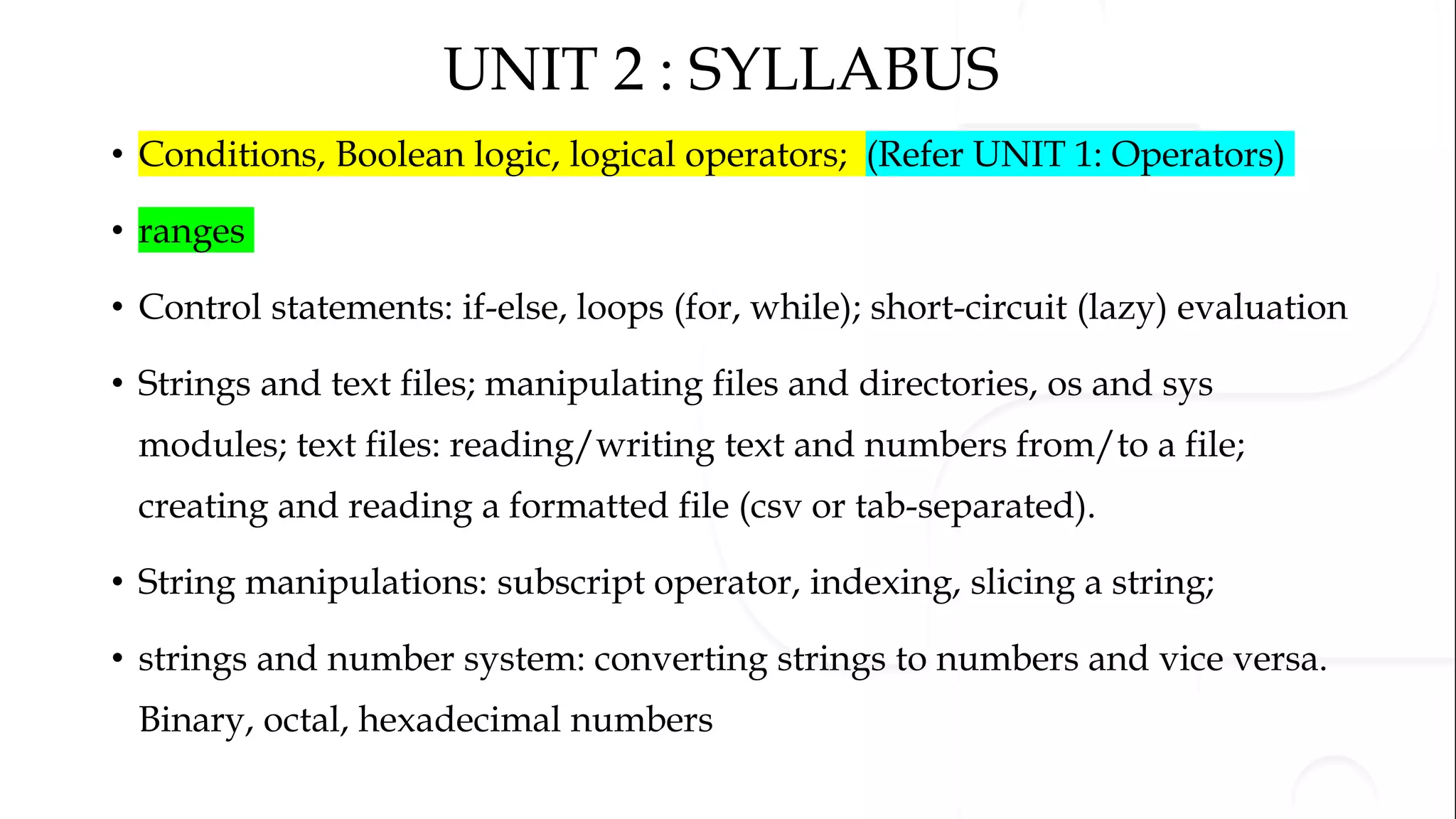
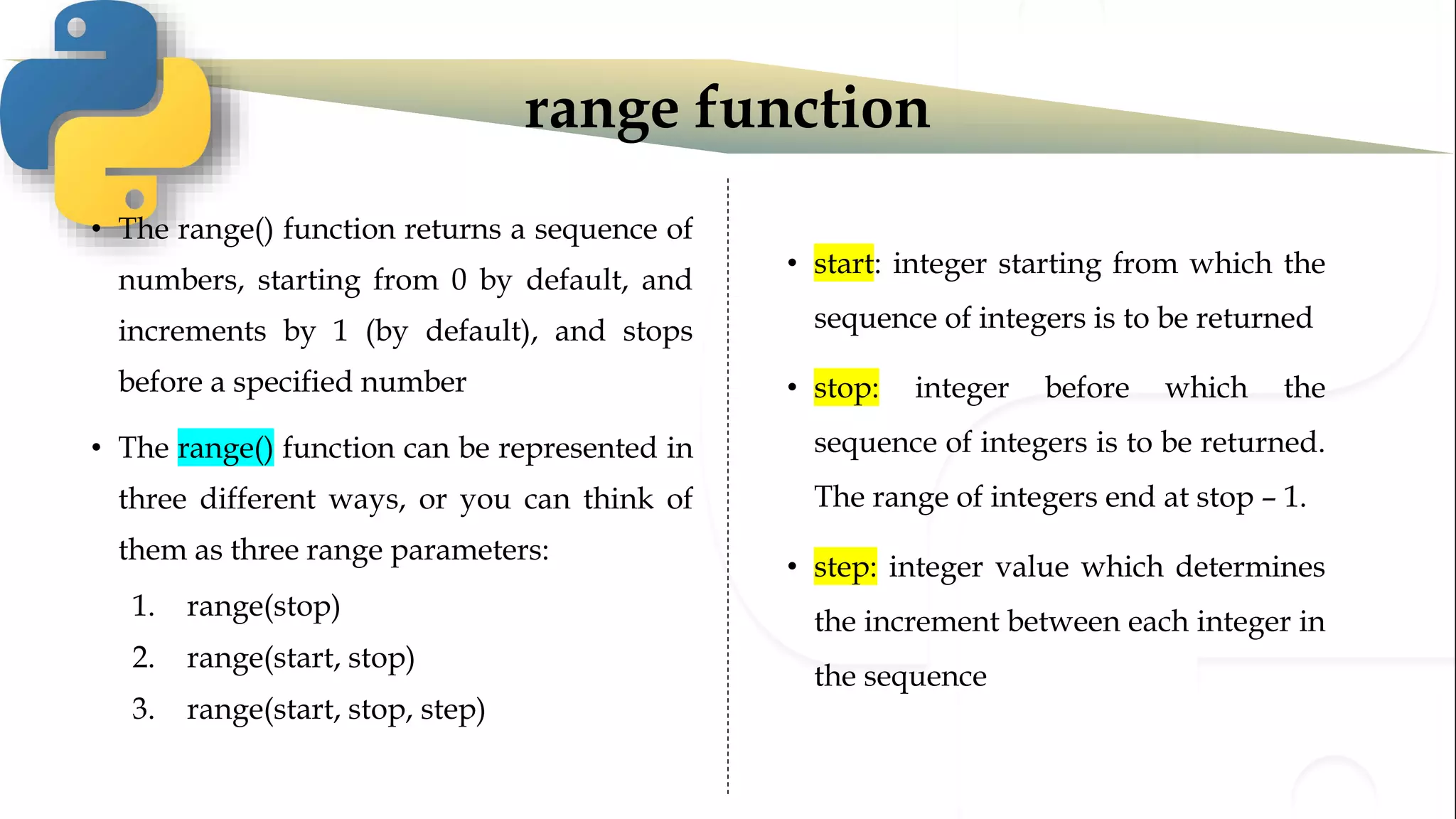
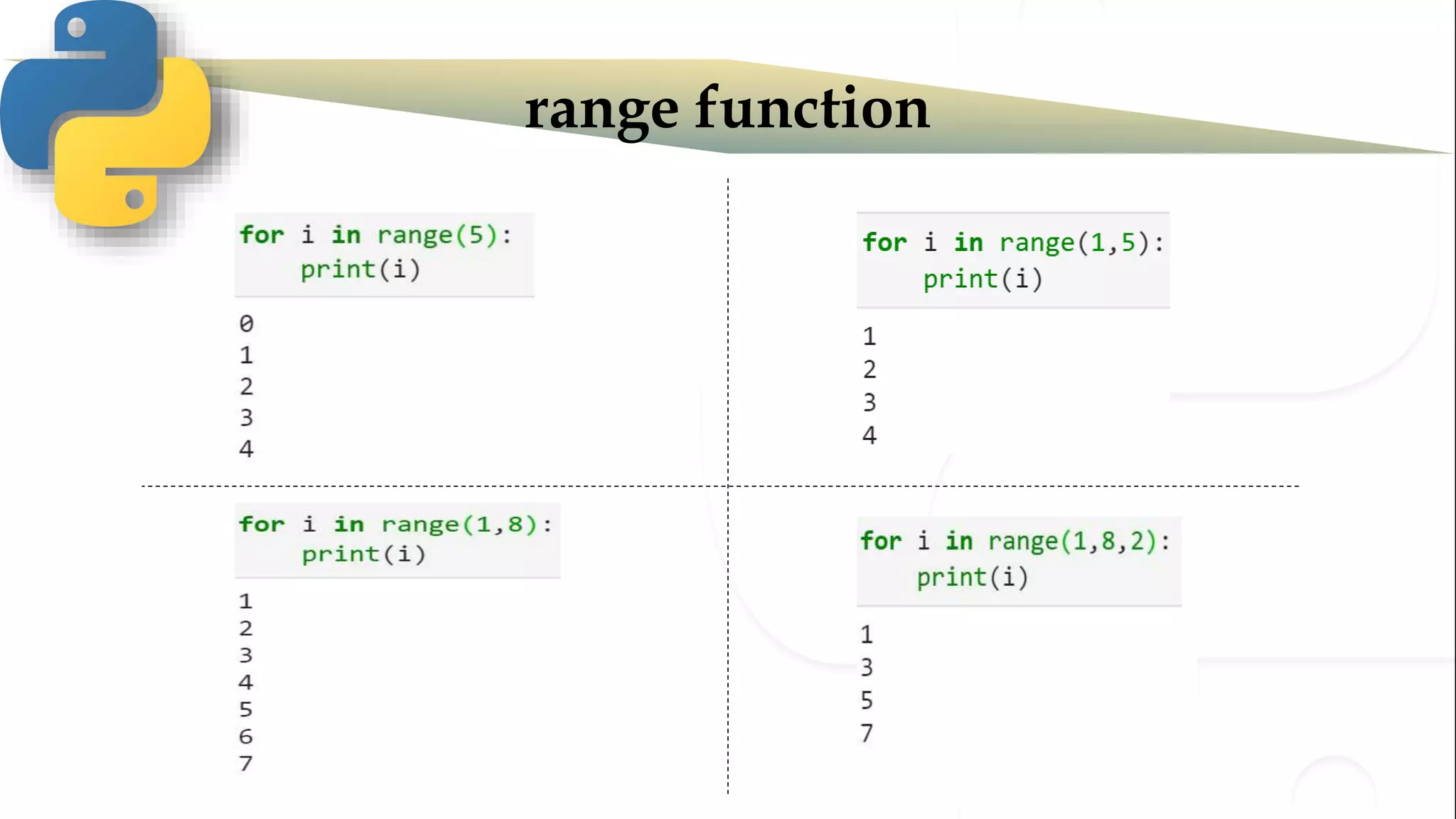
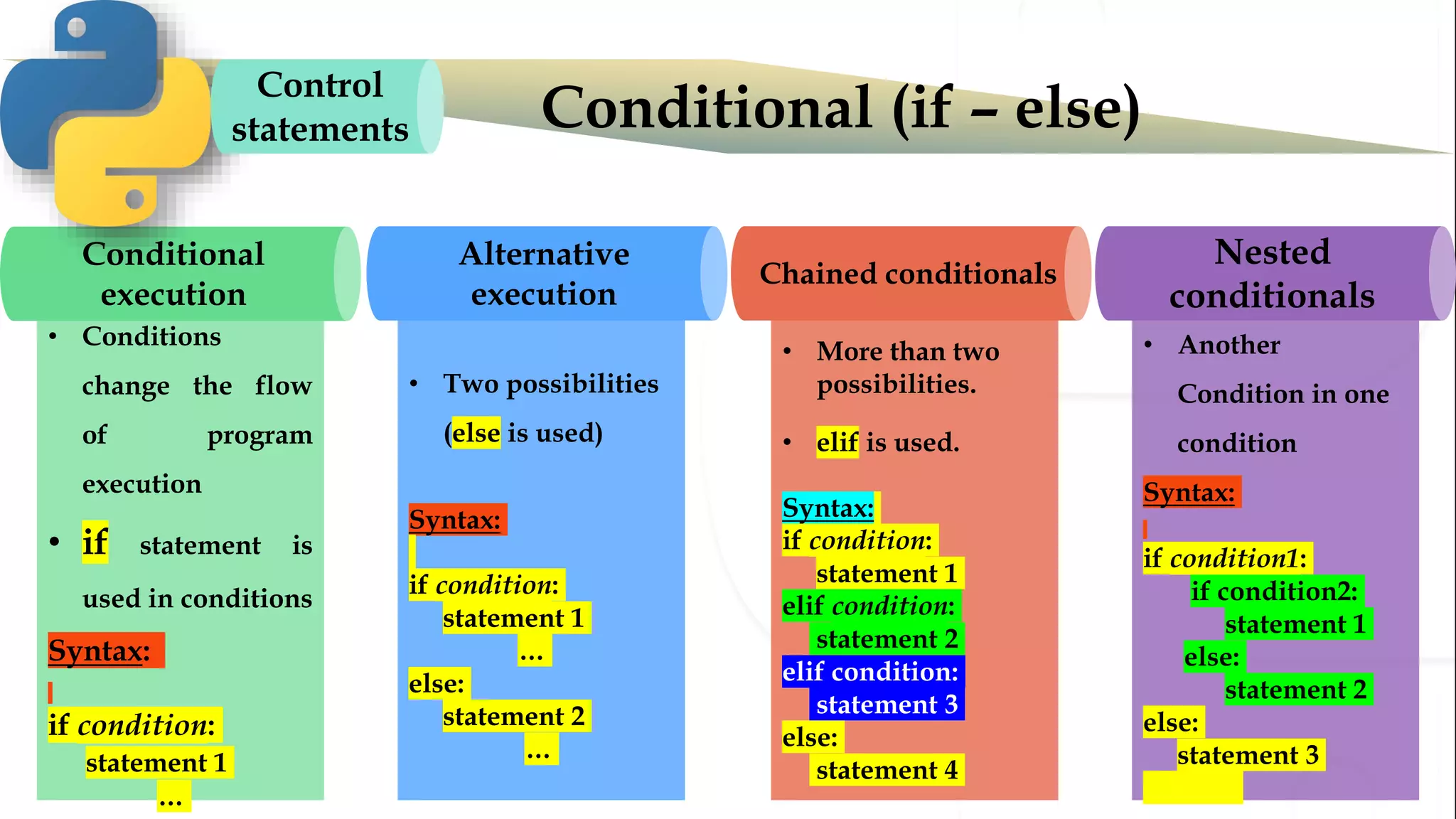
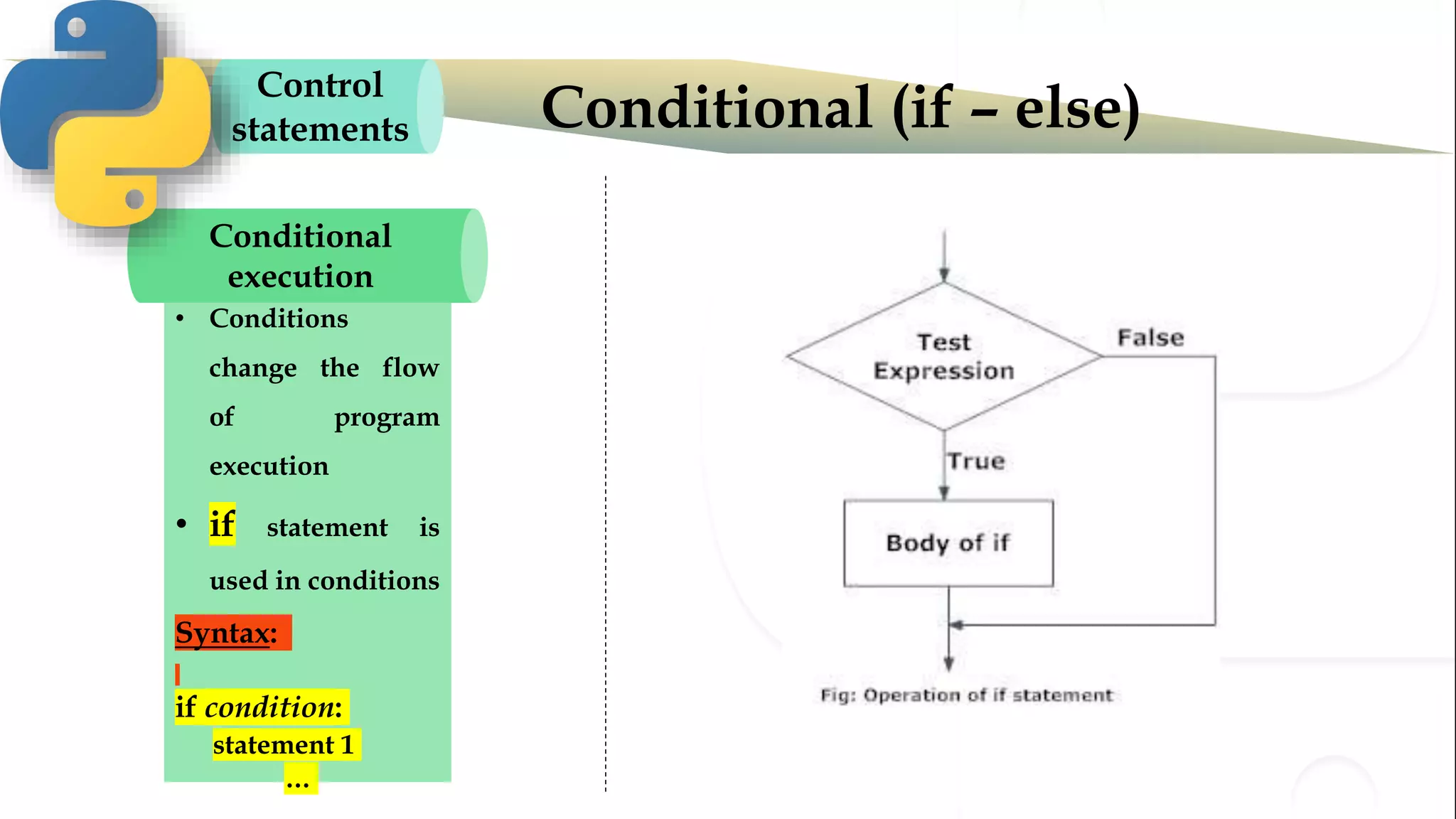
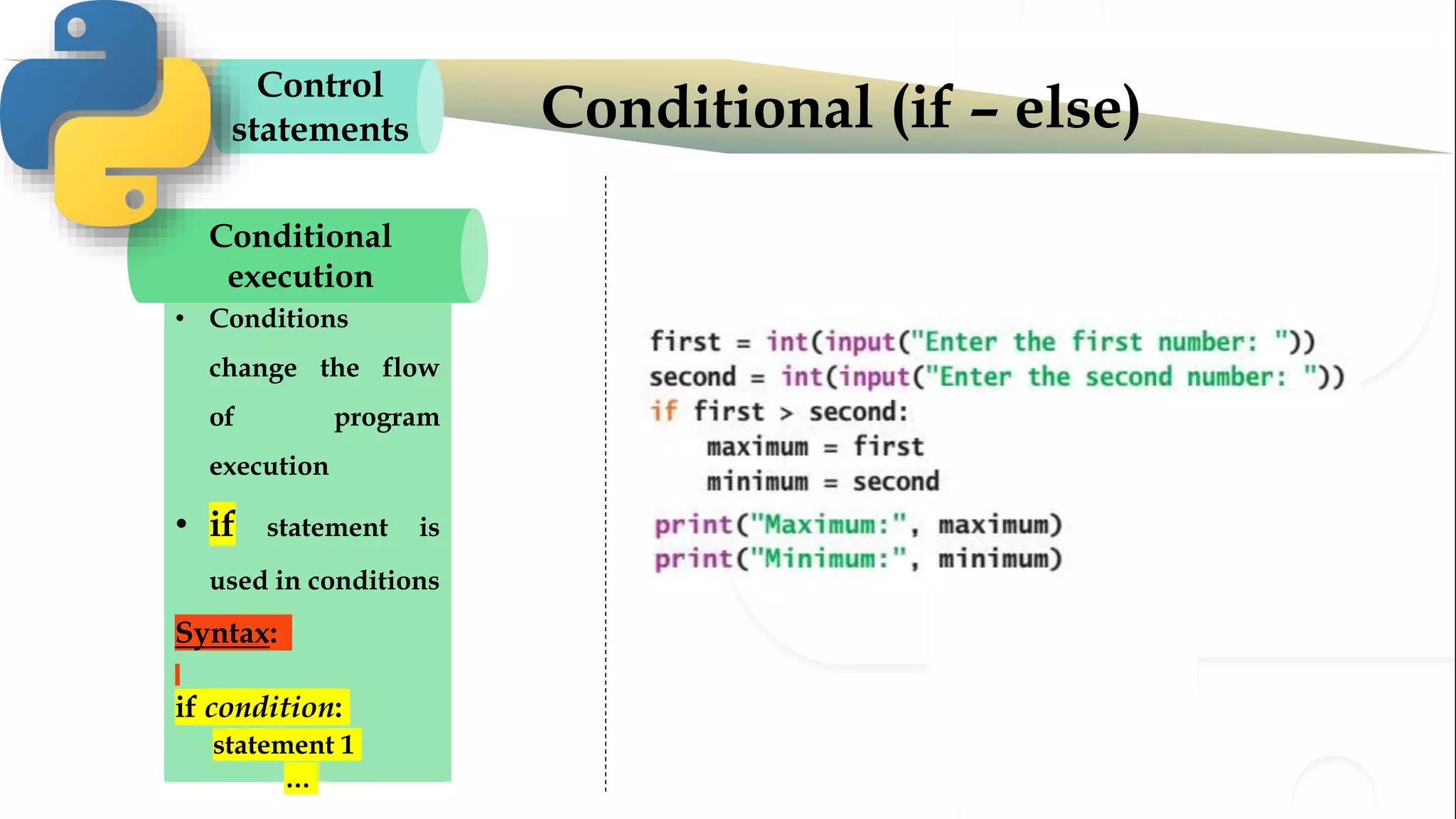
