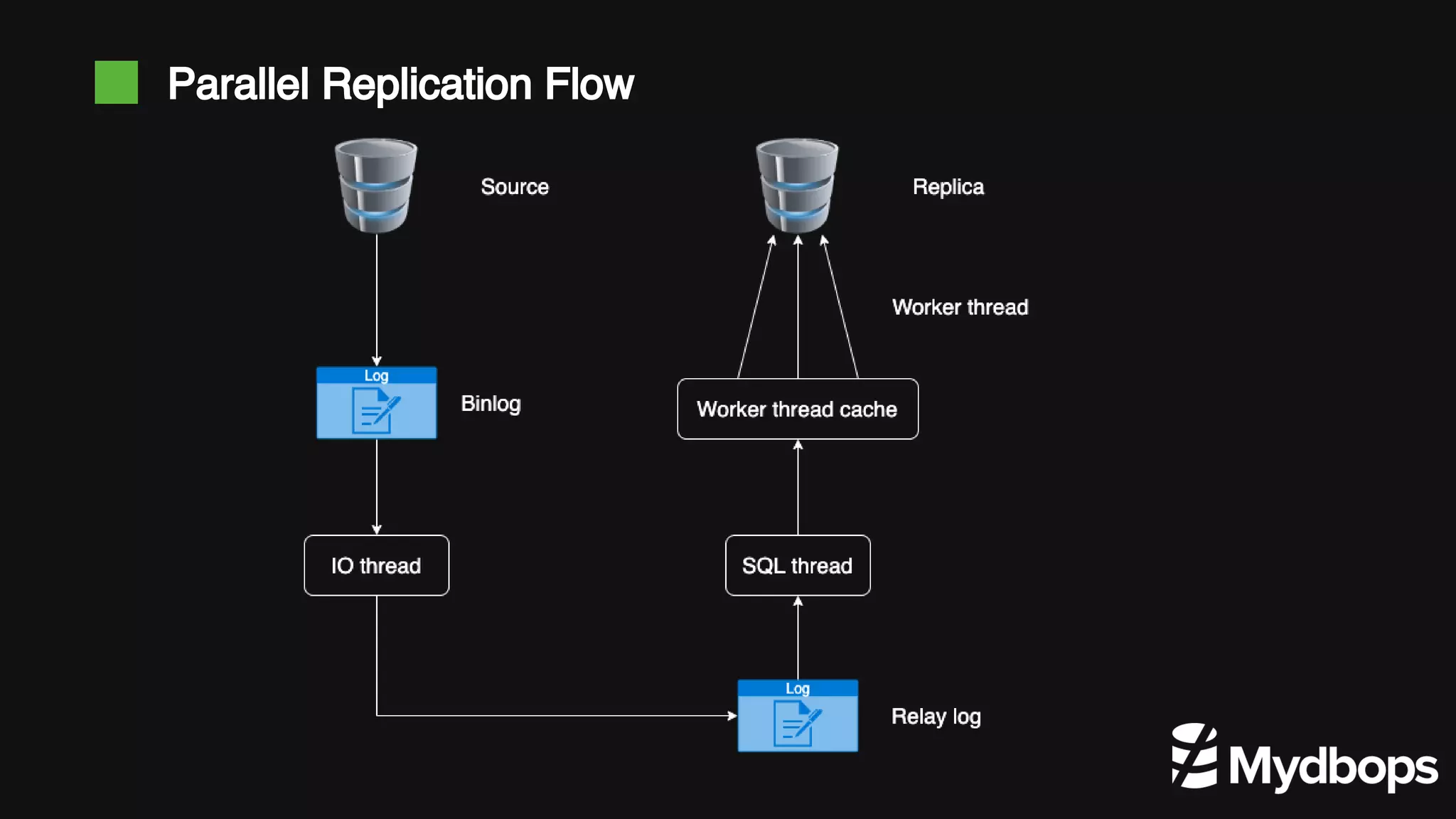
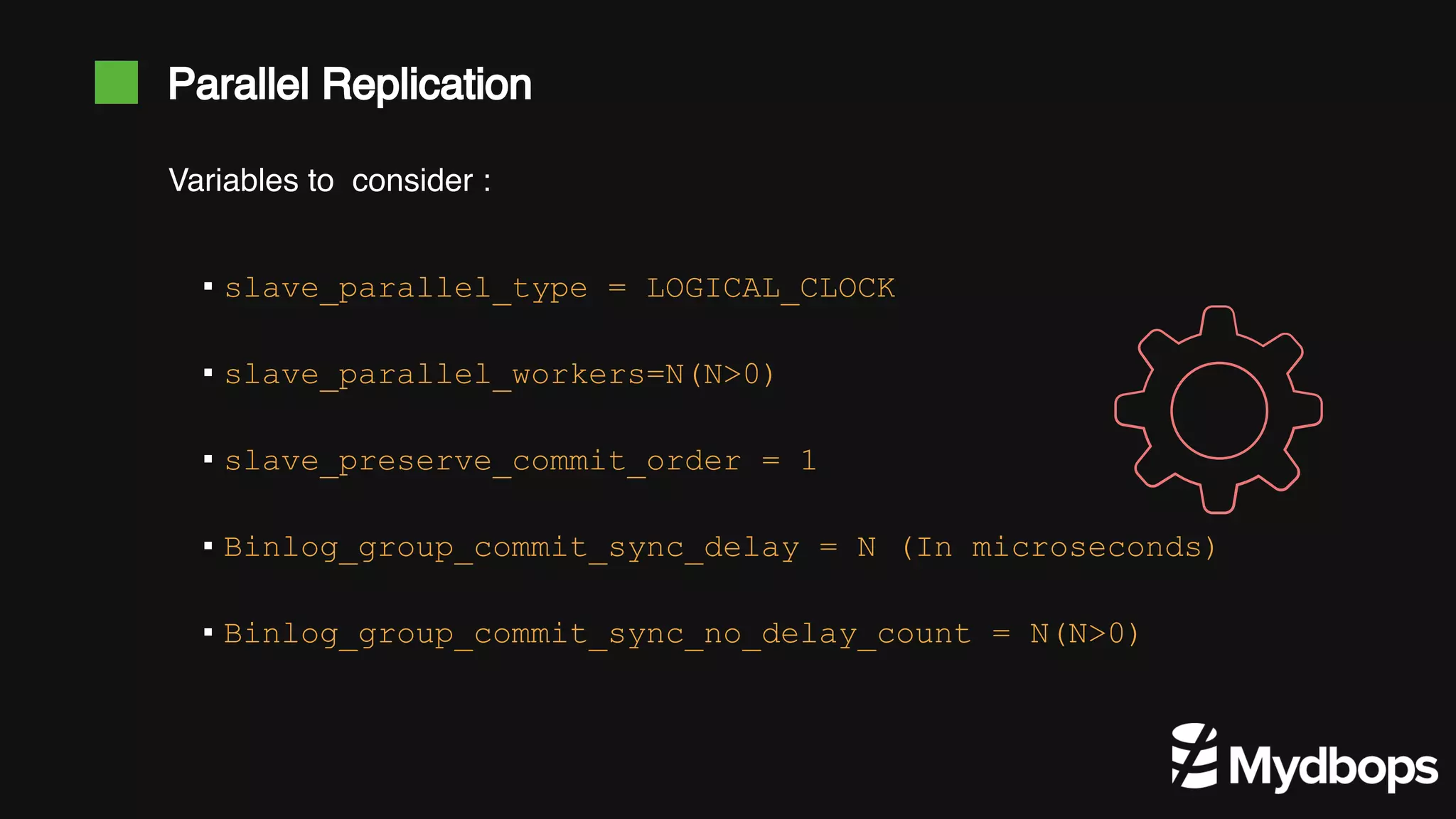
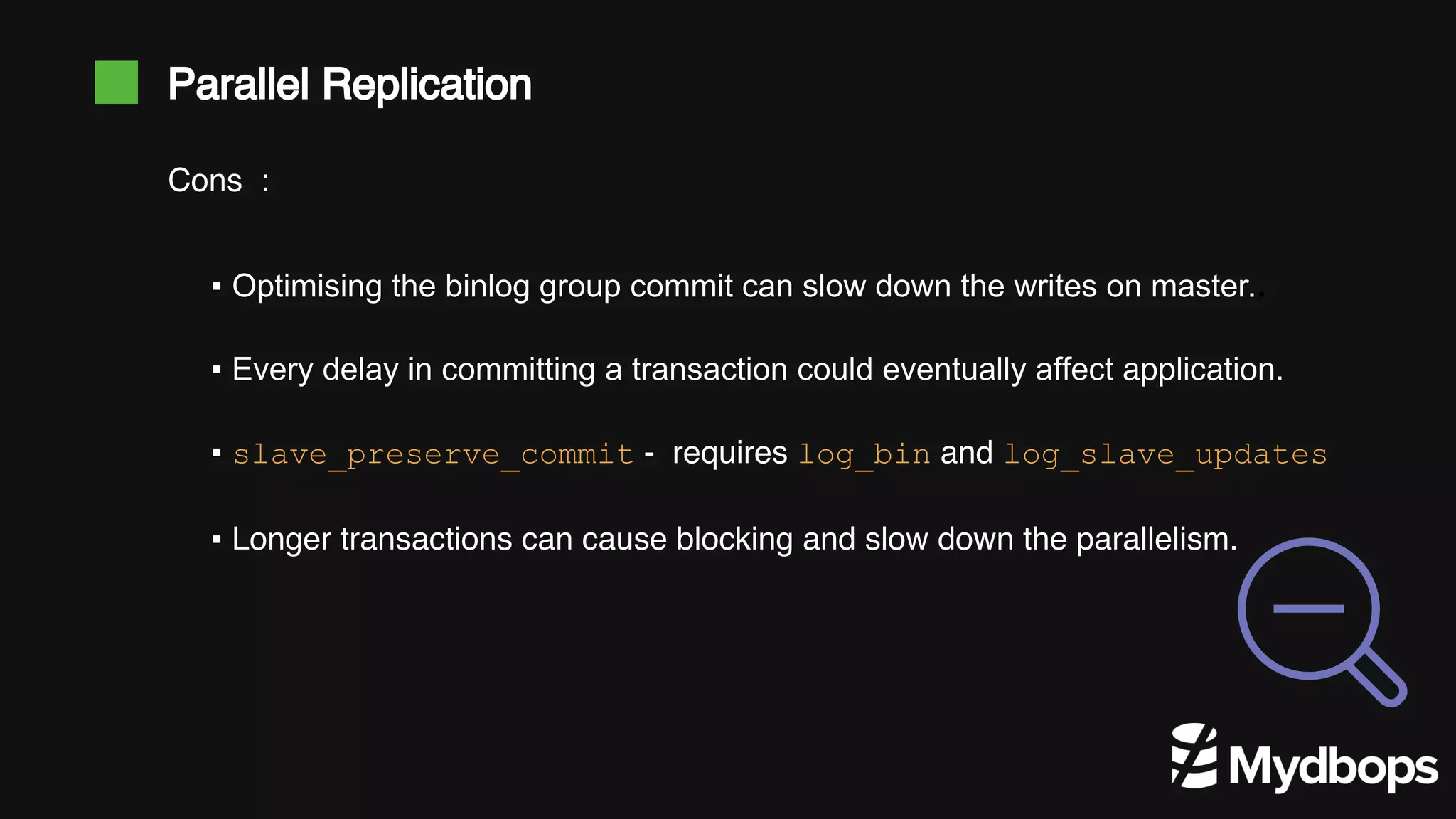
