The document serves as an introduction to Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) and Java fundamentals, covering concepts like abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism. It details Java's characteristics such as platform independence, robustness, security, and object management, alongside fundamental programming structures including data types, variables, operators, and control flow. Additionally, it elaborates on classes, objects, methods, access specifiers, constructors, and arrays in Java.











![PROGRAM public class JavaPrograms { public static void main(String[] args) { int id=10; System.out.println("id="+id); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uniti-250210033053-49bae445/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-unit-1-content-for-students-19-2048.jpg)

![class Student { int id=1; String name=“XXX”; int age=15; void display() { System.out.println(id+" "+name+" "+age); } public static void main(String args[]) { } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uniti-250210033053-49bae445/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-unit-1-content-for-students-23-2048.jpg)


![class Student { int id=1; String name=“XXX”; int age=15; void display() { System.out.println(id+" "+name+" "+age); } public static void main(String args[]) { Student s = new student(); s.display(); } } Note: If we are using methods inside a class, then we must create an object inside the main method()to invoke the method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uniti-250210033053-49bae445/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-unit-1-content-for-students-26-2048.jpg)



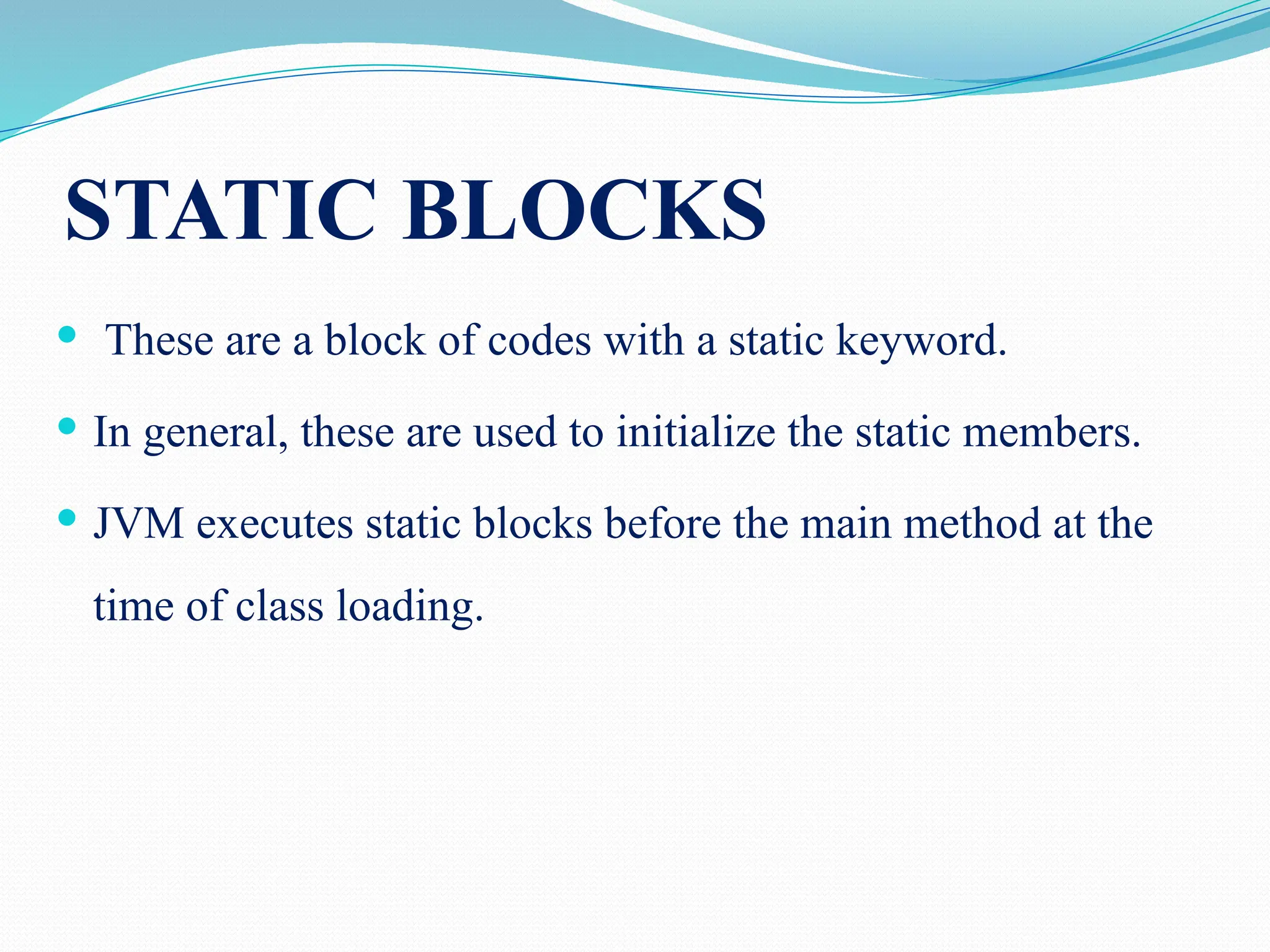
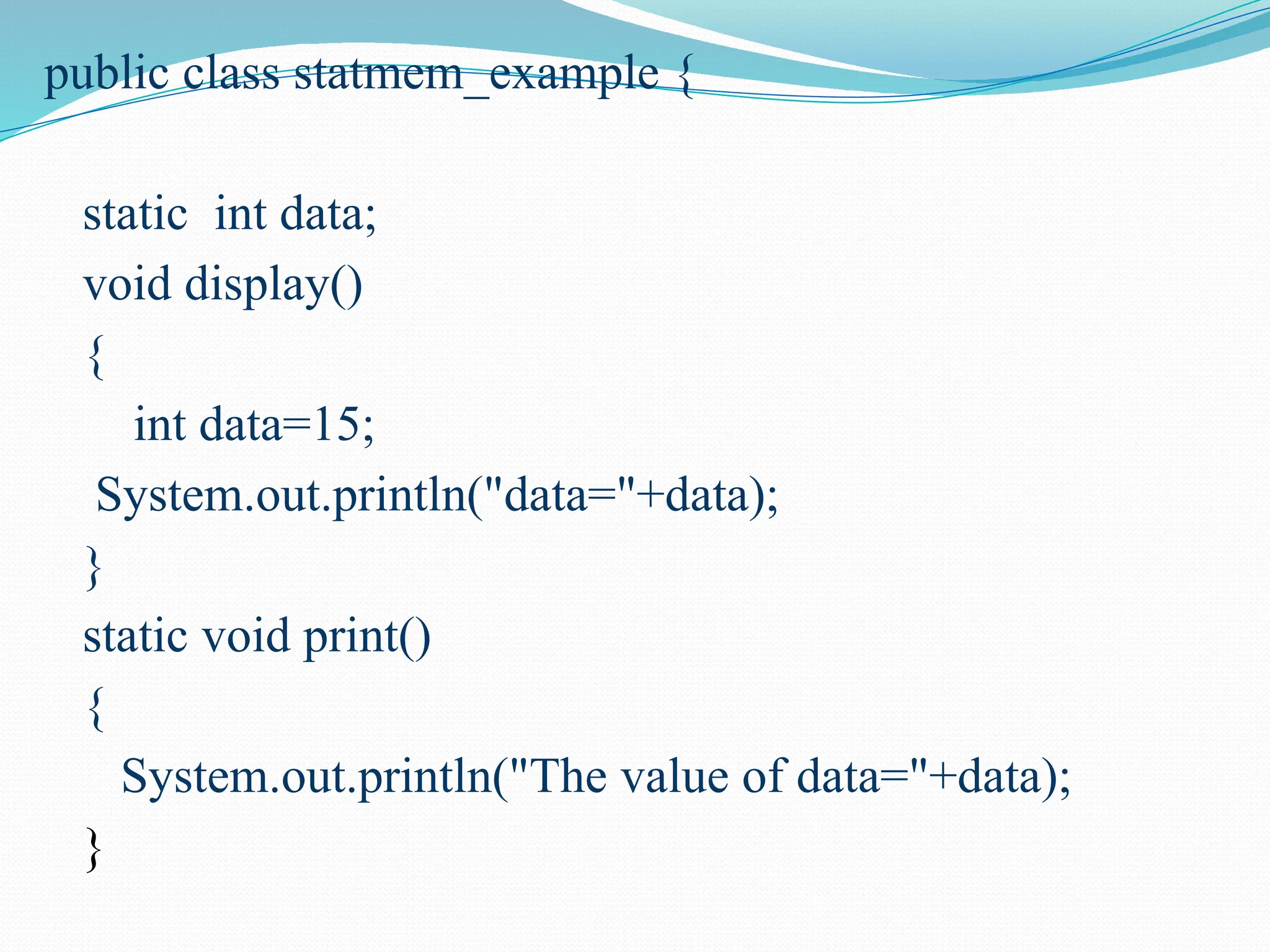
![static { data=10; System.out.println("The static method is invoked"); } public static void main(String args[]) { statmem_example ex=new statmem_example(); statmem_example.print(); ex.display(); } } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uniti-250210033053-49bae445/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-unit-1-content-for-students-35-2048.jpg)