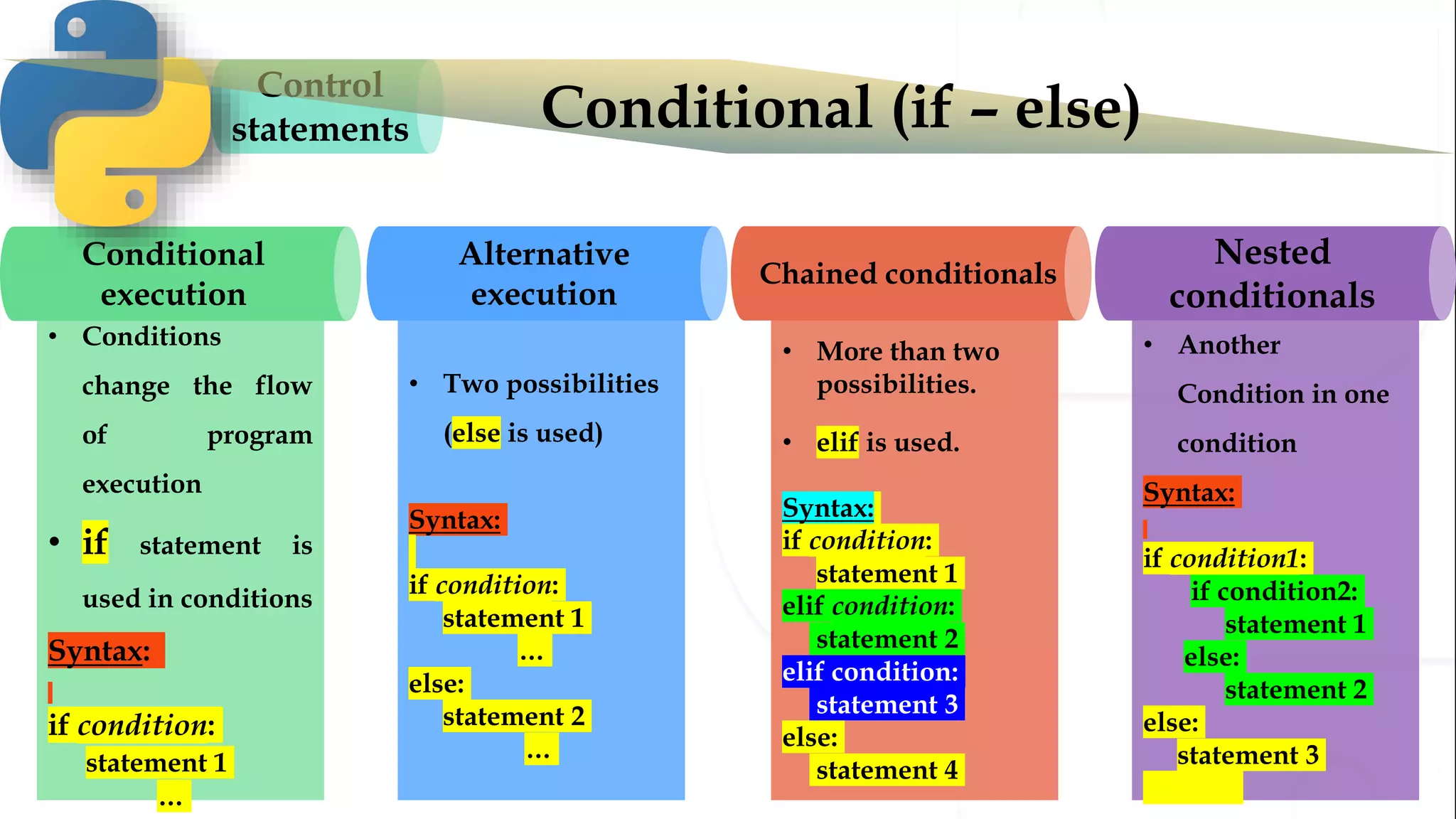
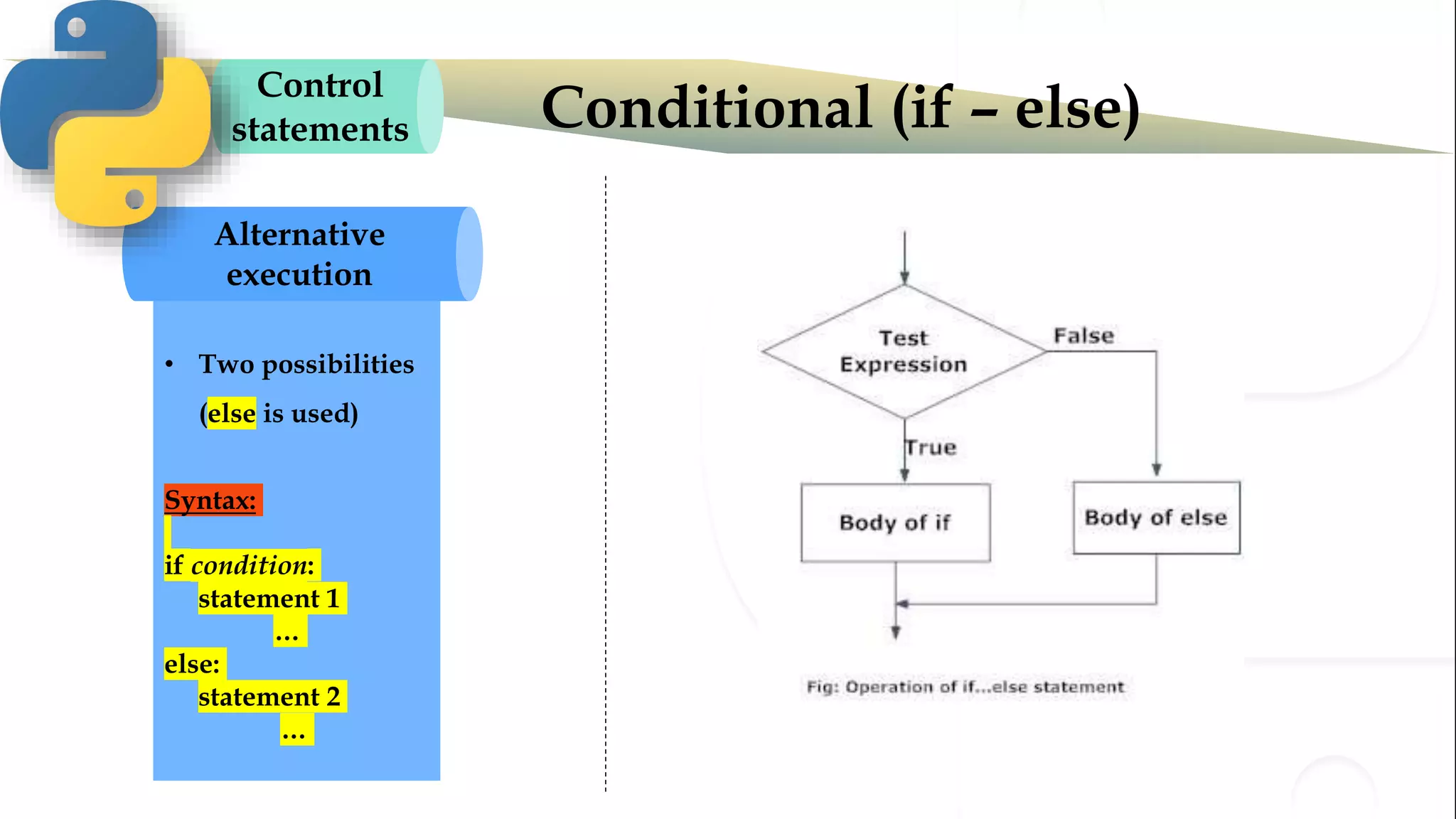
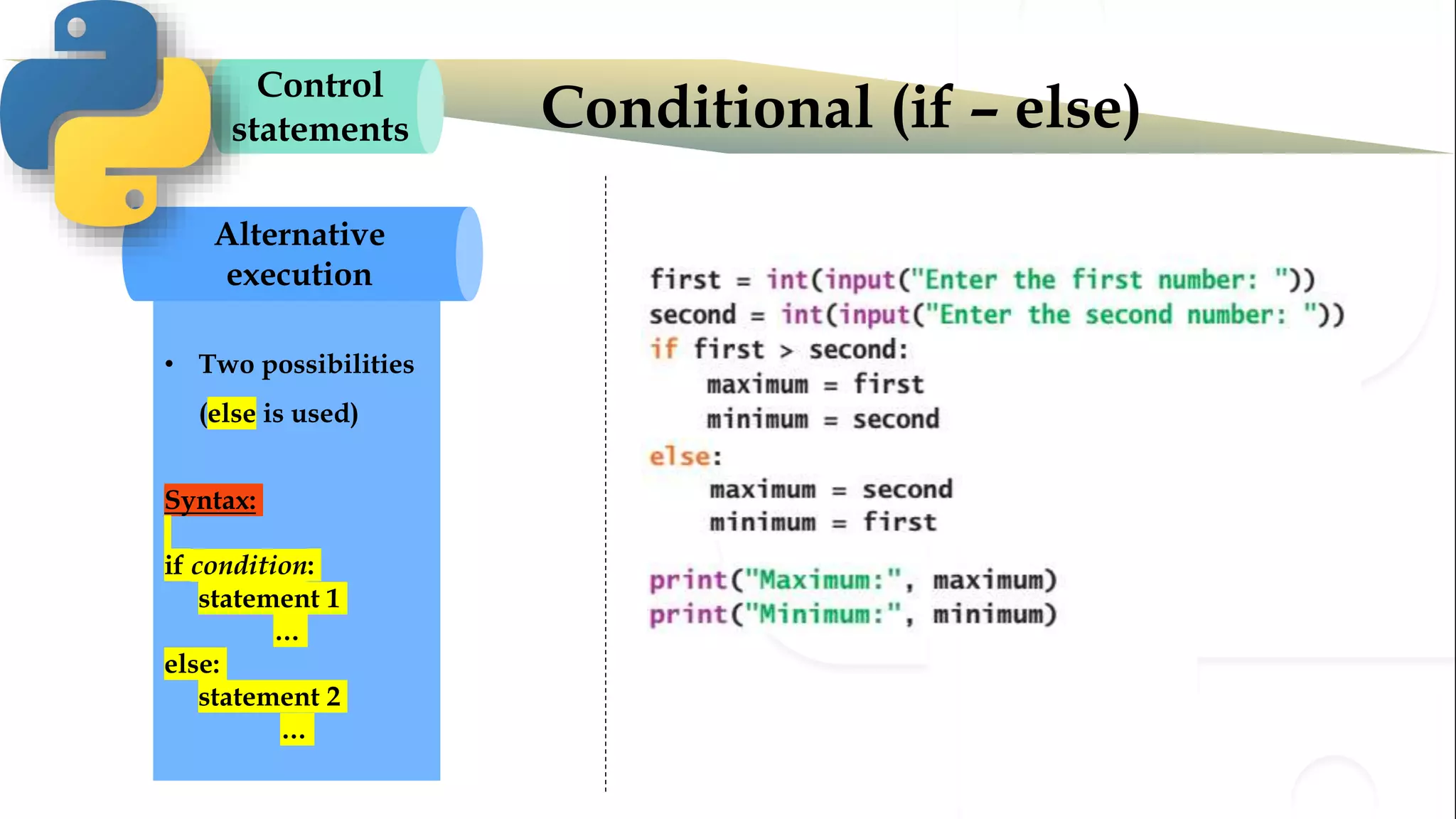
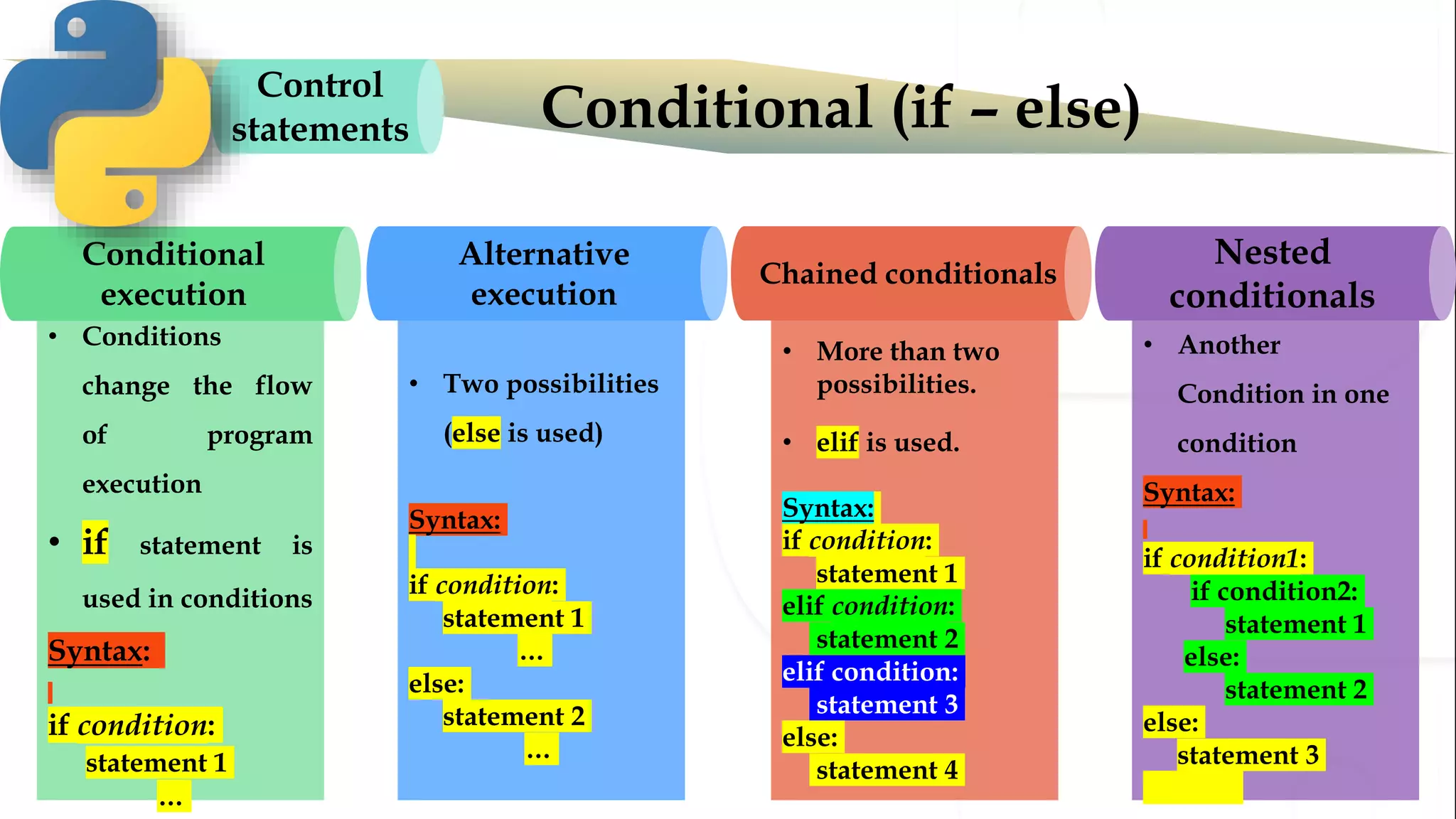
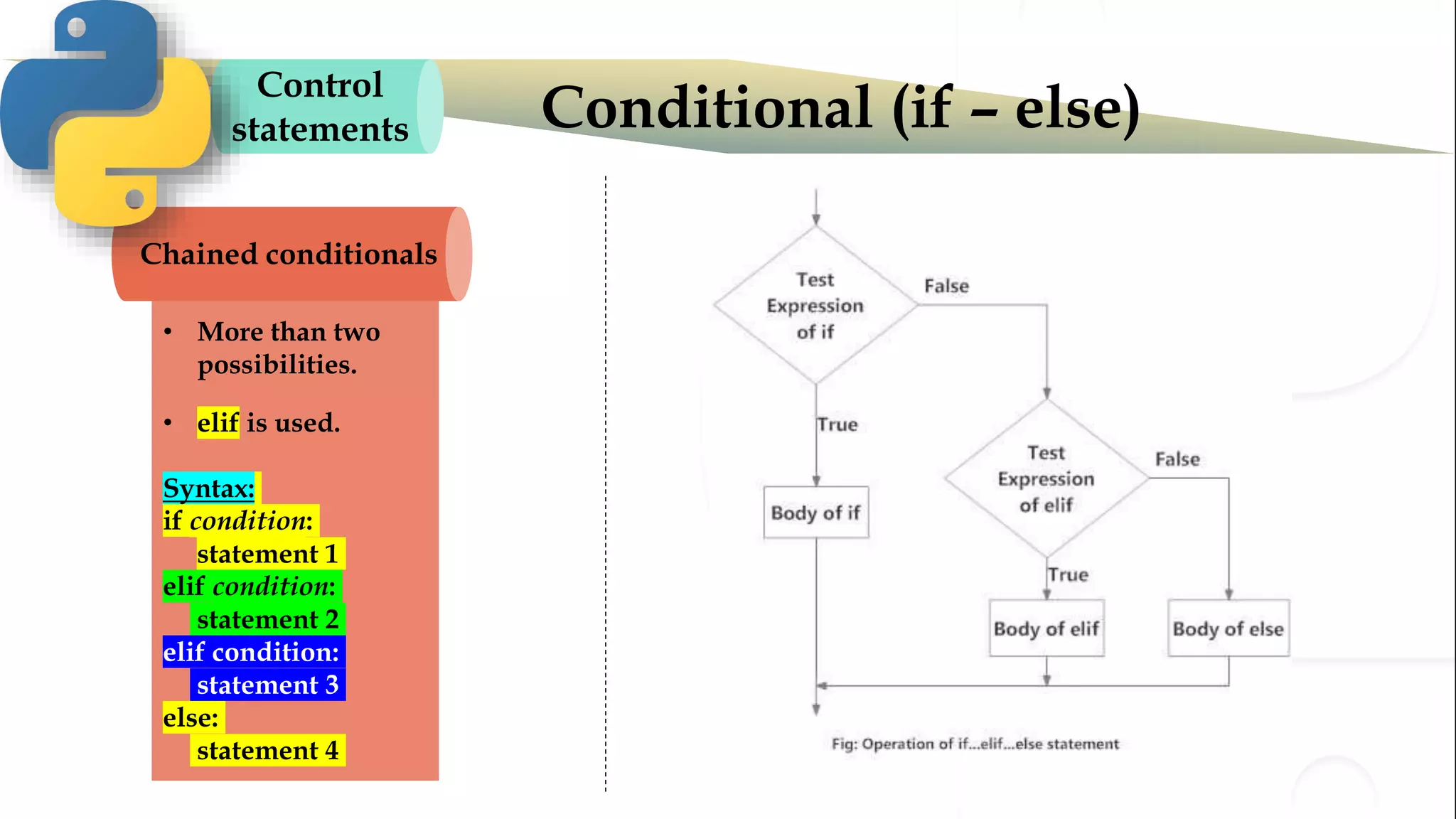
