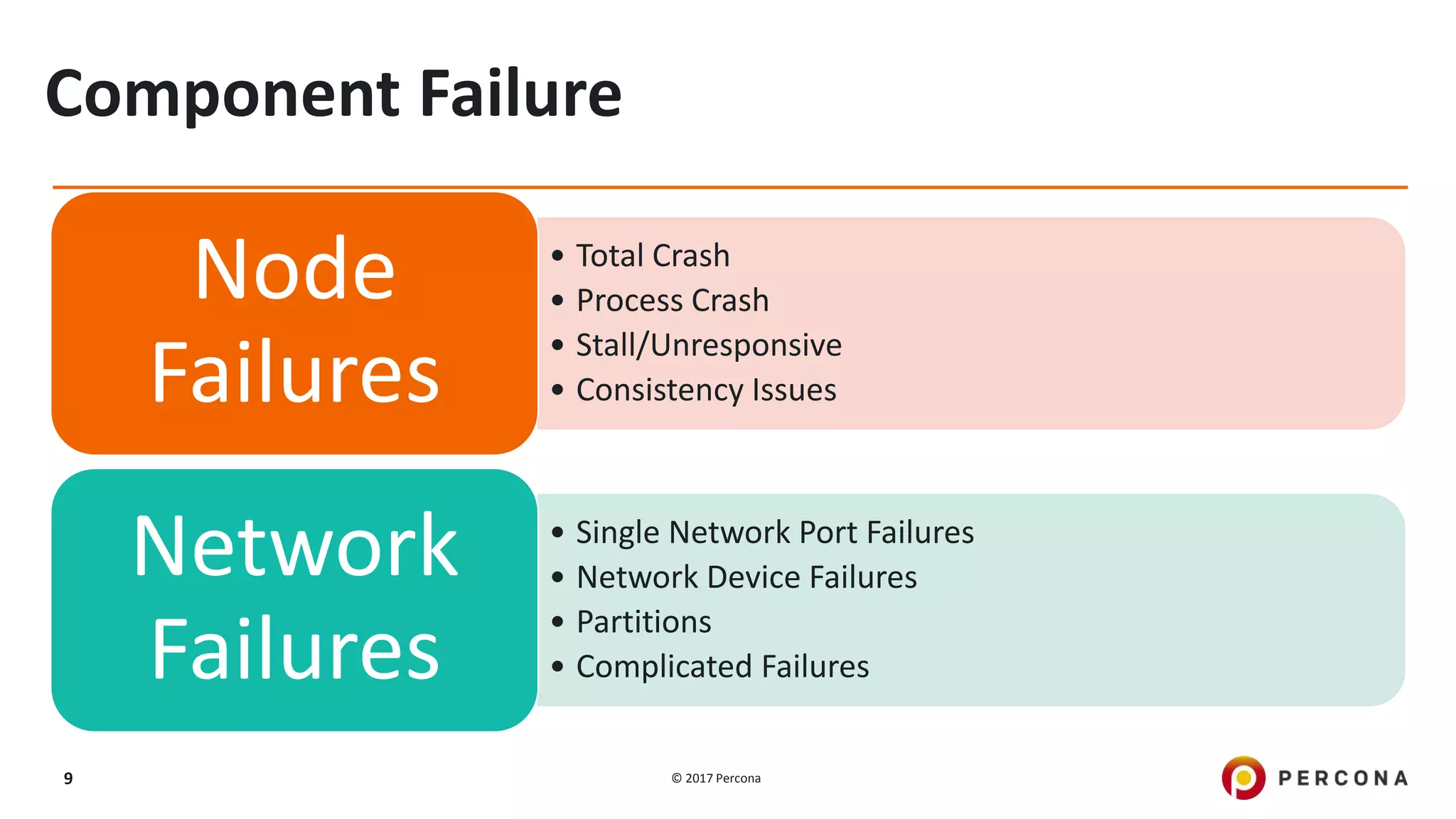
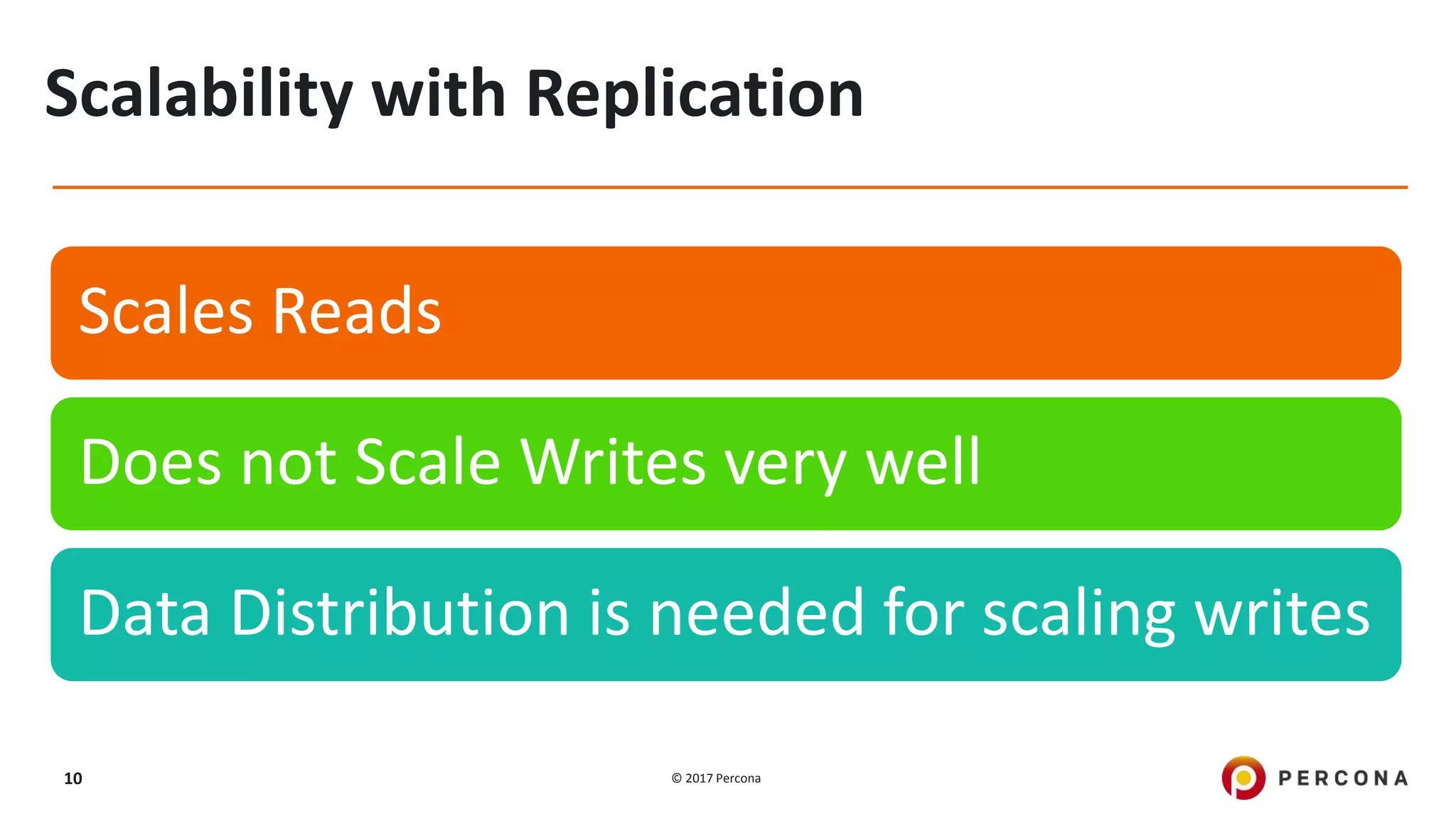
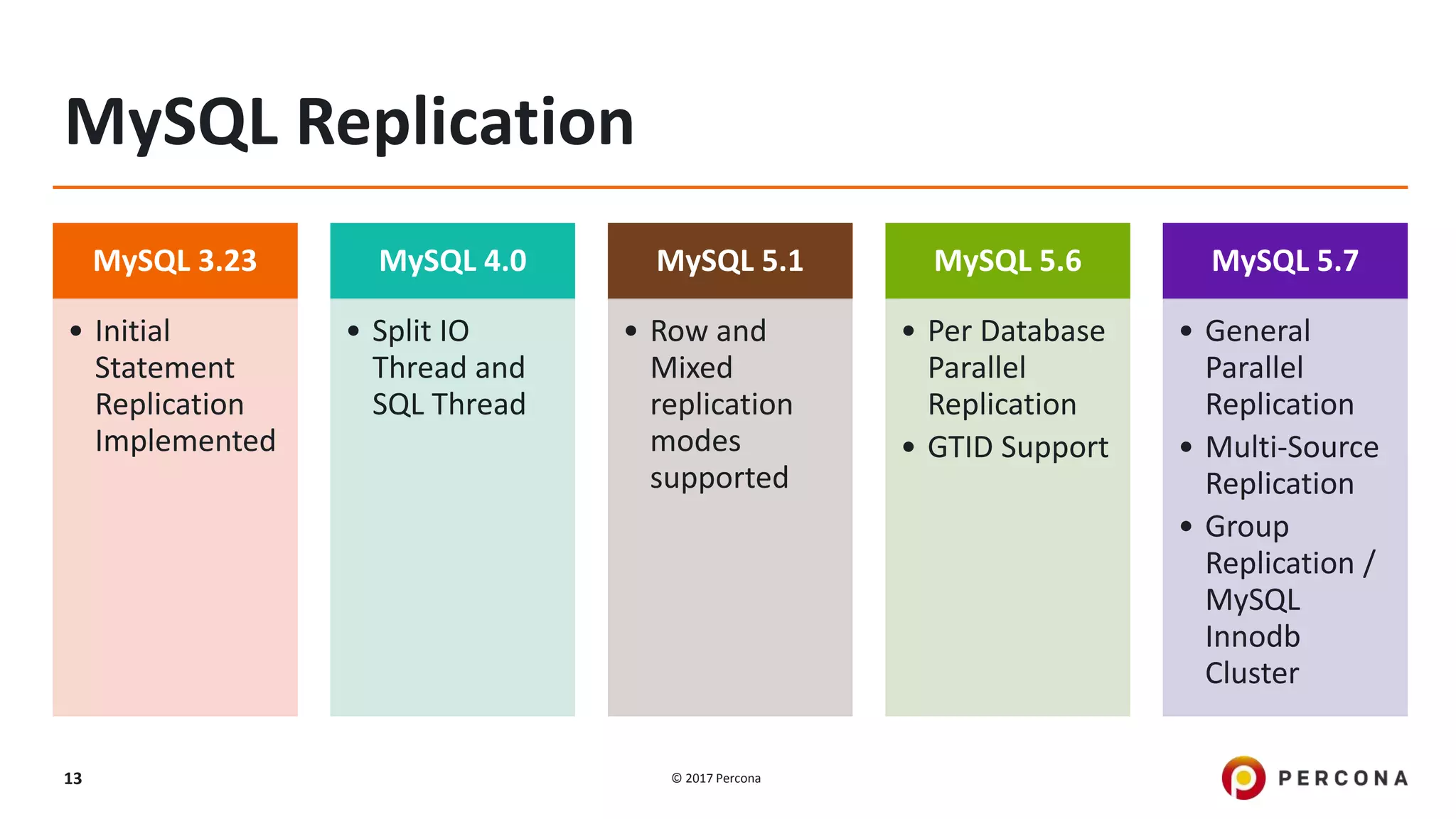
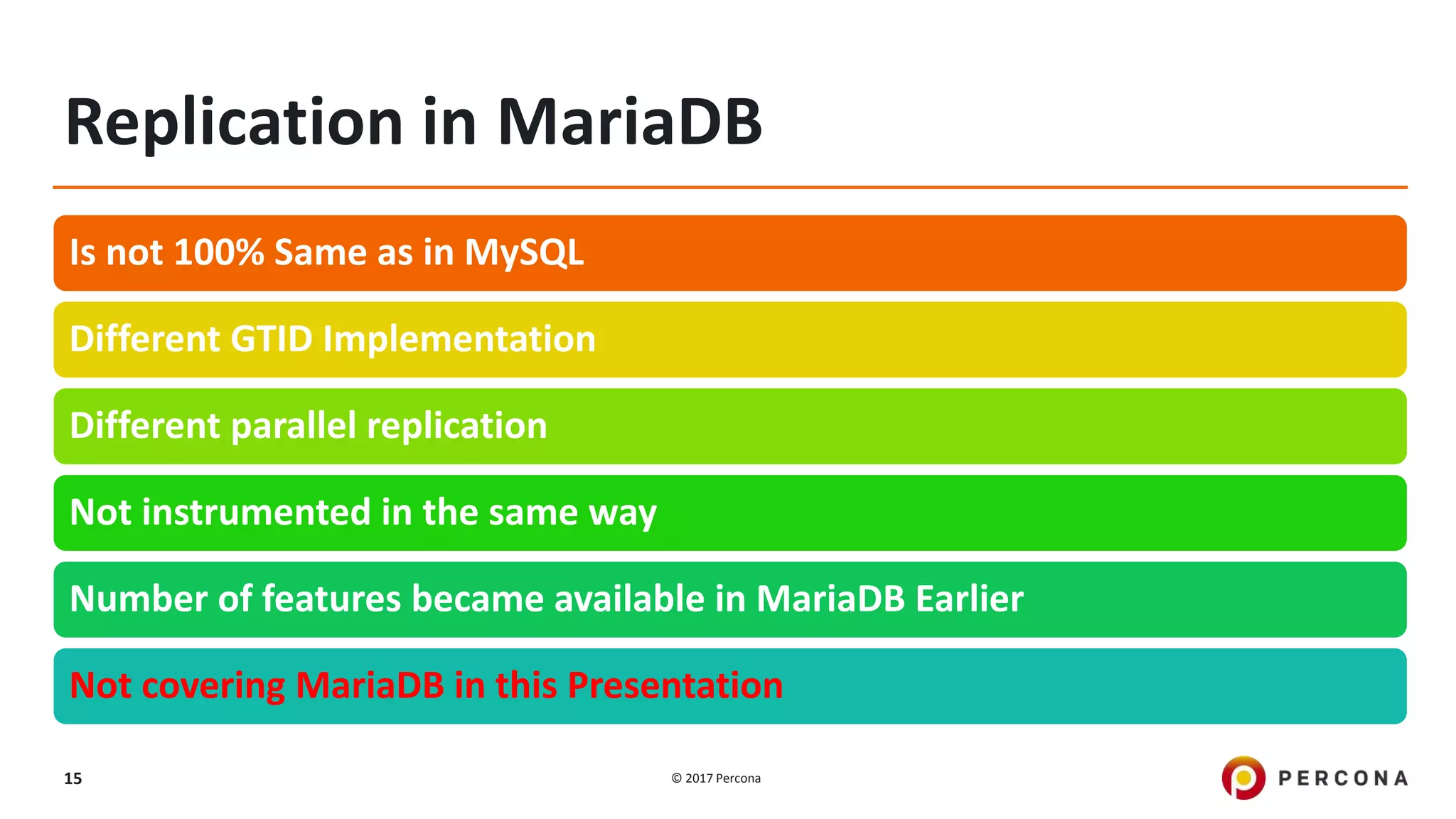
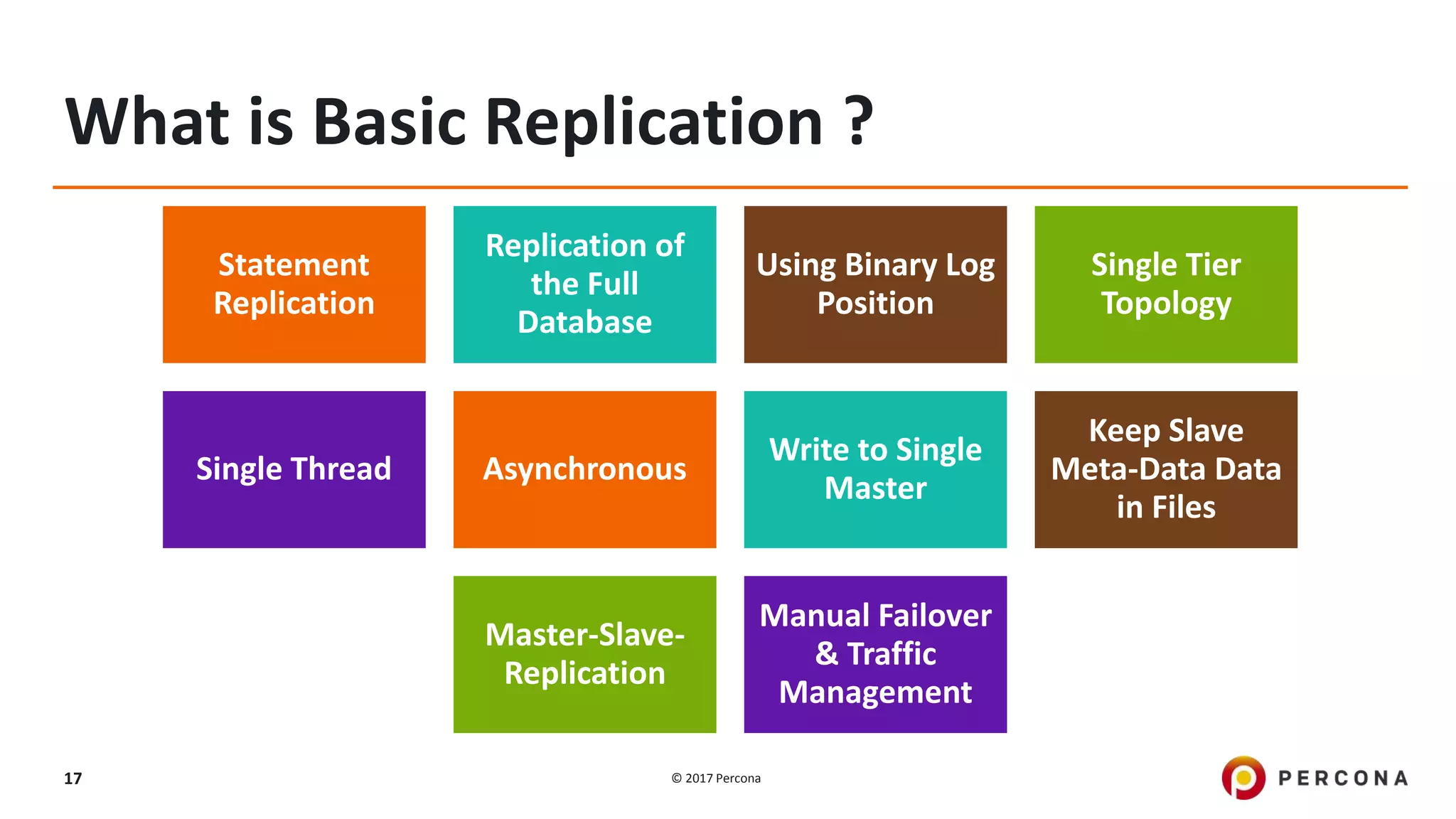
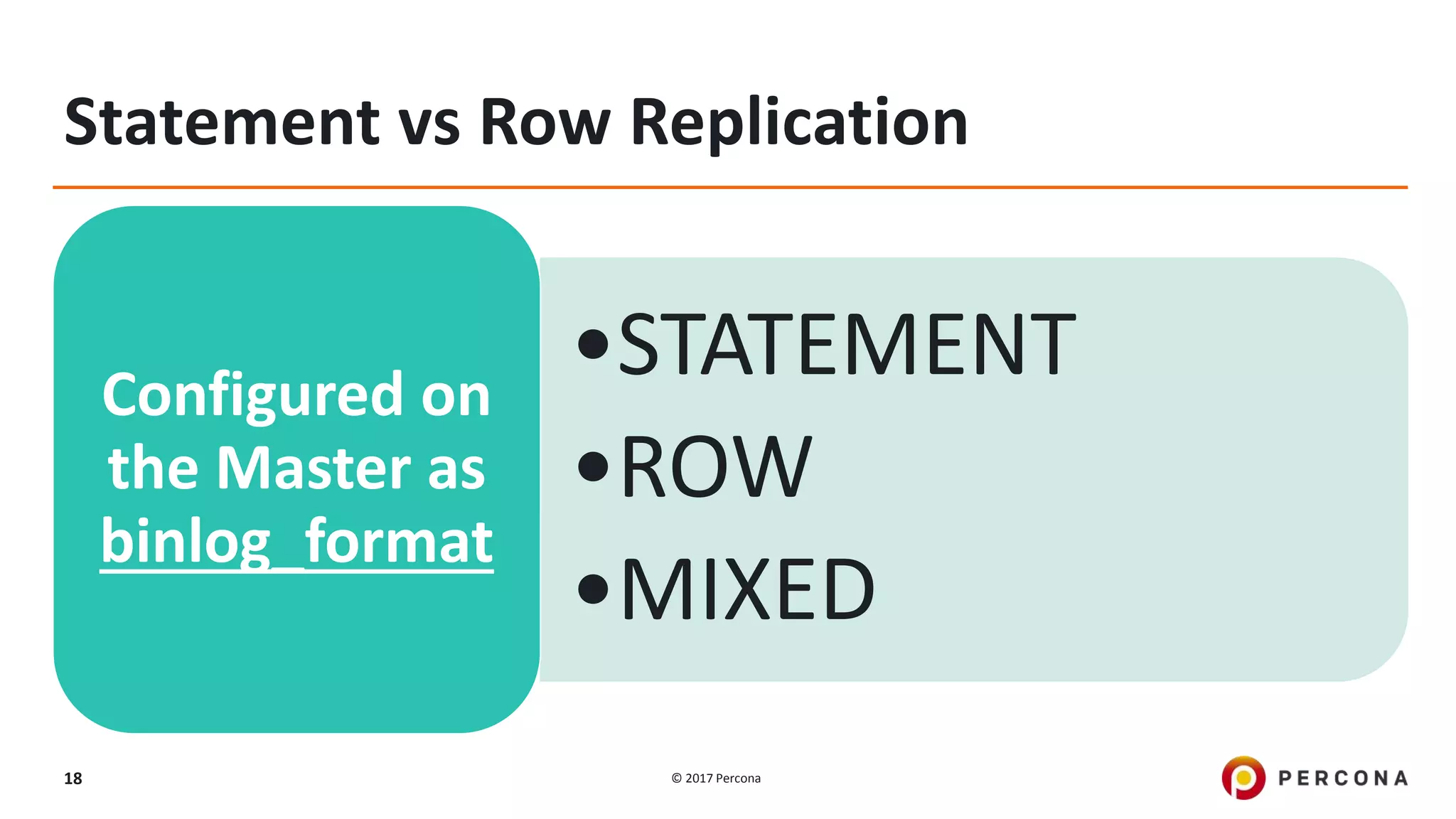
