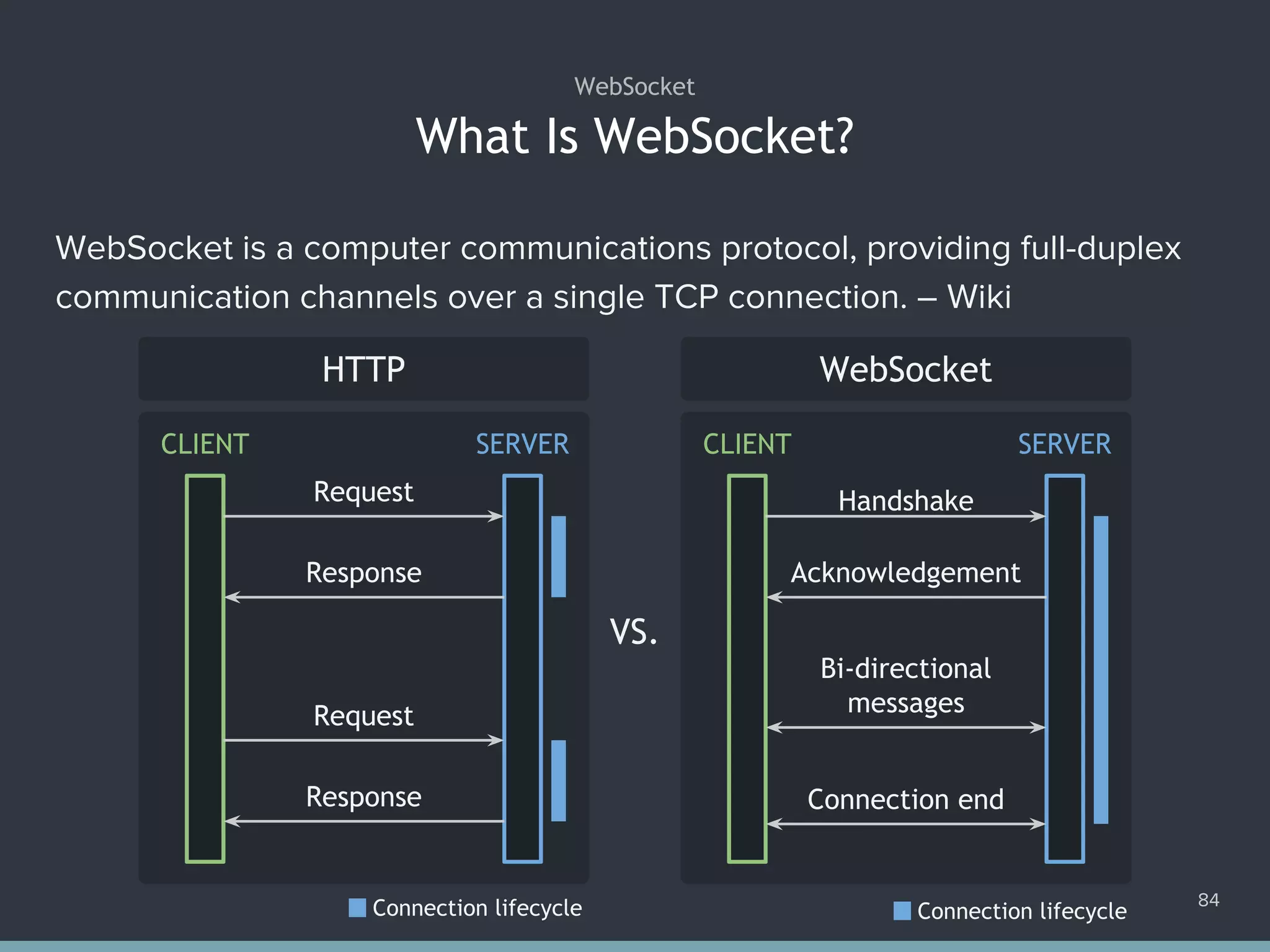
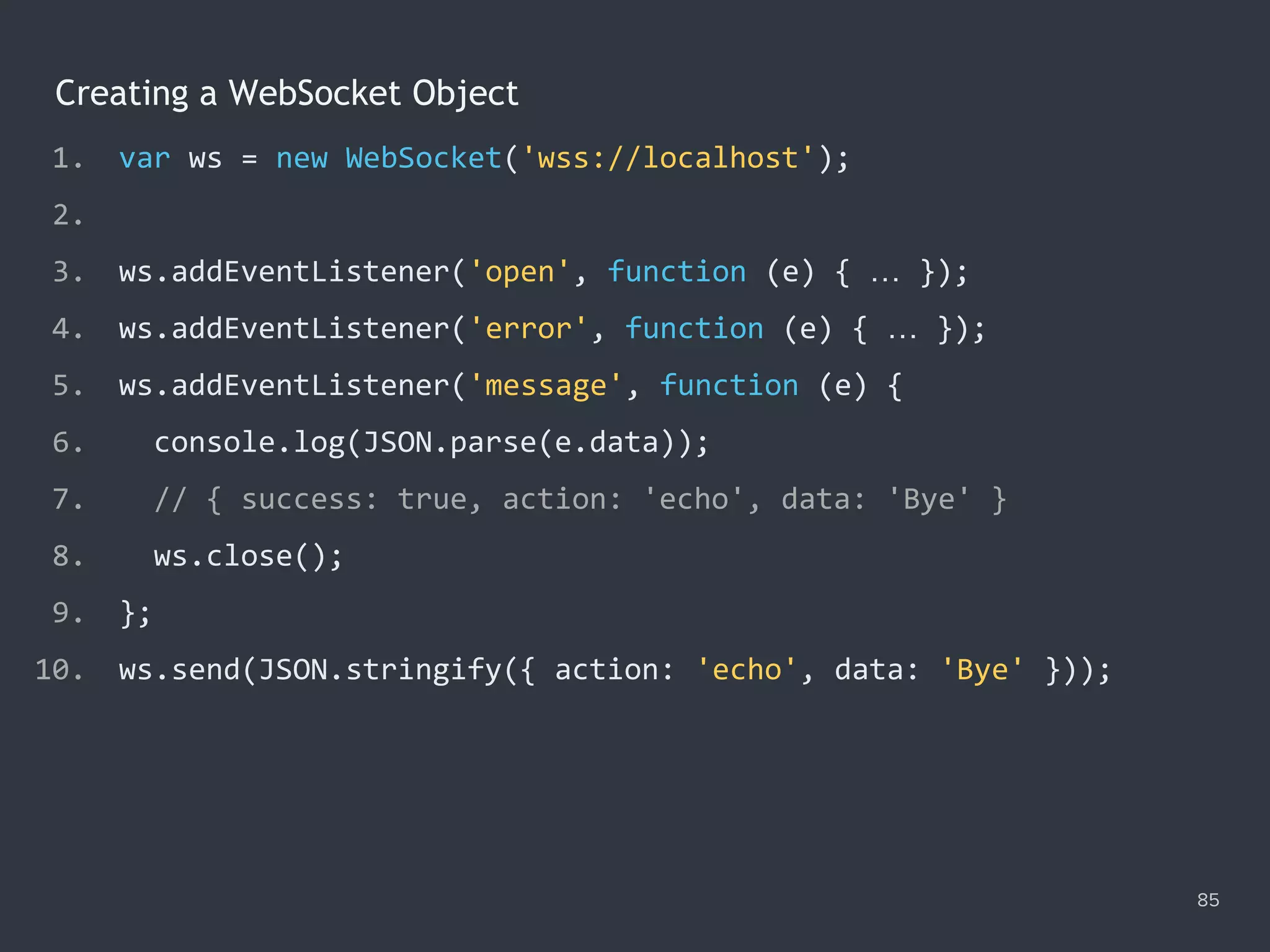
This document provides an overview of practical JavaScript programming focusing on forms and Ajax. It covers form elements, events, data access, validations, and creating custom components using various HTML and JavaScript techniques. The content is detailed with code snippets and examples for practical implementation.






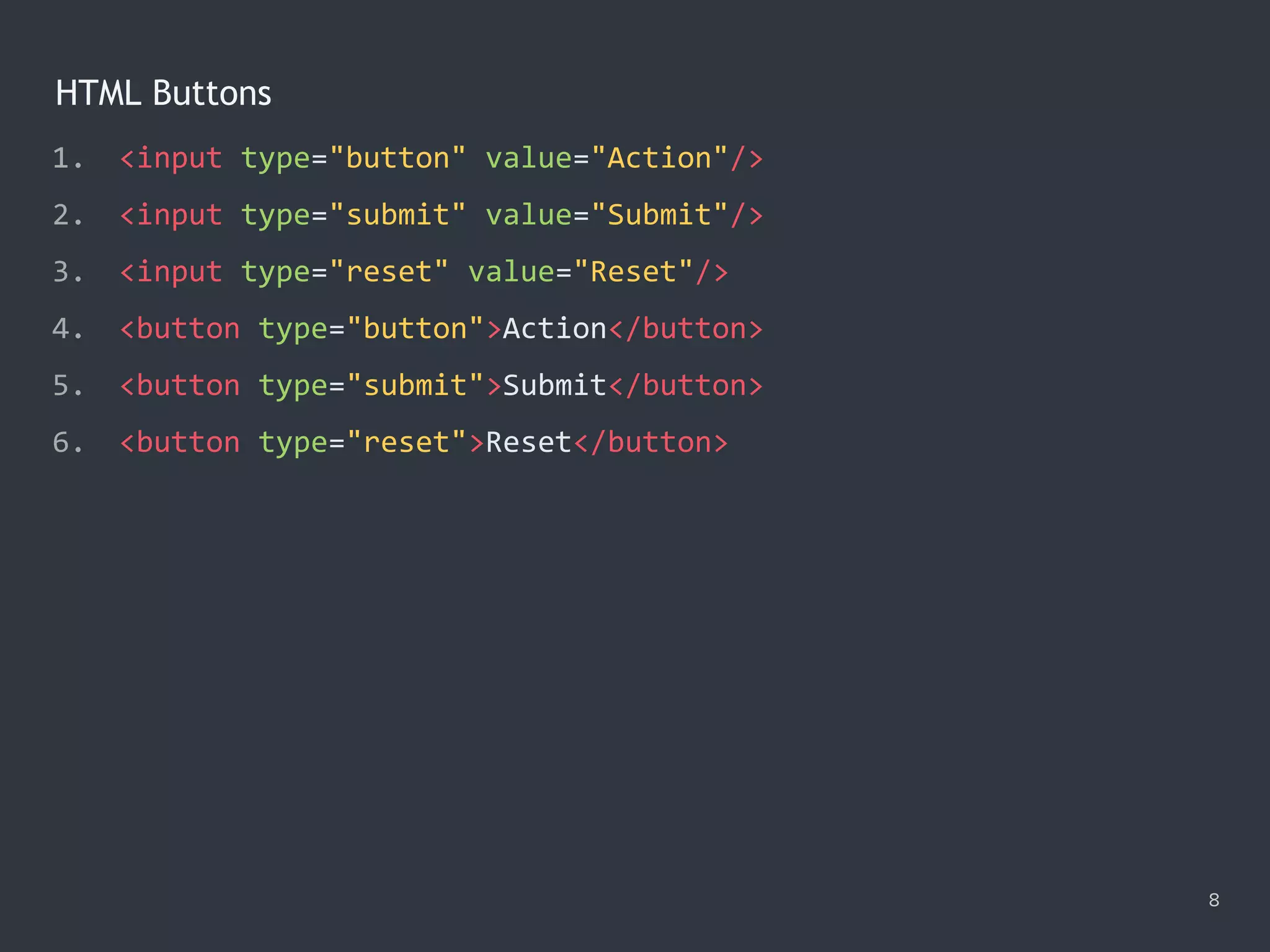
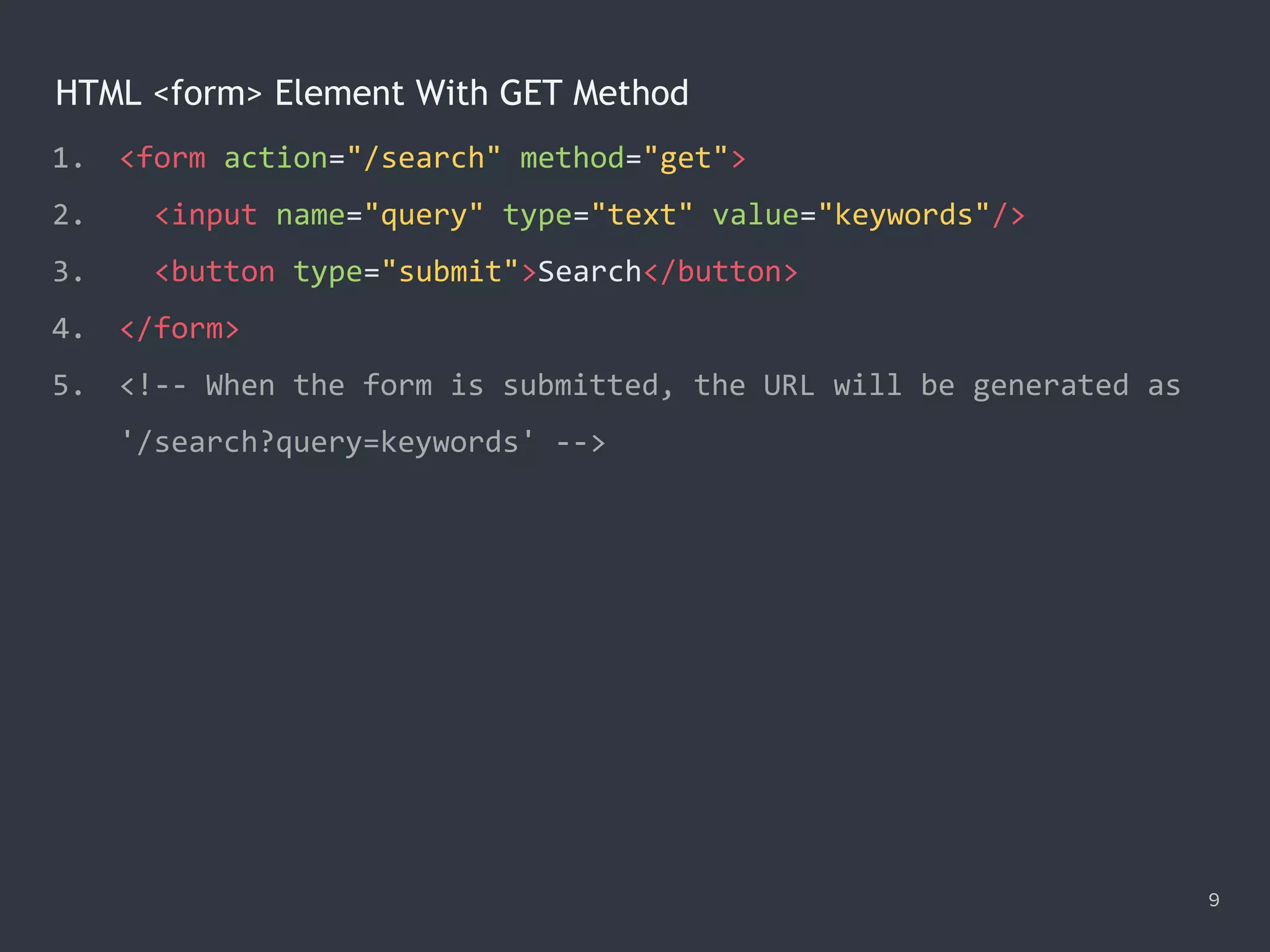
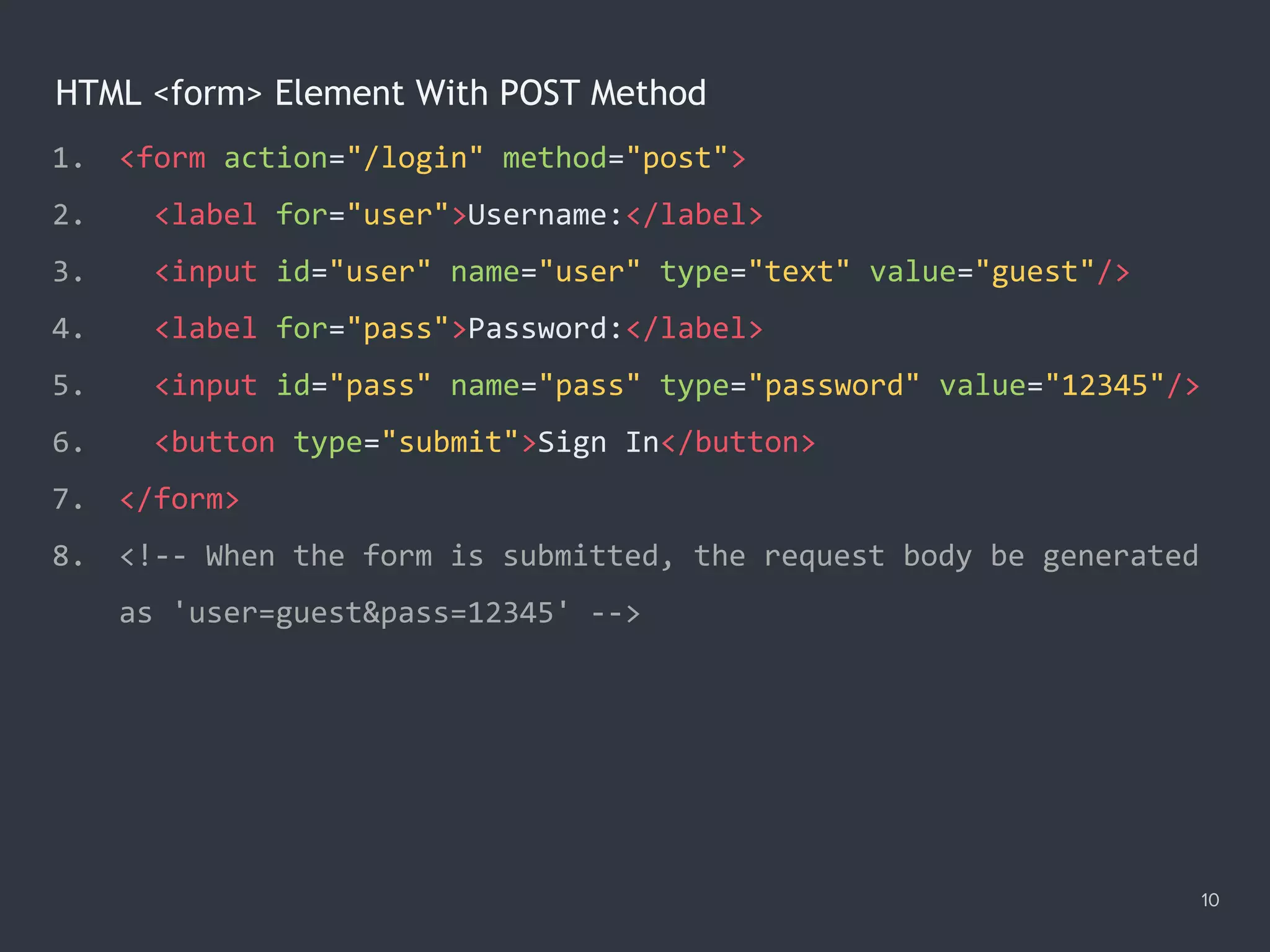
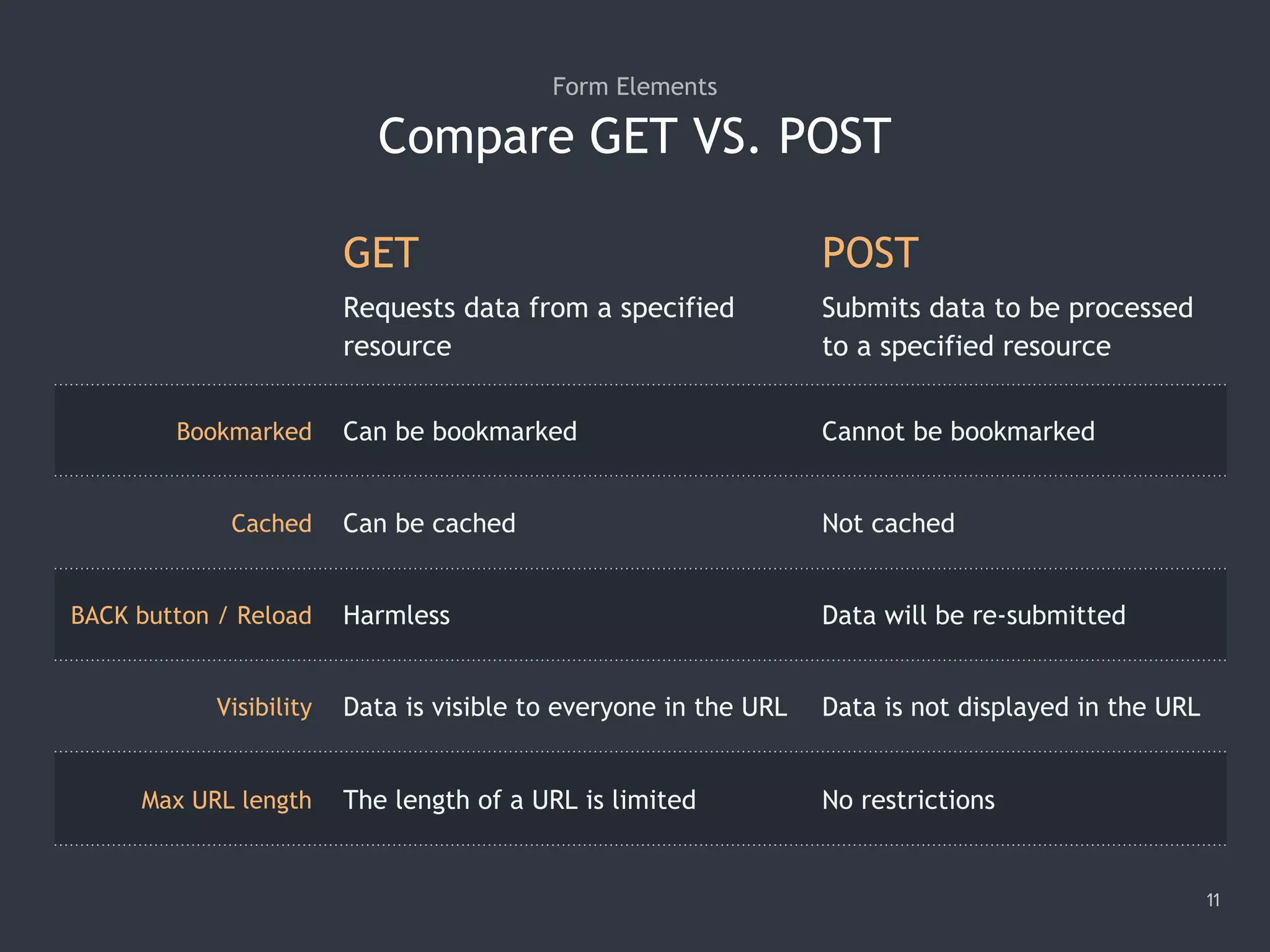


![Selecting Text on Focus 18 1. <input type="text" value="Hello"/> 2. <textarea cols="30" rows="5">Aloha</textarea> 3. <script> 4. var body = document.body; 5. var selectors = 'input[type="text"], textarea'; 6. var onFocus = function (e) { e.target.select(); }; 7. delegator(body)('focusin', selectors, onFocus); 8. delegator(body)('focus', selectors, onFocus, true); 9. </script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practicaljavascriptprogramming-session5-170719054827/75/Practical-JavaScript-Programming-Session-5-8-18-2048.jpg)
![Filtering a List Using input Event 19 1. <input id="filter" type="text"/> 2. <div id="output"></div> 3. <script> 4. var filter = document.querySelector('#filter'); 5. var output = document.querySelector('#output'); 6. var items = ['JS', 'JAVA', 'PHP', 'NODEJS']; 7. filter.addEventListener('input', function (e) { 8. output.textContent = items.filter(item => { 9. return item.indexOf(e.target.value) > -1; 10. }); 11. }); 12. </script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practicaljavascriptprogramming-session5-170719054827/75/Practical-JavaScript-Programming-Session-5-8-19-2048.jpg)
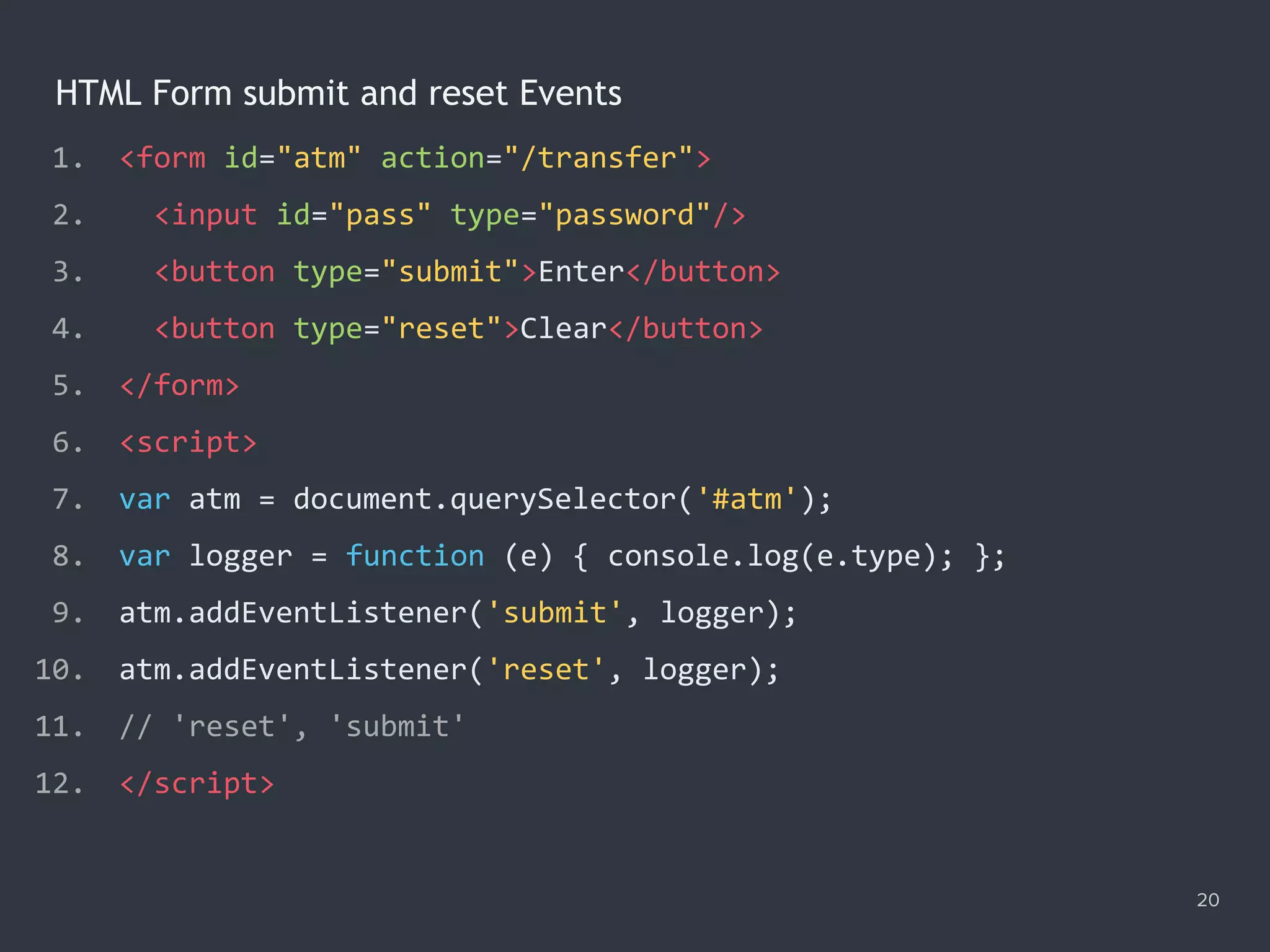



![Getting Values of Checked Checkboxes 24 1. <input name="order" id="1" type="checkbox" value="50" checked> 2. <label for="1">French fries</label> 3. <input name="order" id="2" type="checkbox" value="30" checked> 4. <label for="2">Sprite</label> 5. <script> 6. var selector = '[name="order"]:checked'; 7. var selected = document.querySelectorAll(selector); 8. var values = [...selected].map(elem => elem.value); 9. var total = values.reduce((a, b) => +a + +b); 10. console.log(total); // 80 11. </script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practicaljavascriptprogramming-session5-170719054827/75/Practical-JavaScript-Programming-Session-5-8-24-2048.jpg)
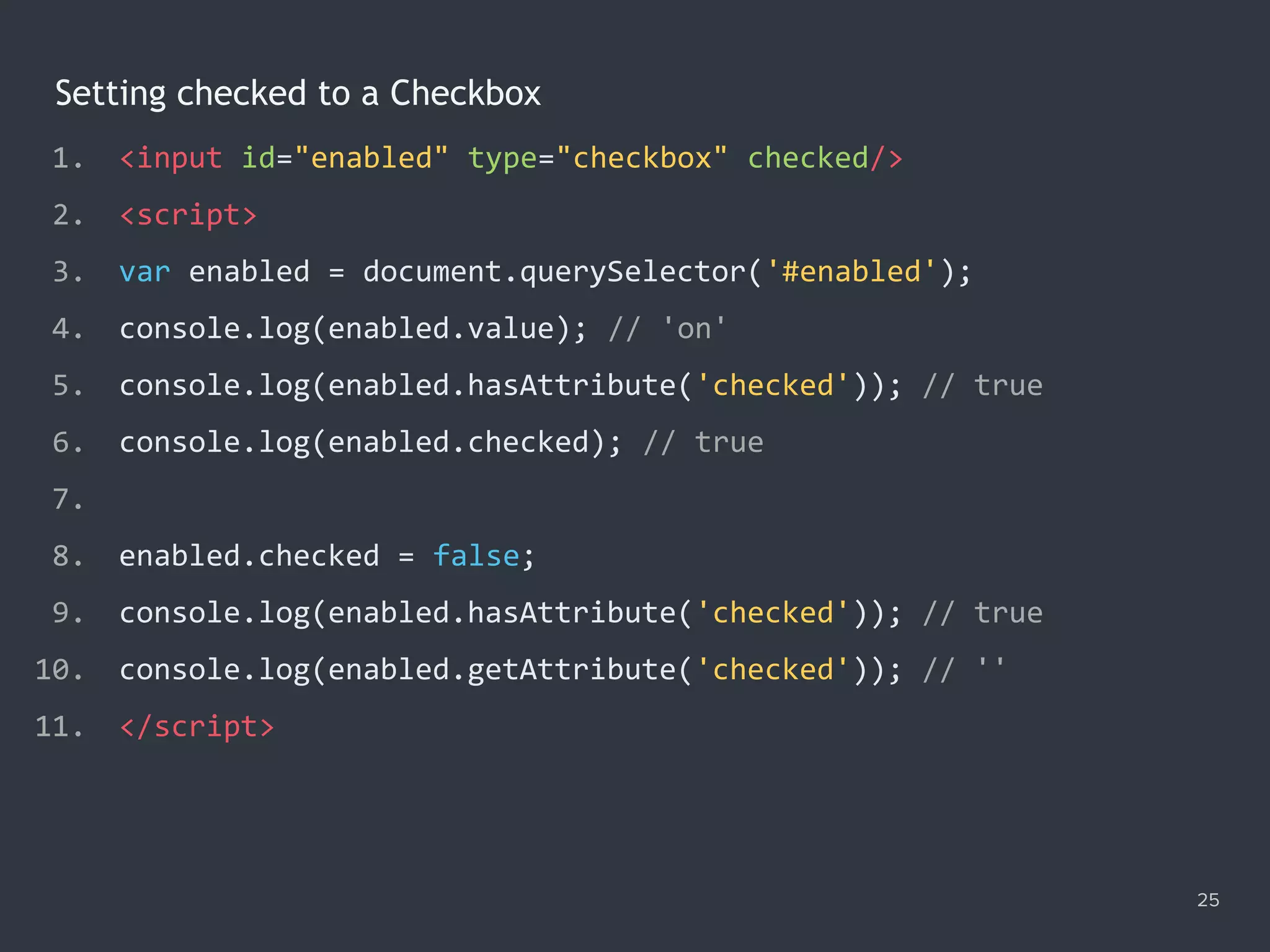
![Getting and Setting Value of Radio Button Group 26 1. <form name="profile"> 2. <input name="gender" type="radio" value="M" checked/> Male 3. <input name="gender" type="radio" value="F"/> Female 4. </form> 5. <script> 6. var selector = '[name="gender"]:checked'; 7. var selected = document.querySelector(selector); 8. console.log(selected.value); // 