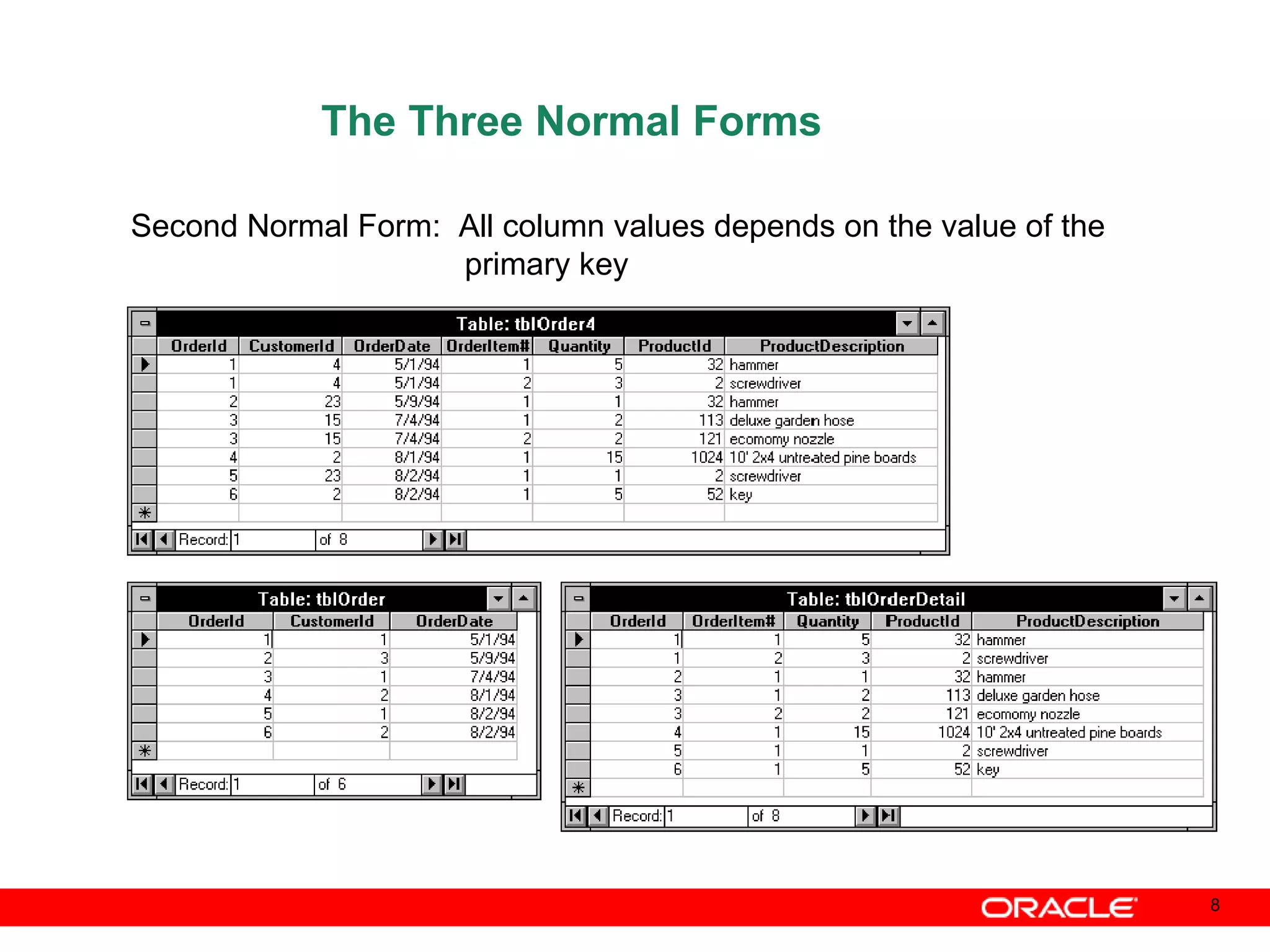
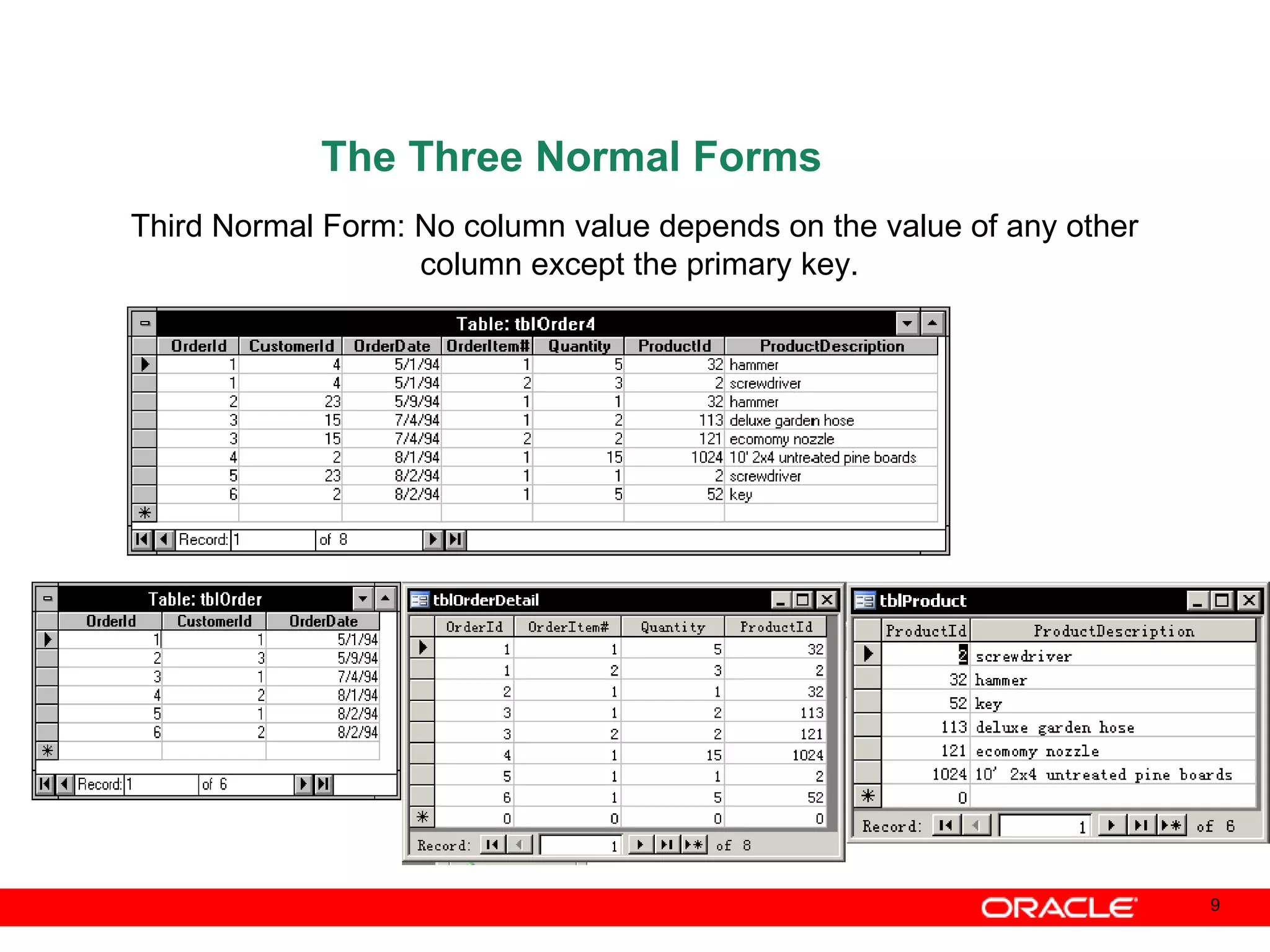
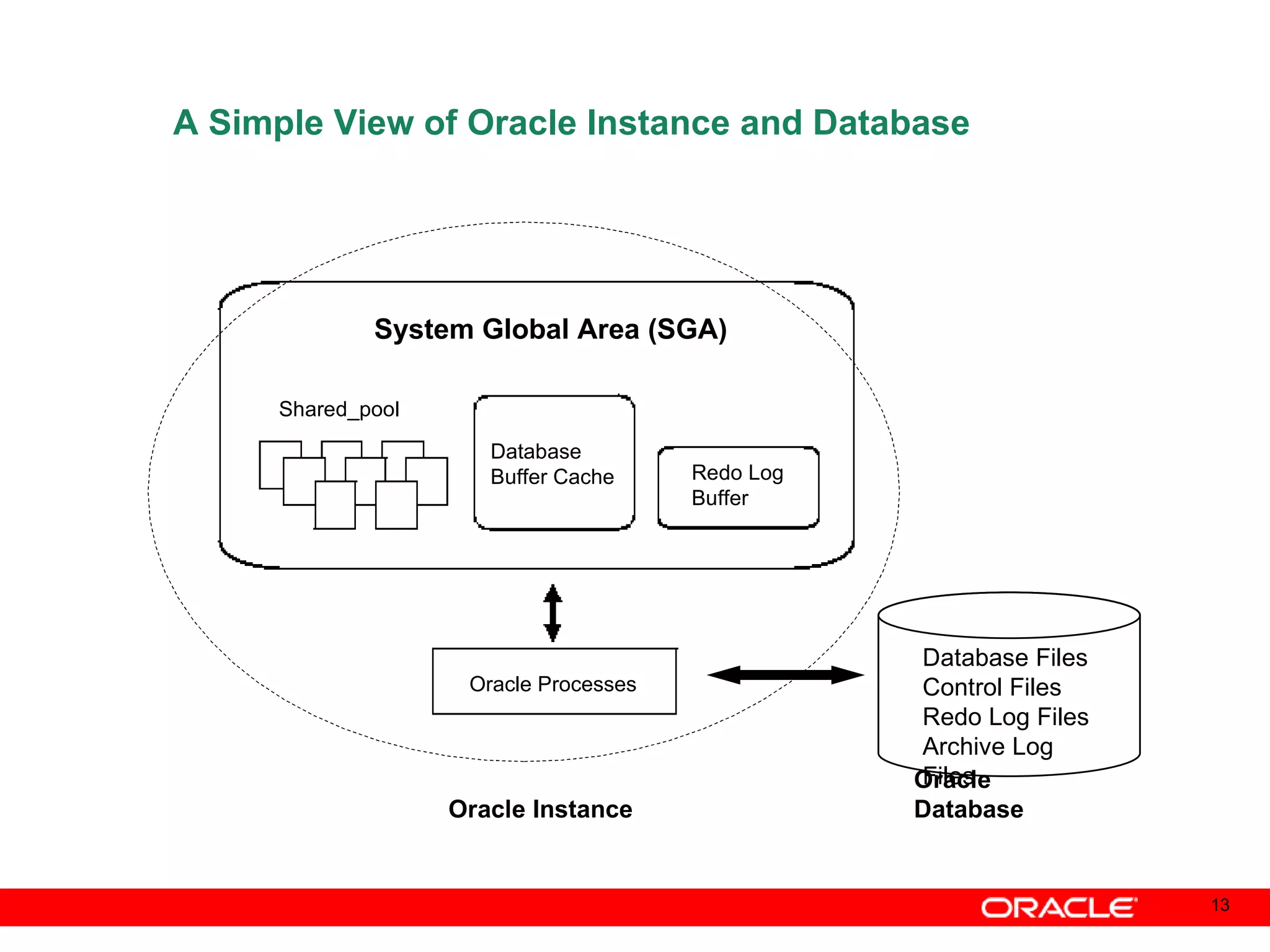
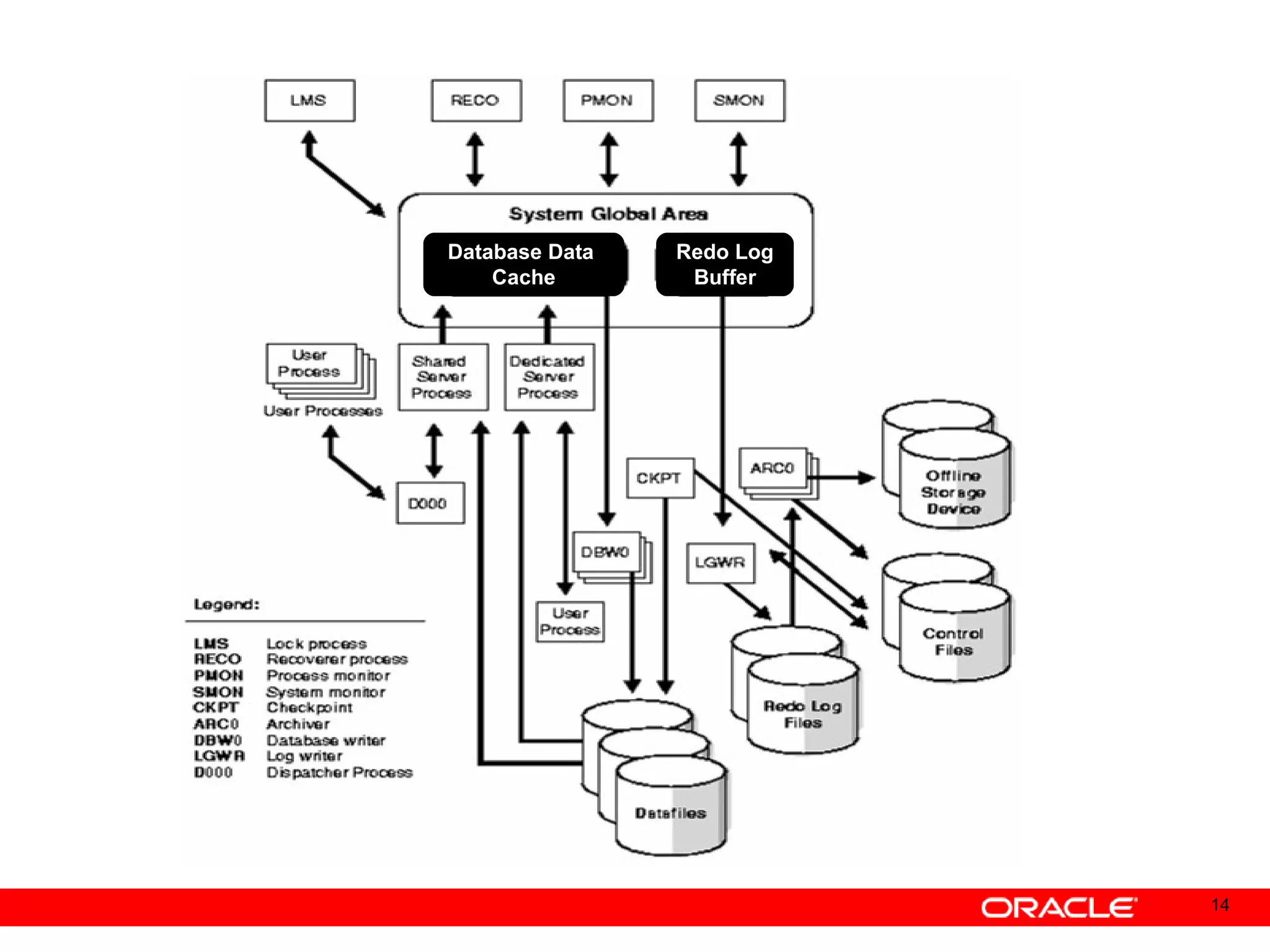
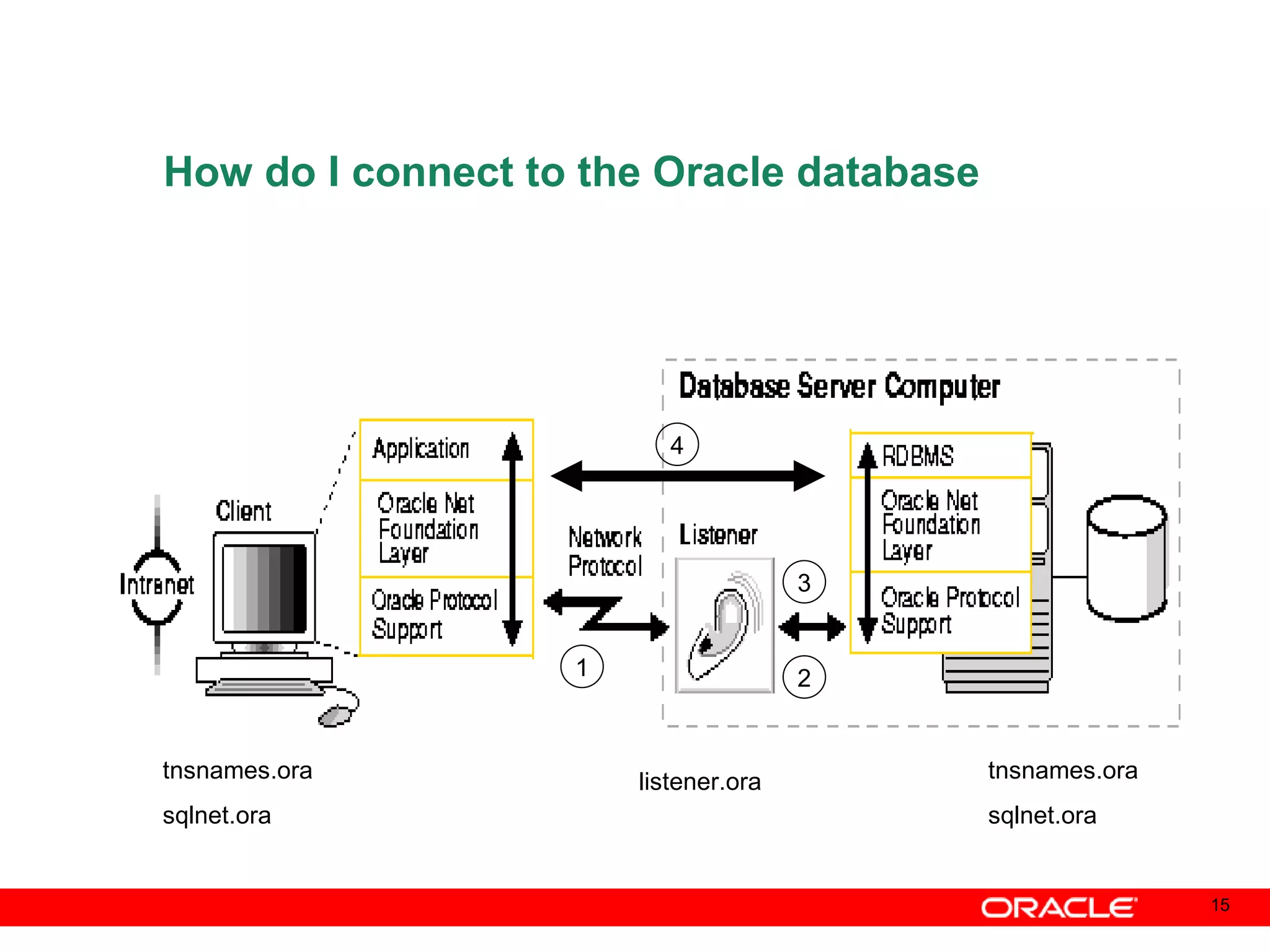
