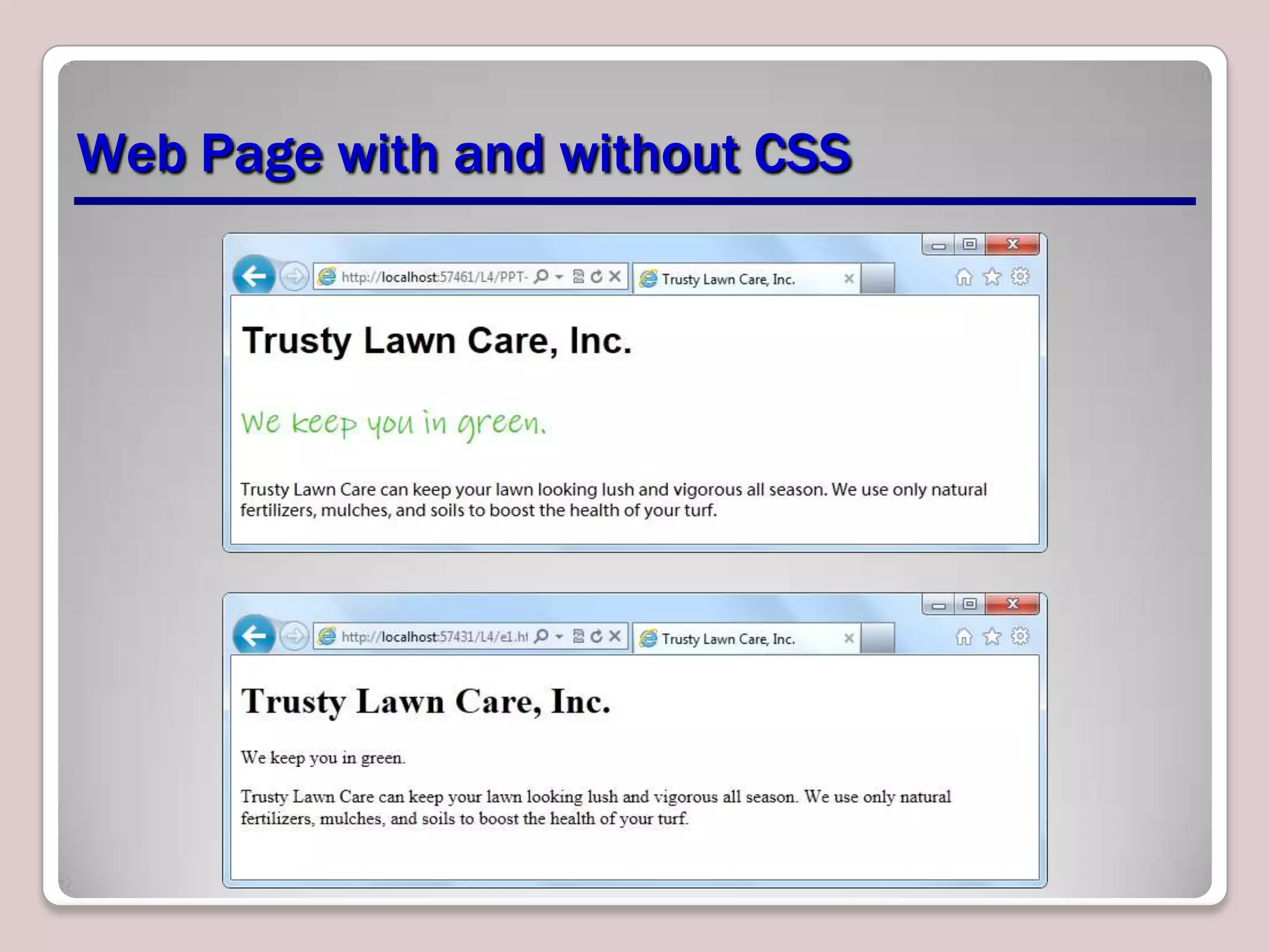
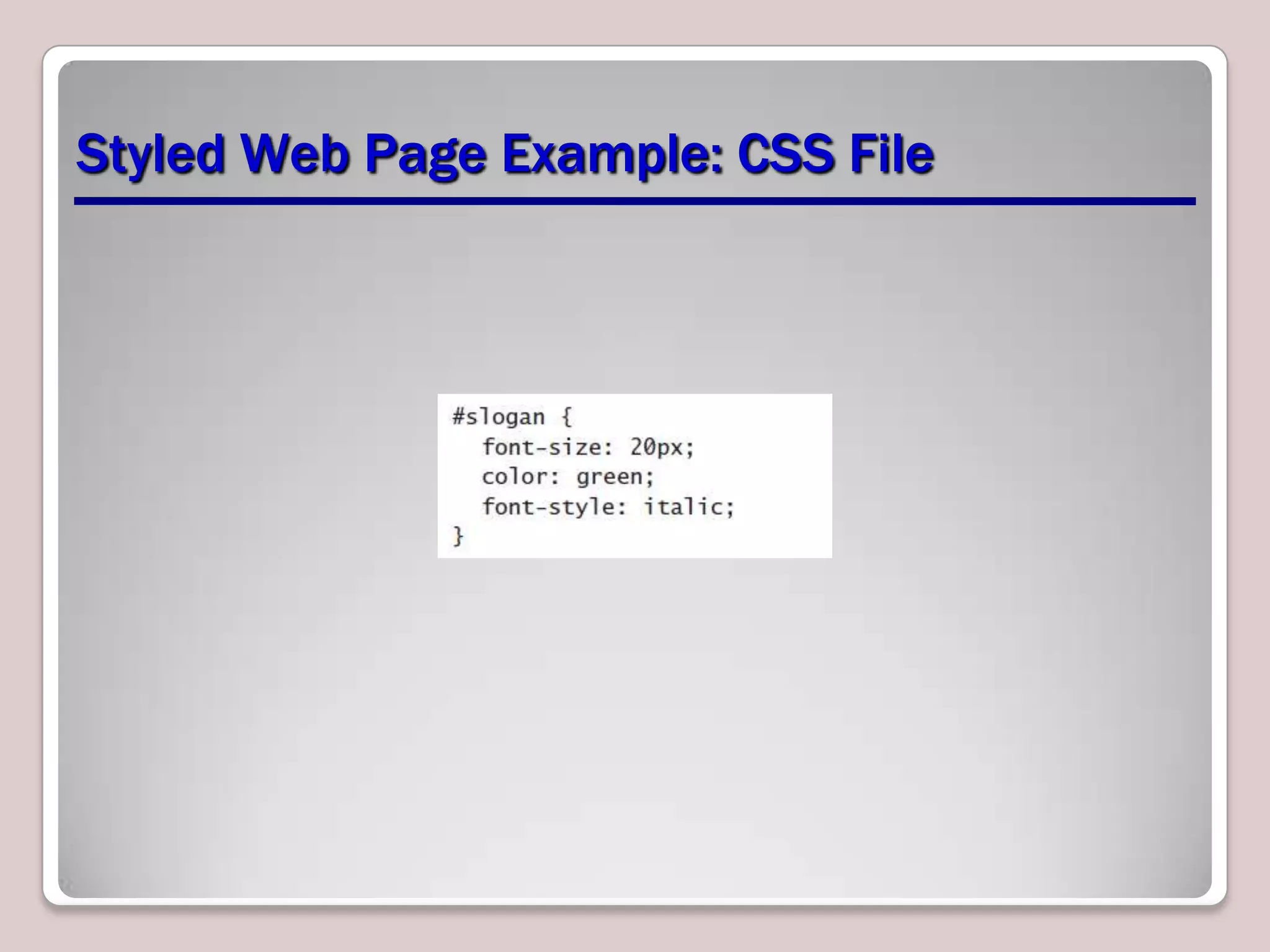
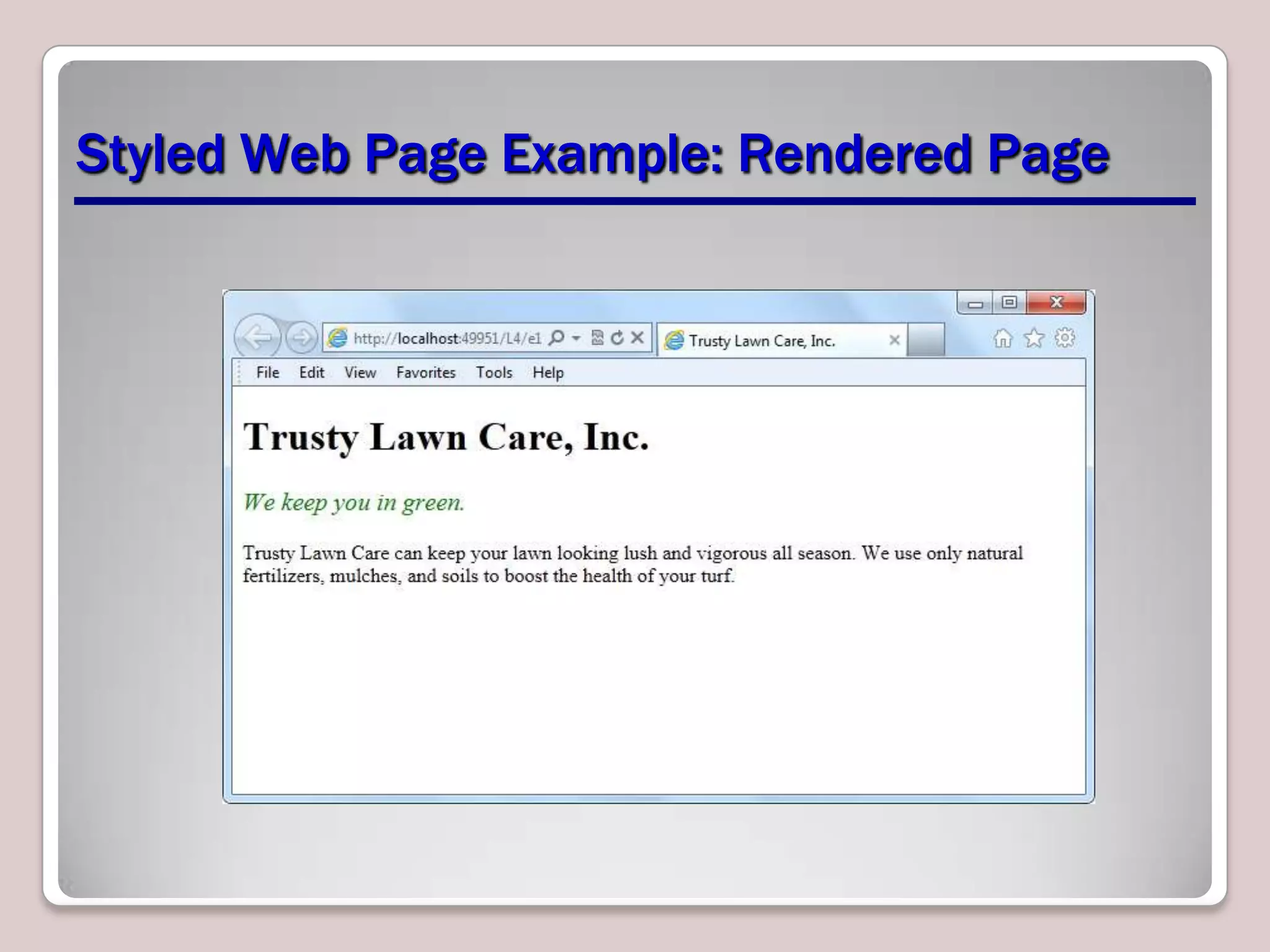
