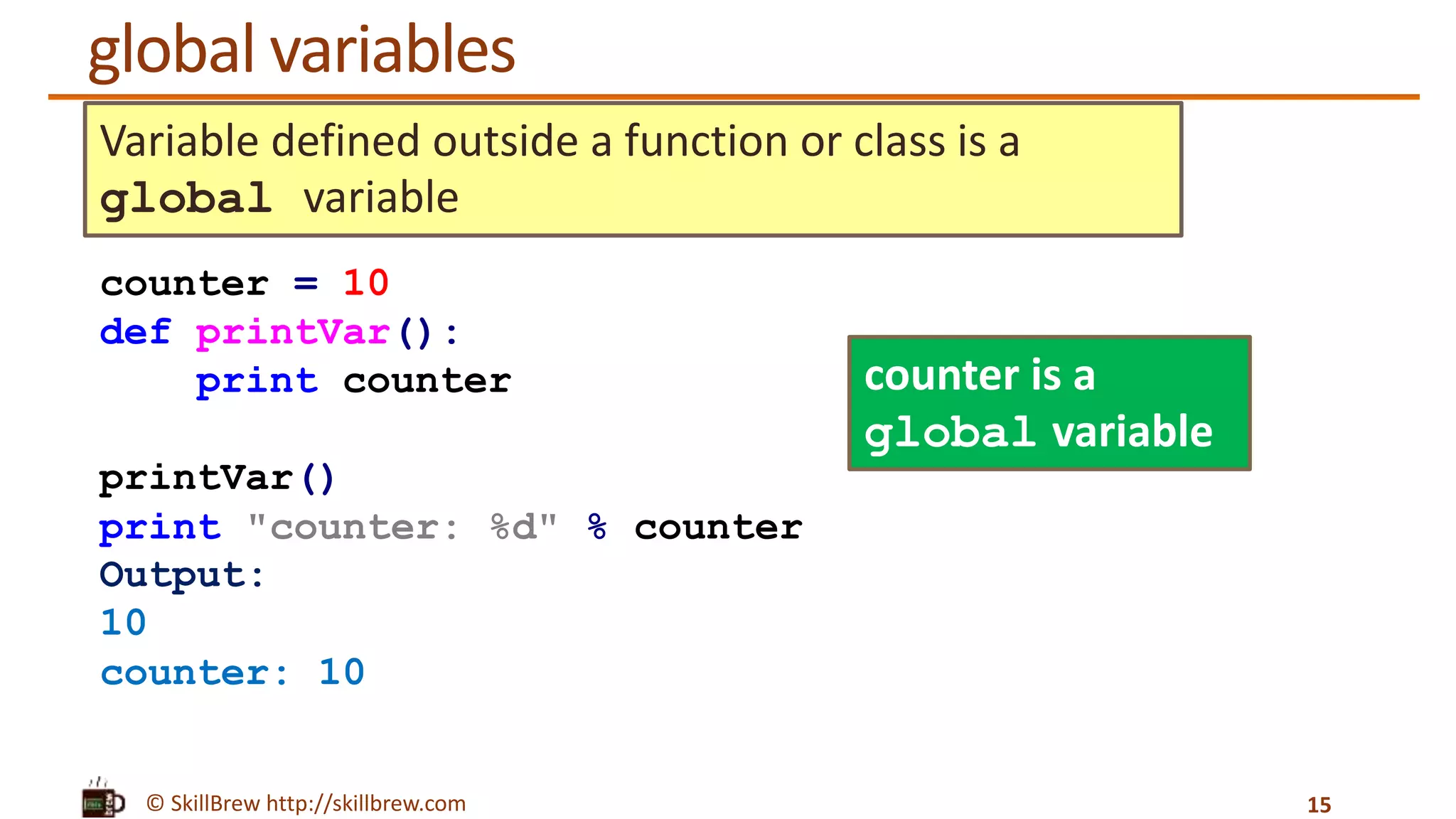
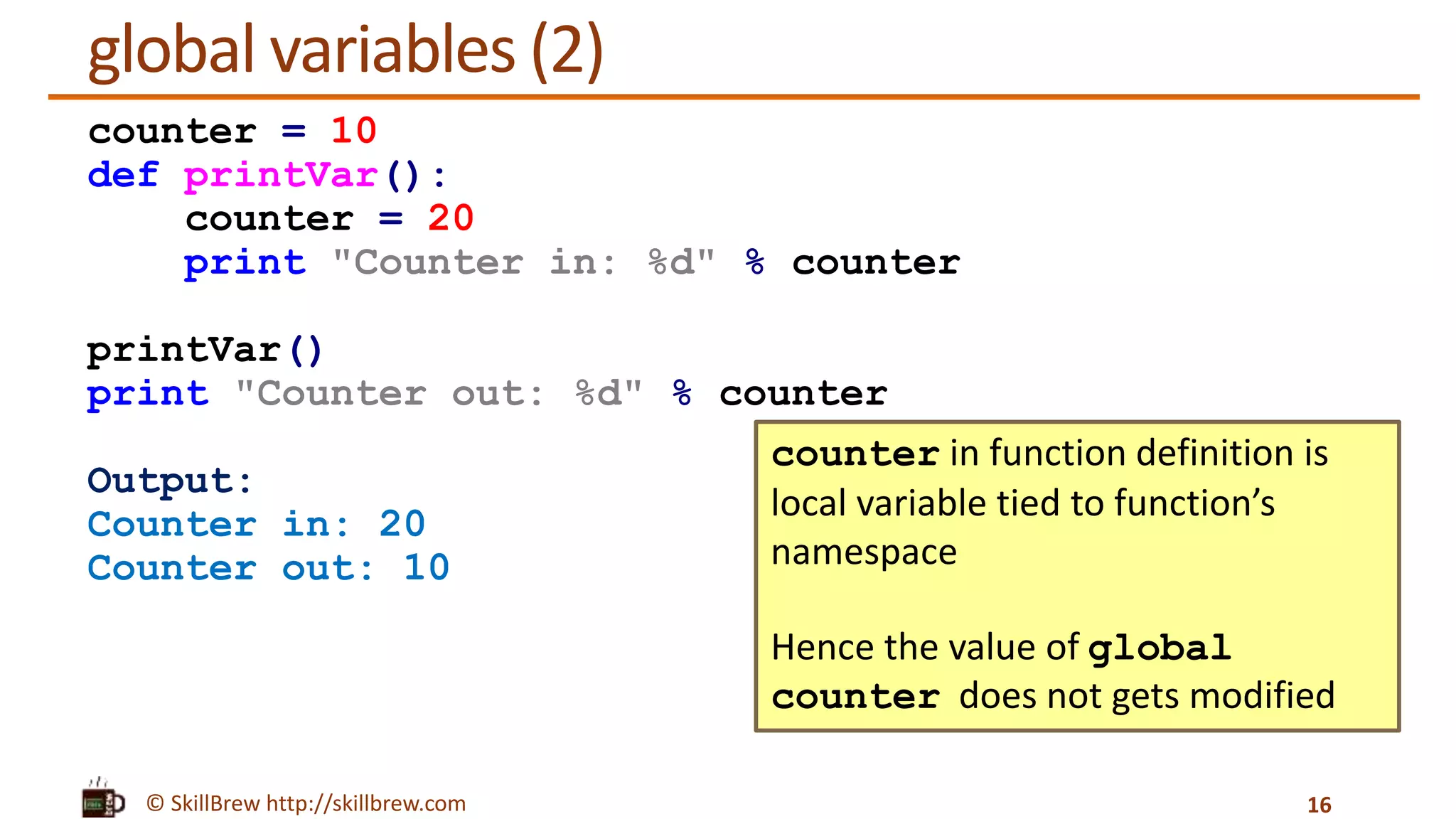
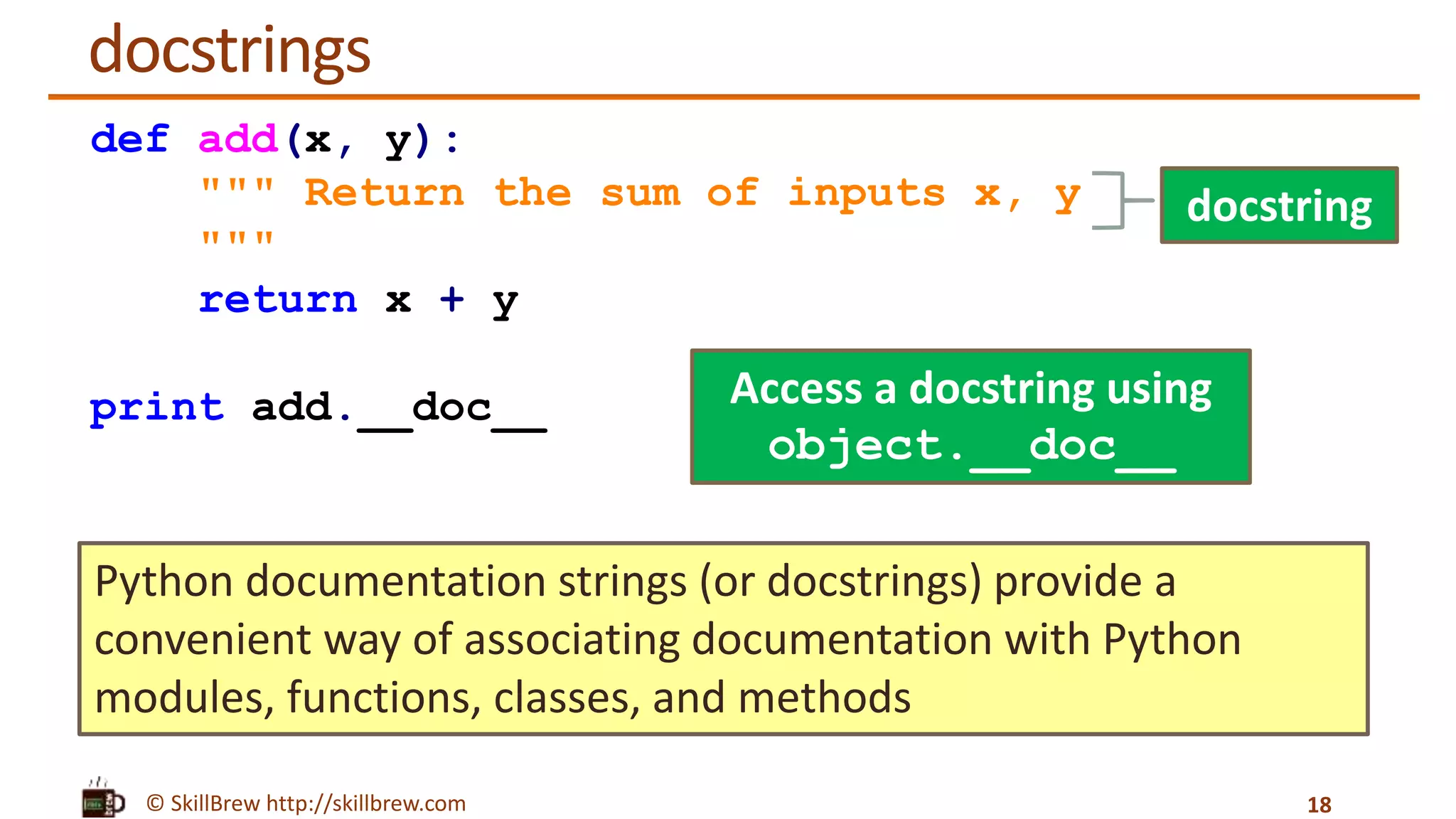
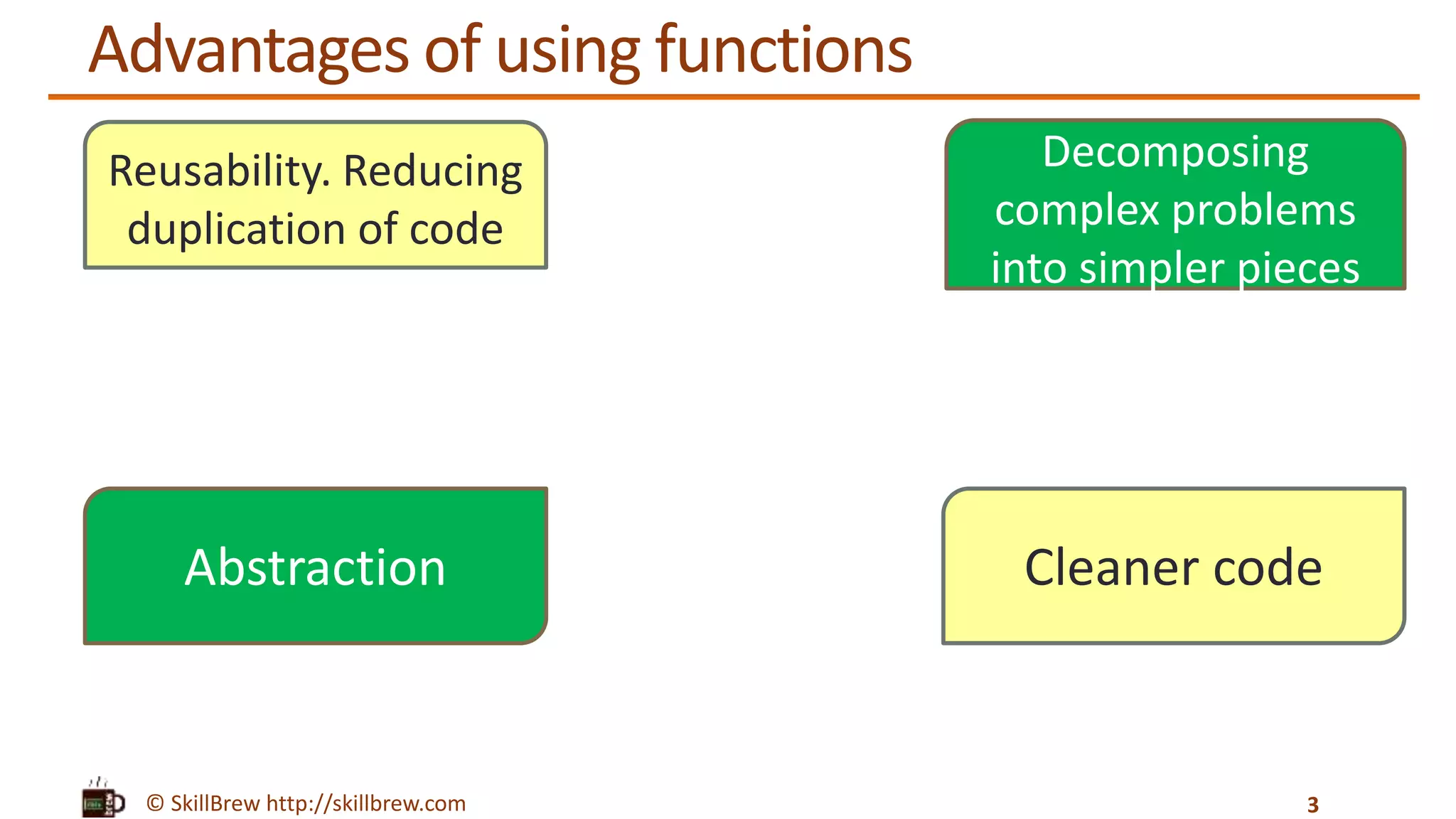
The document discusses the basics of functions in Python, including what a function is, the advantages of using functions, how to define and call functions, and how to use parameters, return values, global variables, default arguments, keyword arguments, and docstrings when