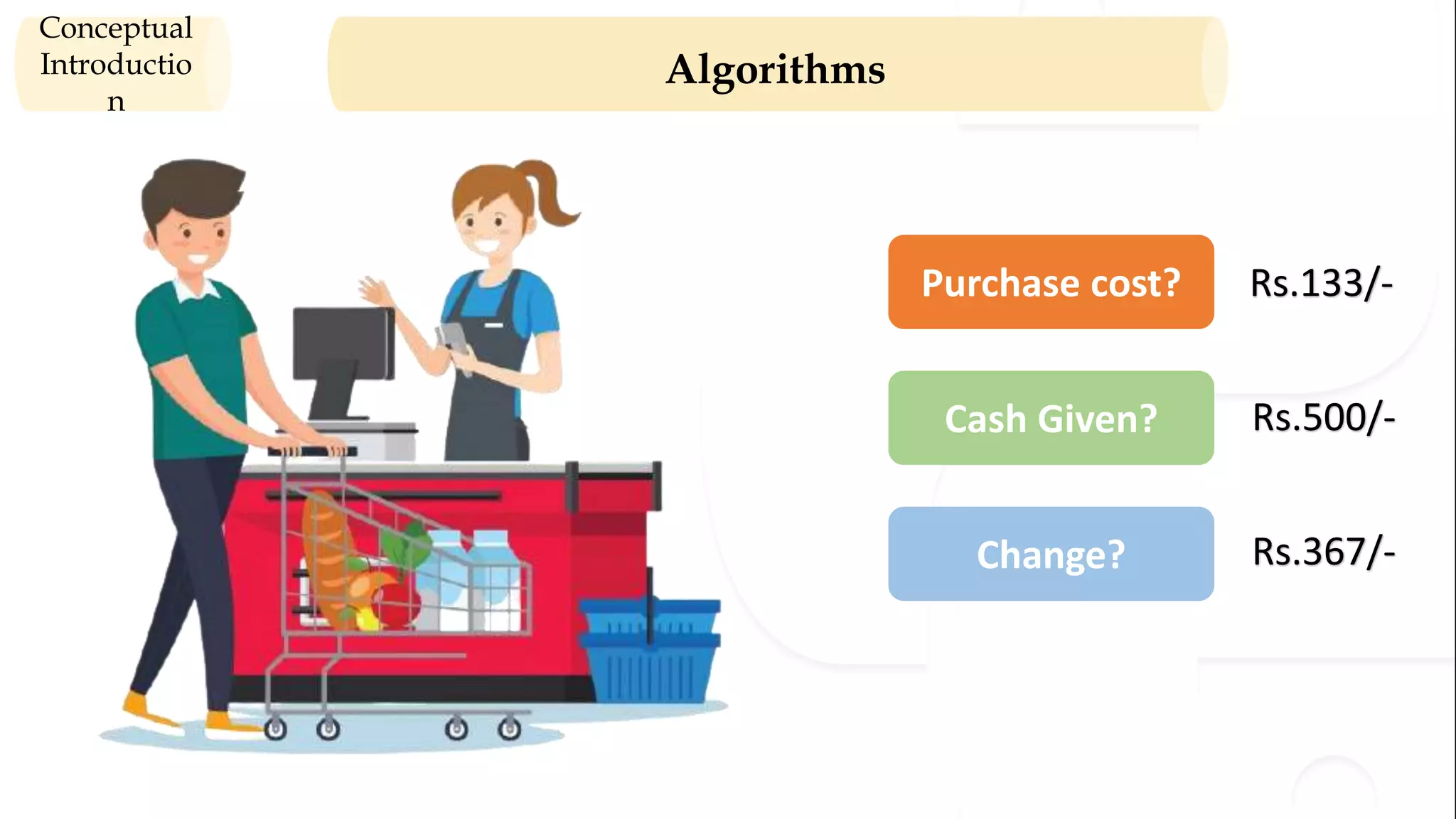
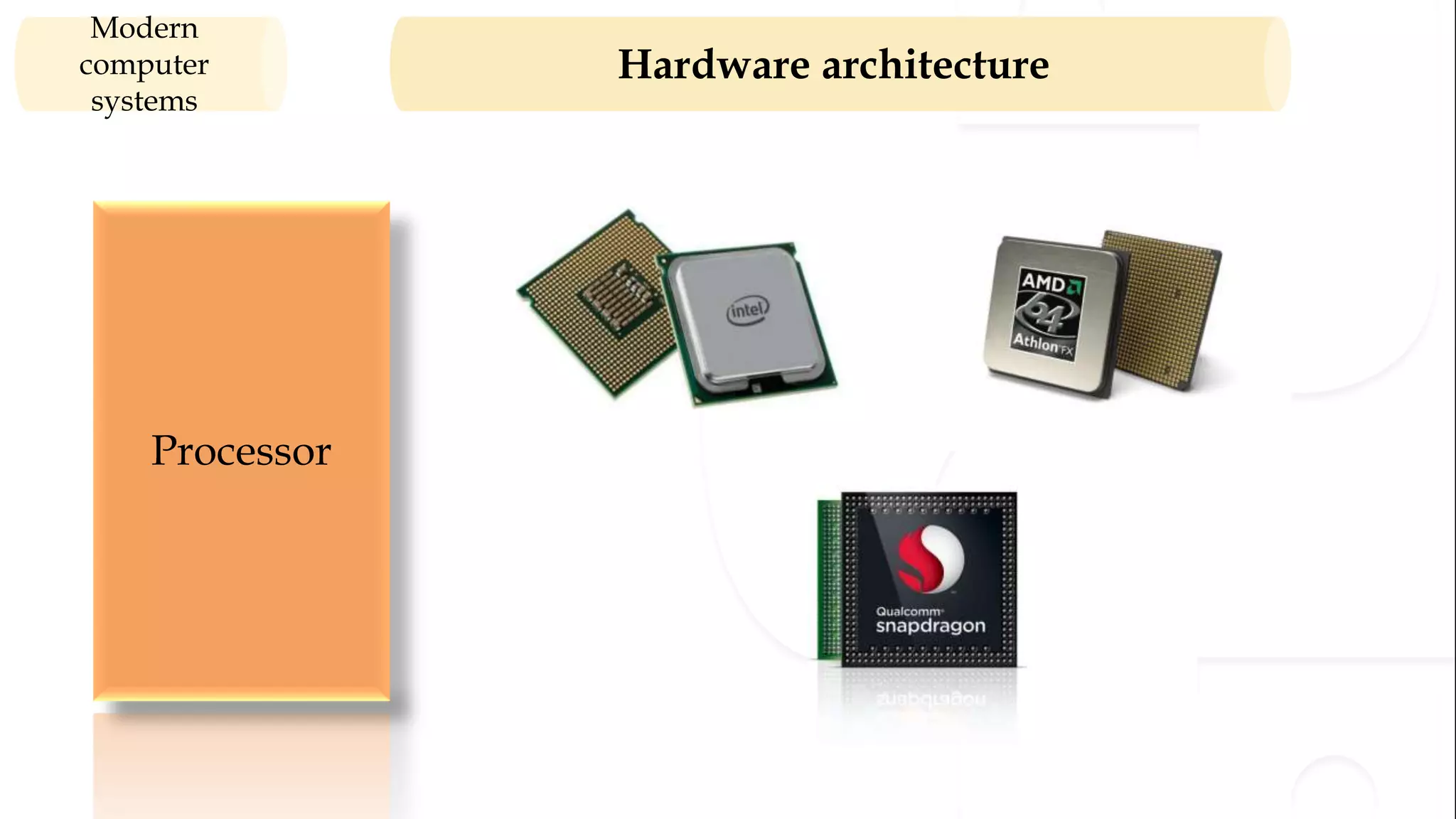
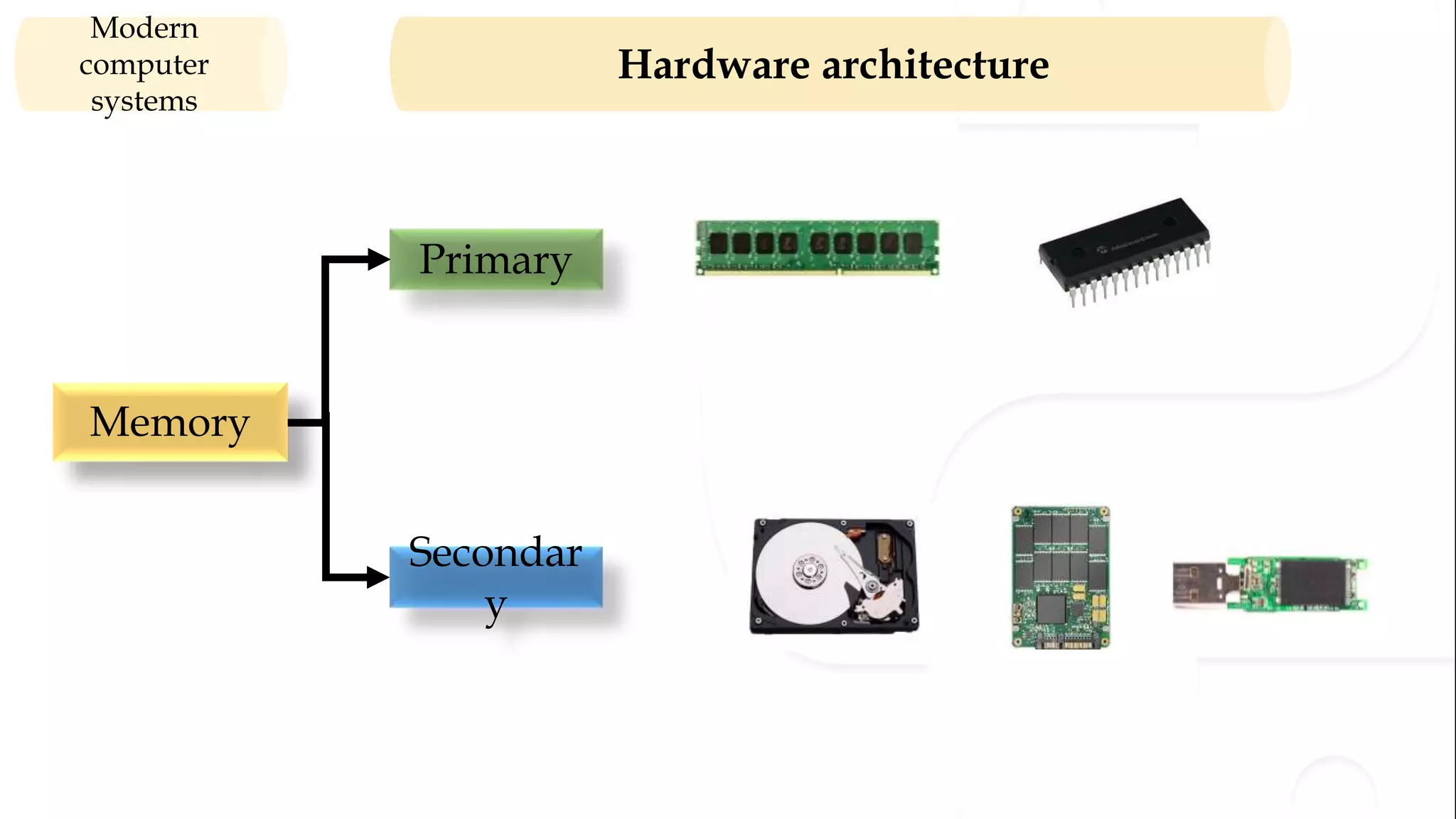