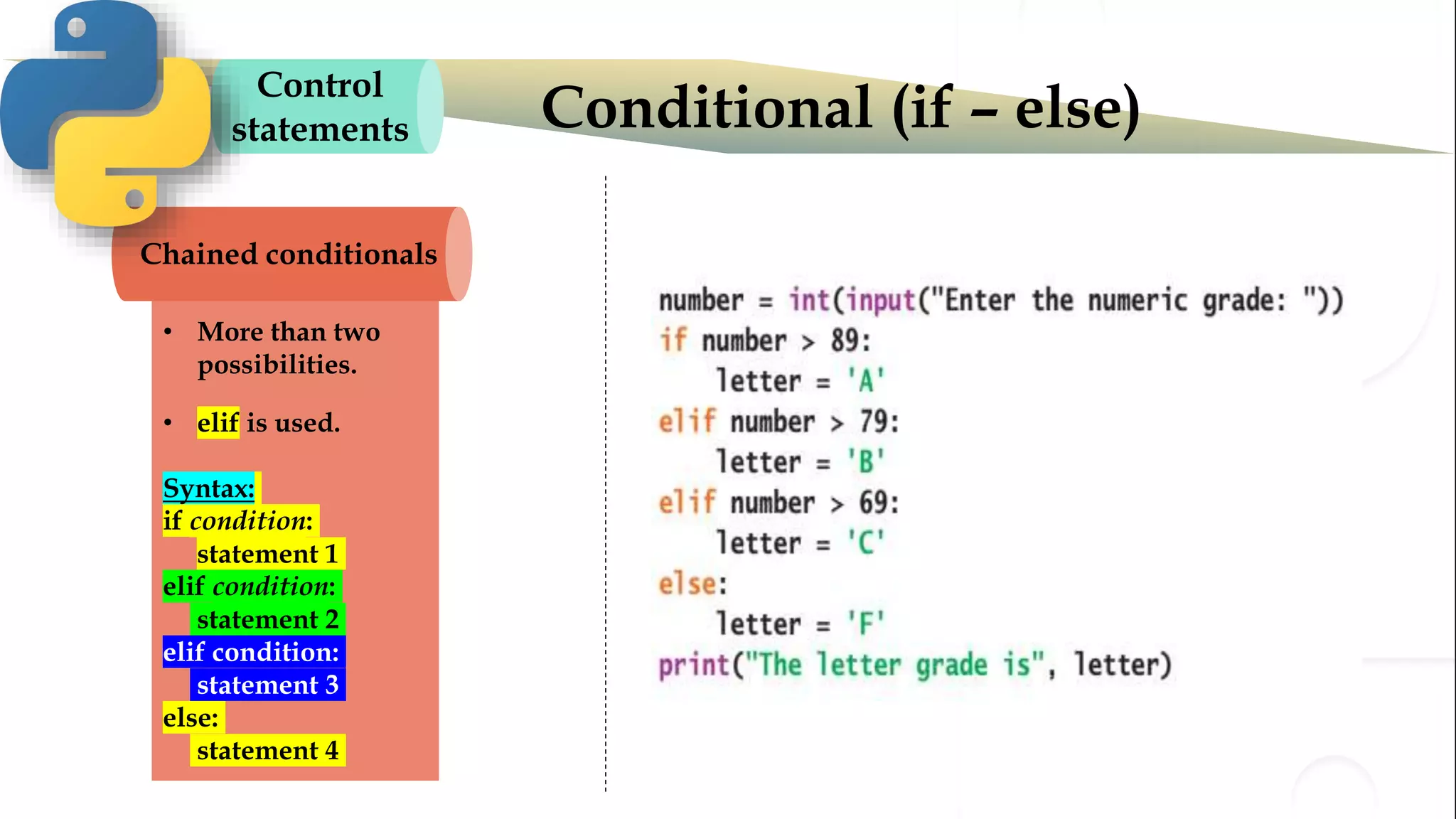
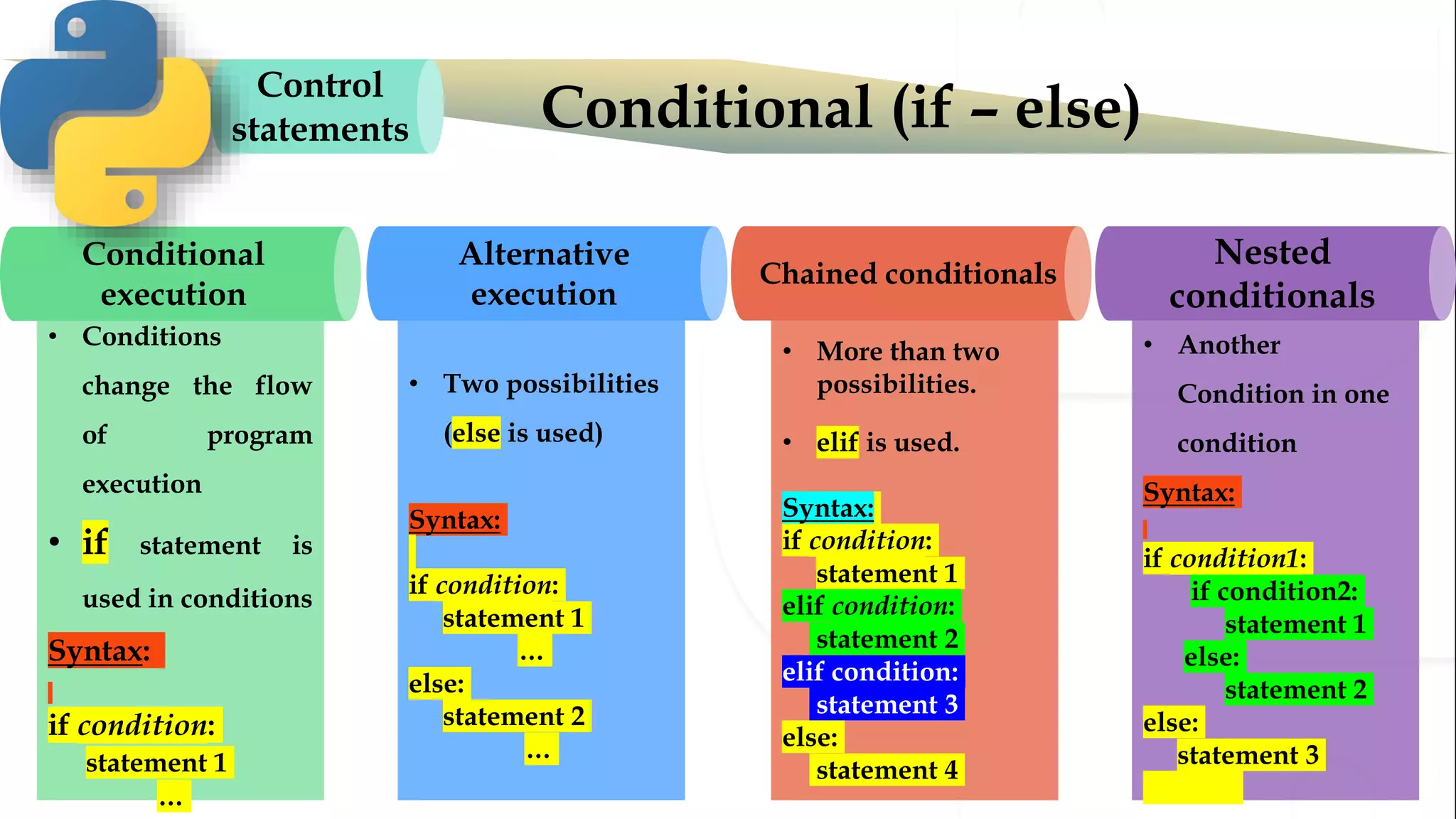
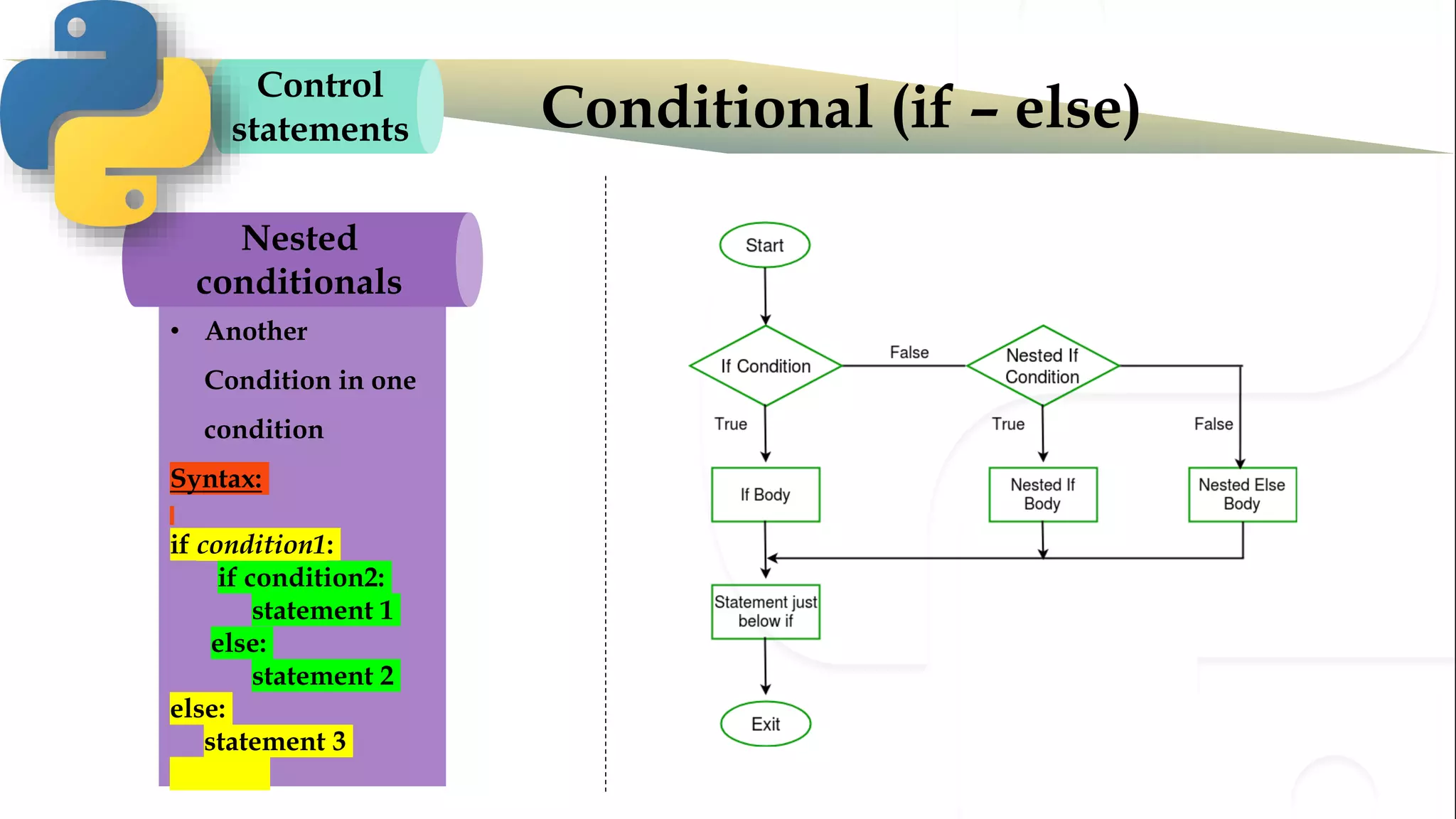
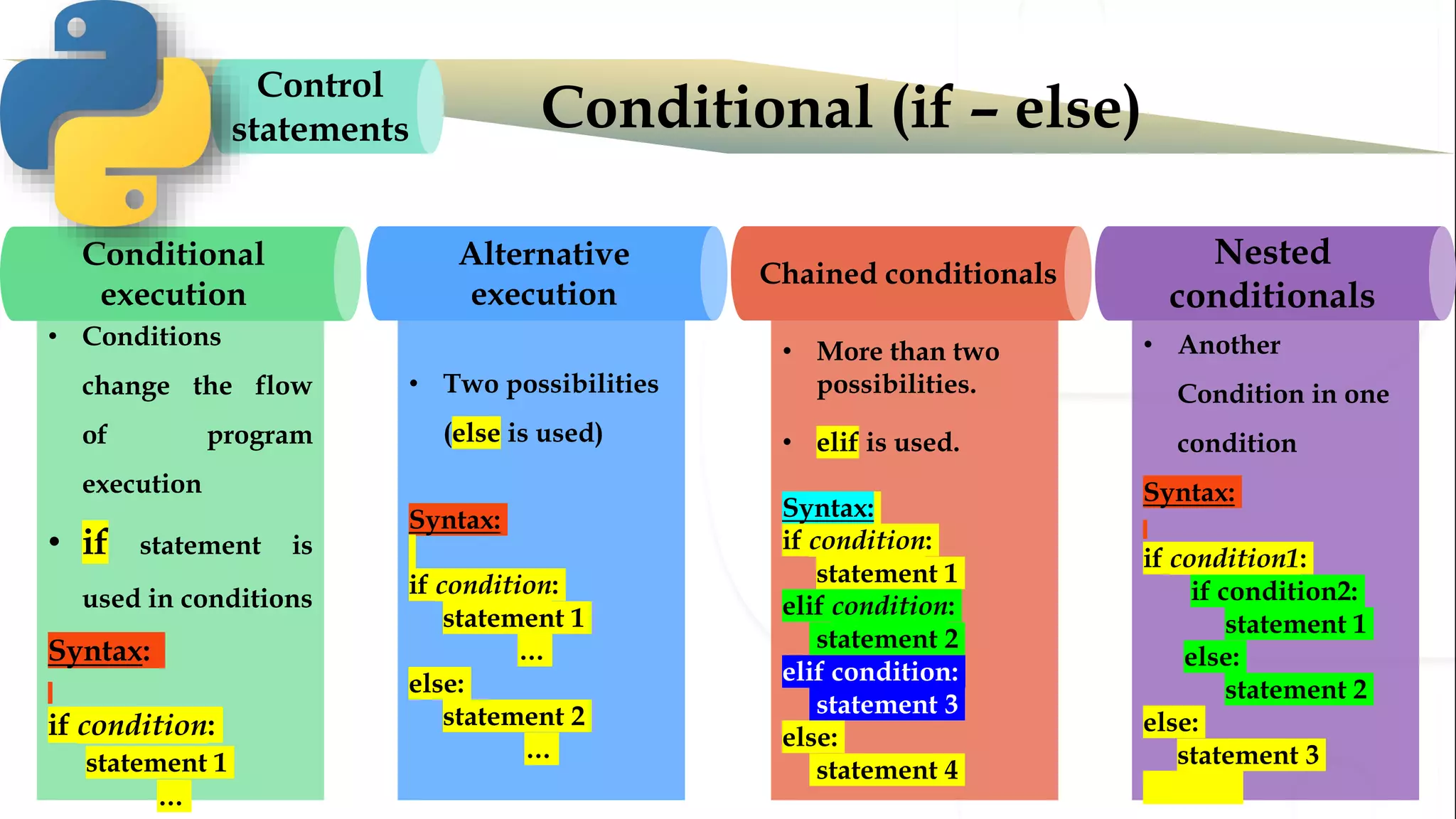
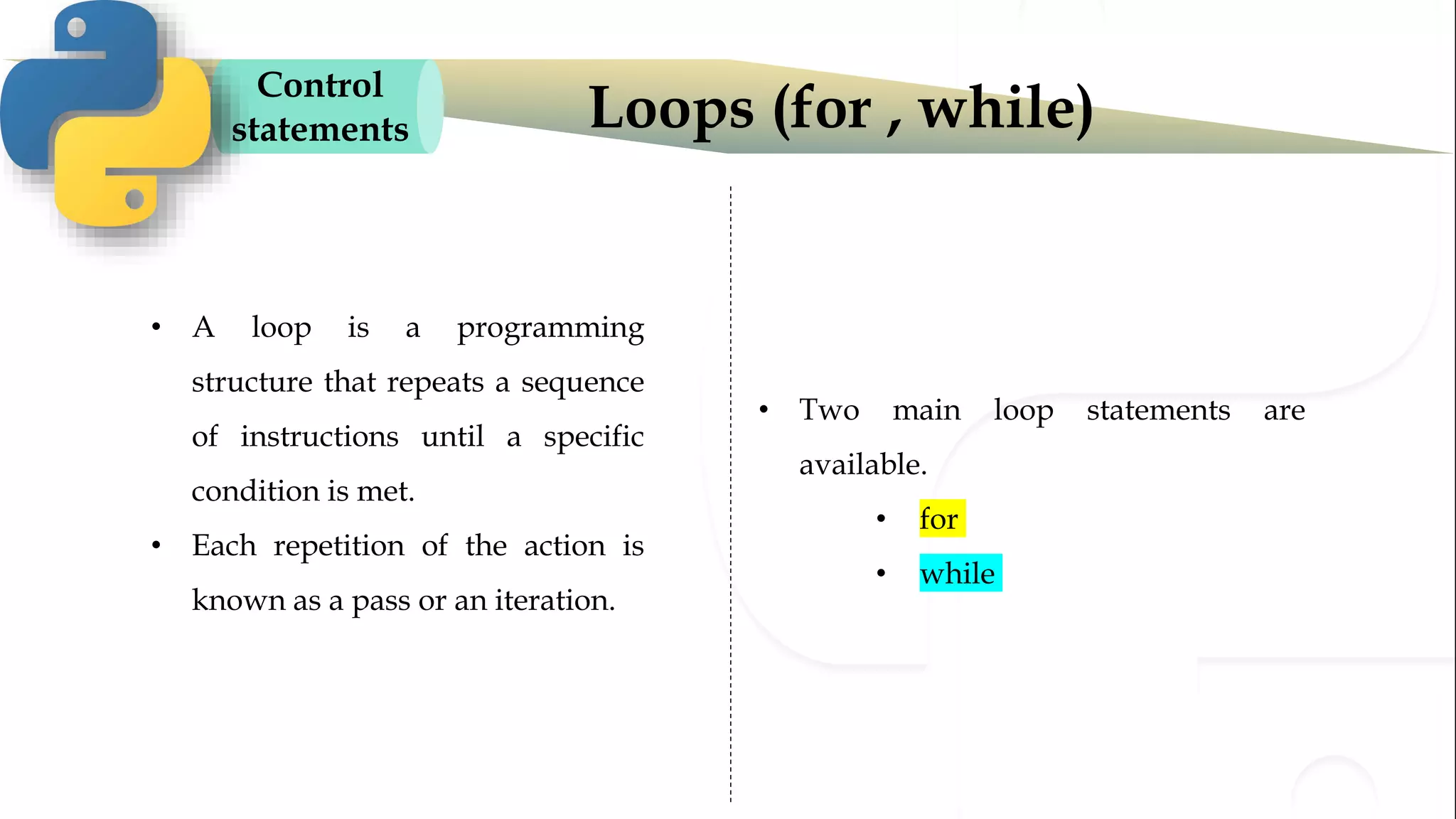
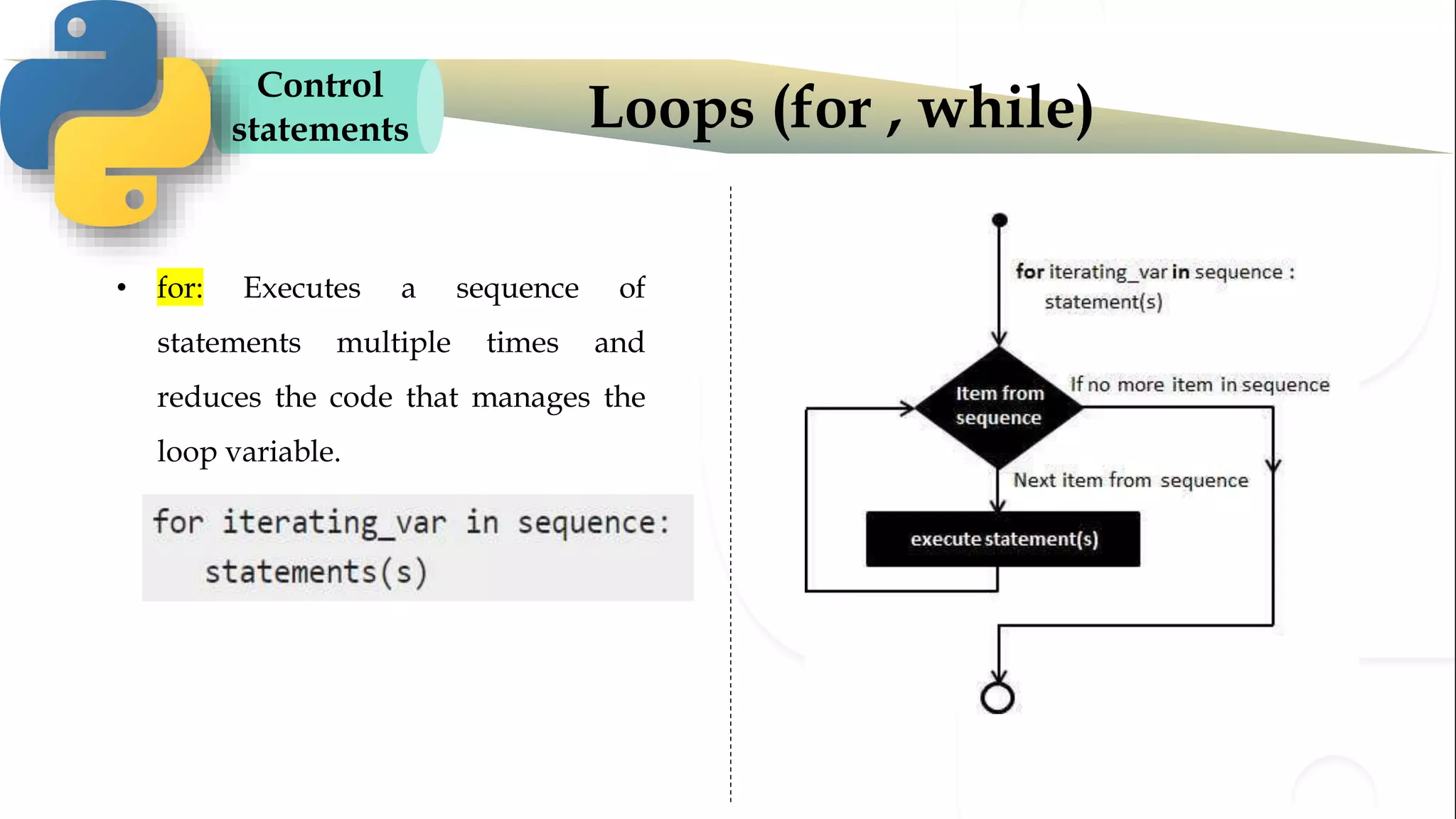