![public class Unary_Example { public static void main(String args[]) { int a=10; System.out.println("Value of a=“+(-a)); System.out.println("Value of a=“+(a++)); System.out.println("Value of a="+(--a)); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uniti-250210033053-49bae445/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-unit-1-content-for-students-39-2048.jpg)





![PROGRAM public class instanceof_example { public static void main(String args[]){ instanceof_example s=new instanceof_example(); System.out.println(s instanceof instanceof_example);//true } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uniti-250210033053-49bae445/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-unit-1-content-for-students-45-2048.jpg)
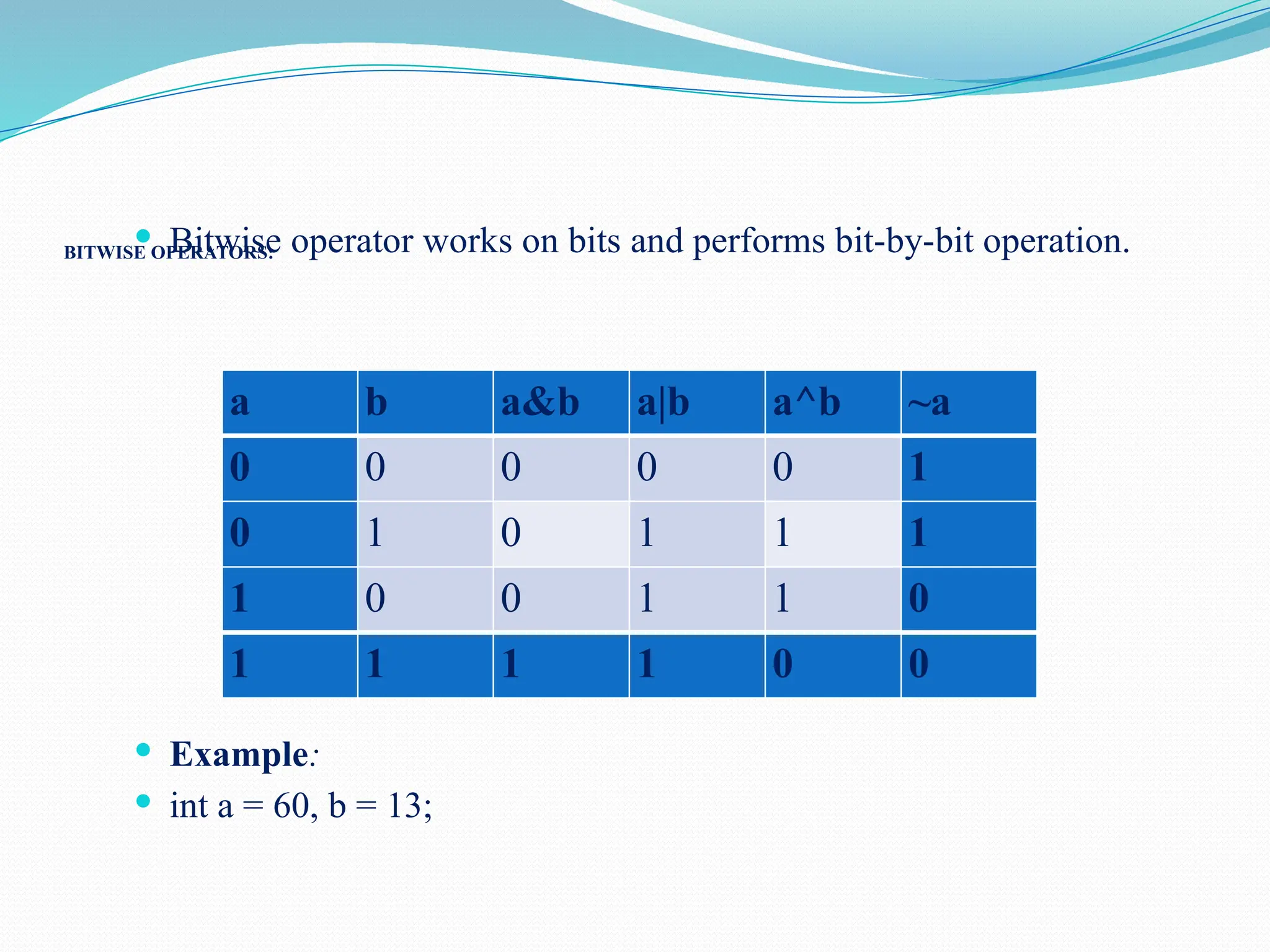