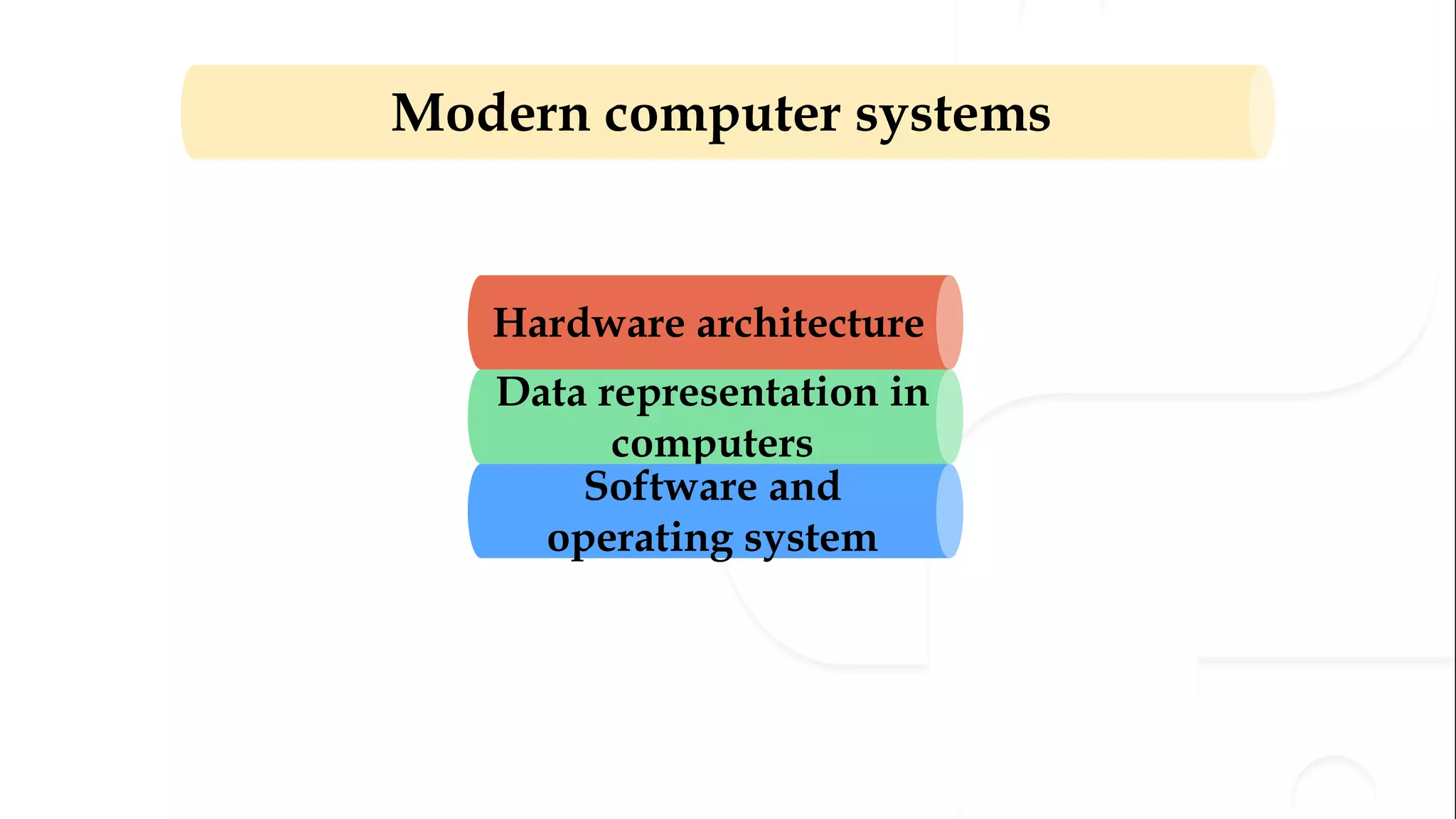
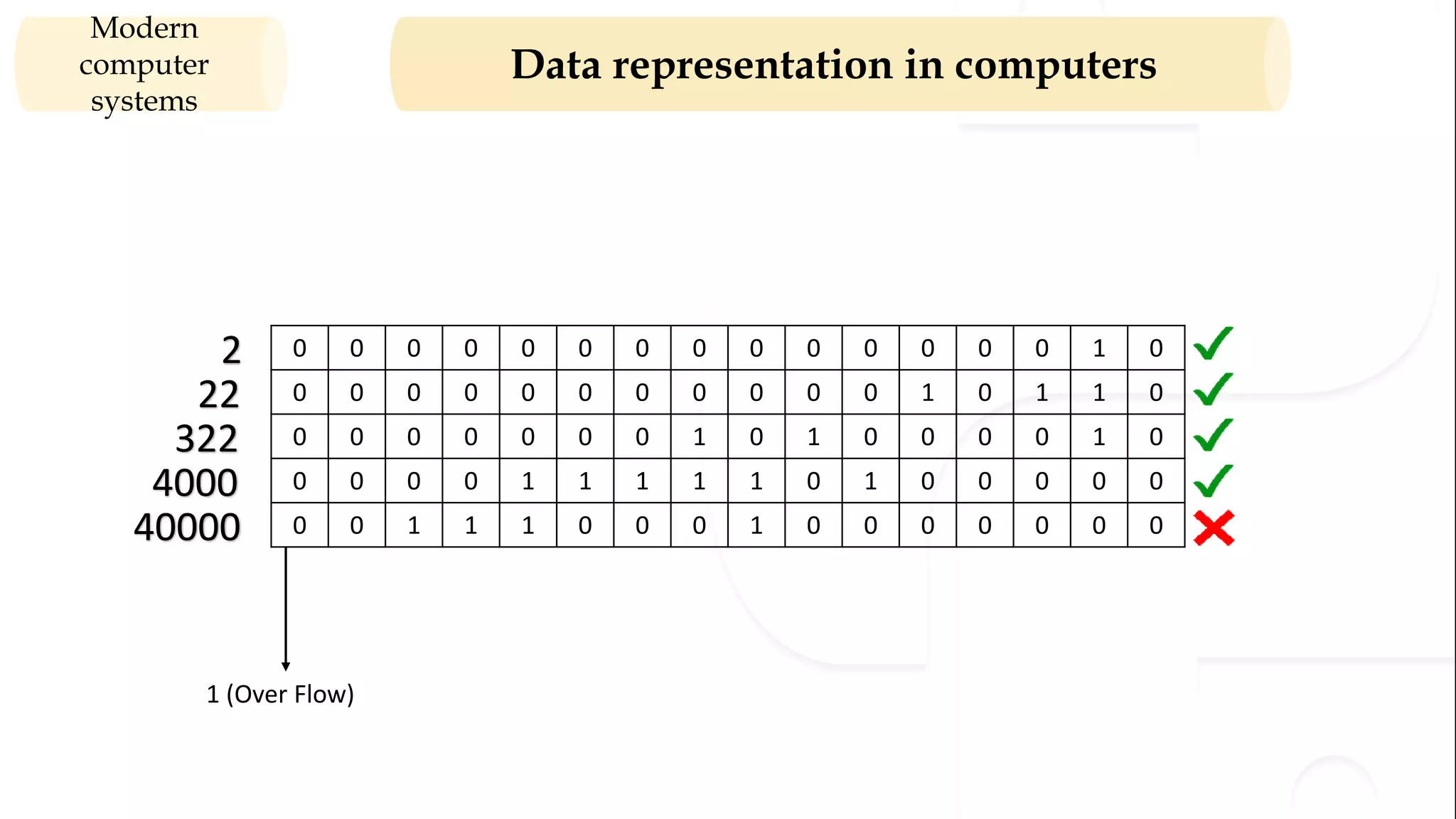