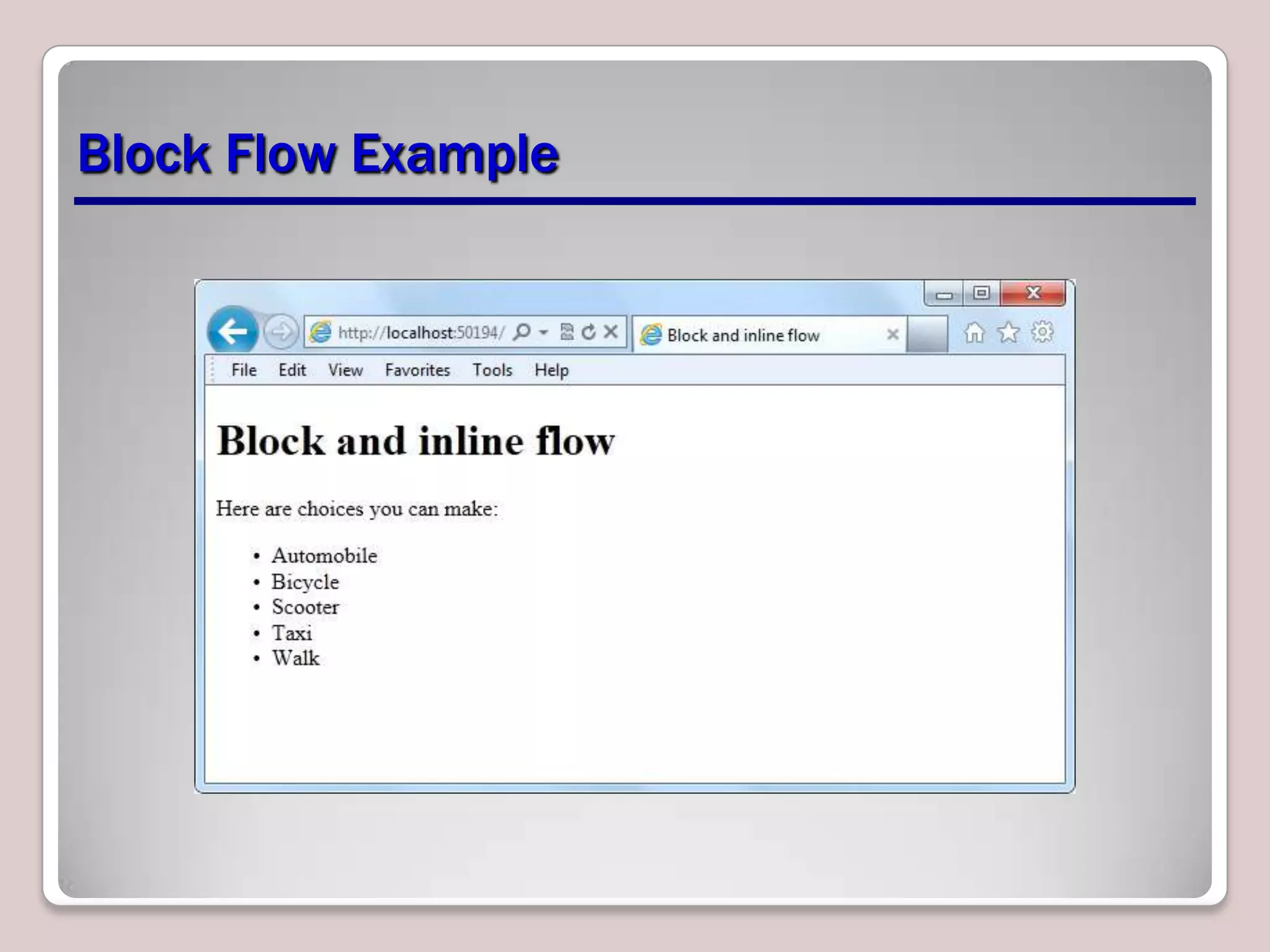
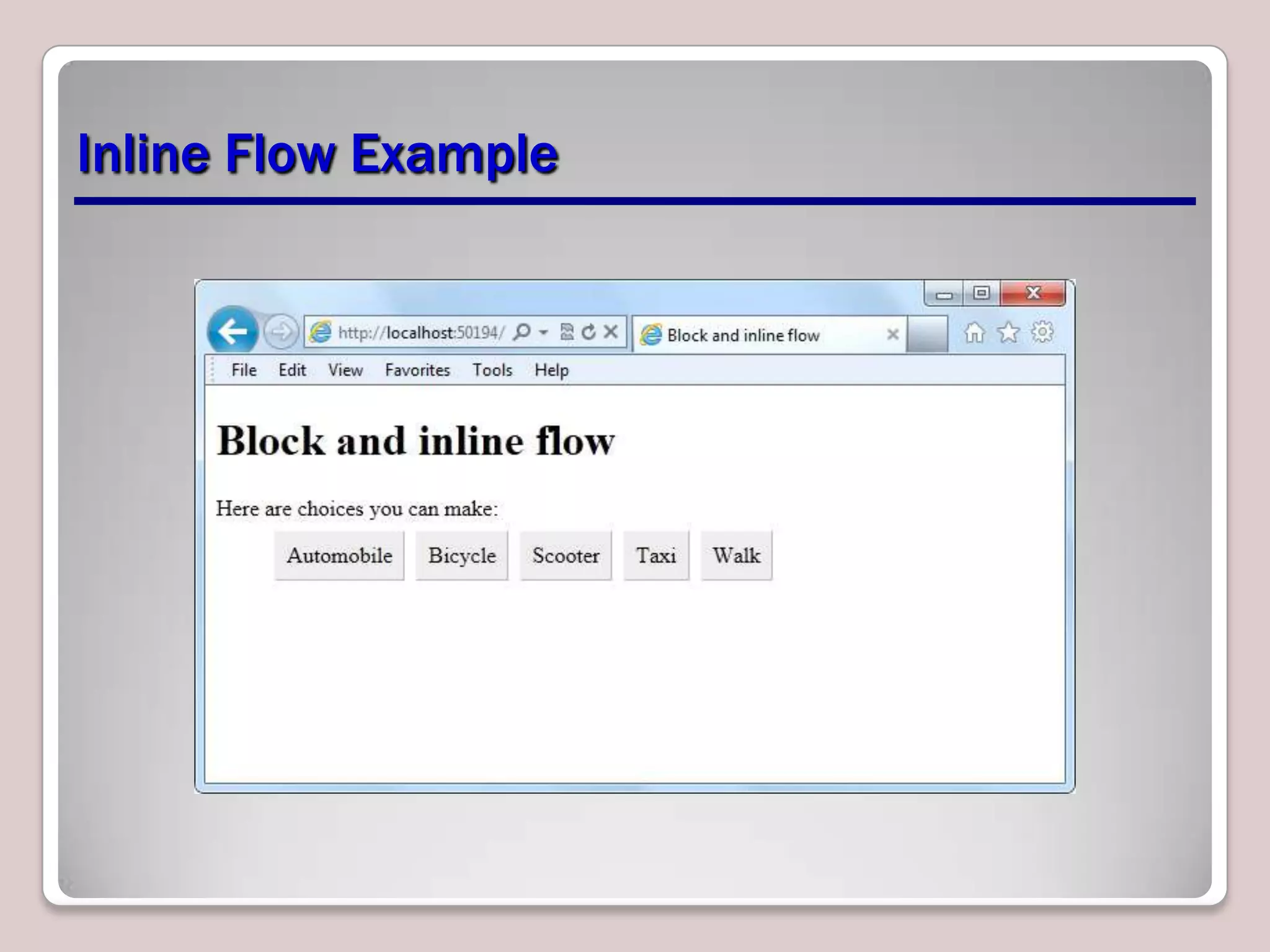
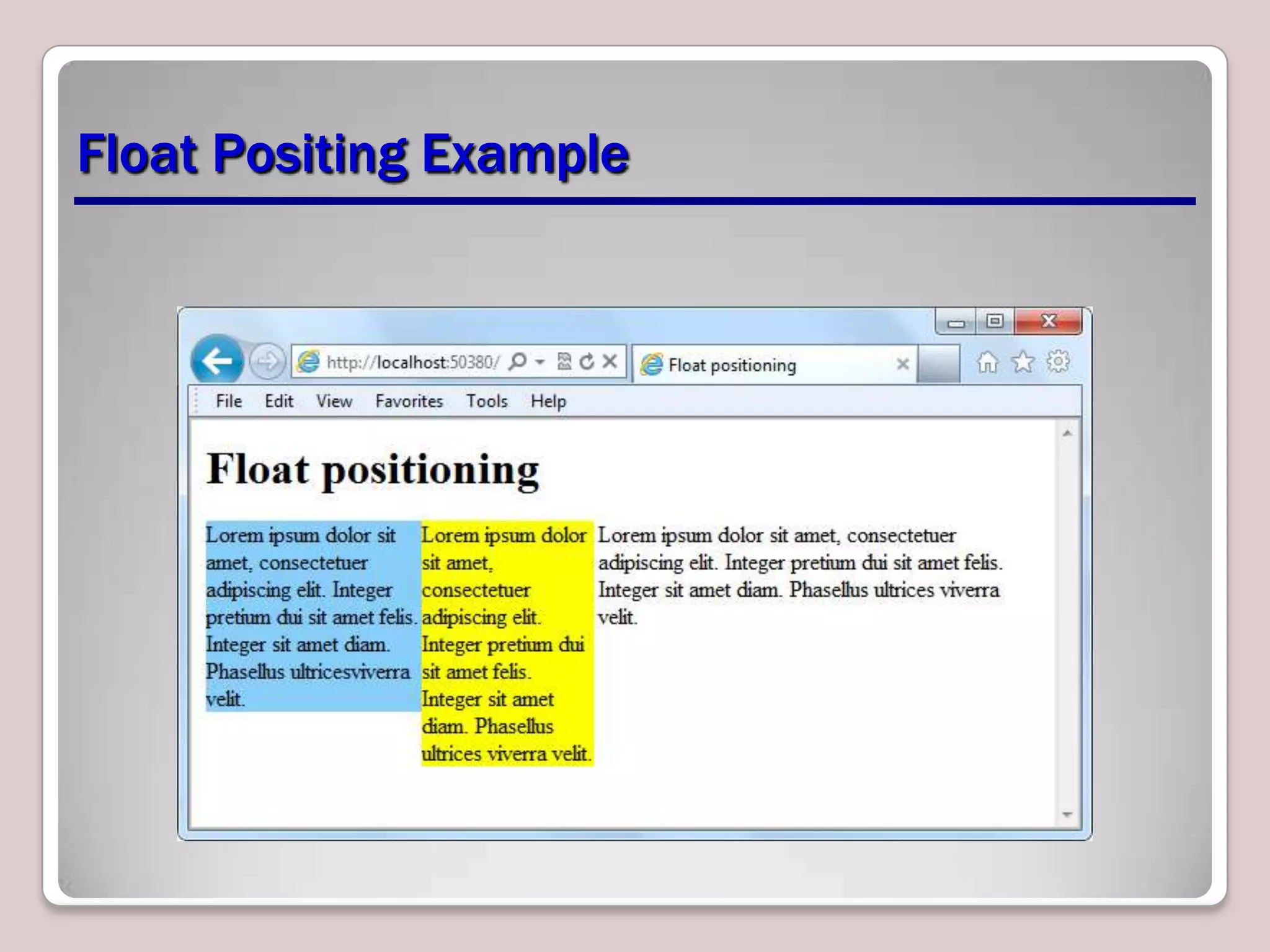
