The document outlines key concepts of functional programming, including the distinctions between functional and imperative programming, the importance of pure and impure functions, and the characteristics of first-class and higher-order functions. It provides examples of lambda functions, recursion, and built-in functional programming functions like map, filter, and reduce, highlighting their use in Python. The text also discusses the proxy function, demonstrating how it enables structural design patterns for object functionality.


![Functional Programming #Example Impure: def remove_last(input_list): input_list.pop() names = [‘A', ‘B', ‘C'] remove_last(names) print(names) remove_last(names) print(names) #Example Pure: def remove_last(input_list): new_list = input_list.copy() new_list.pop() return new_list names = ['A', 'B', 'C'] new_names = remove_last(names) print(names) print(new_names) [‘A', ‘B'] [‘A'] [‘A', ‘B‘,’C’] [‘A‘,’B’]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1oopsunit-iii-240907054102-8c9354d3/75/OOPS-Object-oriented-Programming-PPT-Tutorial-5-2048.jpg)



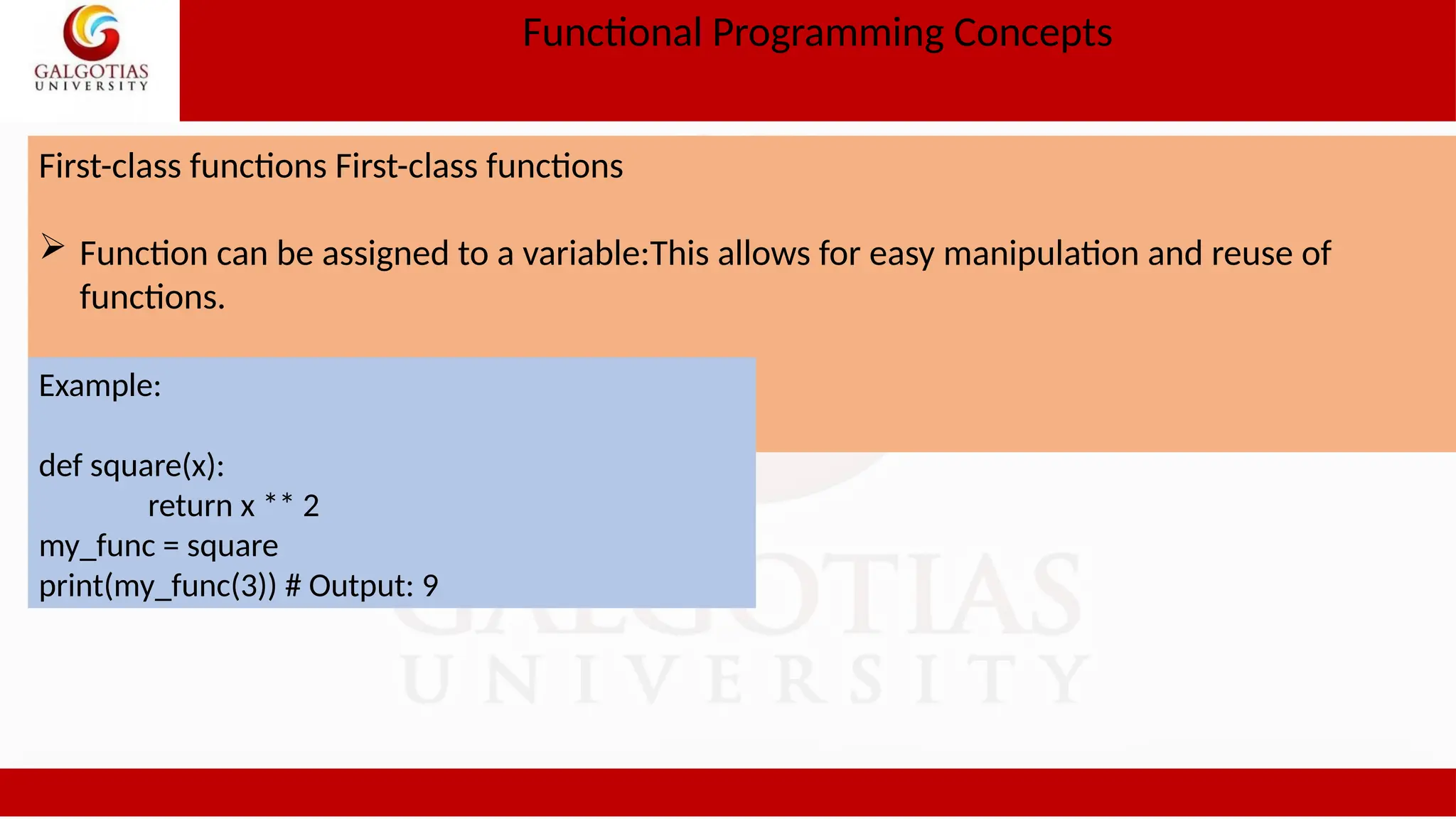
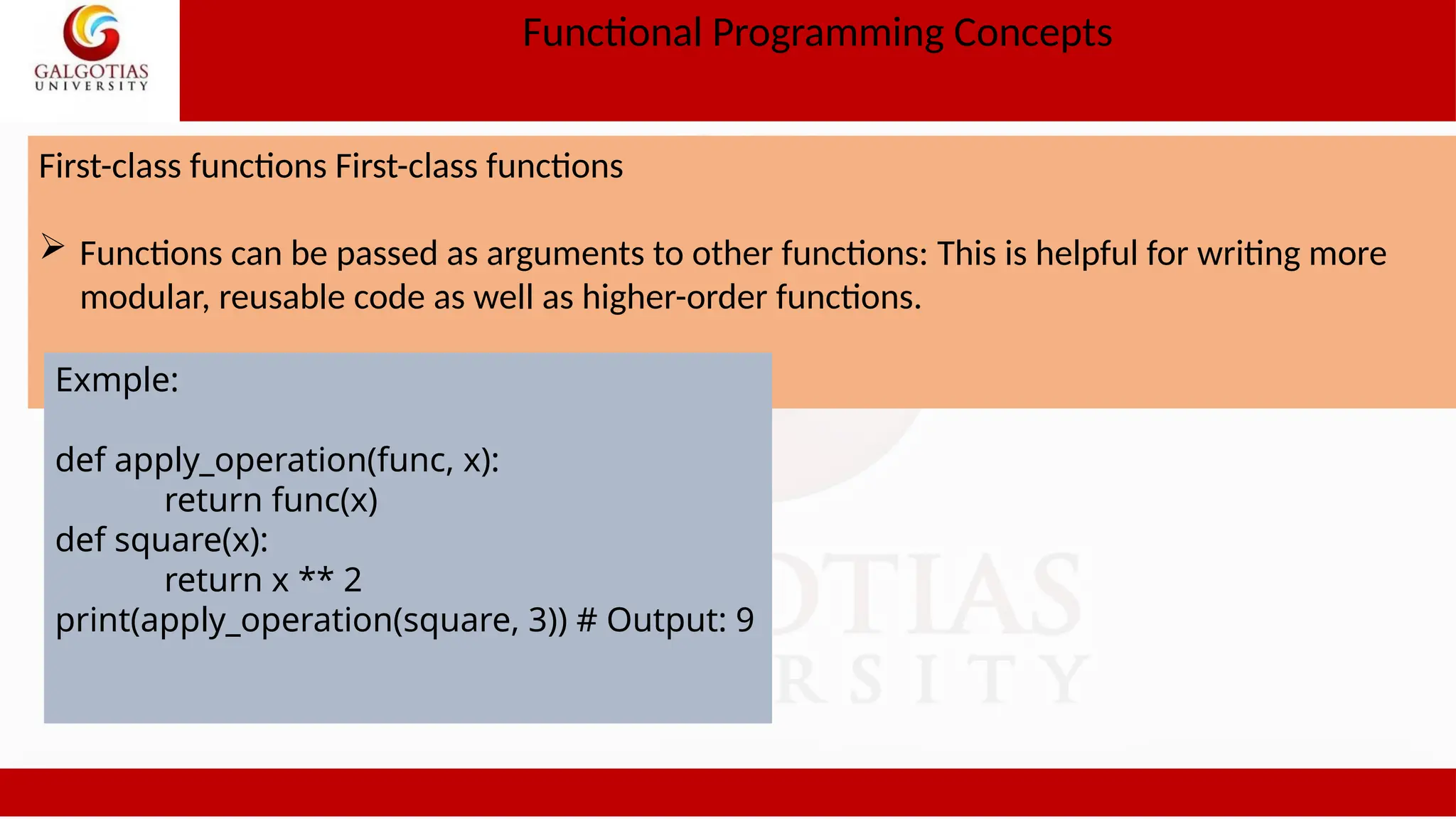
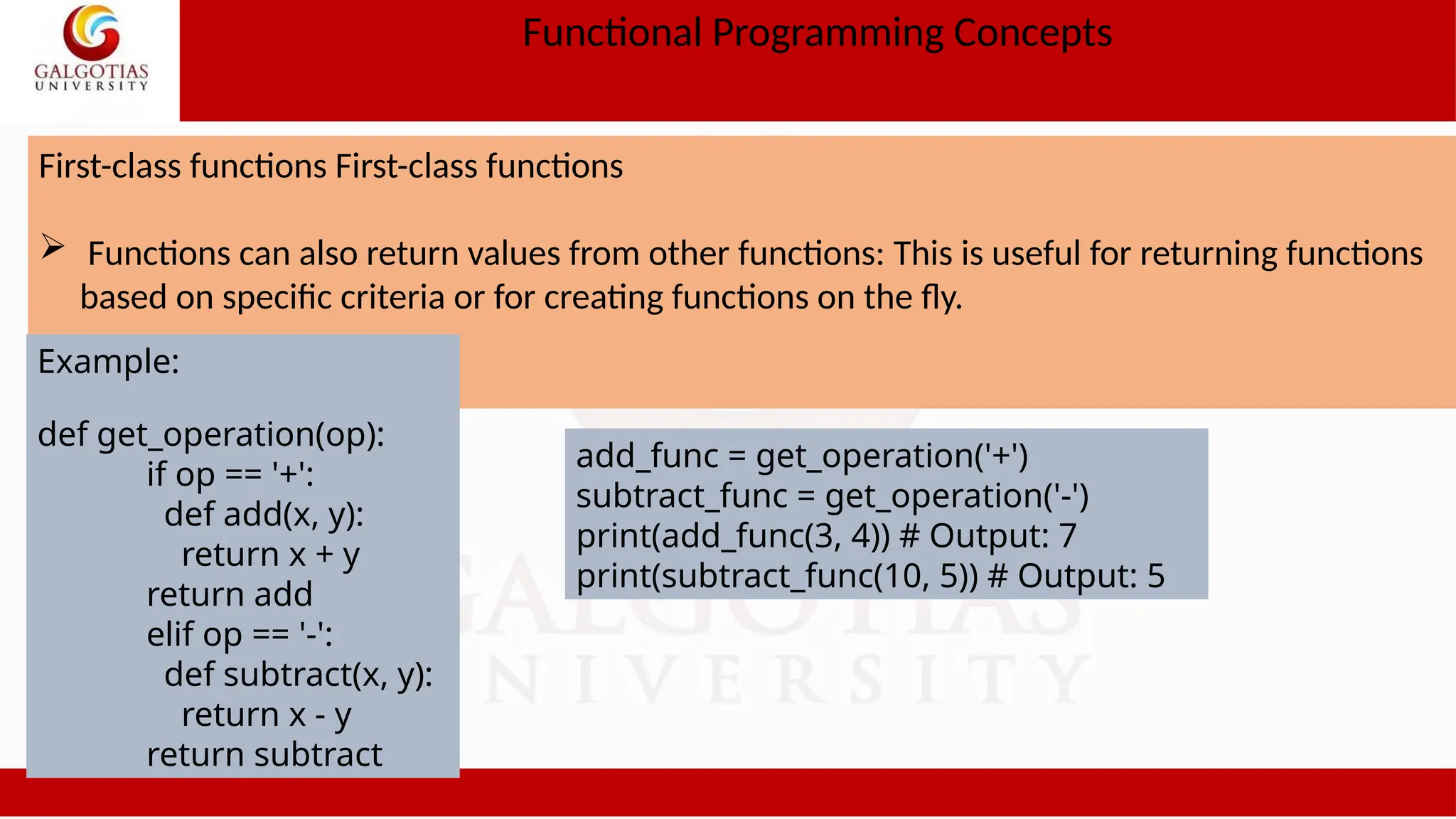
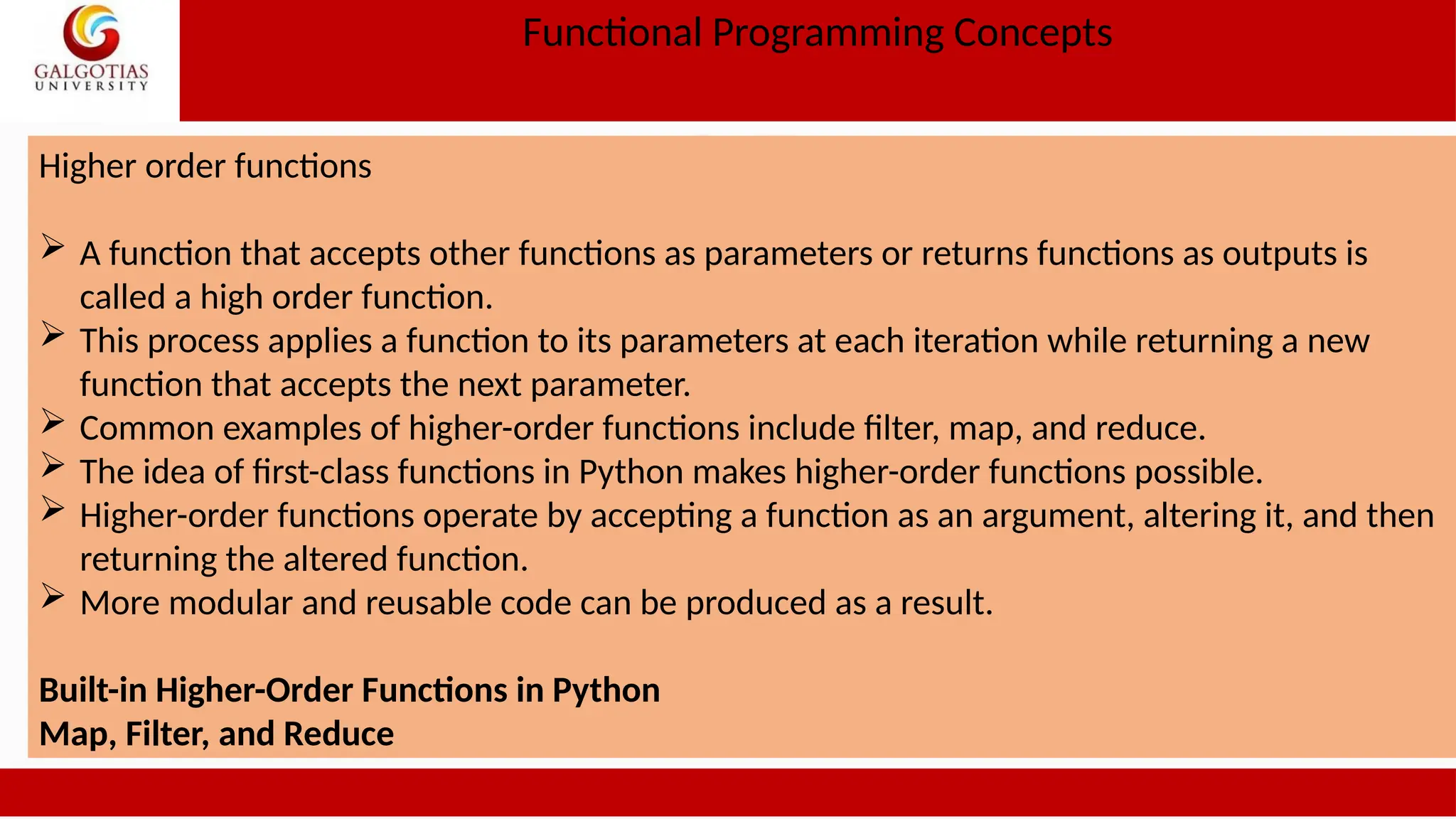
