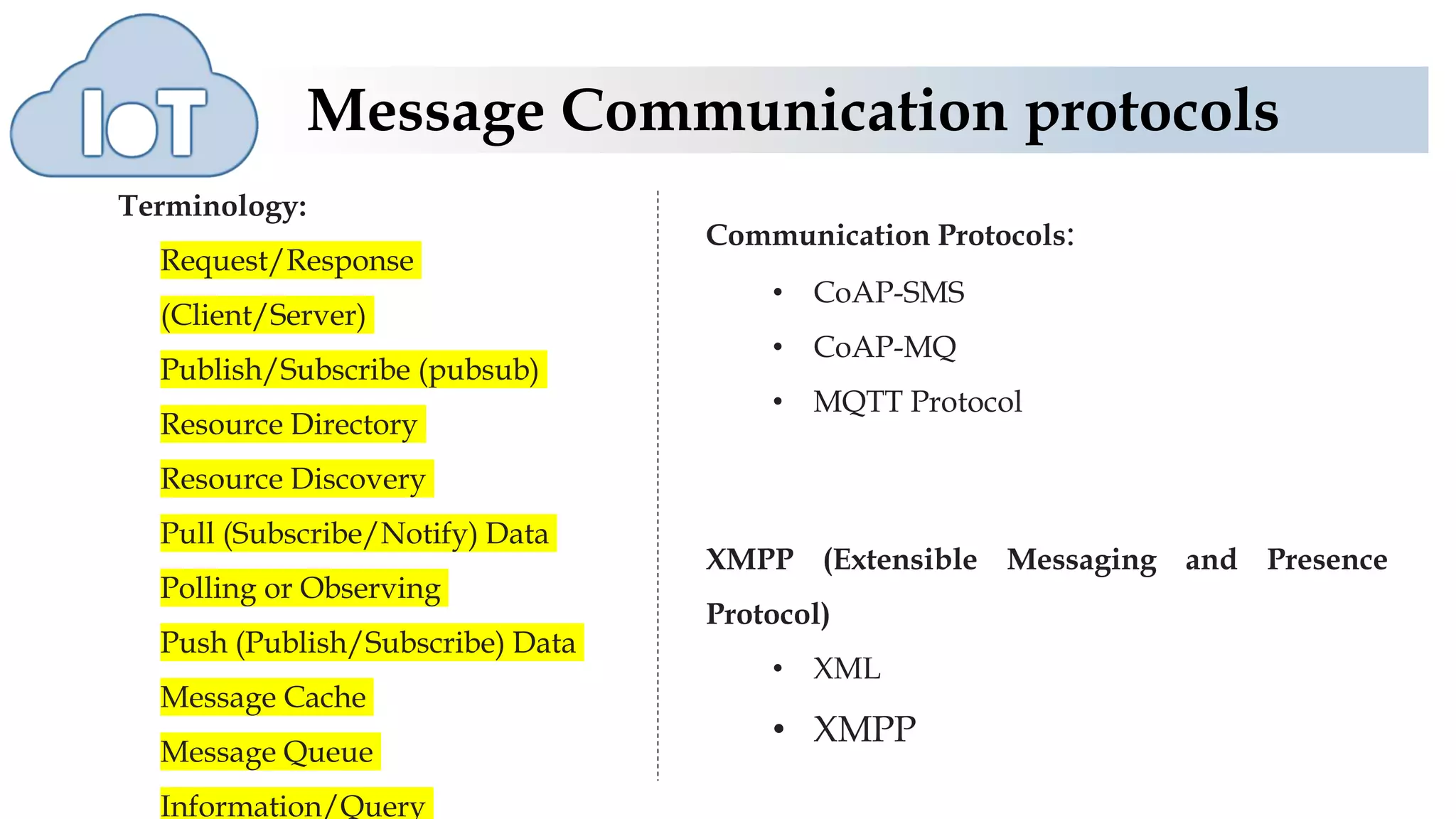
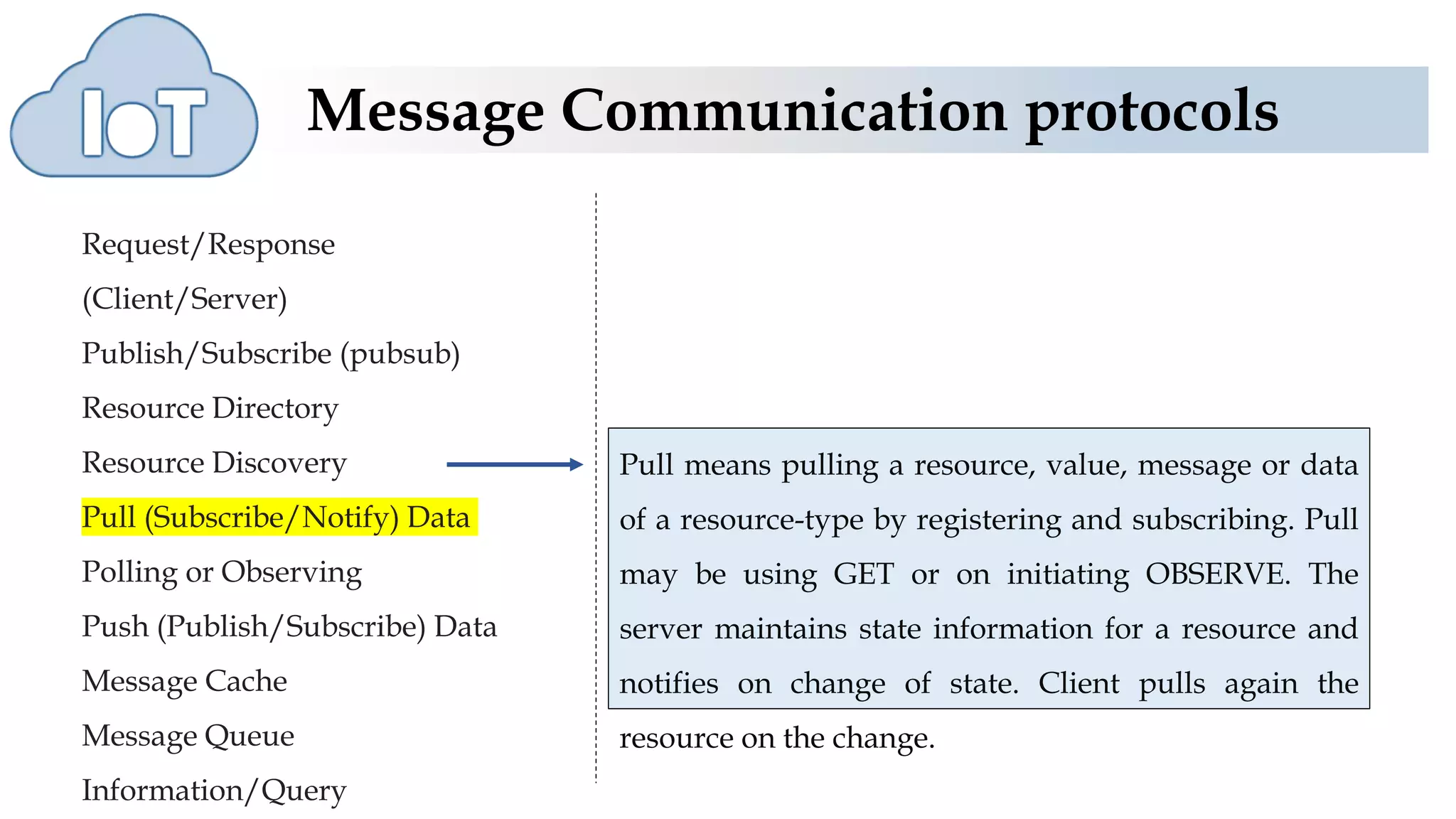