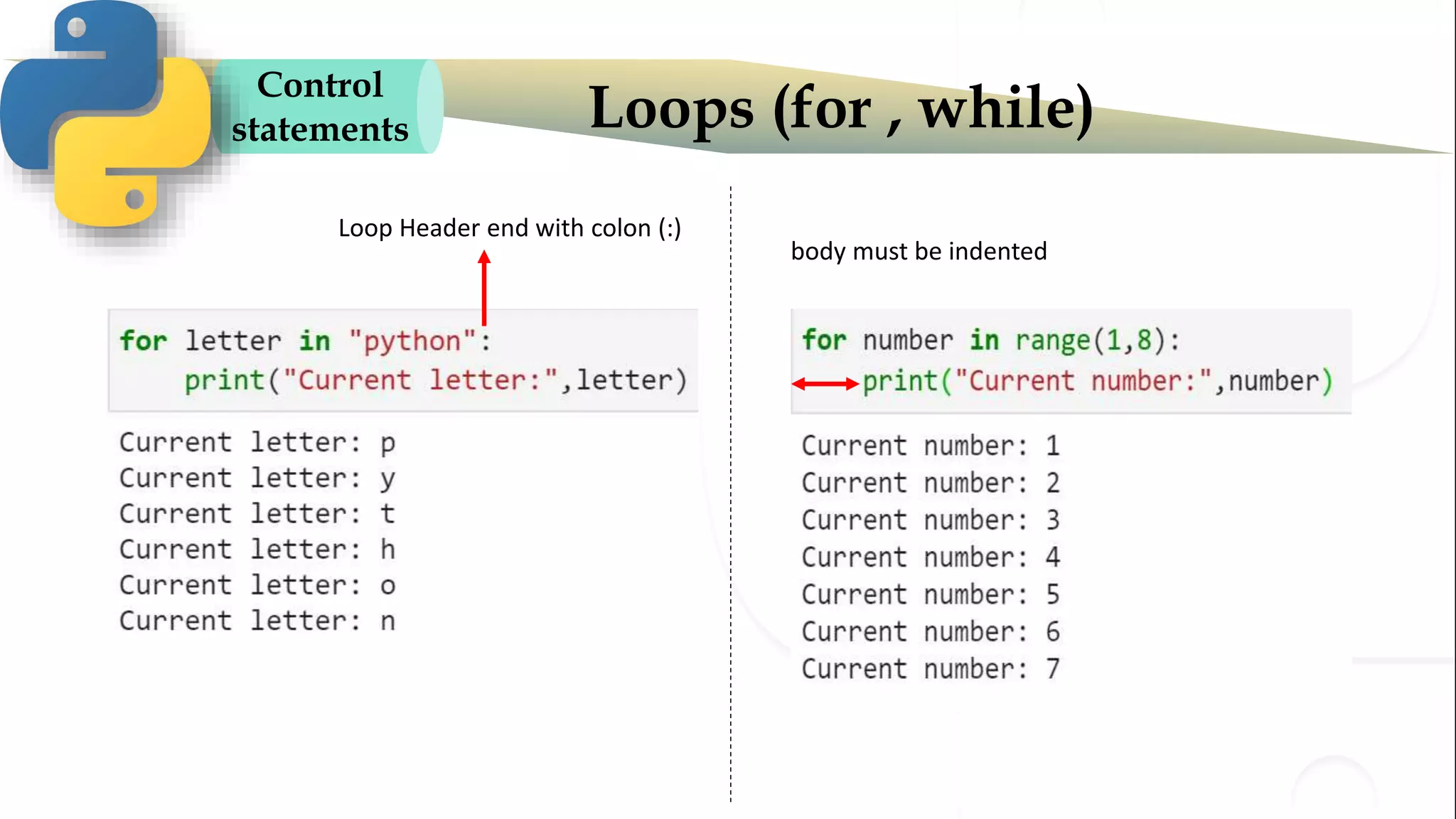
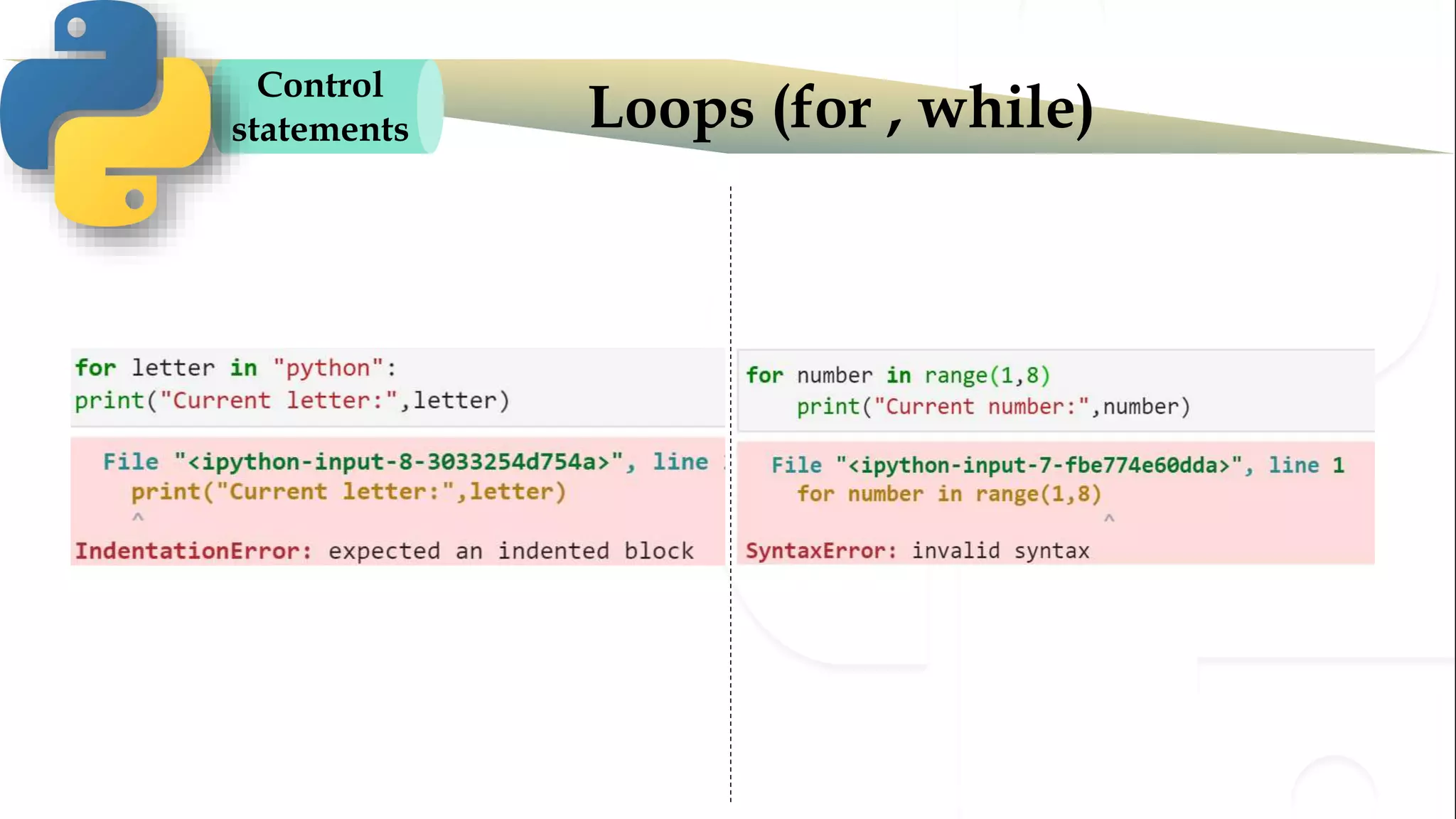
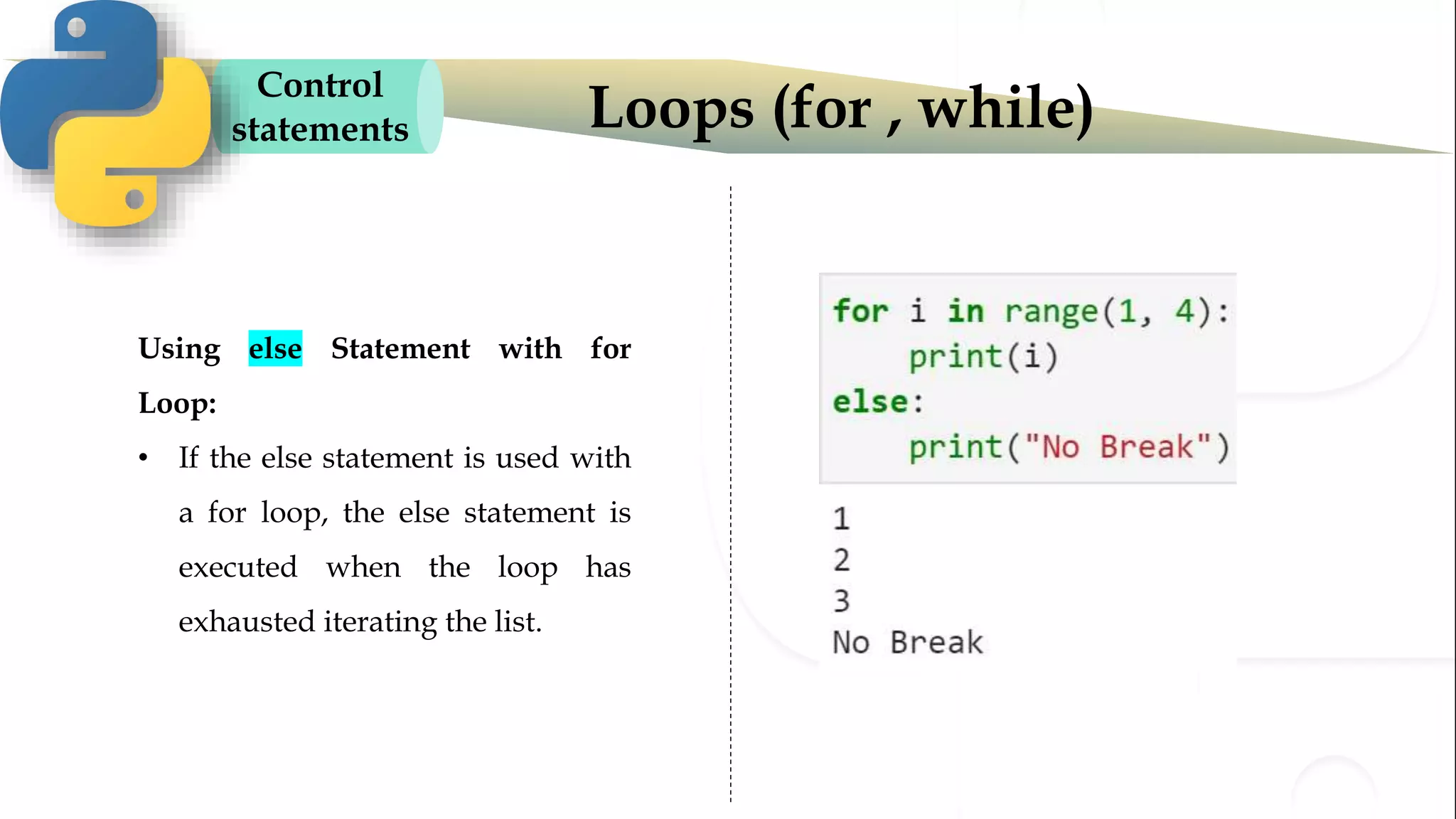
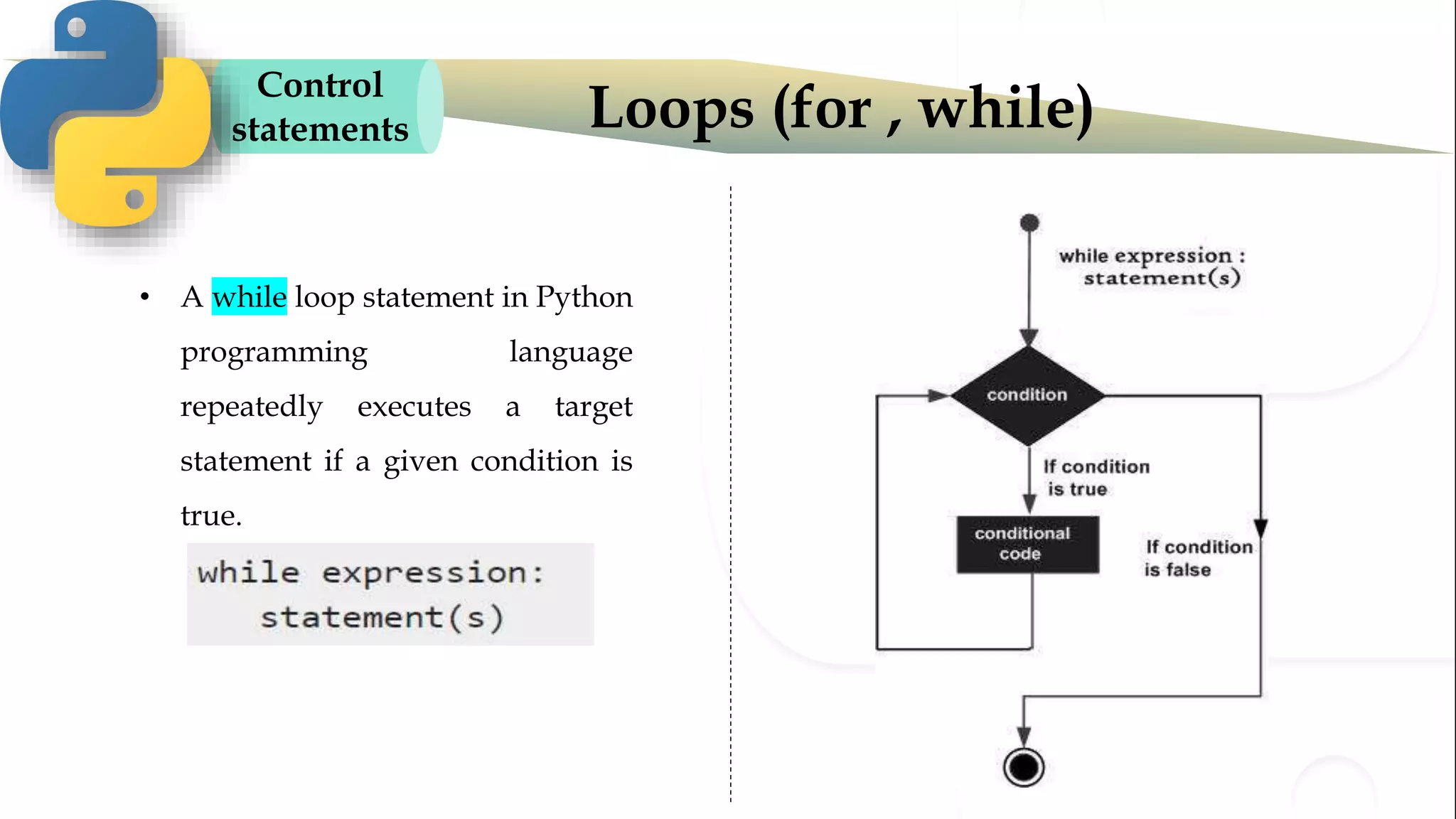
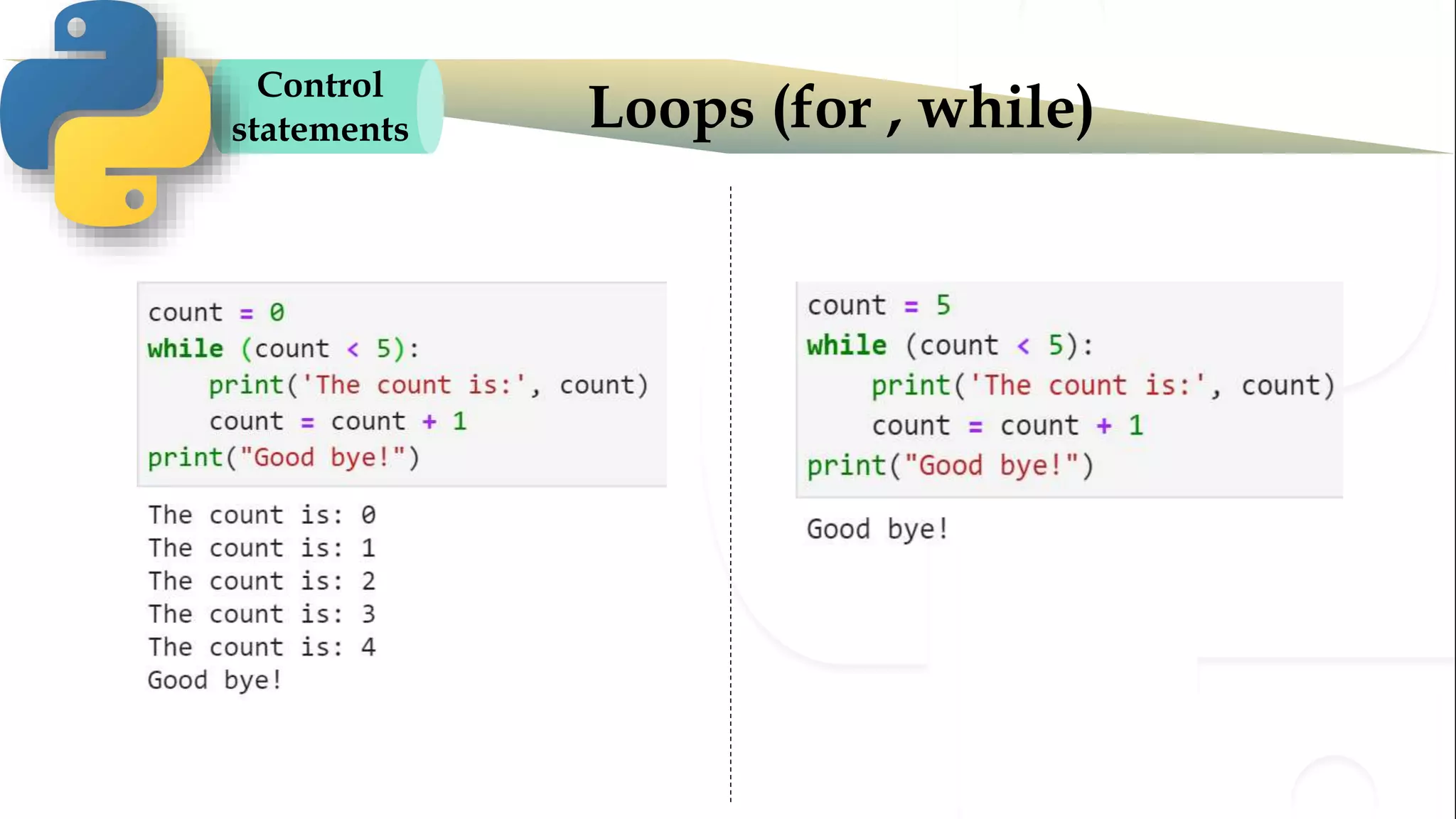