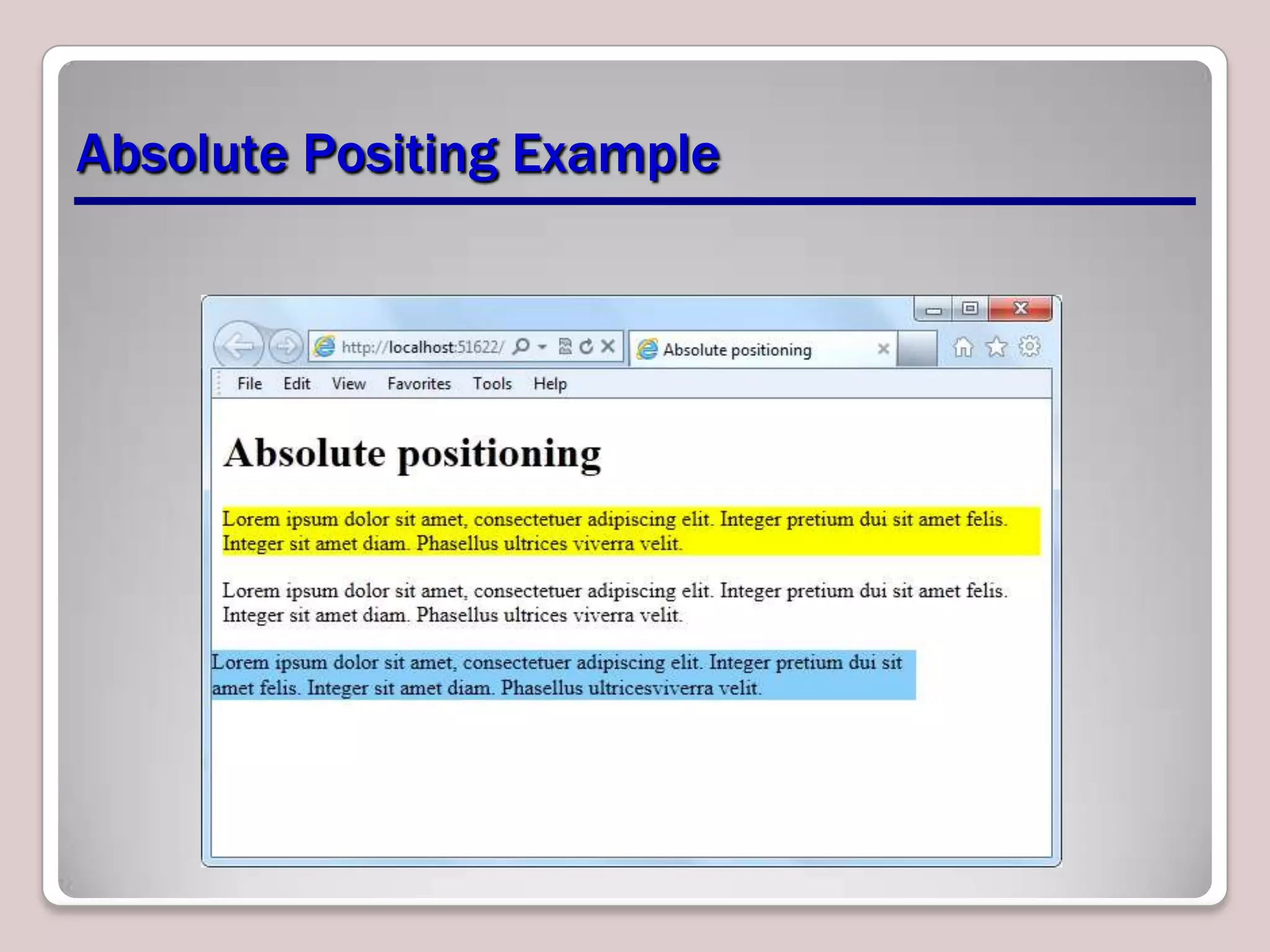
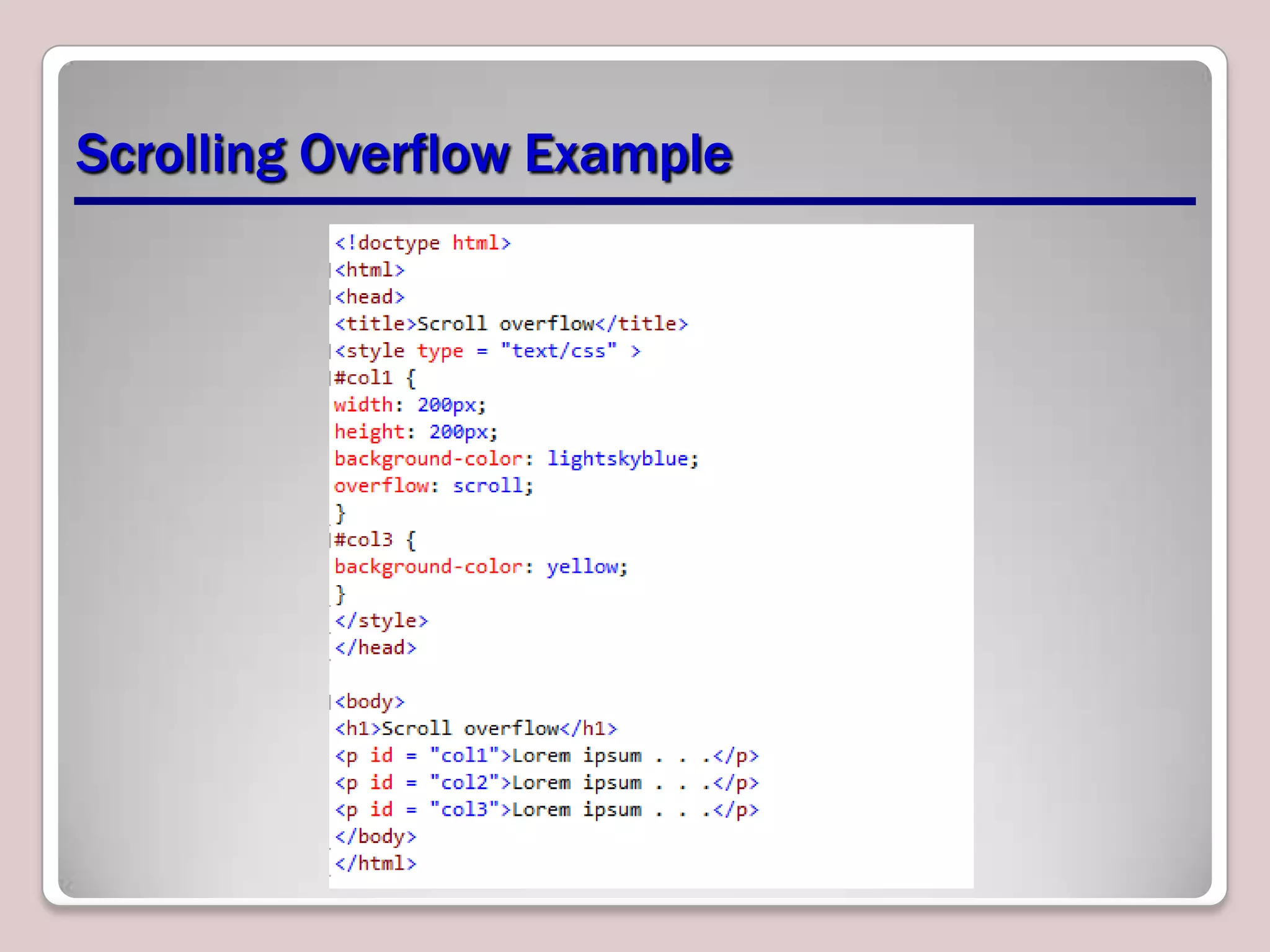
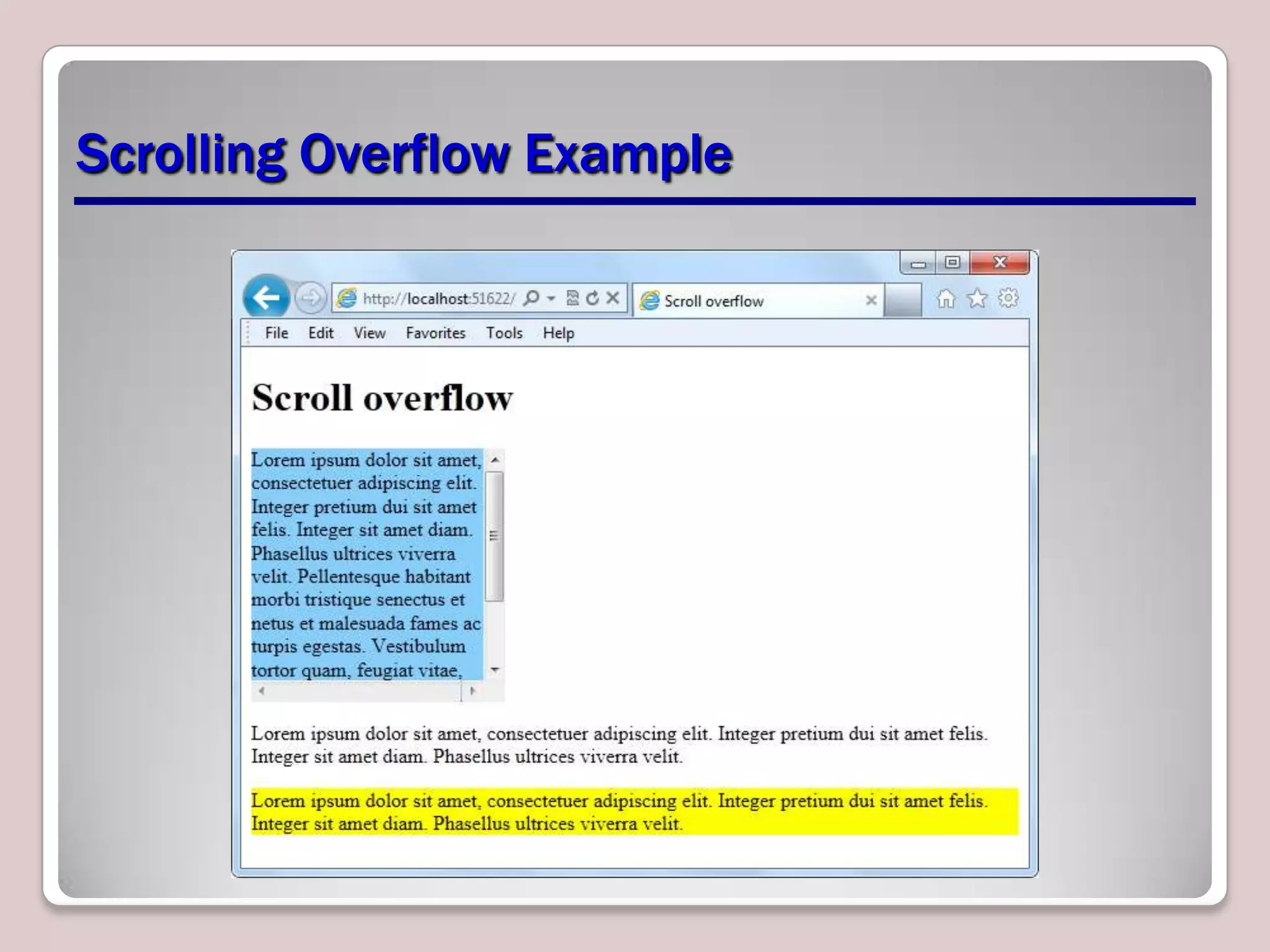
