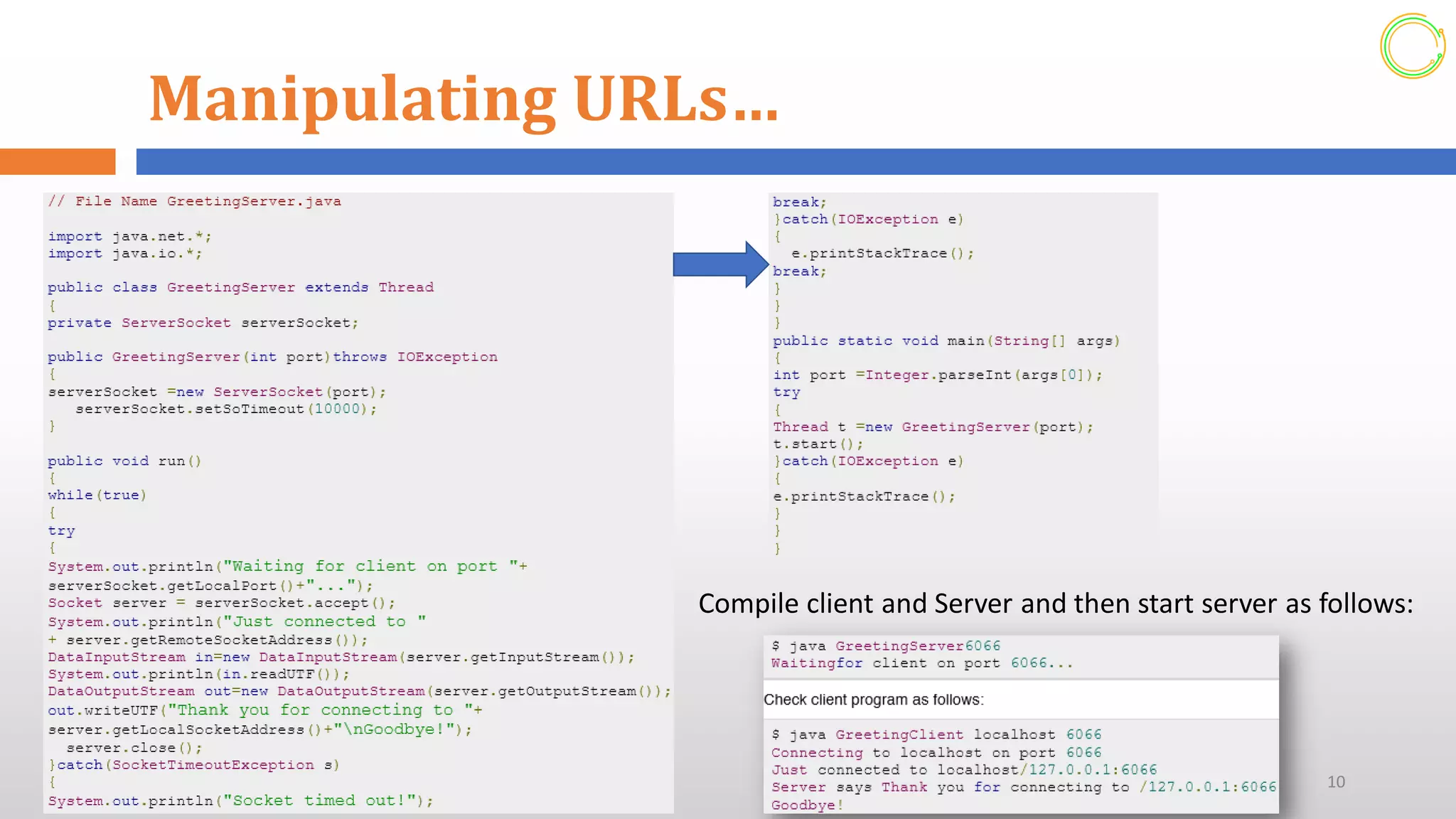
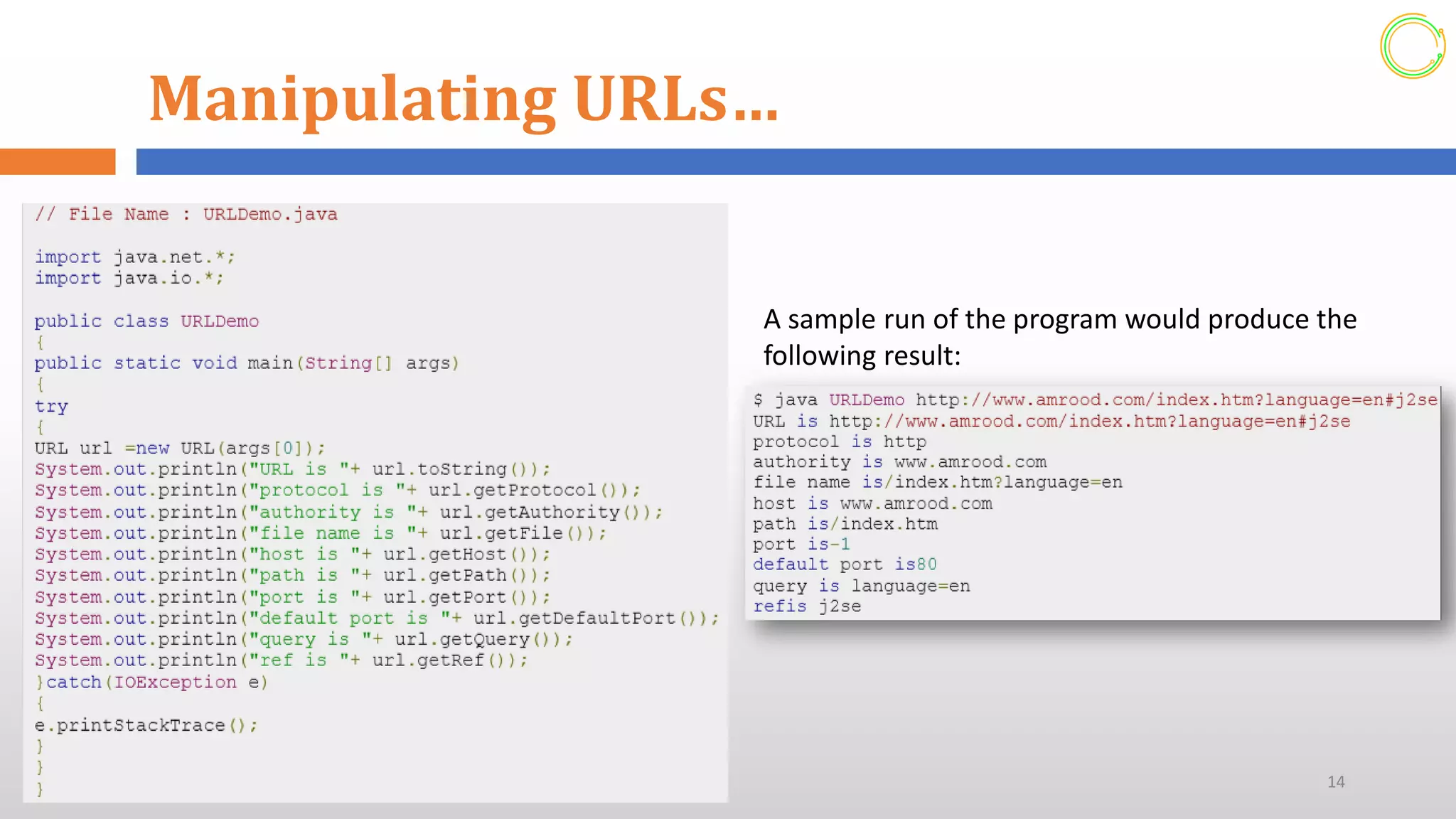
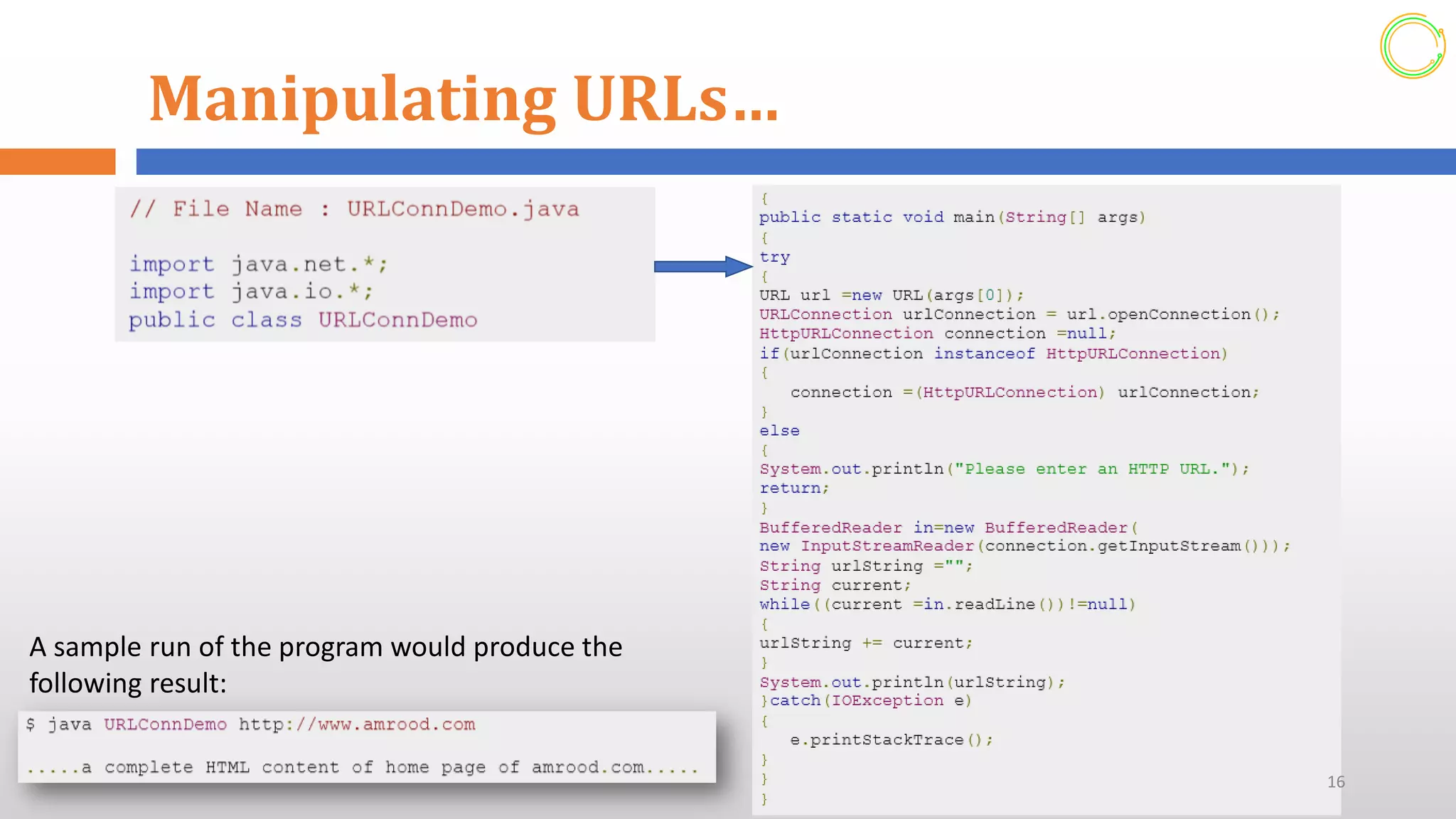
This document provides an overview of networking concepts in Java. It discusses how Java makes network programming easier than C/C++. The java.net package contains classes and interfaces that handle low-level communication details. It supports both TCP and UDP network protocols. The document demonstrates how to create servers and sockets in Java to establish connections between clients and servers for communication. It also shows how to manipulate URLs to access resources on the web and process URL components.