'M' 9. console.log(document.forms.profile.gender.value); // 'M' 10. document.forms.profile.gender.value = 'F'; 11. </script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practicaljavascriptprogramming-session5-170719054827/75/Practical-JavaScript-Programming-Session-5-8-26-2048.jpg)
![Getting Selected Value of a Select 27 1. <select id="lang"> 2. <option value="en-US">English</option> 3. <option value="zh-TW" selected>繁體中文</option> 4. </select> 5. <script> 6. var lang = document.querySelector('#lang'); 7. var options = lang.options; 8. console.log(lang.value); // 'zh-TW' 9. console.log(lang.selectedIndex); // 1 10. console.log(options[lang.selectedIndex].text); // '繁體中文' 11. lang.value = 'en-US'; 12. console.log(options[1].selected); // false 13. </script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practicaljavascriptprogramming-session5-170719054827/75/Practical-JavaScript-Programming-Session-5-8-27-2048.jpg)
![Getting Selected Values of a Multiple Select 28 1. <select id="beverage" multiple> 2. <option value="tea" selected>Tea</option> 3. <option value="soda">Soda</option> 4. <option value="coffee" selected>Coffee</option> 5. </select> 6. <script> 7. var beverage = document.querySelector('#beverage'); 8. var options = drink.options; 9. var selected = [...options].filter(o => o.selected); 10. var values = selected.map(o => o.value); 11. console.log(values); // (2) ['tea', 'coffee'] 12. </script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practicaljavascriptprogramming-session5-170719054827/75/Practical-JavaScript-Programming-Session-5-8-28-2048.jpg)