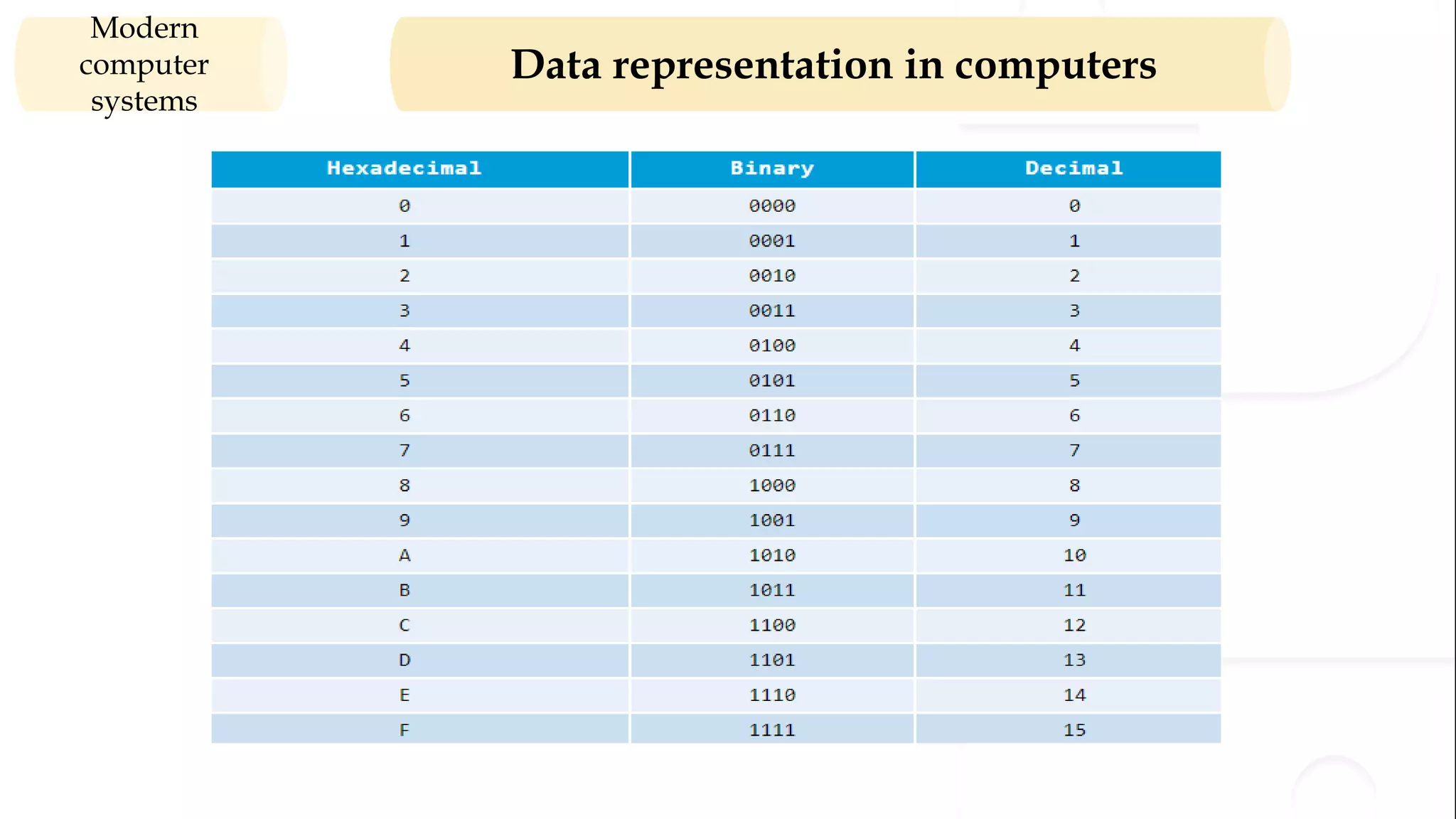
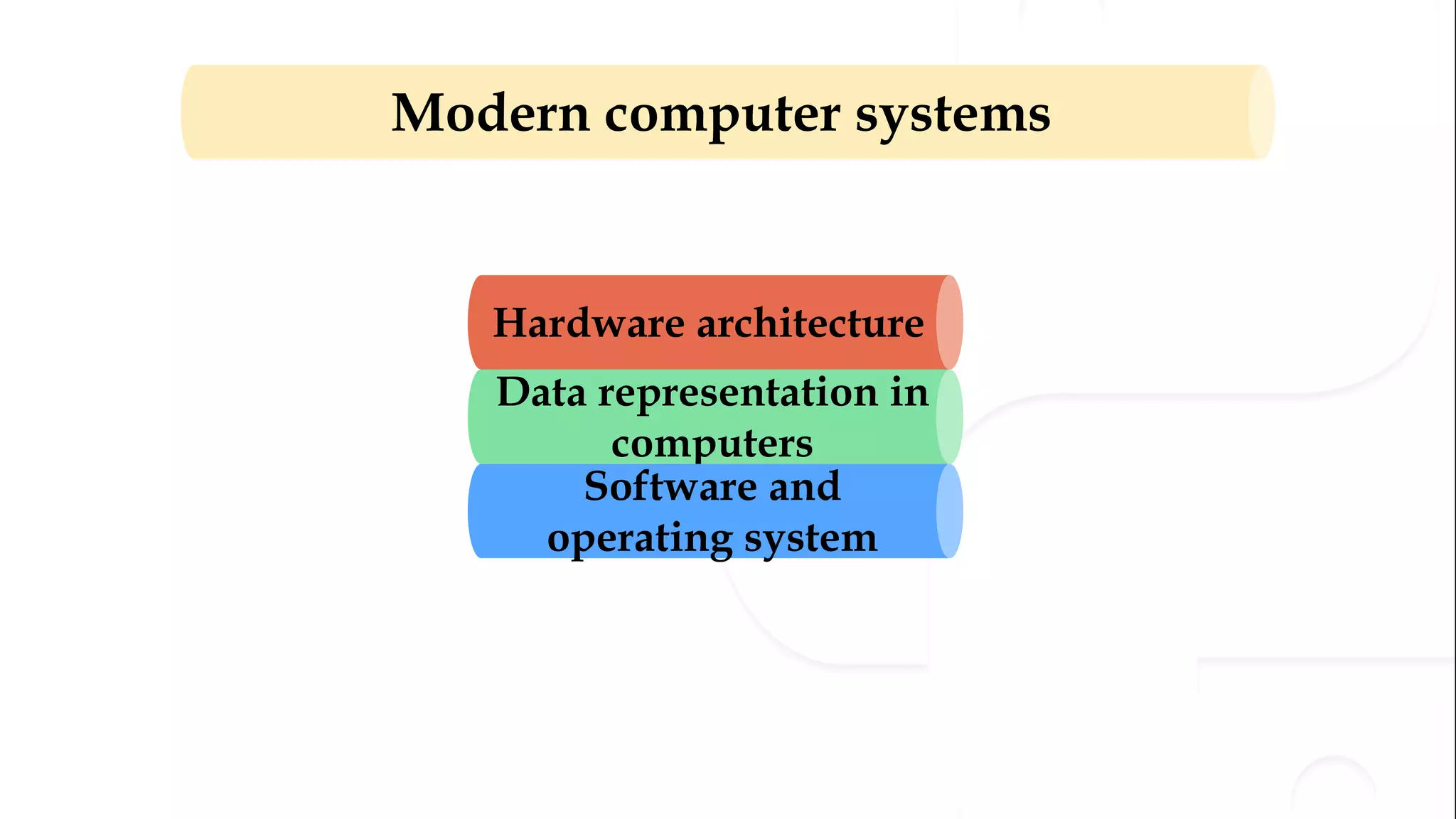
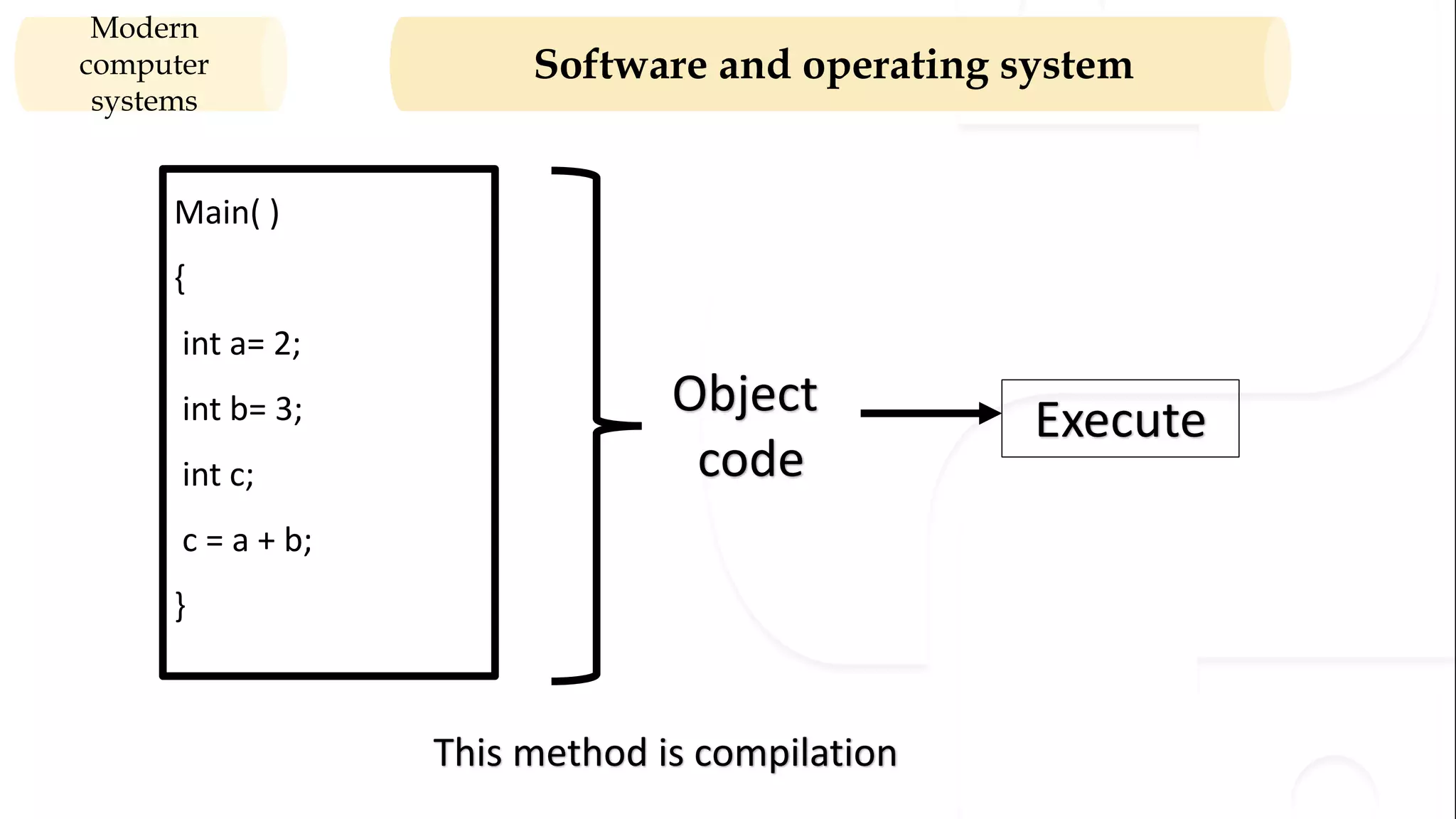