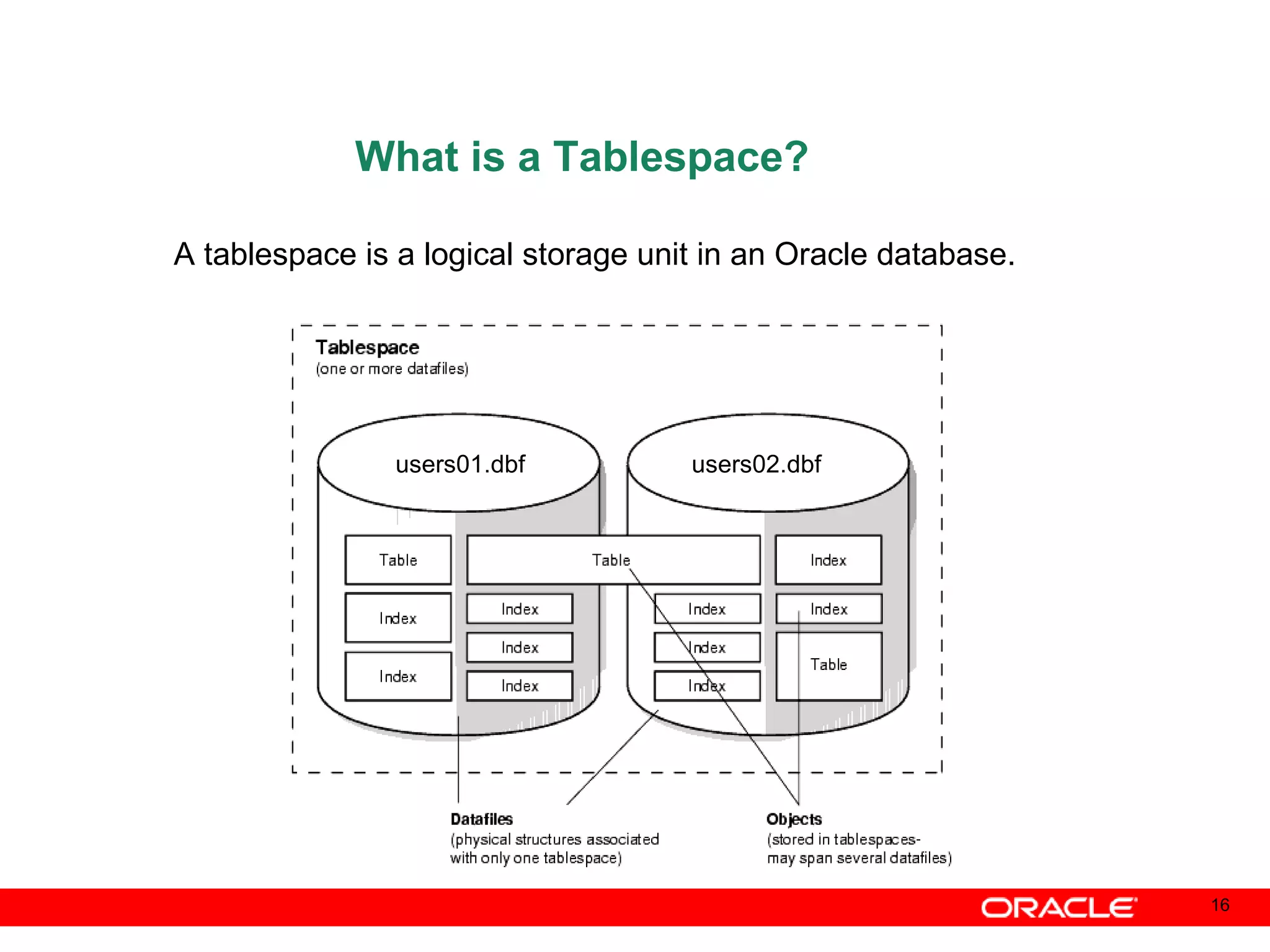
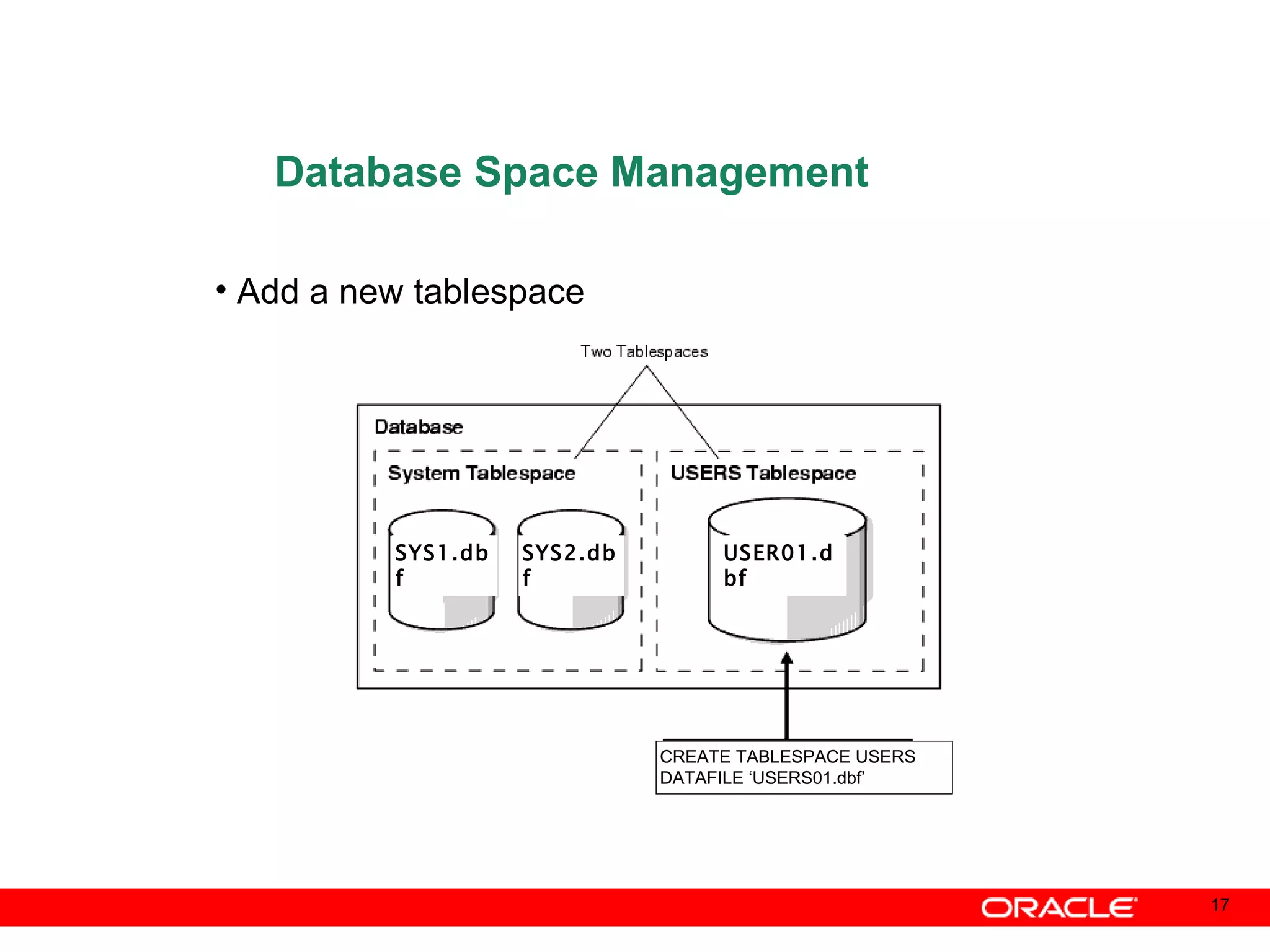
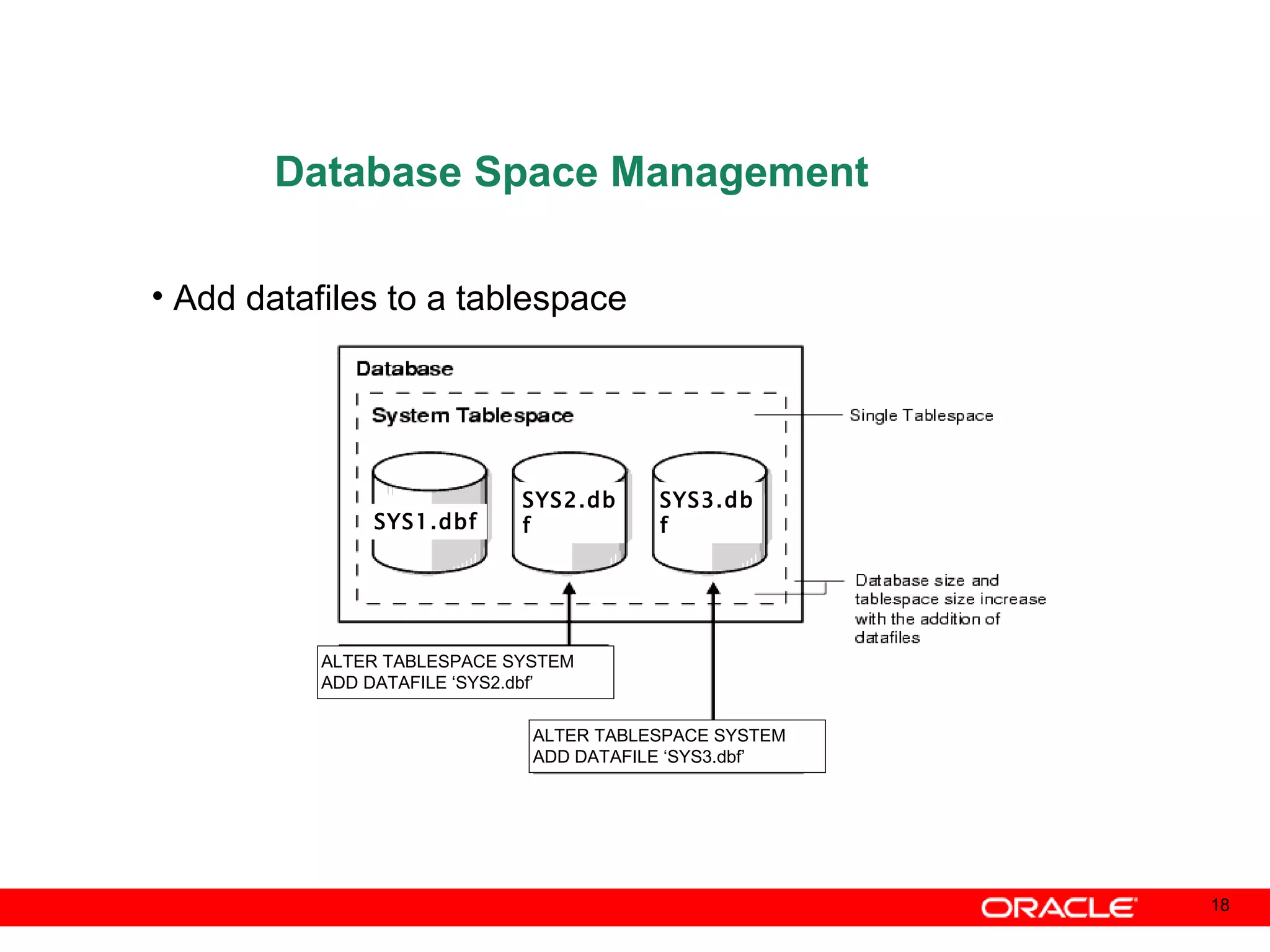
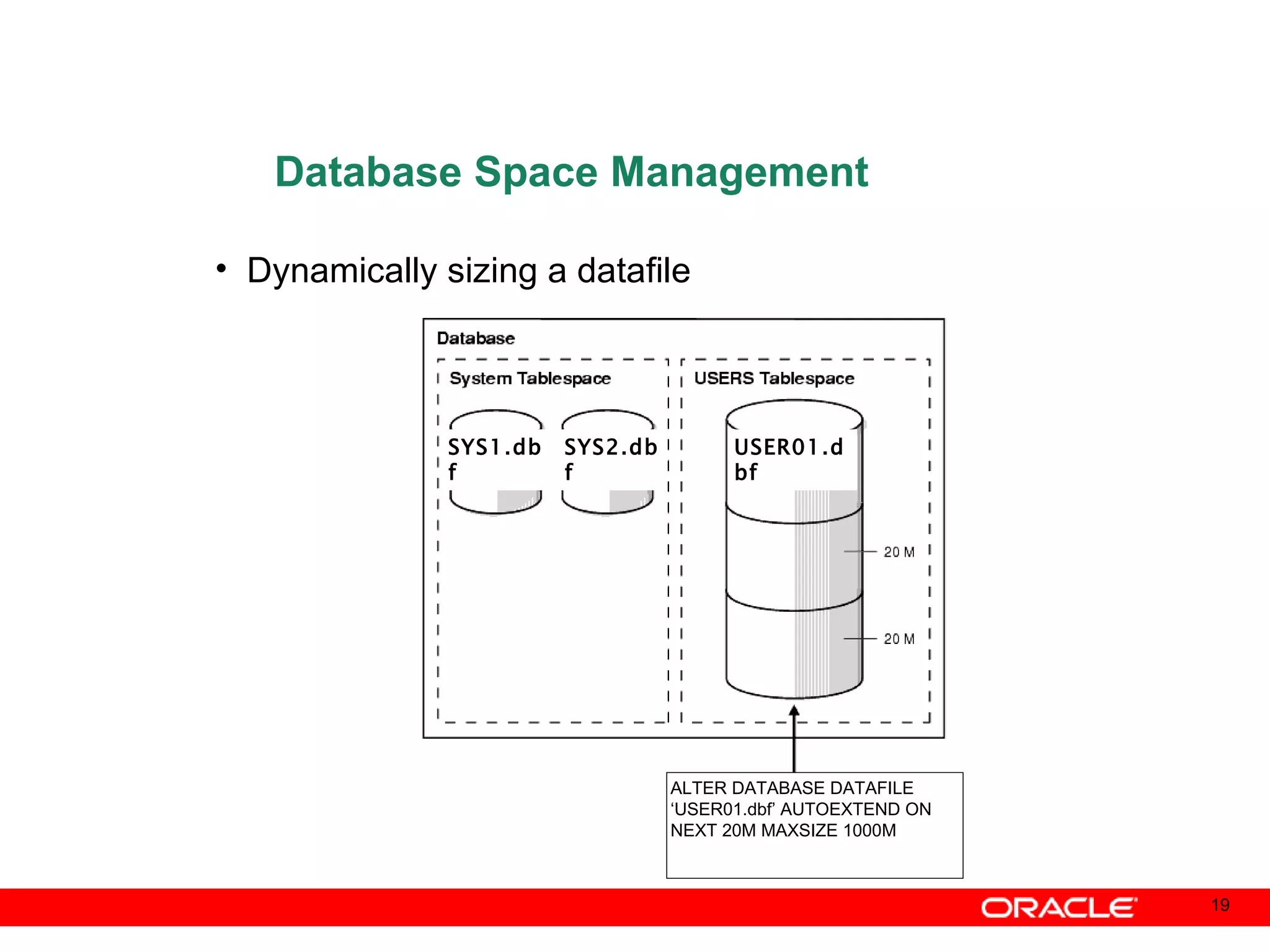
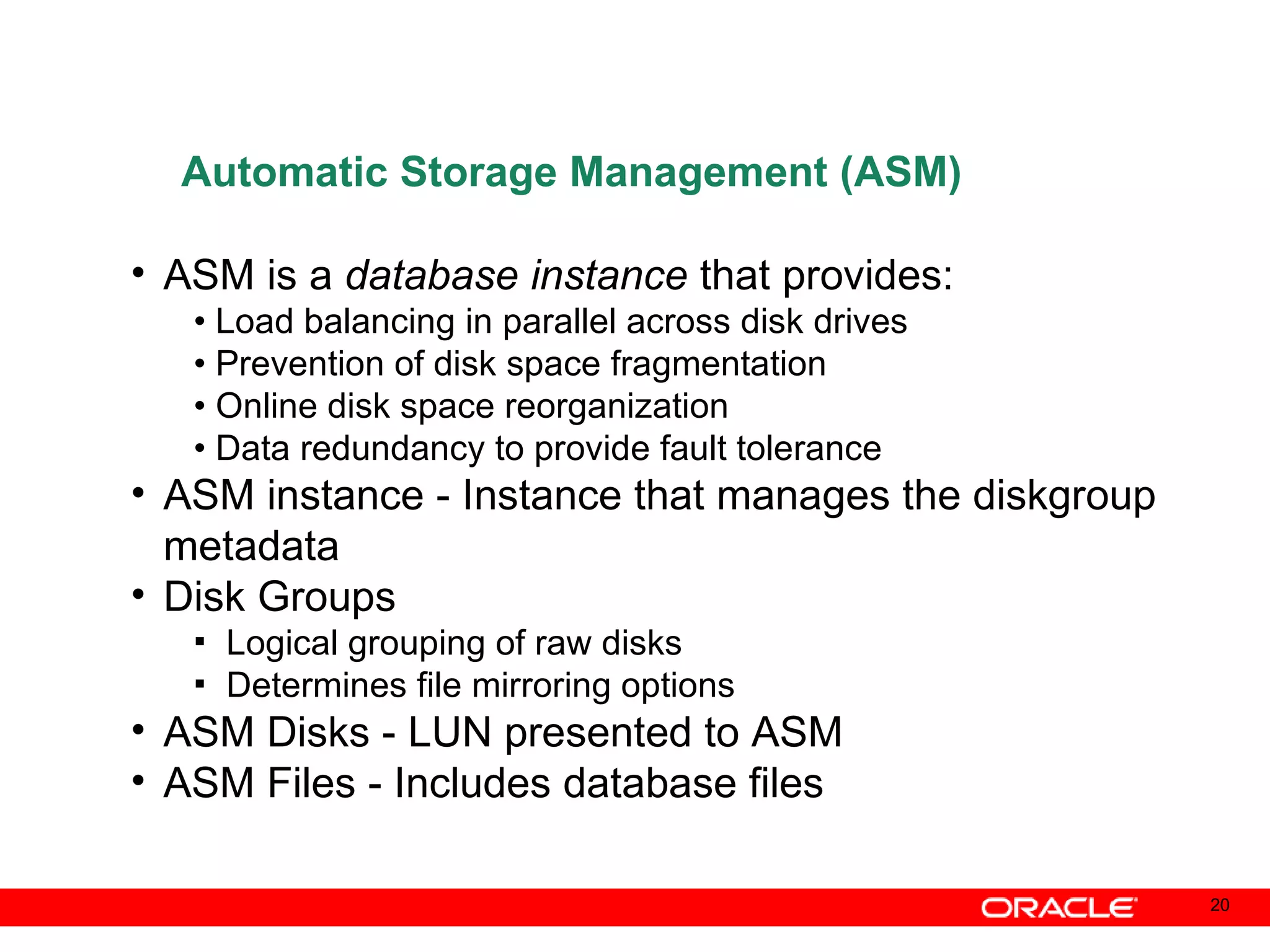