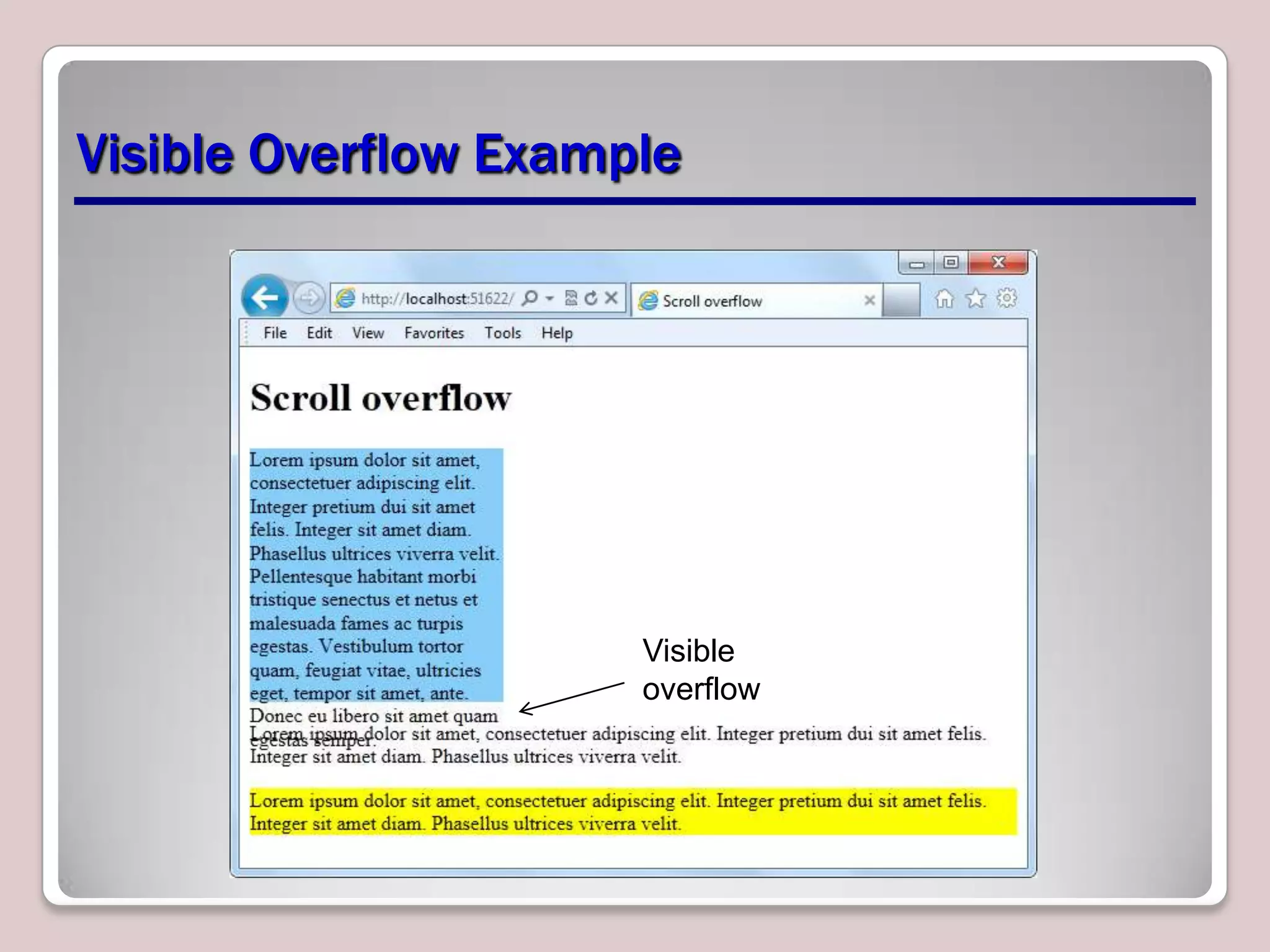
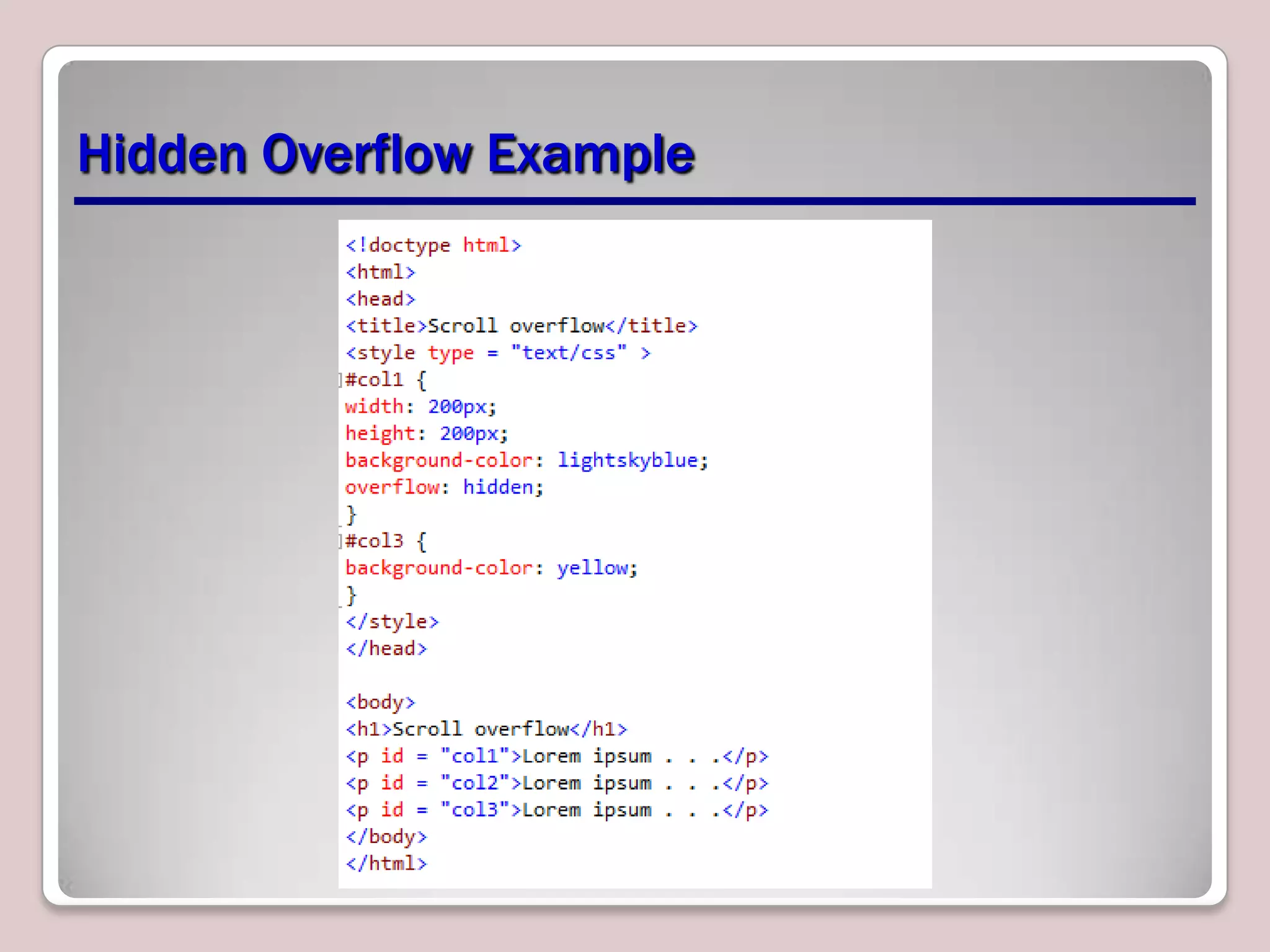
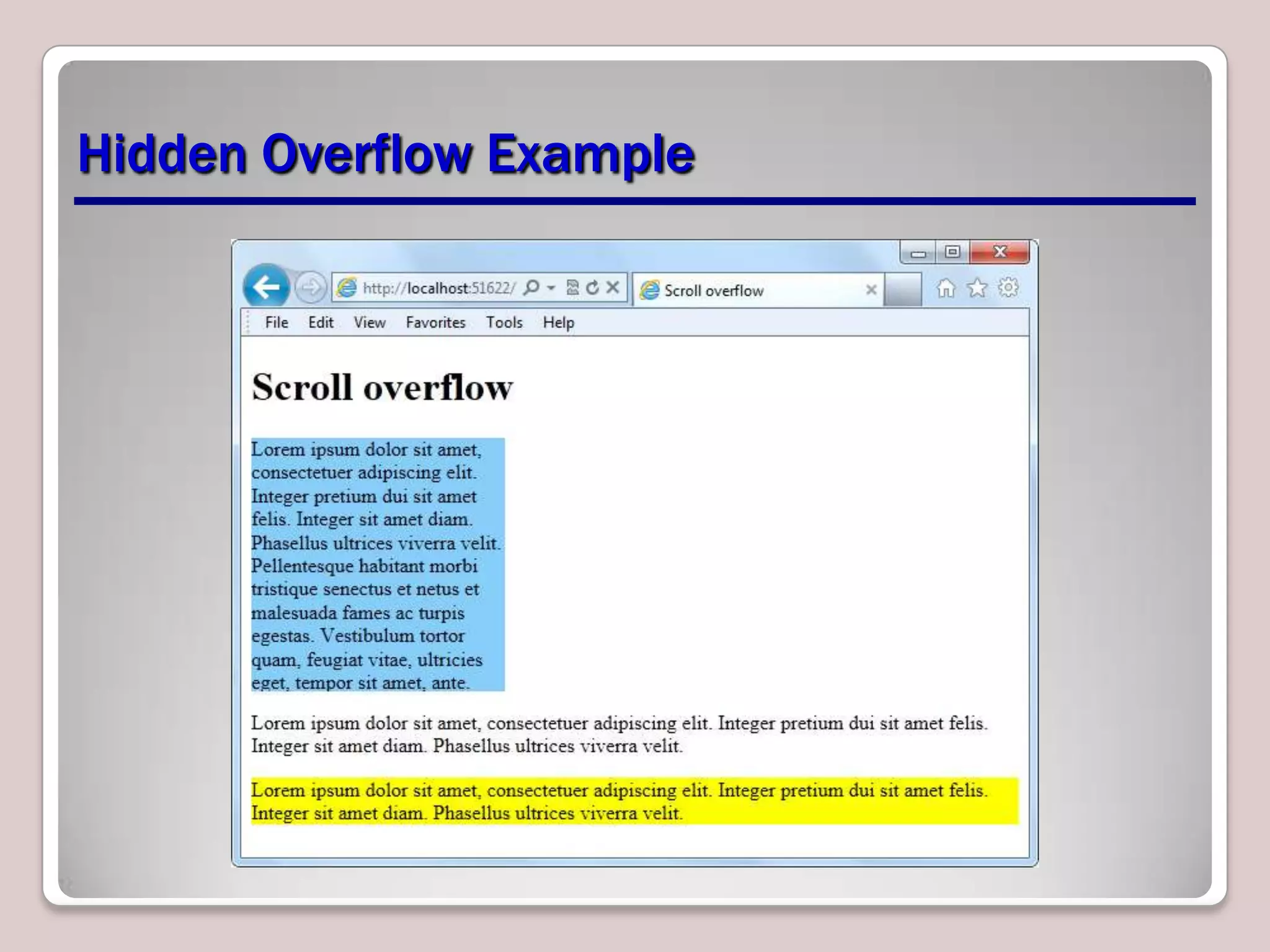
This document provides an overview of CSS essentials including the separation of content and presentation with CSS, linking CSS to HTML, CSS selectors and declarations, fonts, positioning with float and absolute positioning, and overflow properties. It includes examples of inline and block flow, floating and absolutely positioned elements, and using the overflow property to create scrolling, visible and hidden overflow. The goal is to understand core CSS concepts needed to pass the MTA Exam Objective on understanding CSS essentials.