![public class AssignmentOp_Example { public static void main(String[] args) { int a= 20, b = 15; System.out.println("a+=b="+(a+=b)); System.out.println("a-=b="+(a-=b)); System.out.println("a*=b="+(a*=b)); System.out.println("a/=b="+(a/=b)); System.out.println("a%=b="+(a%=b)); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uniti-250210033053-49bae445/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-unit-1-content-for-students-50-2048.jpg)



![Category Operator Associativity Postfix >() [] . (dot operator) Left to right Unary >++ - - ! ~ Right to left Multiplicative >* / Left to right Additive >+ - Left to right Shift >>> >>> << Left to right Relational >> >= < <= Left to right Equality >== != Left to right Bitwise AND >& Left to right Bitwise XOR >^ Left to right Bitwise OR >| Left to right Logical AND >&& Left to right Logical OR >|| Left to right Conditional ?: Right to left Assignment >= += -= *= /= %= >>= <<= &= ^= |= Right to left](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uniti-250210033053-49bae445/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-unit-1-content-for-students-54-2048.jpg)


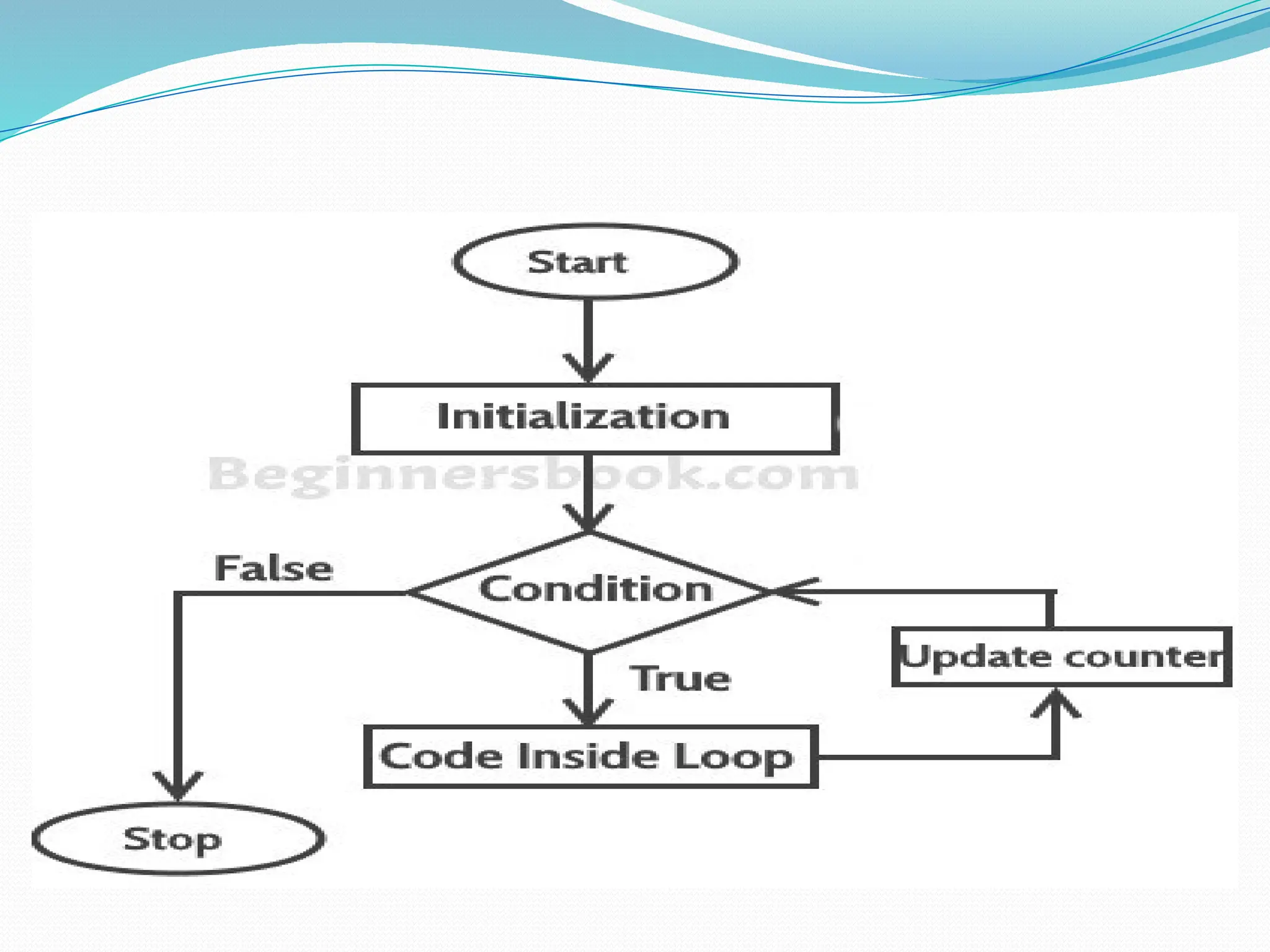

![public class ProgramContinue { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(“Odd Numbers”); for (int i = 1; i <= 10; ++i) { if (i % 2 == 0) continue; System.out.println(i + “t”); } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uniti-250210033053-49bae445/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-unit-1-content-for-students-59-2048.jpg)

![PROGRAM FOR BREAK STATEMENTS public class ProgramBreak { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(“Numbers 1 - 10”); for (int i = 1;; ++i) { if (i == 11) break; System.out.println(i + “t”); } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uniti-250210033053-49bae445/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-unit-1-content-for-students-61-2048.jpg)

