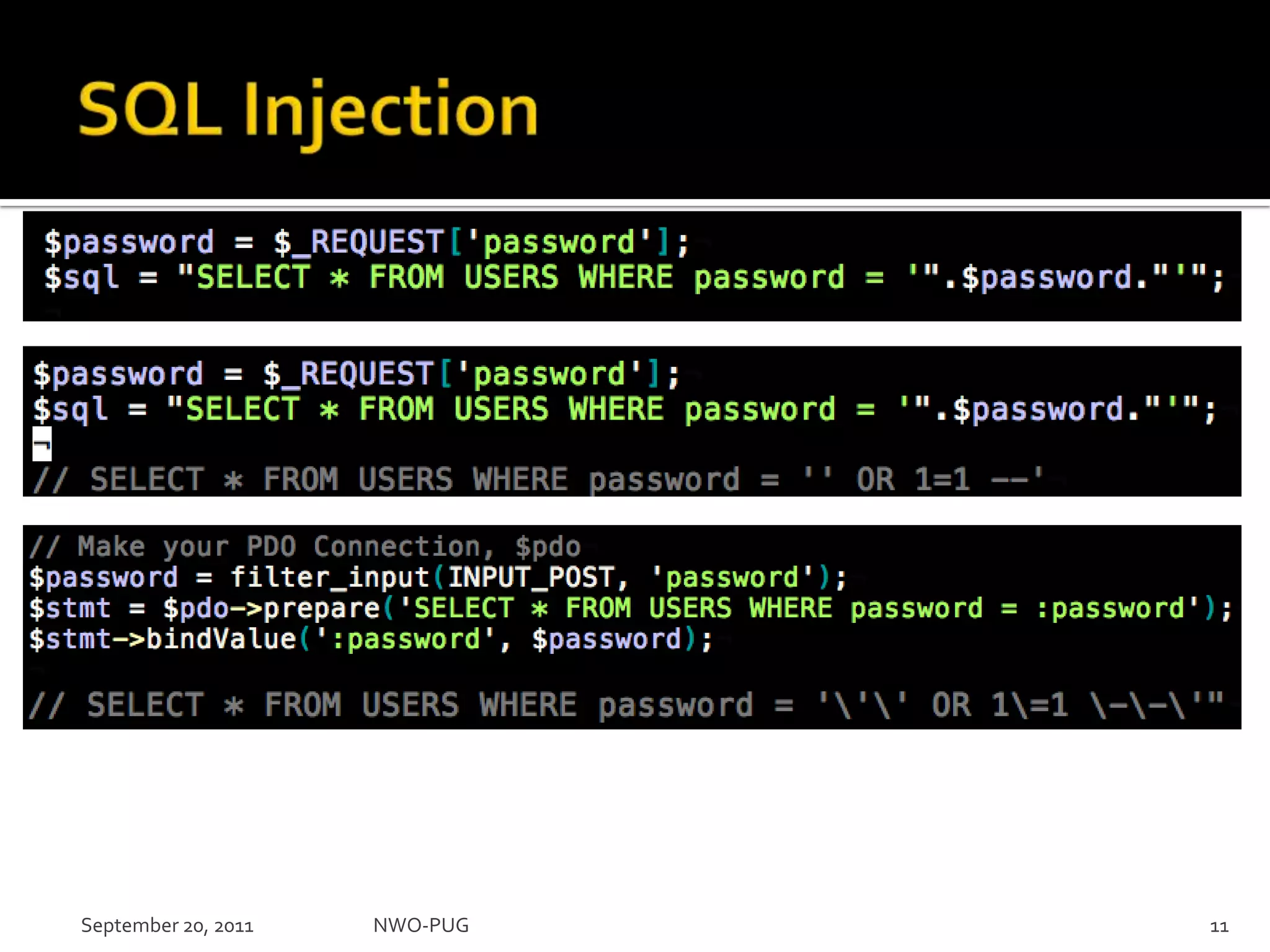
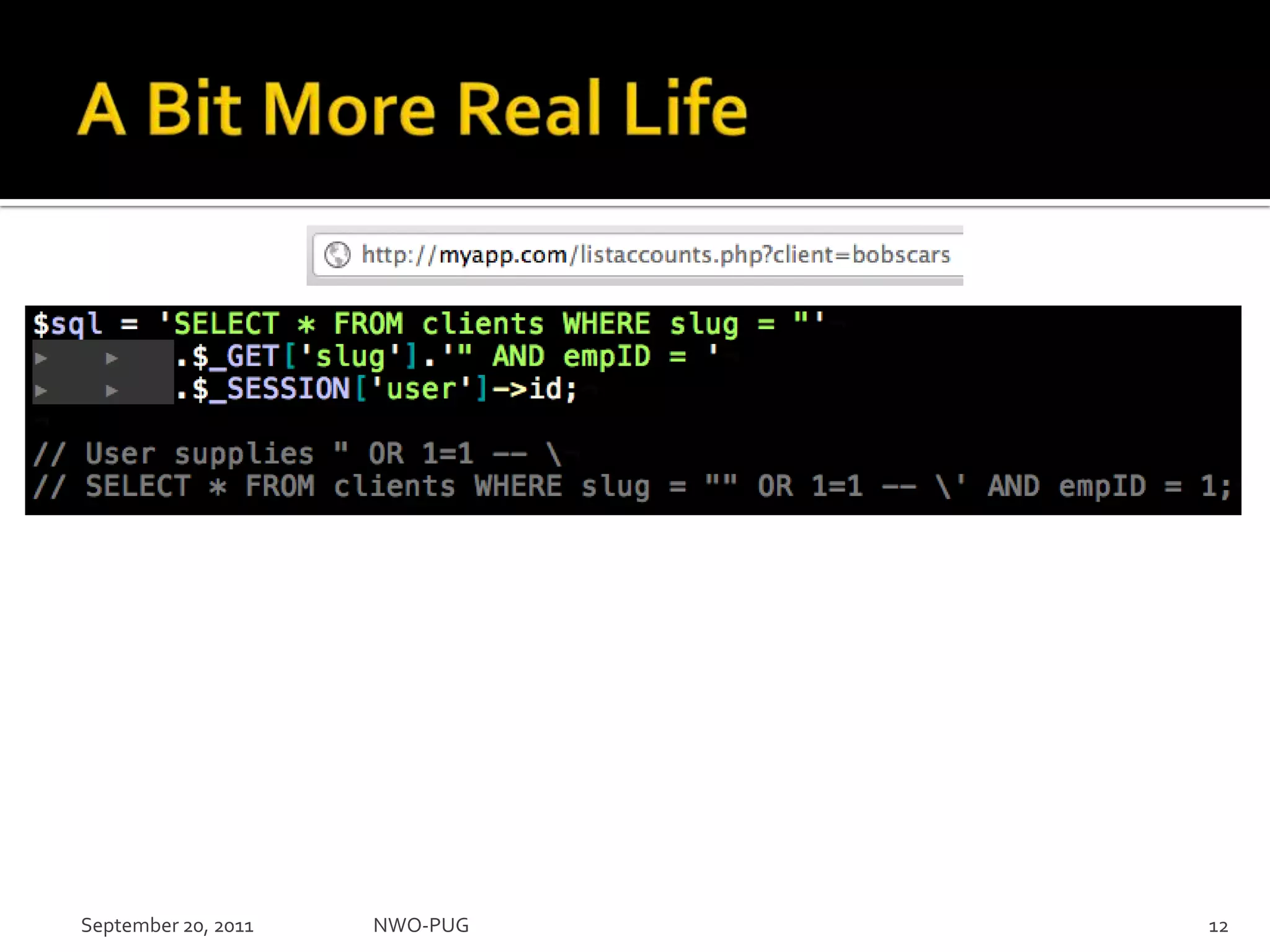
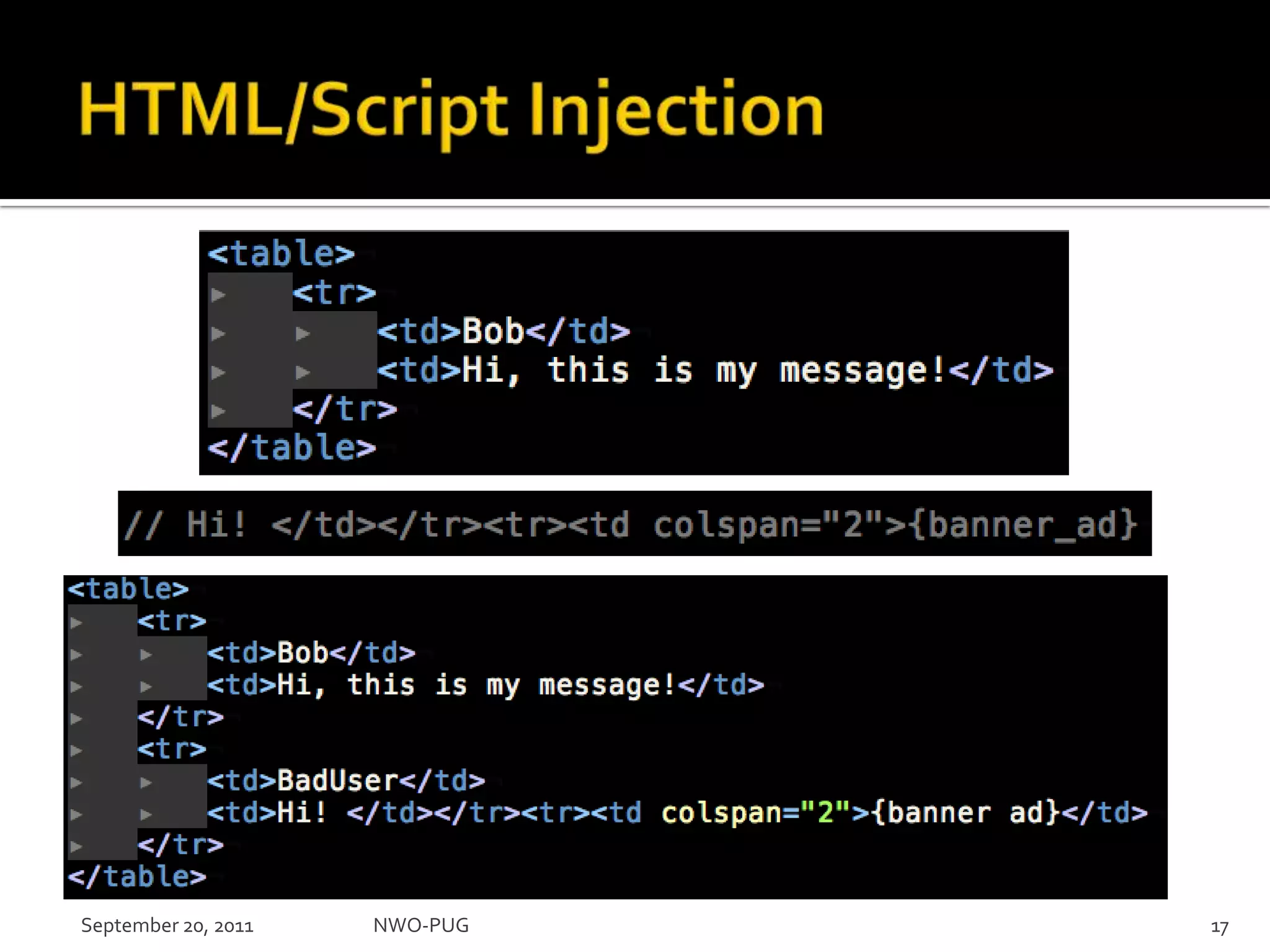
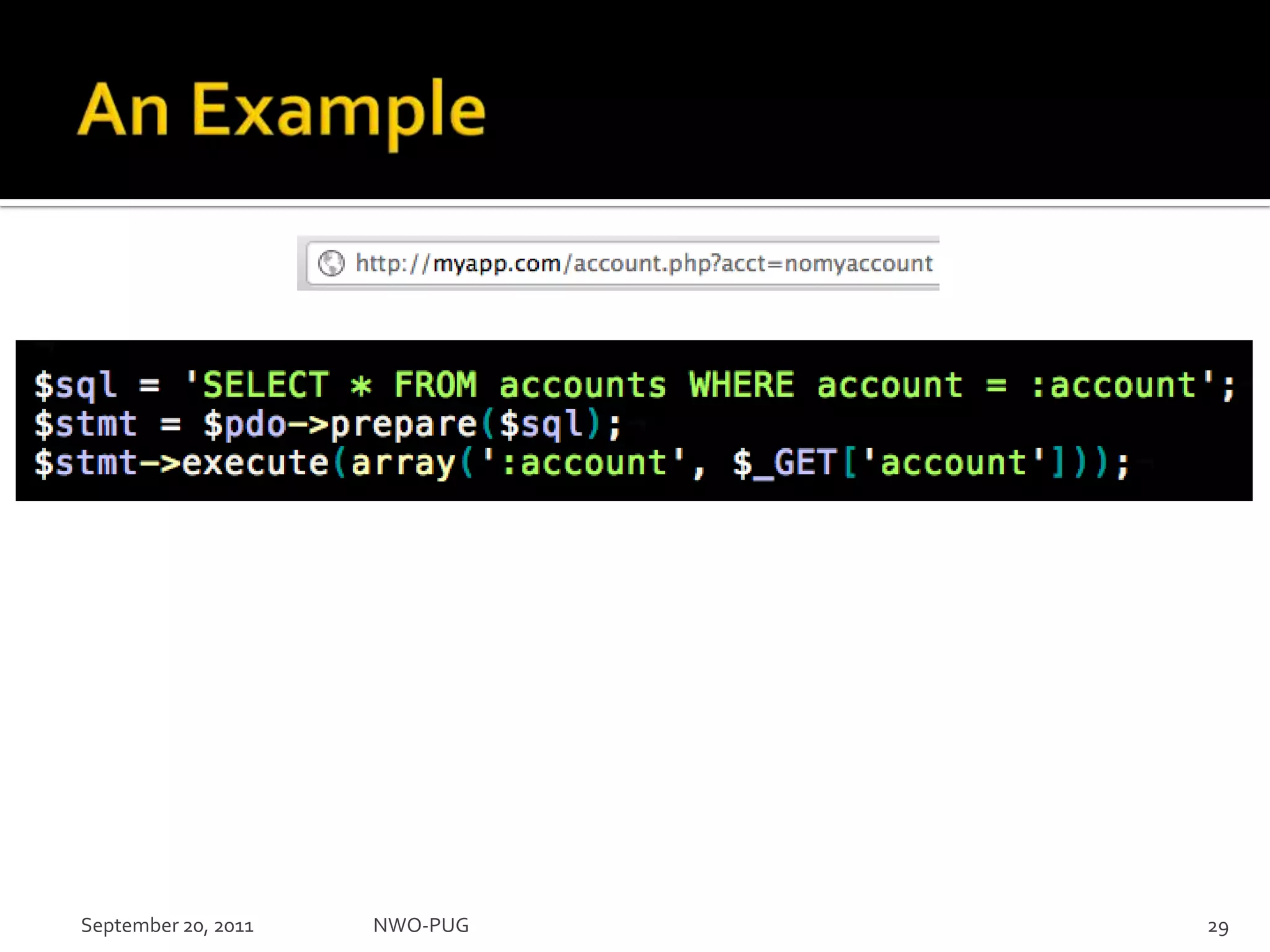