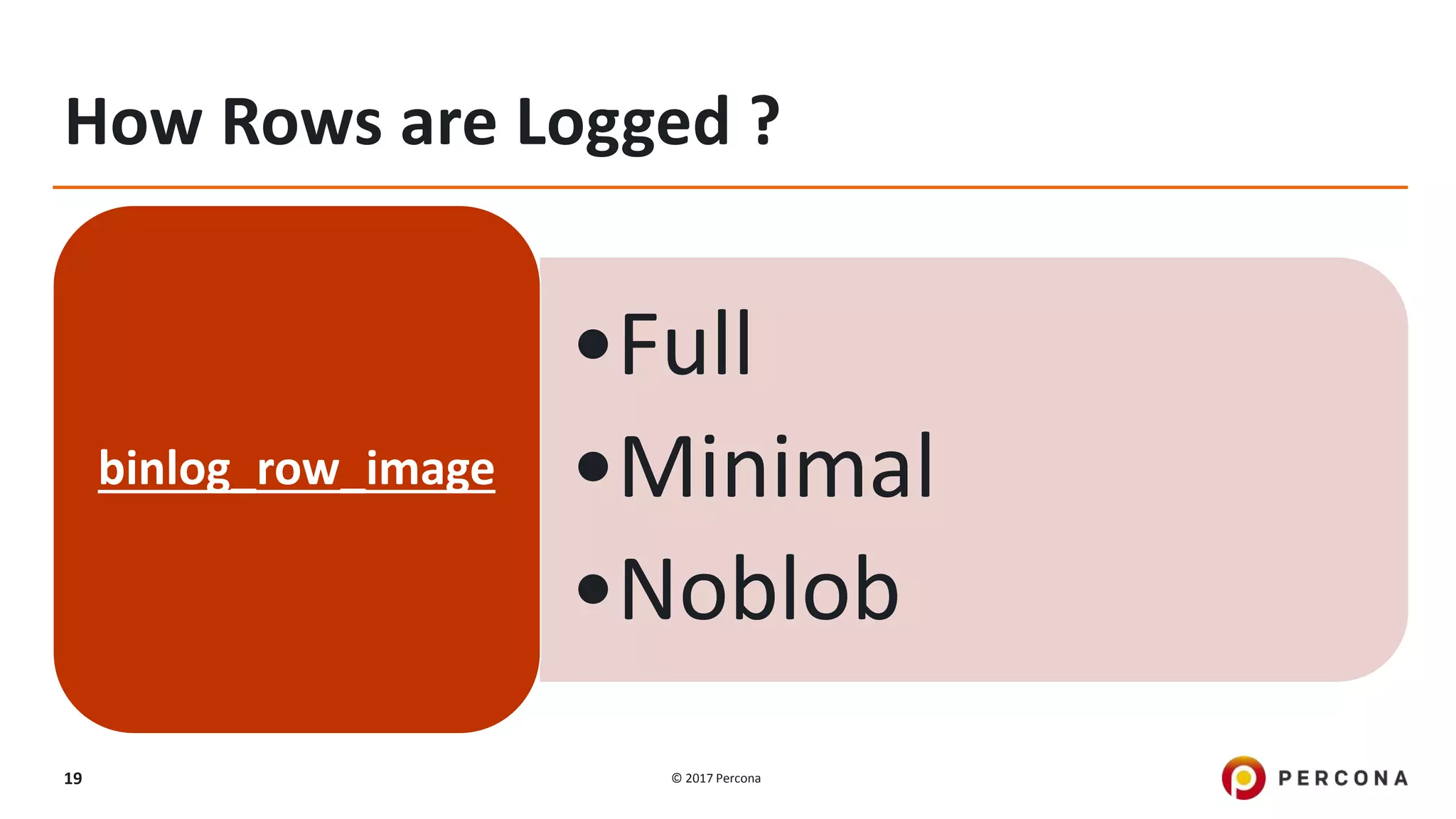
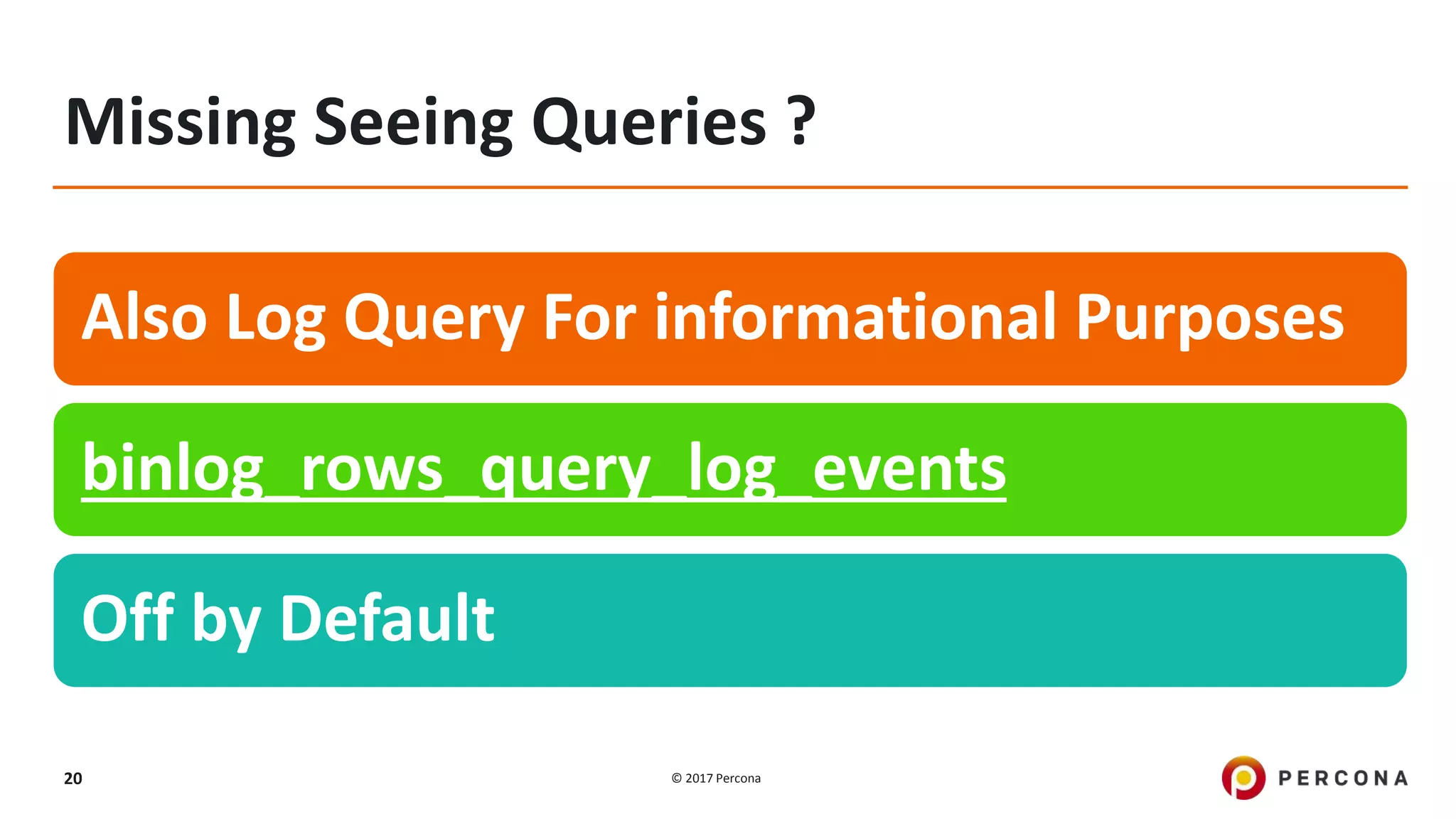
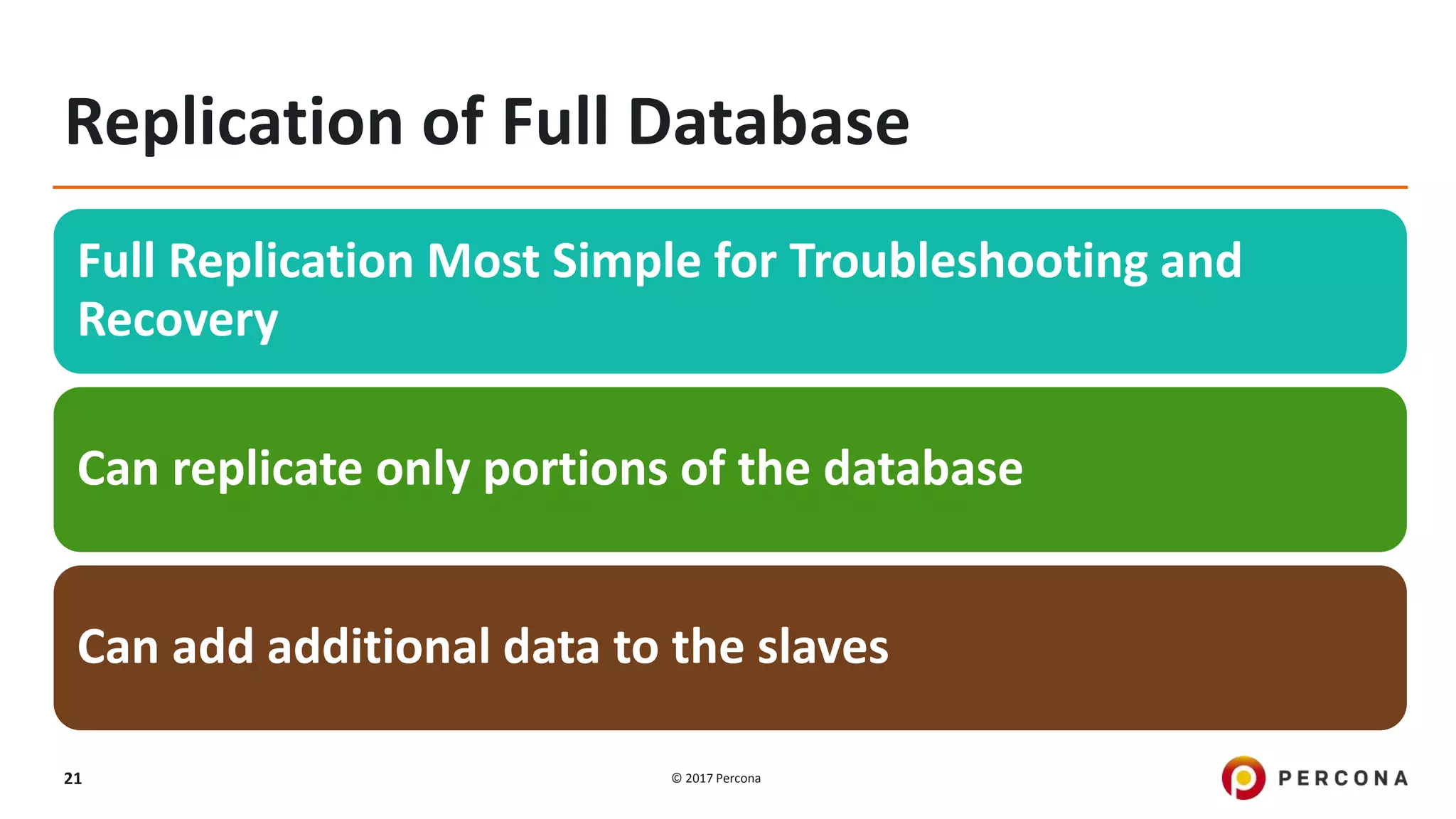
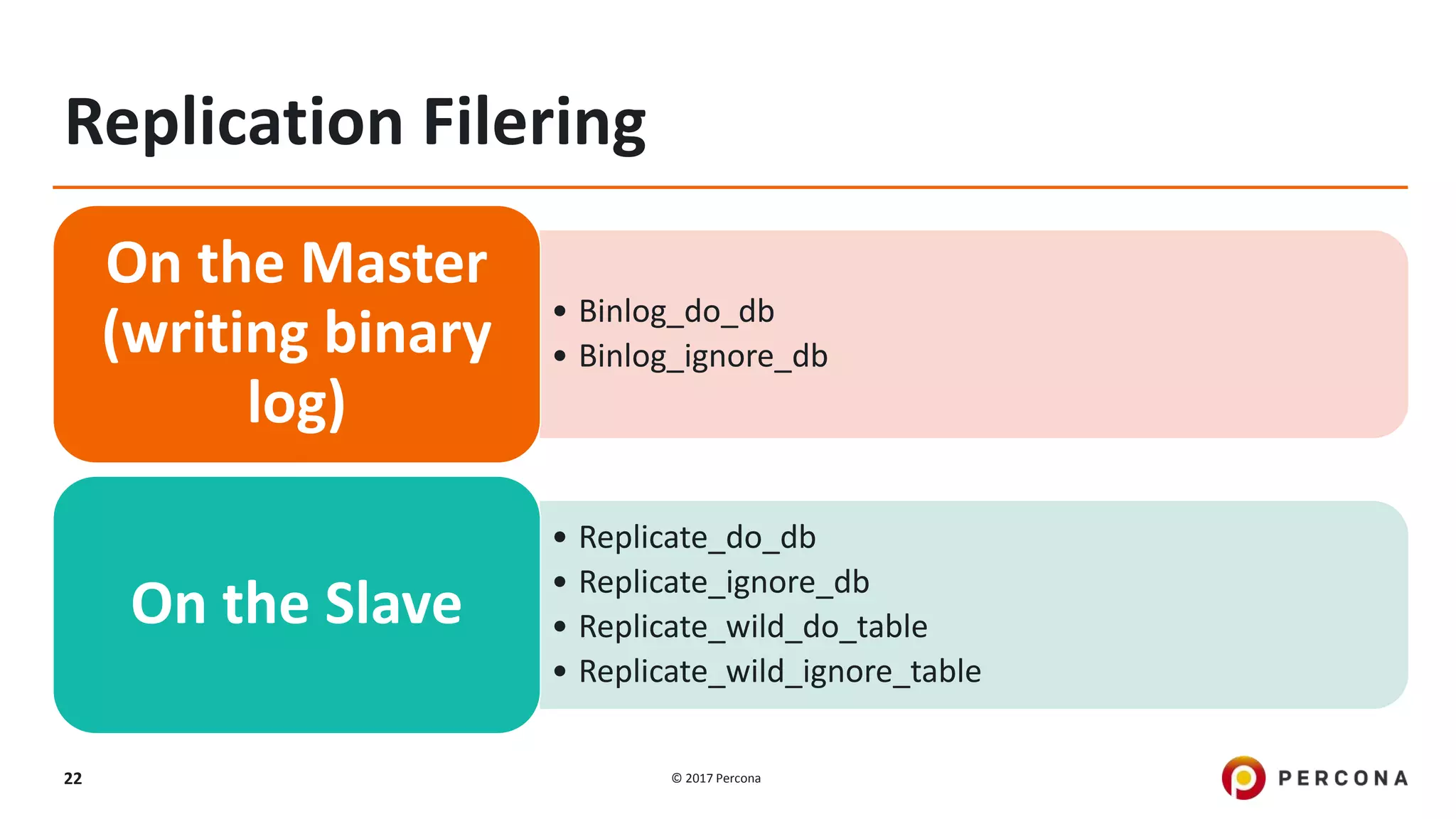
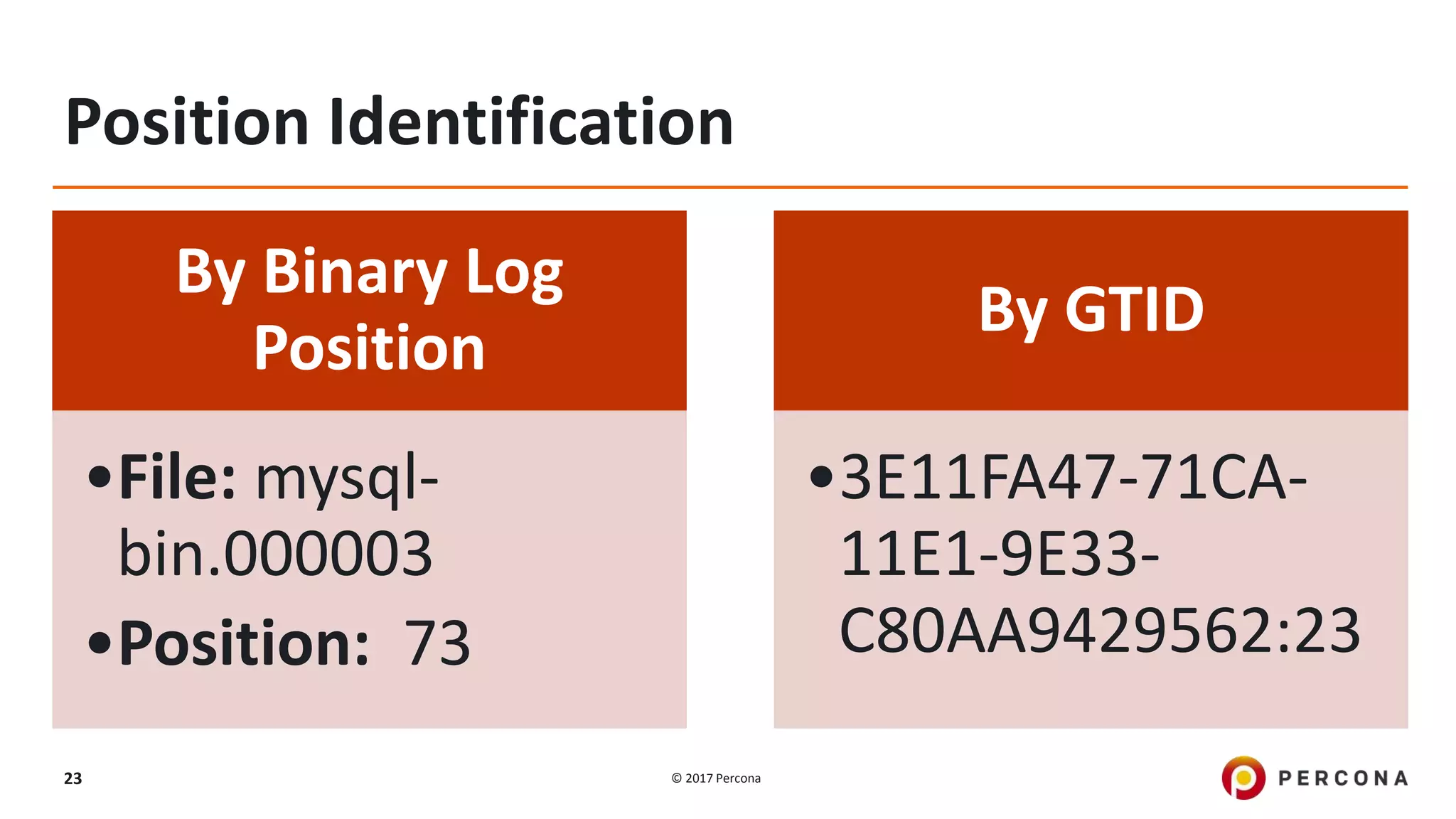
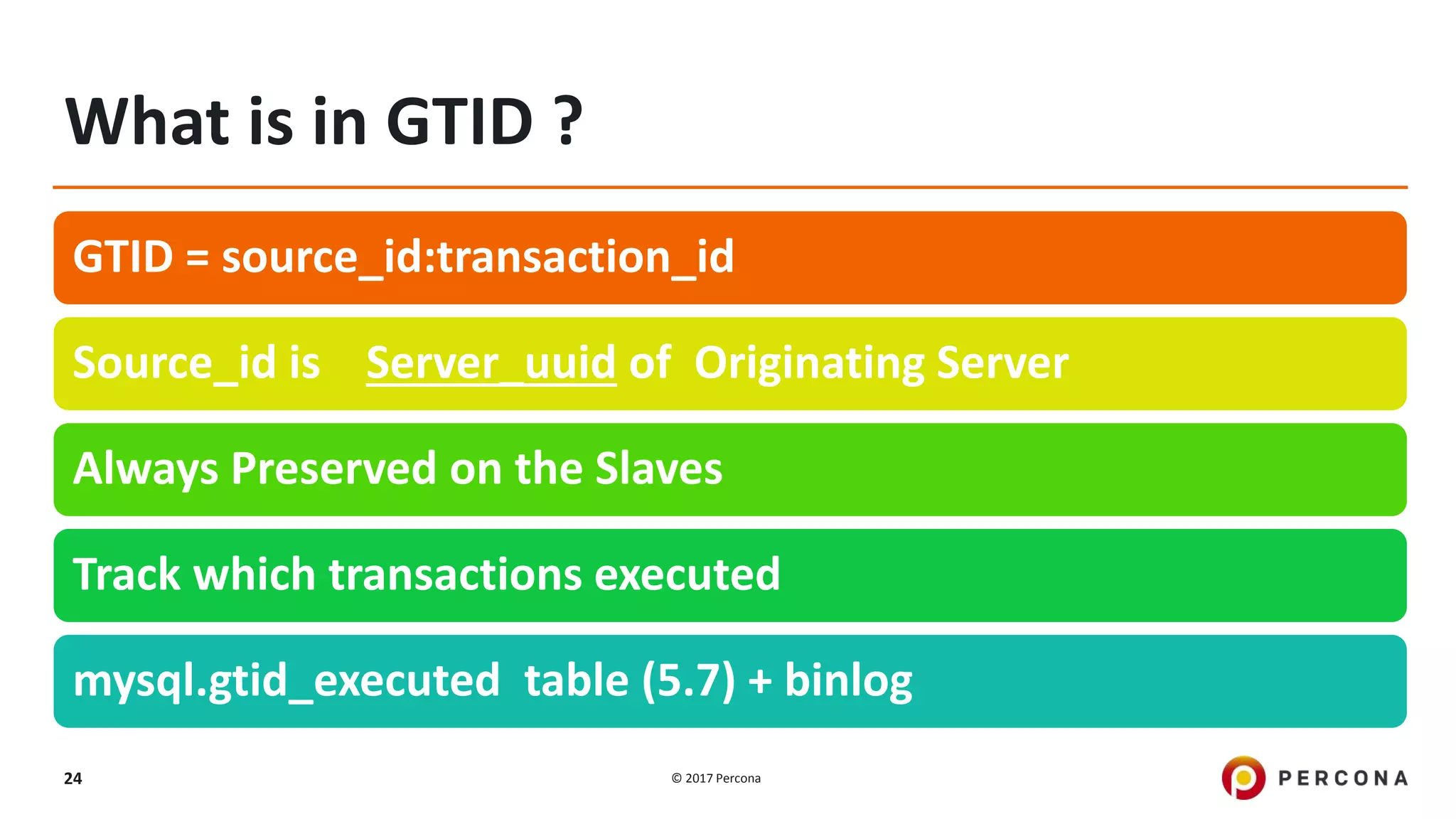
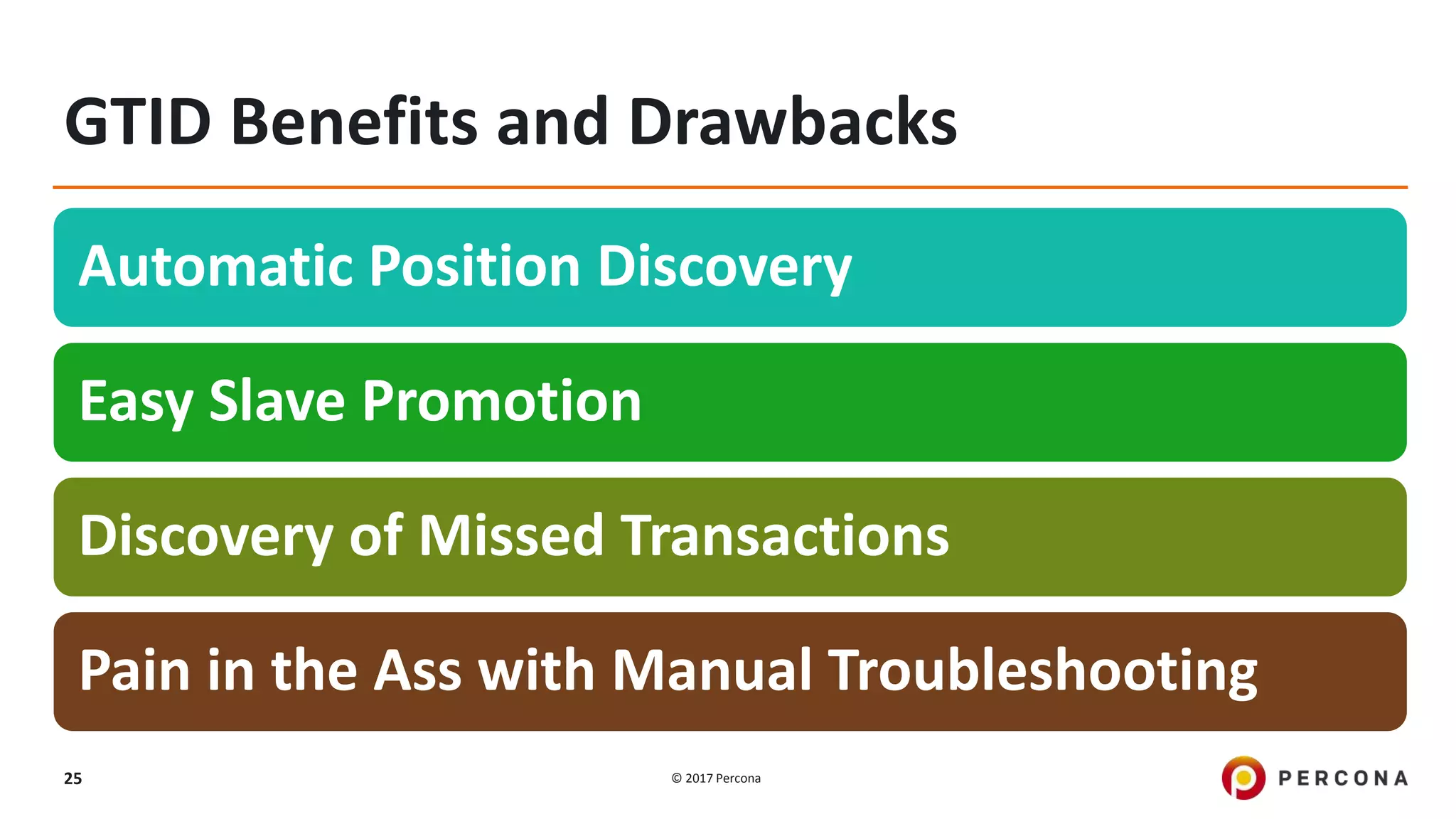