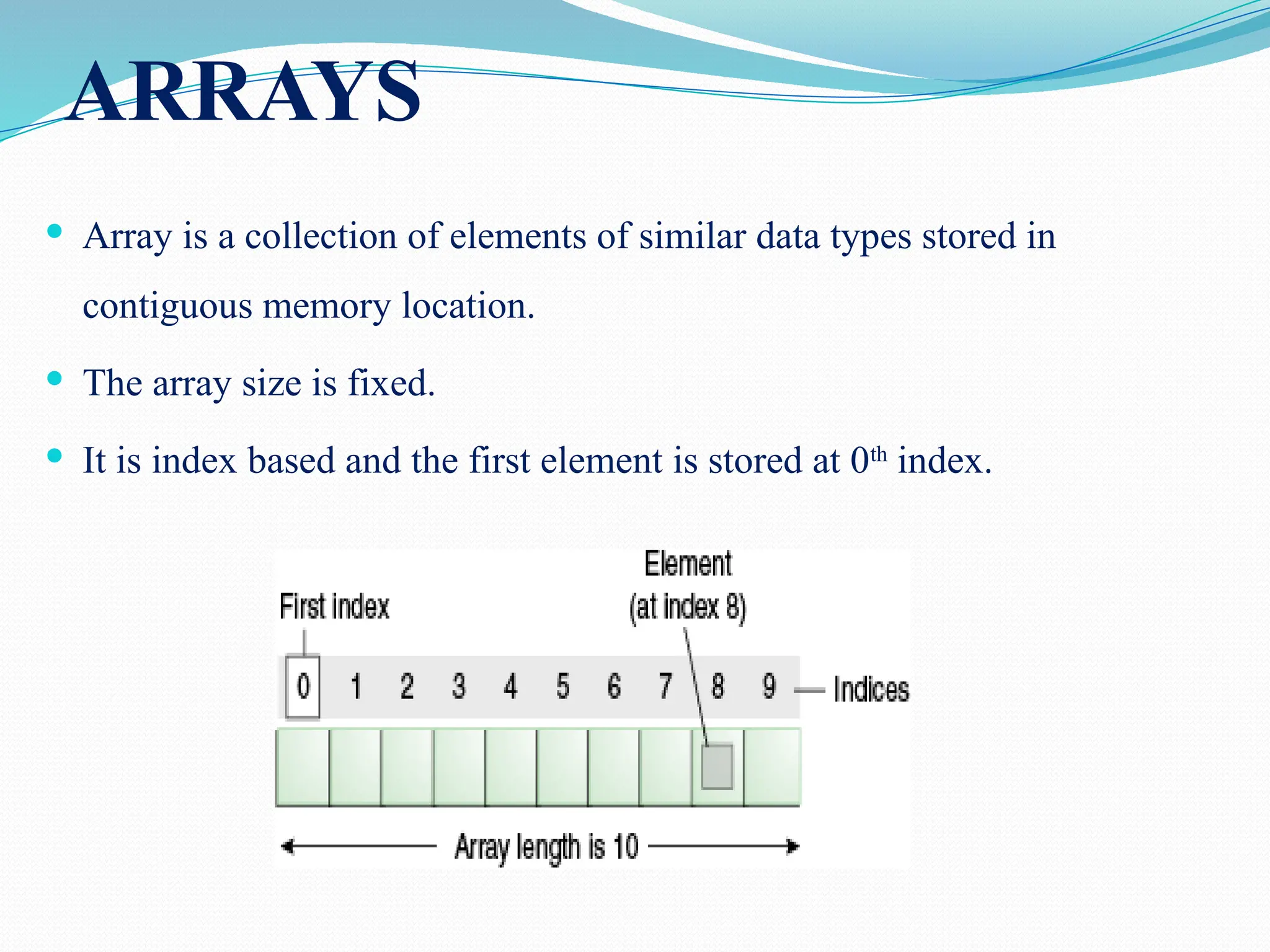

![One Dimensional Array: One-Dimensional Array is the simplest form of an Array in which the elements are stored linearly and can be accessed individually by specifying the index value of each element stored in the array. Syntax: dataType[] arrayName=new datatype[size]; Or dataType arrayName []=new datatype[size]; Example: int[] a=new int[5];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uniti-250210033053-49bae445/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-unit-1-content-for-students-65-2048.jpg)

![Syntax: dataType arrayName[]=new datatype[size]; Or dataType[] arrayName=new datatype[size]; Example: int[] a=new int[5]; OR int a[]=new int[5];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uniti-250210033053-49bae445/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-unit-1-content-for-students-67-2048.jpg)
![INITIALIZING AN ARRAY: SYNTAX: dataType[] arrayName=new datatype[]{list of values separated by comma}; Example: int[] a=new int[]{12,13,14};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uniti-250210033053-49bae445/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-unit-1-content-for-students-68-2048.jpg)
![import java.util.*; public class Array_Example { public static void main(String args[]) { int number[]=new int[3]; System.out.println("Enter the array elements"); Scanner s=new Scanner(System.in); number[0]=s.nextInt(); number[1]=s.nextInt(); number[2]=s.nextInt(); System.out.println("The numbers entered are"+number[0]+" t"+number[1]+"t"+number[2]); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uniti-250210033053-49bae445/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-unit-1-content-for-students-69-2048.jpg)
![MULTIDIMENSIONALARRAYS: A multidimensional array is an array with more than two dimensions. In multi dimensional array the elements are stored in the form of rows and columns. Syntax: dataType[][] arrayName=new datatype[rowsize][columnnsize]; Example: int[][] a=new int[3][4];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uniti-250210033053-49bae445/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-unit-1-content-for-students-70-2048.jpg)
![JAGGED ARRAY Jagged array is an array of arrays with different row size i.e. with different dimensions. Example: int[][] a = { {11, 3, 43}, {3, 5, 8, 1}, {9}, };](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uniti-250210033053-49bae445/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-unit-1-content-for-students-71-2048.jpg)