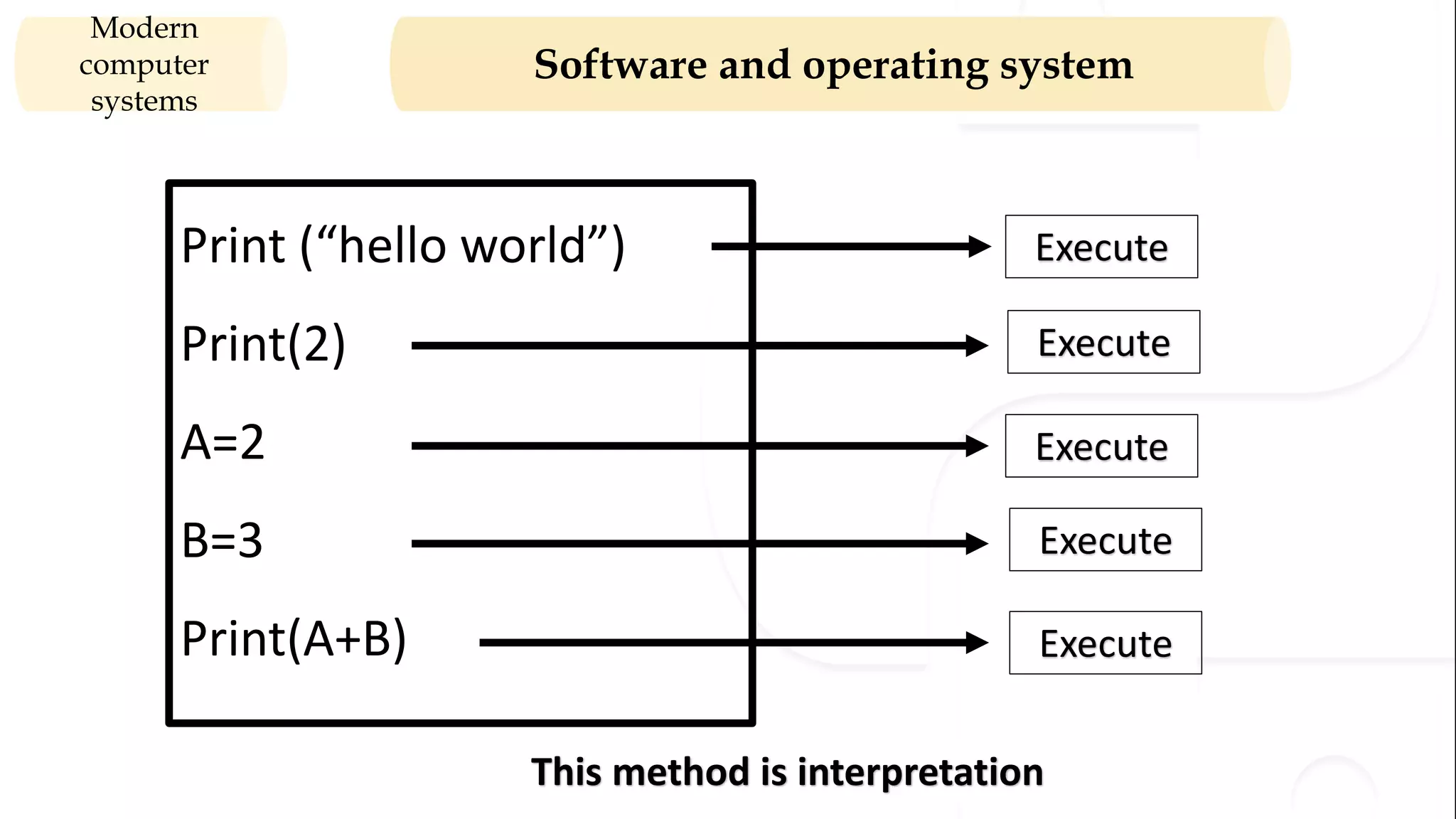
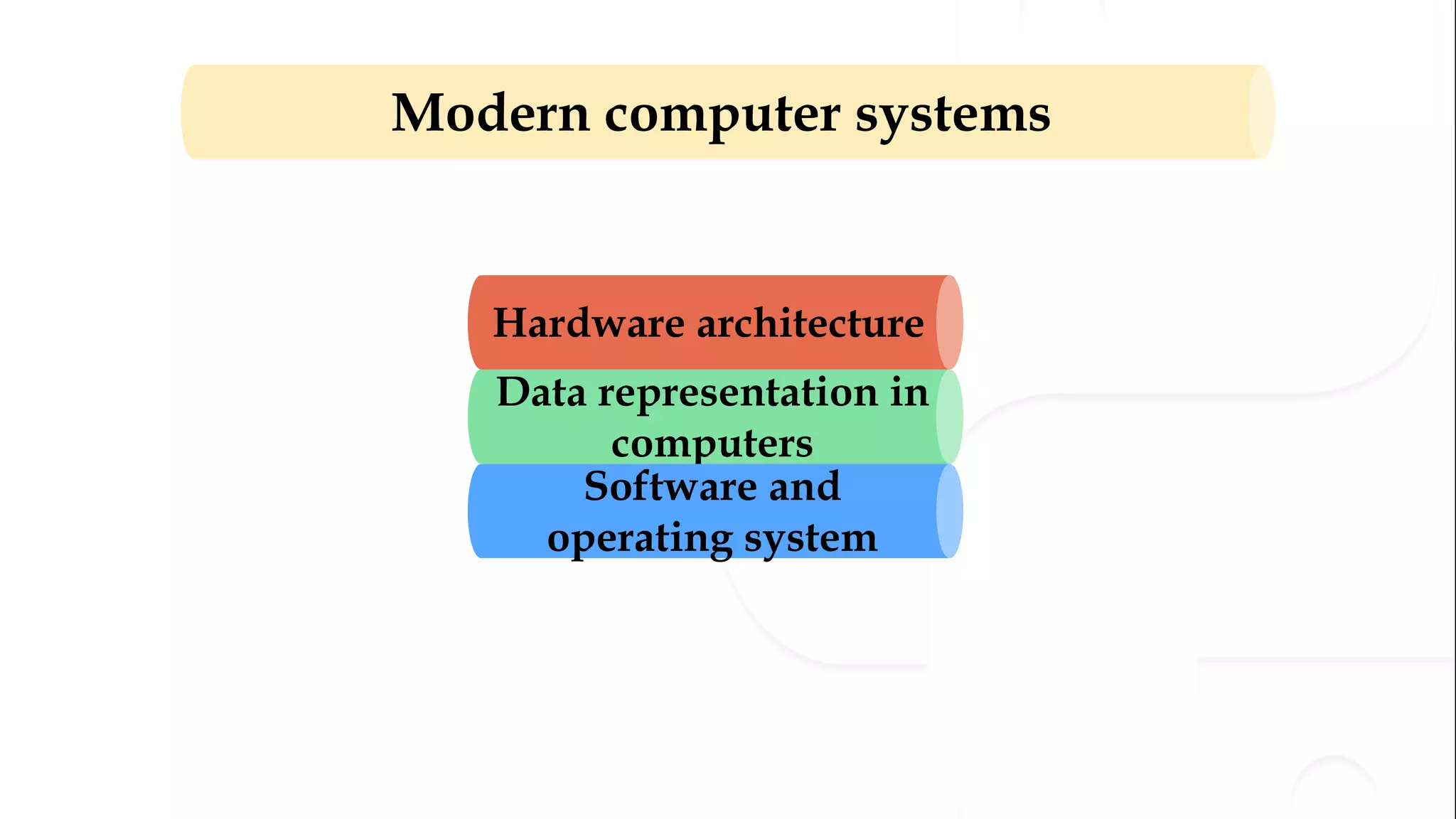
The document provides an overview of the syllabus for a Python programming course. It covers conceptual introductions to topics in computer science and algorithms. It also covers modern computer systems including hardware architecture, data representation, software, and operating systems. The course will teach students how to install Python and cover basic syntax, data types, variables, arithmetic operators, and understanding errors.