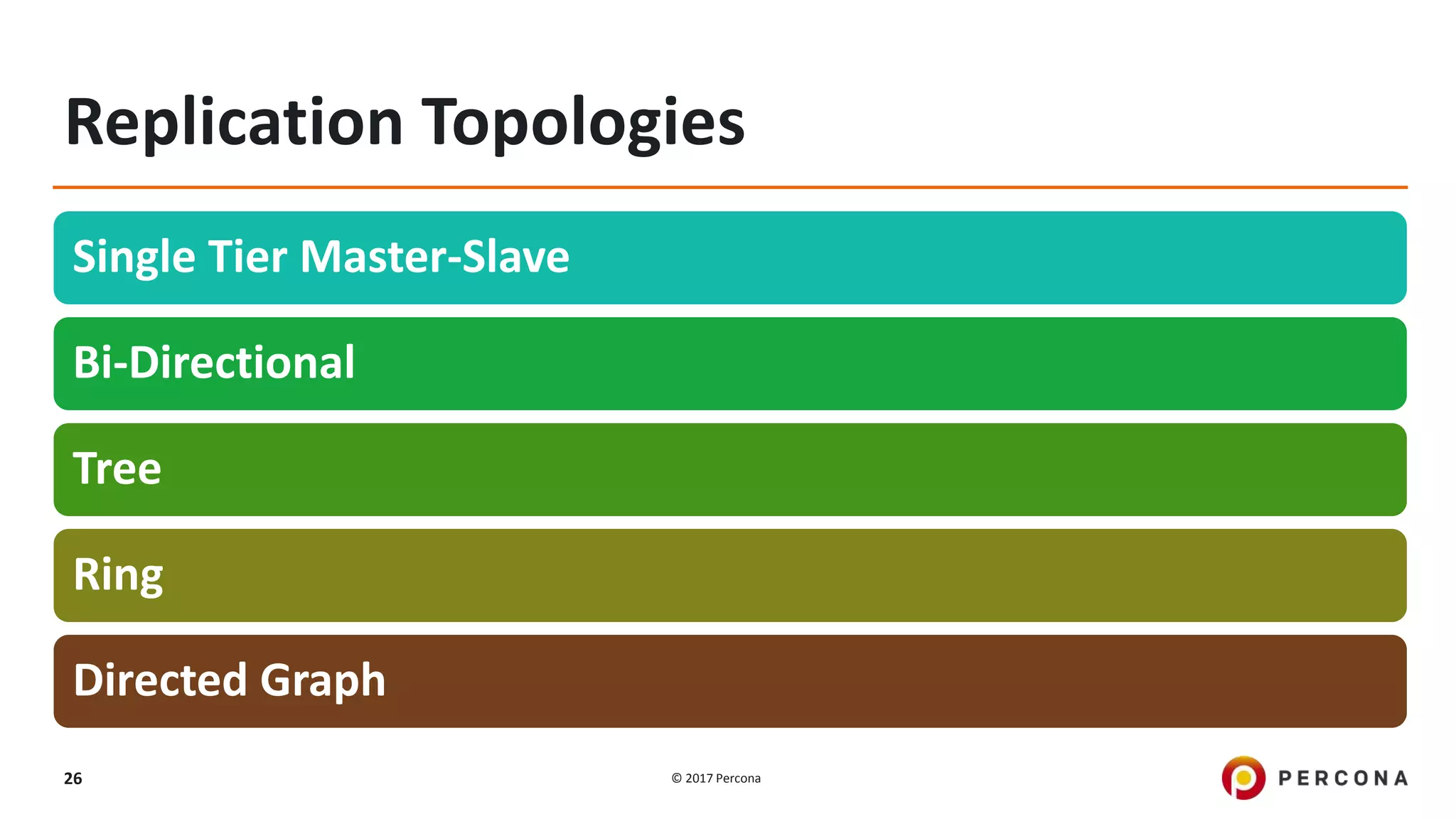
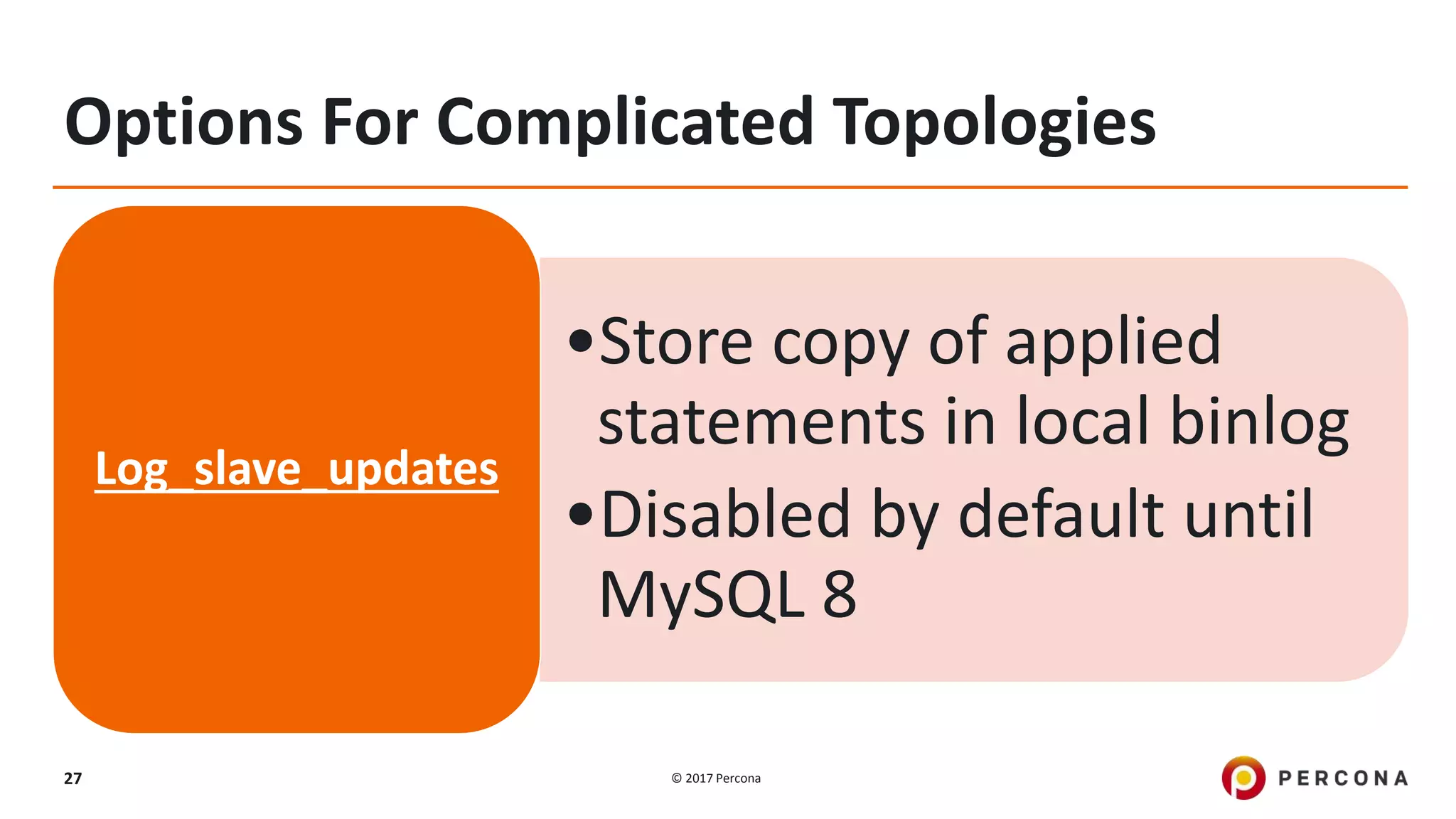
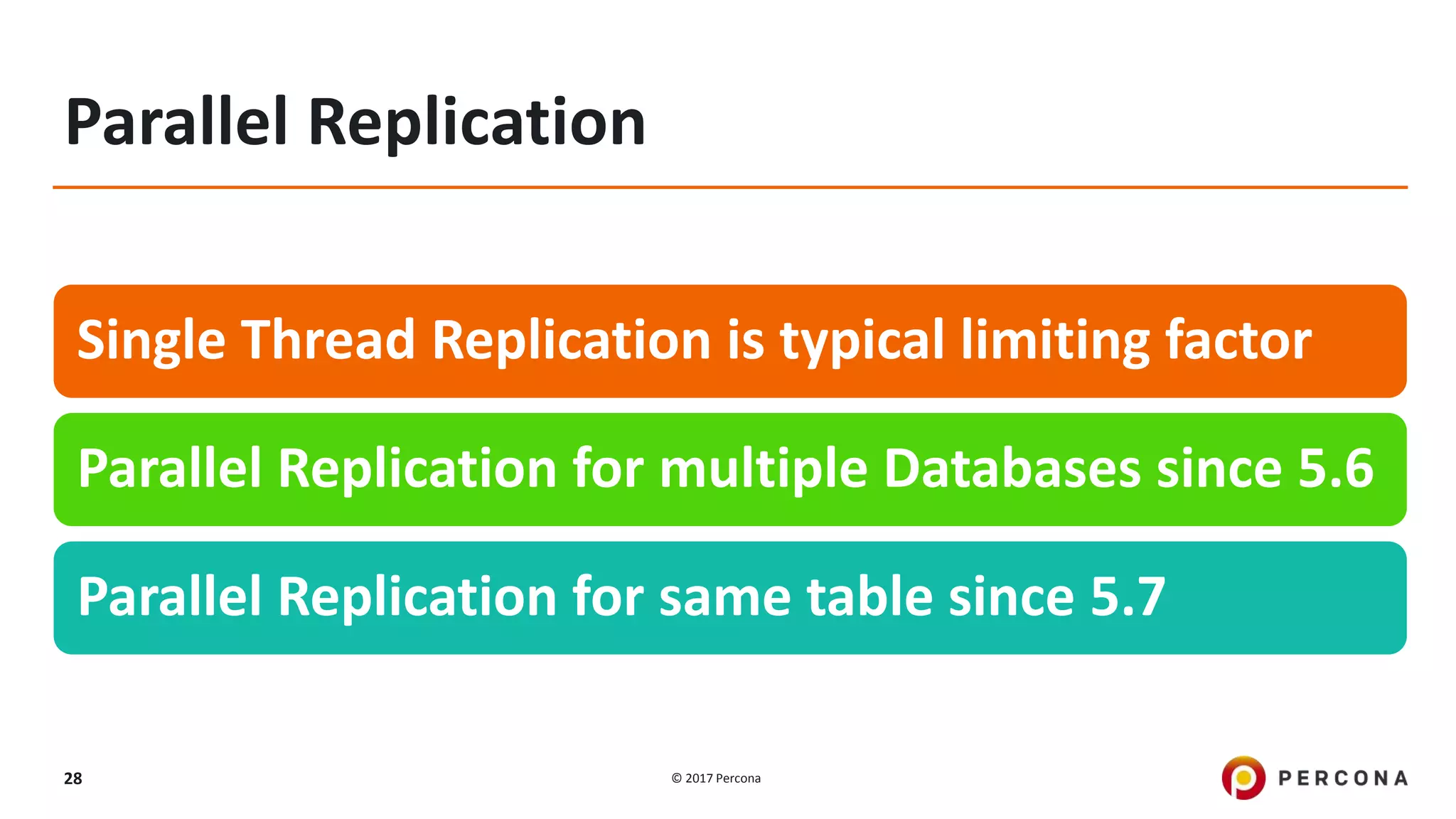
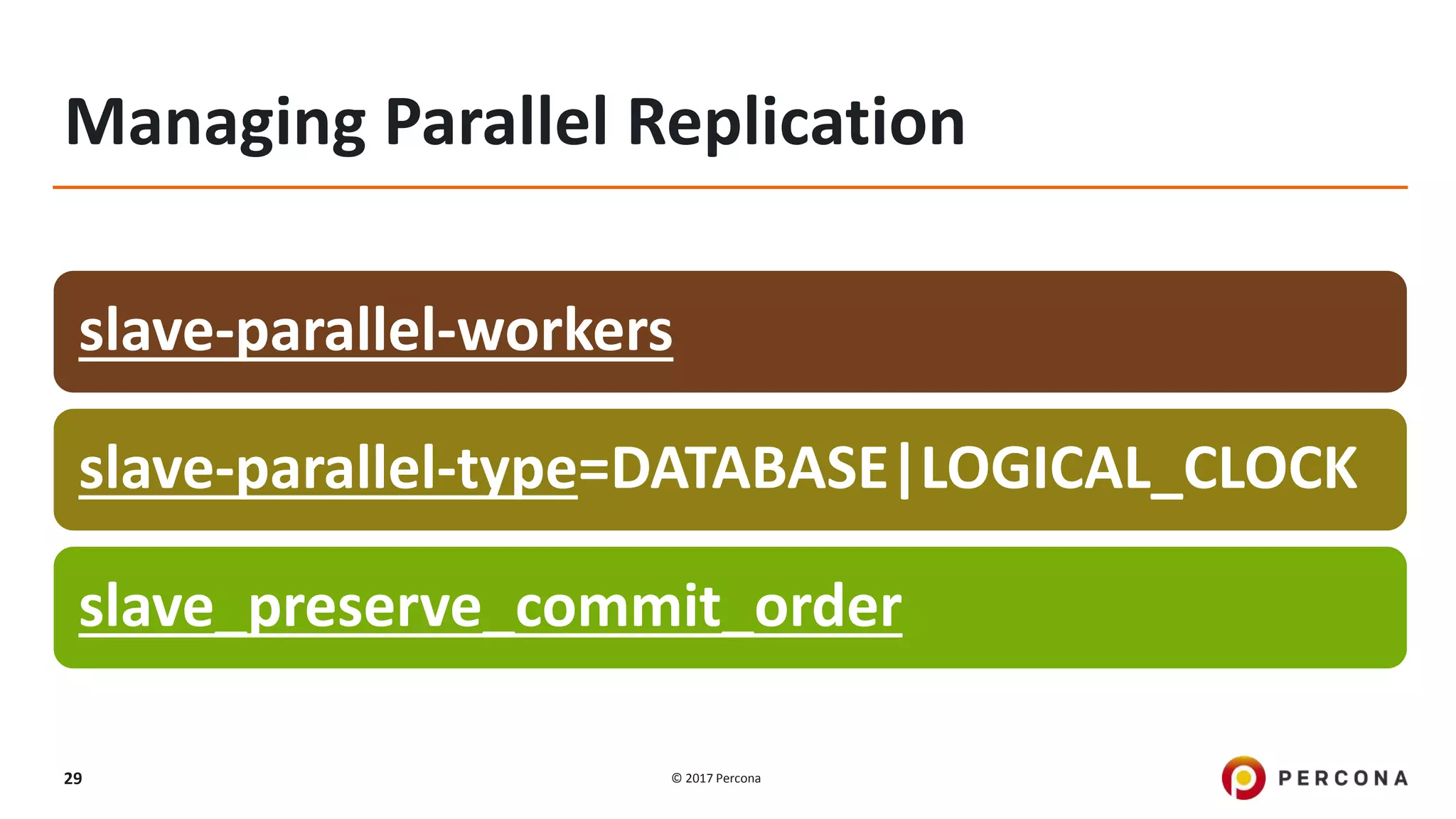
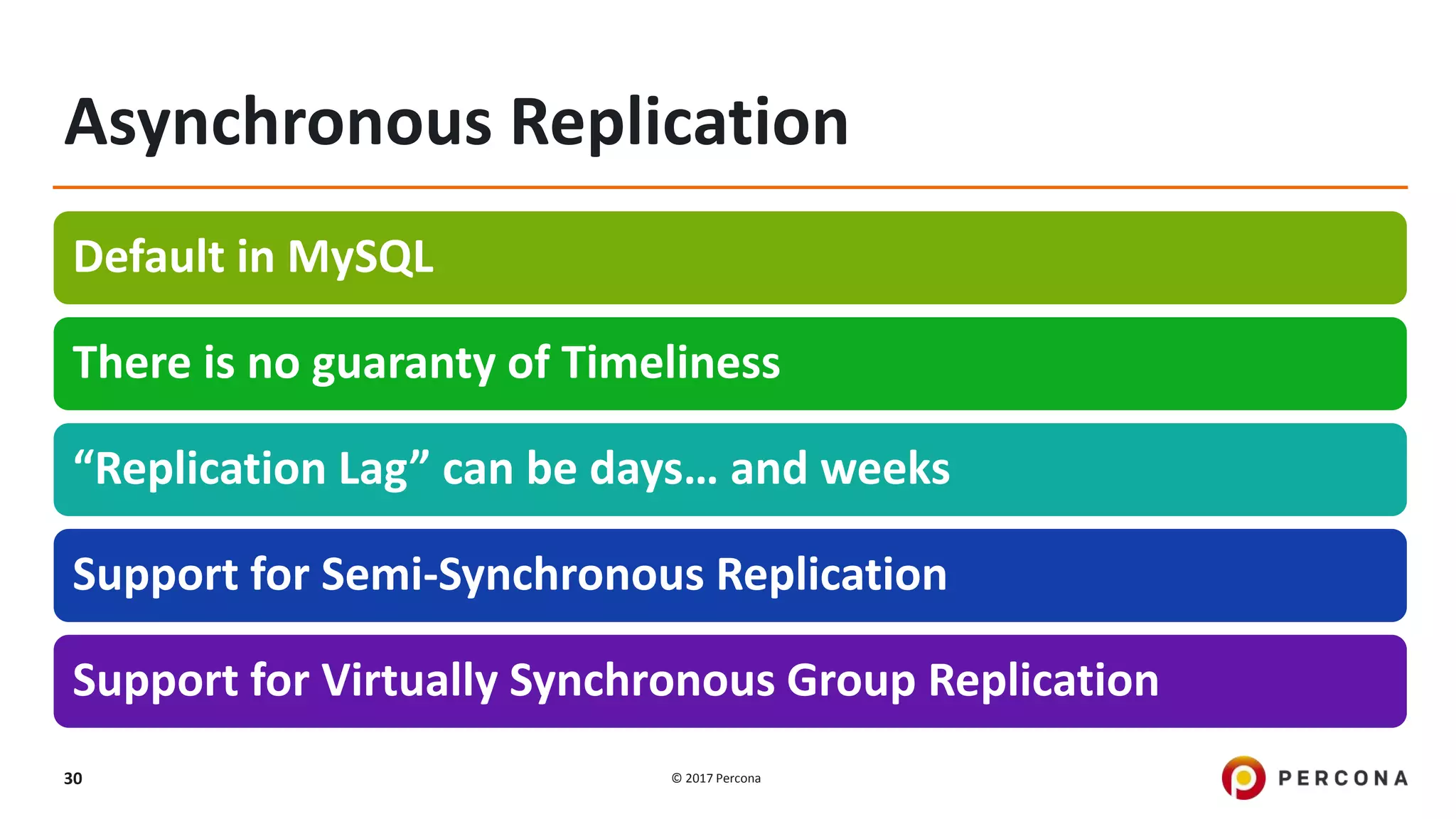
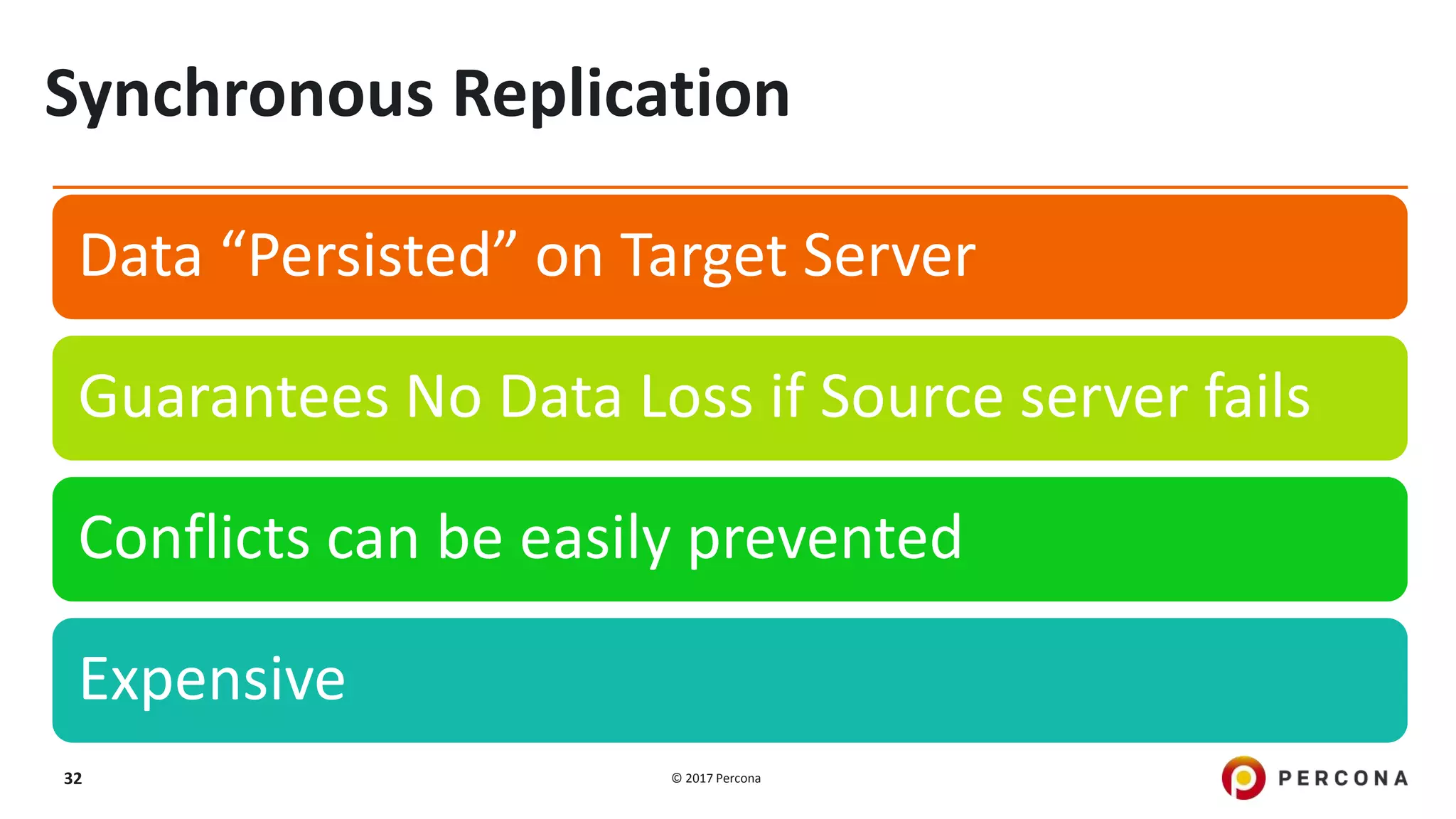