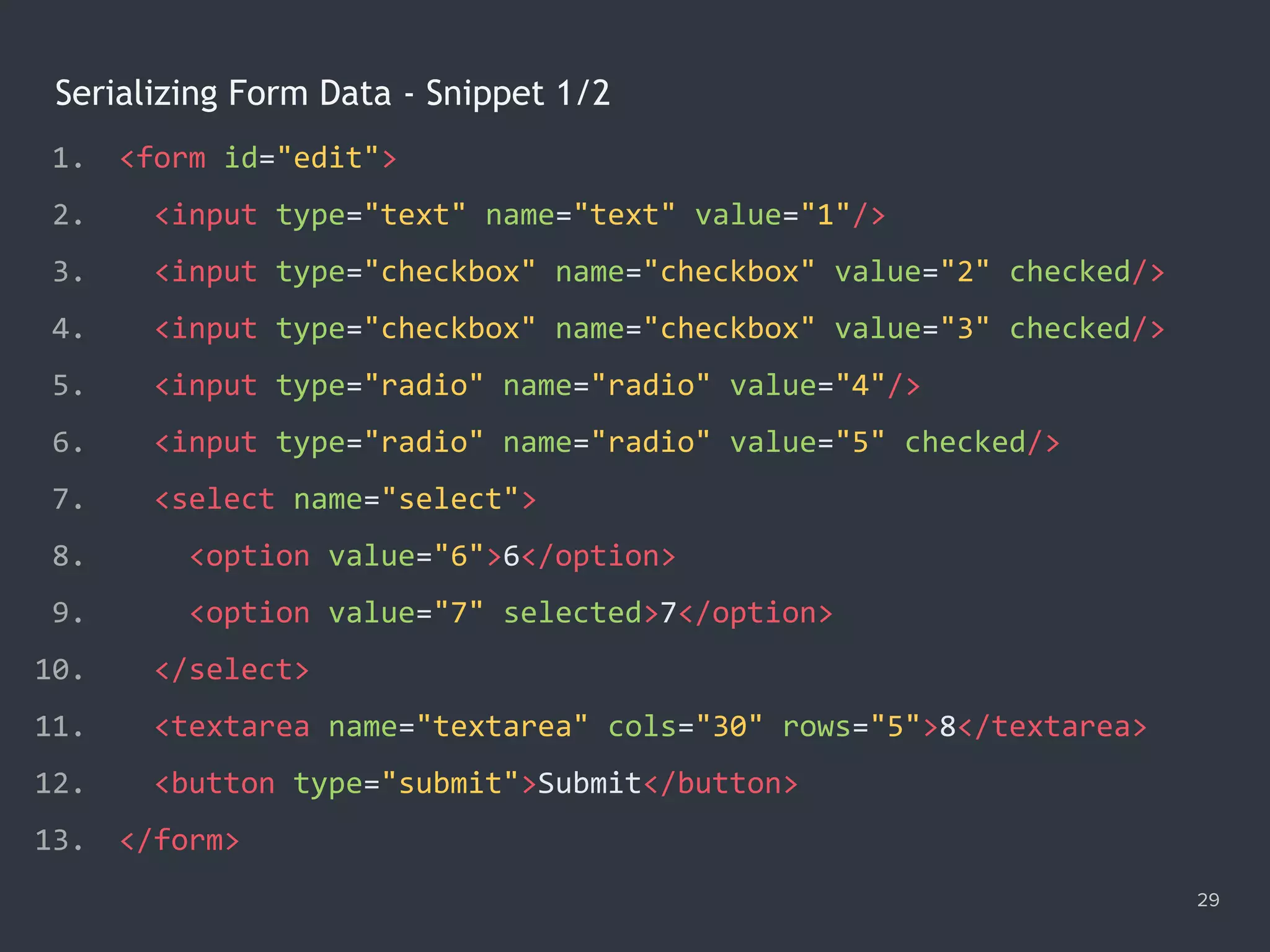
![Serializing Form Data - Snippet 2/2 30 1. function serialize (form) { 2. var key, val, output = [...form.elements].map(elem => { 3. key = elem.name, val = elem.value; 4. if (elem.type === 'checkbox' || elem.type === 'radio') { 5. val = elem.checked ? val : null; 6. } 7. if (!key || val === null) { return false; } 8. return `${key}=${val}`; 9. }); 10. return output.filter(v => v).join('&'); 11. } 12. console.log(serialize(document.querySelector('#edit'))); 13. // 'text=1&checkbox=2&checkbox=3&radio=5&select=7&textarea=8'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practicaljavascriptprogramming-session5-170719054827/75/Practical-JavaScript-Programming-Session-5-8-30-2048.jpg)


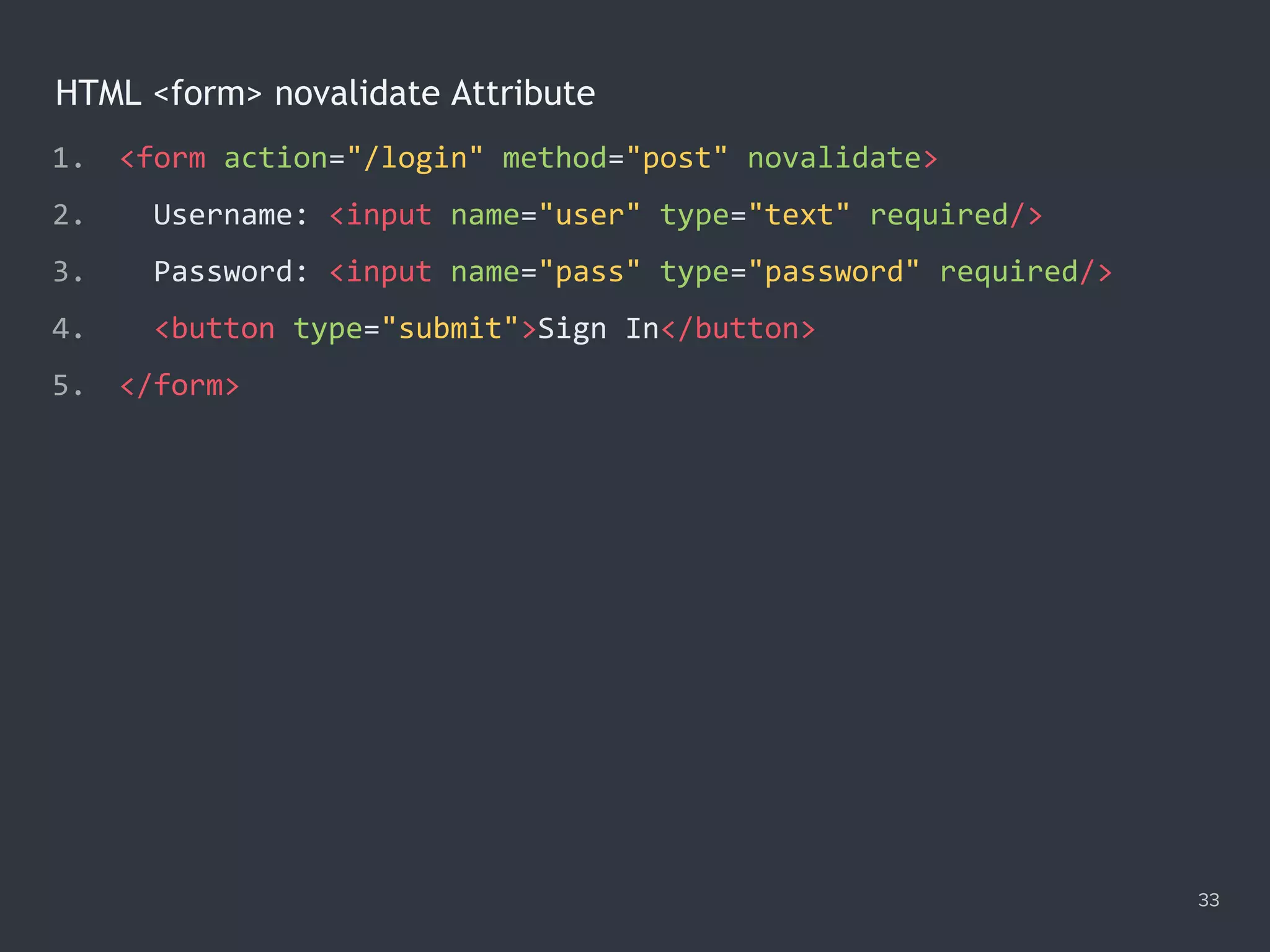
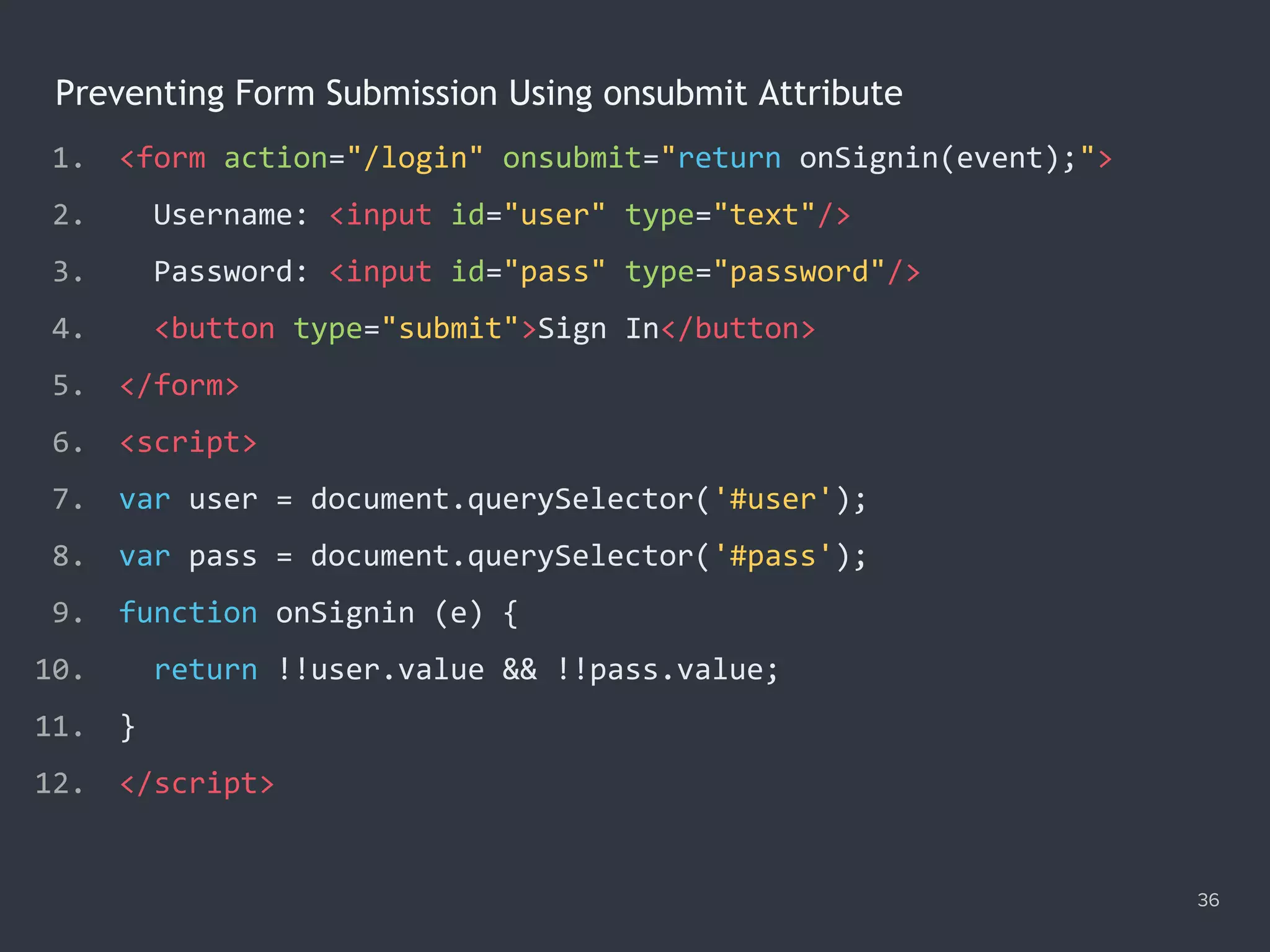
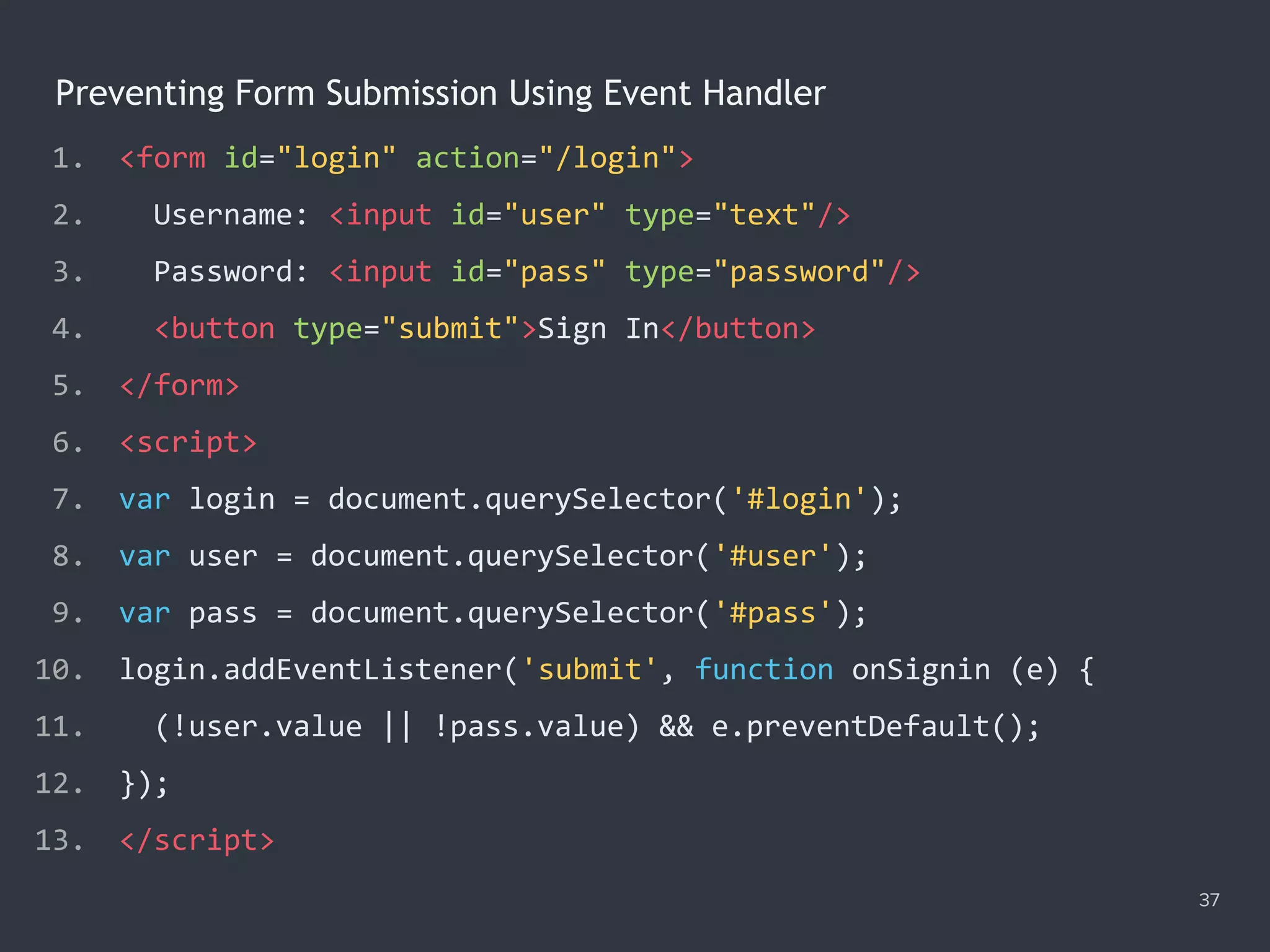
![Checking Required Fields 34 1. <form id="login" action="/login" method="post" novalidate> 2. Username: <input name="user" type="text" required/> 3. Password: <input name="pass" type="password" required/> 4. <button type="submit">Sign In</button> 5. </form> 6. <script> 7. var login = document.querySelector('#login'), required; 8. login.addEventListener('submit', function (e) { 9. required = document.querySelectorAll(':required'); 10. if ([...required].filter(el => !el.value).length) { 11. e.preventDefault(); 12. } 13. }); 14. </script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practicaljavascriptprogramming-session5-170719054827/75/Practical-JavaScript-Programming-Session-5-8-34-2048.jpg)
![Preventing User From Typing Non-numeric Values 35 1. <input id="phone" type="text"/> 2. <script> 3. var phone = document.querySelector('#phone'); 4. phone.addEventListener('keypress', function (e) { 5. if (e.key && !/^[0-9]+$/.test(e.key)) { 6. e.preventDefault(); 7. } 8. }); 9. </script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practicaljavascriptprogramming-session5-170719054827/75/Practical-JavaScript-Programming-Session-5-8-35-2048.jpg)

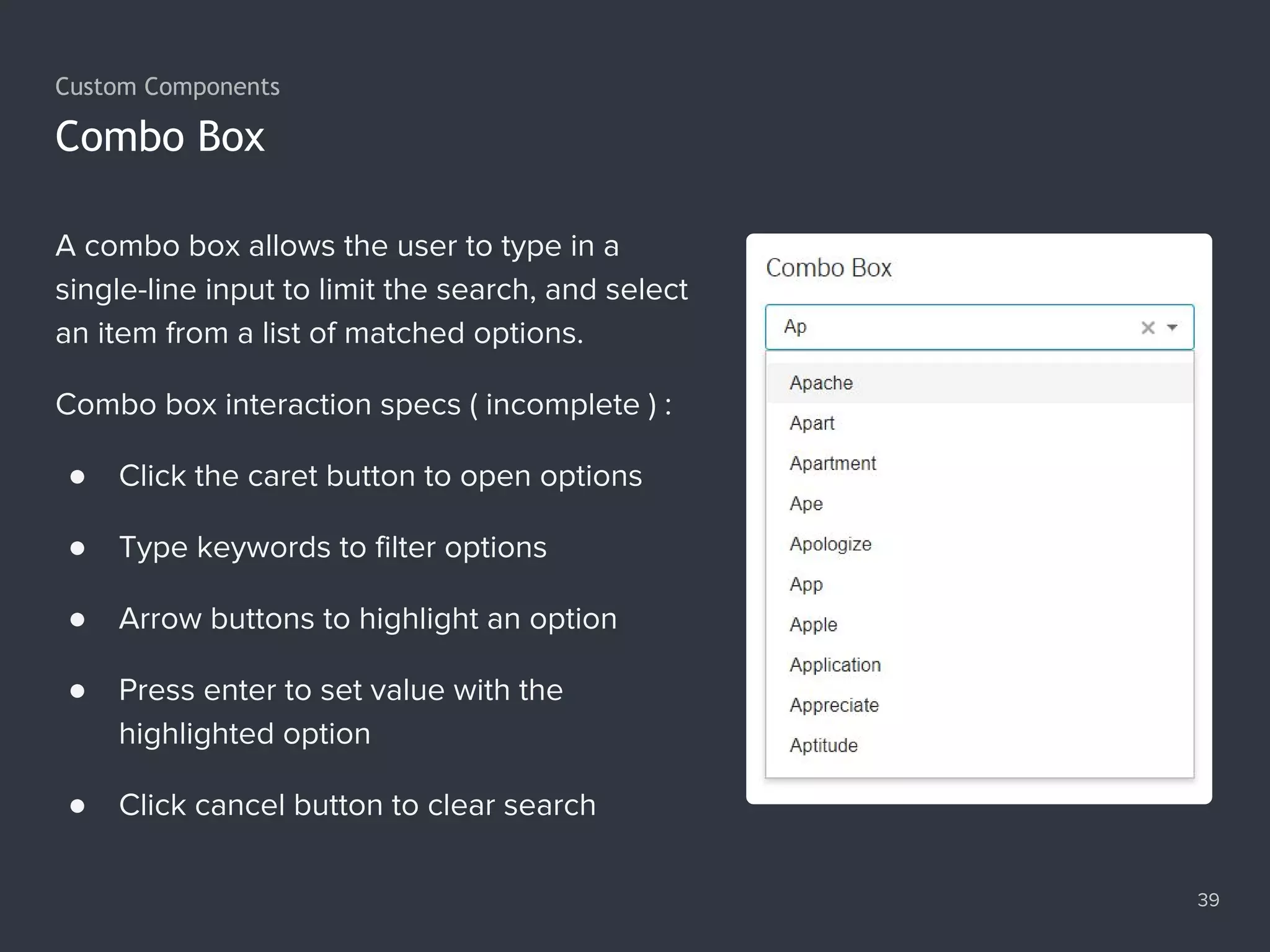
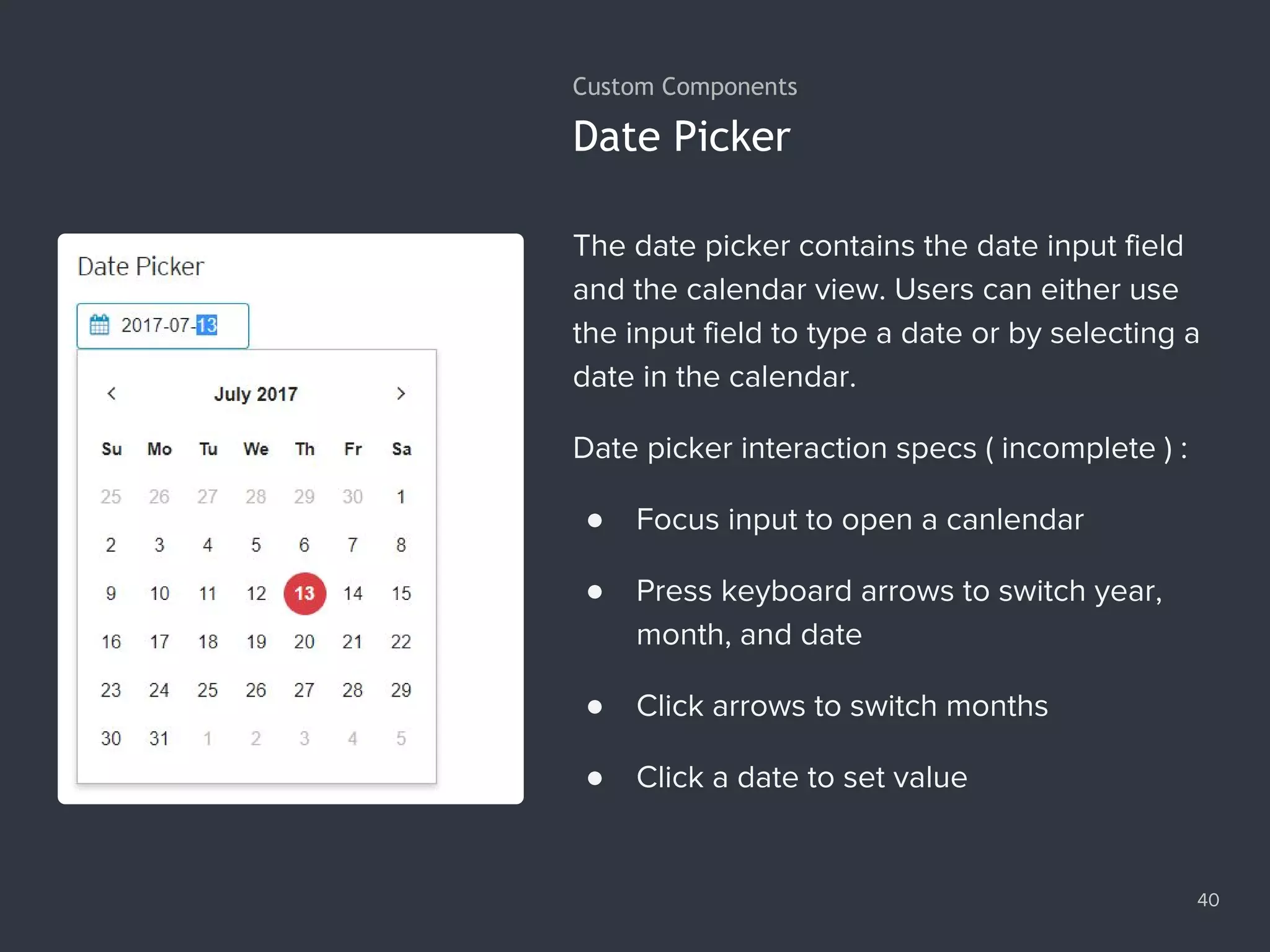



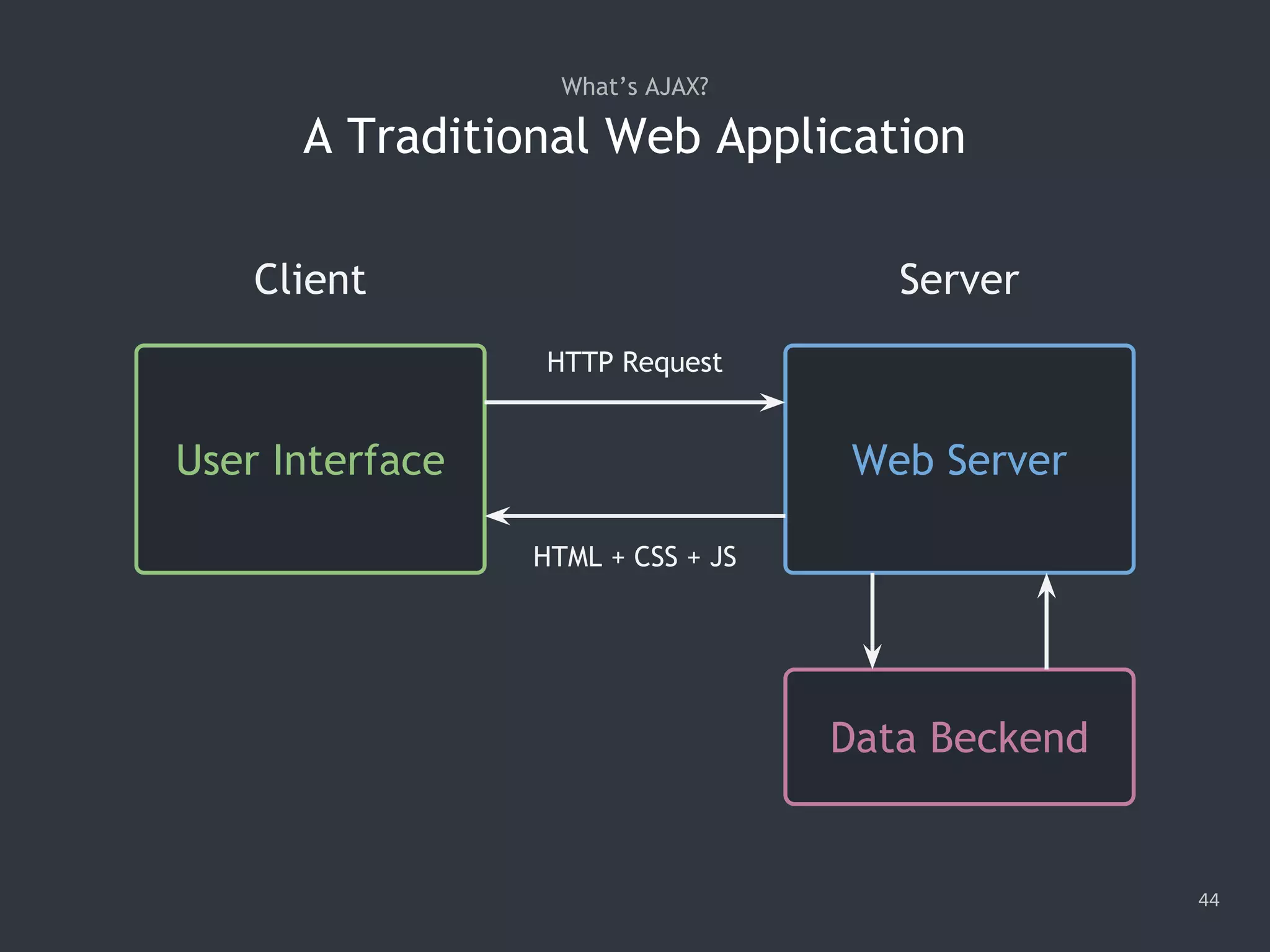
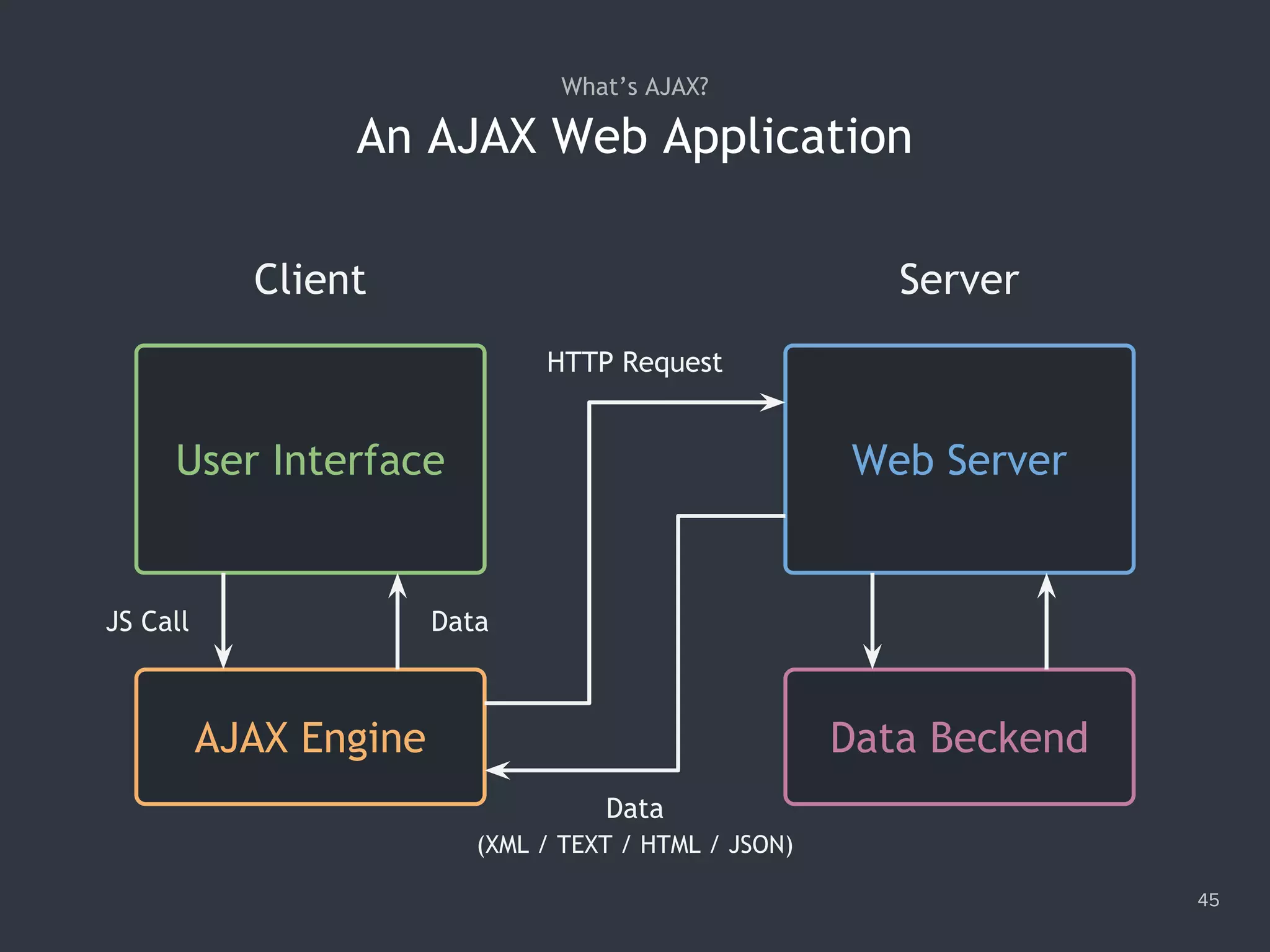

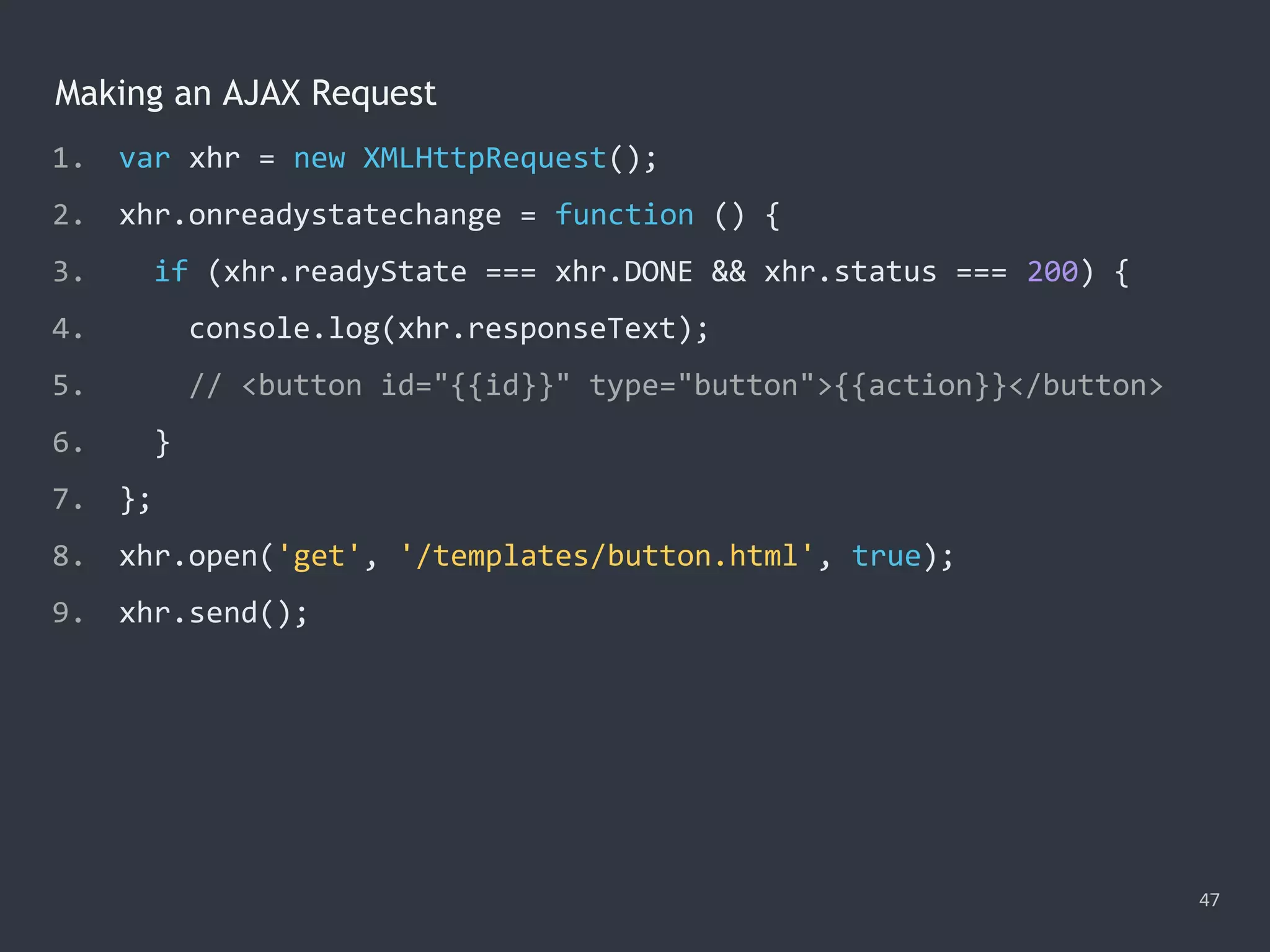
![Making a Synchronous Request 48 1. var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest(); 2. xhr.open('GET', '/data/cars.json', false); 3. xhr.send(); 4. console.log(xhr.responseText); 5. // '["audi","benz","bmw"]'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practicaljavascriptprogramming-session5-170719054827/75/Practical-JavaScript-Programming-Session-5-8-48-2048.jpg)