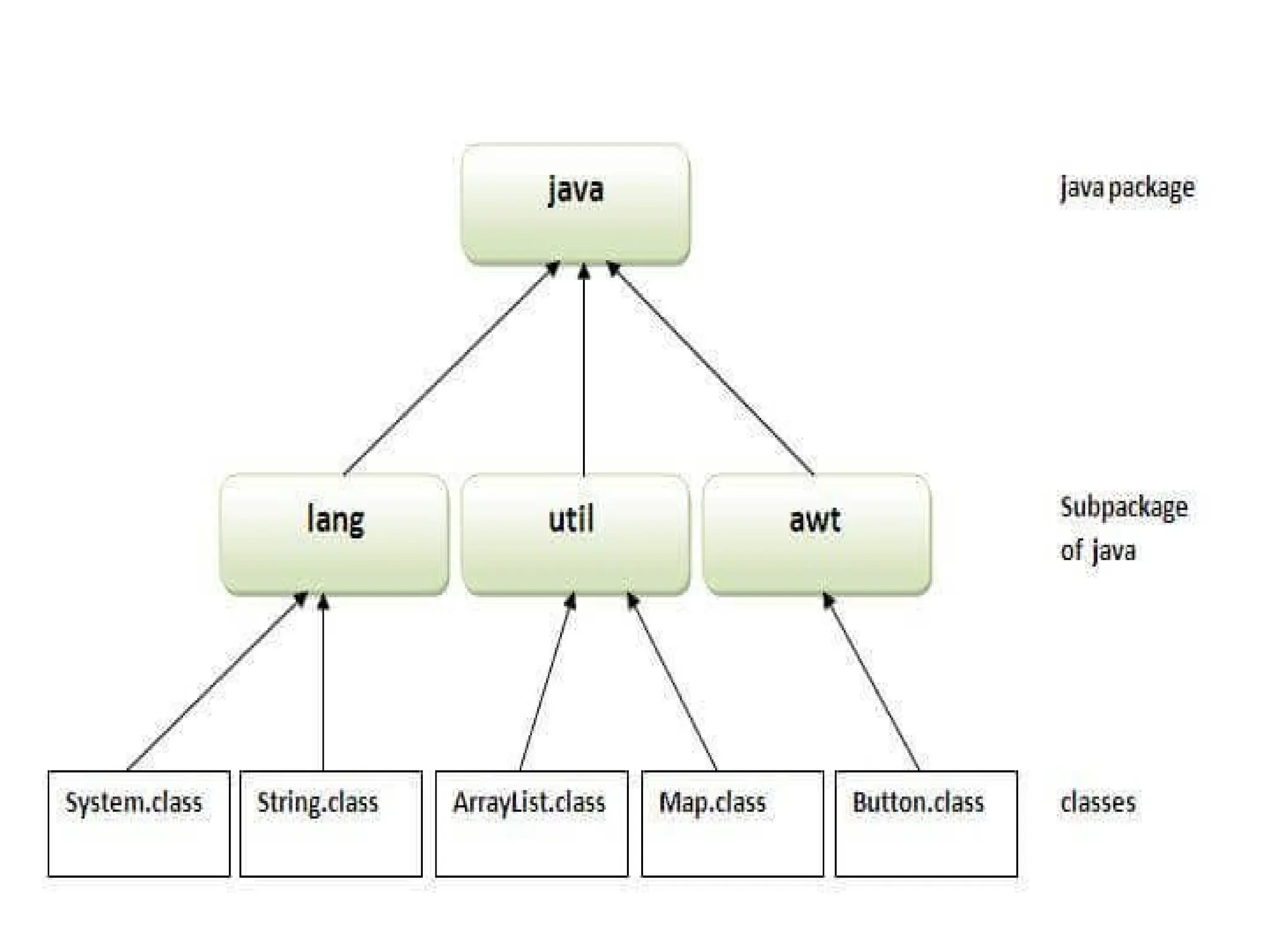


![import java.util.*; import Package_Example.*; public class Package_Example { public static void main(String args[]) { System.out.println("Enter the student name"); Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); String name=in.next(); Hello h=new Hello(); System.out.println(h.display()+"t"+name); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uniti-250210033053-49bae445/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-unit-1-content-for-students-76-2048.jpg)