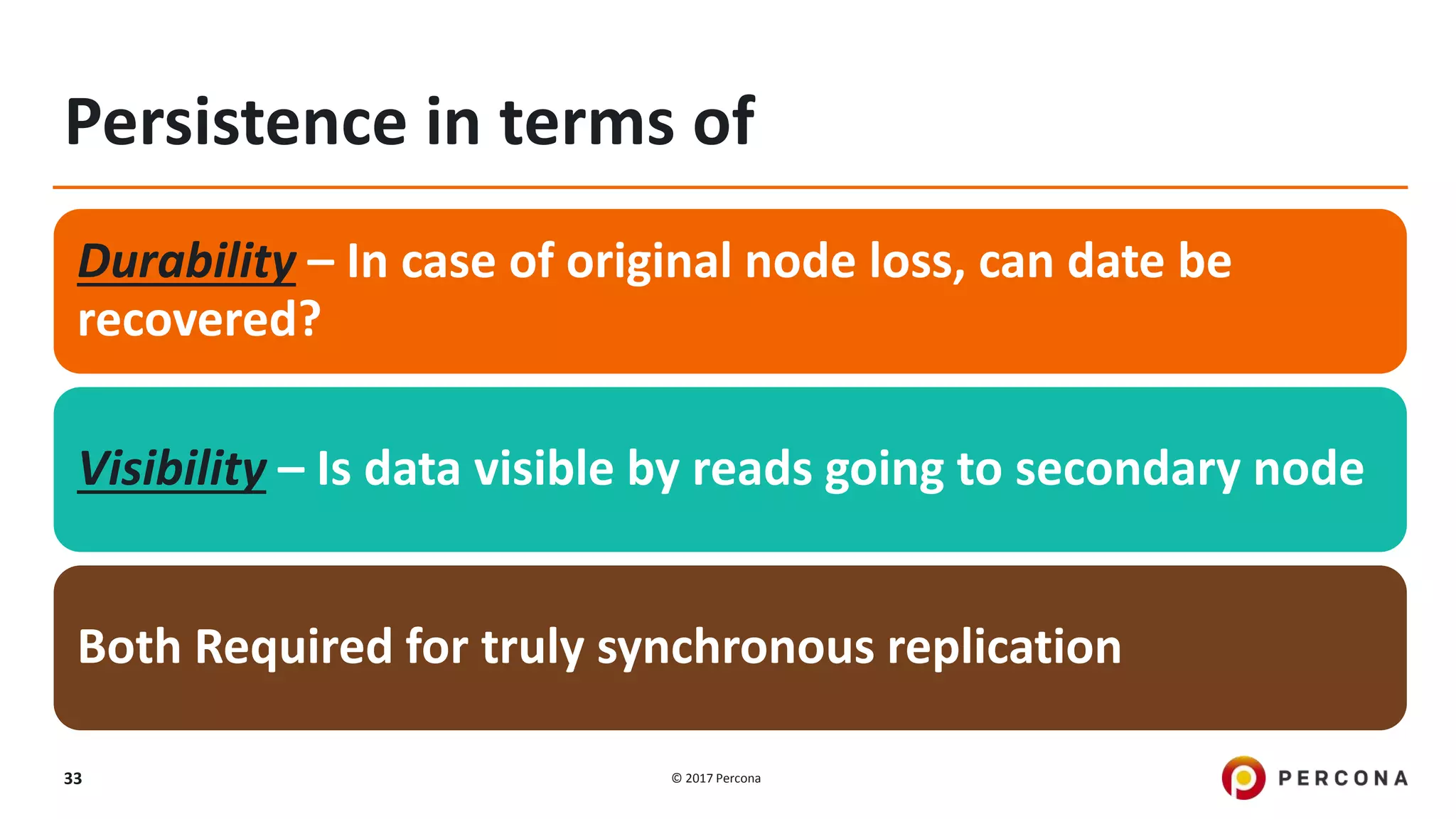
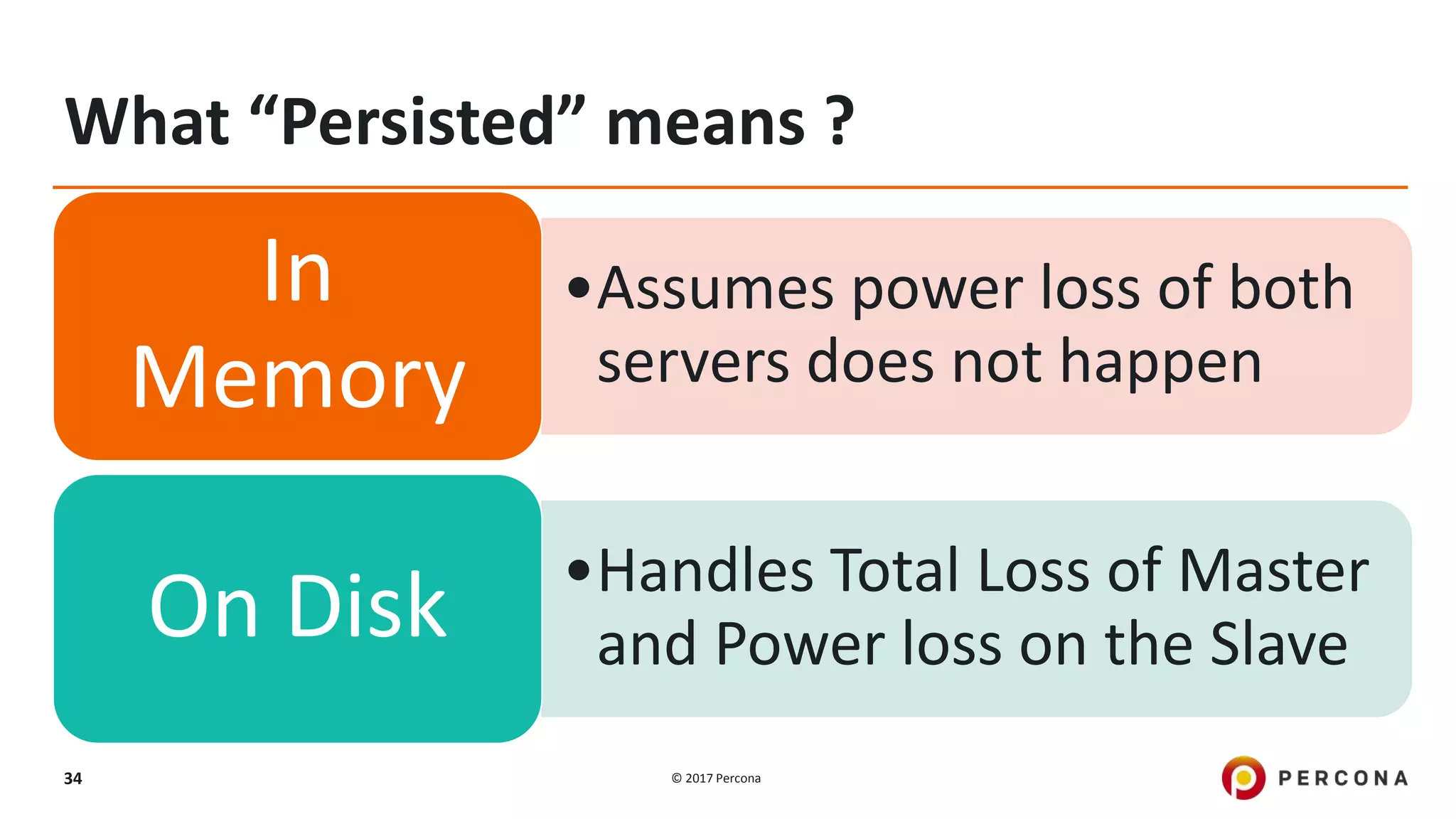
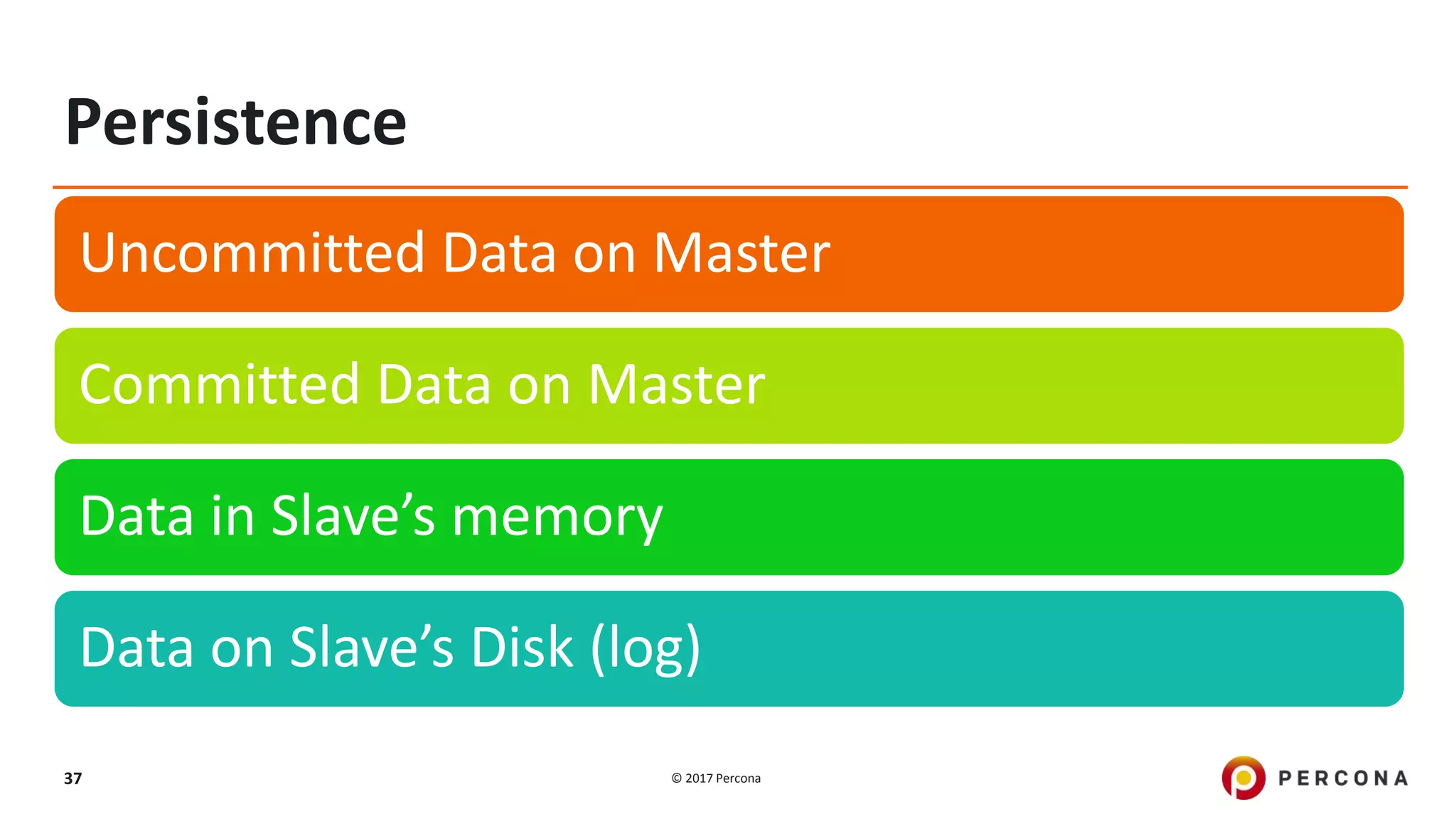
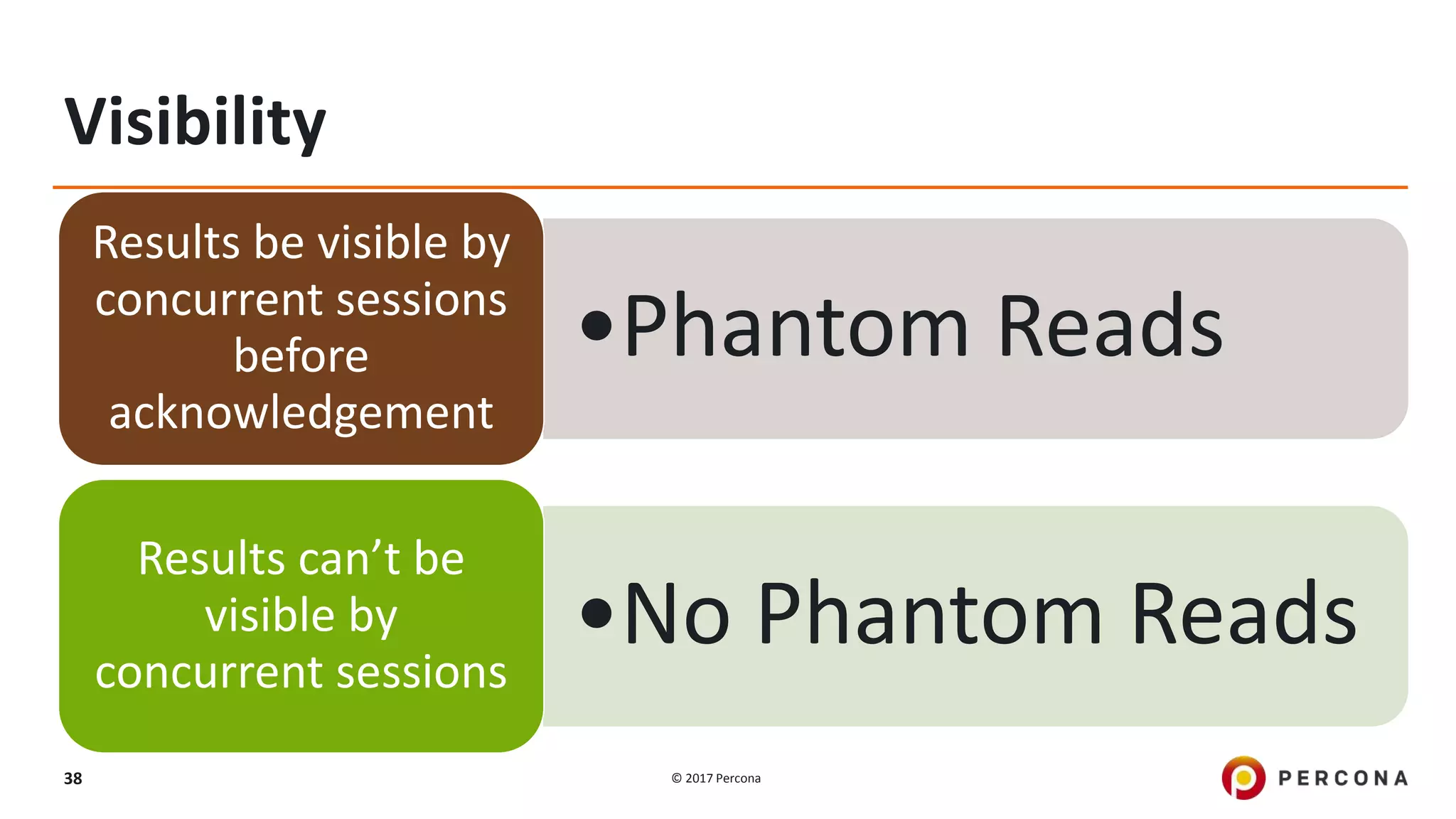
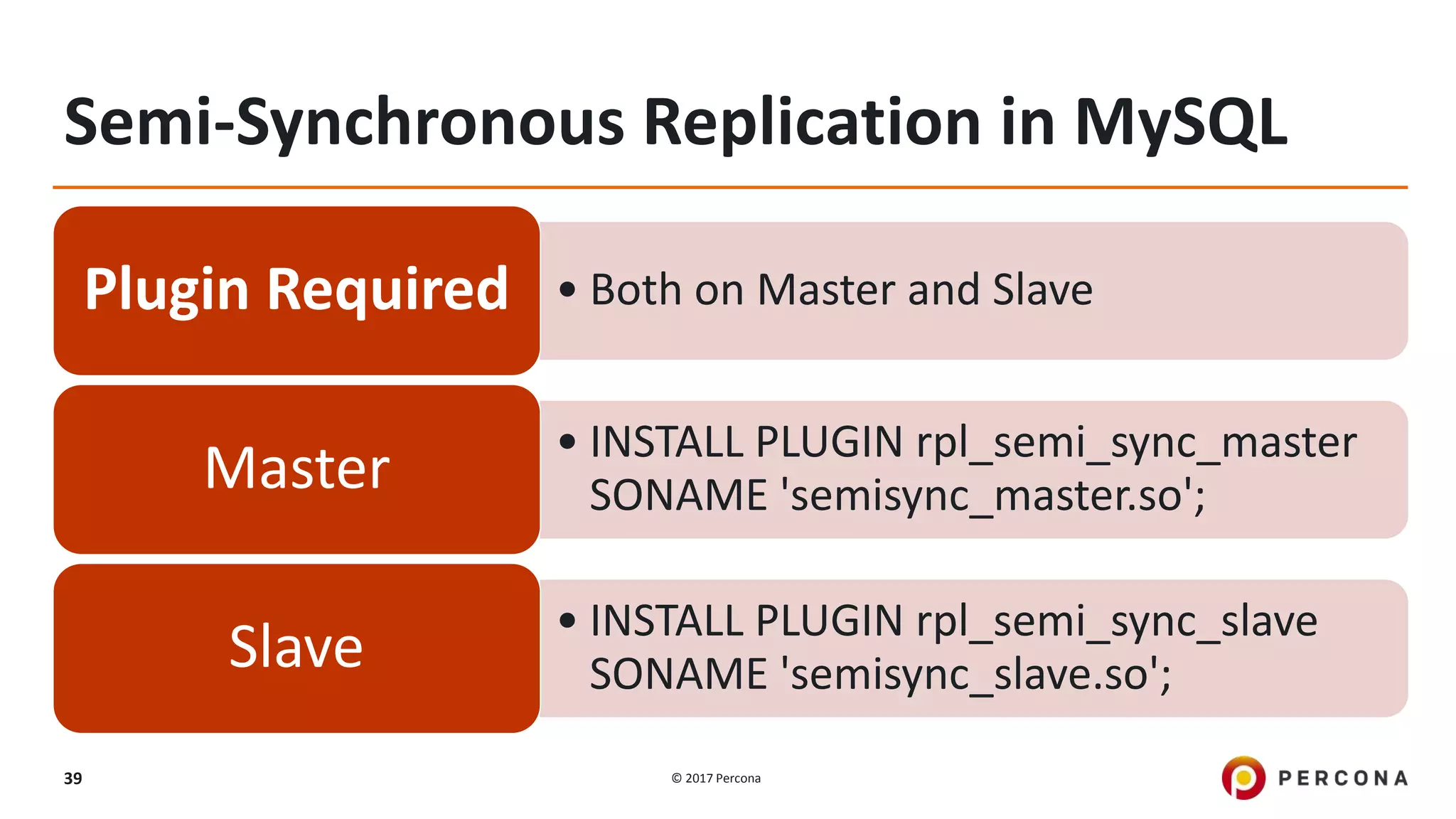
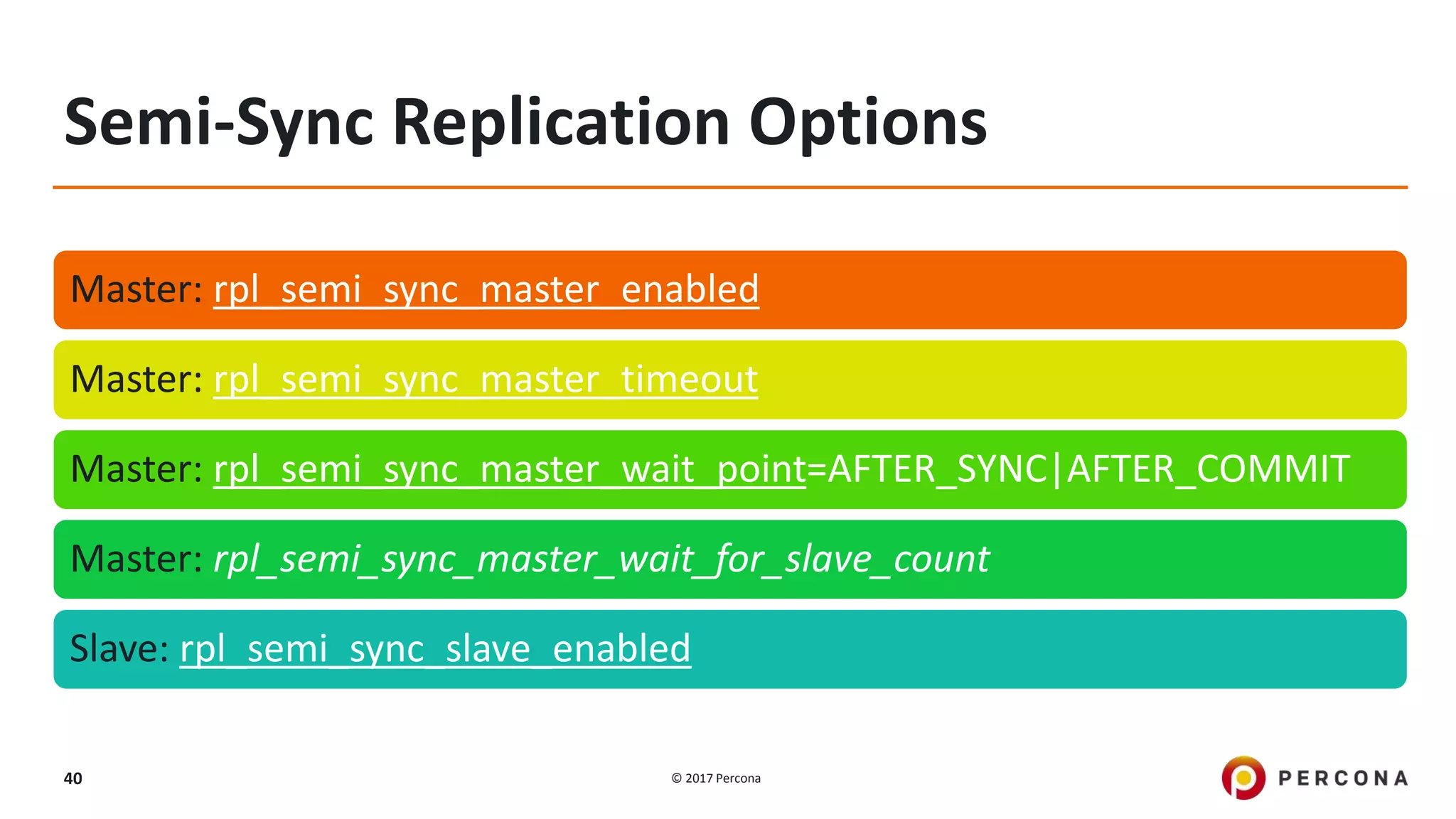