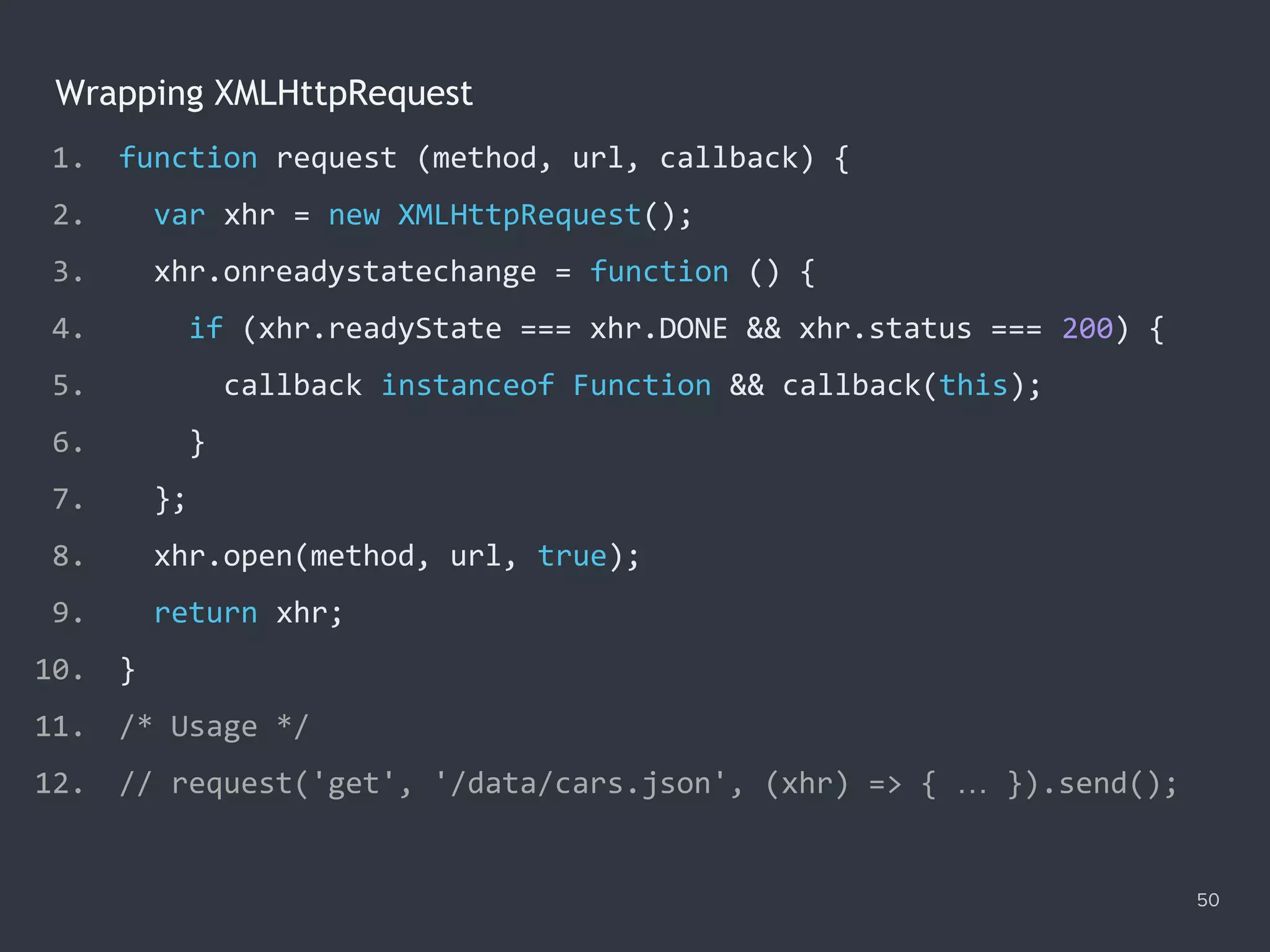
![Handling the Server Response 51 1. request('get', '/data/numbers.json', function (xhr) { 2. console.log(xhr.status); // 200 3. console.log(xhr.statusText); // 'OK' 4. console.log(xhr.responseText); // '[100,200,300]' 5. console.log(xhr.getResponseHeader('Content-type')); 6. // 'application/json' 7. }) 8. .send();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practicaljavascriptprogramming-session5-170719054827/75/Practical-JavaScript-Programming-Session-5-8-51-2048.jpg)
![Working with XML Data 52 1. /* Given a XML file 'food.xml' as follows: 2. <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 3. <root><food>Pizza</food><food>Bread</food></root> 4. */ 5. request('get', '/data/food.xml', function (xhr) { 6. var nodes = xhr.responseXML.getElementsByTagName('food'); 7. var data = [...nodes].map(node => node.textContent); 8. console.log(data); // (2) ['Pizza', 'Bread'] 9. }) 10. .send();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practicaljavascriptprogramming-session5-170719054827/75/Practical-JavaScript-Programming-Session-5-8-52-2048.jpg)
![Using POST Method in XMLHTTPRequest 53 1. var item = 'item=iphone'; 2. var amount = 'amount=99'; 3. var params = [item, amount].join('&'); 4. var contentType = 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'; 5. var xhr = request('post', '/order', function (xhr) { 6. console.log(xhr.responseText); 