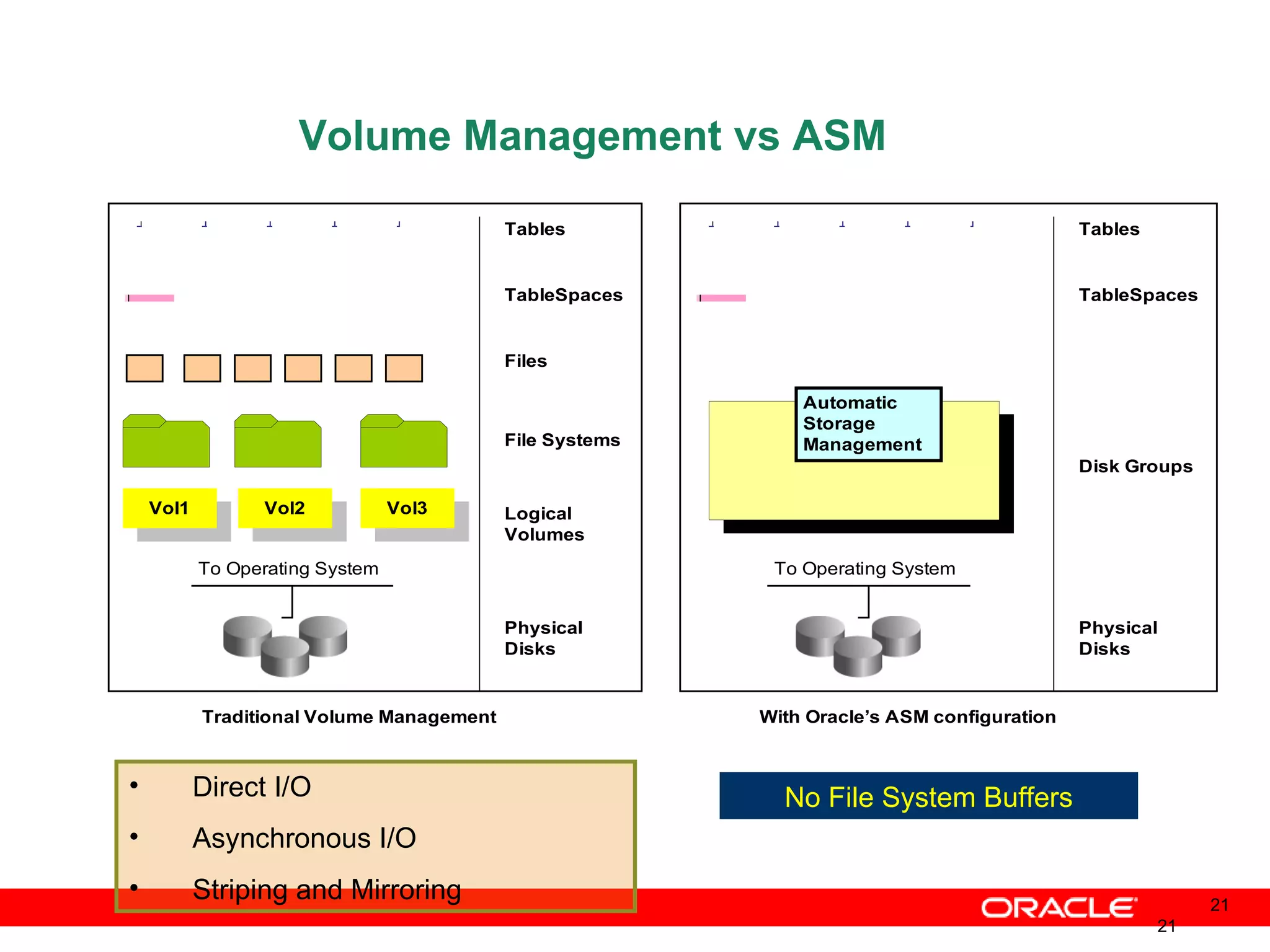
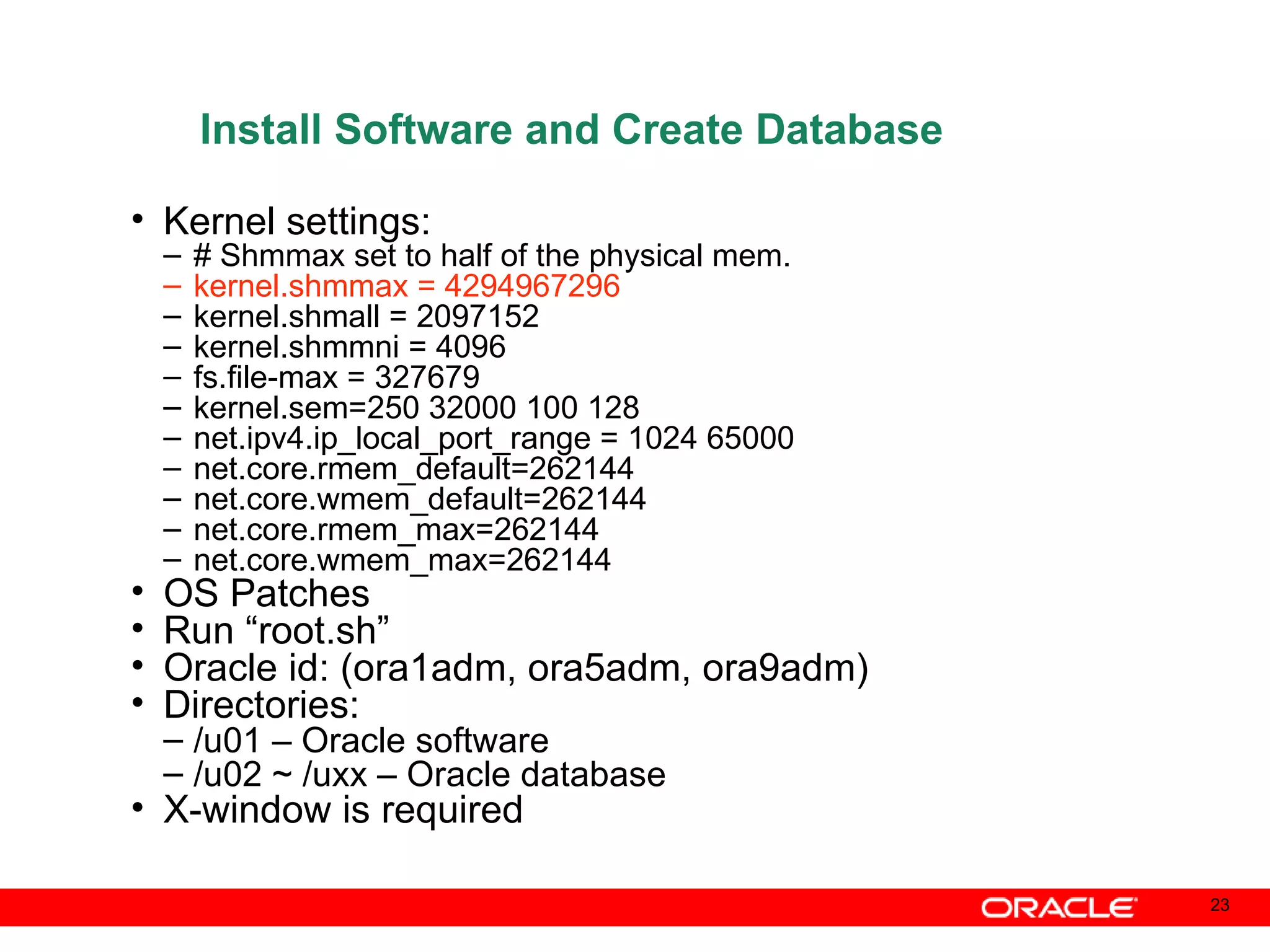
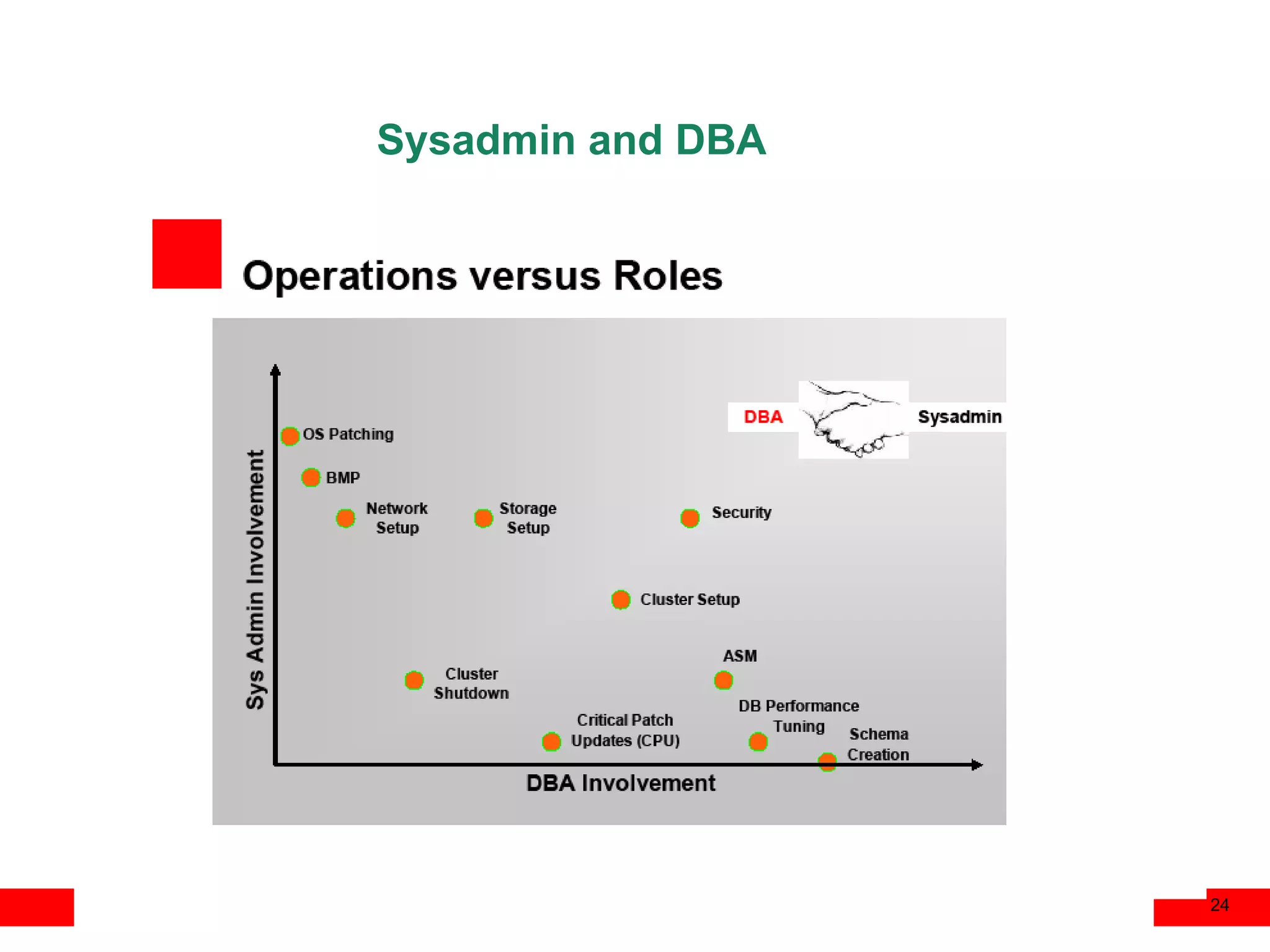
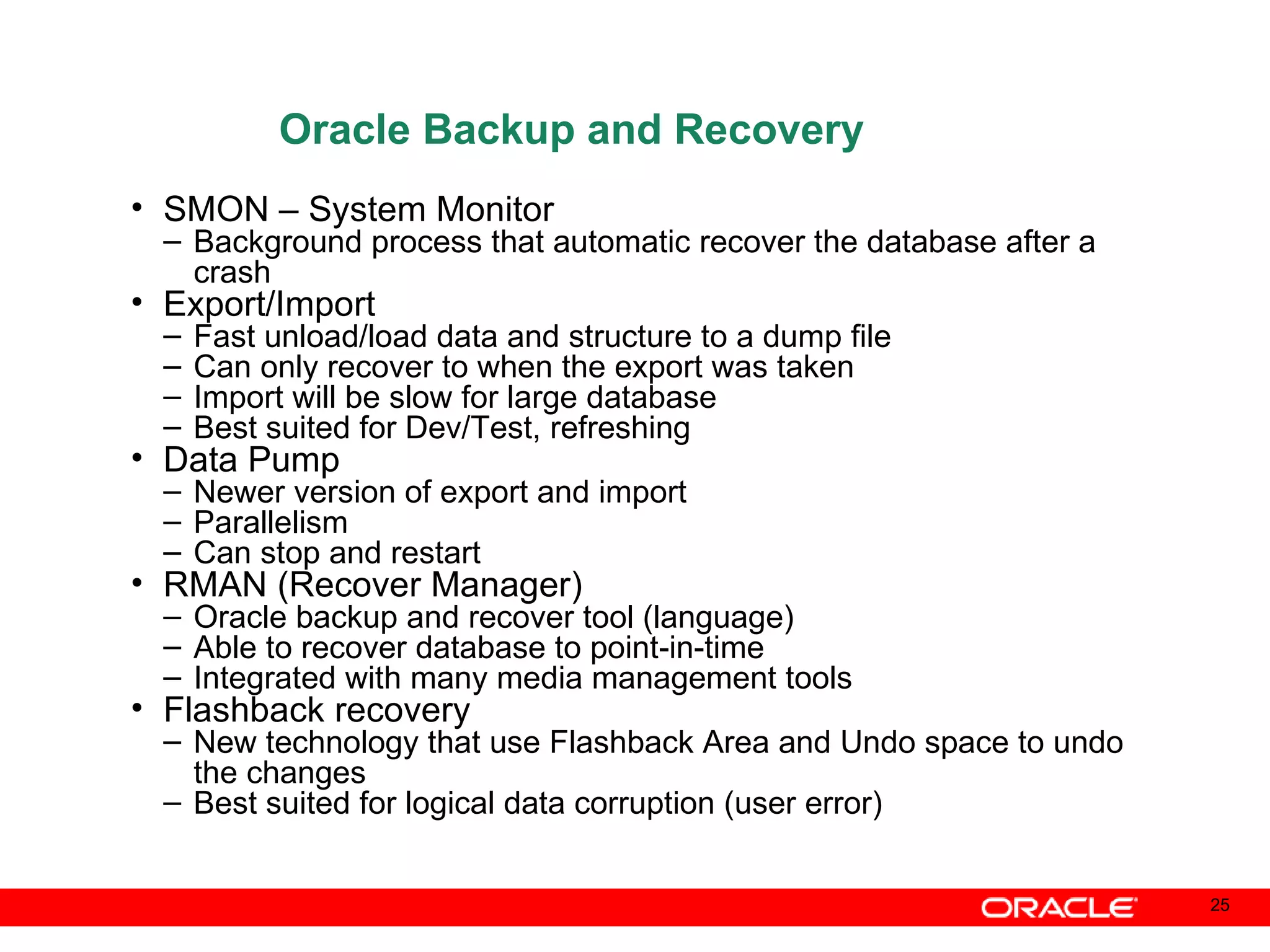
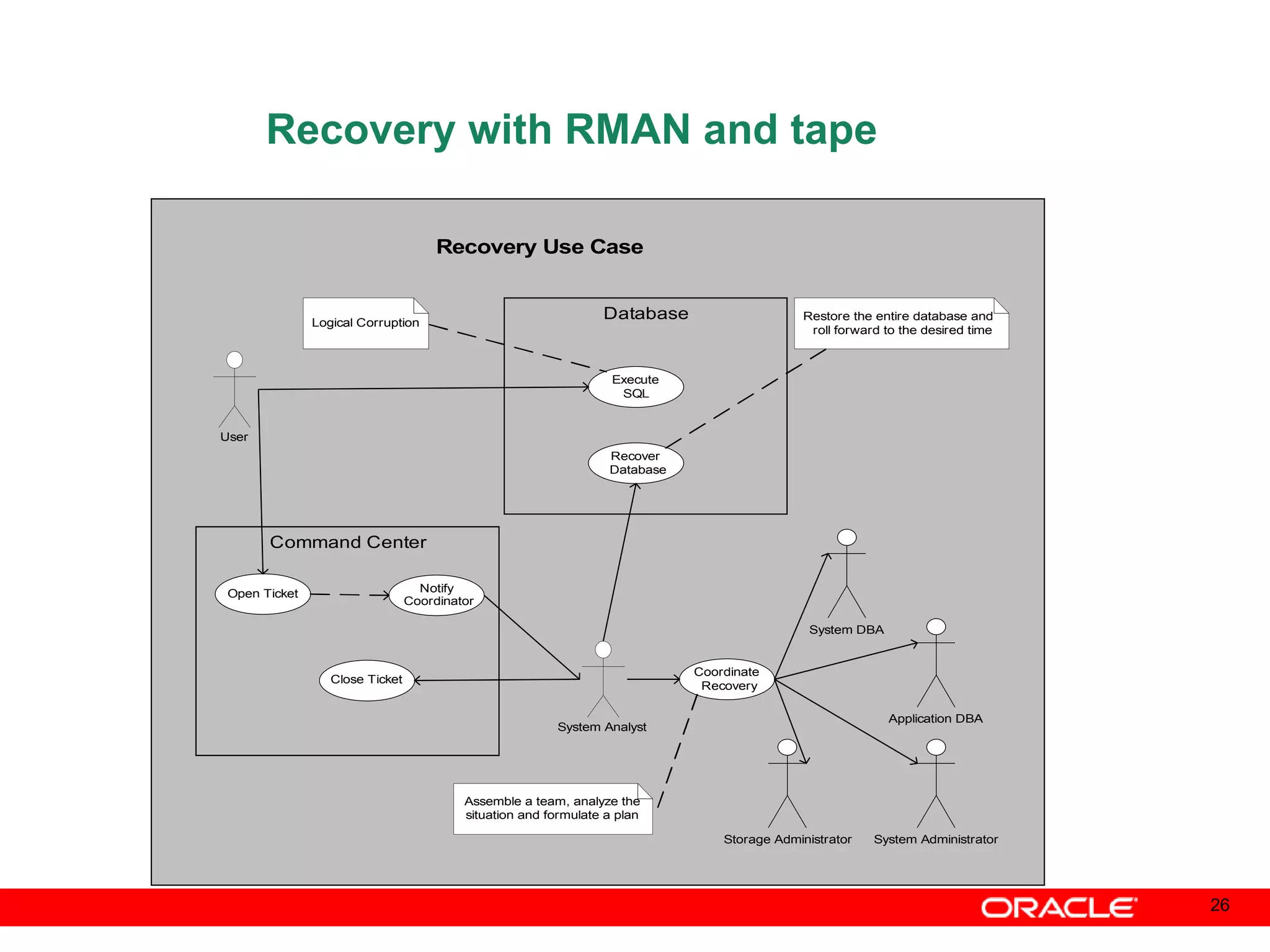
