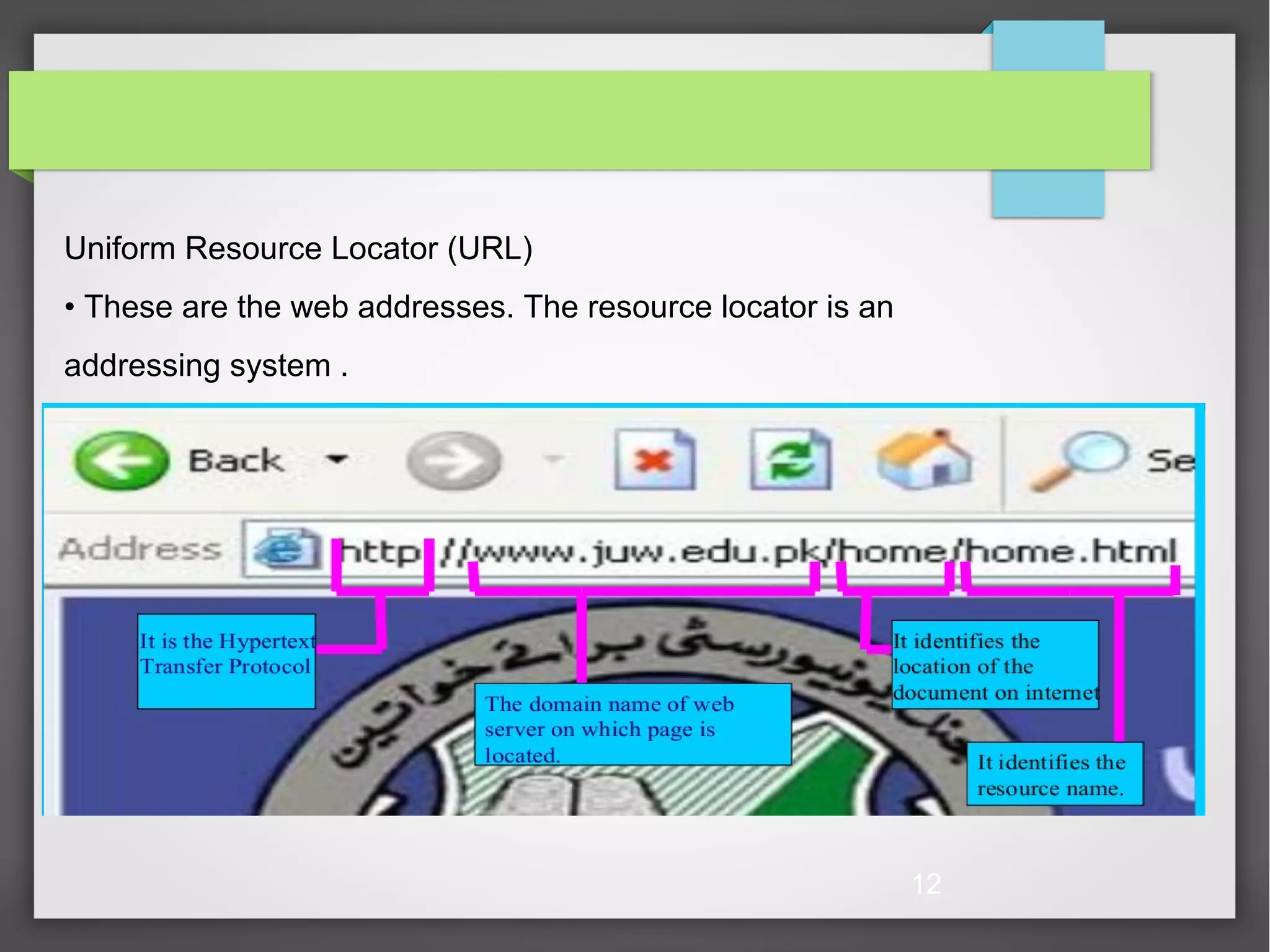
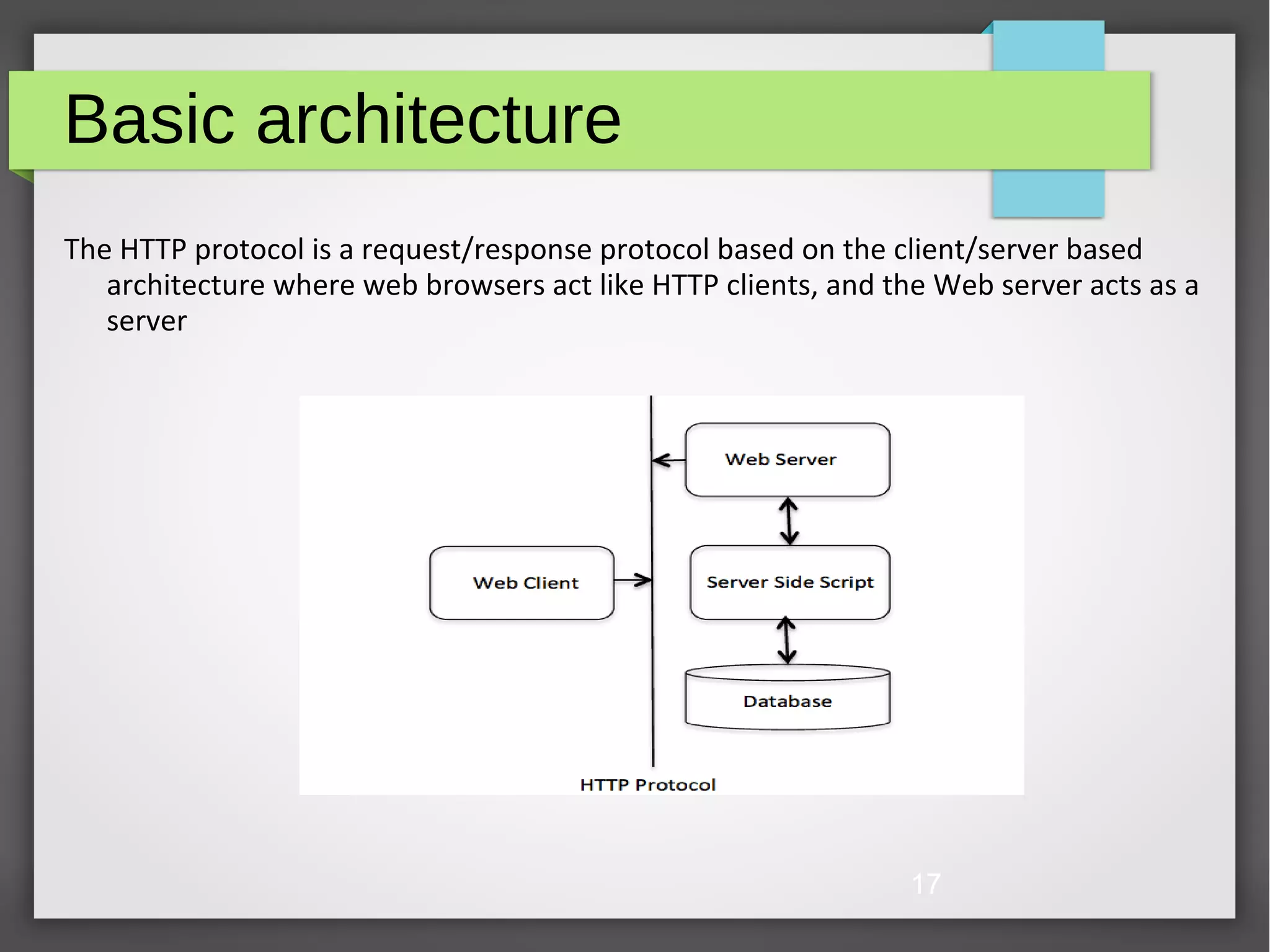
The document provides an overview of the World Wide Web (WWW) and Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). It discusses the structure of the WWW including clients, servers, caches and components like HTML, URLs, and browsers. HTTP is described as the application protocol that allows for data communication across the internet using requests and responses. Key aspects of HTTP like features, architecture, status codes, and request methods are summarized.