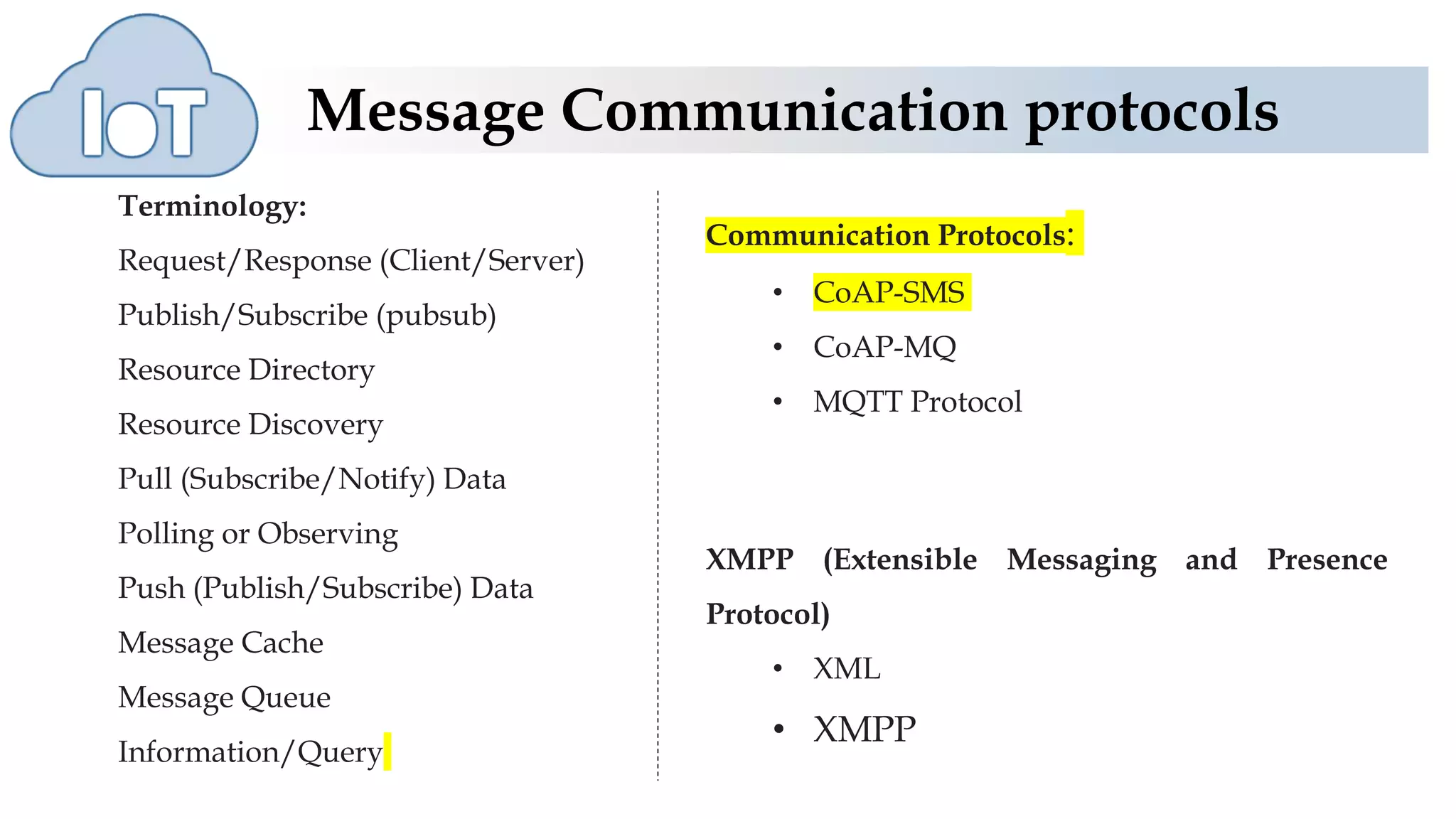
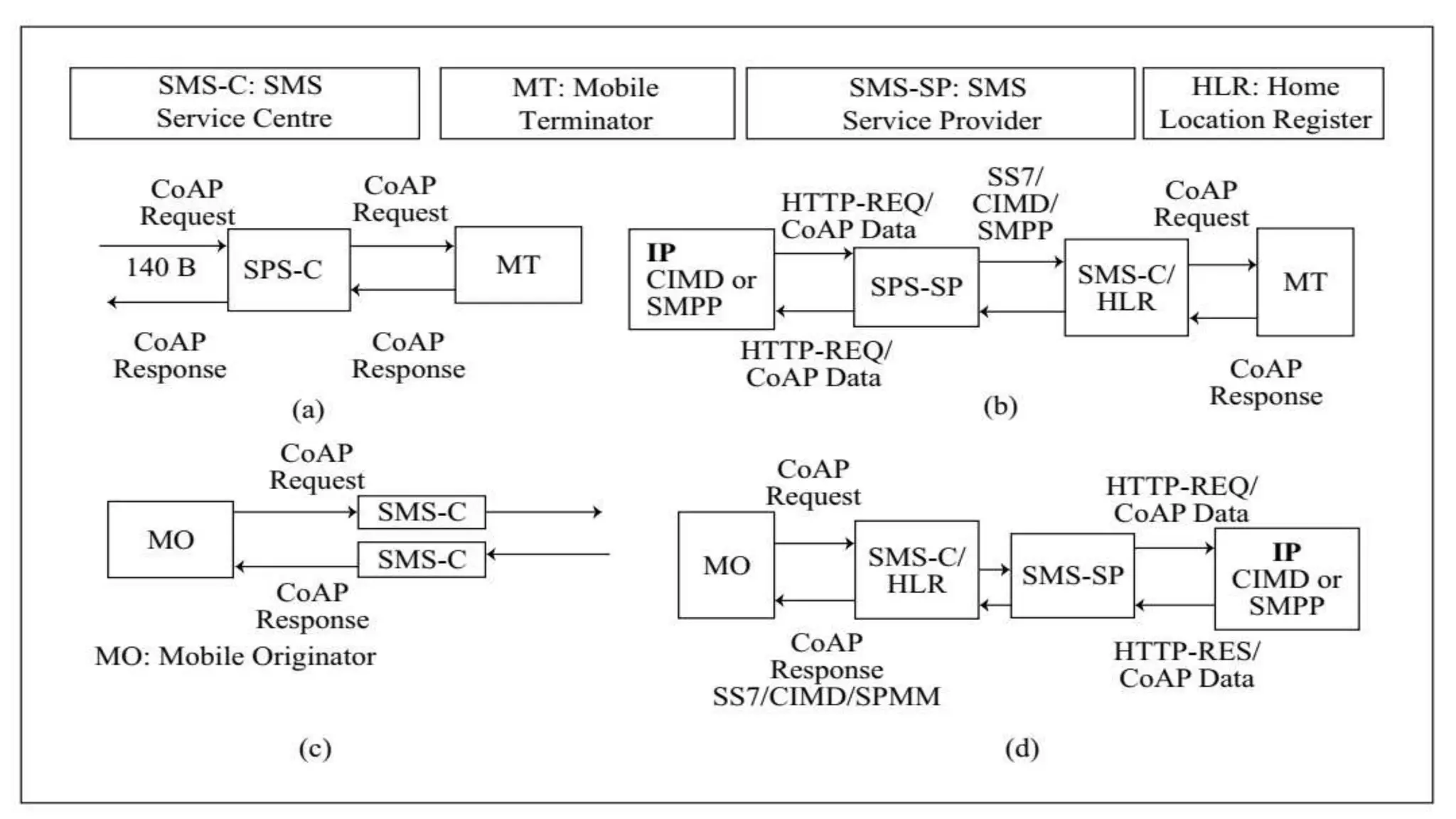
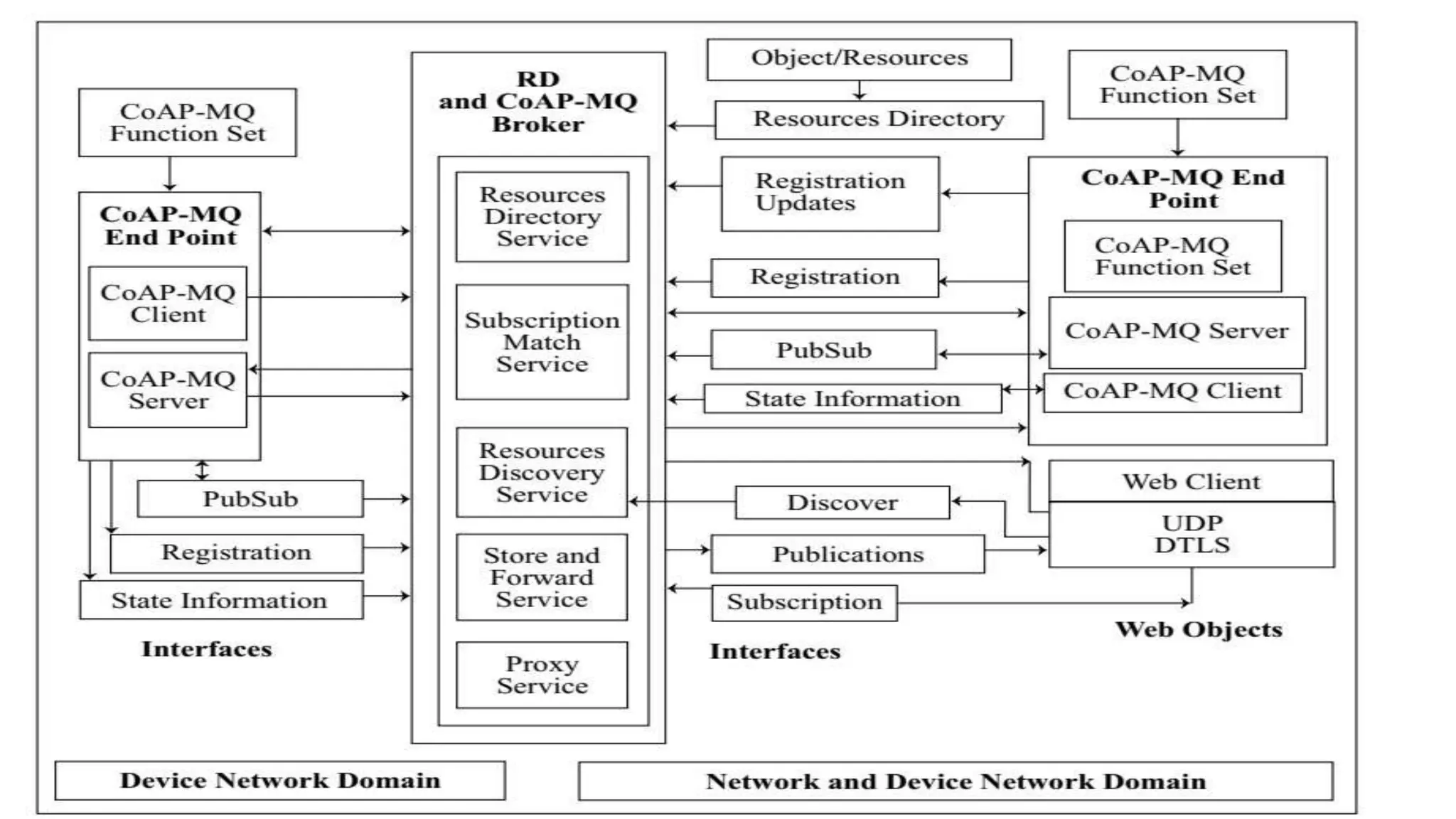