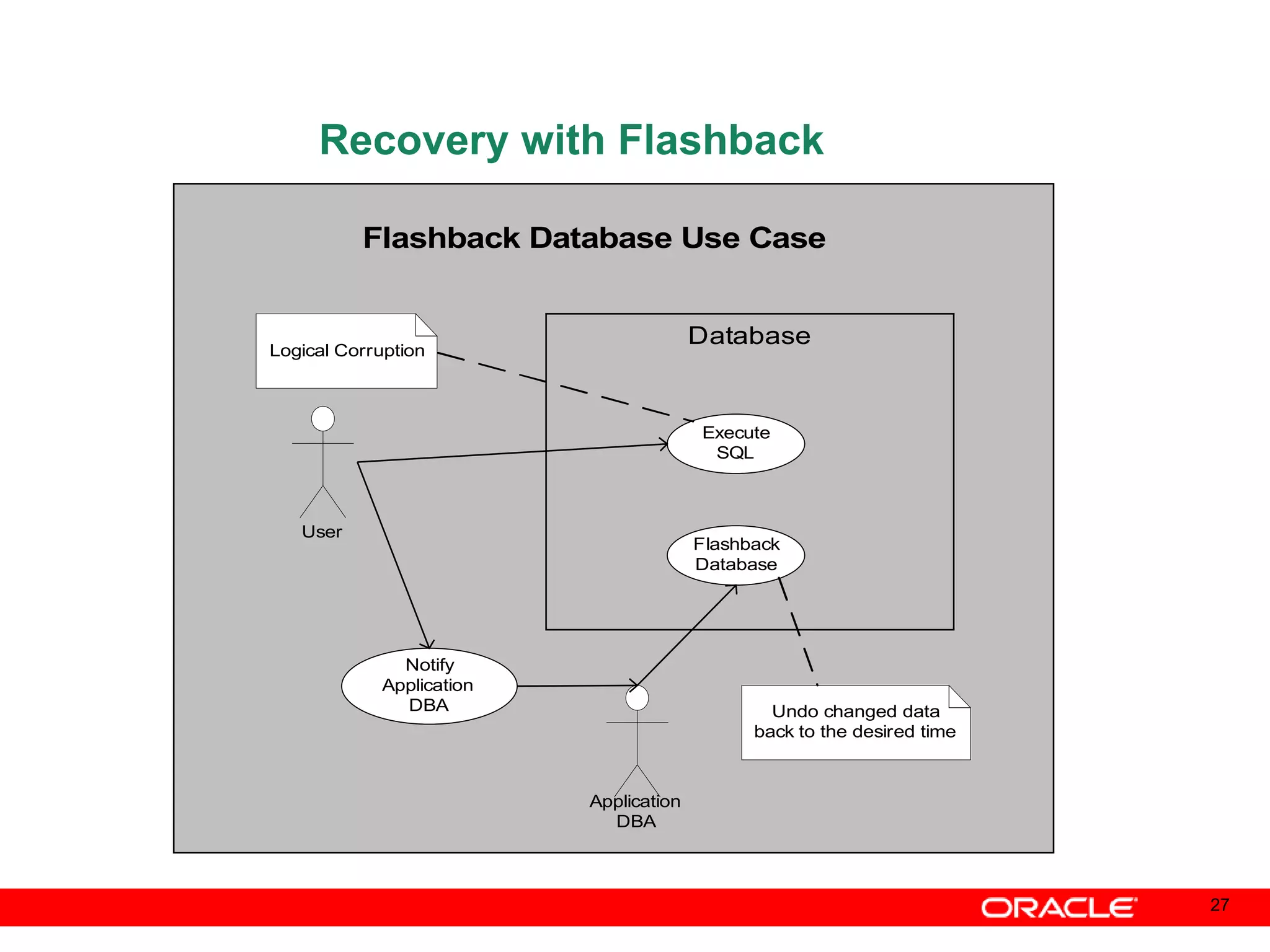
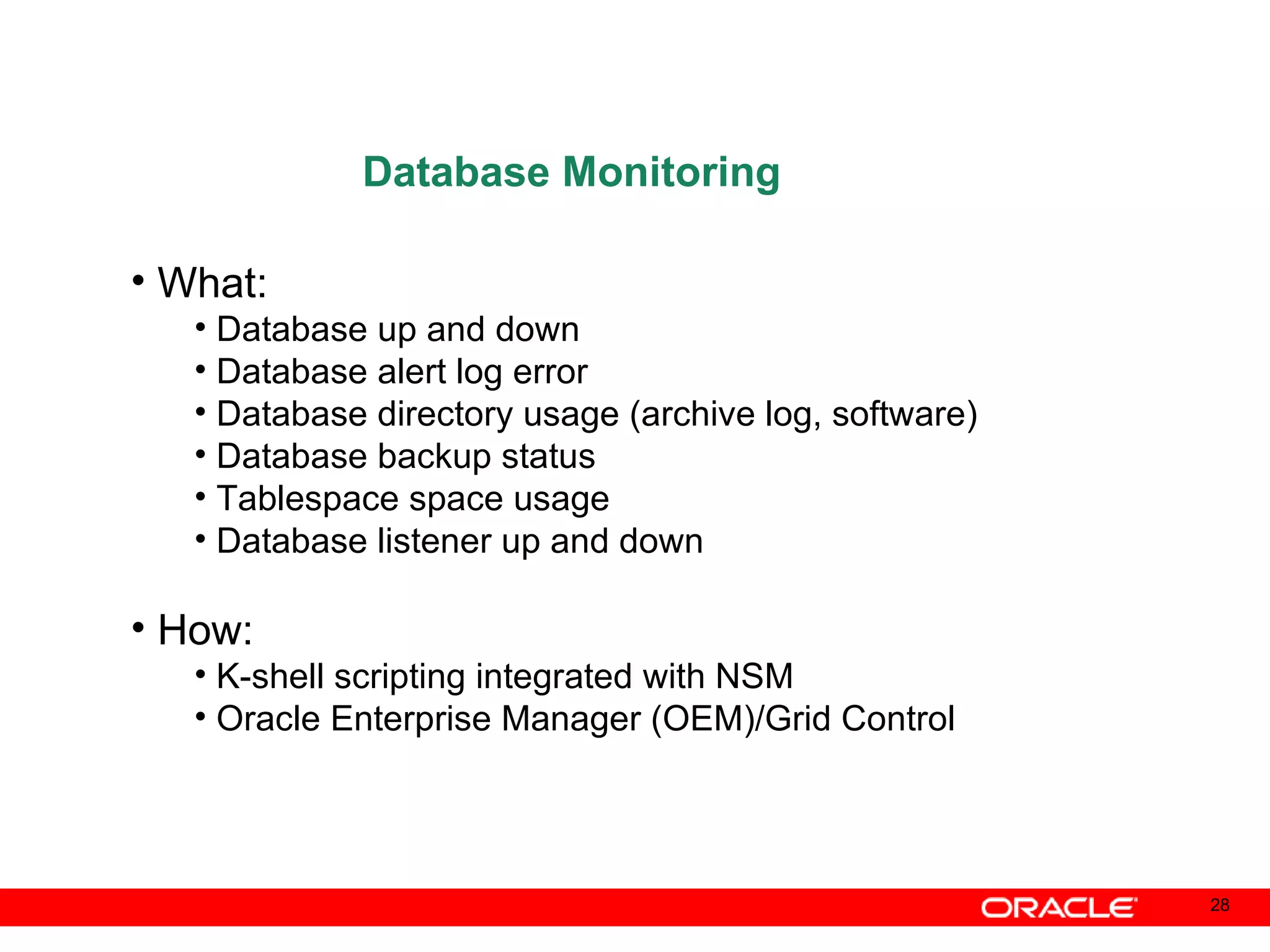
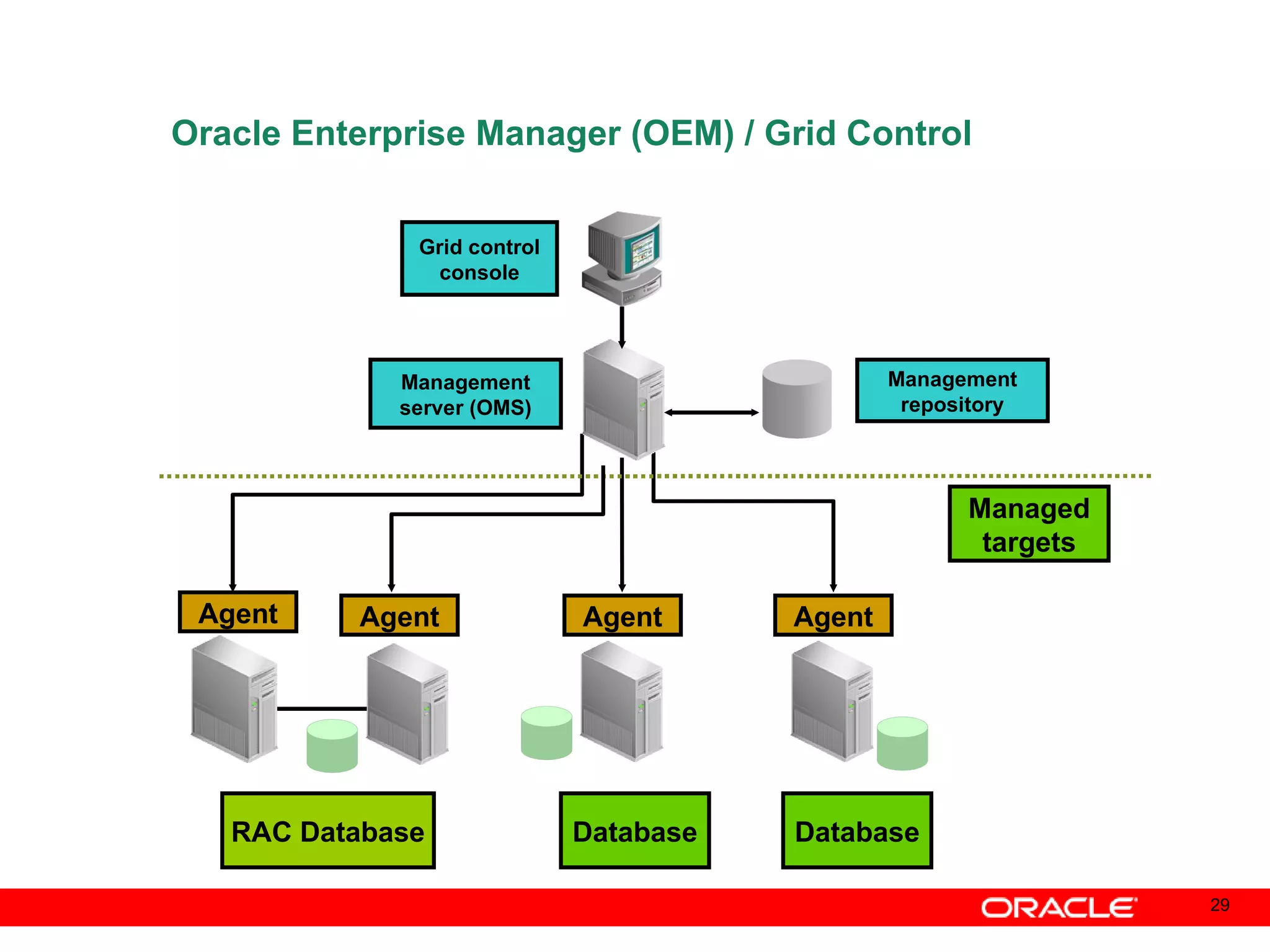
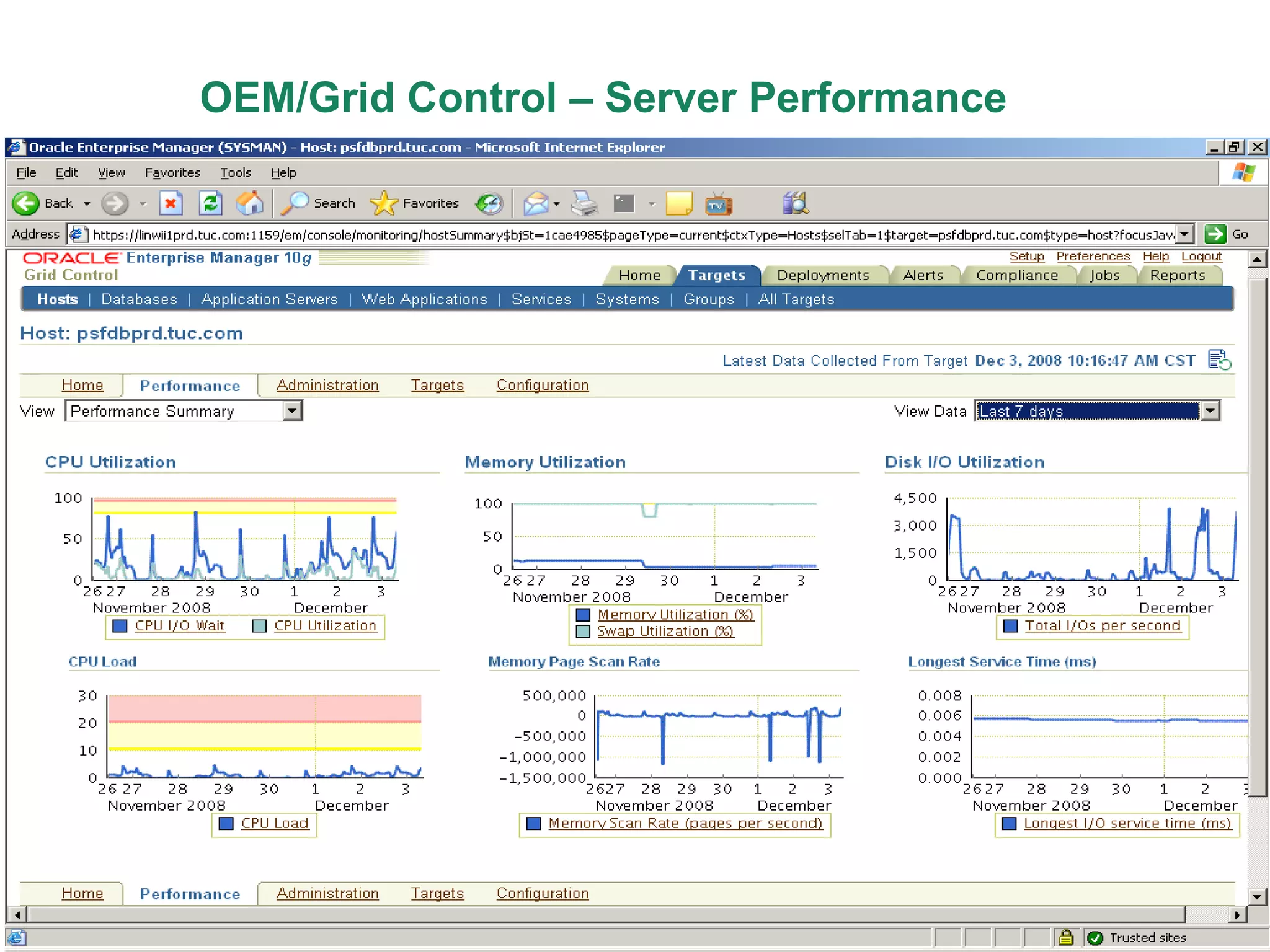
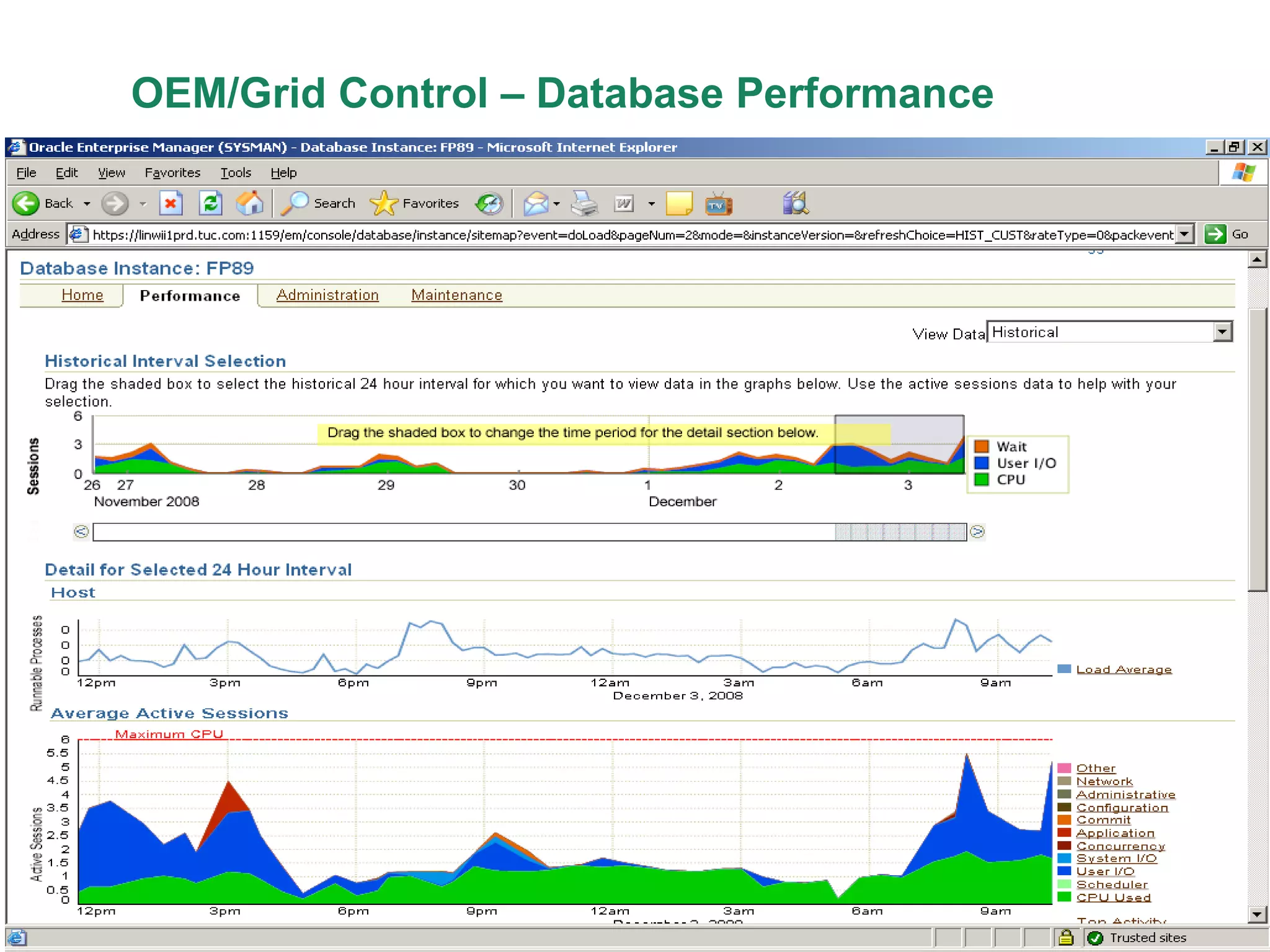