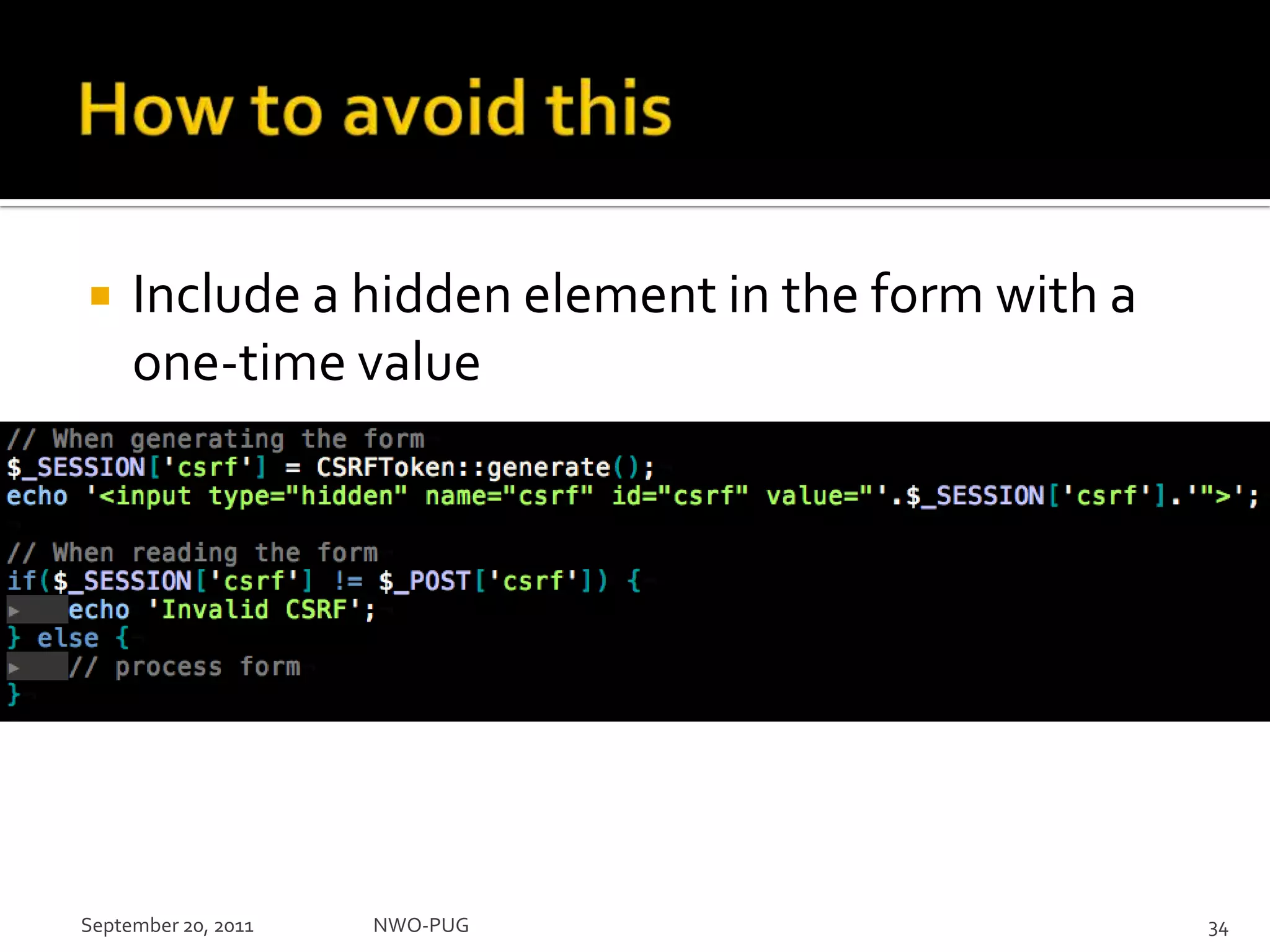
This document summarizes a presentation on PHP security given to the NWO-PUG group. The presentation covers the most common web application attacks like injection, cross-site scripting, insecure authentication, and how to prevent them following secure coding principles. It discusses the OWASP Top 10 security risks and how to avoid each one through input validation, output encoding, authorization checking, secure session handling and encryption. The presentation emphasizes defense in depth and that attackers may combine different vulnerabilities.