working with functions. Key points covered include how functions allow code reuse and decomposition of complex problems, how to define a function using the def keyword, how to call a defined function by name, and how docstrings provide documentation for functions and other objects.

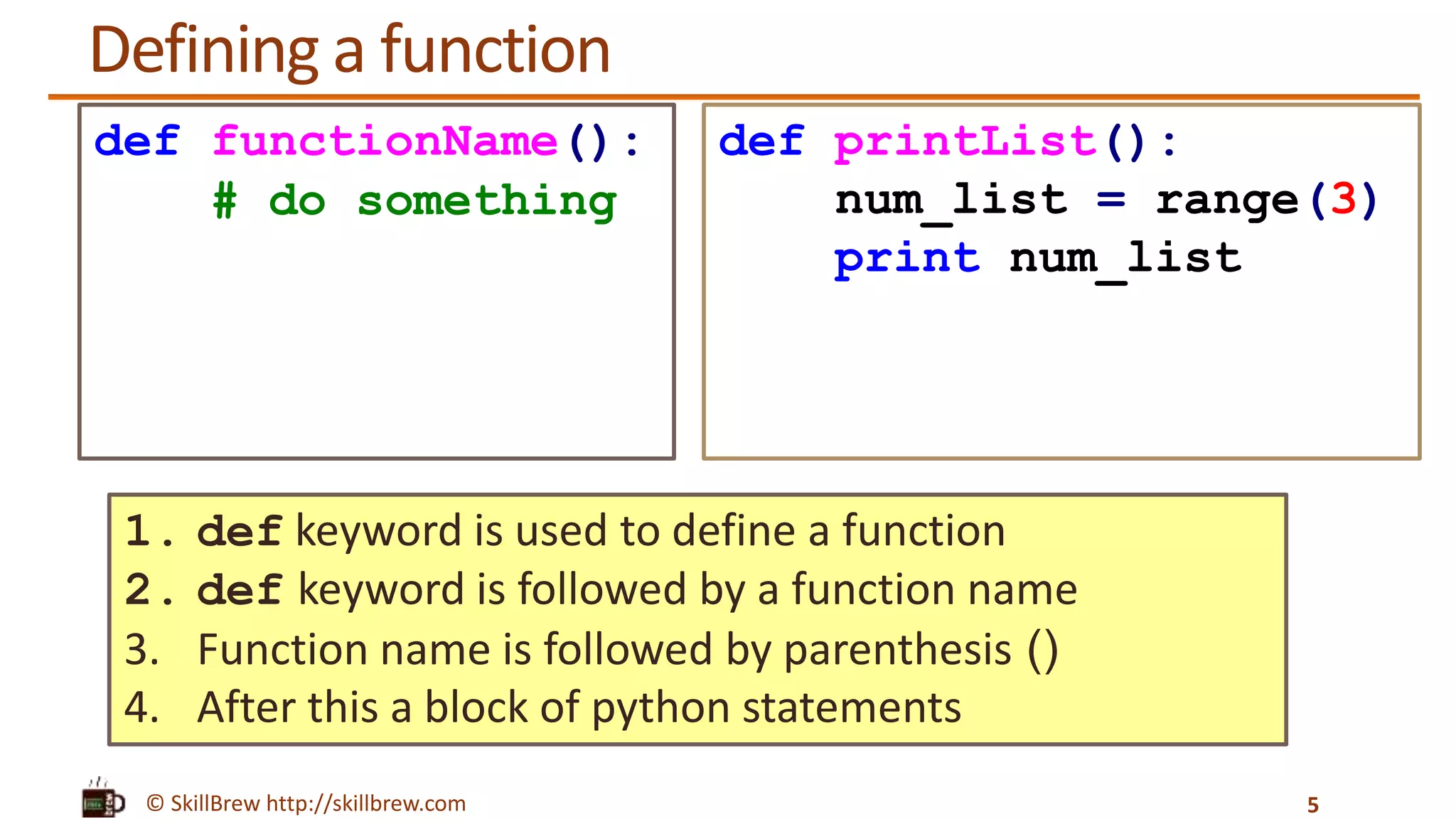
![© SkillBrew http://skillbrew.com Calling a Function 6 def printList(): num_list = range(3) print num_list printList() Output: [0, 1, 2] To call a function, we specify the function name with the round brackets Call to function](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonprogrammingessentials-m17-functions-140819043207-phpapp01/75/Python-Programming-Essentials-M17-Functions-6-2048.jpg)
![© SkillBrew http://skillbrew.com return keyword 7 def printList(): num_list = range(3) return num_list my_list = printList() print my_list Output: [0, 1, 2] 1. The return keyword is used to return values from a function 2. A function implicitly returns None by default even if you don’t use return keyword](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonprogrammingessentials-m17-functions-140819043207-phpapp01/75/Python-Programming-Essentials-M17-Functions-7-2048.jpg)
![© SkillBrew http://skillbrew.com Parameterized functions 8 def printList(upper_limit): num_list = range(upper_limit) print "list: %s" % num_list printList(5) printList(2) Output: list: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4] list: [0, 1] 1. Names given in the function definition are called parameters 2. The values you supply in the function call are called arguments](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonprogrammingessentials-m17-functions-140819043207-phpapp01/75/Python-Programming-Essentials-M17-Functions-8-2048.jpg)
![© SkillBrew http://skillbrew.com Default arguments 9 def printList(upper_limit=4): print "upper limit: %d" % upper_limit num_list = range(upper_limit) print "list: %s" % num_list printList(5) printList() Output: upper limit: 5 list: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4] upper limit: 4 list: [0, 1, 2, 3] value 4 1. When function is called without any arguments default value is used 2. During a function call if argument is passed