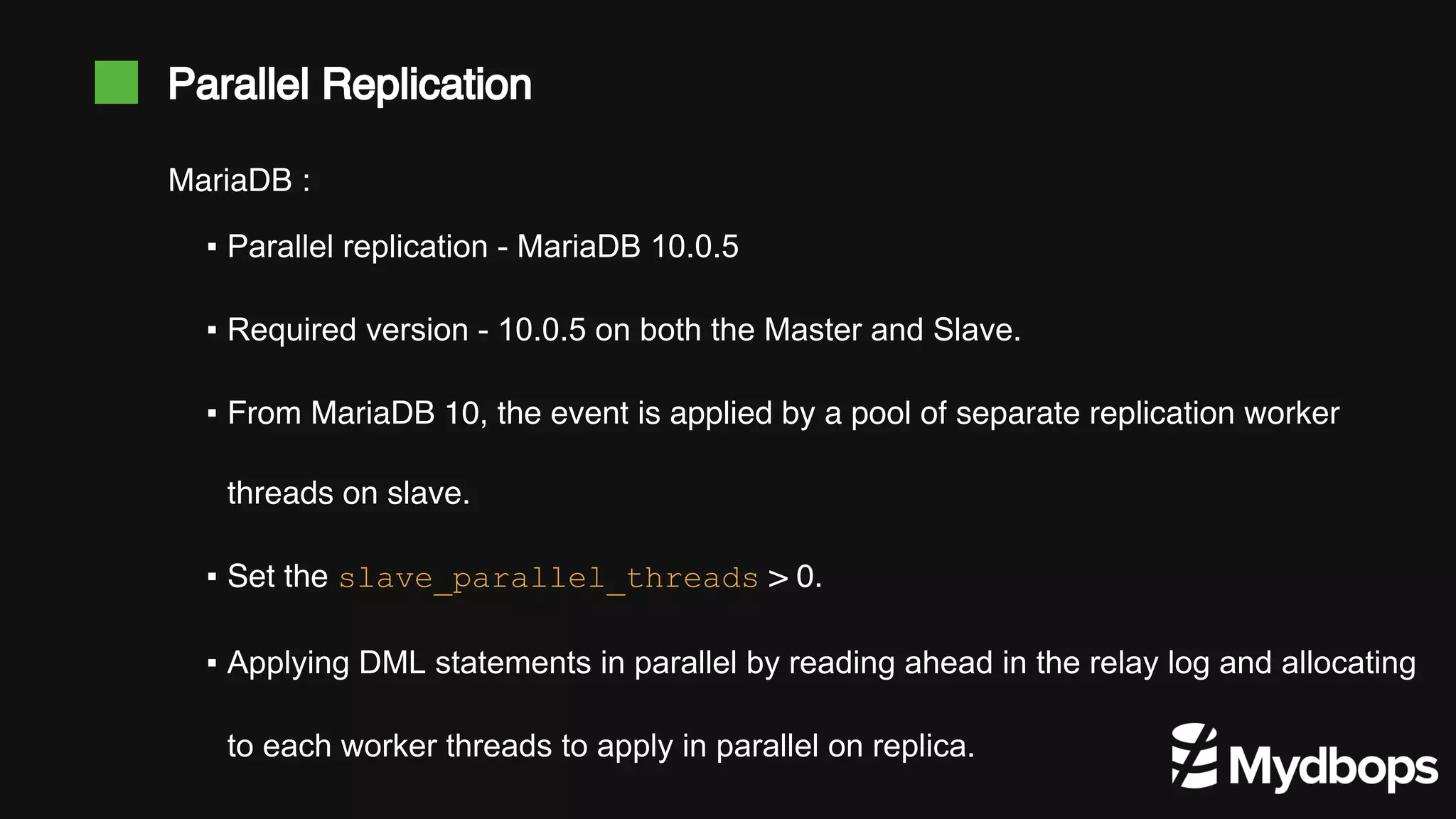
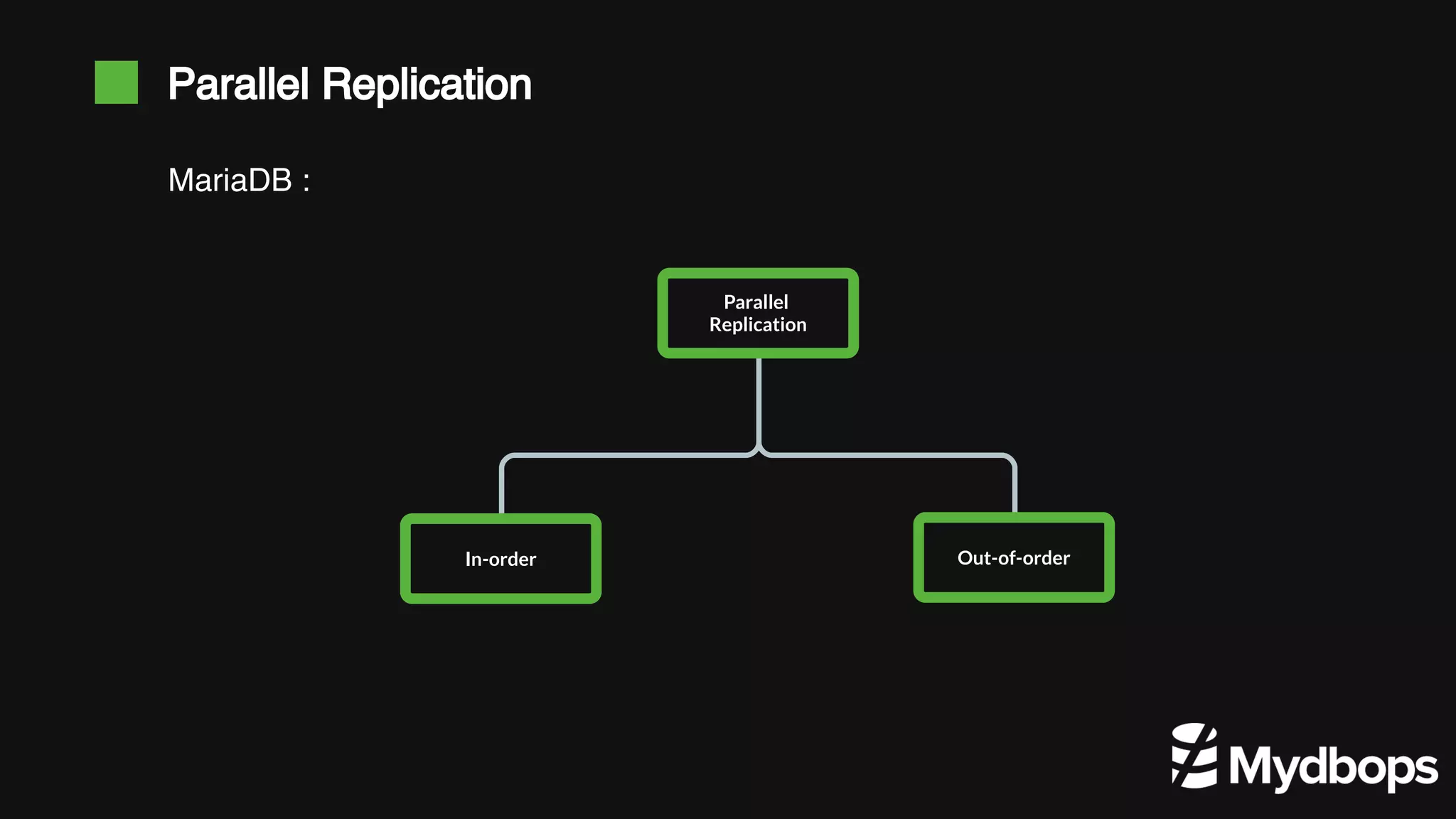