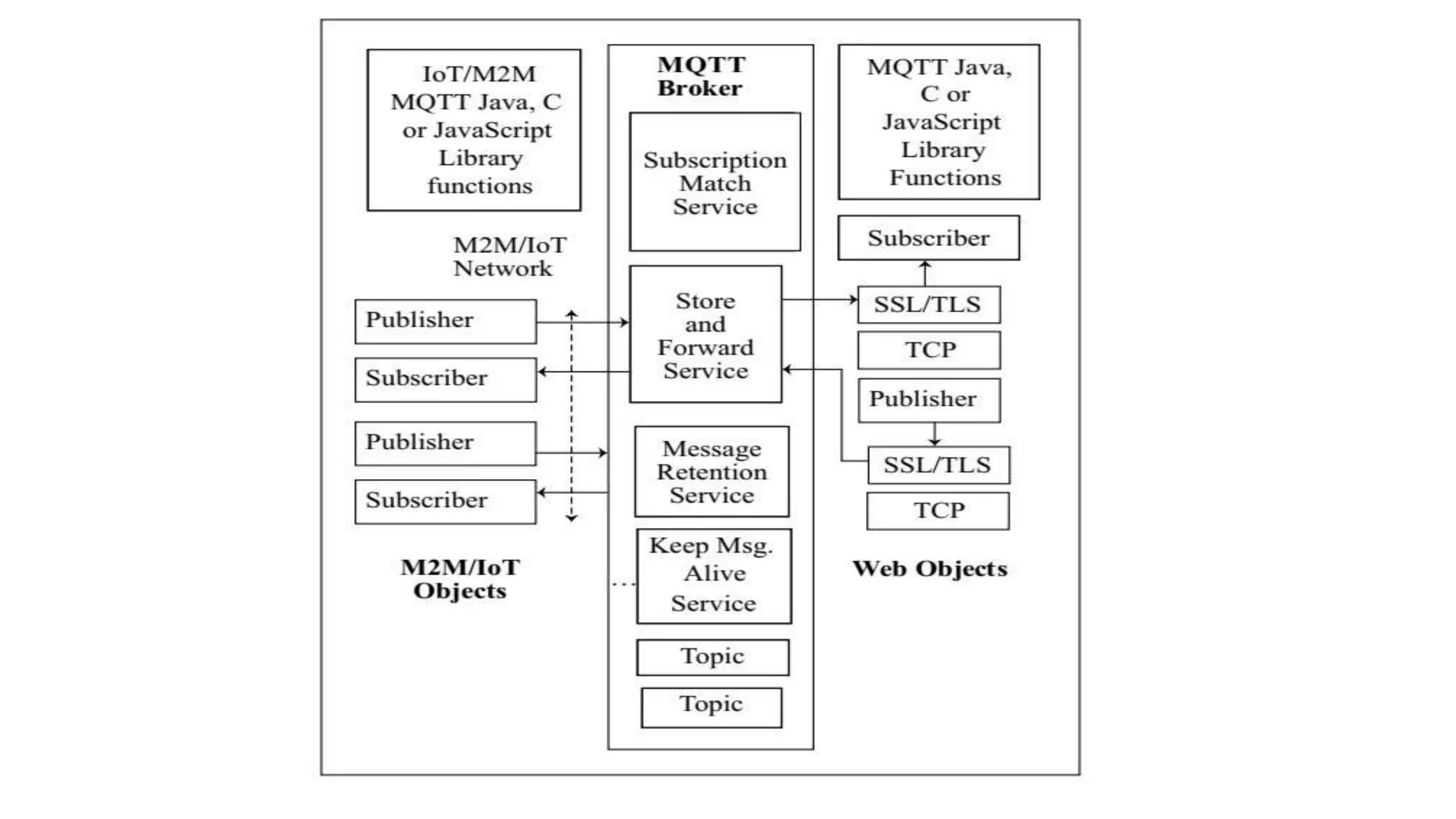
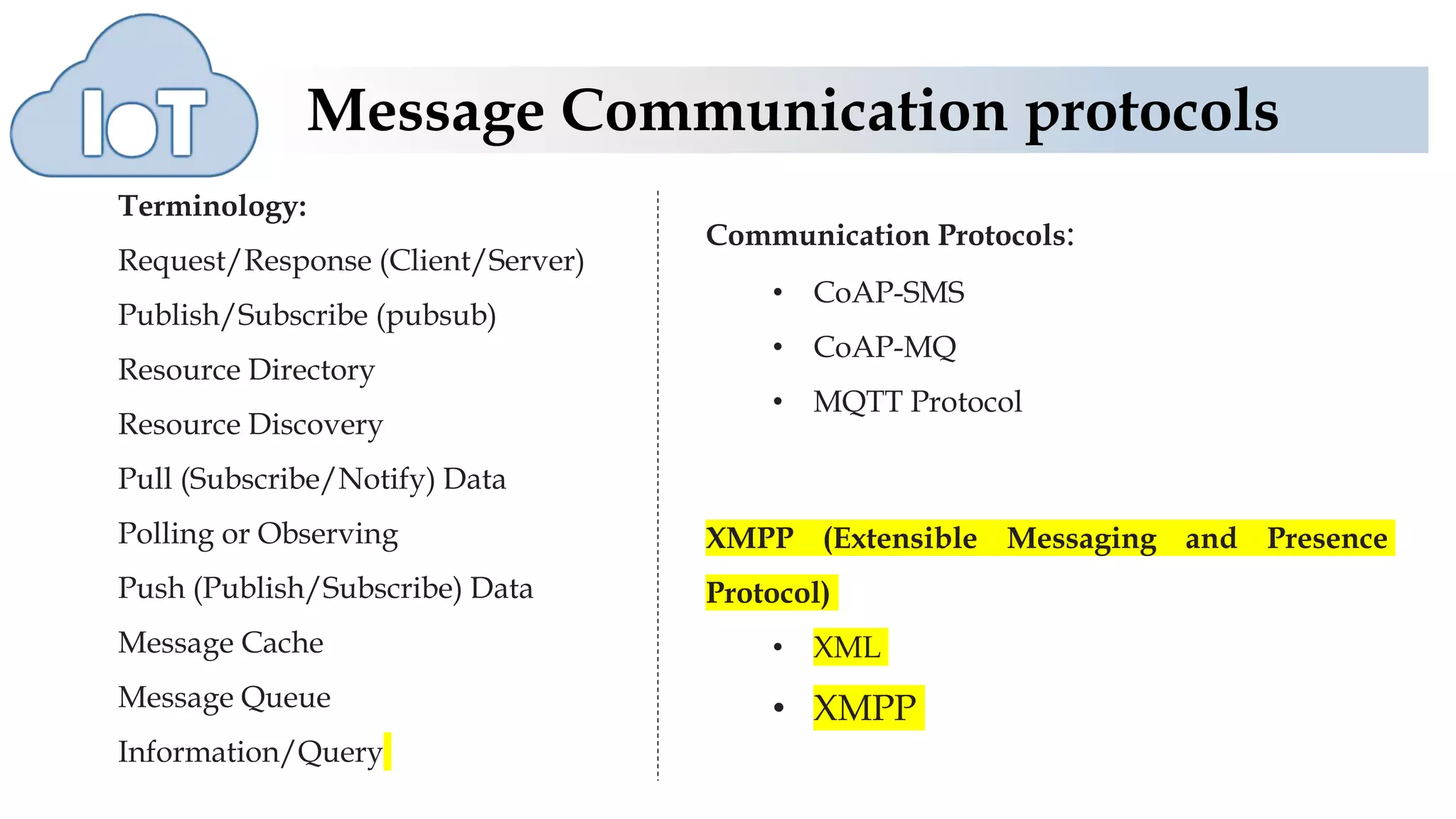