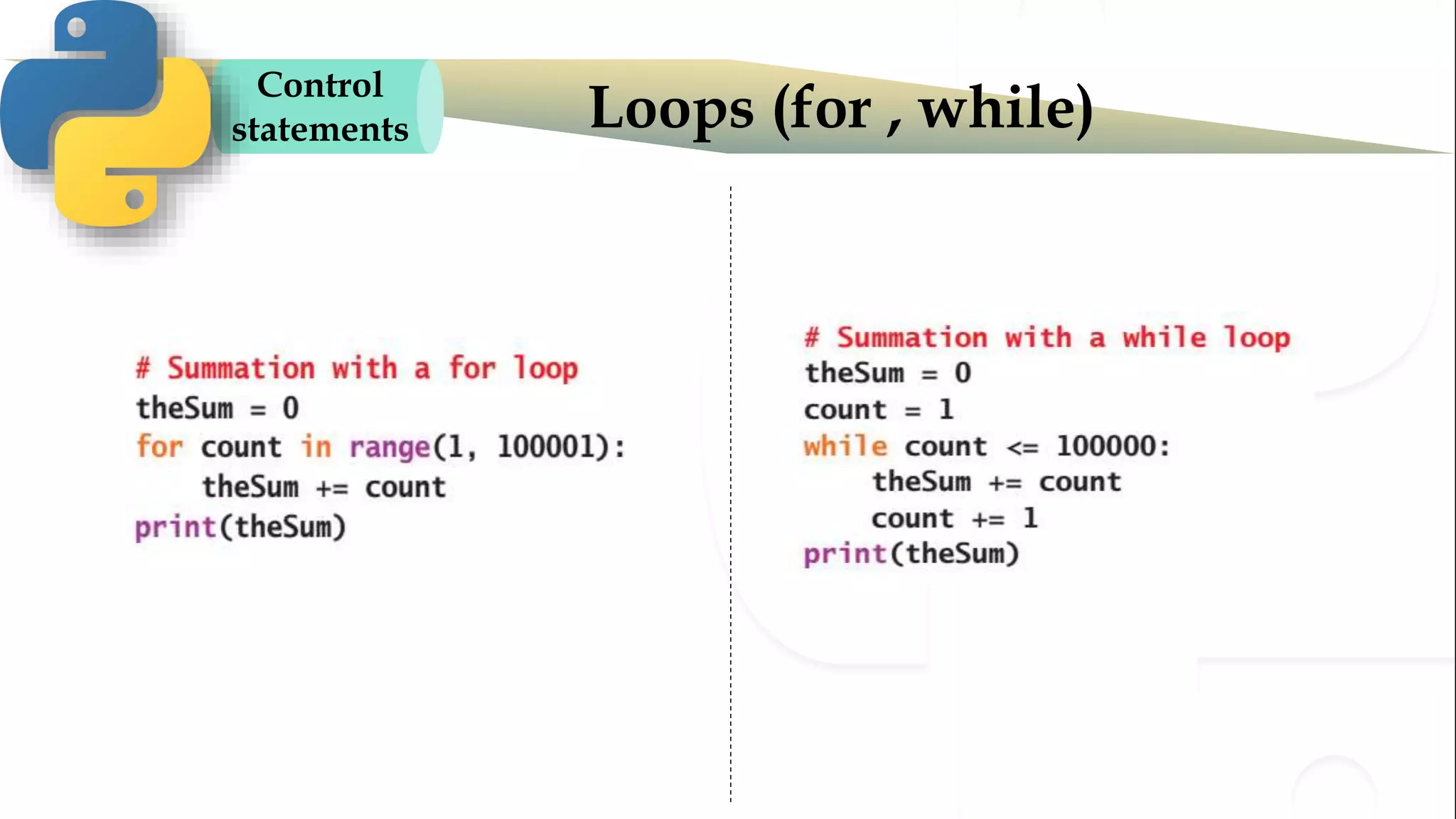
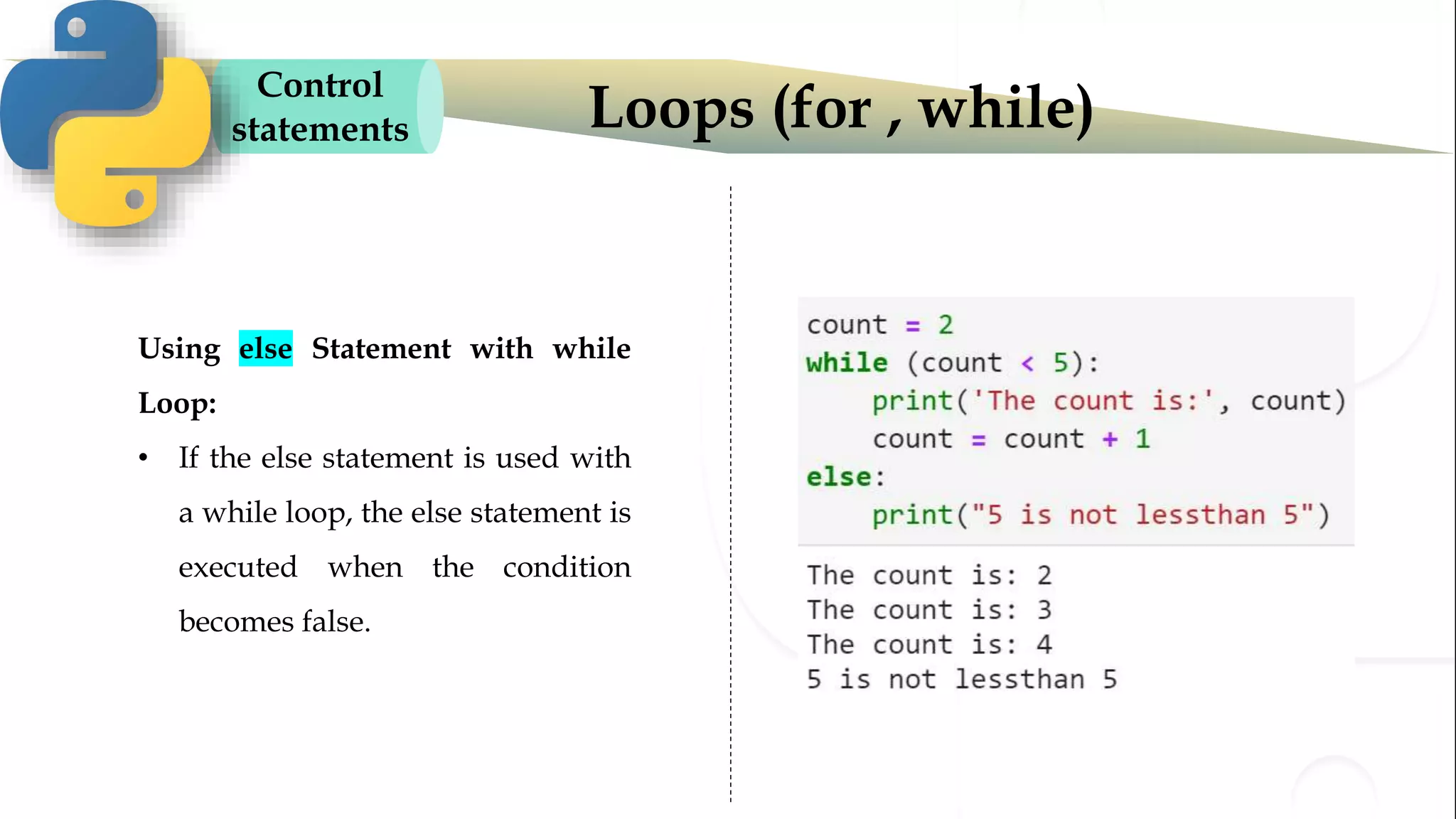
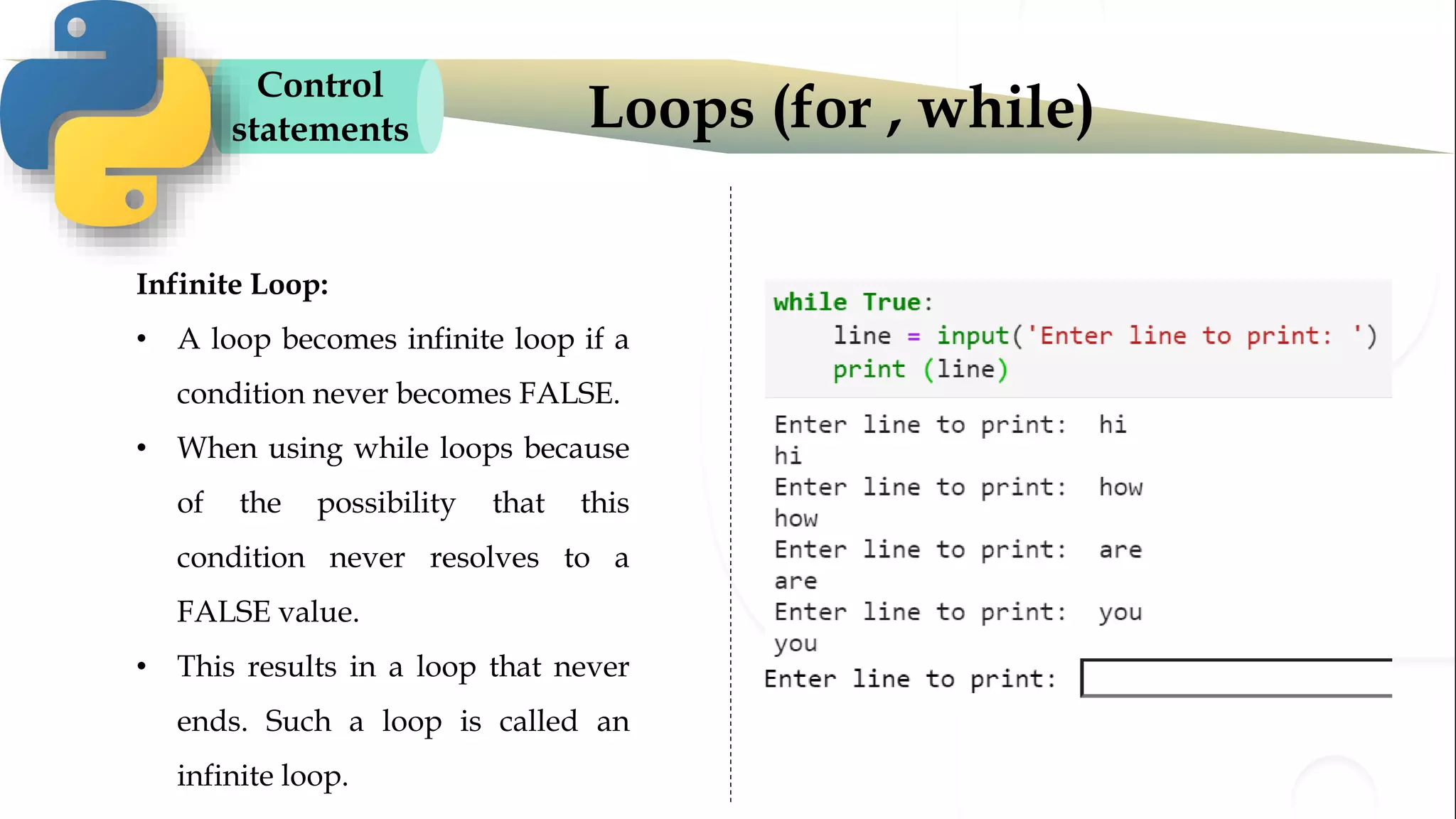
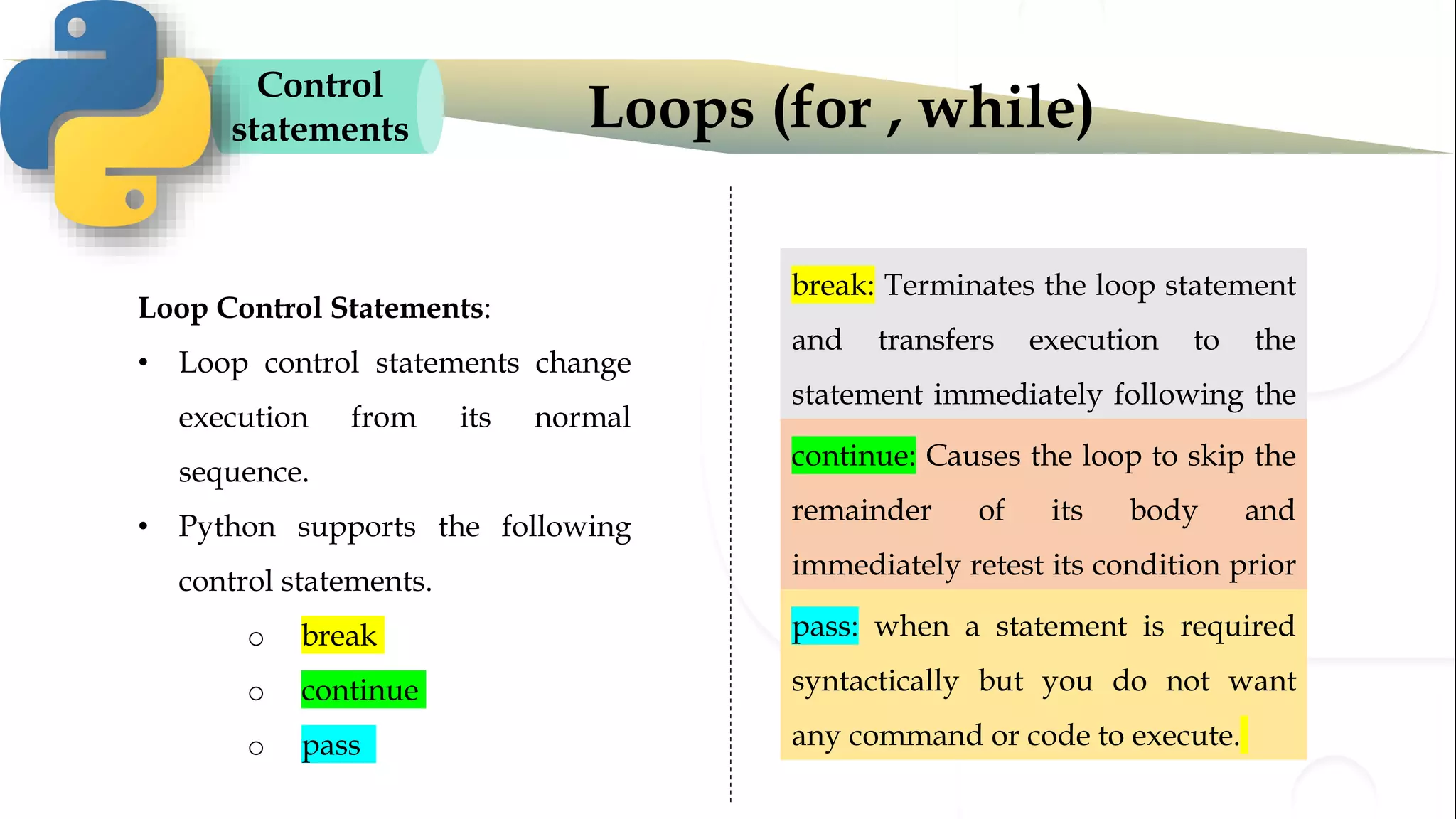
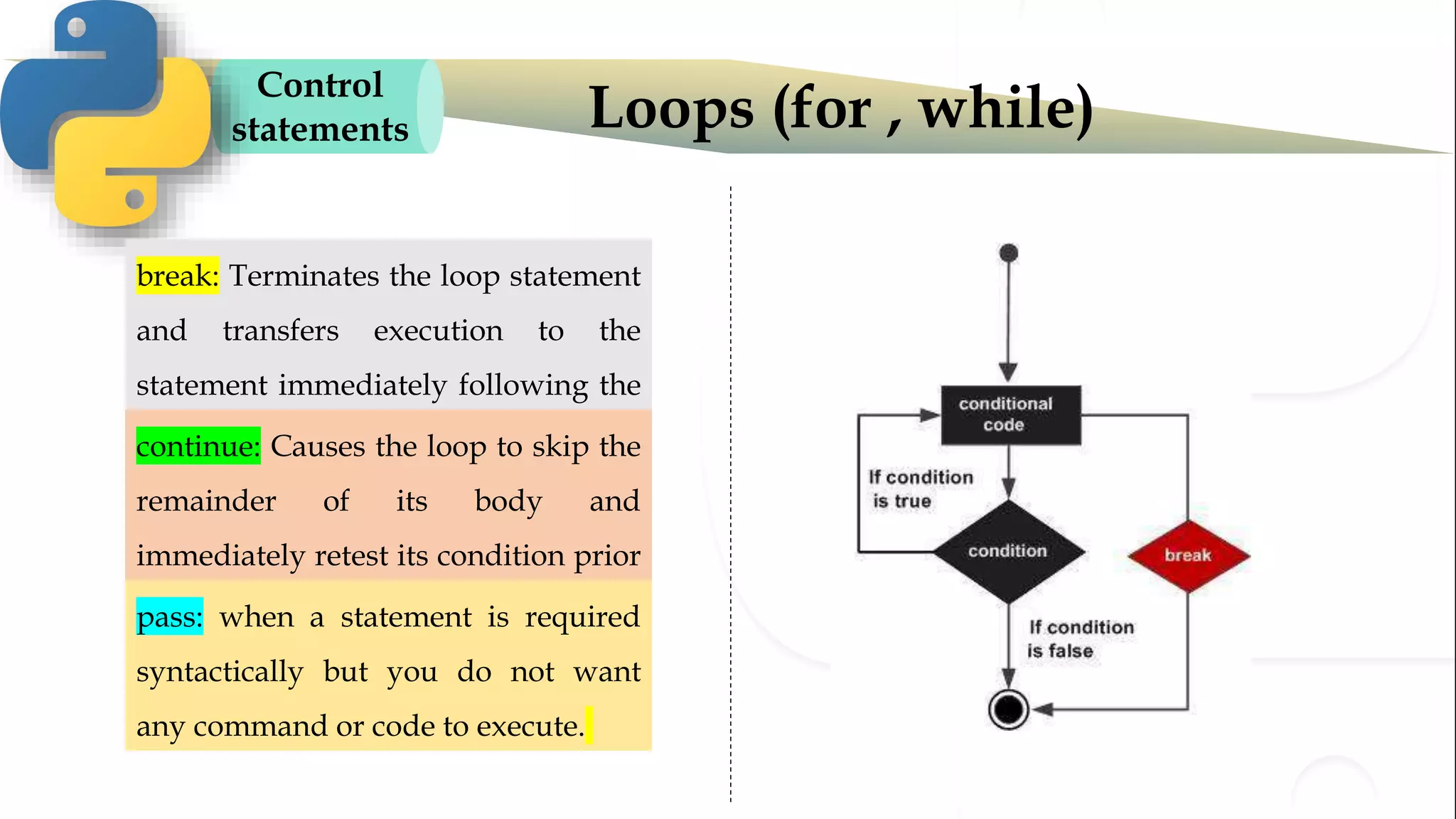
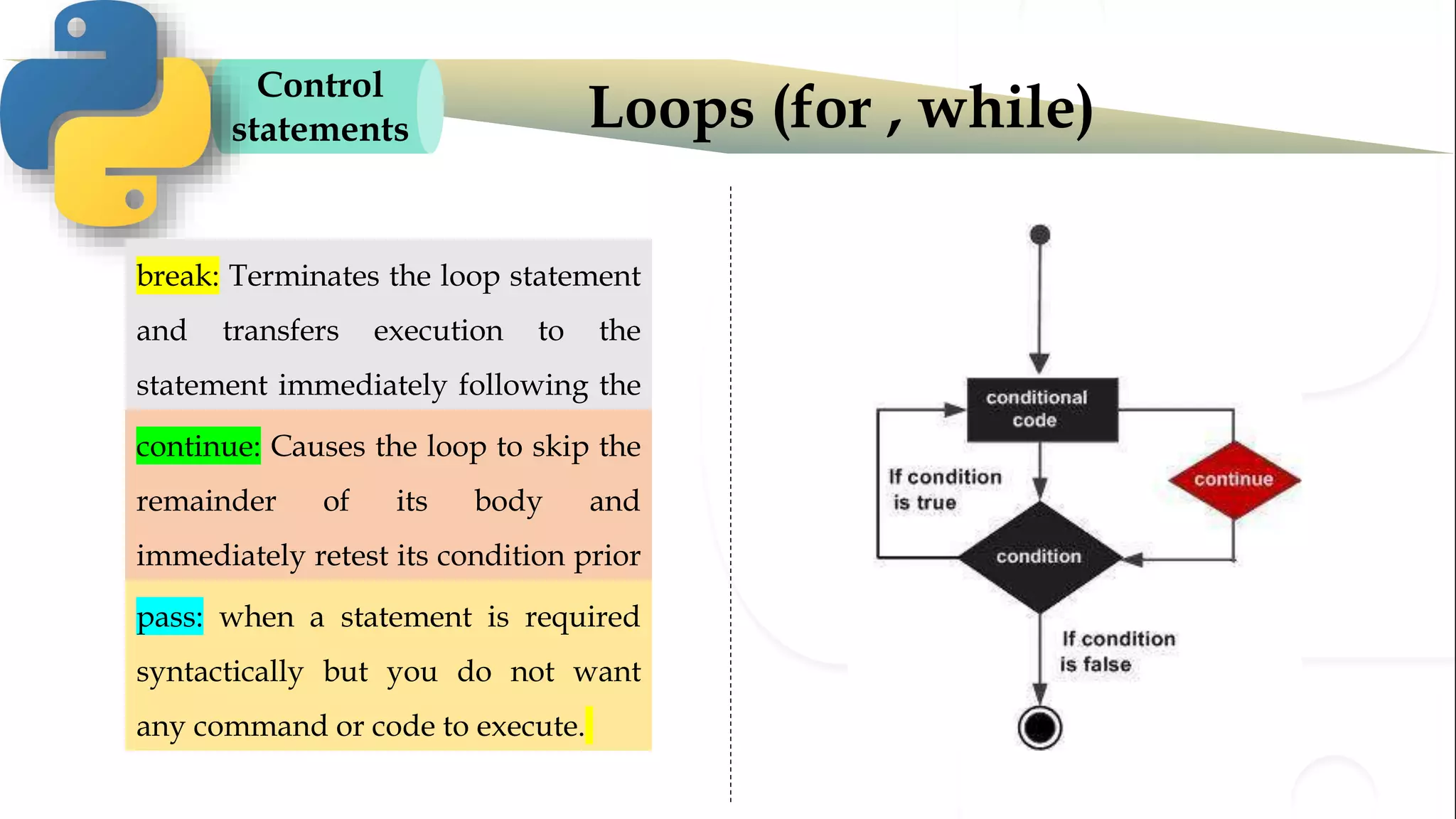