7. // '{"data":{"item":"iphone","amount":"99"}}' 8. }); 9. xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-type', contentType); 10. xhr.send(params);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practicaljavascriptprogramming-session5-170719054827/75/Practical-JavaScript-Programming-Session-5-8-53-2048.jpg)
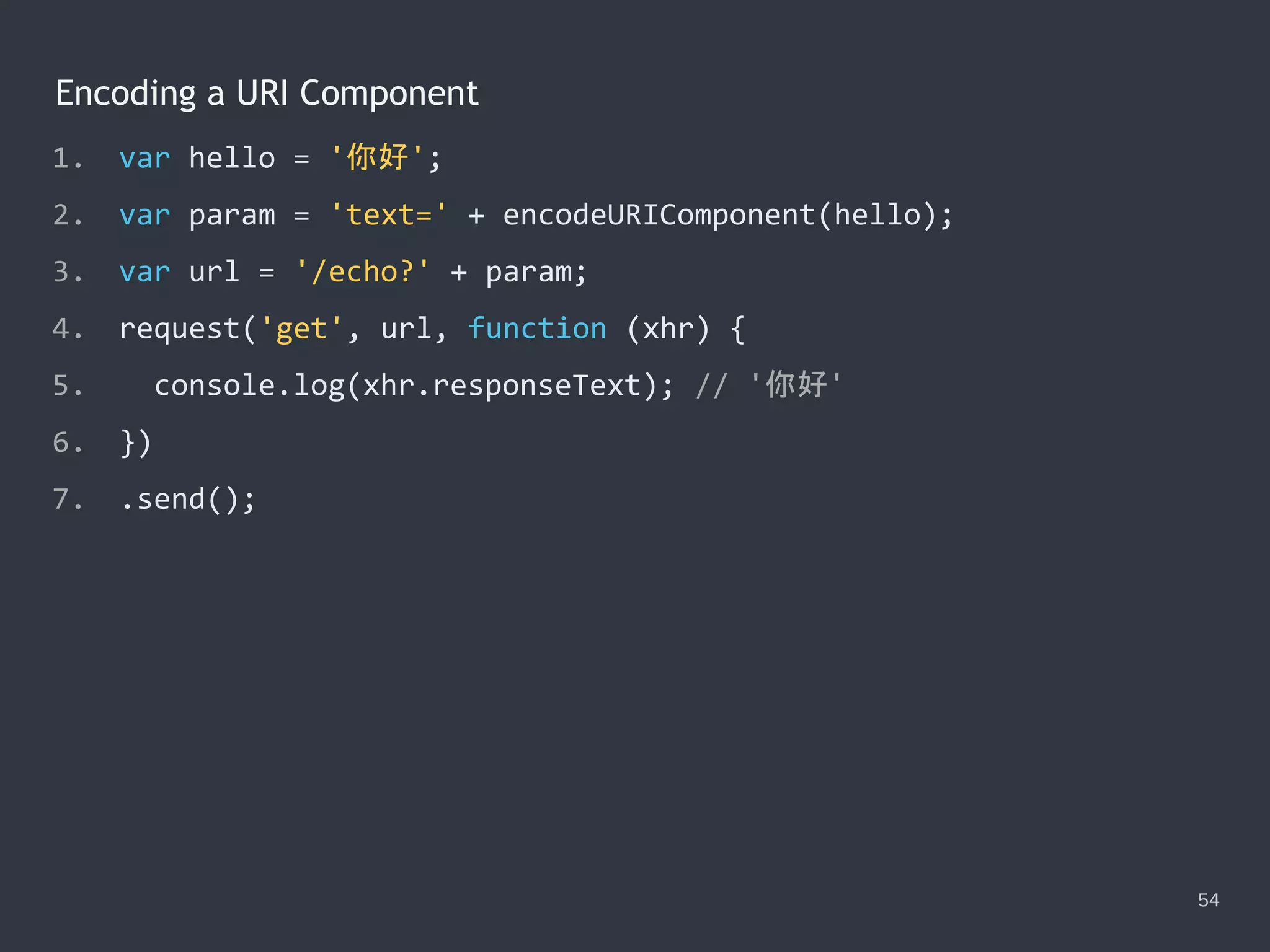
![Uploading a File 55 1. <input id="file" type="file"/> 2. <script> 3. var file = document.querySelector('#file').files[0]; 4. var data = new FormData(); 5. var xhr = request('post', '/upload'); 6. data.append('target', 'images'); 7. data.append('file', file, 'sky.jpg'); 8. xhr.send(data); 9. </script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practicaljavascriptprogramming-session5-170719054827/75/Practical-JavaScript-Programming-Session-5-8-55-2048.jpg)
![Monitoring Progress of a File Upload 56 1. var file = document.querySelector('#file').files[0]; 2. var data = new FormData(); 3. var xhr = request('post', '/upload'); 4. data.append('file', file); 5. xhr.upload.addEventListener('progress', function (e) { 6. if (e.lengthComputable) { 7. console.log(Math.floor(e.loaded / e.total * 100)); 8. } 9. }); 10. xhr.send(data);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practicaljavascriptprogramming-session5-170719054827/75/Practical-JavaScript-Programming-Session-5-8-56-2048.jpg)


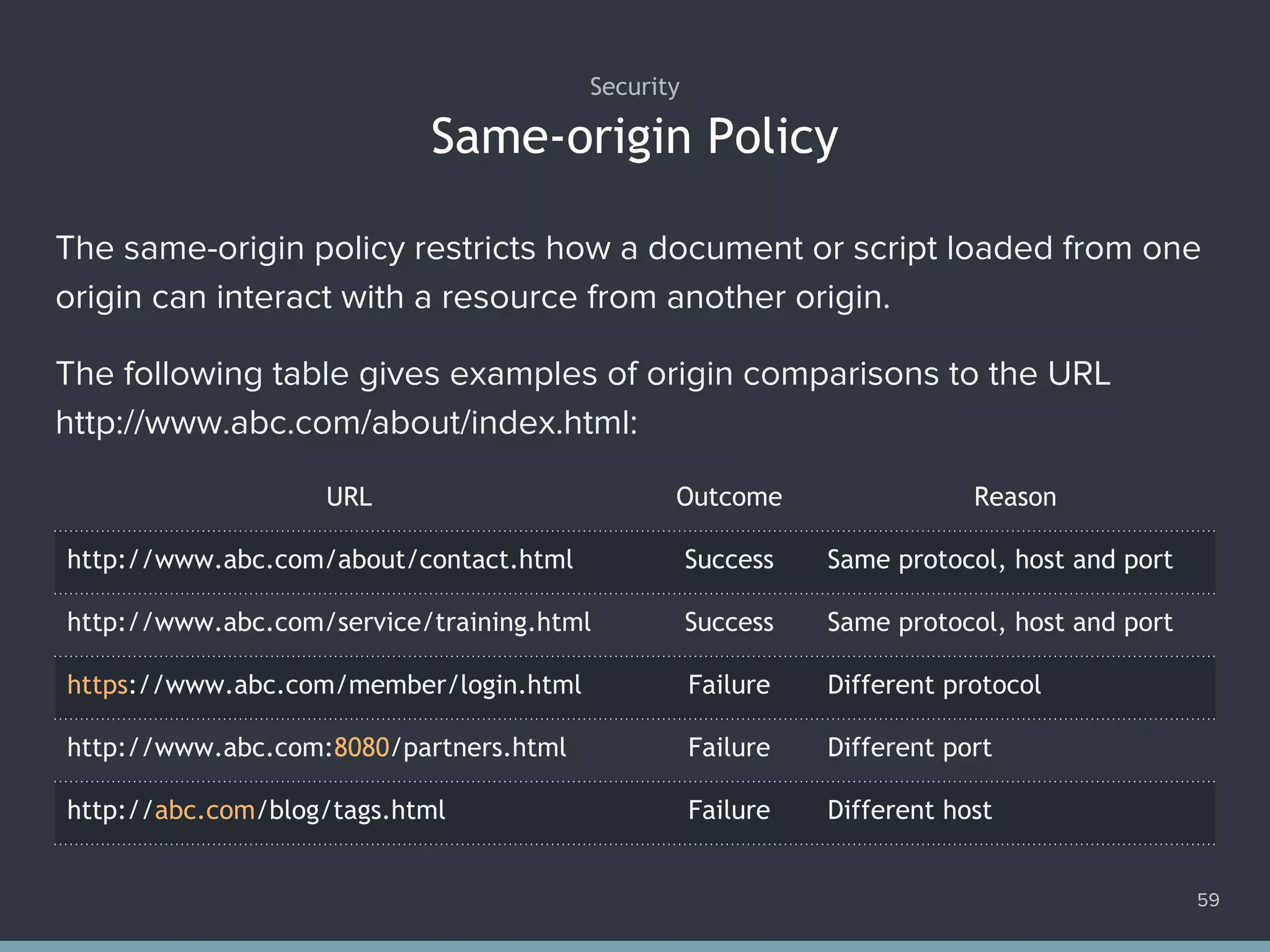