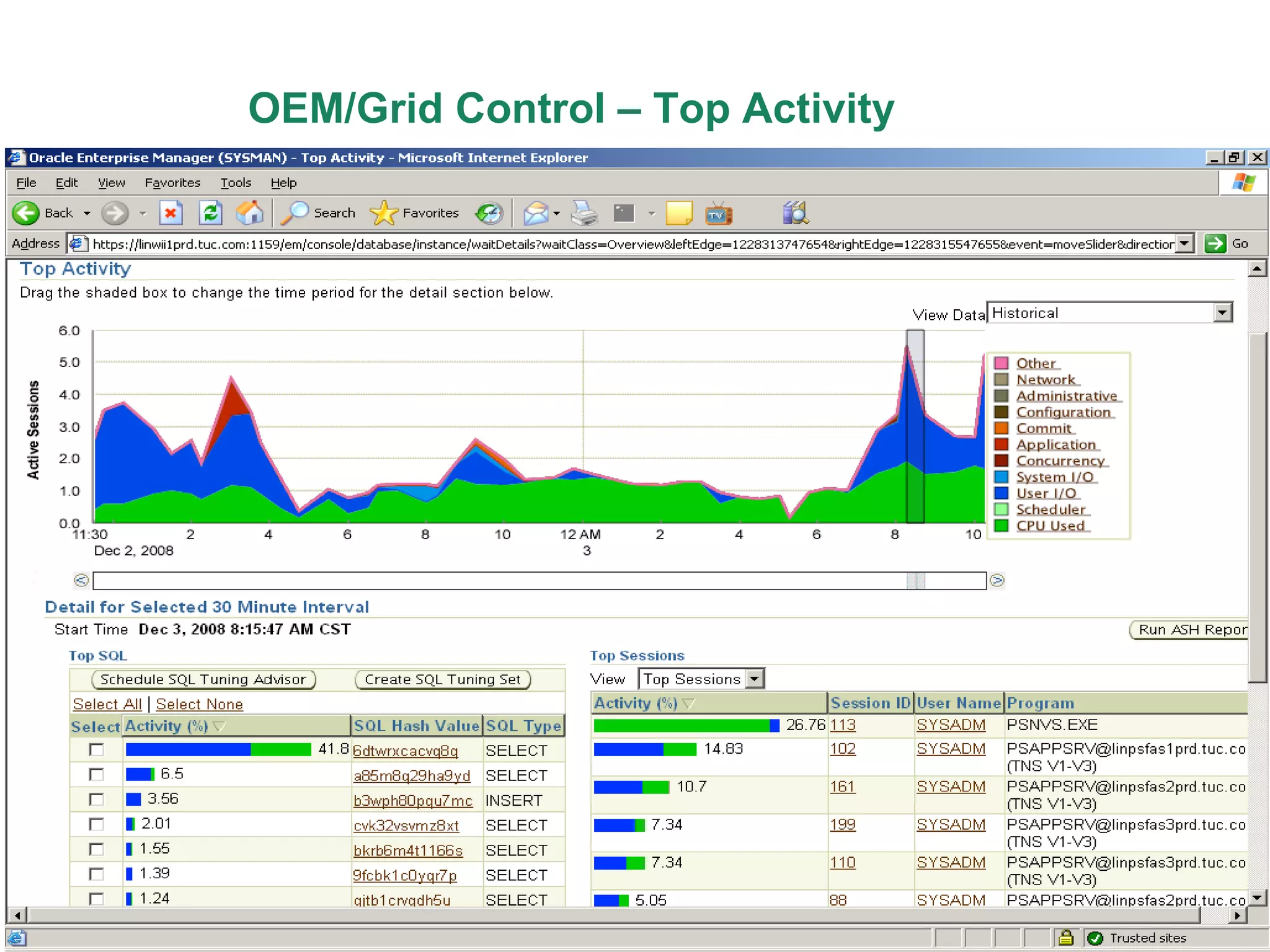
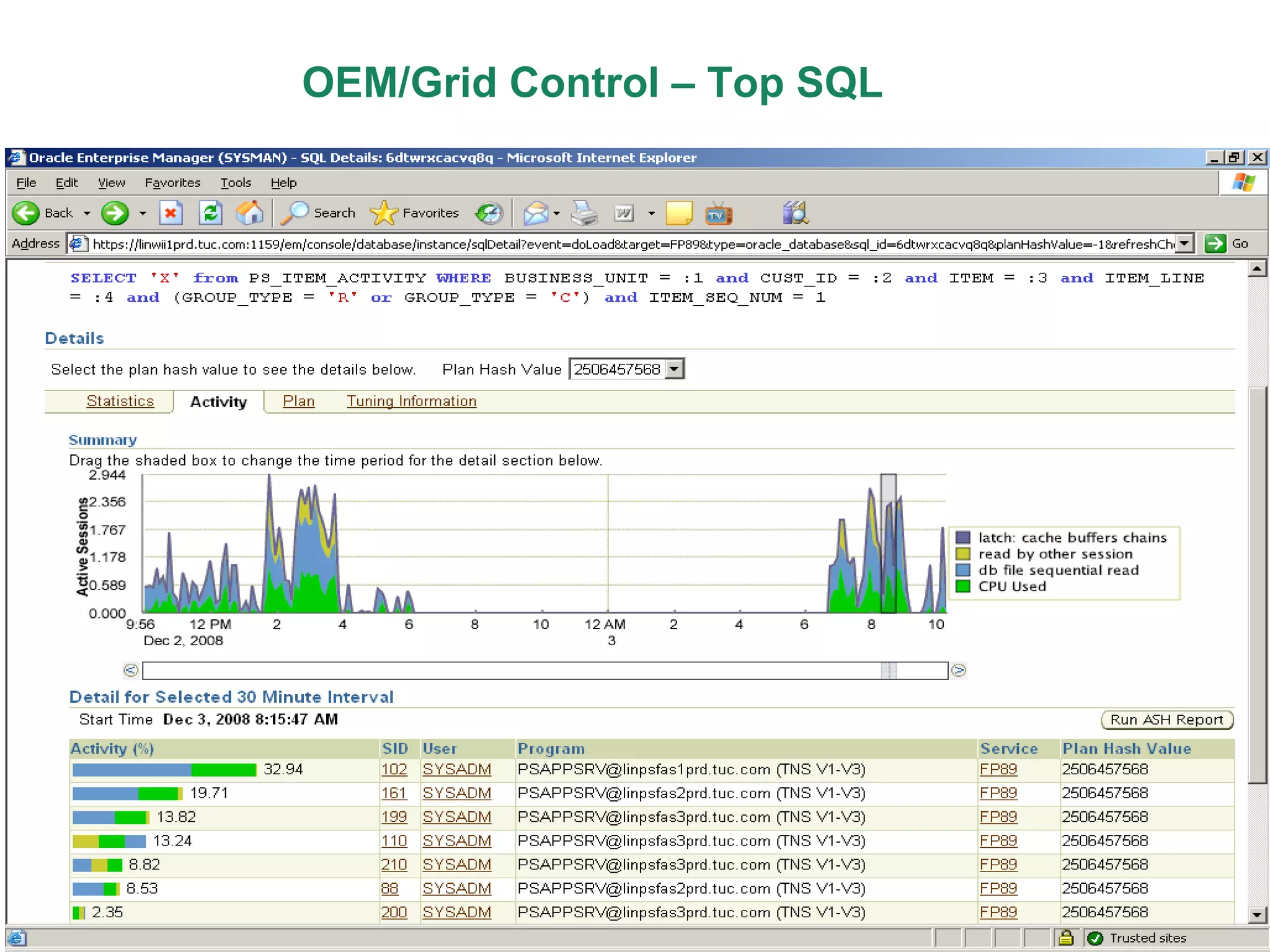
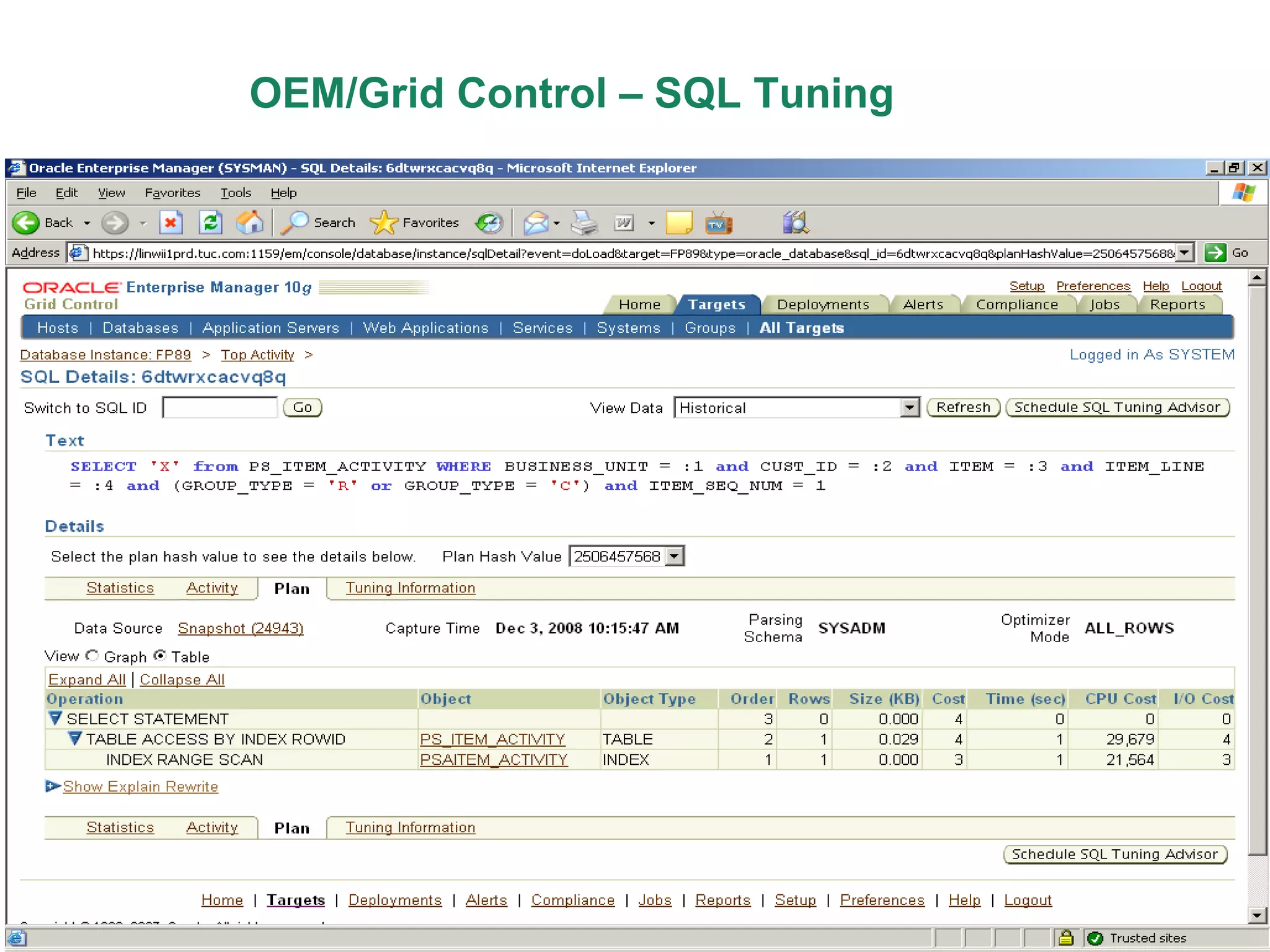
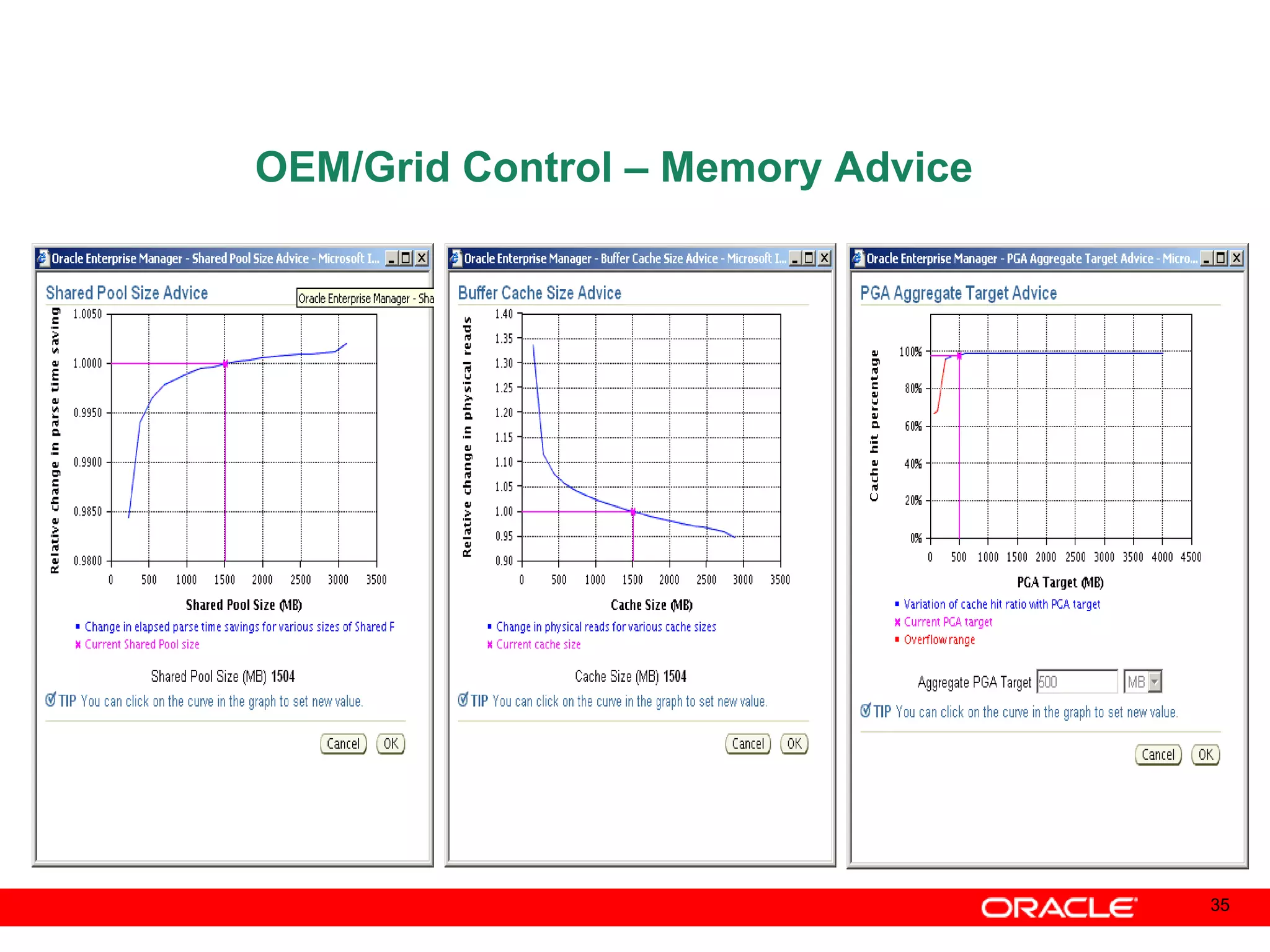
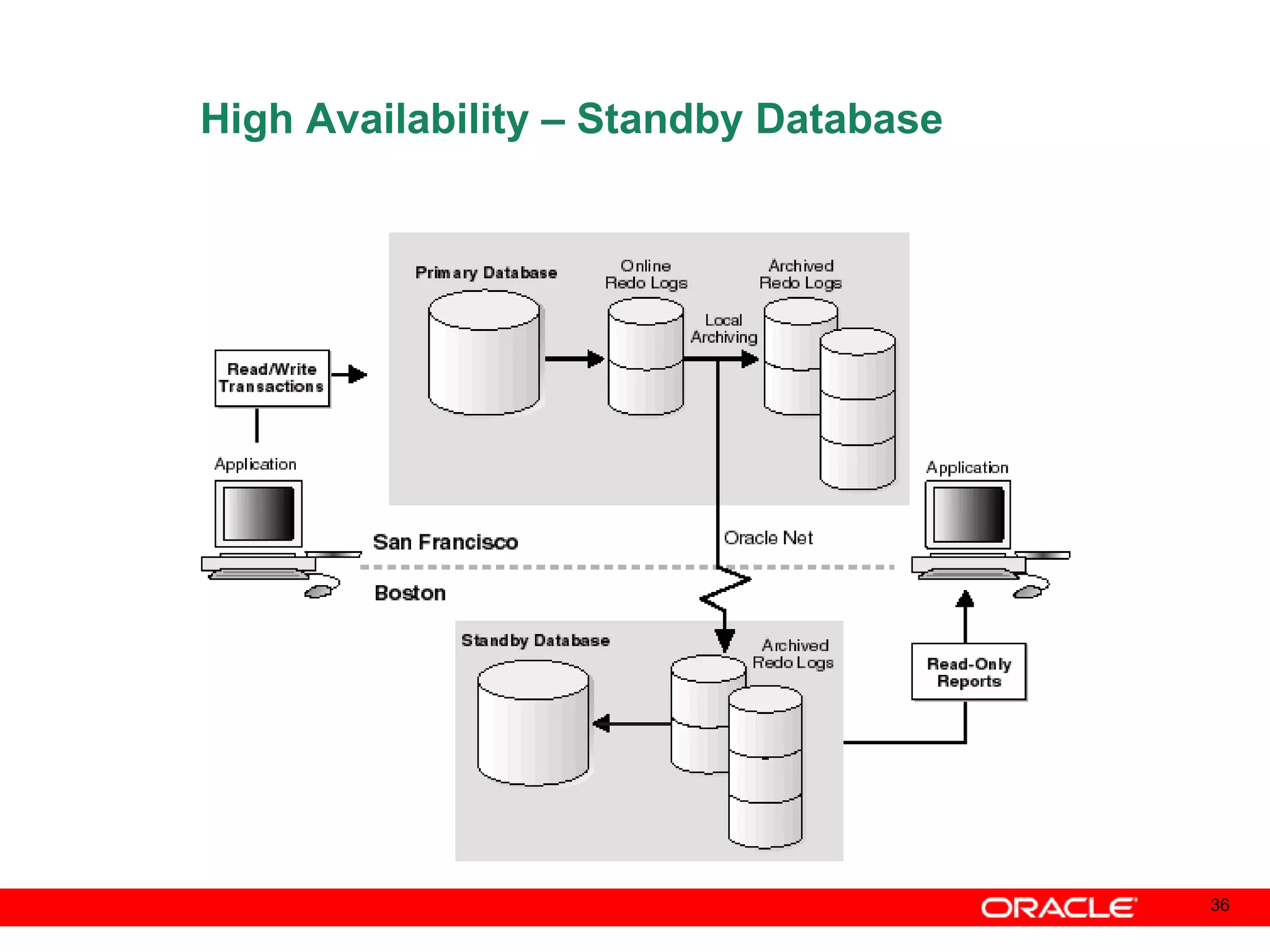