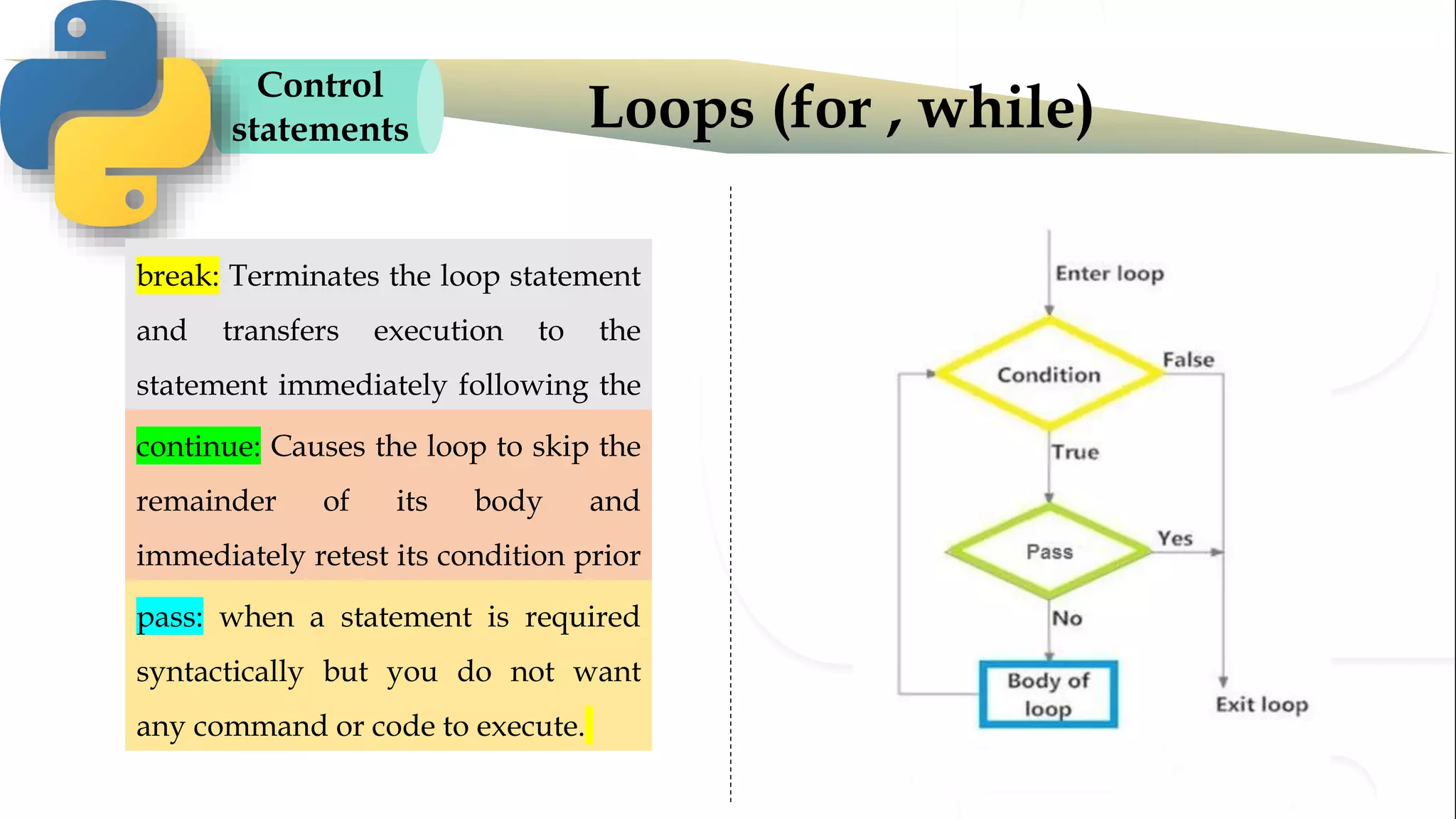
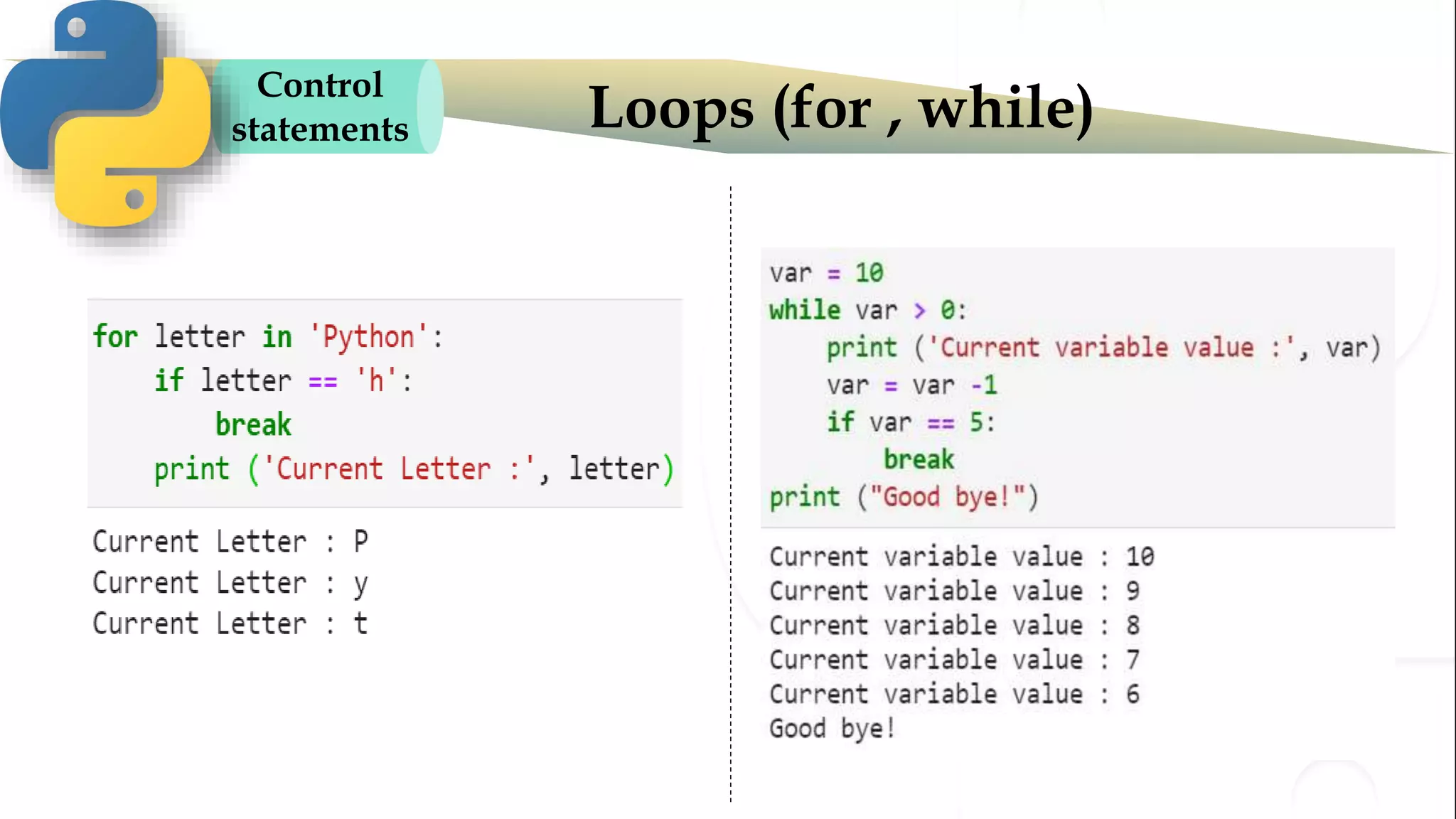
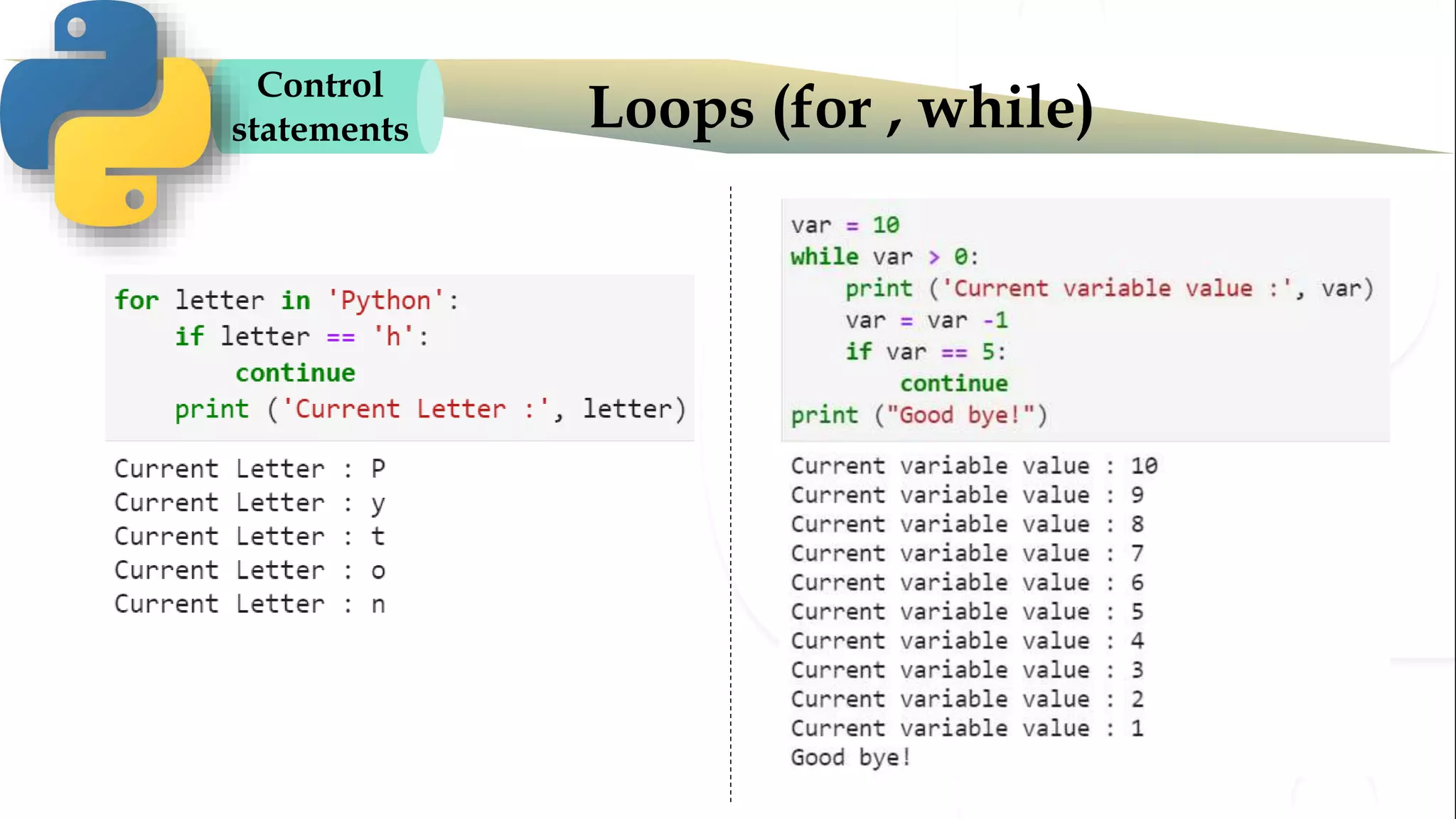
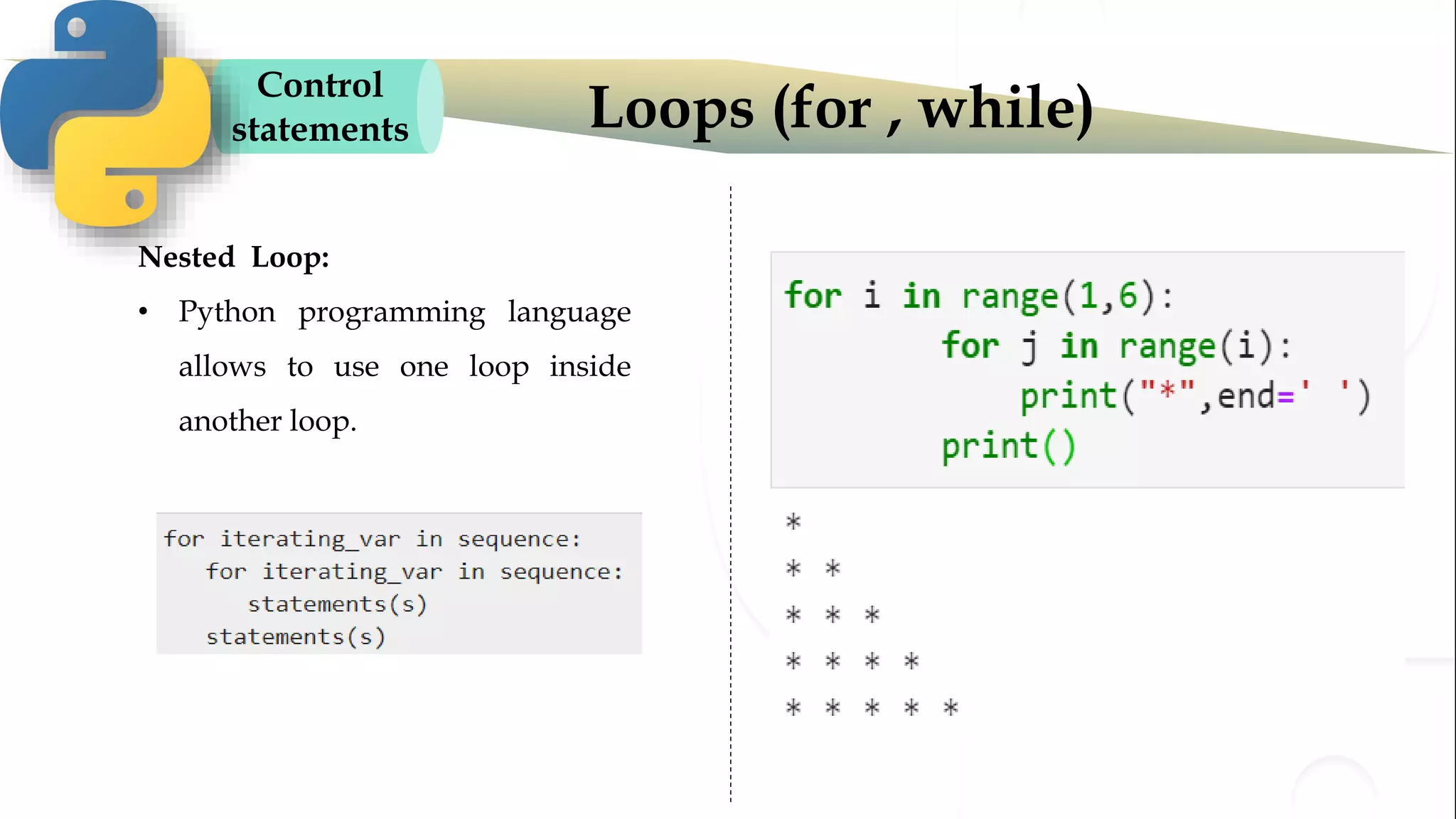
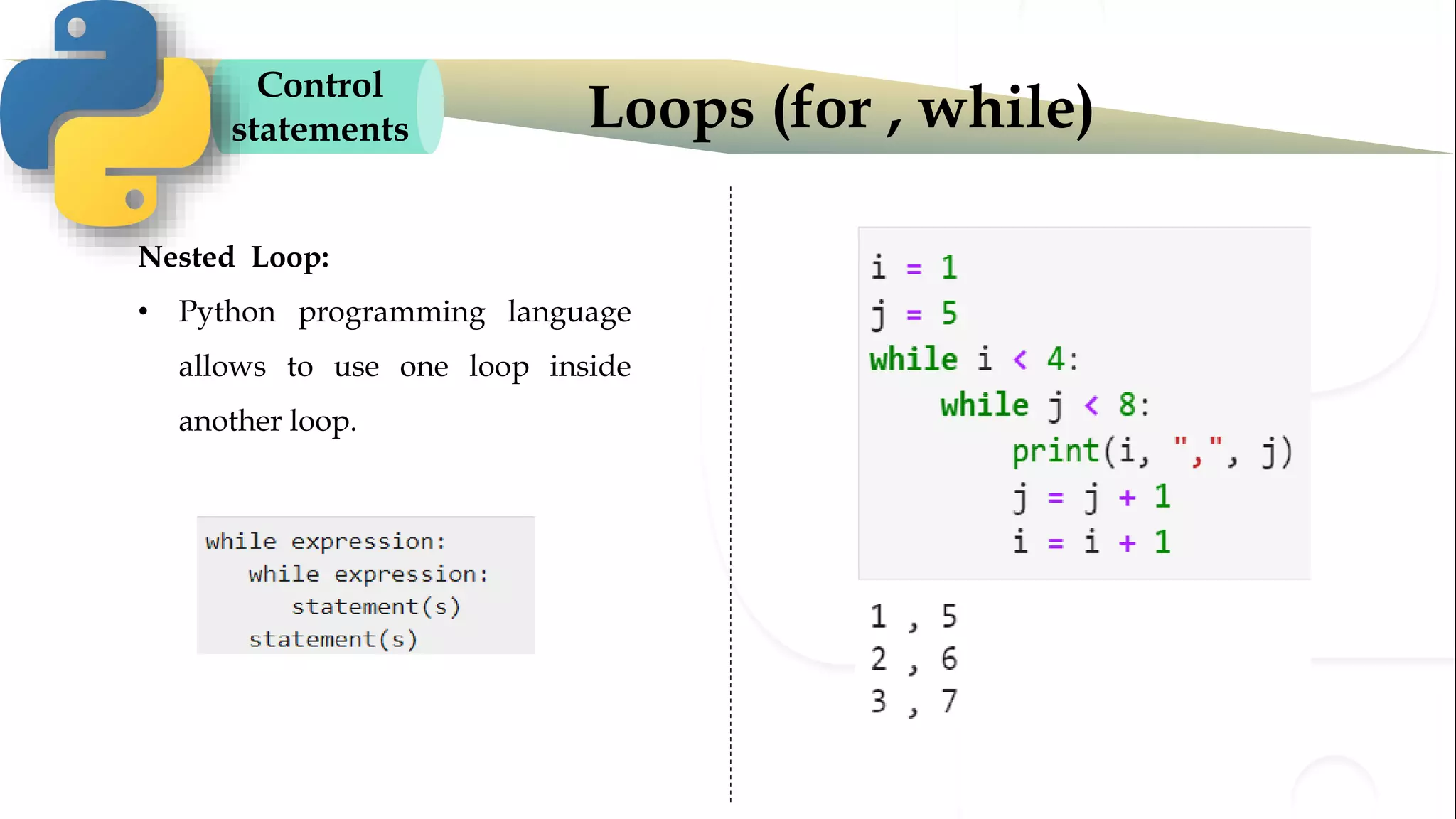
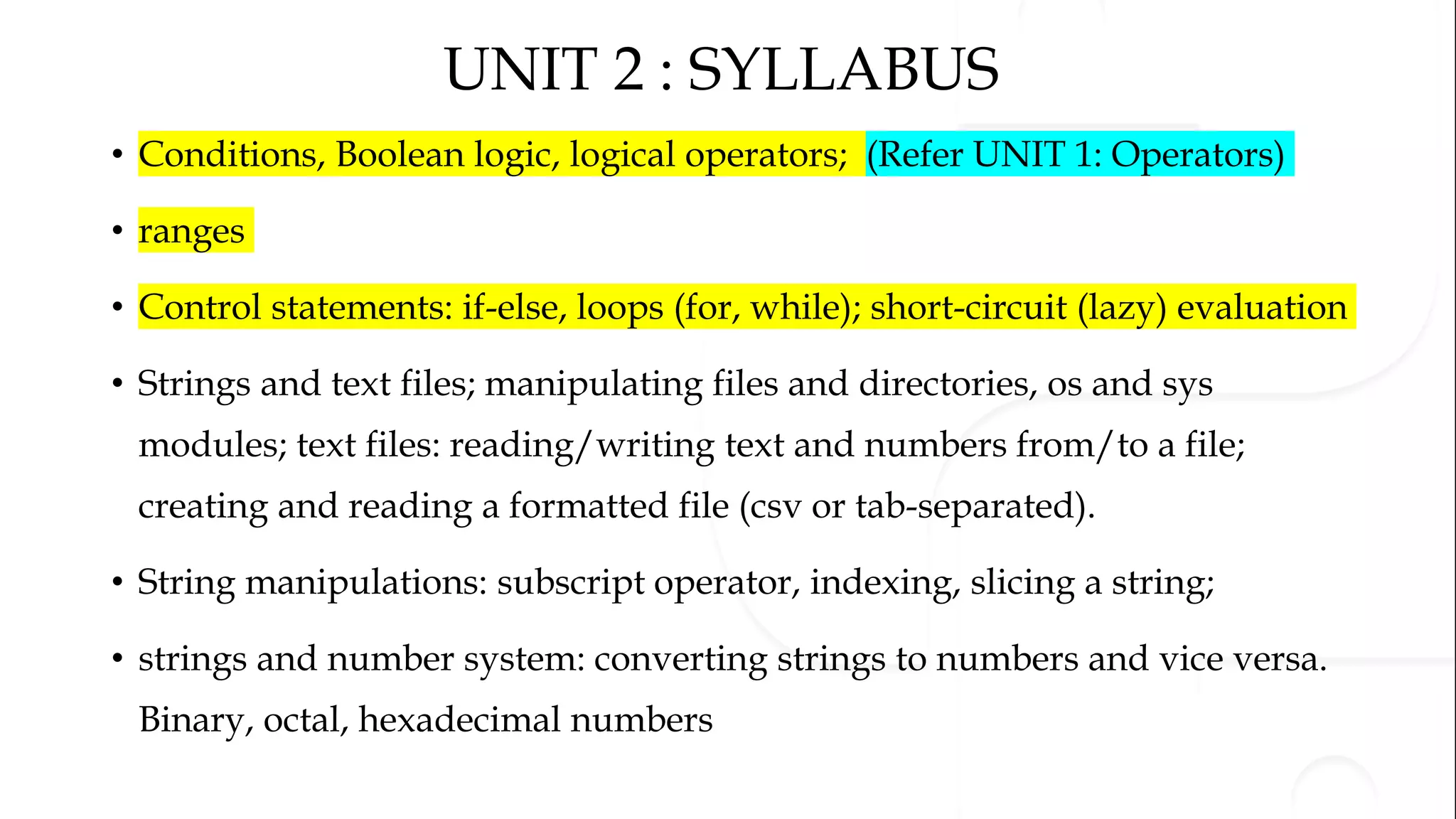
The document discusses various Python programming concepts including control statements, loops, strings, files and string manipulation. Control statements like if-else are used to conditionally execute code. Loops like for and while are used to repeatedly execute code while a condition is true. Strings can be manipulated using indexing, slicing and other string methods. Files can be read from and written to using file handling methods in Python.