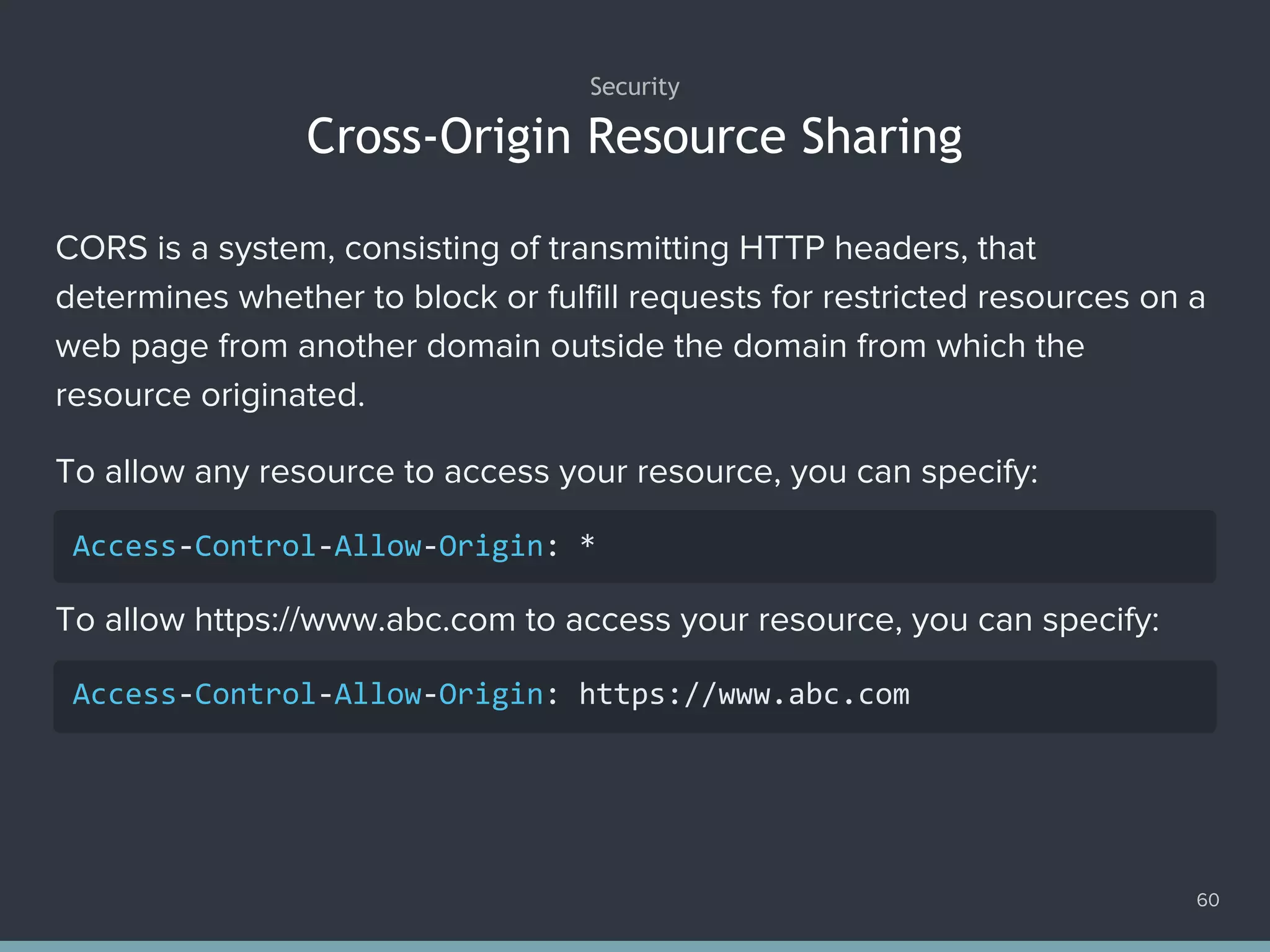
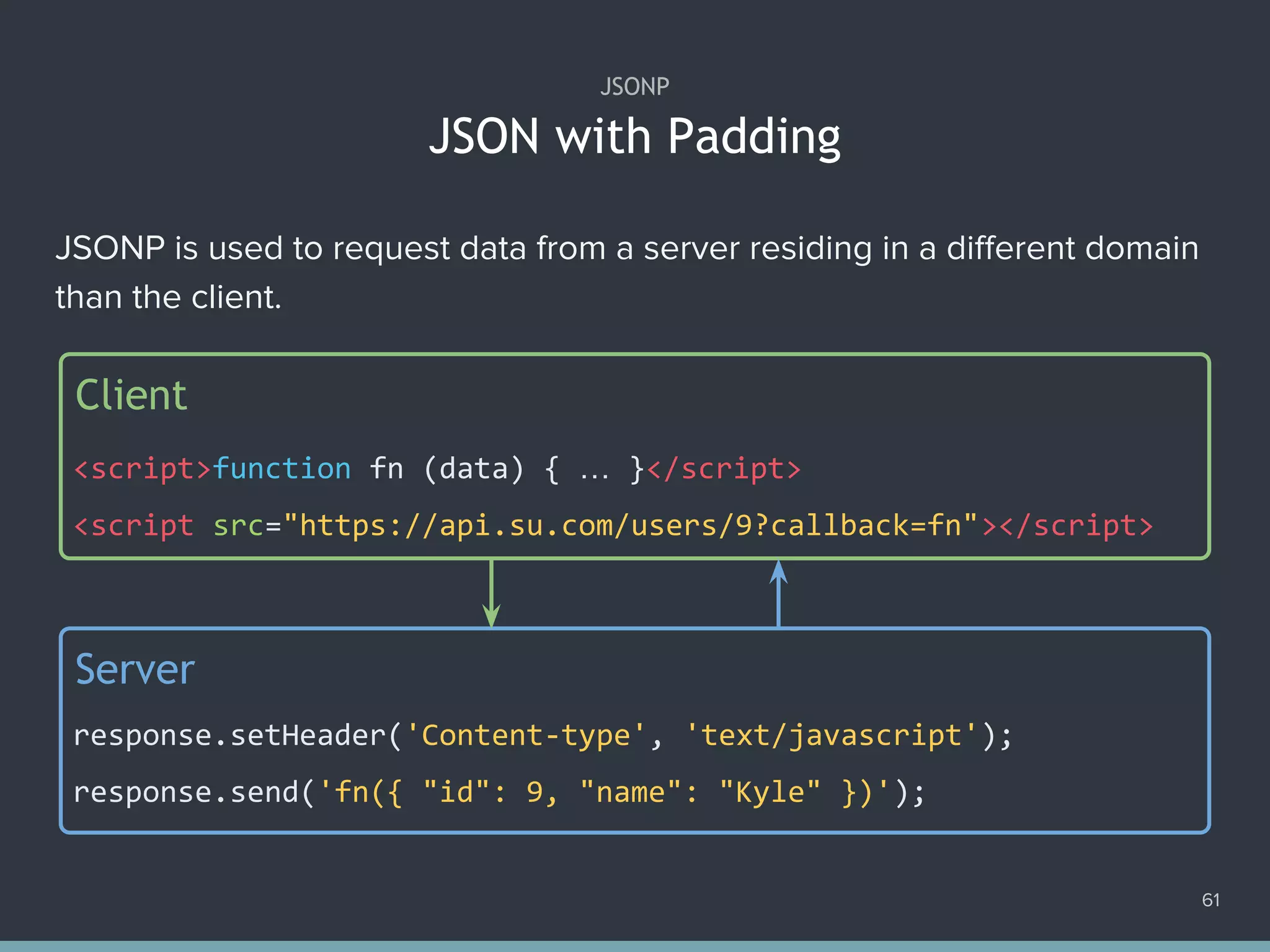

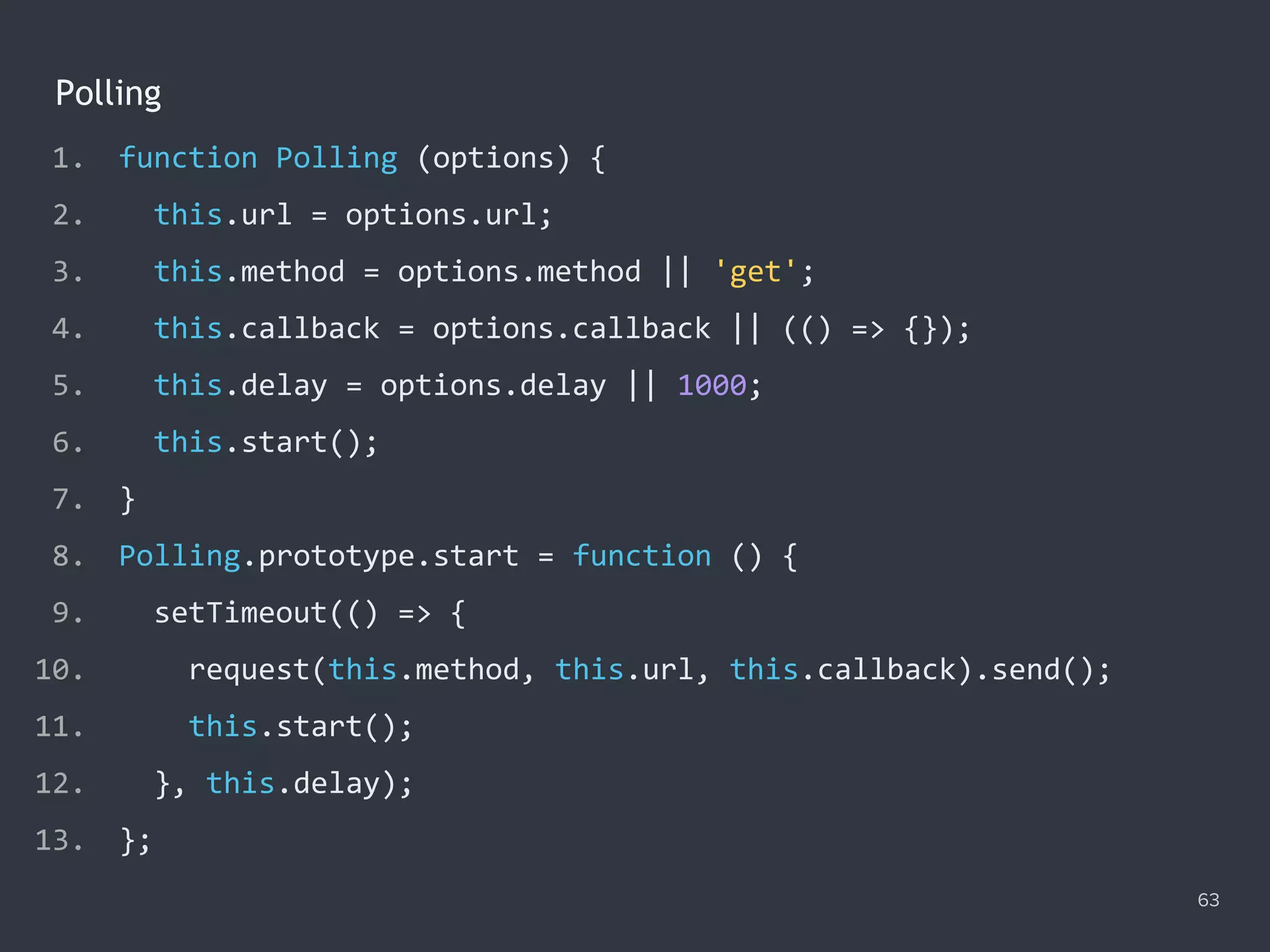



![Disabling Submit Button When Request Is In-progress 68 1. var profile = document.querySelector('form#profile'); 2. var save = document.querySelector('[type="submit"]#save'); 3. profile.addEventListener('submit', function (e) { 4. e.preventDefault(); 5. request('post', 'submit', function (xhr) { 6. save.disabled = false; 7. }).send(); 8. save.disabled = true; 9. });](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practicaljavascriptprogramming-session5-170719054827/75/Practical-JavaScript-Programming-Session-5-8-68-2048.jpg)
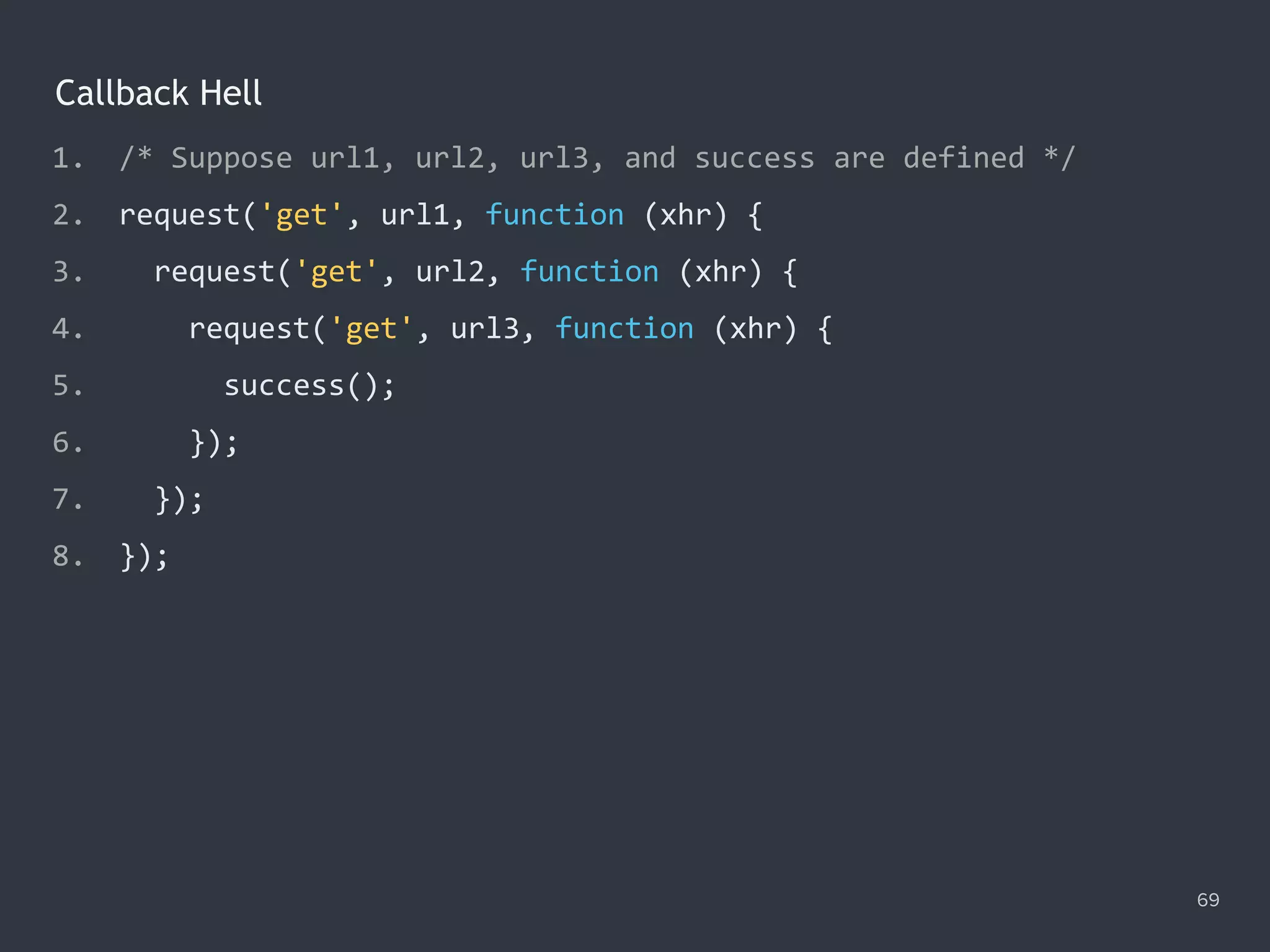
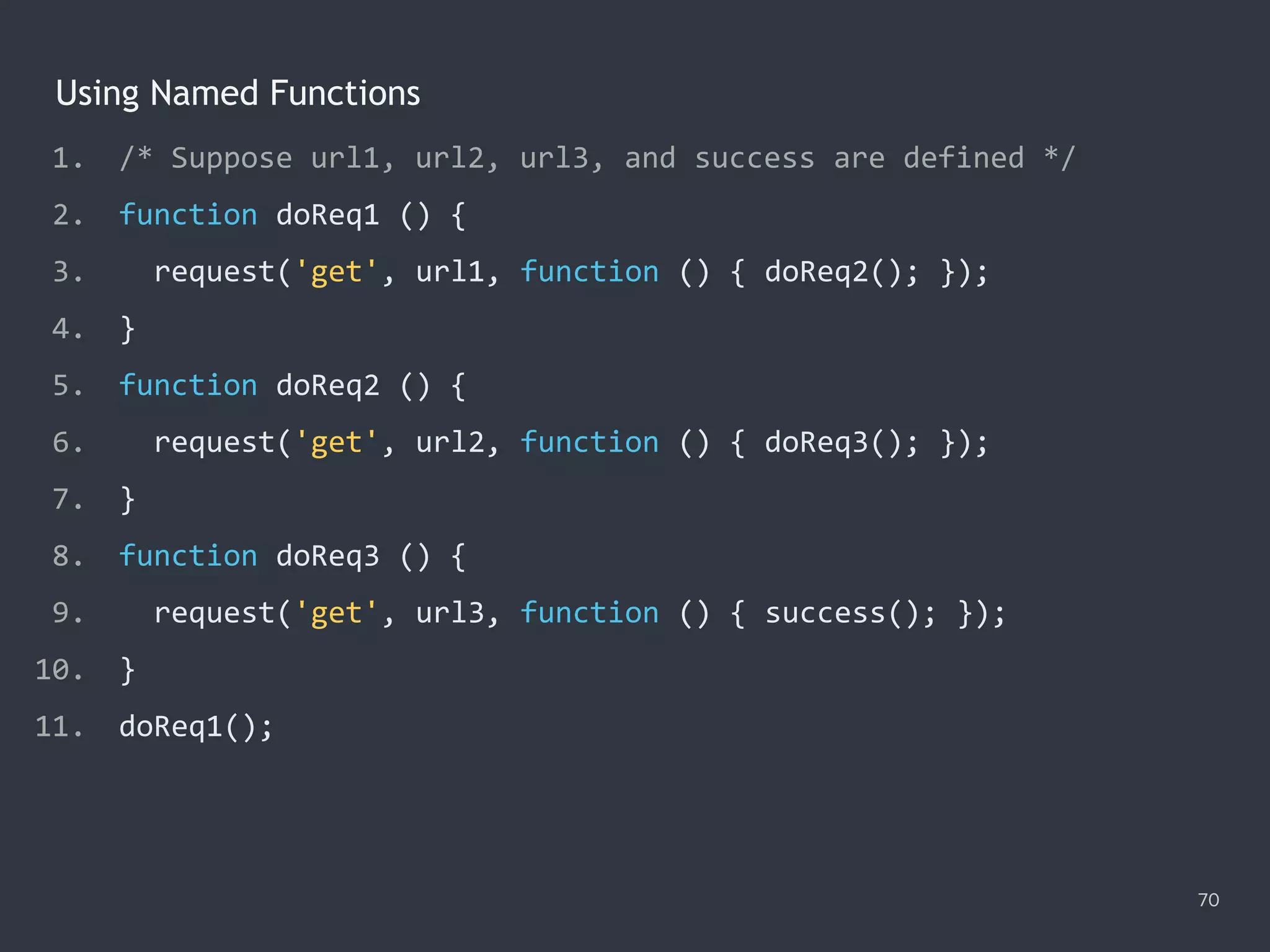

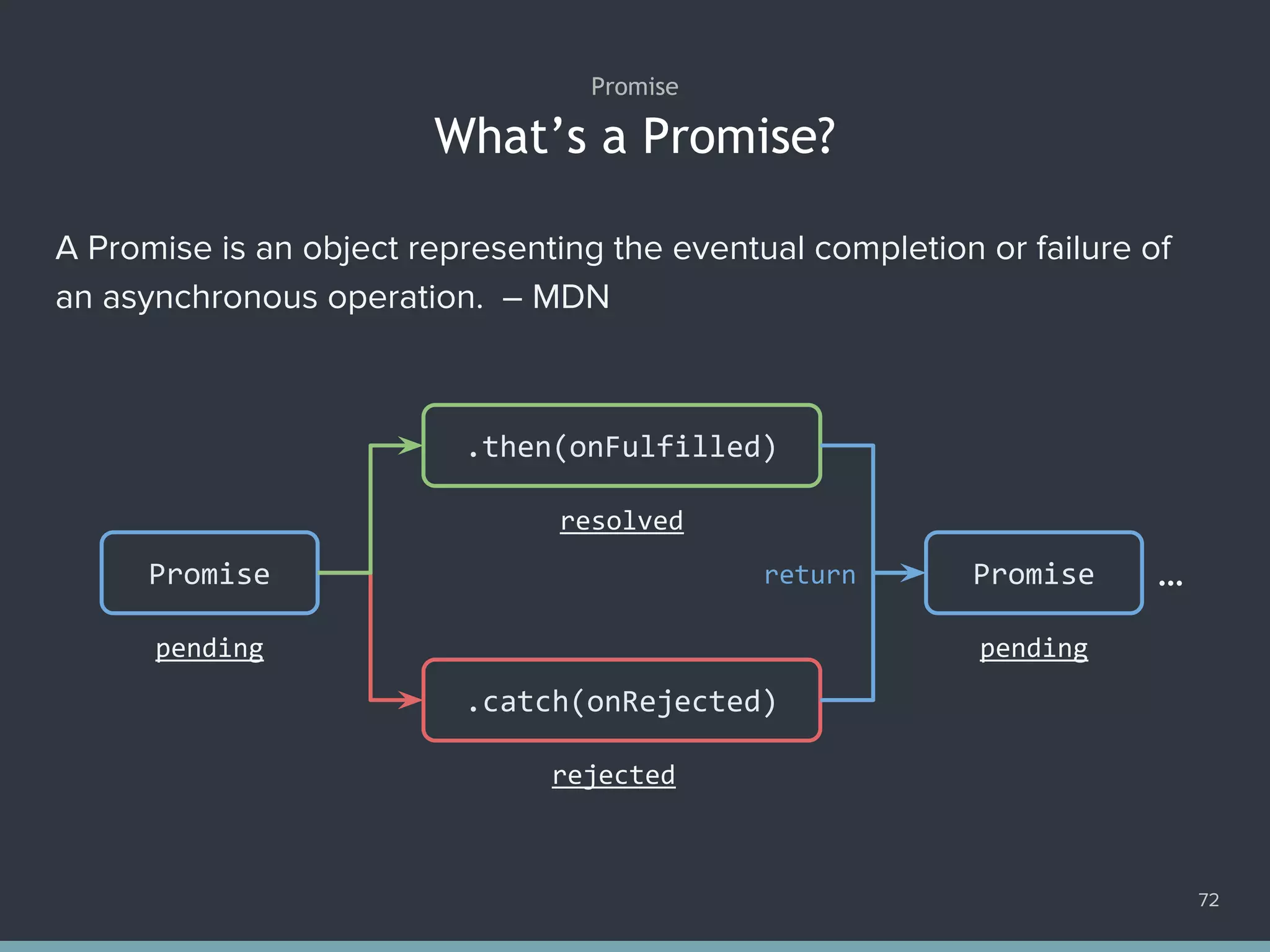
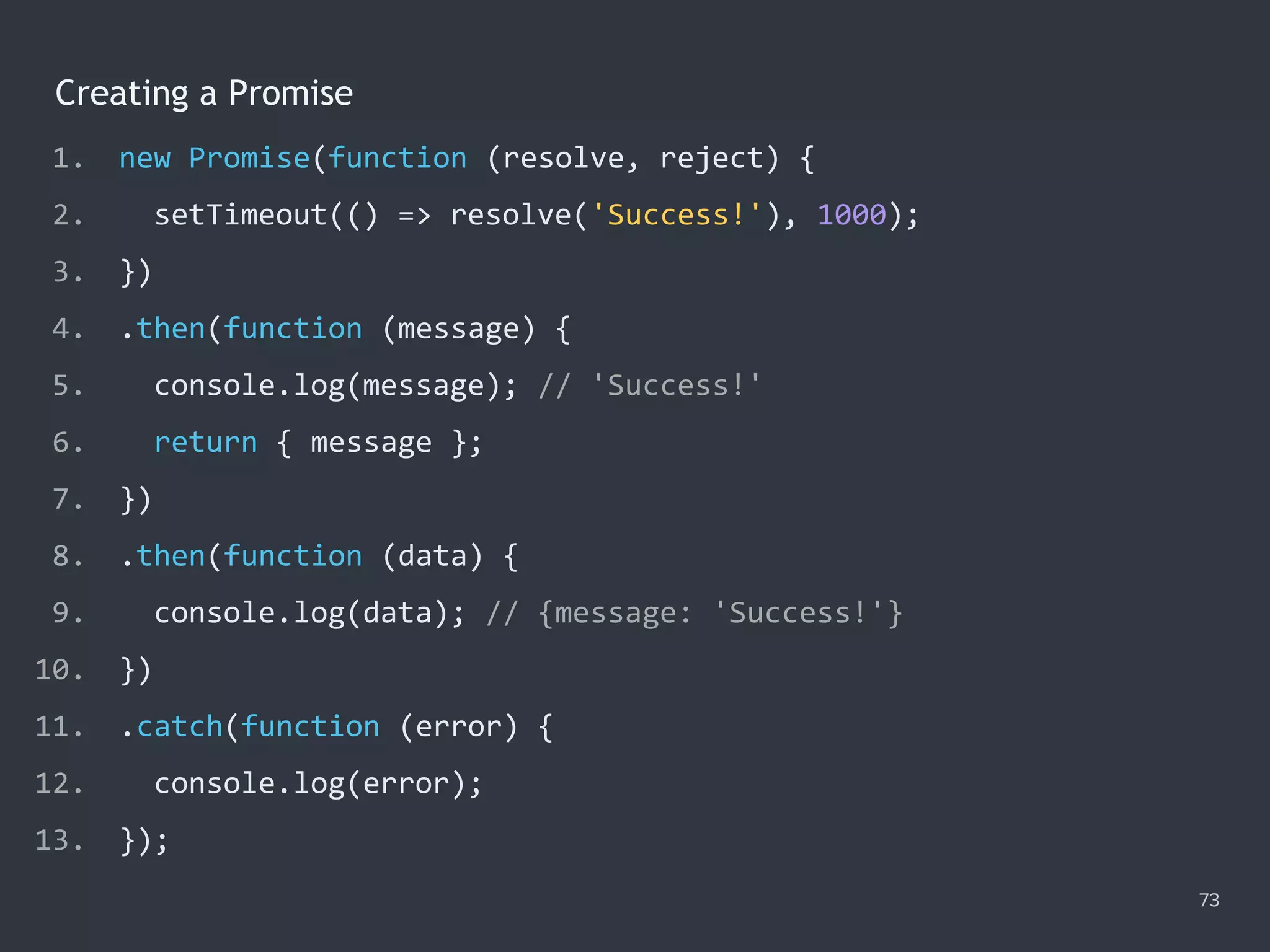


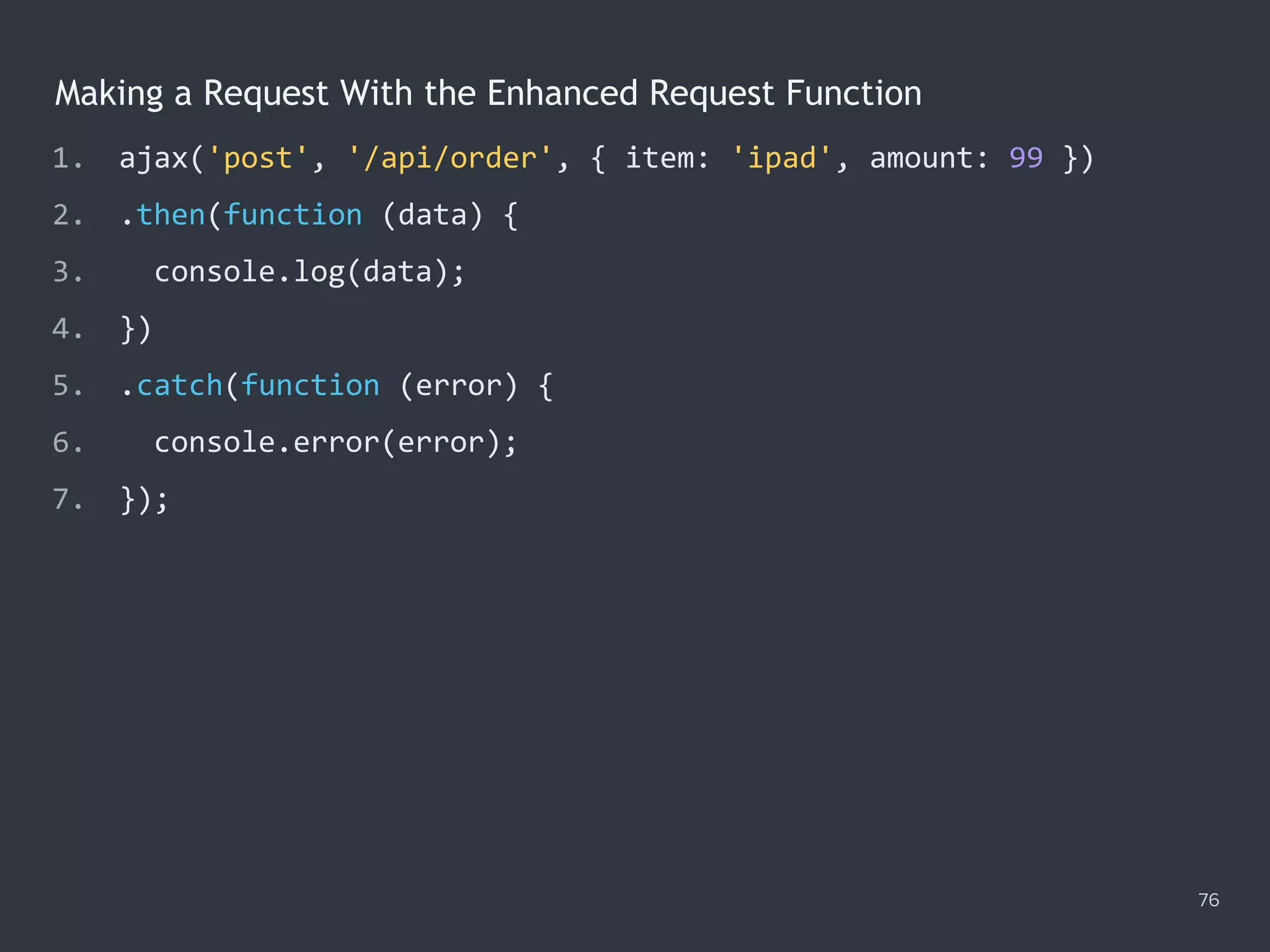
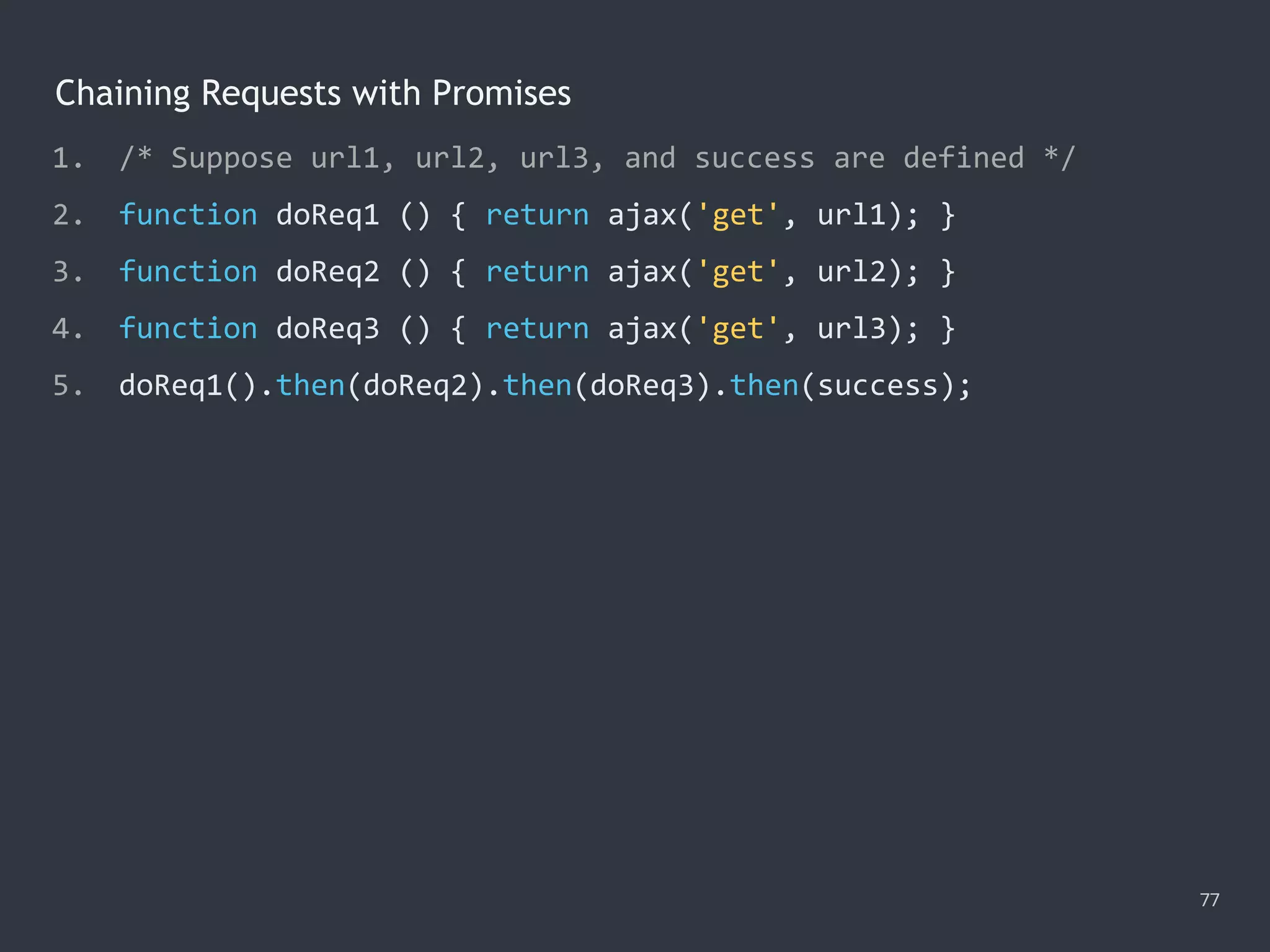
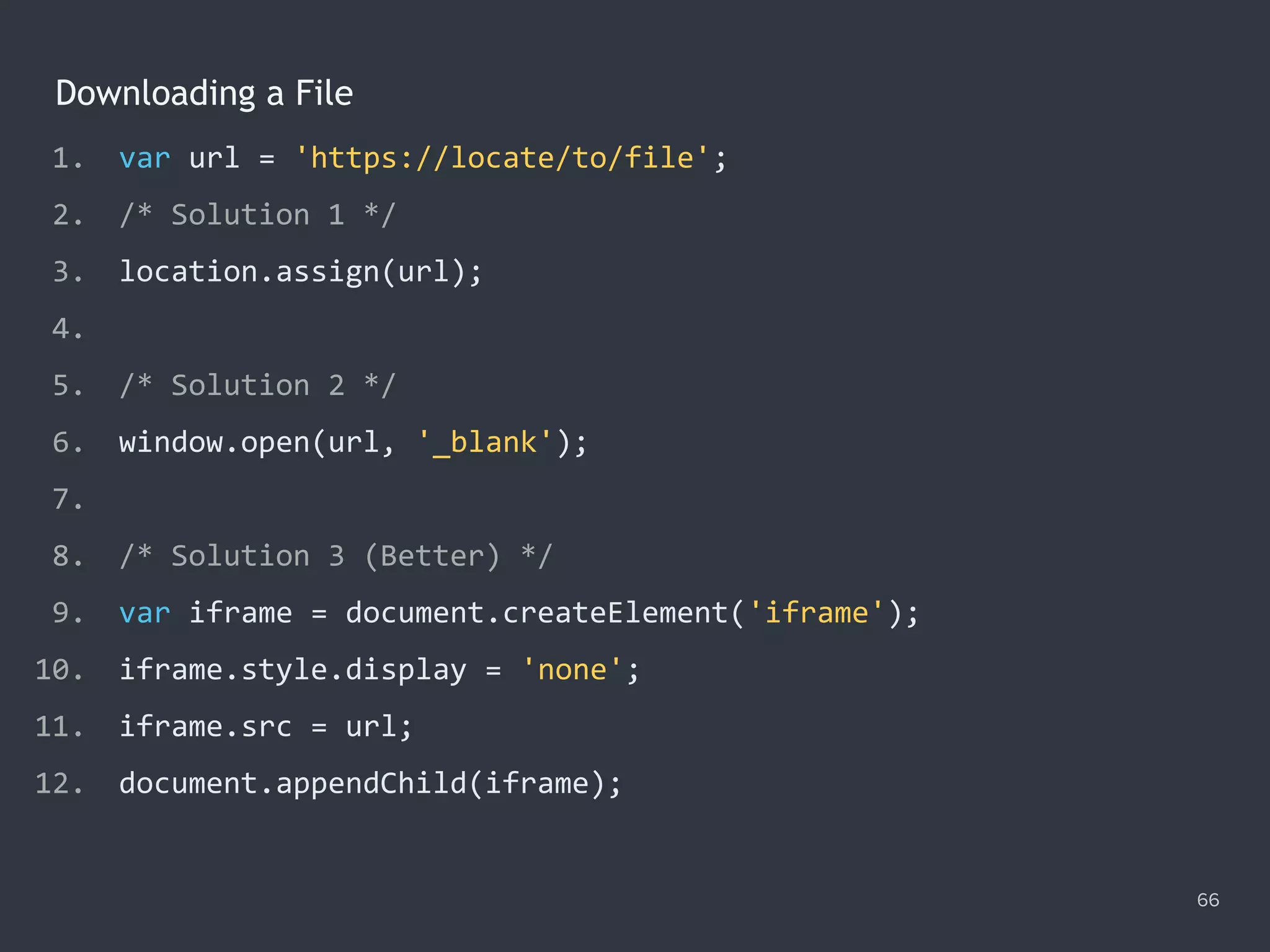
![The Promise.all() Method 78 1. Promise.all([ 2. ajax('get', '/data/hosts.json'), 3. ajax('get', '/data/users.json') 4. ]) 5. .then(function ([hosts, users]) { 6. console.log(hosts); 7. console.log(users); 8. }) 9. .catch(function (error) { 10. console.error(error); 11. });](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practicaljavascriptprogramming-session5-170719054827/75/Practical-JavaScript-Programming-Session-5-8-78-2048.jpg)