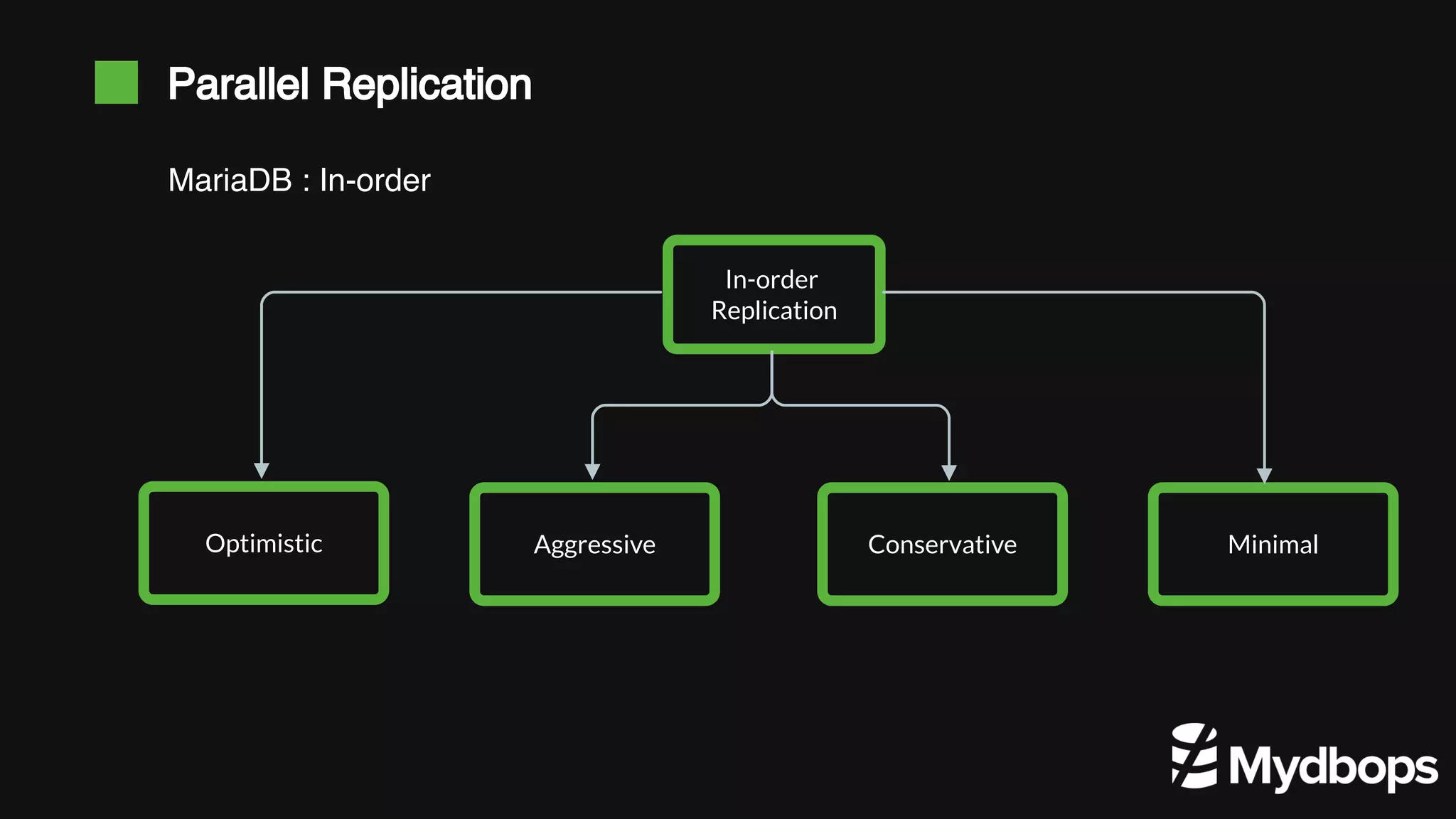
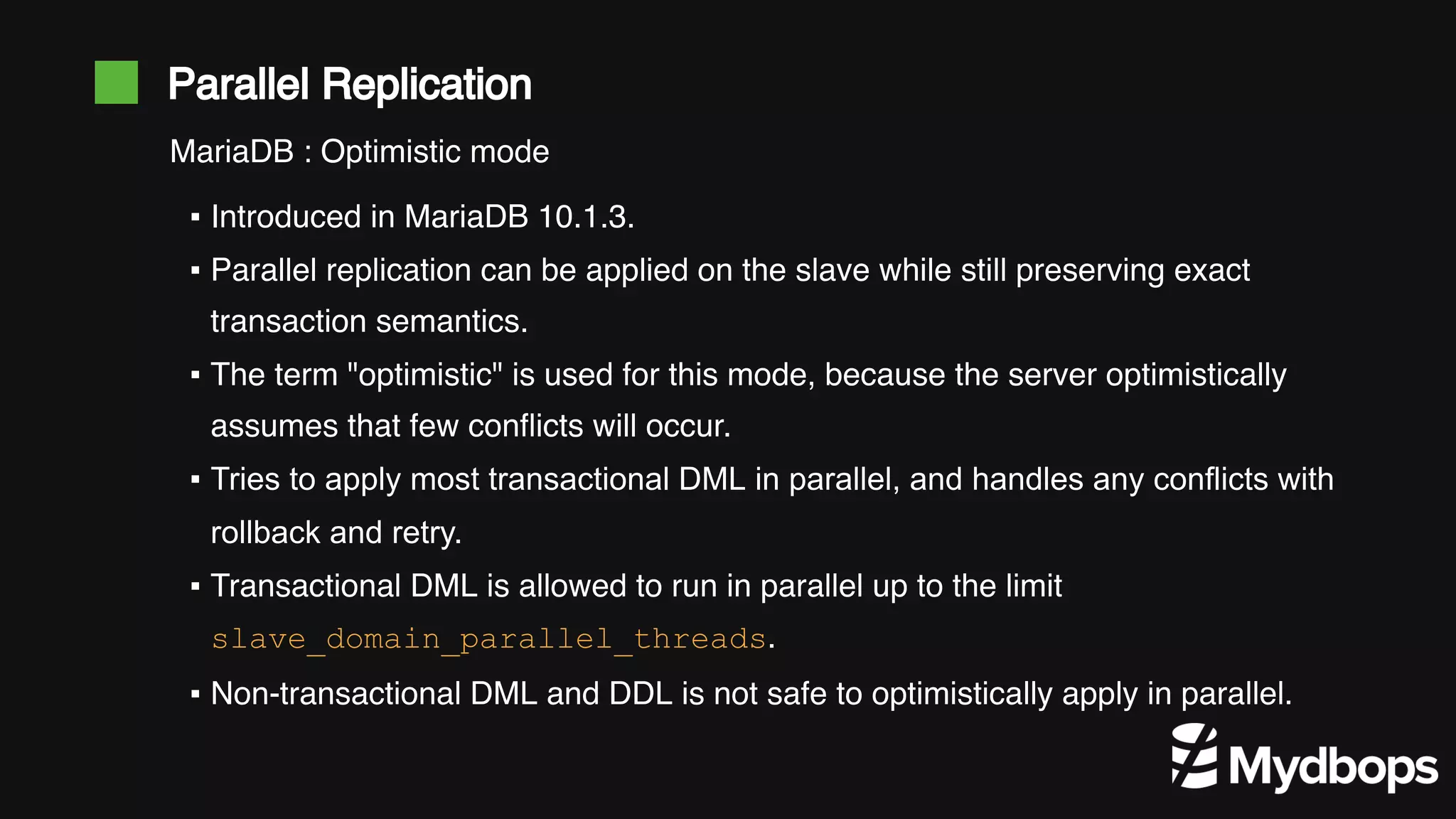
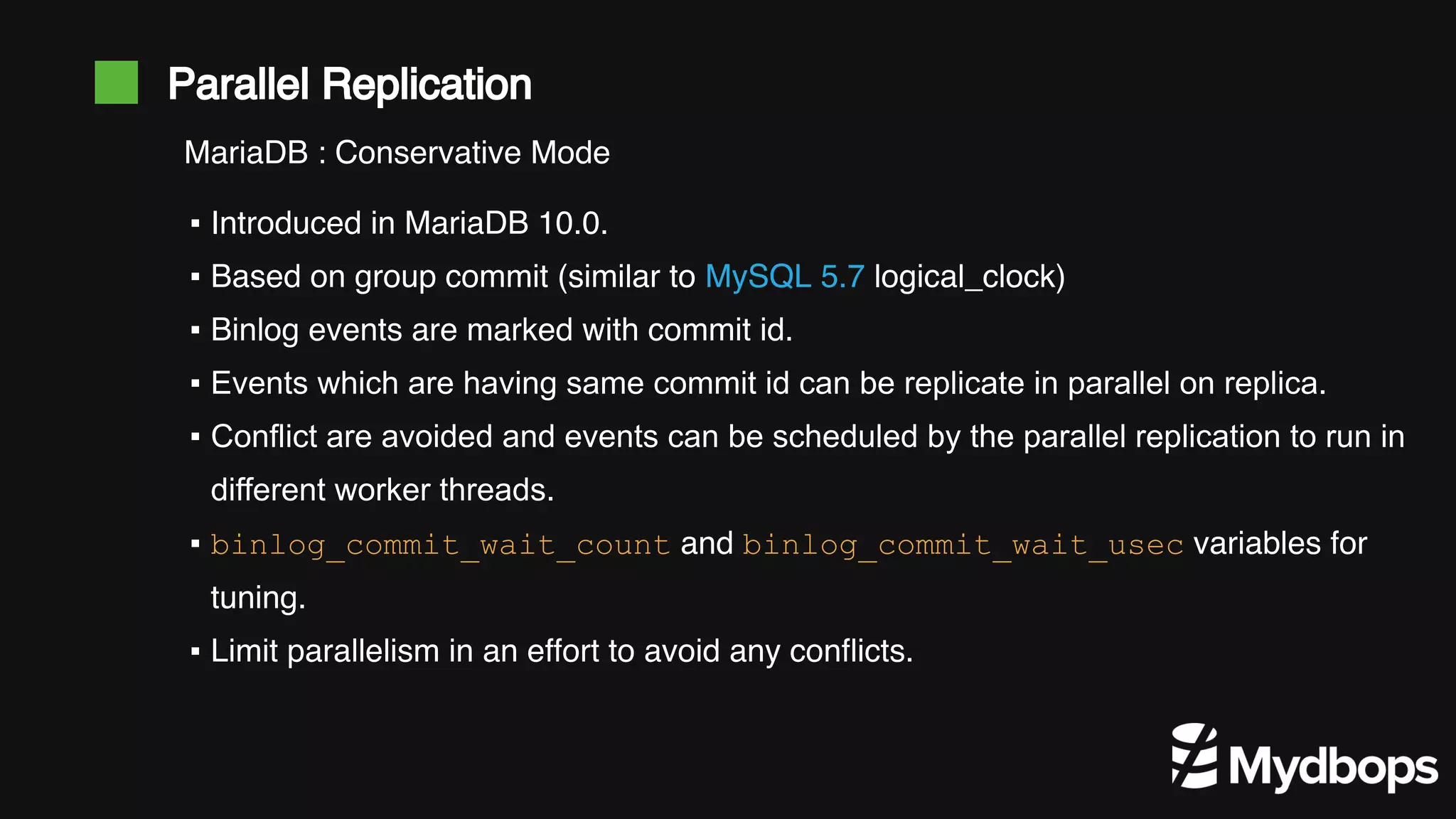