![Functional Programming Concepts Higher order functions Example def apply_func(func, lst): return [func(x) for x in lst] def square(x): return x ** 2 numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] squared_numbers = apply_func(square, numbers) print(squared_numbers) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25] Example 2 def make_adder(n): def adder(x): return x + n return adder add_five = make_adder(5) print(add_five(10)) # Output: 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1oopsunit-iii-240907054102-8c9354d3/75/OOPS-Object-oriented-Programming-PPT-Tutorial-15-2048.jpg)



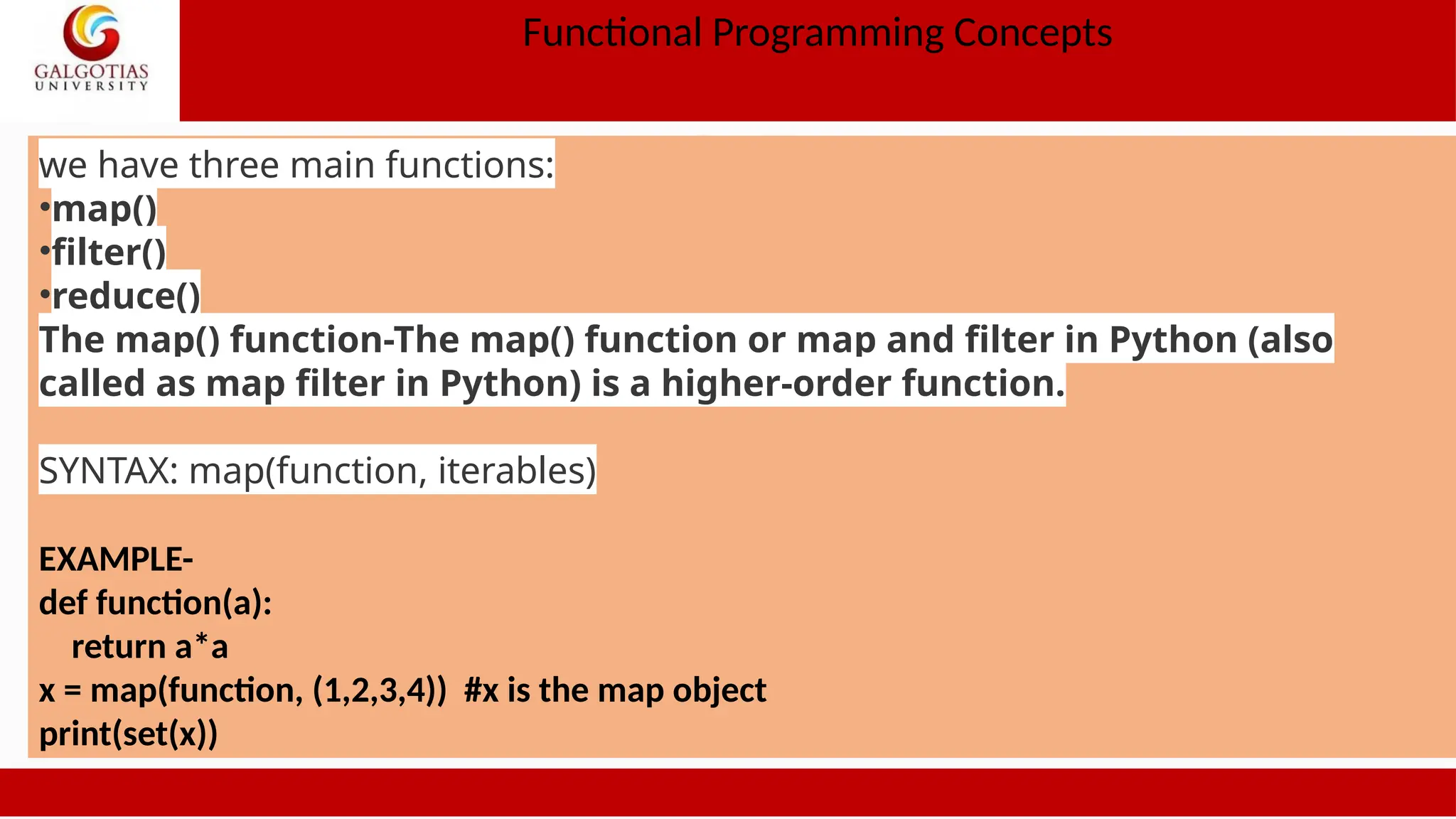
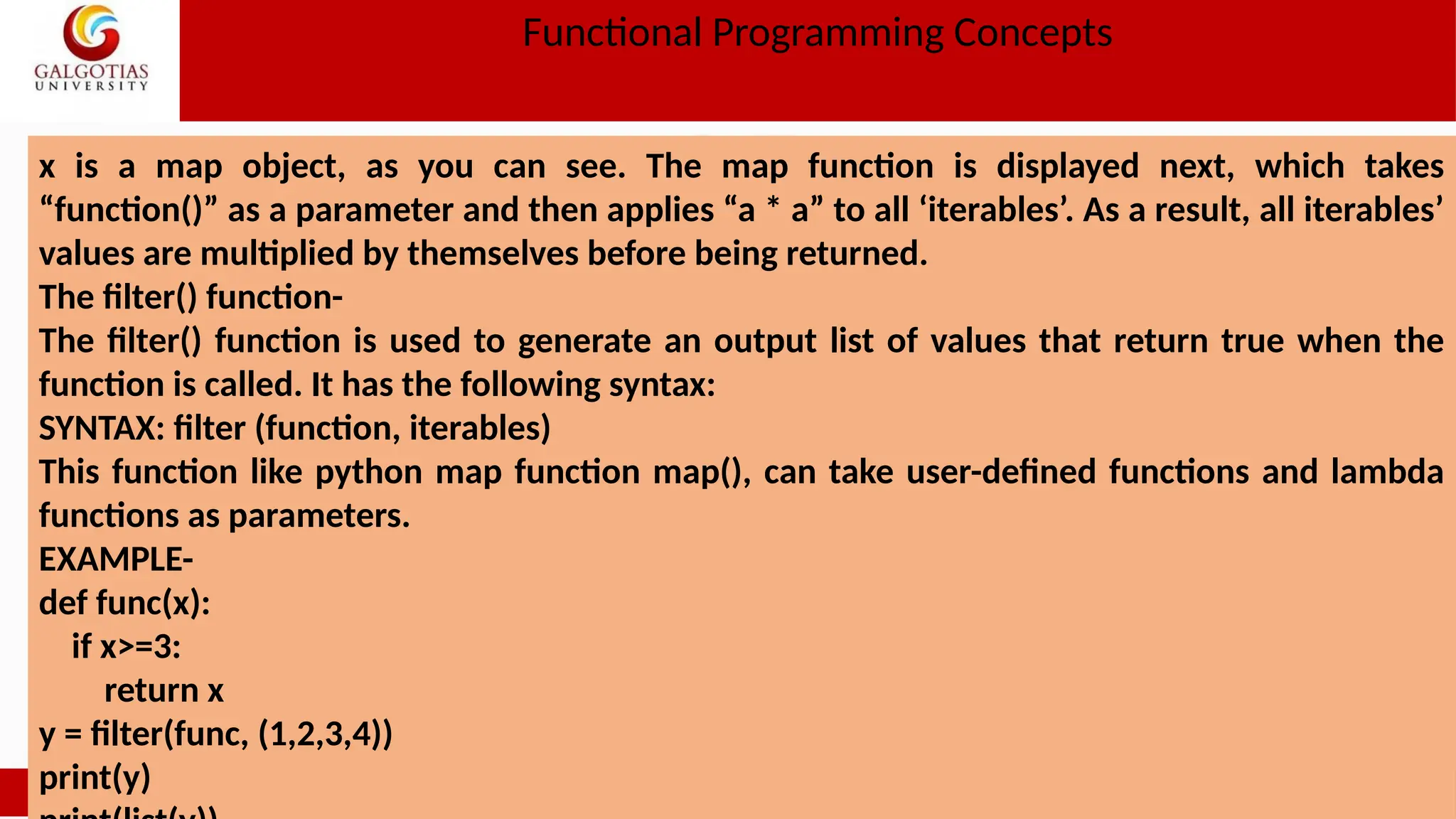
![OUTPUT-[3, 4] As you can see, y is the filter object, and the list is a collection of true values for the condition (x>=3). The reduce() function- The reduce() function applies a provided function to ‘iterables’ and returns a single value, as the name implies. SYNTAX: reduce(function, iterables) The function specifies which expression should be applied to the ‘iterables’ in this case. The function tools module must be used to import this function. EXAMPLE- from functools import reduce reduce(lambda a,b: a+b,[23,21,45,98]) OUTPUT-187](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1oopsunit-iii-240907054102-8c9354d3/75/OOPS-Object-oriented-Programming-PPT-Tutorial-29-2048.jpg)