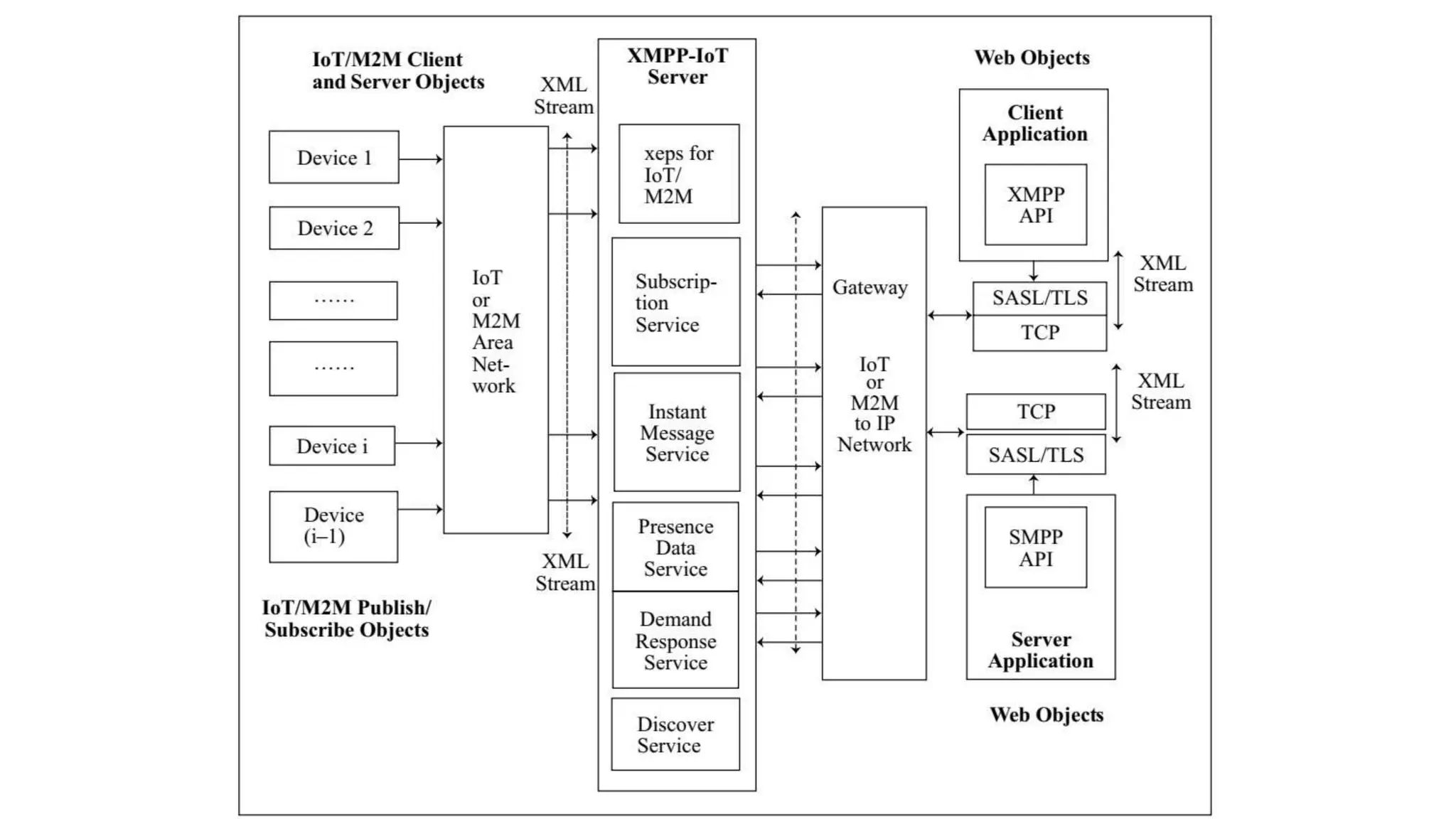
The document discusses various protocols for web connectivity and message communication, including request/response, publish/subscribe, resource directories, and pull/push data models. It defines terminology and describes several protocols in more detail, such as CoAP-SMS which uses SMS for message transport, CoAP-MQ which uses a message queue, and MQTT which is an open-source M2M protocol that uses topics and a broker.