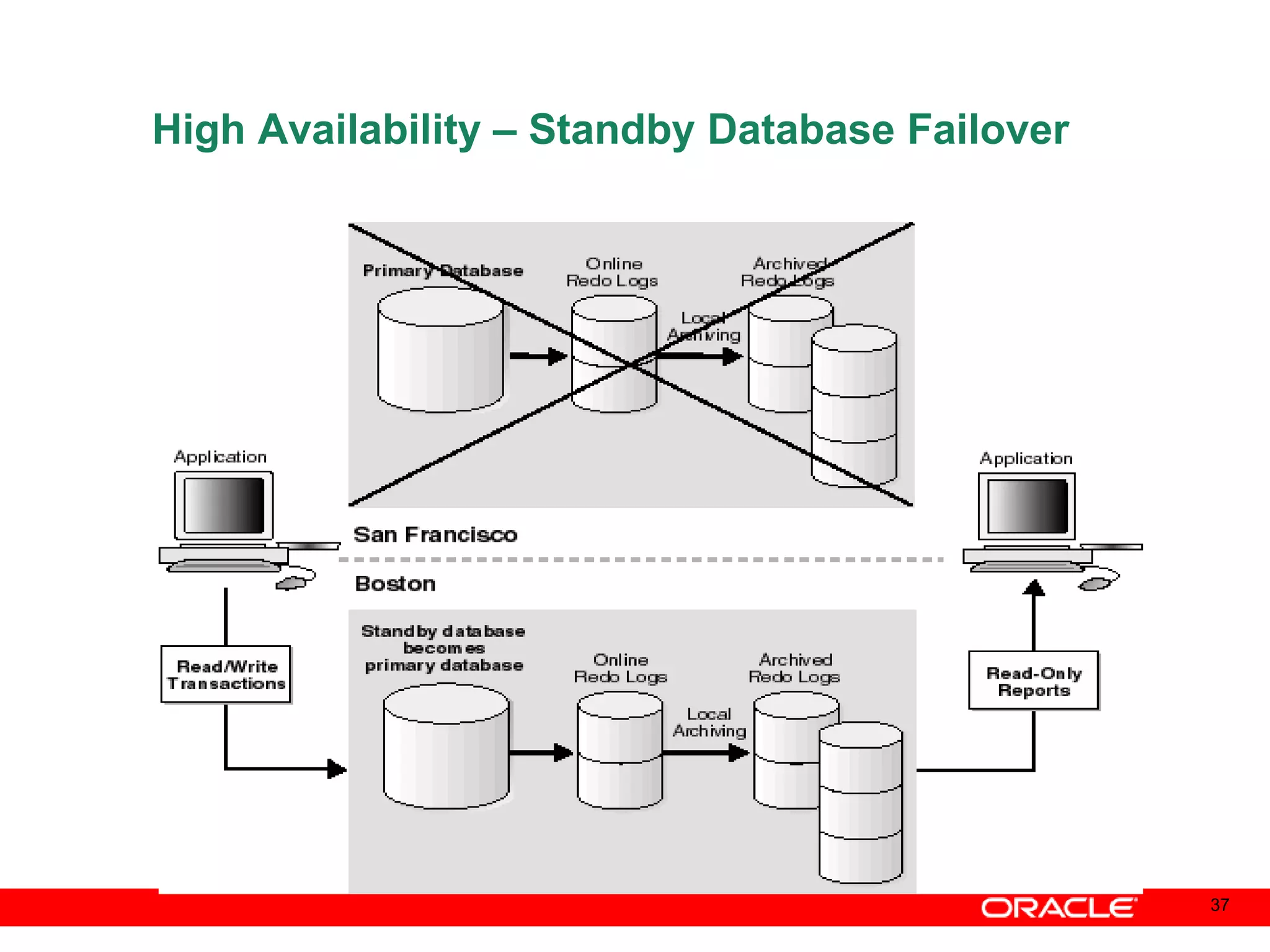
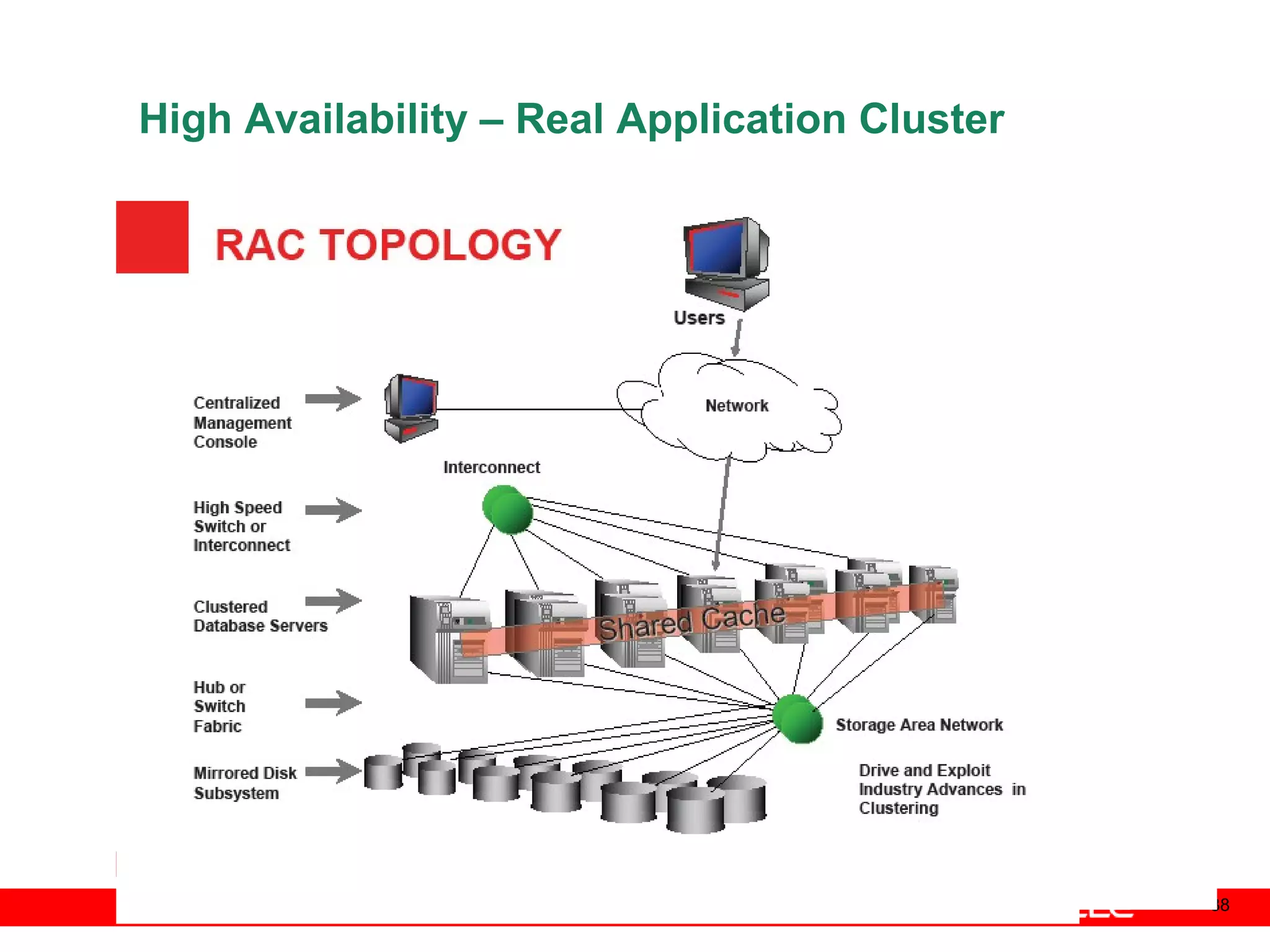
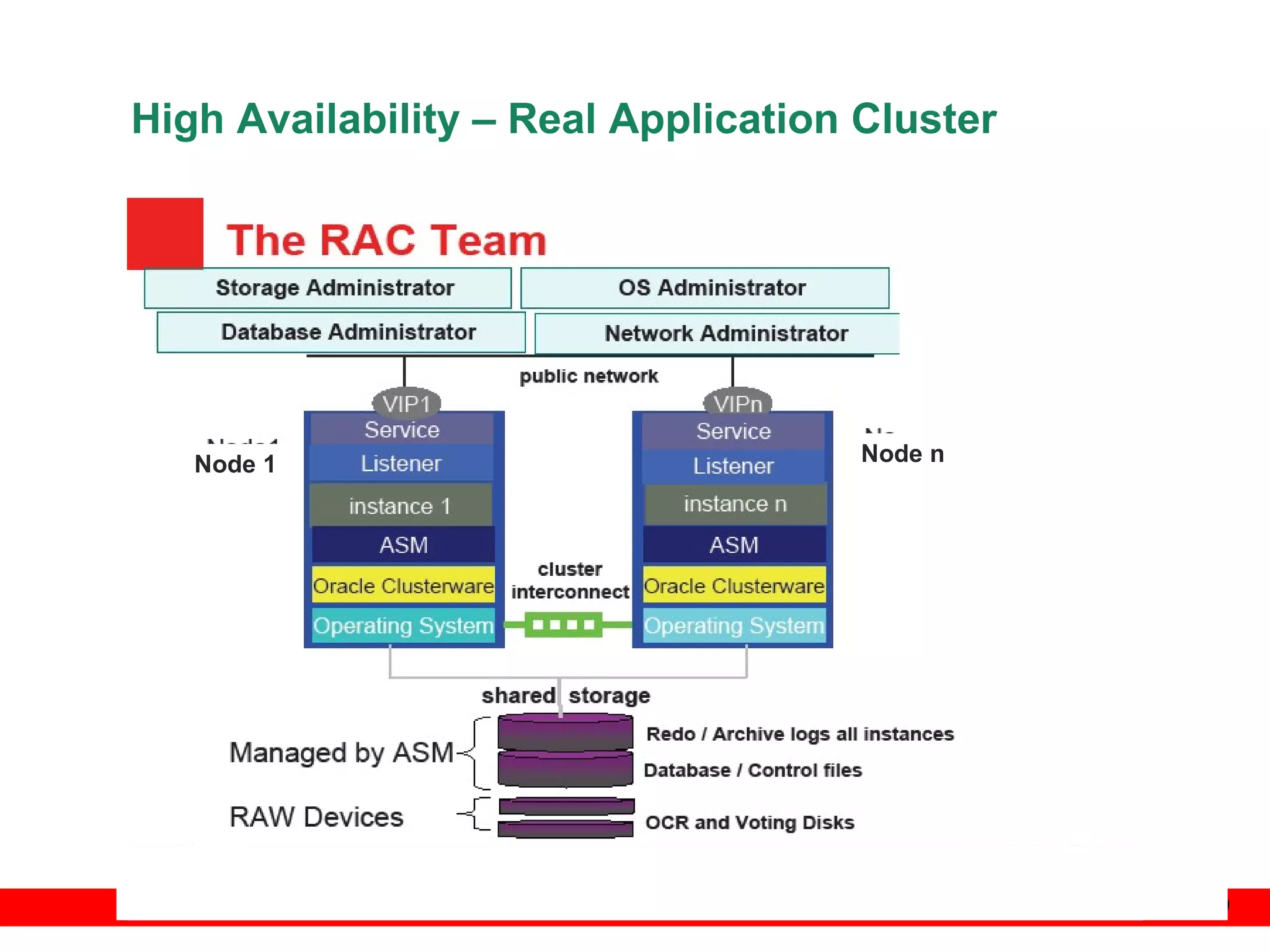
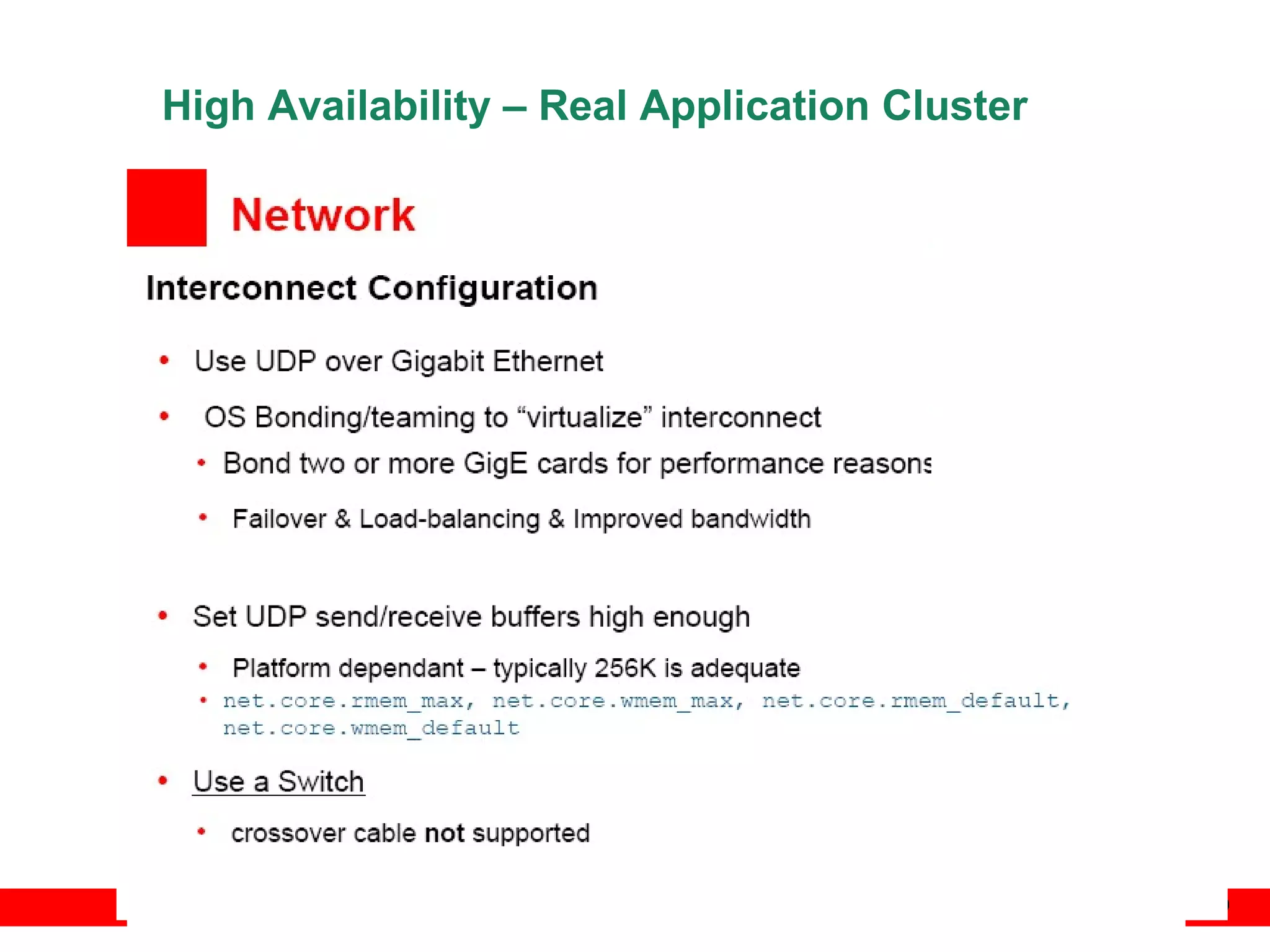
An Oracle database instance consists of background processes that control one or more databases. A schema is a set of database objects owned by a user that apply to a specific application. Tables store data in rows and columns, and indexes and constraints help maintain data integrity and improve query performance. Database administrators perform tasks like installing and upgrading databases, managing storage, security, backups and high availability.