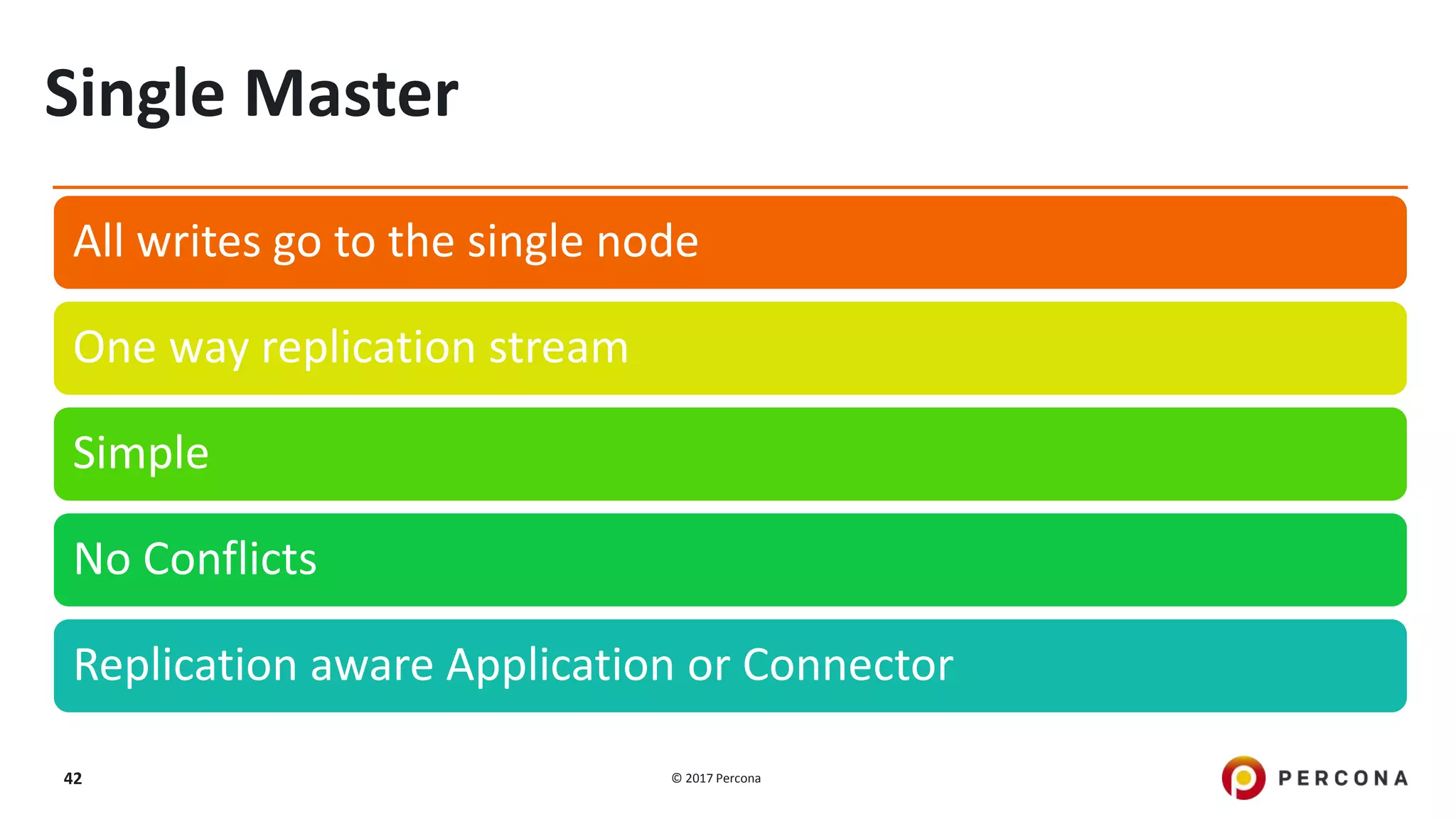
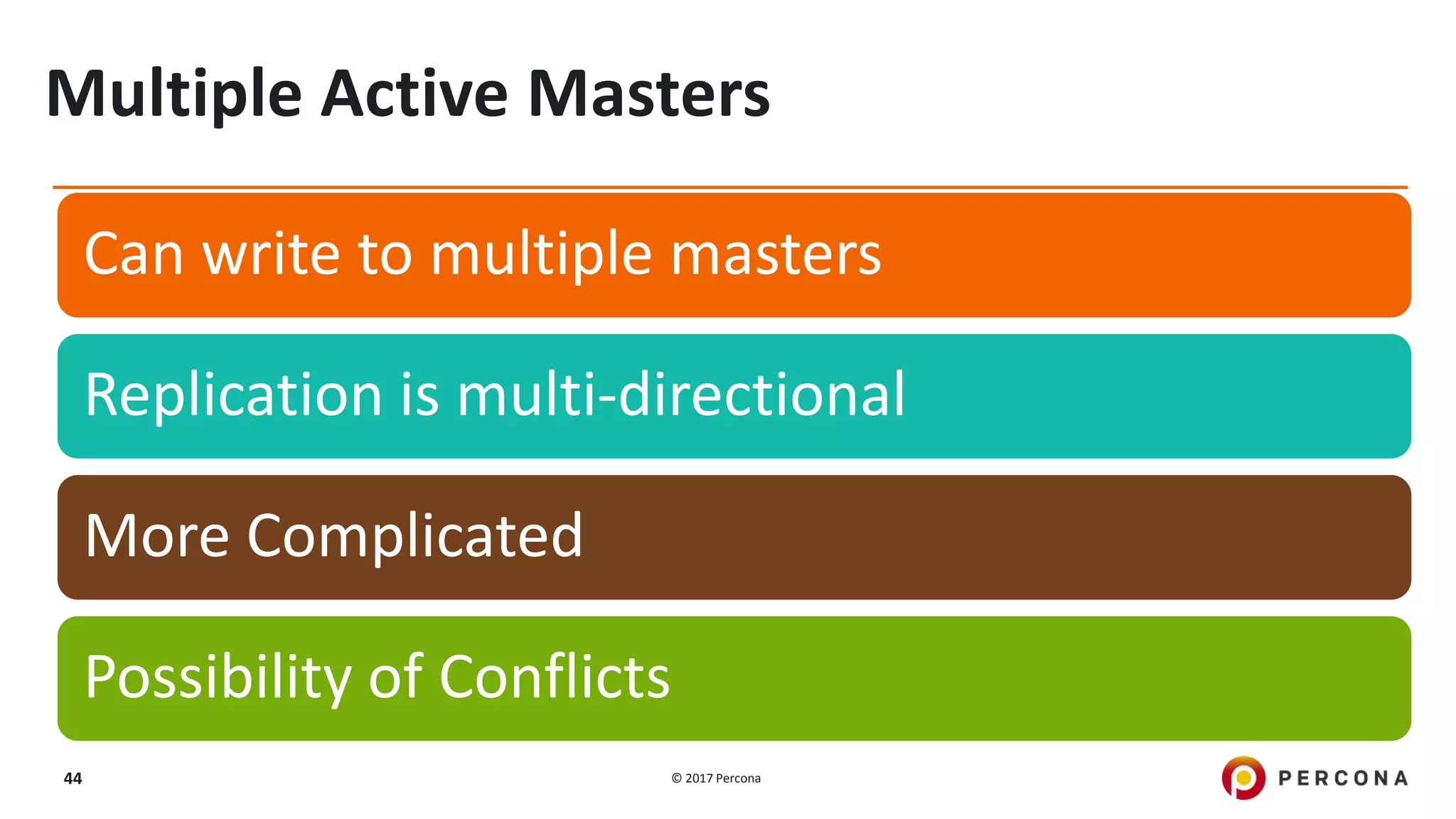
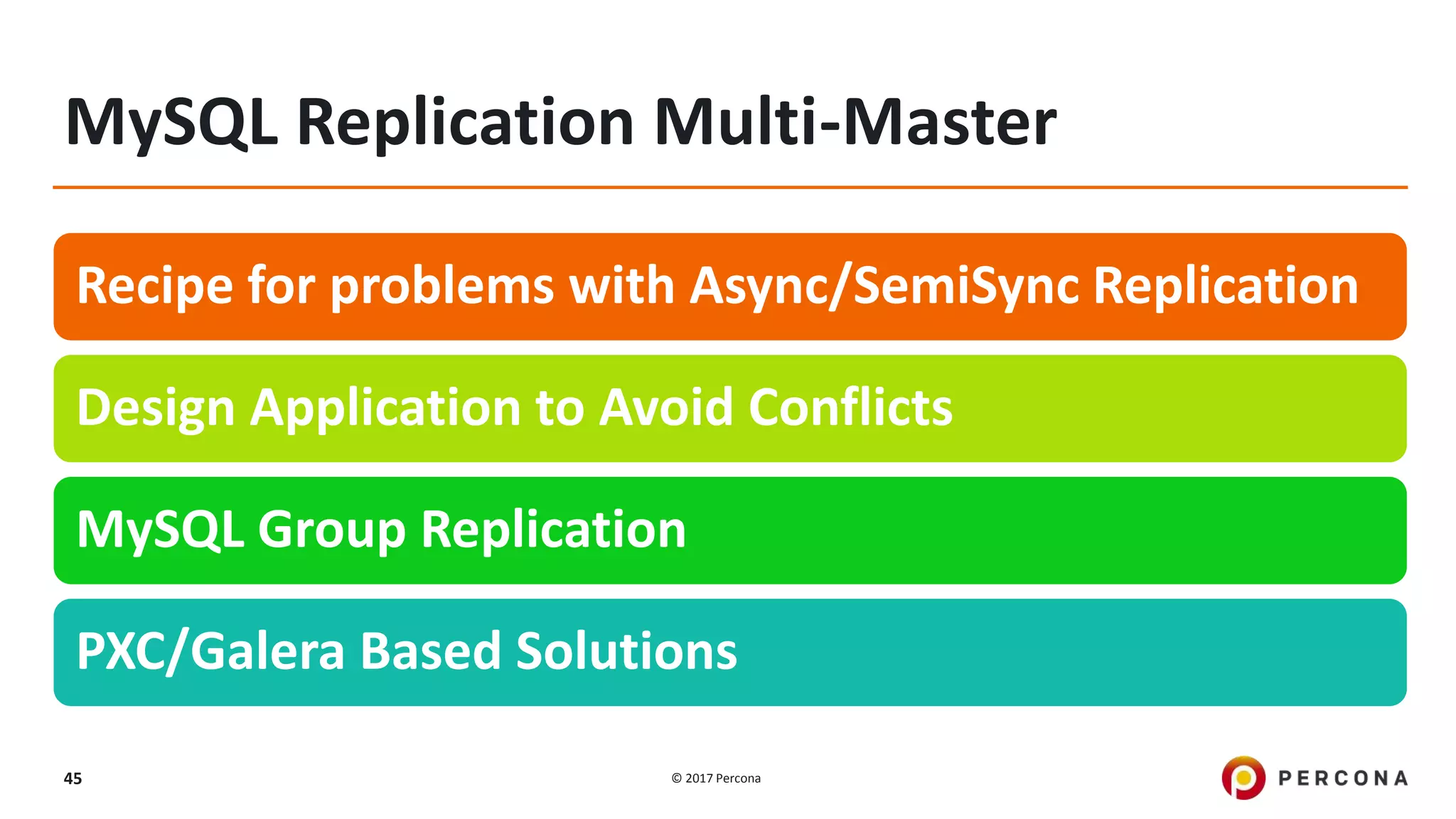
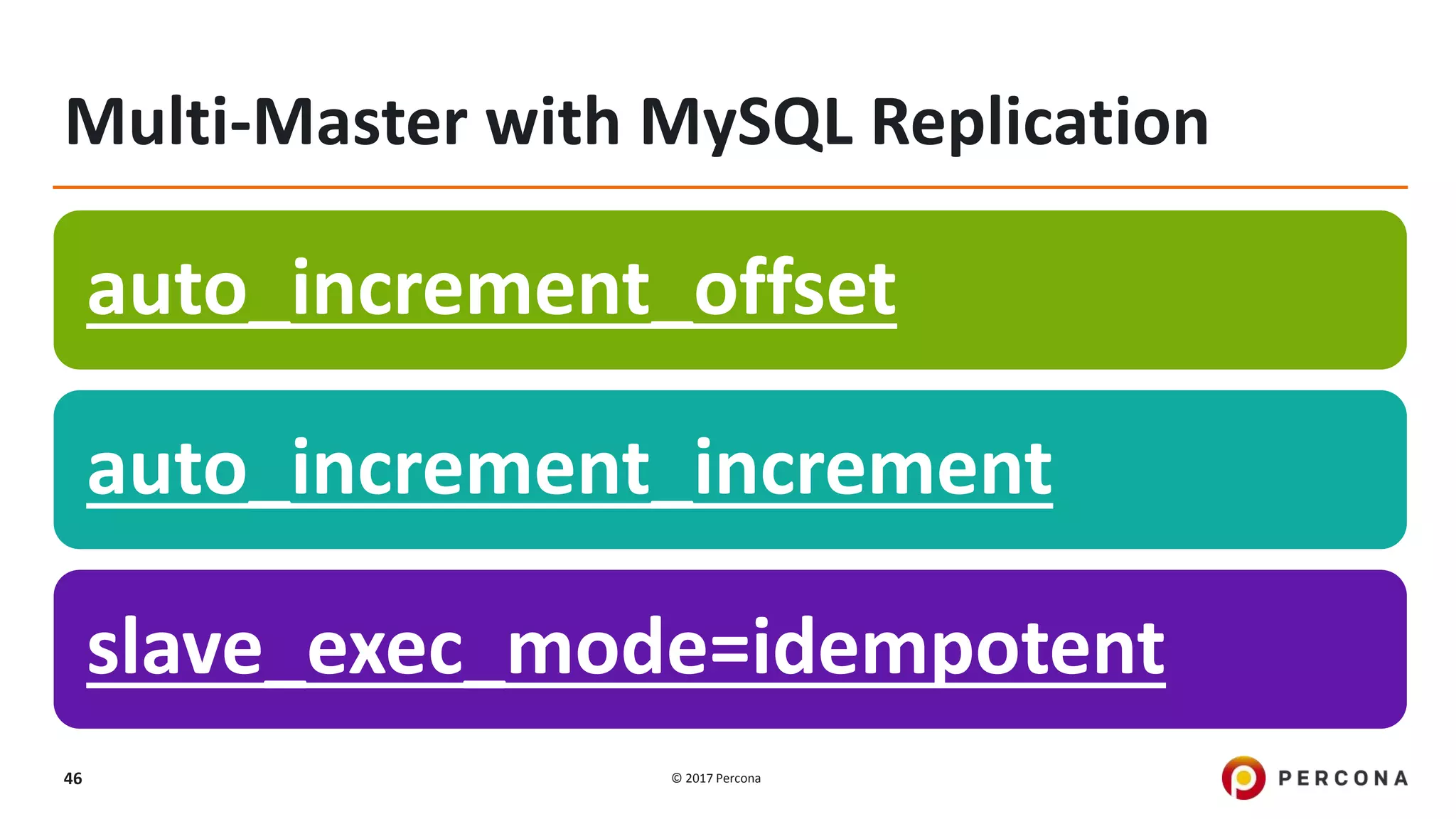
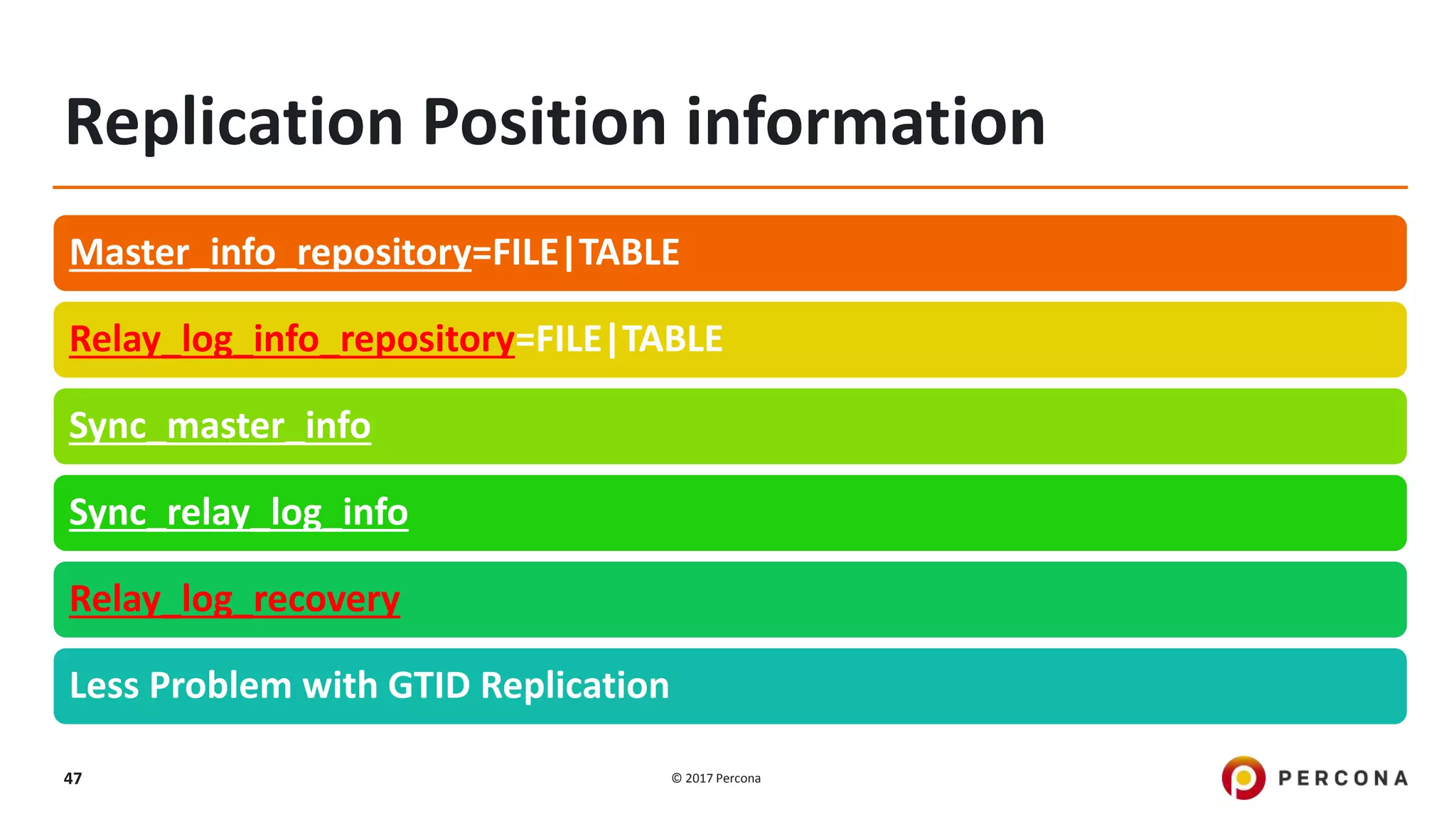
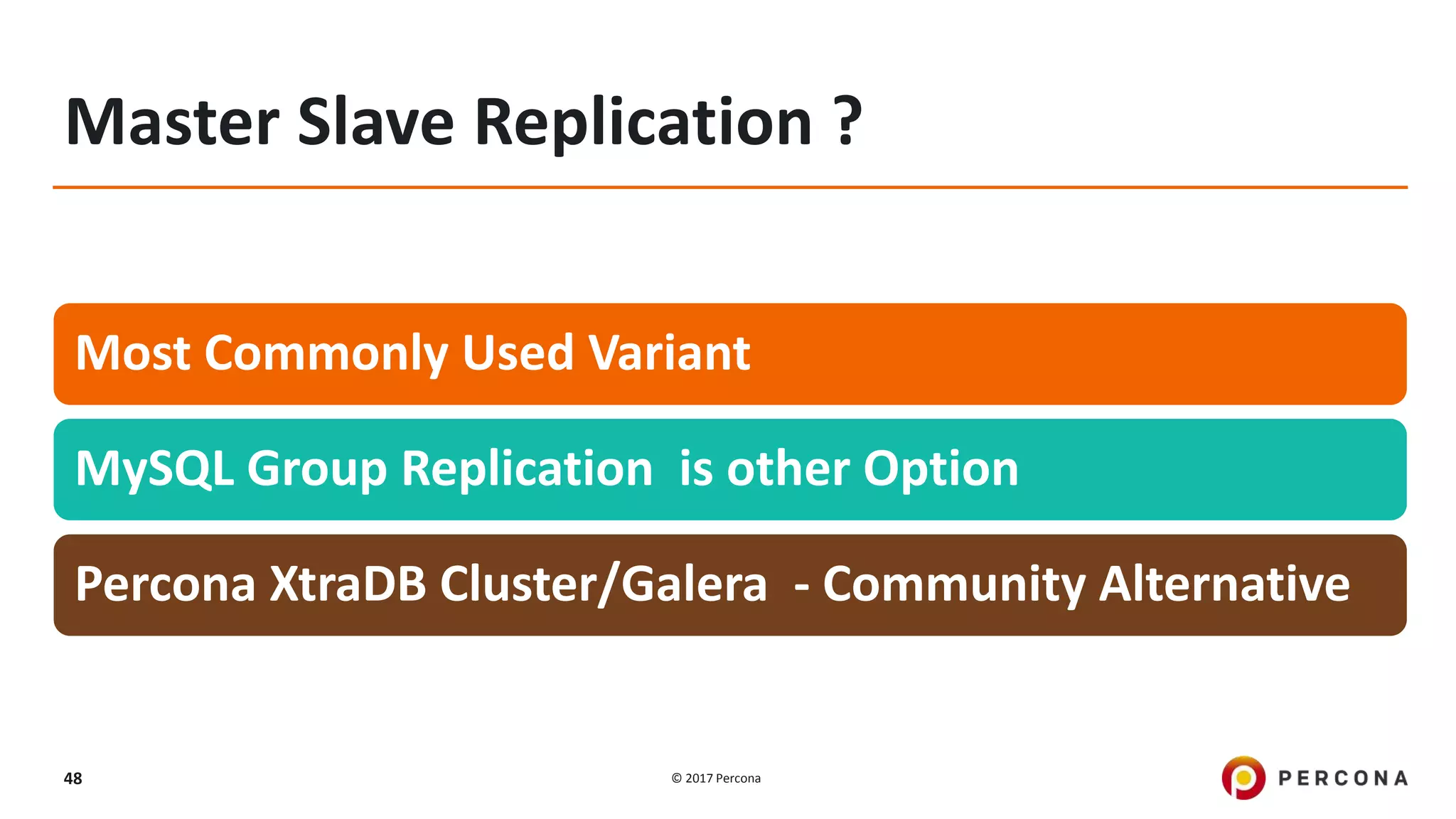
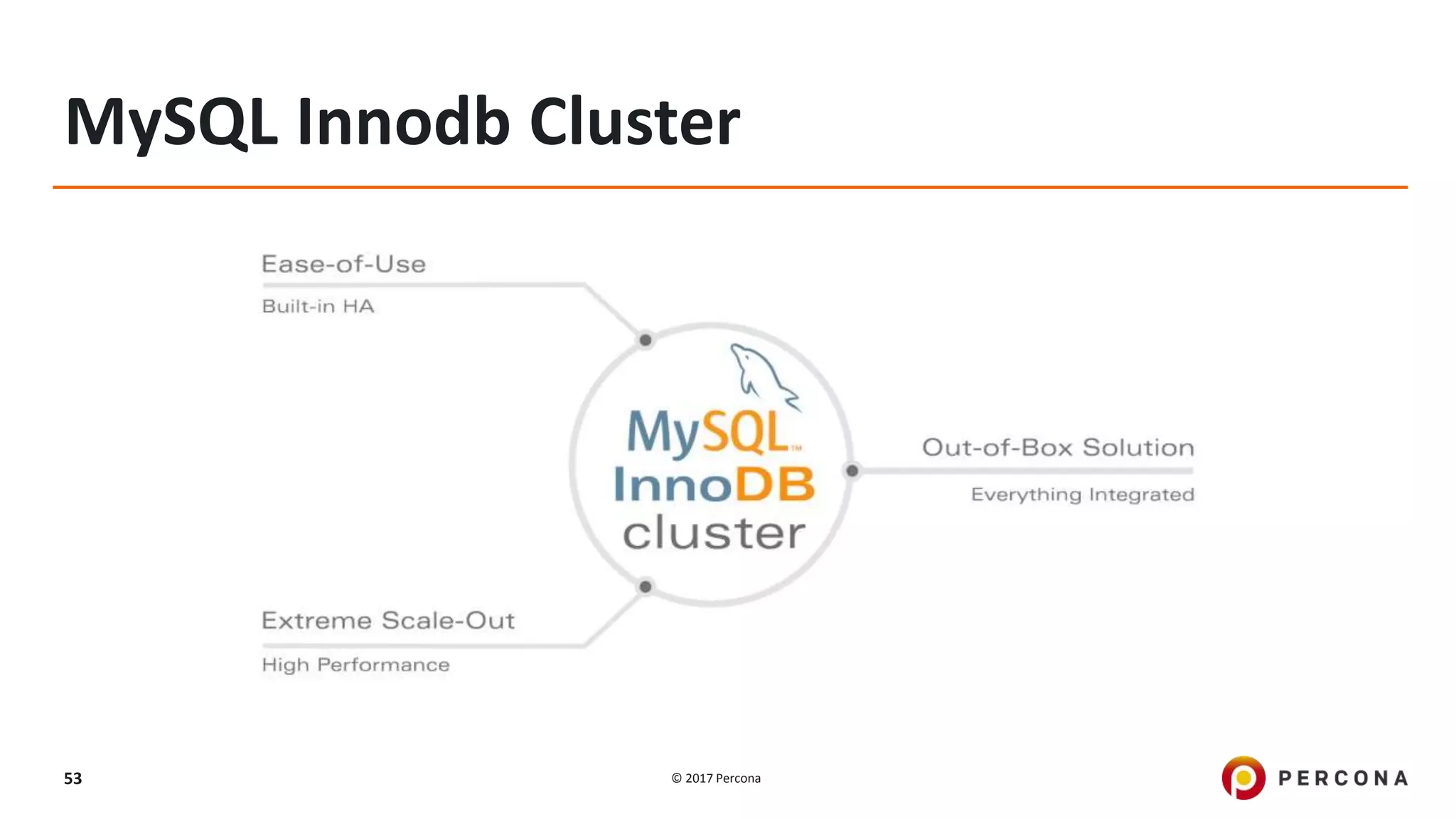