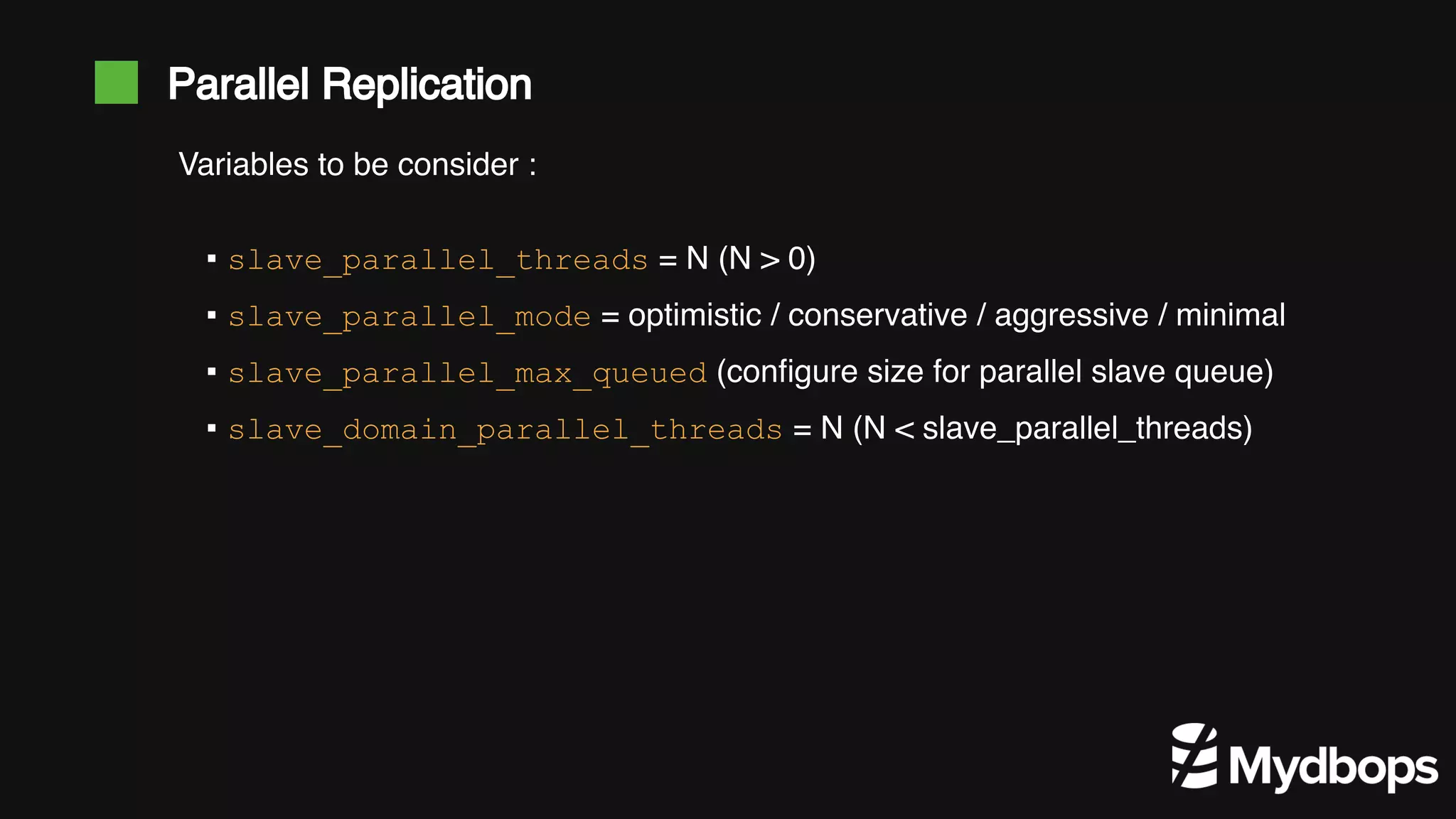
The document discusses parallel replication in MySQL and MariaDB, detailing its evolution, benefits, and various configurations. It explains the mechanics of replication, including the differences between single-threaded and multi-threaded processes, and highlights the improvements introduced in different MySQL and MariaDB versions. Additionally, it covers the implications, limitations, and recommended practices for effective parallel replication in both database systems.