then the passed value is used](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonprogrammingessentials-m17-functions-140819043207-phpapp01/75/Python-Programming-Essentials-M17-Functions-9-2048.jpg)
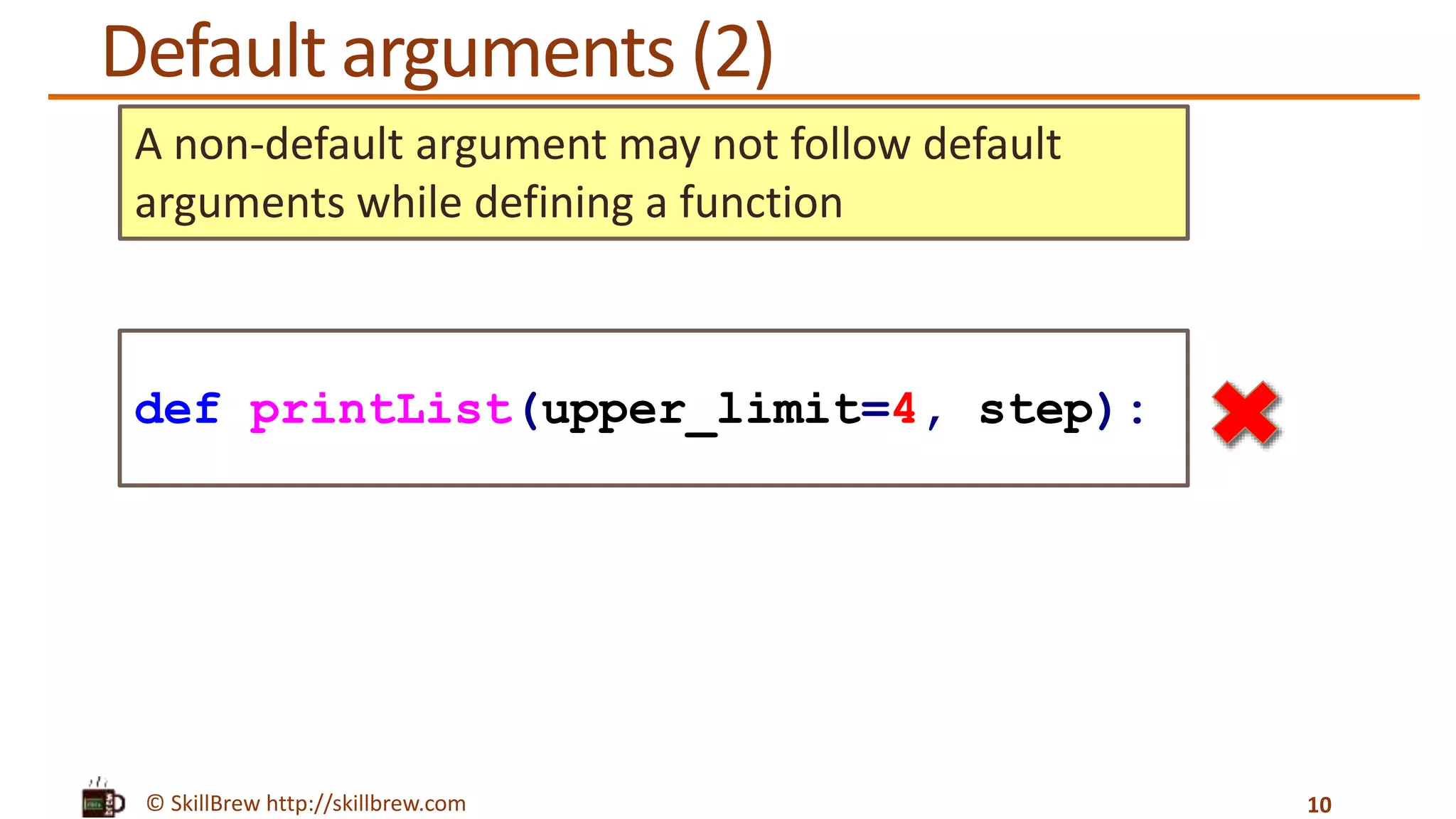
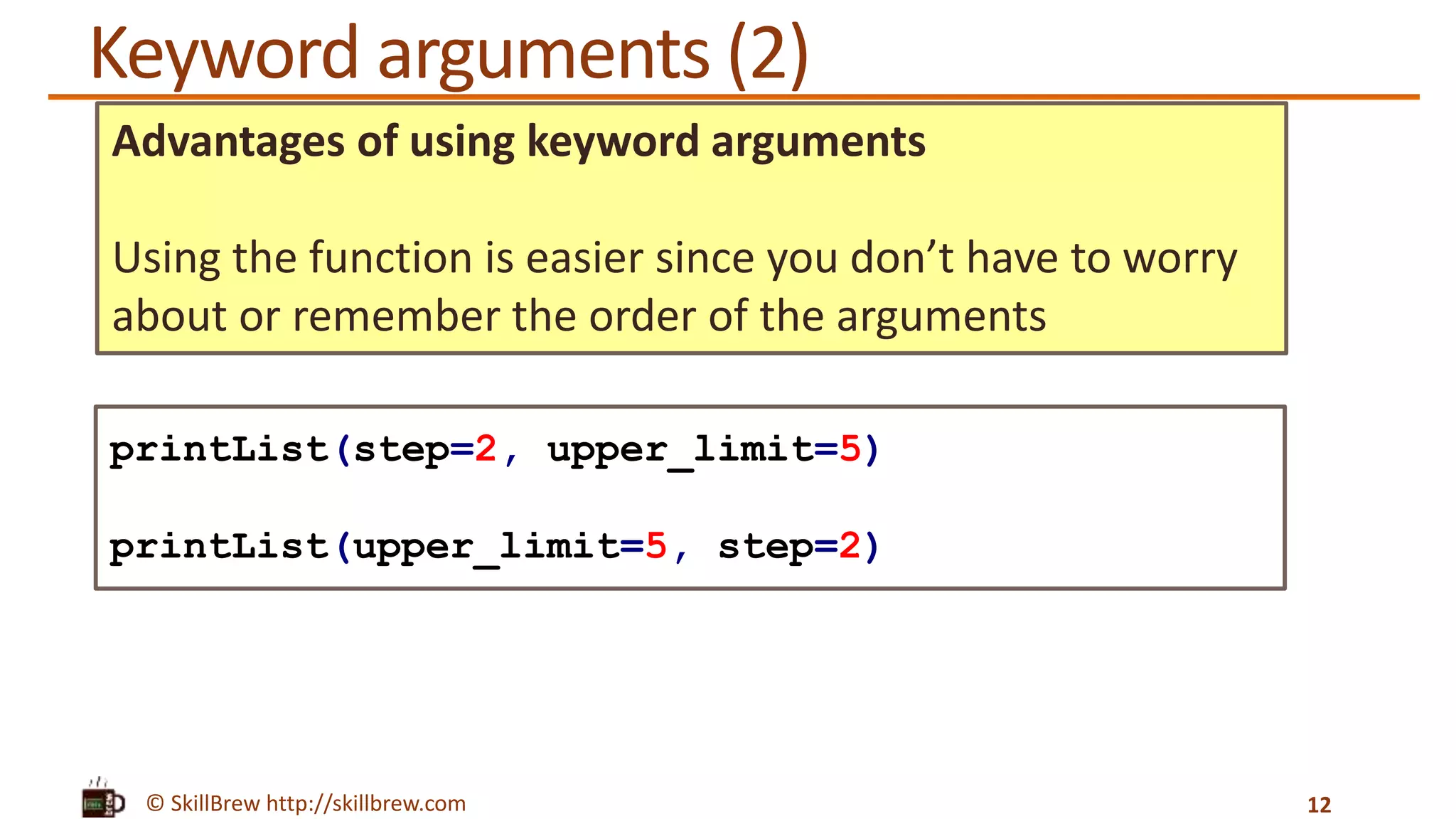
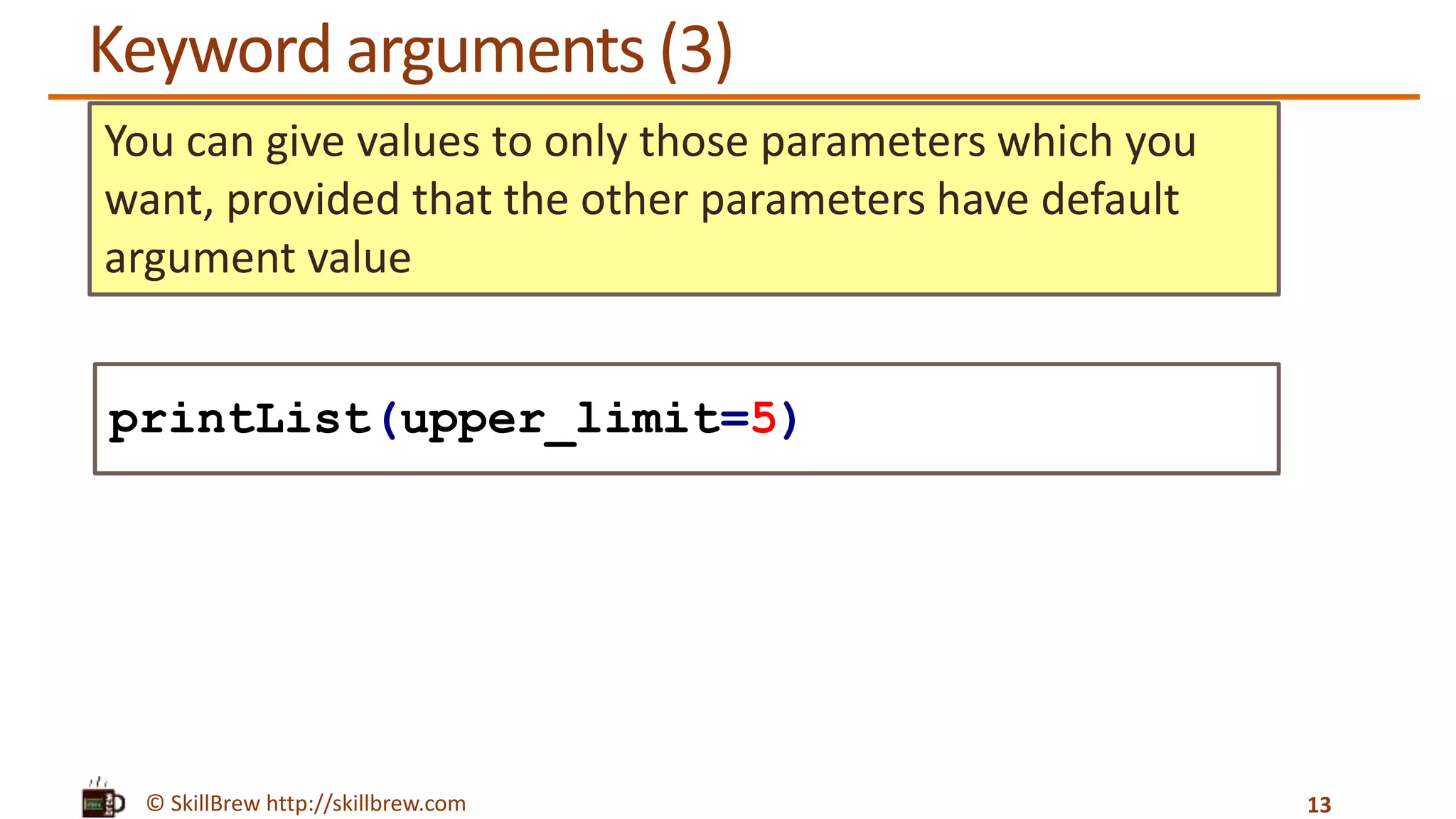
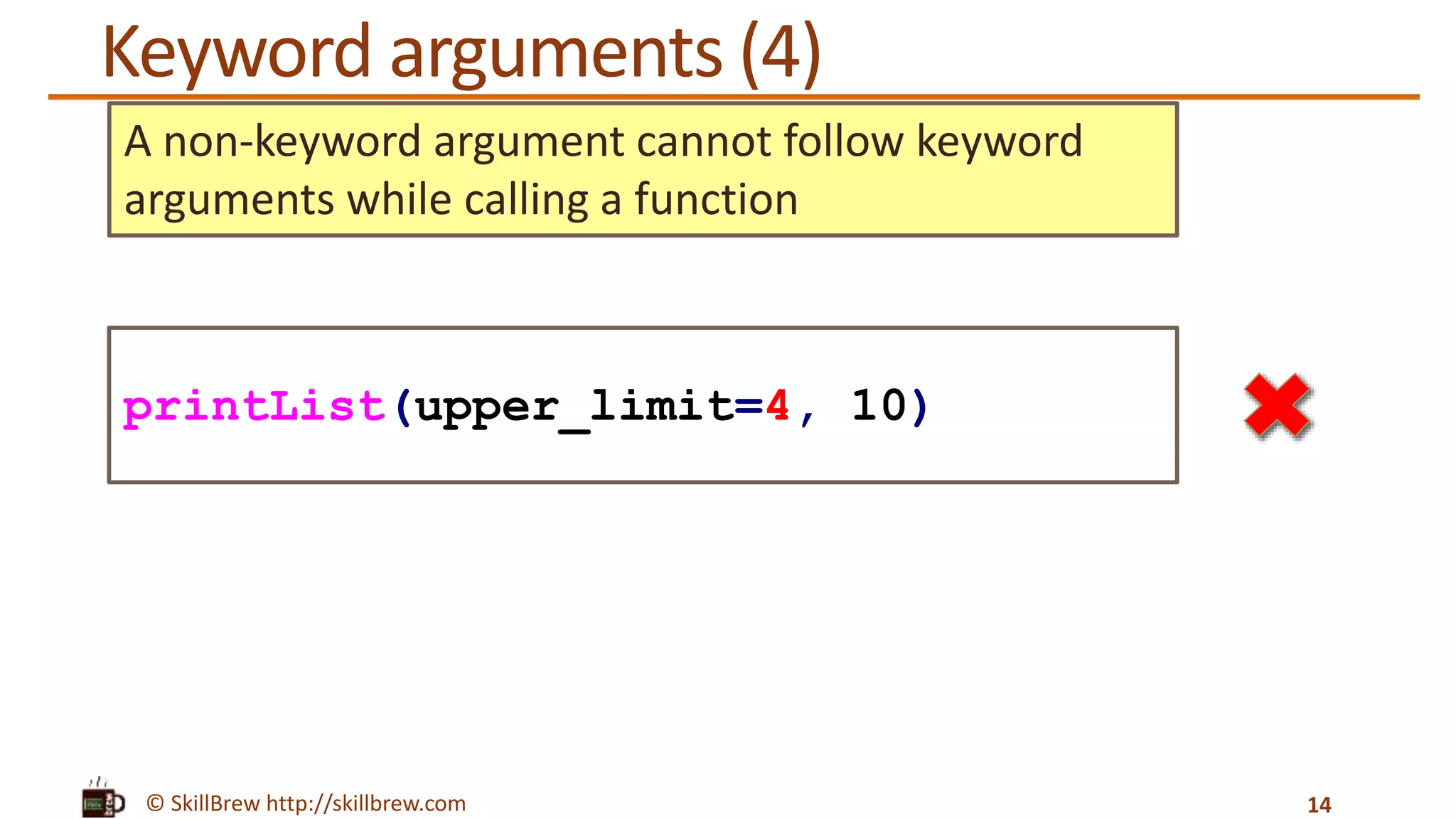
![© SkillBrew http://skillbrew.com Keyword arguments 11 def printList(upper_limit, step=1): print "upper limit: %d" % upper_limit num_list = range(0, upper_limit, step) print "list: %s" % num_list printList(upper_limit=5, step=2) Output: upper limit: 5 list: [0, 2, 4] range() function has two variations: 1.range(stop) 2.range(start, stop[, step])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonprogrammingessentials-m17-functions-140819043207-phpapp01/75/Python-Programming-Essentials-M17-Functions-11-2048.jpg)