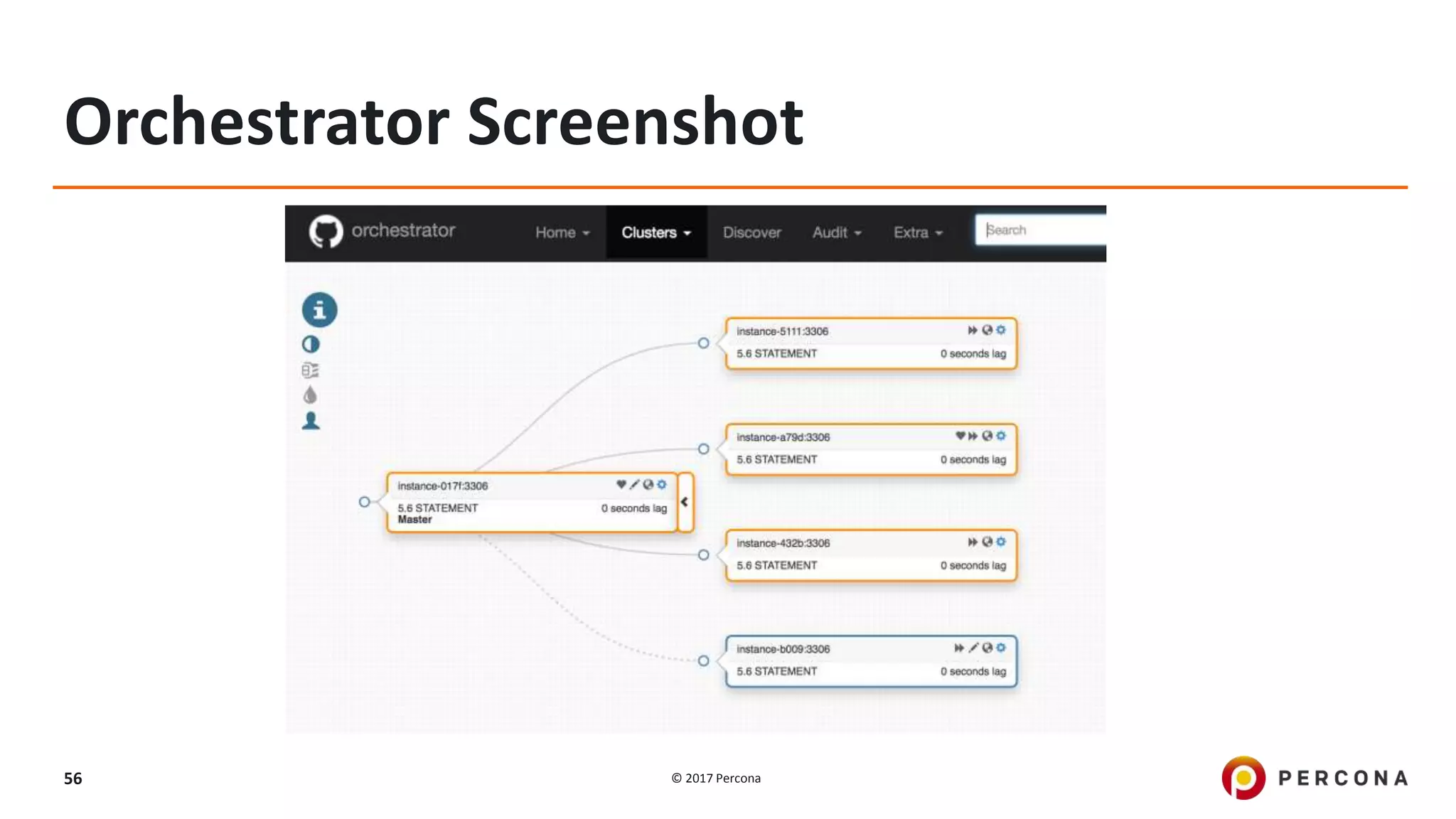
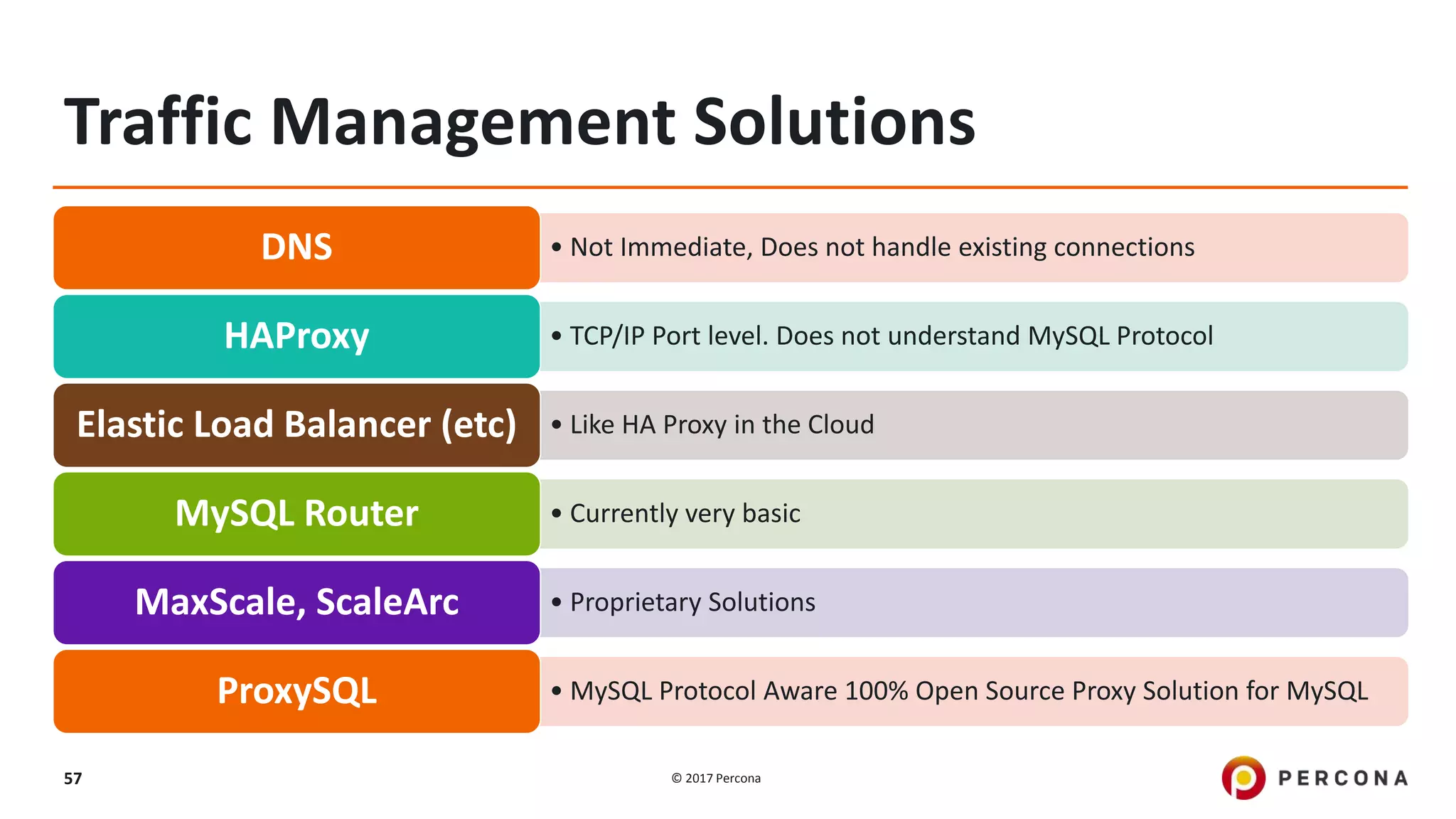
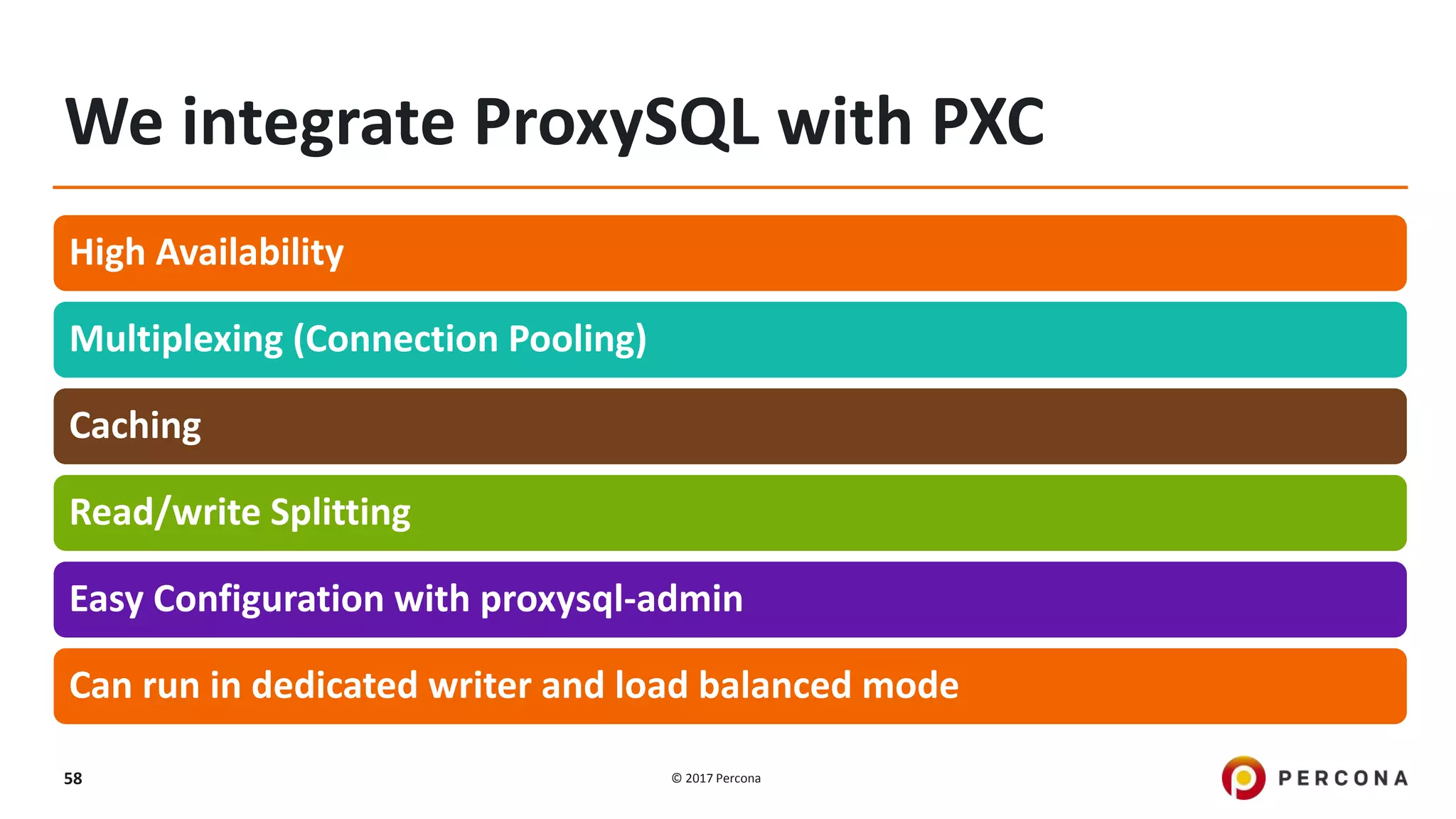
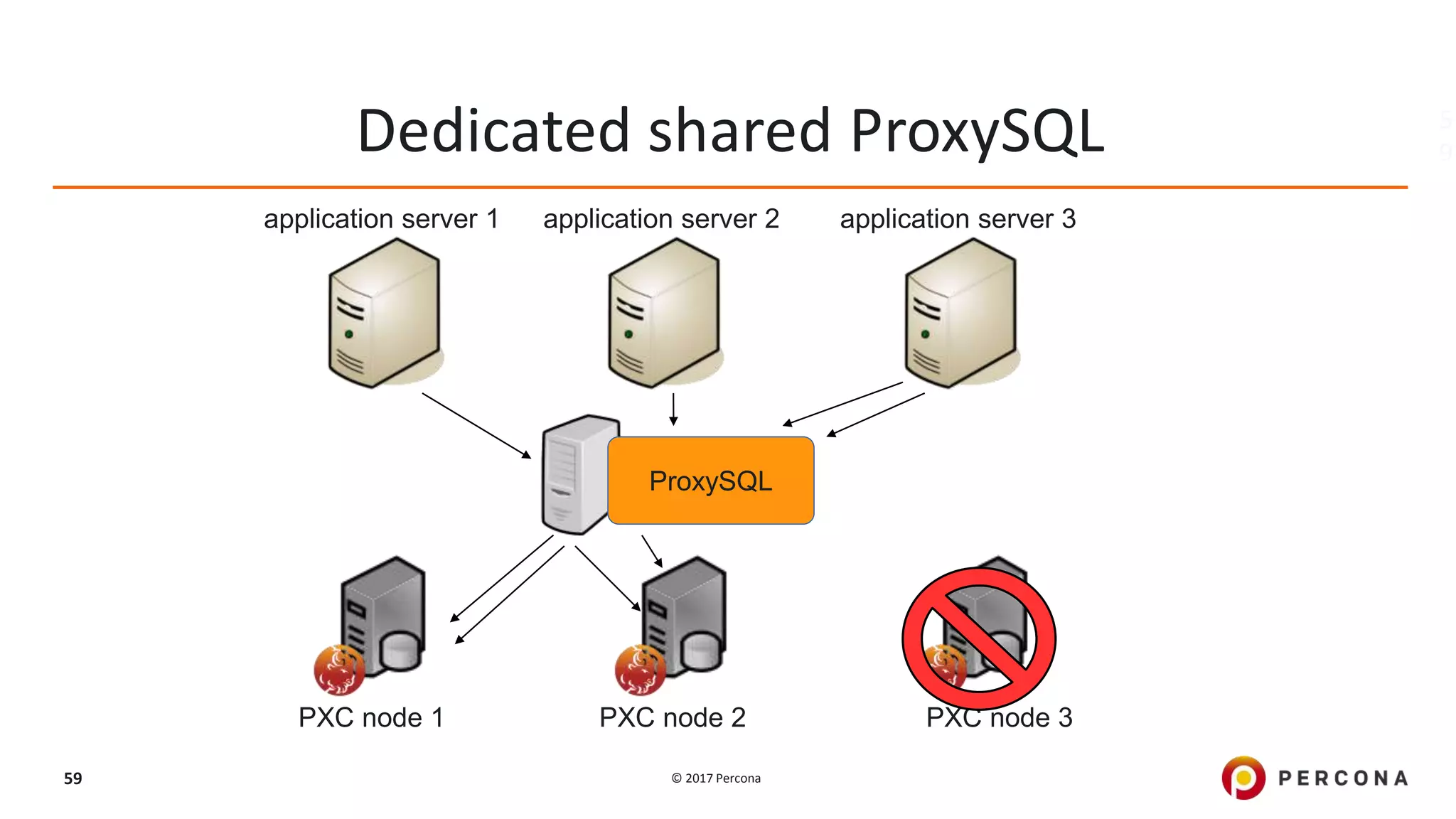
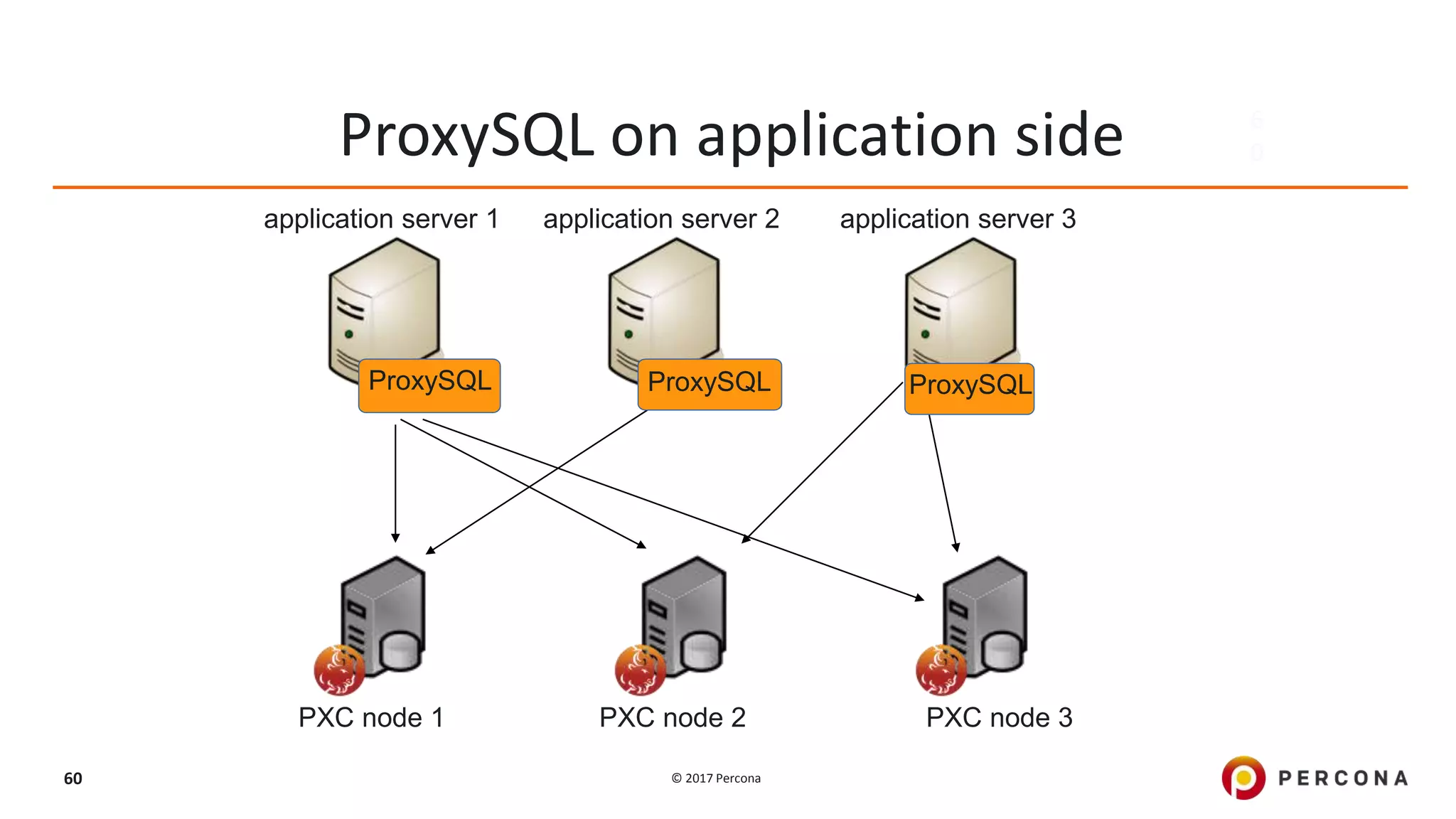
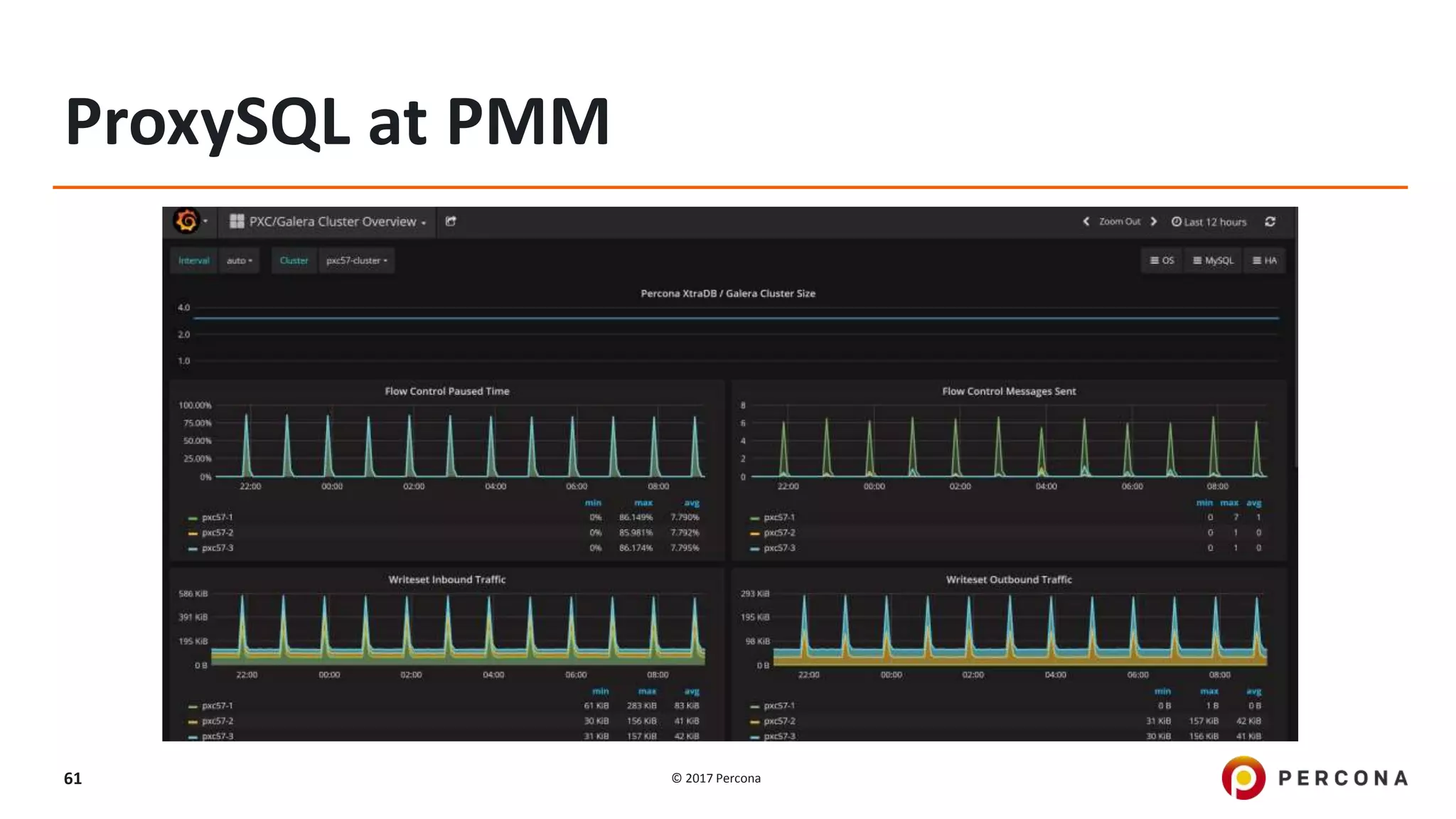
This presentation covers advanced MySQL replication features, emphasizing the importance of replication for availability, scalability, and performance. It outlines the evolution of MySQL replication through various versions, discusses different replication types such as synchronous and asynchronous, and introduces alternatives like MySQL Group Replication. Additionally, it addresses the complexities of multi-master setups and highlights traffic management solutions for better replication configuration and failover management.